Selective Doping in Silicon Carbide Power Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background on Selective Doping in SiC Power Devices
3. n-Type and p-Type Ion-Implantation Doping of SiC
4. Surface Roughness of SiC Implanted Layers
5. Effects of Selective Implantation Doping on Relevant SiC Devices Parameters
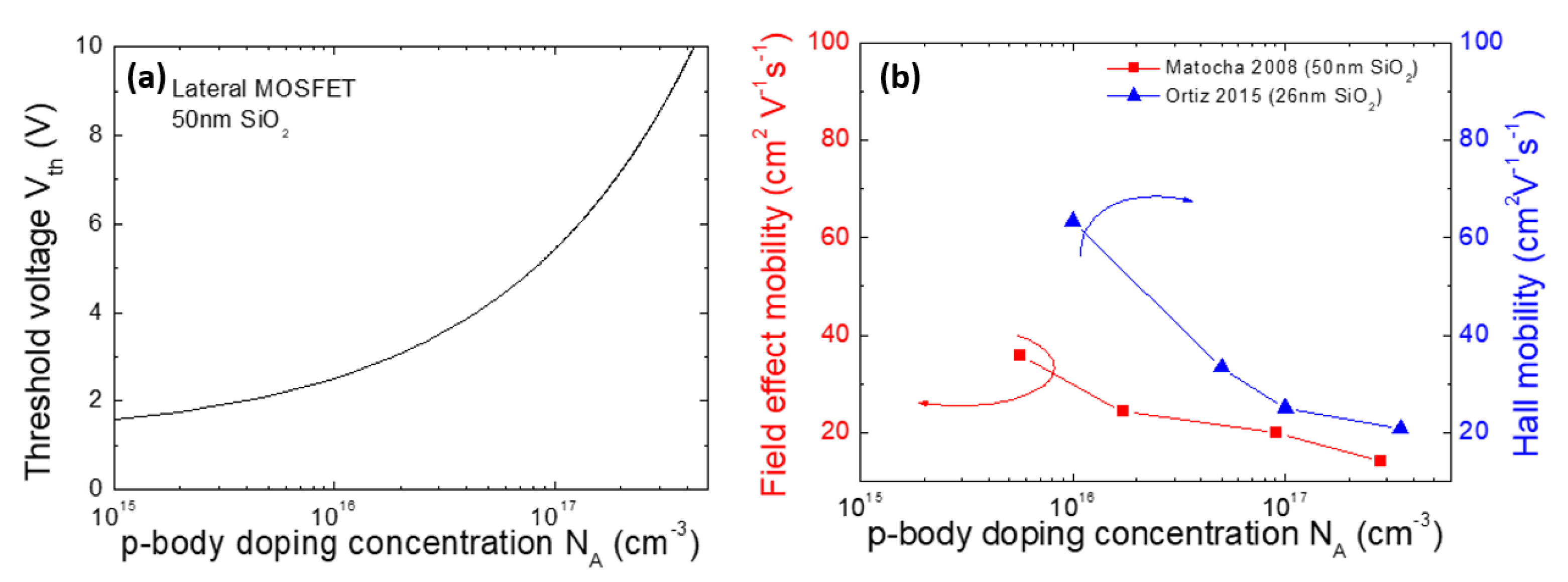
5.1. Doping Effects on Threshold Voltage and Channel Mobility of 4H-SiC MOSFET
5.2. “Counter Doping” of 4H-SiC MOSFET Channel
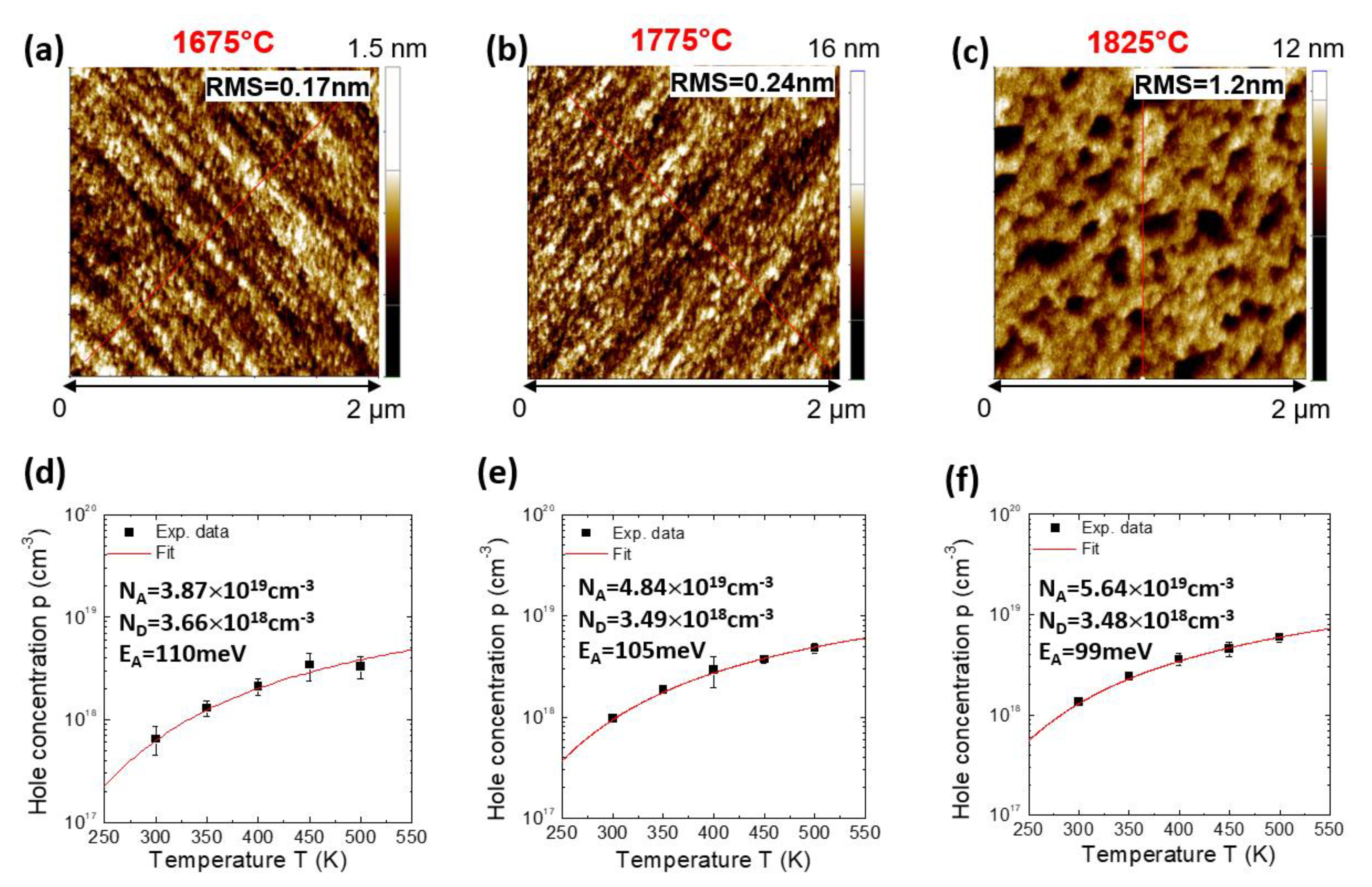
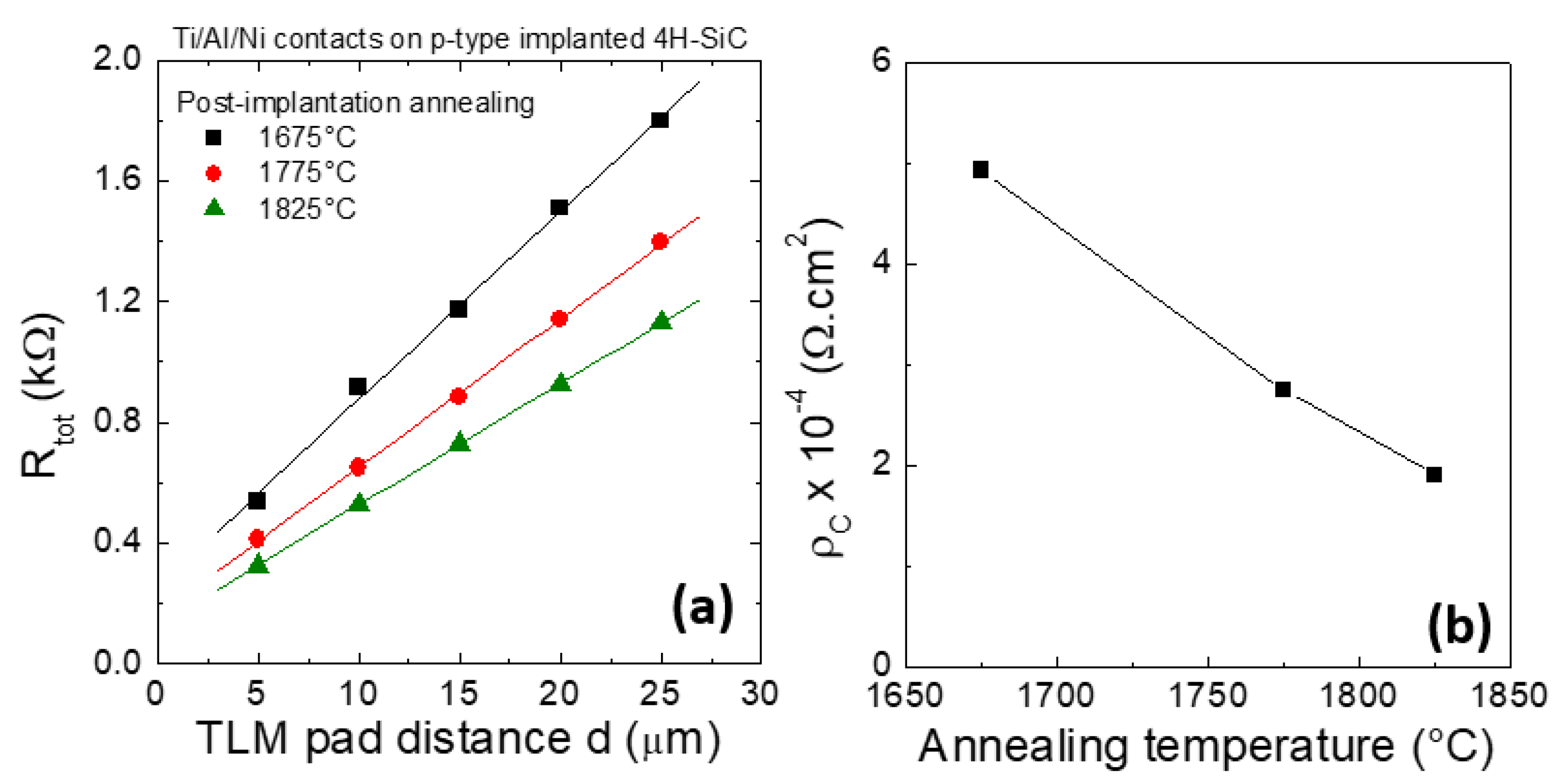
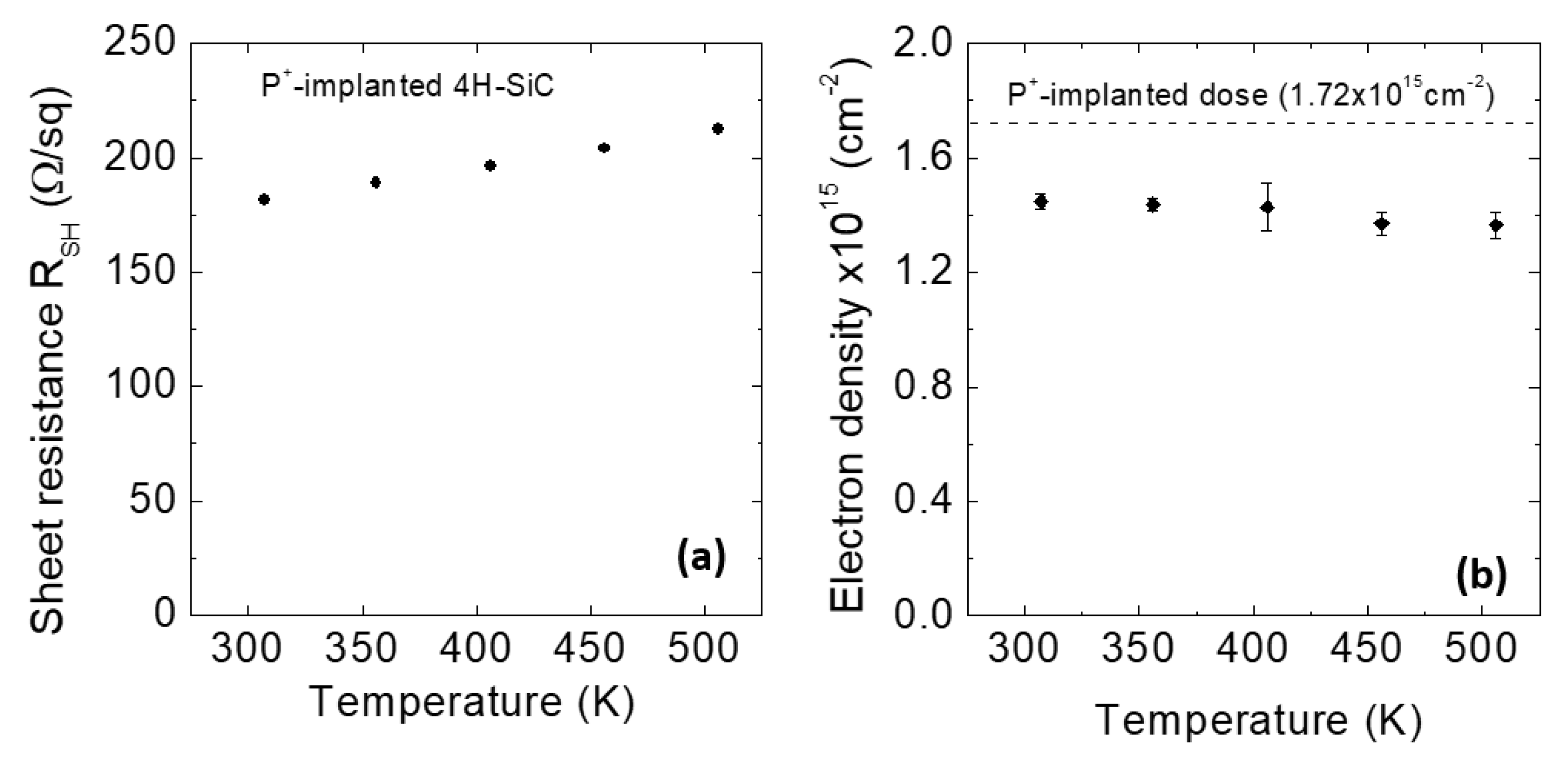
5.3. High-Dose n-Type and p-Type Doping for Ohmic Contacts in SiC Devices
6. Non-Conventional Annealing and Doping Methods
6.1. Laser, Microwave and Plasma Annealing Technniques
6.2. Laser Irradiation Doping of SiC Immersed in a Liquid Containing Dopant Species
6.3. Other p-Type Doping Methods Based on Al Melting
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimoto, T.; Cooper, J.A. Fundamentals of Silicon Carbide Technology, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Greco, G.; Lo Nigro, R.; Giannazzo, F.; Patti, A.; Saggio, M. Challenges for energy efficient wide band gap semiconductor power devices. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensl, G.; Ciobanu, F.; Frank, T.; Krieger, M.; Reshanov, S.; Schmid, F.; Weidner, M. SiC Material Properties. In SiC Materials and Devices; Shur, M., Rumyanstev, S., Levinshtein, M., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2006; Volume I, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, T. Material science and device physics in SiC technology for high-voltage power devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 040103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Huang, A.Q.; Lucía, Ó.; Ozpineci, B. Review of silicon carbide power devices and their applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8193–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Greco, G.; Lo Nigro, R.; Giannazzo, F.; Iucolano, F.; Saggio, M. Emerging trends in wide band gap semiconductors (SiC and GaN) technology for power devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187–188, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, G.L. Diffusion of impurities and ion implantation. In Properties of Silicon Carbide; Harris, G.L., Ed.; INSPEC, the Institution of Electrical Engineers: London, UK, 1995; pp. 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Heera, V.; Skorupa, W. Ion implantation and annealing effects in silicon carbide. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1997, 438, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, B.G.; Hallén, A.; Linnarsson, M.K.; Kuznetsov, A.Y.; Janson, M.S.; Formanek, B.; Österman, J.; Persson, P.O.; Hultman, L.; Storasta, L.; et al. Doping of silicon carbide by ion implantation. Mater. Sci. Forum 2001, 353–356, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallén, A.; Janson, M.S.; Kuznetsov, A.Y.; Åberg, D.; Linnarsson, M.K.; Svensson, B.G.; Persson, P.O.; Carlsson, F.H.; Storasta, L.; Bergman, J.P.; et al. Ion implantation of silicon carbide. Nuclear Instr. Methods Phys. Res. B 2002, 186, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Leung, J.; Janson, M.S.; Kuznetsov, A.; Svensson, B.G.; Linnarsson, M.K.; Hallén, A.; Jagadish, C.; Cockayne, D.J.H. Ion implantation in 4H-SiC. Nuclear Instr. Methods Phys. Res. B 2008, 266, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, T.; Kawahara, K.; Niwa, H.; Kaji, N.; Suda, J. Ion implantation technology in SiC for power device applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Workshop on Junction Technology (IWJT), Shanghai, China, 18–20 May 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Carole, D.; Raynaud, C.; Ferro, G.; Sejil, S.; Laariedh, F.; Brylinski, C.; Planson, D.; Morel, H. Classic and alternative methods of p-type doping 4H-SiC for integrated lateral devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2015 International Semiconductor Conference (CAS), Sinaia, Romania, 12–14 October 2015; pp. 