Evaluation of the Environmental Impact and Efficiency of N-Doping Strategies in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Carbon Dots
2.2. Characterization of CDs
2.3. Calculation of Fluorescence Quantum Yield
2.4. Scope and System Boundaries
2.5. Life Cycle Inventory Data
- Citric acid {GLO} | market;
- Urea, as N {GLO} | market;
- Ethylenediamine {RER} | market;
- N,N-dimethylformamide {GLO} | market;
- Acetonitrile {GLO} | market;
- Pyridine {GLO} | market;
- Water, deionized, from tap water, at user {Europe without Switzerland} market;
- Electricity, medium voltage {PT} | market;
- Chemical waste, unspecified.
2.6. Environmental Impact Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Carbon Dots
3.2. Optical Properties of Carbon Dots
3.3. Improvement on the Purification of CA-urea Carbon Dots
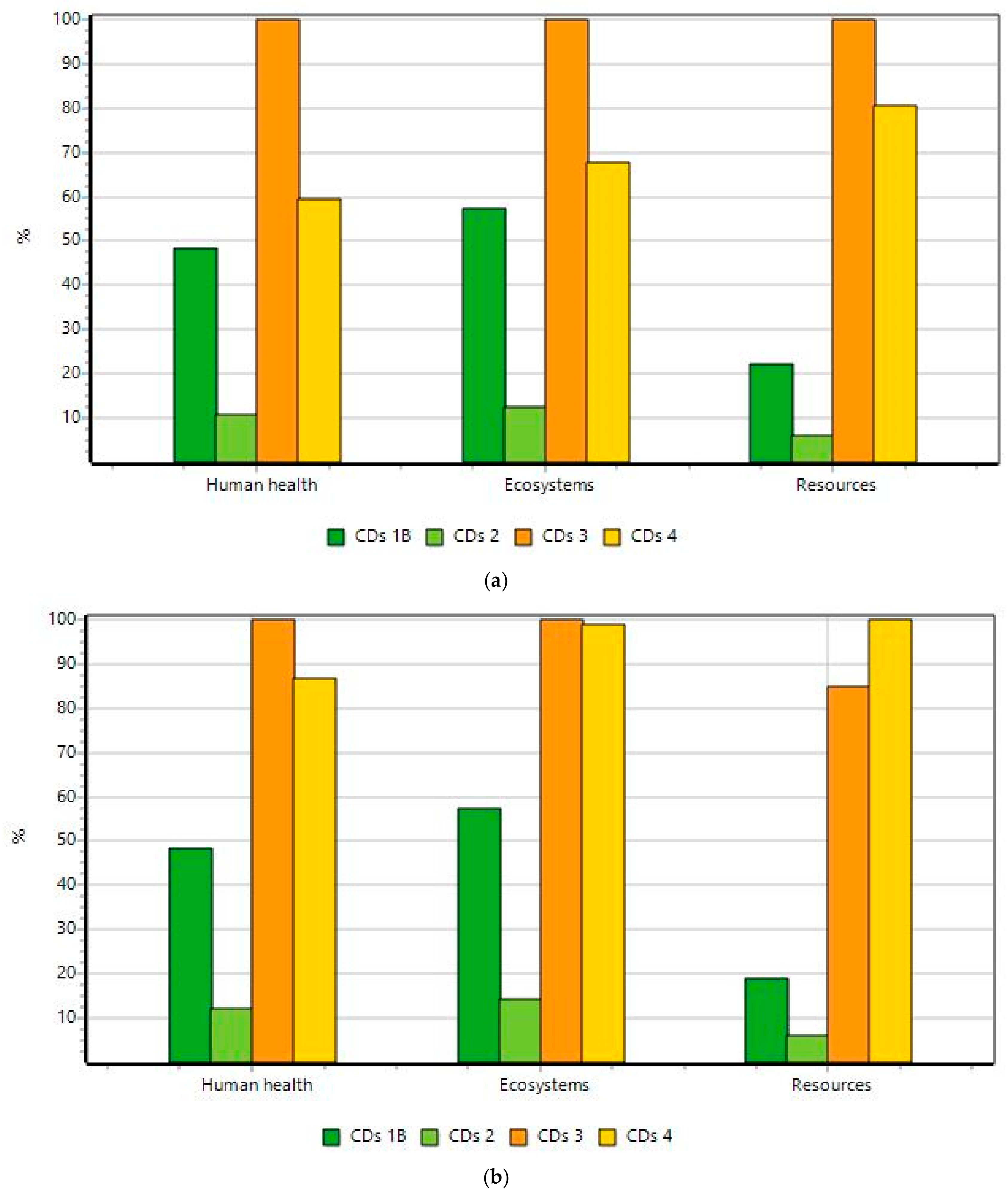
3.4. Life Cycle Assessment Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva, J.C.E.; Gonçalves, H.M. Analytical and bioanalytical applications of carbon dots. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lu, K.-Q.; Tang, Z.-R.; Xu, Y.-J. Recent progress in carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications in photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3717–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, H.; Tang, J.; Deng, S.; Yan, F.; Li, W.; Qu, M. Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: A review. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Dong, P.; Huang, J. A Mini Review on Carbon Quantum Dots: Preparation, Properties, and Electrocatalytic Application. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, A.; Sun, S. Recent applications of carbon nanomaterials in fluorescence biosensing and bioimaging. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11346–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarra, M.; Orfãos, L.D.; Alves, C.S.; Moreno-Tost, R.; Pino-González, M.S.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Eliche-Quesada, D.; Castro, E.; Luque, R. Sustainable Production of Carbon Nanoparticles from Olive Pit Biomass: Understanding Proton Transfer in the Excited State on Carbon Dots. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10493–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, H.; Song, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, M. Presence of photoluminescent carbon dots in Nescafe® original instant coffee: Applications to bioimaging. Talanta 2014, 127, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, E.F.C.; da Silva, L.P.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; Leitão, J.M.M. Hypochlorite fluorescence sensing by phenylboronic acid-alizarin adduct based carbon dots. Talanta 2020, 208, 120447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, G.P.C.; Simões, E.F.C.; Crista, D.M.A.; Leitão, J.M.M.; Pinto da Silva, L.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Glucose Sensing by Fluorescent Nanomaterials. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crista, D.M.A.; Mello, G.P.C.; Shevchuk, O.; Sendão, R.M.S.; Simões, E.F.C.; Leitão, J.M.M.; da Silva, L.P.