Highly Ductile and Ultra-Thick P-Doped FeSiB Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
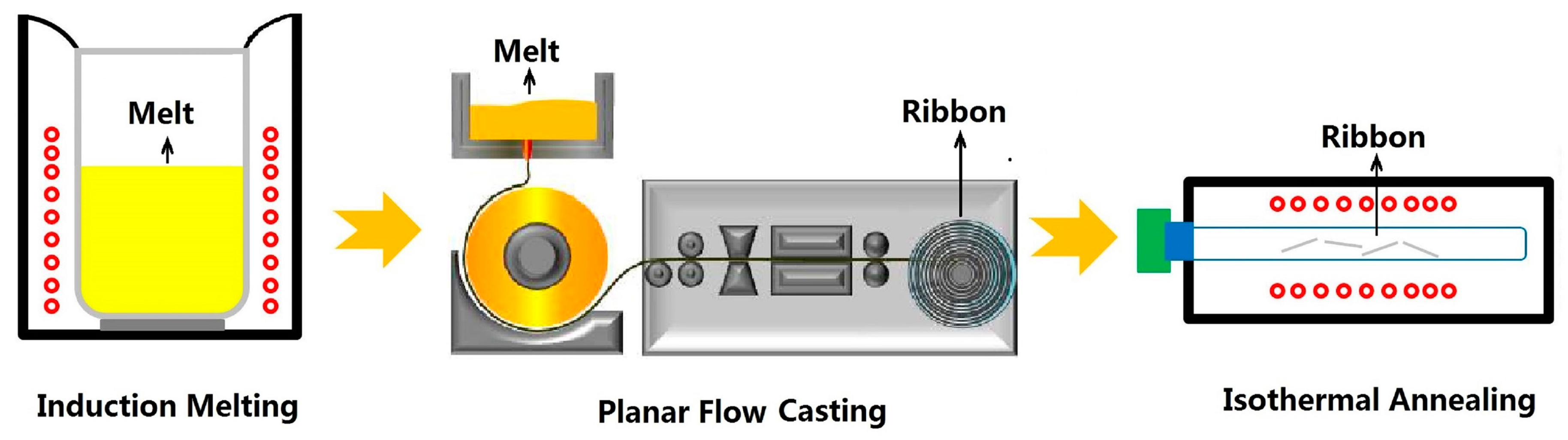
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results
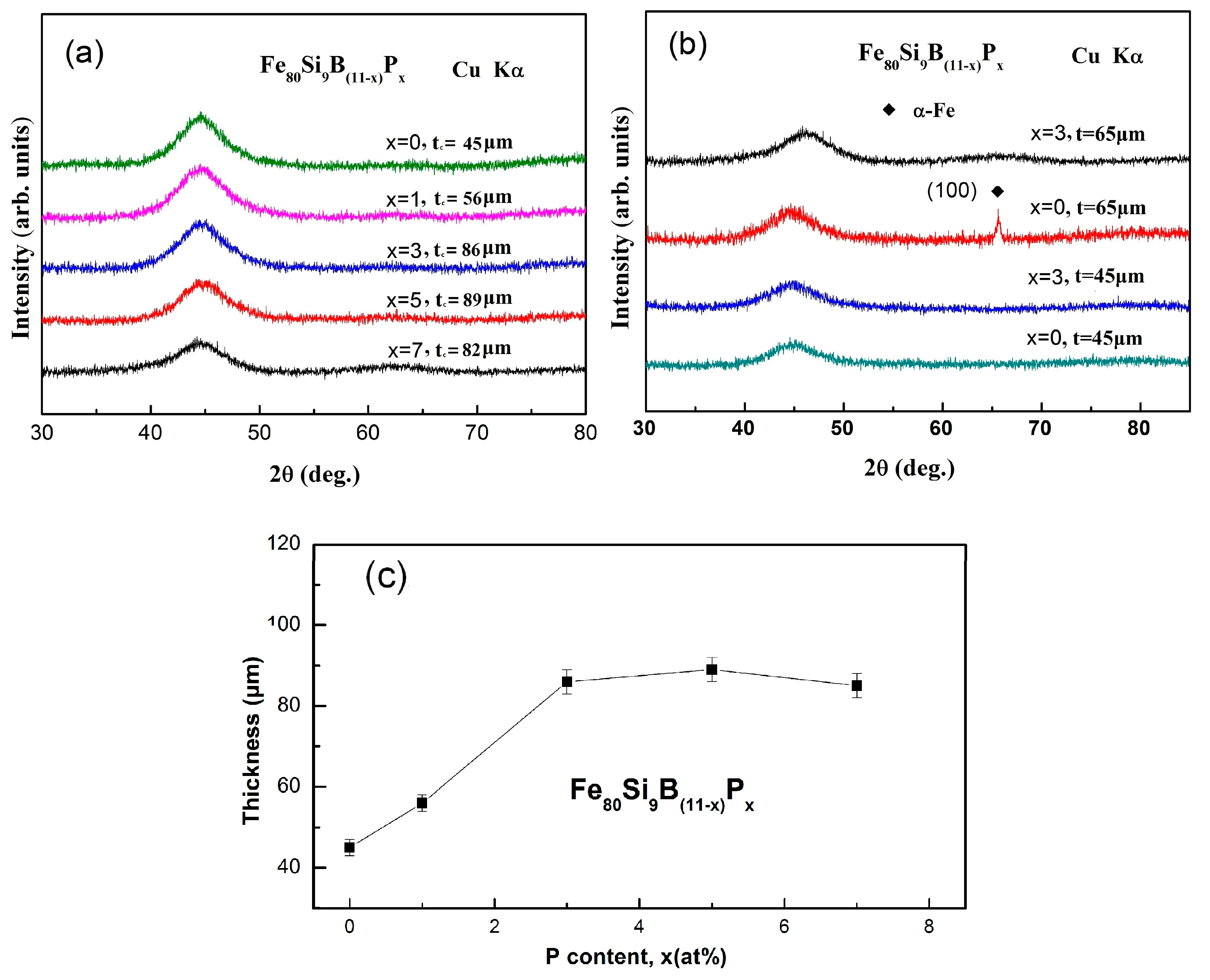
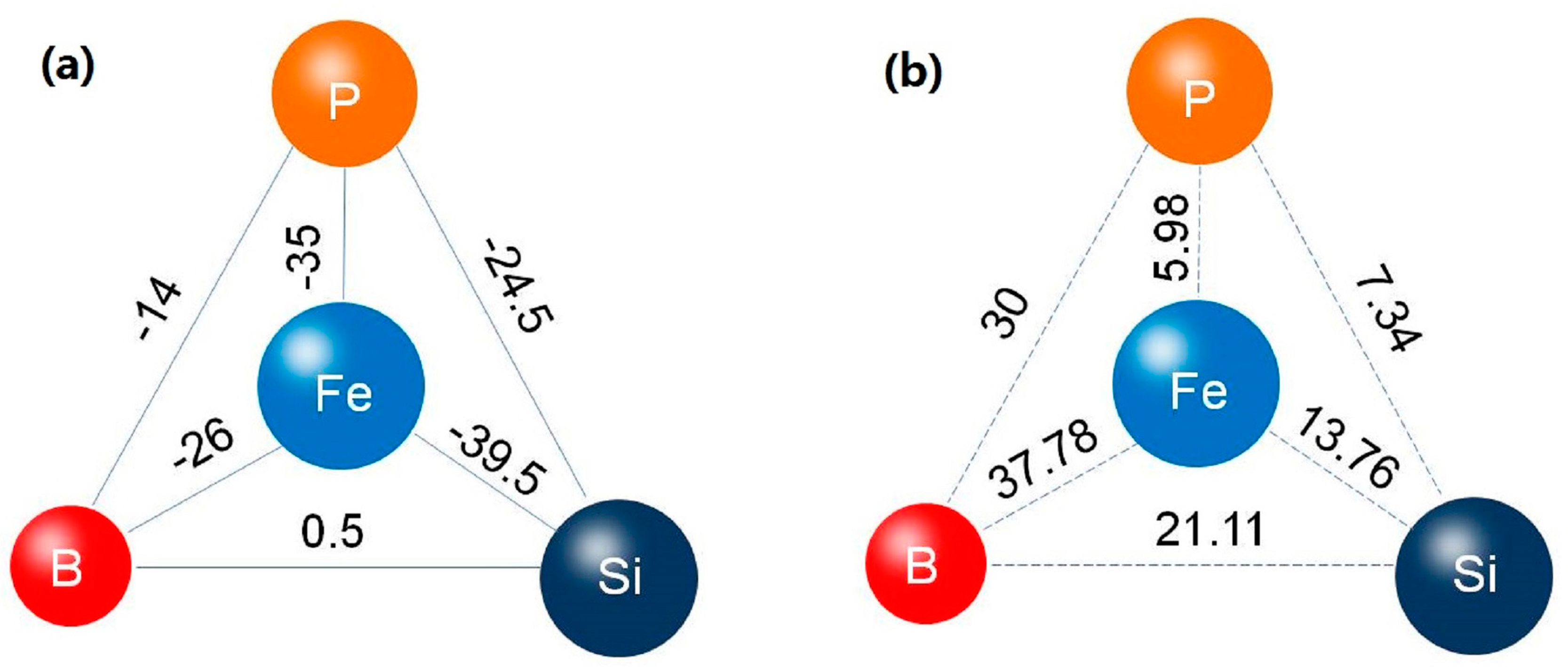
3.1. Glass Forming Ability (GFA) Analysis
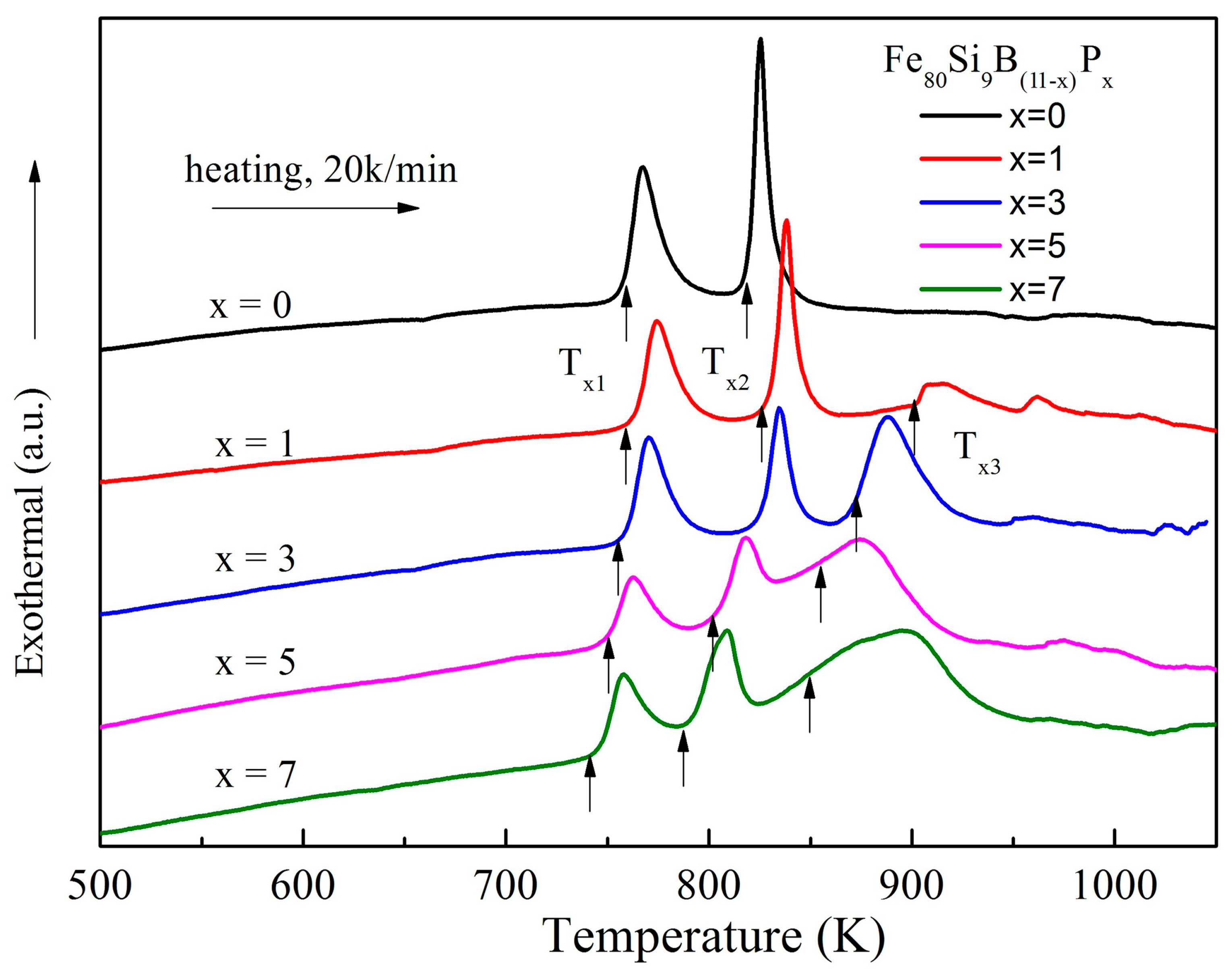
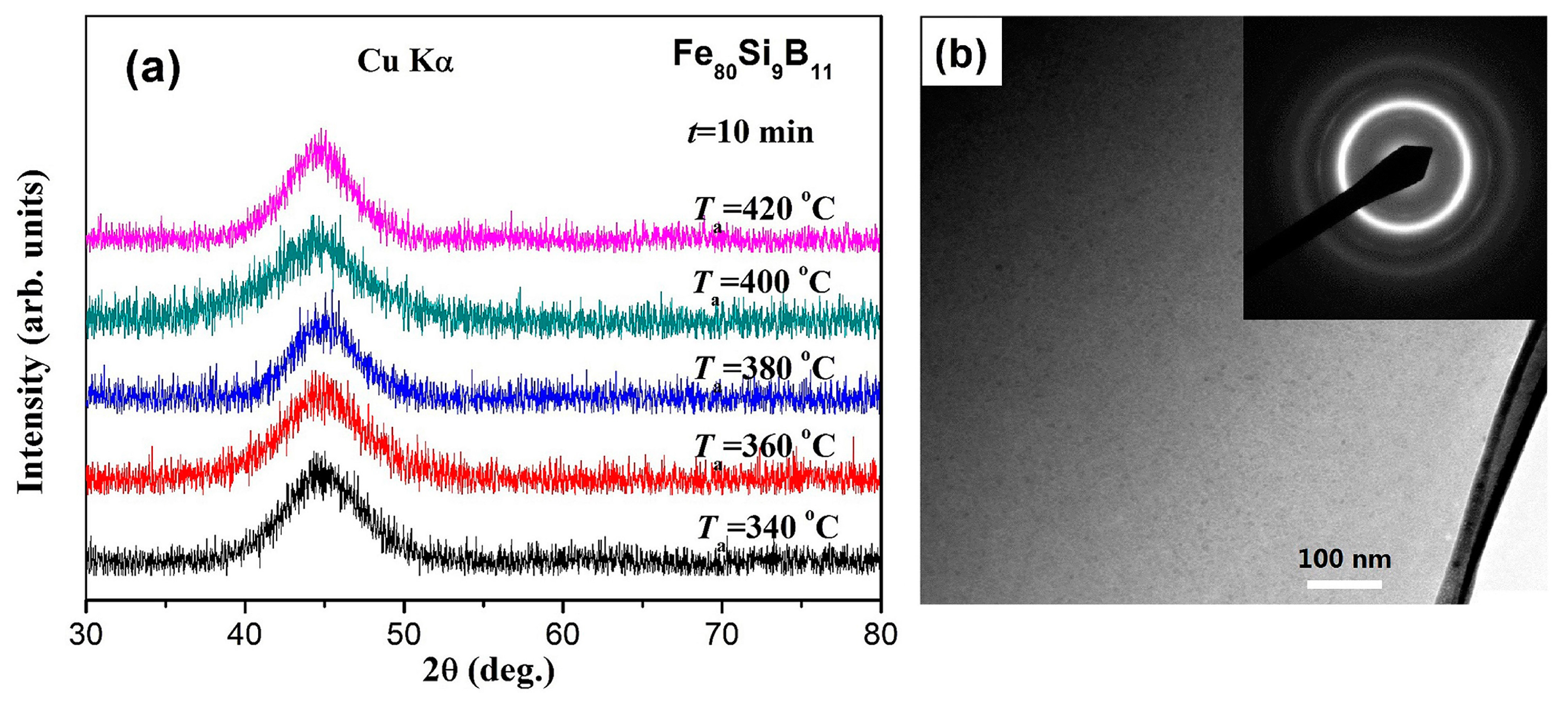
3.2. Crystallization Characteristics
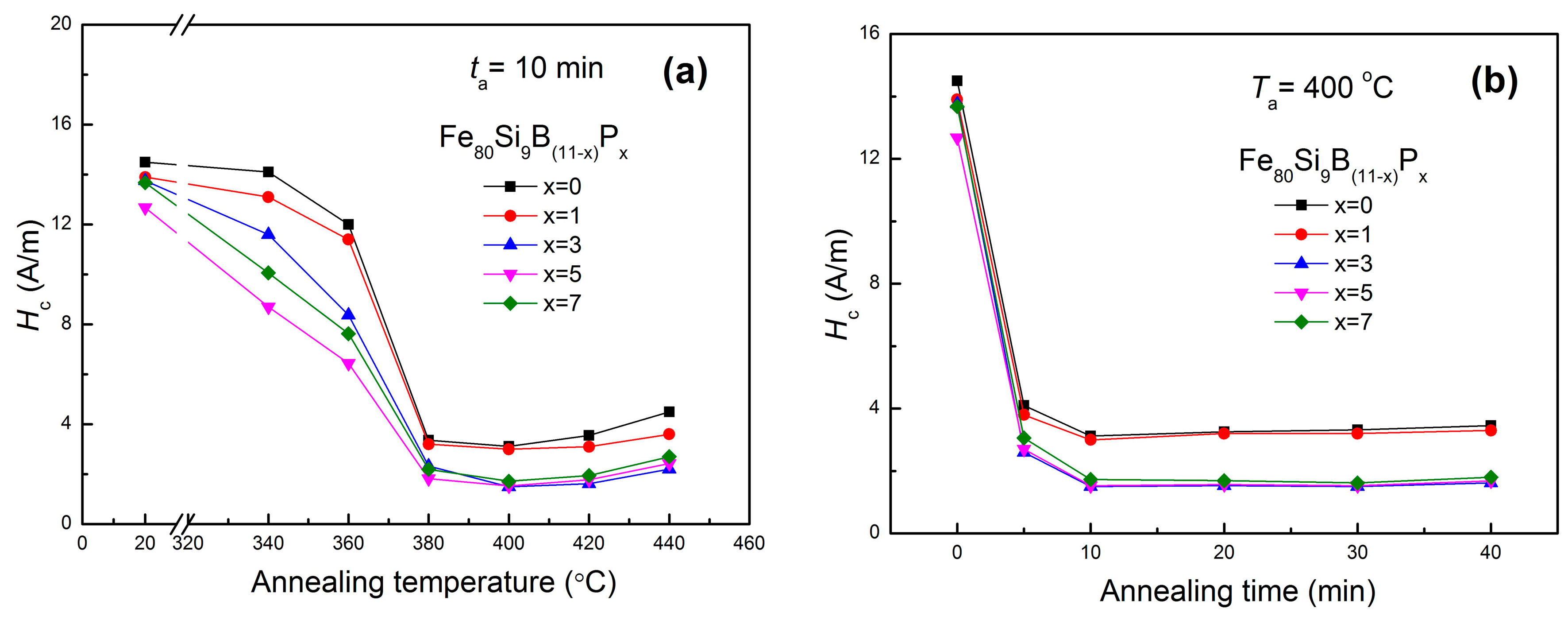
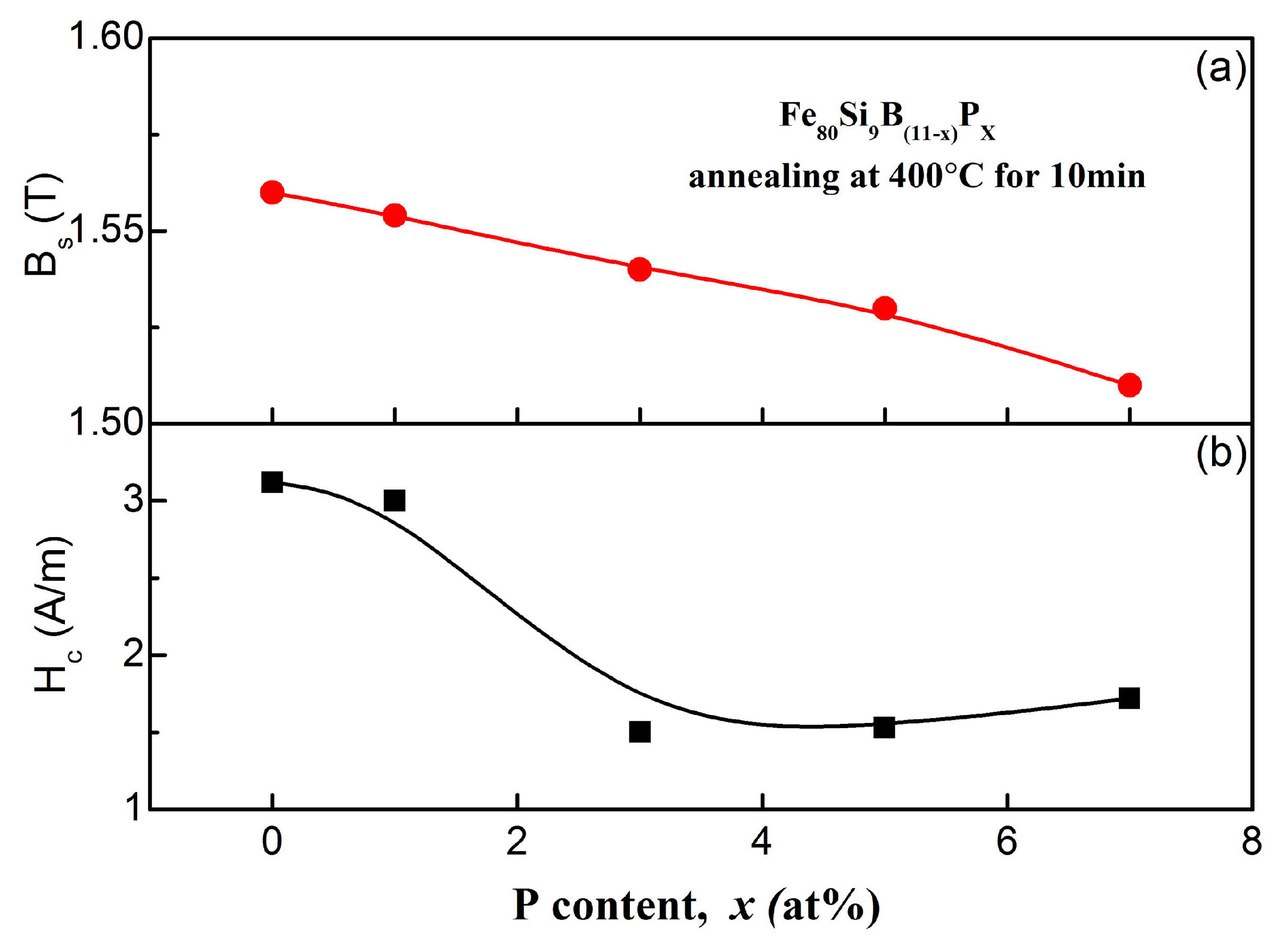
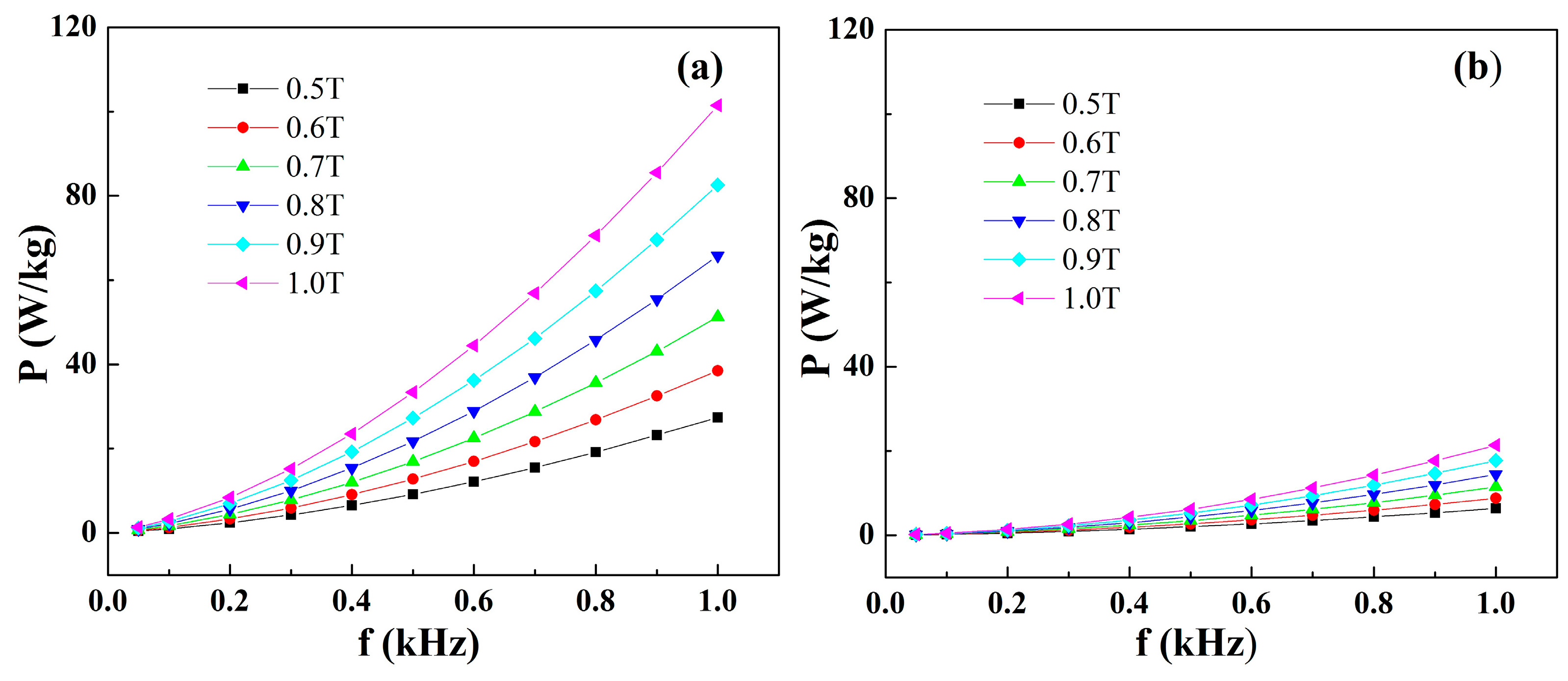
3.3. Soft Magnetic Characteristics
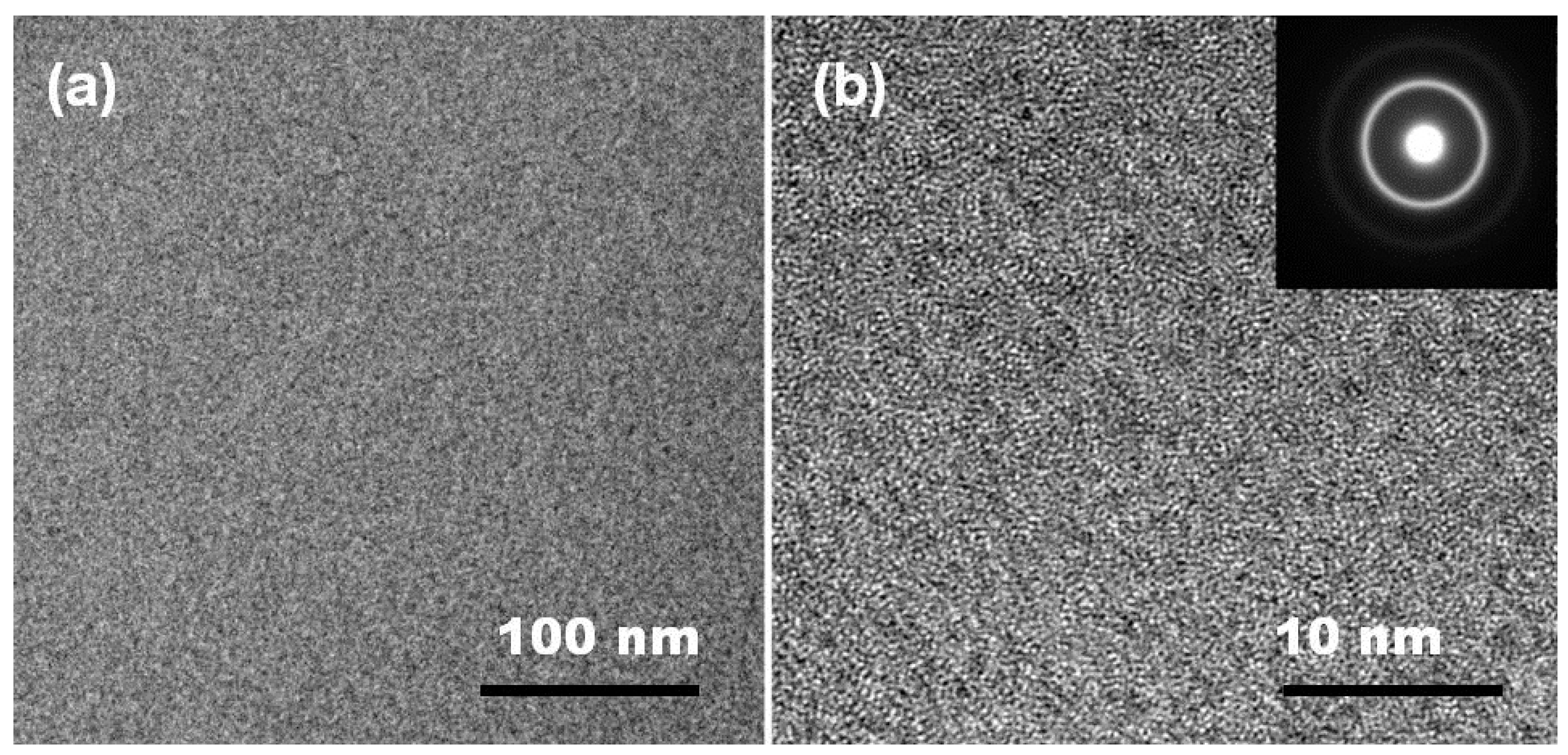
3.4. Microstructural Analysis
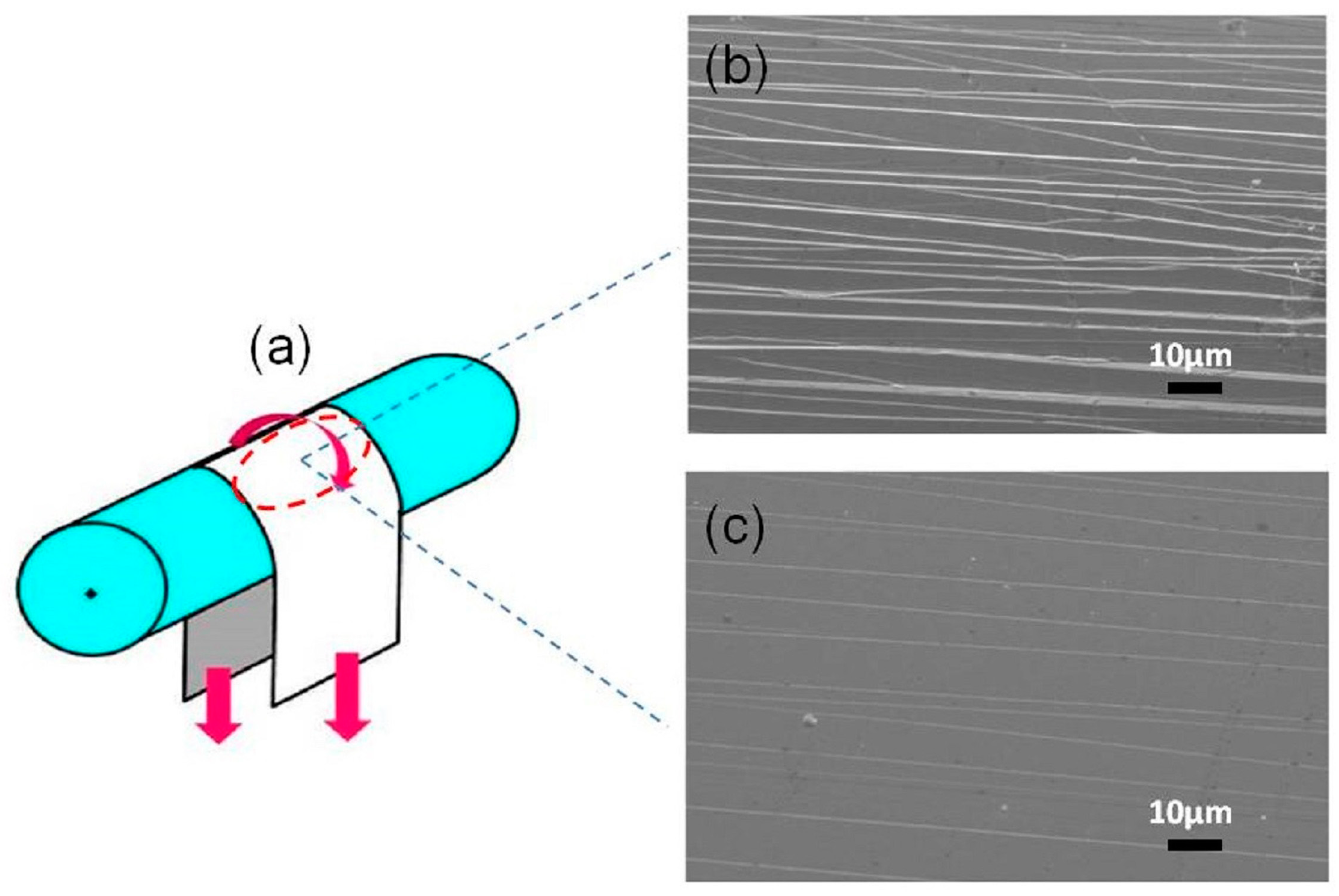
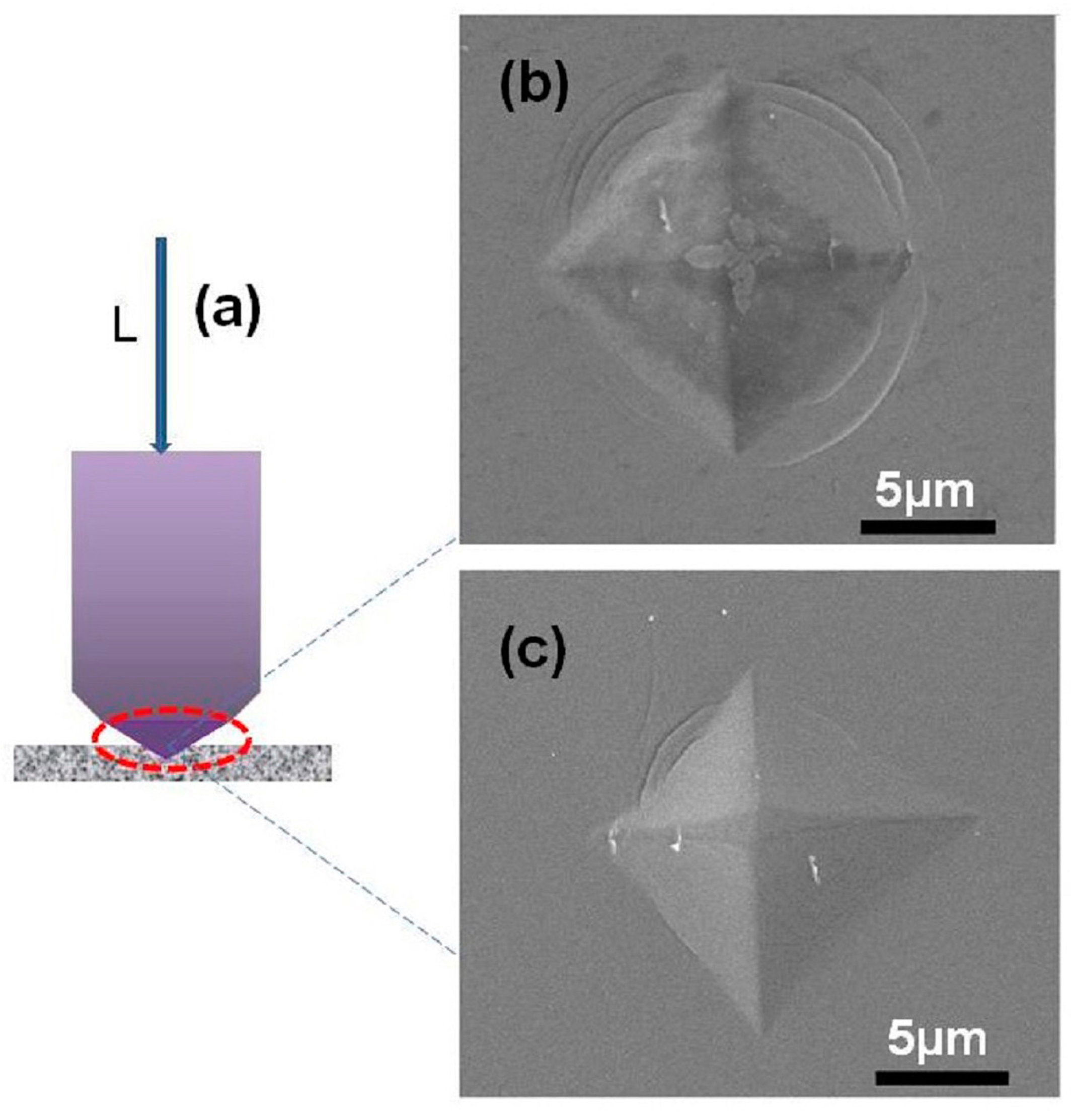
3.5. Mechanical Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amjad, S.; Neelakrishnan, S.; Rudramoorthy, R. Review of design considerations and technological challenges for successful development and deployment of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, Y.; Sun, X.; Jiang, L.; Pong, P.W. Magnetics in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soinski, M.; Leszczynski, J.; Swieboda, C.; Kwiecien, M. Nanocrystalline block cores for high-frequency chokes. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 2801904:1–2801904:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, A.M.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; McHenry, M.E. Soft magnetic materials in high-frequency, high-power conversion applications. JOM 2012, 64, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, R.; Azuma, D. Impacts of amorphous metal-based transformers on energy efficiency and environment. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2451–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simizu, S.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; McHenry, M.E. Metal amorphous nanocomposite soft magnetic material-enabled high power density, rare earth free rotational machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Li, Q.; Wen, X. Development of a high power density motor made of amorphous alloy cores. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 4510–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, H.; Chu, D.; Xie, S.; Sun, H.; Ferry, M.; Li, S. Composition dependence of the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys: A review study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 391, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y. Loss deterioration in amorphous cores for distribution transformers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 160, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolano, R.; Kolano-Burian, A.; Polak, M.; Szynowski, J. Application of rapidly quenched soft magnetic materials in energy-saving electric equipment. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 2004804:1–2004804:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, R.; Mechler, G.; Zhou, G. Calculation of core hot-spot temperature in power and distribution transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2002, 17, 991–995. [Google Scholar]
- Kefalas, T.D.; Magdaleno-Adame, S. Techno-economic comparative evaluation of mixed and conventional magnetic wound cores for three-phase distribution transformers. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 155, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauder, T.; Hameyer, K. Performance factor comparison of nanocrystalline, amorphous, and crystalline soft magnetic materials for medium-frequency applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, P.; Biela, J. Influence of material properties and geometric shape of magnetic cores on acoustic noise emission of medium-frequency transformers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 32, 7916–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgilakis, P.S.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Doulamis, N.D.; Doulamis, A.D.; Kollias, S.D. Prediction of iron losses of wound core distribution transformers based on artificial neural networks. Neurocomputing 1998, 23, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, I.; Olivares-Galván, J.C.; Georgilakis, P.S.; Cañedo, J.M. A novel octagonal wound core for distribution transformers validated by electromagnetic field analysis and comparison with conventional wound core. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoiralis, E.I.; Tsili, M.A.; Kladas, A.G. Transformer design and optimization: A literature survey. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2009, 24, 1999–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Ohnuma, M.; Furubayashi, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. Thermal embrittlement of Fe-based amorphous ribbons. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Bian, X.; Wang, W. Origin of ductile–brittle transition of amorphous Fe78Si9B13 ribbon during low temperature annealing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 341, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Naoe, M.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Hasegawa, R. Magnetic properties of high Bs Fe-based amorphous material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Inoue, A. On glass-forming ability of Fe-based amorphous alloys. Mater. Lett. 1999, 38, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kim, K.; Yi, S. Enhanced glass-forming ability of Fe-based bulk metallic glasses prepared using hot metal and commercial raw materials through the optimization of mo content. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-H.; Dong, C.; Shek, C. Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2004, 44, 45–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Martin, L.; Luzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Inoue, A. Role of alloying additions in glass formation and properties of bulk metallic glasses. Materials 2010, 3, 5320–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, A.; Kubota, T.; Chang, C.; Makabe, M.; Inoue, A. Fe-metalloids bulk glassy alloys with high Fe content and high glass-forming ability. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, Q.; Li, Q.; Jiang, B.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y. Development of Fe-based bulk metallic glasses as potential biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Yang, W.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z. Influences of oxygen on plastic deformation of a Fe-based bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2017, 135, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Iron-based bulk metallic glasses. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 131–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J. Short-range order and thermal stability in amorphous alloys. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1984, 14, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.L. Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the crystal to glass transformation in metallic materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1986, 30, 81–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.K.; Sheng, H.W.; Alamgir, F.M.; Bai, J.M.; He, J.H.; Ma, E. Icosahedral short-range order in amorphous alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 145502:1–145502:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egami, T. Structural relaxation in amorphous alloys—compositional short range ordering. Mater. Res. Bull. 1978, 13, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z.; Wang, A.D.; Chang, C.T.; Wang, Y.G.; Dong, B.S.; Zhou, S.X. Synthesis of fesibpnbcu nanocrystalline soft-magnetic alloys with high saturation magnetization. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 611, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Liu, H.S.; Dou, L.T.; Yang, W.M.; Chang, C.T.; Inoue, A.; Wang, X.M.; Li, R.W.; Shen, B.L. Soft magnetic properties and microstructure of Fe84−xNb2B14Cux nanocrystalline alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmaier, W. A method for the determination of ductility for thin metallic materials. ASTM Spec. Tech. Publ. 1982, 753, 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.P.; Bei, H.; Liu, C.T. Recent progress in quantifying glass-forming ability of bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B. Effect of the atomic size distribution on glass forming ability of amorphous metallic alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 2001, 36, 2183–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R.; Schroers, J.; Wang, W. Thermodynamics and kinetics of bulk metallic glass. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, M.; Majumdar, B.; Phanikumar, G.; Akhtar, D. Effect of Planar Flow Melt Spinning Parameters on Ribbon Formation in Soft Magnetic Fe68.5Si18.5B9Nb3Cu1 Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2011, 42, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, H.; Mühlbach, H.; Stephani, G. The effect of the main processing parameters on the geometry of amorphous metal ribbons during planar flow casting (PFC). J. Mater. Sci. 1984, 19, 3229–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axinte, E. Metallic glasses from “alchemy” to pure science: Present and future of design, processing and applications of glassy metals. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 518–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z.; Wang, A.D.; Chang, C.T.; Wang, Y.G.; Dong, B.S.; Zhou, S.X. FeSiBPNbCu alloys with high glass-forming ability and good soft magnetic properties. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsepelev, V.; Konashkov, V.; Starodubtsev, Y.; Belozerov, V.; Gaipishevarov, D. Optimum regime of heat treatment of soft magnetic amorphous materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapperi, S.; Cizeau, P.; Durin, G.; Stanley, H.E. Dynamics of a ferromagnetic domain wall: Avalanches, depinning transition, and the barkhausen effect. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 6353–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitoh, T.; Makino, A.; Inoue, A. Origin of low coercivity of (Fe0.75B0.15Si0.10)100−xNbx (x = 1–4) glassy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08F102:1–08F102:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Lass, E.A.; Poon, S.J.; Shiflet, G.J.; Rawlings, M.; Daniil, M.; Willard, M.A. Magnetic properties and thermal stability of (Fe,Co)-Mo-B-P-Si metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 063906:1–063906:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Bae, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, T.; Lavernia, E.; Lee, Z. Ordering–disordering phenomena and micro-hardness characteristics of B2 phase in Fe–(5–6.5%) Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 407, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. Mechanical behavior of metallic glasses: Microscopic understanding of strength and ductility. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 445–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Park, K.-W.; Kim, K.-H.; Fleury, E.; Lee, B.-J.; Wakeda, M.; Shibutani, Y. Origin of the plasticity in bulk amorphous alloys. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, A.J.; Sheng, H.; Ma, E. Local order influences initiation of plastic flow in metallic glass: Effects of alloy composition and sample cooling history. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 5263–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, W. Highly Ductile and Ultra-Thick P-Doped FeSiB Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071148
Li Z, Zhou S, Zhang G, Zheng W. Highly Ductile and Ultra-Thick P-Doped FeSiB Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071148
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zongzhen, Shaoxiong Zhou, Guangqiang Zhang, and Wei Zheng. 2018. "Highly Ductile and Ultra-Thick P-Doped FeSiB Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties" Materials 11, no. 7: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071148
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhou, S., Zhang, G., & Zheng, W. (2018). Highly Ductile and Ultra-Thick P-Doped FeSiB Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials, 11(7), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071148