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallén, A.; Linnarson, M.K. Ion implantation technology for silicon carbide. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 306, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipoti, R.; Ayedh, H.M.; Svensson, B.G. Defects related to electrical doping of 4H-SiC by ion implantation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2018, 78, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godignon, P.; Torregrosa, F.; Zekentes, K. Silicon carbide doping by ion implantation. Mater. Res. Found. 2020, 69, 107–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troffer, T.; Schadt, M.; Frank, T.; Itoh, H.; Pensl, G.; Heindl, J.; Strunk, H.P.; Maier, M. Doping of SiC by implantatin of boron and aluminum. Phys. Stat. Sol. A 1997, 162, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmody, C.; Goldsman, N. Incomplete ionization in aluminum-doped4H-silicon carbide. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 145701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.L.; Bardeen, J. Electrical properties of pure silicon and silicon alloys containing boron and phosphorous. Phys. Rev. 1949, 75, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efros, A.L.; Lien, N.V.; Shklovskii, B.I. Impurity band structure in lightly dopedsemiconductors. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1979, 12, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimini, E. Ion Implantation: Basics to Device Fabrication; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroko, L.J.; Milnes, A.G. Diffusion of nitrogen into silicon carbide single crystals doped with aluminum. Solid State Electron. 1966, 9, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhov, E.N.; Vodakov, Y.A.; Lomakina, G.A. Diffusion of aluminum in silicon carbide. Sov. Phys. Solid State 1969, 11, 415–416. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, O.; Ryssel, H.; Pichler, P. Determination of aluminum diffusion parameters in silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 5645–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhov, E.N. Doping of SiC crystals during sublimation growth and diffusion. In Cystal Growth; Glebovsky, V., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heera, V.; Stoemenos, J.; Kögler, R.; Skorupa, W. Amorphization and recrystallization of 6H-SiC by ion-beam irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolse, W.; Conrad, J.; Rödle, T.; Weber, T. Ion-beam-induced amorphization of 6H-SiC. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 74–75, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, T.; Inoue, N. Nitrogen ion implantation into -SiC epitaxial layers. Phys. Stat. Sol. A 1997, 162, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, Y.; Miyamoto, N.; Kimoto, T.; Matsunami, H. Remarkable lattice recovery and low sheet resistance of phosphorus implanted 4H-SiC (11–20). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimoto, T.; Takemura, O.; Matsunami, H.; Nakata, T.; Inoue, M. Al+ and B+ implantation into 6H-SiC epilayers and application to pn junction diodes. J. Electr. Mater. 1998, 27, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, Y.; Kimoto, T.; Matsunami, H.; Schmid, F.; Pensl, G. Electrical activation of high-concentration aluminum implanted in 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 4916–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capano, M.A.; Santhakumar, R.; Venugopal, R.; Melloch, M.R.; Cooper, J.A. Phosphorus implantation into 4H-silicon carbide. J. Electron. Mater. 2000, 29, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laube, M.; Schmid, F.; Pensl, G.; Wagner, G.; Linnarsson, M.; Maier, M. Electrical activation of high concentrations of N+ and P+ ions implanted into 4H–SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, E.; Heft, A.; Wesh, W. Ion-beam induced damage and annealing behaviour in SiC. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. B 1998, 141, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itho, H.; Troffer, T.; Peppermuller, C.; Pensl, G. Effects of C or Si co-implantation on the electrical activation of B atoms implanted in 4H–SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Chow, T.P. N-type doping of 4H-SiC with phosphorus co-implanted with C or Si. J. Electron. Mater. 2001, 30, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensl, G.; Ciobanu, F.; Frank, T.; Kirmse, D.; Krieger, M.; Reshanov, S.; Schmid, F.; Weidner, W.; Ohshima, T.; Itoh, H.; et al. Defect-engineering in SiC by ion implantation and electron irradiation. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambach, M.; Frey, L.; Bauer, A.J.; Ryssel, H. Extracting activation and compensation ratio from aluminum implanted 4H-SiC by modeling of resistivity measurements. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 527–529, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, H.; Suda, J.; Kimoto, T. Electrical properties of n- and p-type 4H–SiC formed by ion implantation into high-purity semi-insulating substrates. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 070306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiße, J.; Hauck, M.; Sledziewski, T.; Tschiesche, M.; Krieger, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Mitlehner, H.; Frey, L.; Erlbacher, T. Analysis of compensation effects in aluminum-implanted 4H–SiC devices. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 924, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiße, J.; Hauck, M.; Krieger, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Erlbacher, T. Aluminum acceptor activation and charge compensation in implanted p-type 4H-SiC. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 055308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capano, M.A.; Cooper, J.A.; Melloch, M.R.; Saxler, A.; Mitchel, W.C. Ionization energies and electron mobilities in phosphorus- and nitrogen-implanted 4H-silicon carbide. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 8773–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saks, N.S.; Agarwal, A.K.; Ryu, S.H.; Palmour, J.W. Low-dose aluminum and boron implants in 4H and 6H silicon carbide. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senzaki, J.; Fukuda, K.; Arai, K. Influences of postimplantation annealing conditions on resistance lowering in high-phosphorus-implanted 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 2942–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, S.G.; Rao, M.V.; Tian, Y.-l.; Ridgway, M.C.; Schreifels, J.A.; Kopanski, J.J. Ultrahigh-temperature microwave annealing of Al+- and P+-implanted 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 73708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, T.; Yan, G.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wen, J. Effect of annealing process on the surface roughness in multiple Al implanted 4H-SiC. J. Semicond. 2011, 32, 72002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipoti, R.; Scaburri, R.; Hallén, A.; Parisini, A. Conventional thermal annealing for a more efficient p-type doping of Al+ implanted 4H-SiC. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipoti, R.; Carnera, A.; Alferi, G.; Kranz, L. About the electrical activation of 1 × 1020 cm−3 ion implanted Al in 4H–SiC at annealing temperatures in the range 1500–1950 °C. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 924, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toifl, A. Modeling and Simulation of Thermal Annealing of Implanted GaN and SiC. Master’s Thesis, Technical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2018. Available online: https://www.iue.tuwien.ac.at/uploads/tx_sbdownloader/toifl.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2021).