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. 3-Hydroxyphenylboronic Acid-Based Carbon Dot Sensors for Fructose Sensing. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-H.; Fang, Y.-W.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X.-M.; Yin, X.-B. Carbon Quantum Dots for Zebrafish Fluorescence Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhuo, P.; Yin, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z. Solid-State Fluorescent Carbon Dots with Aggregation-Induced Yellow Emission for White Light-Emitting Diodes with High Luminous Efficiencies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24395–24403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hu, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, Q. Polymer-Assisted Self-Assembly of Multicolor Carbon Dots as Solid-State Phosphors for Fabrication of Warm, High-Quality, and Temperature-Responsive White-Light-Emitting Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 22332–22338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, H.; Jorge, P.A.S.; Fernandes, J.R.A.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Hg(II) sensing based on functionalized carbon dots obtained by direct laser ablation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendão, R.M.S.; Crista, D.M.A.; Afonso, A.C.P.; Martínez de Yuso, M.d.V.; Algarra, M.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.; Pinto da Silva, L. Insight into the hybrid luminescence showed by carbon dots and molecular fluorophores in solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 20919–20926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, F.; Hosseini, M.; Zare-Dorabei, R.; Salehnia, F.; Ganjali, M.R. Fluorescent turn on sensing of Caffeine in food sample based on sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots and optimization of process parameters through response surface methodology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri, S.; Kumar, R.; Panda, A.K.; Solanki, P.R. Highly Biocompatible, Fluorescence, and Zwitterionic Carbon Dots as a Novel Approach for Bioimaging Applications in Cancerous Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 37835–37845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, E.F.C.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; Leitão, J.M.M. Carbon dots from tryptophan doped glucose for peroxynitrite sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 852, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Gao, P.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Hu, J. Bottom-up synthesis and structural design strategy for graphene quantum dots with tunable emission to the near infrared region. Carbon 2019, 142, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Das, J. Small molecules derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Xie, Z. Three Colors Emission from S,N Co-doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Visible Light H2 Production and Bioimaging. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Shao, D.; He, X.; Ren, Z.; Ji, W.; Shan, C.; Qu, S.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Q. Carbon dots as a trackable drug delivery carrier for localized cancer therapy in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5119–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Ushakova, E.V.; Rogach, A.L. Influence of molecular fluorophores on the research field of chemically synthesized carbon dots. Nano Today 2018, 23, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, W.; Świergosz, T.; Bednarz, S.; Walas, K.; Bashmakova, N.V.; Bogdał, D. Luminescence phenomena of carbon dots derived from citric acid and urea—A molecular insight. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13889–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martindale, B.C.M.; Hutton, G.A.M.; Caputo, C.A.; Reisner, E. Solar Hydrogen Production Using Carbon Quantum Dots and a Molecular Nickel Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6018–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, L. Nitrogen-Doping Enhanced Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Green Synthesis and Their Applications for Bioimaging and Label-Free Detection of Au 3+ Ions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3053–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; He, G.; Li, Z.; He, F.; Gao, F.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. A green heterogeneous synthesis of N-doped carbon dots and their photoluminescence applications in solid and aqueous states. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10307–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, B.; Fan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Xu, S.; Luo, X. Nitrogen doped carbon dots: Mechanism investigation and their application for label free CA125 analysis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3053–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Tang, Y.; Lu, H.; Yu, S.; Ding, X.; Xu, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Highly Photoluminescent and Stable N-Doped Carbon Dots as Nanoprobes for Hg2+ Detection. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, E.F.C.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.; Leitão, J.M.M. Peroxynitrite and nitric oxide fluorescence sensing by ethylenediamine doped carbon dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Anastas, P.T. Toward Green Nano. J. Ind. Ecol. 2008, 12, 316–328. [Google Scholar]
- Pourzahedi, L.; Eckelman, M.J. Comparative life cycle assessment of silver nanoparticle synthesis routes. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafana, A.; Kumar, S.V.; Temizel-Sekeryan, S.; Dahoumane, S.A.; Haselbach, L.; Jeffryes, C.S. Evaluating microwave-synthesized silver nanoparticles from silver nitrate with life cycle assessment techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Tang, F.; Adam, P.; Laratte, B.; Ionescu, R.E. Fate and Characterization Factors of Nanoparticles in Seventeen Subcontinental Freshwaters: A Case Study on Copper Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9370–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyayula, V.K.K.; Meyer, D.E.; Curran, M.A.; Gonzalez, M.A. Life cycle assessment as a tool to enhance the environmental performance of carbon nanotube products: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 26, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, S.; González-García, S.; Moldes-Diz, Y.; Vazquez-Vazquez, C.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Comparative life cycle assessment of different synthesis routes of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Teixeira, C.A.; Rouboa, A. Assessment study of an advanced gasification strategy at low temperature for syngas generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 10155–10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Afonso Teixeira, C.; Rouboa, A. Environmental Analysis of Waste-to-Energy—A Portuguese Case Study. Energies 2018, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Lakowicz, J.R., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 390, ISBN 978-0-387-31278-1. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.W. Quantitative Spectrofluorimetry—The Fluorescence Quantum Yield Of Quinine Sulfate. Photochem. Photobiol. 1967, 6, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannon, J.H.; Magde, D. Absolute quantum yield determination by thermal blooming. Fluorescein. J. Phys. Chem. 1978, 82, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hischier, R.; Walser, T. Life cycle assessment of engineered nanomaterials: State of the art and strategies to overcome existing gaps. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Steinmann, Z.J.N.; Elshout, P.M.F.; Stam, G.; Verones, F.; Vieira, M.; Zijp, M.; Hollander, A.; van Zelm, R. ReCiPe2016: A harmonised life cycle impact assessment method at midpoint and endpoint level. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Hultman, L. C 1s Peak of Adventitious Carbon Aligns to the Vacuum Level: Dire Consequences for Material’s Bonding Assignment by Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2017, 18, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Dickinson, C.; Lafir, F.; Brougham, D.F.; Marsili, E. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles biosynthesized with Rhizopus oryzae protein extract. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Song, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Pang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, B.; Peng, X. Carbon Dots with Red Emission for Sensing of Pt2+, Au3+, and Pd2+ and Their Bioapplications in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Yu, J.-S. How do nitrogen-doped carbon dots generate from molecular precursors? An investigation of the formation mechanism and a solution-based large-scale synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5608–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Ma, J.; Shan, X.; Feng, H.; Shao, L.; Chen, J. Highly luminescent N-doped carbon quantum dots as an effective multifunctional fluorescence sensing platform. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, T.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, F.-L.; Liu, Y. Microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization, cell imaging of fluorescent carbon dots using l-asparagine as precursor. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3323–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X.; Luo, Y.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Hydrothermal Treatment of Grass: A Low-Cost, Green Route to Nitrogen-Doped, Carbon-Rich, Photoluminescent Polymer Nanodots as an Effective Fluorescent Sensing Platform for Label-Free Detection of Cu(II) Ions. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Xiong, Y.; von Seckendorff, M.; Susha, A.S.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Molecular Fluorescence in Citric Acid-Based Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.B.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Bandosz, T.J.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; Algarra, M. Carbon dots coated with vitamin B 12 as selective ratiometric nanosensor for phenolic carbofuran. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Weng, L.-T.; Li, Y.; Lau, A.; Chan, C.K.; Chan, C.-M. Surface Chemical Composition of Size-Fractionated Urban Walkway Aerosols Determined by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchii, D.Y.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Bavykina, A.V.; Gascon, J. Revisiting Nitrogen Species in Covalent Triazine Frameworks. Langmuir 2017, 33, 14278–14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; He, F.; Gao, F.; Su, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Y. Nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.; Bin Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon dots: Synthesis, formation mechanism, fluorescence origin and sensing applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; Guardia, M. De la Optical bio(sensing) using nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots: Recent advances and future challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usachov, D.; Vilkov, O.; Grüneis, A.; Haberer, D.; Fedorov, A.; Adamchuk, V.K.; Preobrajenski, A.B.; Dudin, P.; Barinov, A.; Oehzelt, M.; et al. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene: Efficient Growth, Structure, and Electronic Properties. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5401–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, C.-M.; Liu, Z.; Lai, C.-S. N-Doped Graphene with Low Intrinsic Defect Densities via a Solid Source Doping Technique. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Isotani, S.; Mansano, R.D.; Sucasaire, W.; Pinto, R.A.C.; Mittani, J.C.R.; Ogata, K.; Kuratani, N. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Raman Spectroscopy Studies on Thin Carbon Nitride Films Deposited by Reactive RF Magnetron Sputtering. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2012, 02, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Mauro, N.; Buscarino, G.; Sciortino, L.; Popescu, R.; Schneider, R.; Giammona, G.; Gerthsen, D.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F. β-C3N4 Nanocrystals: Carbon Dots with Extraordinary Morphological, Structural, and Optical Homogeneity. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B. Investigation from chemical structure to photoluminescent mechanism: A type of carbon dots from the pyrolysis of citric acid and an amine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5976–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

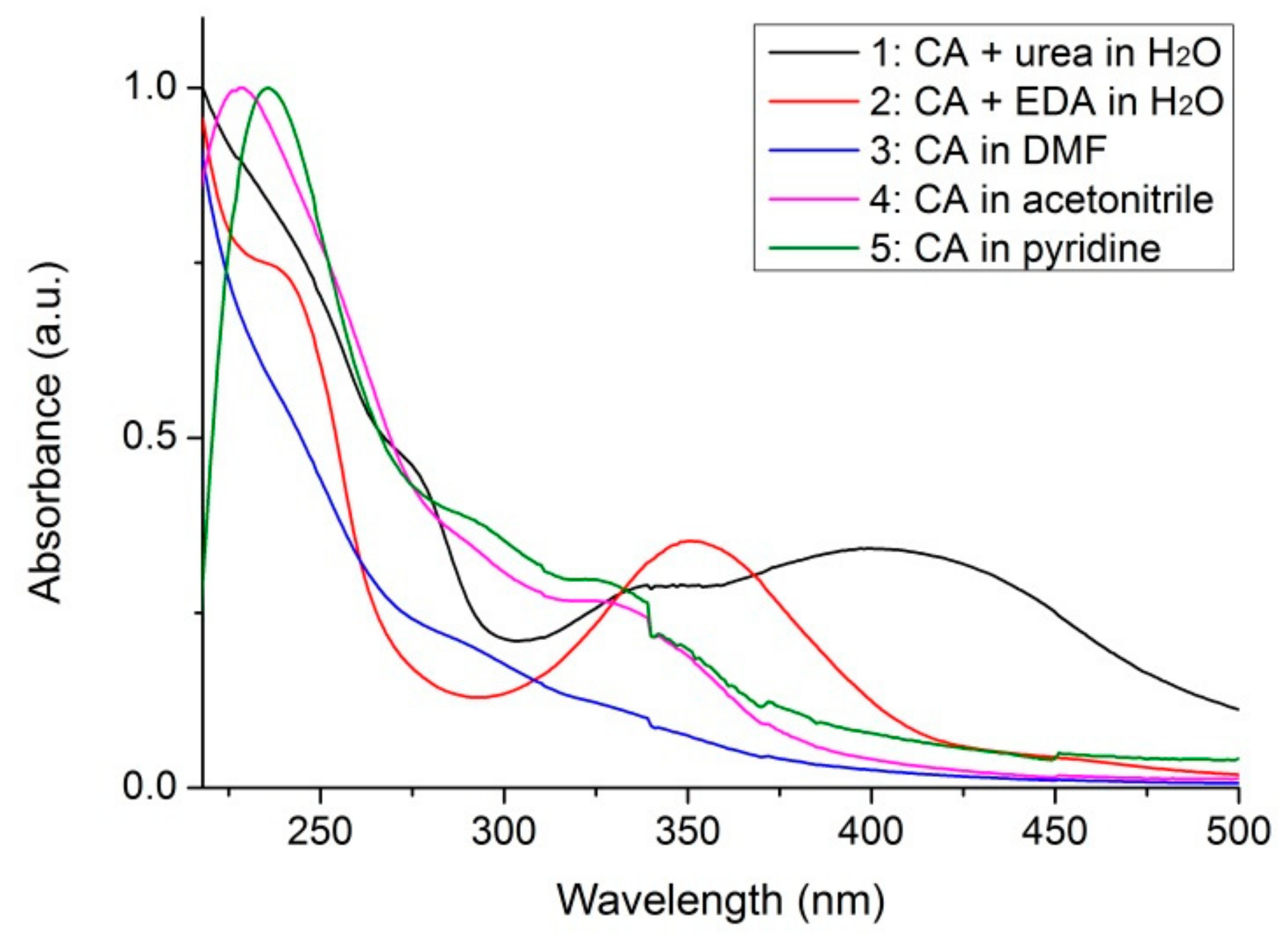

| CDs | 1: Citric Acid (CA) + Urea in H2O | 2: CA + Ethylenediamine (EDA) in H2O | 3: CA in n,n-Dimethylformamide (DMF) | 4: CA in Acetonitrile | 5: CA in Pyridine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction yield (%) | 7.9 | 7.3 | 4.4 | 7.3 | 0.4 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −0.6 | −0.2 | 0.6 | 2.1 | −2.4 |
| C 1s (at.%) | 60.9 | 68.5 | 70.9 | 63.1 | 74.8 |
| O 1s (at.%) | 23.7 | 16.5 | 22.2 | 36.4 | 23.6 |
| N 1s (at.%) | 15.4 | 15.0 | 6.9 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
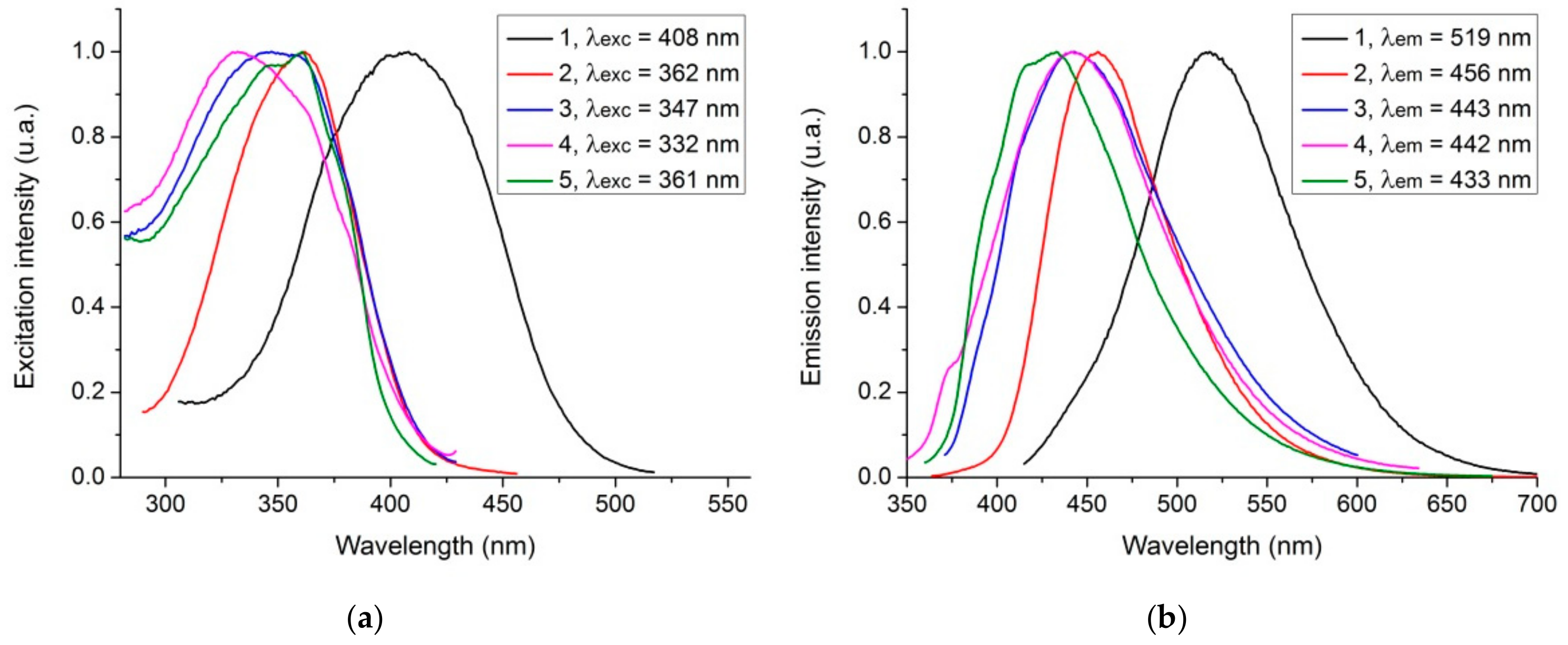
| CDs | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QYFL (%) | 37.4 | 3.1 | 3.5 | 2.4 | 2.3 |
| λexc (nm) | 410 | 360 | 350 | 330 | 360 |
| λem (nm) | 520 | 460 | 440 | 440 | 430 |
| CDs | 1A | 1B | 1C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction yield (%) | 7.9 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −0.6 | −1.4 | −3.3 |
| C 1s (at.%) | 60.9 | 61.7 | 65.2 |
| O 1s (at.%) | 23.7 | 22.8 | 21.0 |
| N 1s (at.%) | 15.4 | 15.6 | 13.9 |
| QYFL (%) | 37.4 | 3.5 | 3.3 |
| λexc (nm) | 410 | 370 | 370 |
| λem (nm) | 520 | 460 | 460 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christé, S.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.; Pinto da Silva, L. Evaluation of the Environmental Impact and Efficiency of N-Doping Strategies in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots. Materials 2020, 13, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030504
Christé S, Esteves da Silva JCG, Pinto da Silva L. Evaluation of the Environmental Impact and Efficiency of N-Doping Strategies in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots. Materials. 2020; 13(3):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030504
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristé, Suzanne, Joaquim C.G. Esteves da Silva, and Luís Pinto da Silva. 2020. "Evaluation of the Environmental Impact and Efficiency of N-Doping Strategies in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots" Materials 13, no. 3: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030504
APA StyleChristé, S., Esteves da Silva, J. C. G., & Pinto da Silva, L. (2020). Evaluation of the Environmental Impact and Efficiency of N-Doping Strategies in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots. Materials, 13(3), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030504