- Nipoti, R.; Parisini, A. Al+ ion implanted 4H-SiC: Electrical activation versus annealing time. ECS Trans. 2019, 92, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimonka, V.; Toifl, A.; Hössinger, A.; Selberherr, S.; Weinbub, J. Transient model for electrical activation of Aluminium and phosphorus-implanted silicon carbide. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 235701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toifl, A.; Šimonka, V.; Hössinger, A.; Selberherr, S.; Grasser, T. Simulation of the effects of postimplantation annealing on silicon carbide DMOSFET characteristics. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2019, 66, 3060–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capano, M.A.; Ryu, S.; Cooper, J.A.; Melloch, M.R.; Rottner, K.; Karlsson, S.; Nordell, N.; Powell, A.; Walker, D.E. Surface roughening in ion implanted 4H-silicon carbide. J. Electron. Mater. 1999, 28, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanqué, S.; Pérez, R.; Godignon, P.; Mestres, N.; Morvan, E.; Kerlain, A.; Dua, C.; Brylinski, C.; Zielinski, M.; Camassel, J. Room Temperature Implantation and Activation Kinetics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in 4H-SiC Crystals. Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 457–460, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddow, S.E.; Williams, J.; Isaacs-Smith, T.; Capano, M.A.; Cooper, J.A.; Mazzola, M.S.; Hsieh, A.J.; Casady, J.B. High temperature implant activation in 4H and 6H-SiC in a silane ambient to reduce step bunching. Mater. Sci. Forum 2000, 338–342, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambach, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Ryssel, H. Electrical and topographical characterization of aluminum implanted layers in 4H silicon carbide. Phys. Stauts Solidi B 2008, 245, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.H.; Roccaforte, F.; Giannazzo, F.; Di Franco, S.; Bongiorno, C.; Zanetti, E.; Ruggiero, A.; Saggio, M.; Raineri, V. Correlation study of morphology, electrical activation and contact formation of ion implanted 4H-SiC. Solid State Phenom. 2010, 156–158, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, Y.; Katsumoto, K.; Kimoto, T.; Matsunami, H. Flat surface after high-temperature annealing for phosphorus-ion implanted 4H-SiC(0001) using graphite cap. Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 457–460, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilevski, K.V.; Wright, N.G.; Nikitina, I.P.; Horsfall, A.B.; O’Neill, A.G.; Uren, M.J.; Hilton, K.P.; Masterton, A.G.; Hydes, A.J.; Johnson, C.M. Protection of selectively implanted and patterned silicon carbide surfaces with graphite capping layer during post-implantation annealing. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipoti, R.; Mancarella, F.; Moscatelli, F.; Rizzoli, R.; Zampolli, S.; Ferri, M. Carbon-cap for ohmic contacts on ion-implanted 4H–SiC. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2010, 13, H432–H435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzetto, A.; Giannazzo, F.; Lo Nigro, R.; Raineri, V.; Roccaforte, F. Structural and transport properties in alloyed Ti/Al Ohmic contacts formed on p-type Al-implanted 4H-SiC annealed at high temperature. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 255302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haney, S.; Agarwal, A. The effects of implant activation anneal on the effective inversion layer mobility of 4H-SiC MOSFETs. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 37, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, H.; Tang, K.; Chow, T.P. Effect of graphite cap for implant activation on inversion channel mobility in 4H-SiC MOSFETs. Mater. Sci. Forum 2009, 615–617, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Ohshima, T.; Ohi, A.; Itoh, H.; Pensl, G. Anomalous increase in effective channel mobilityon gamma-irradiated p-channel SiC metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors containing step bunching. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 6830–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzetto, A.; Giannazzo, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Raineri, V.; Roccaforte, F. Limiting mechanism of inversion channel mobility in Al-implanted lateral 4H-SiC metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 072117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tuttle, B.R.; Dhar, S. Silicon carbide: A unique platform for metal oxide-semiconductor physics. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 021307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, P.; Giannazzo, F.; Frazzetto, A.; Roccaforte, F. Influence of the surface morphology on the channel mobility of lateral implanted 4H-SiC(0001) metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 084501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Burk, A.; Callanan, R.; Capell, C.; Das, M.; Haney, S.; Hull, B.; Jonas, C.; O’Loughlin, M.; O’Neil, M.; et al. Critical technical issues in high voltage SiC power devices. Mater. Sci. Forum 2009, 600–603, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.M.; Ng, K.K. Physics of Semiconductor Devices; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Matocha, K. Challenges in SiC power MOSFET design. Solid-State Electron. 2008, 52, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tomás, A.; Brosselard, P.; Godignon, P.; Millán, J.; Mestres, N.; Jennings, M.R.; Covington, J.A.; Mawby, P.A. Field-effect mobility temperature modeling of 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 114508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannazzo, F.; Roccaforte, F.; Raineri, V. Acceptor, compensation, and mobility profiles in multiple Al implanted 4H-SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 202104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, P.; Alessandrino, M.S.; Carbone, B.; Russo, A.; Roccaforte, F.; Giannazzo, F. High resolution two dimensional imaging of the 4H-SiC MOSFET channel by scanning capacitance microscopy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, G.; Strenger, C.; Uhnevionak, V.; Burenkov, A.; Bauer, A.J.; Pichler, P.; Cristiano, F.; Bedel-Pereira, E.; Mortet, V. Impact of acceptor concentration on electrical properties and density of interface states of 4H-SiC n-metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors studied by Hall effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 062104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, K.; Oikawa, T. Counter-doped MOSFETs of 4H-SiC. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 1999, 20, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, F.; Poggi, A.; Solmi, S.; Nipoti, R. Nitrogen implantation to improve electron channel mobility in 4H-SiC MOSFET. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2008, 55, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, M.; Soler, V.; Rius, G.; Montserrat, J.; Rebollo, J.; Godignon, P. Advanced processing for mobility improvement in 4H-SiC MOSFETs: A review. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2018, 78, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, L.K.; Fiorenza, P.; Giannazzo, F.; Frazzetto, A.; Roccaforte, F. Correlating macroscopic and nanoscale electrical modifications of SiO2/4H-SiC interfaces upon post-oxidation-annealing in N2O and POCl3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 193501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, P.; Giannazzo, F.; Vivona, M.; La Magna, A.; Roccaforte, F. SiO2/4H-SiC interface doping during post-deposition-annealing of the oxide in N2O or POCl3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 153508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, P.; Di Franco, S.; Giannazzo, F.; Roccaforte, F. Nanoscale probing of the lateral homogeneity of donors concentration in nitridated SiO2/4H–SiC interfaces. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 315701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modic, A.; Liu, G.; Ahyi, A.C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, P.; Hamilton, M.C.; Williams, J.R.; Feldman, L.C.; Dhar, S. High channel mobility 4H-SiC MOSFETs by antimony counter-doping. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2014, 35, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, M.; Iwamatsu, T.; Amishiro, H.; Watanabe, H.; Kita, K.; Miura, N. Channel engineering of 4H-SiC MOSFETs using sulphur as a deep level donor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM2018), San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 December 2018; pp. 8.3.1–8.3.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernot, J.; Contreras, S.; Camassel, J. Electrical transport properties of aluminium implanted 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 023706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisini, A.; Nipoti, R. Analysis of the hole transport through valence band states in heavy Al doped 4H-SiC by ion implantation. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 243703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, S.; Konczewicz, L.; Arvinte, R.; Peyre, H.; Chassagne, T.; Zielinski, M.; Juillaguet, S. Electrical transport properties of p-type 4H-SiC. Phys. Status Solidi A 2017, 214, 1600679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spera, M.; Corso, D.; Di Franco, S.; Greco, G.; Severino, A.; Fiorenza, P.; Giannazzo, F.; Roccaforte, F. Effect of high temperature annealing (T > 1650 °C) on the morphological and electrical properties of p-type implanted 4H-SiC layers. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2019, 93, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pensl, G.; Schmid, F.; Ciobanu, F.; Laube, M.; Reshanov, S.A.; Schulze, N.; Semmelroth, K.; Nagasawa, H.; Schöner, A.; Wagner, G. Electrical and optical characterization of SiC. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 433–436, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, S.; Okuda, T.; Kimoto, T.; Suda, J. Hall scattering factors in p-type 4H-SiC with various doping concentrations. Appl. Phys. Express 2016, 9, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorder, D.K. Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rambach, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Ryssel, H. High temperature implantation of Aluminum in 4H silicon carbide. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 556–557, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaforte, F.; Frazzetto, A.; Greco, G.; Giannazzo, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Lo Nigro, R.; Saggio, M.; Leszczyński, M.; Prystawko, P.; Raineri, V. Critical issues for interfaces to p-type SiC and GaN in power devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8324–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivona, V.; Greco, G.; Giannazzo, F.; Lo Nigro, R.; Rascunà, S.; Saggio, M.; Roccaforte, F. Thermal stability of the current transport mechanisms in Ni-based Ohmic contacts on n- and p-implanted 4H-SiC. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 075018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.A.; Jennings, M.; Sharma, Y.K.; Sanchez-Fuentes, A.; Walker, D.; Gammon, P.M.; Pérez-Tomás, A.; Thomas, S.M.; Burrows, S.E.; Mawby, P.A. On the schottky barrier height lowering effect of Ti3SiC2 in ohmic contacts to P-Type 4H-SiC. Intern. J. Fund. Phys. Sci. 2014, 4, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Tannous, T.; Souedain, M.; Ferro, G.; Lazar, M.; Raynaud, C.; Toury, B.; Beaufort, M.F.; Barbot, J.F.; Dezellus, O.; Planson, D. A Study on the temperature of ohmic contact to p-Type SiC based on Ti3SiC2 phase. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2016, 63, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vivona, A.; Greco, G.; Lo Nigro, R.; Bongiorno, C.; Roccaforte, F. Ti/Al/W Ohmic contacts to p-type implanted 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 035705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivona, M.; Greco, G.; Bongiorno, C.; Lo Nigro, R.; Scalese, S.; Roccaforte, F. Electrical and structural properties of surfaces and interfaces in Ti/Al/Ni Ohmic contacts to p-type implanted 4H-SiC. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spera, M.; Greco, G.; Corso, D.; Di Franco, S.; Severino, A.; Messina, A.A.; Giannazzo, F.; Roccaforte, F. Ohmic contacts on p-Type Al-Implanted 4H-SiC layers after different post-implantation annealings. Materials 2019, 12, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nipoti, R.; Nath, A.; Qadri, S.B.; Tian, Y.-L.; Albonetti, C.; Carnera, A.; Rao, M.V. High-dose phosphorus-implanted 4H-SiC: Microwave and conventional post-implantation annealing at temperatures ≥ 1700 °C. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, F.; Laube, M.; Pensl, G.; Wagner, G.; Maier, M. Electrical activation of implanted phosphorus ions in [0001]- and [11–20]-oriented 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 9182–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spera, M.; Greco, G.; Severino, A.; Vivona, M.; Fiorenza, P.; Giannazzo, F.; Roccaforte, F. Active dopant profiling and Ohmic contacts behavior in degenerate n-type implanted silicon carbide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, A.; Mello, D.; Boninelli, S.; Roccaforte, F.; Giannazzo, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Calabretta, C.; Calcagno, L.; Piluso, N.; Arena, G. Effects of Thermal Annealing Processes in Phosphorous Implanted 4H-SiC Layers. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 963, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaforte, F.; Brezeanu, G.; Gammon, P.M.; Giannazzo, F.; Rascunà, S.; Saggio, M. Schottky contacts to silicon carbide: Physics, technology and applications. In Advancing Silicon Carbide Electronics Technology; Zekentes, K., Vasilevskiy, K., Eds.; Materials Research Foundation: Millersville, PA, USA, 2018; Volume I, pp. 127–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascunà, S.; Badalà, P.; Tringali, C.; Bongiorno, C.; Smecca, E.; Alberti, A.; Di Franco, S.; Giannazzo, F.; Greco, G.; Roccaforte, F.; et al. Morphological and electrical properties of Nickel based Ohmic contacts formed by laser annealing process on n-type 4H-SiC. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2019, 97, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Barbero, C.J.; Sigmon, T.W. Activation of ion implanted dopants in α-SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishida, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Nakashima, K.; Eryu, O. Excimer laser annealing of ion-implanted 6H-silicon carbide. Mater. Sci. Forum 2000, 873, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tanoue, H.; Arai, K. Electrical activation of the ion-implanted phosphorus in 4H-SiC by excimer laser annealing. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 5934–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutto, C.; Fogarassy, E.; Mathiot, D.; Muller, D.; Kern, P.; Ballutaud, D. Long-pulse duration excimer laser annealing of Al+ ion implanted 4H-SiC for pn junction formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 208–209, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutopoulos, C.; Terzis, P.; Zergioti, I.; Kontos, A.G.; Zekentes, K.; Giannakopoulos, K.; Raptis, Y.S. Laser annealing of Al implanted silicon carbide: Structural and optical characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7912–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabretta, C.; Agati, M.; Zimbone, M.; Boninelli, S.; Castiello, A.; Pecora, A.; Fortunato, G.; Calcagno, L.; Torrisi, L.; La Via, F. Laser annealing of P and Al implanted 4H-SiC epitaxial layers. Materials 2019, 12, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, M.V. Ultra-fast microwave heating for large bandgap semiconductor processing. In Advances in Induction and Microwave Heating of Mineral and Organic Materials; Grundas, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 459–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nipoti, R.; Nath, A.; Rao, M.V.; Hallén, A.; Carnera, A.; Tian, Y.-L. Microwave annealing of very high dose Aluminum-implanted 4H-SiC. Appl. Phys. Express 2011, 4, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, S.; Kaku, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Murakami, H.; Miyazaki, S. Crystallization of Si films on glass substrate using thermal plasma jet. Thin Solid Films 2005, 487, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Hanafusa, H.; Ashihara, R.; Hayashi, S.; Murakami, H.; Higashi, S. High-efficiency impurity activation by precise control of cooling rate during atmospheric pressure thermal plasma jet annealing of 4H-SiC wafer. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 06GC01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafusa, H.; Maruyama, K.; Ishimaru, R.; Higashi, S. High efficiency activation of phosphorus atoms in 4H–SiC by atmospheric pressure thermal plasma jet annealing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 858, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.D.; Ramirez, D.A. In situ boron incorporation and activation in silicon carbide using excimer laser recrystallization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 3368–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Salama, I.A.; Quick, N.R.; Kar, A. Effects of different laser sources and doping methods used to dope silicon carbide. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Ikeda, A.; Ikenoue, H.; Asano, T. Phosphorus doping into 4H-SiC by irradiation of excimer laser in phosphoric solution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 06GF02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marui, D.; Ikeda, A.; Nishi, K.; Ikenoue, H.; Asano, T. Aluminum doping of 4H-SiC by irradiation of excimer laser in aluminum chloride solution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 06JF03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Sumina, R.; Ikenoue, H.; Asano, T. Al doping from laser irradiated Al film deposited on 4H-SiC. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 858, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, K.; Park, Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.; Jun, C.-H.; Koo, S.; Ko, S.C. Surface Al doping of 4H-SiC via low temperature annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 031603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, G.; Jacquier, C. Growth by a vapour–liquid–solid mechanism: A new approach for silicon carbide epitaxy. New J. Chem. 2004, 28, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soueidan, M.; Ferro, G.; Jacquier, C.; Godignon, P.; Pezoldt, J.; Lazar, M.; Nsouli, B.; Monteil, Y. Improvement of 4H–SiC selective epitaxial growth by VLS mechanism using Al and Ge-based melts. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejil, S.; Lazar, M.; Carole, D.; Brylinski, C.; Planson, D.; Ferro, G.; Raynaud, C. Further optimization of VLS localized epitaxy for deeper 4H-SiC p–n junctions. Phys. Stat. Sol. A 2017, 214, 1600454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

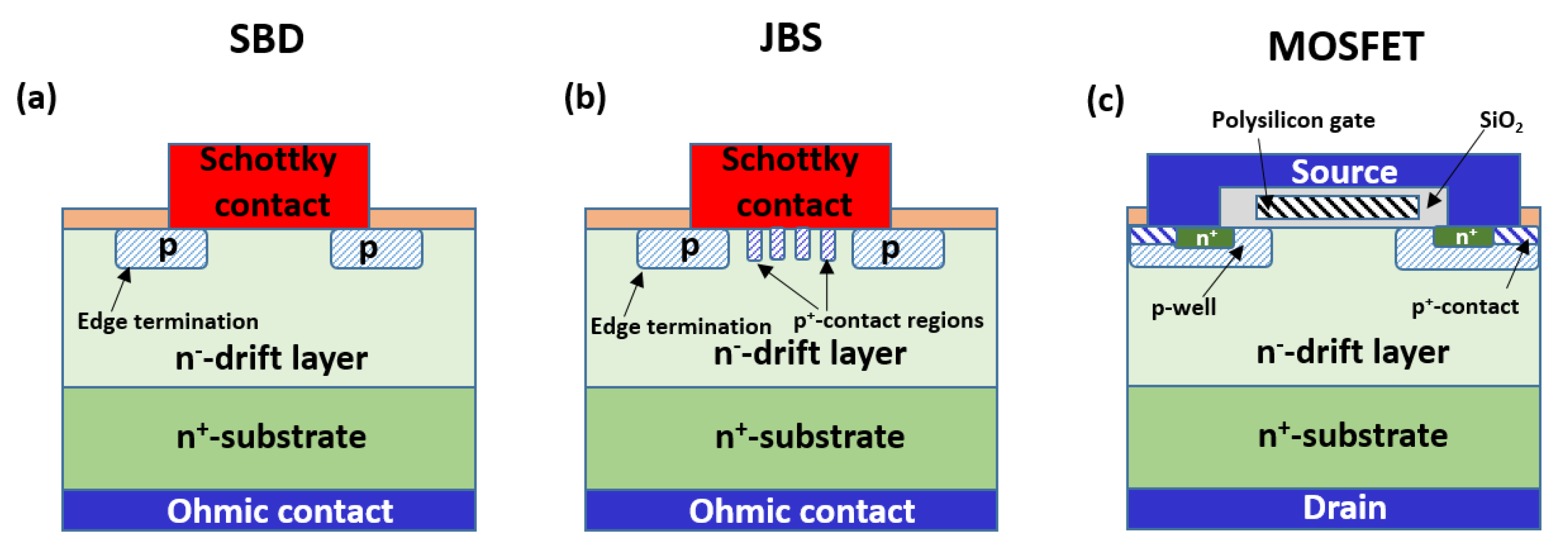
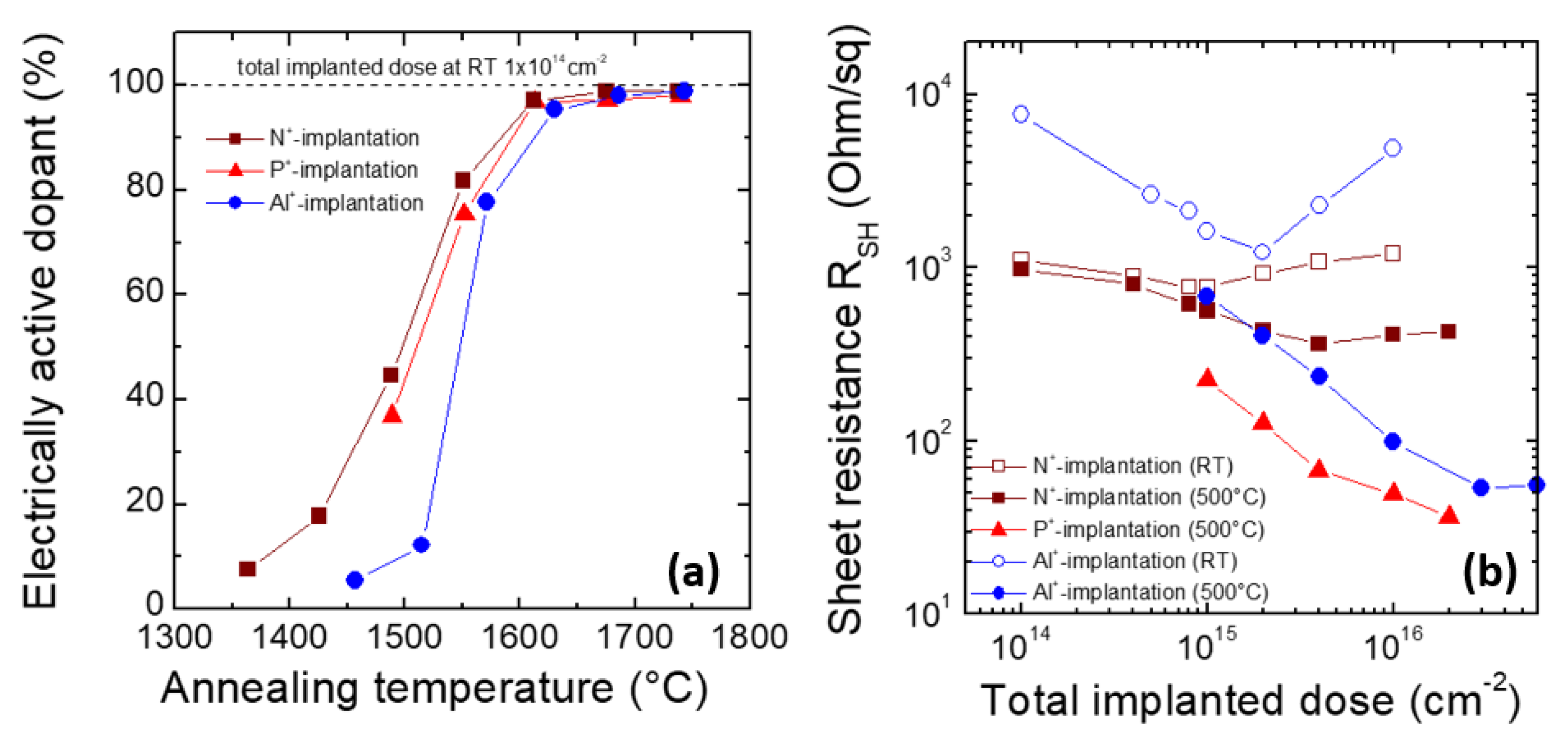
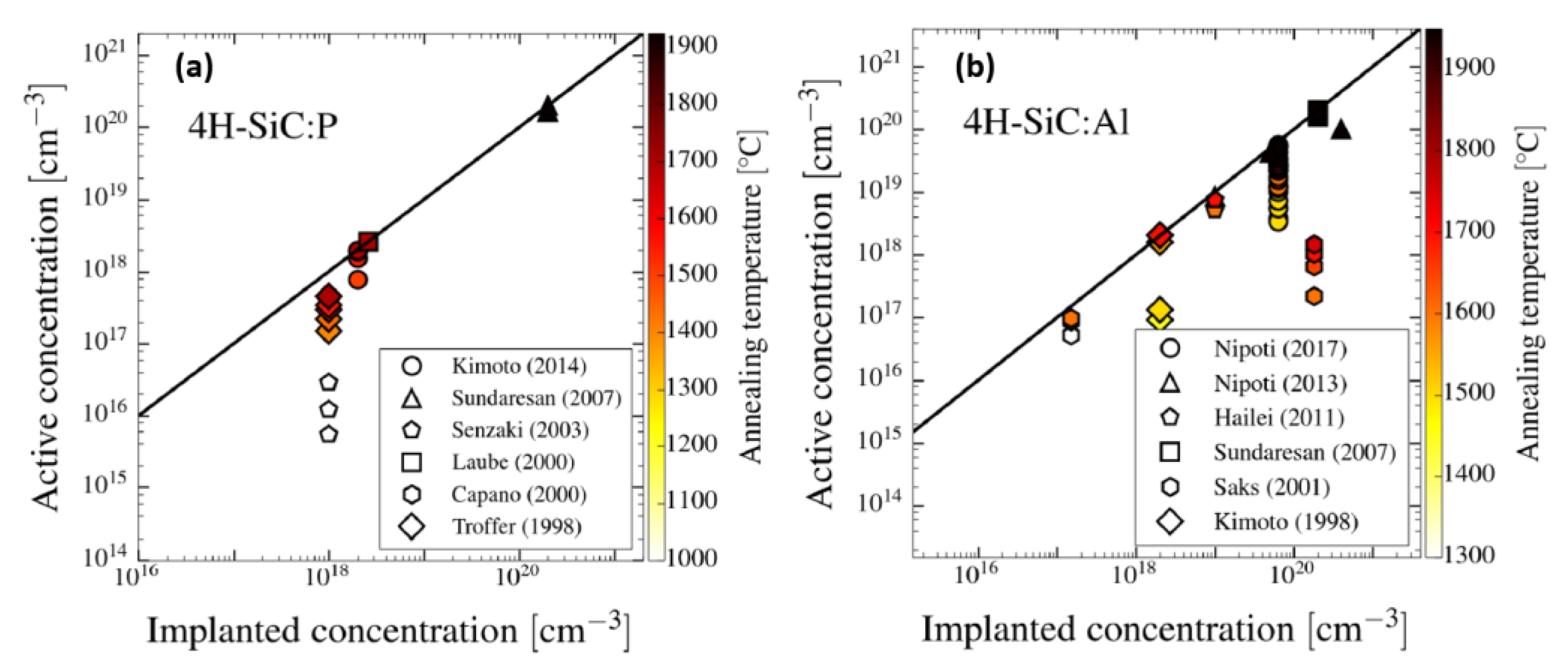

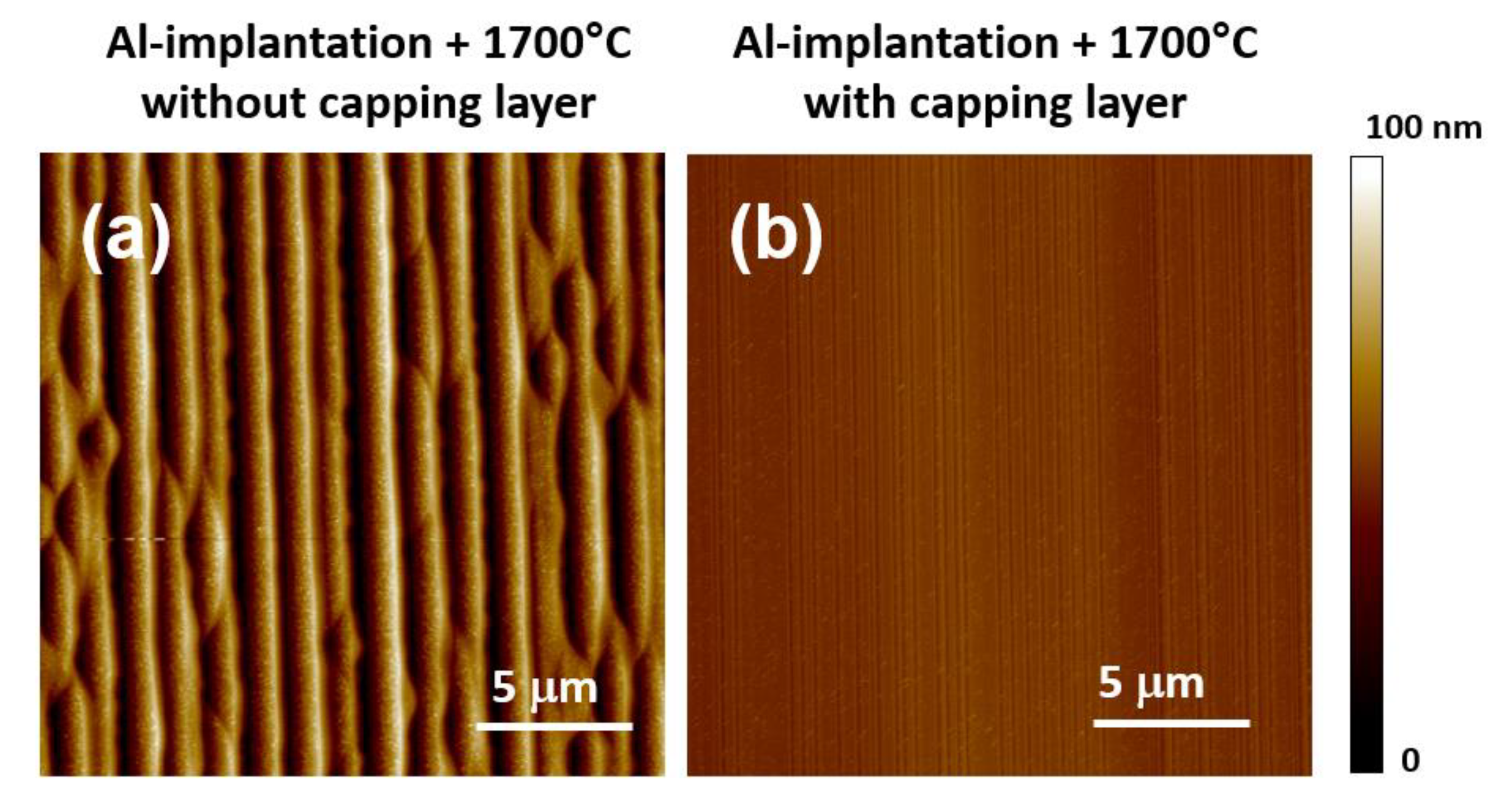

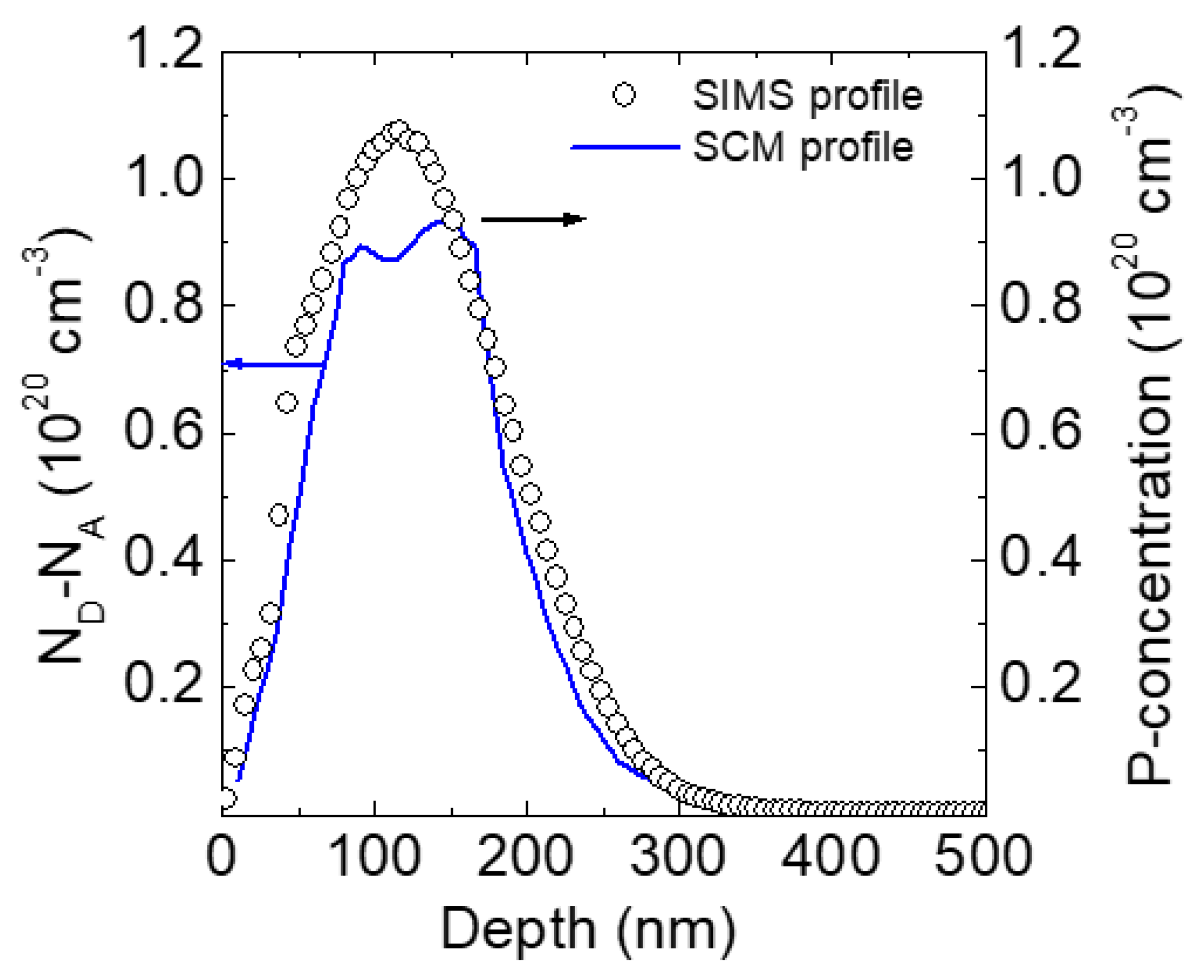

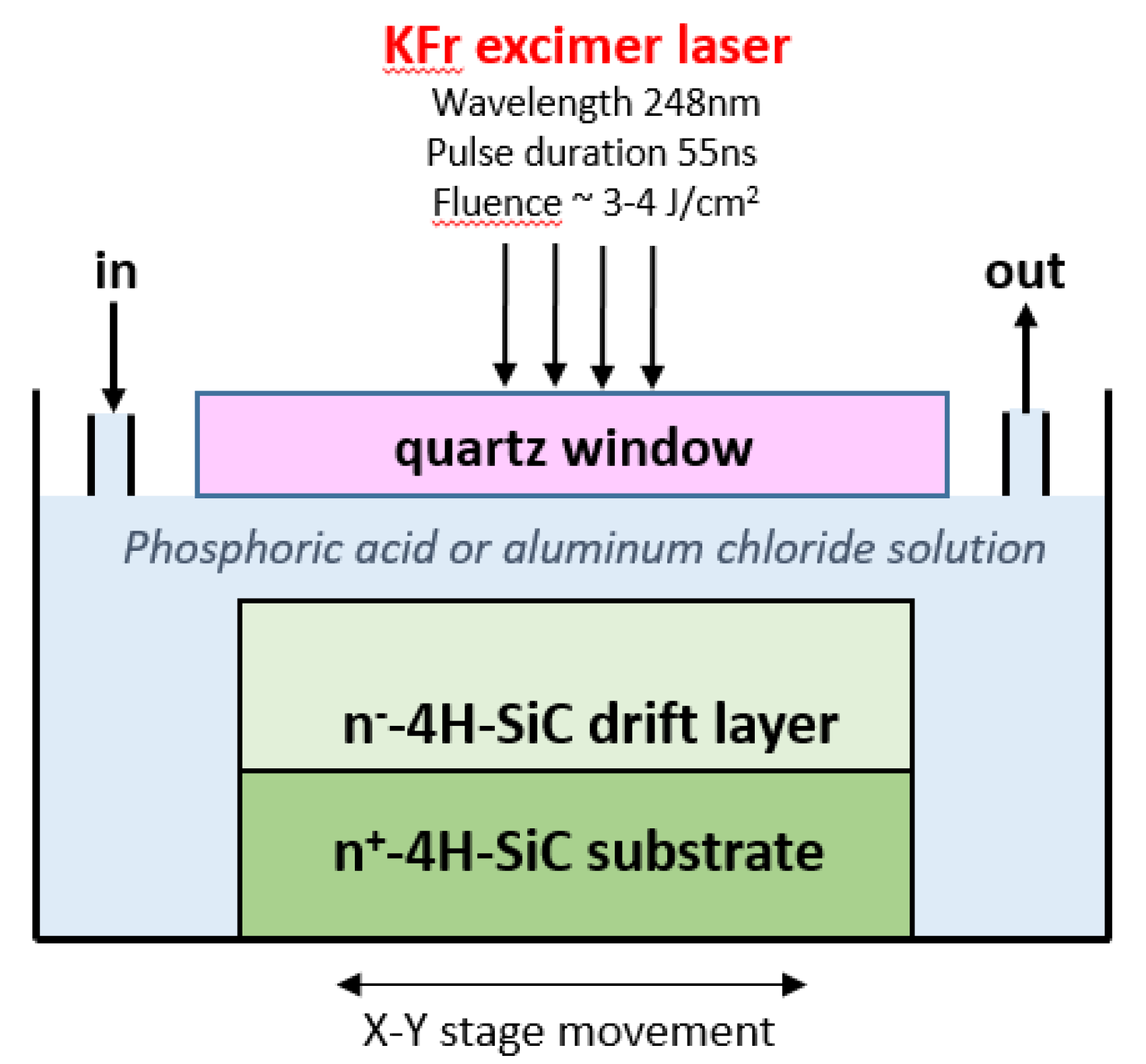
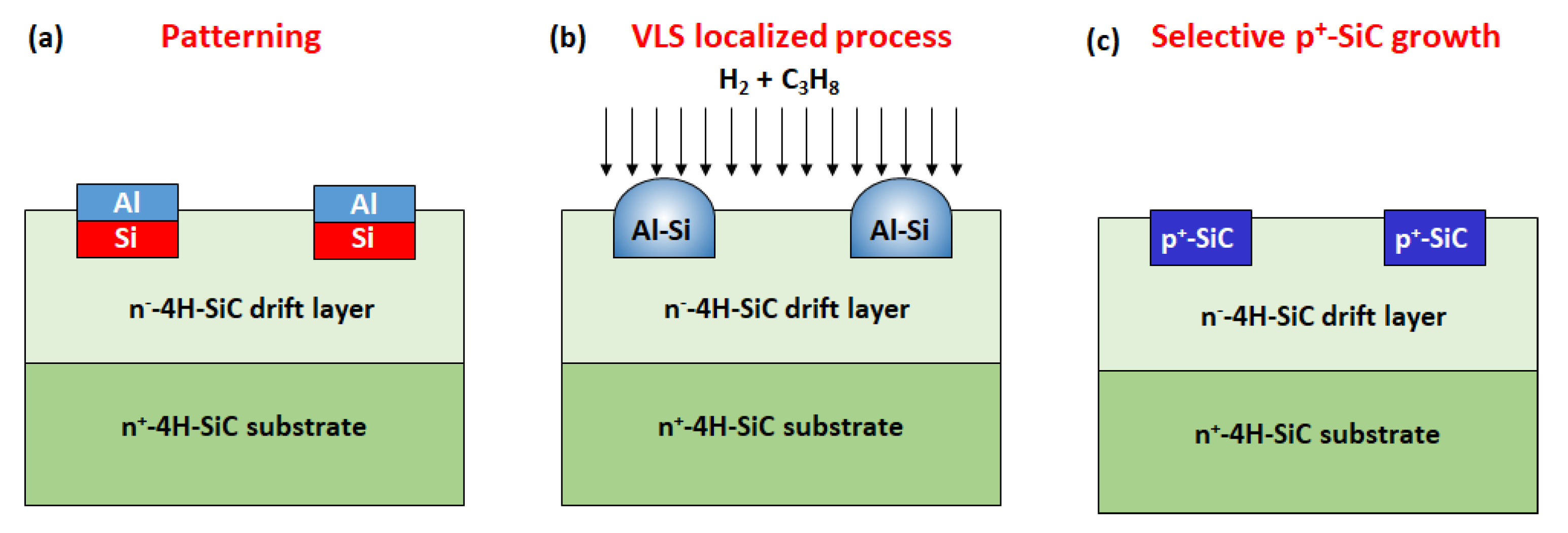
| Dopant | Ionization Energy (meV) | Solubility Limit (cm−3) |
|---|---|---|
| N | 61(h); 126 (k) | 2 × 1020 |
| P | 60 (h); 120 (k) | 1 × 1021 |
| Al | 198 (h); 201 (k) | 1 × 1021 |
| B (shallow) | 280–300 | 2 × 1019 |
| Implanted Region | Doping Level (cm−3) | Implantation Depth (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| Source/Drain | 1019–1020 | 0.2–0.3 |
| MOSFET p-body | 1017–1018 | 0.4–0.8 |
| p+-contacts | 1019–1020 | 0.2–0.3 |
| Edge termination | 1016–1017 | 0.4–0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Vivona, M.; Greco, G.; Giannazzo, F. Selective Doping in Silicon Carbide Power Devices. Materials 2021, 14, 3923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143923
Roccaforte F, Fiorenza P, Vivona M, Greco G, Giannazzo F. Selective Doping in Silicon Carbide Power Devices. Materials. 2021; 14(14):3923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143923
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoccaforte, Fabrizio, Patrick Fiorenza, Marilena Vivona, Giuseppe Greco, and Filippo Giannazzo. 2021. "Selective Doping in Silicon Carbide Power Devices" Materials 14, no. 14: 3923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143923
APA StyleRoccaforte, F., Fiorenza, P., Vivona, M., Greco, G., & Giannazzo, F. (2021). Selective Doping in Silicon Carbide Power Devices. Materials, 14(14), 3923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143923










