Effects of Cutting Edge Microgeometry on Residual Stress in Orthogonal Cutting of Inconel 718 by FEM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
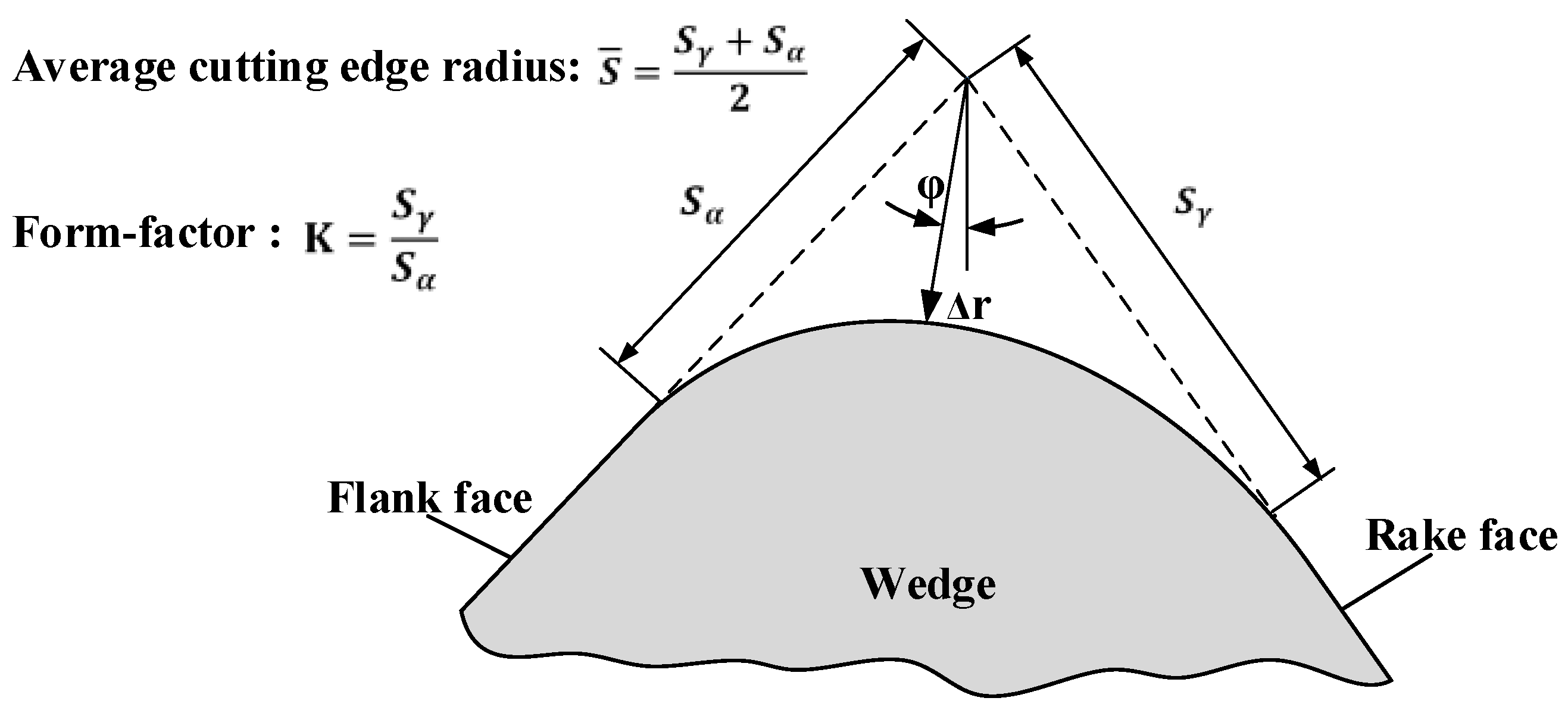
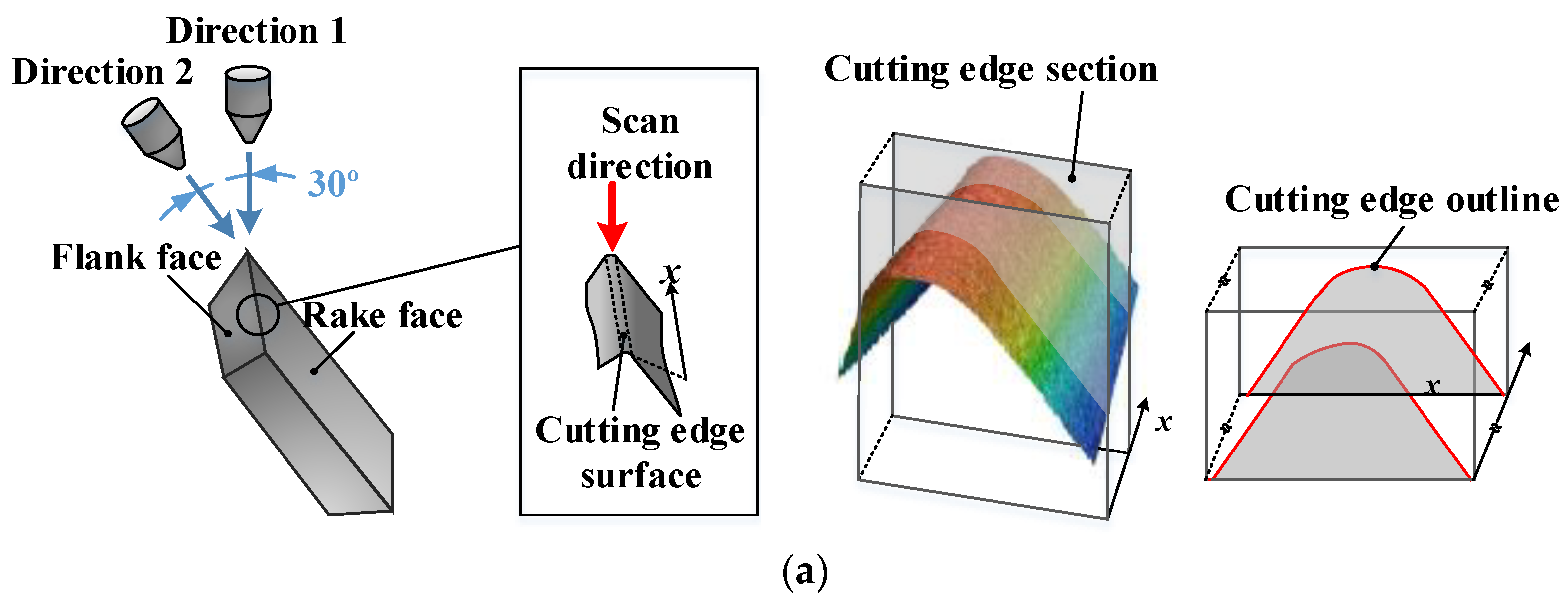
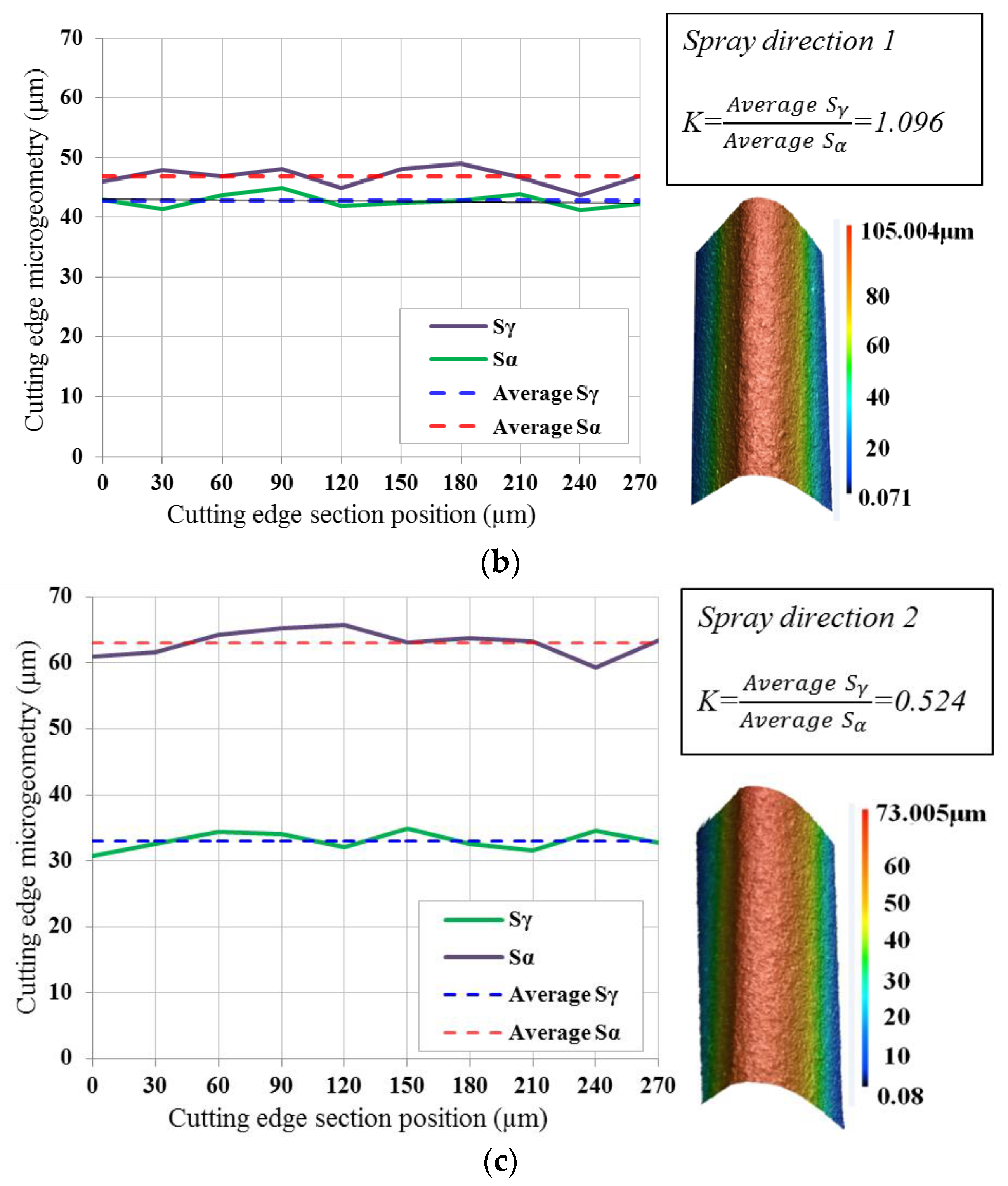
2. Cutting Edge Characterization and Edge Preparation
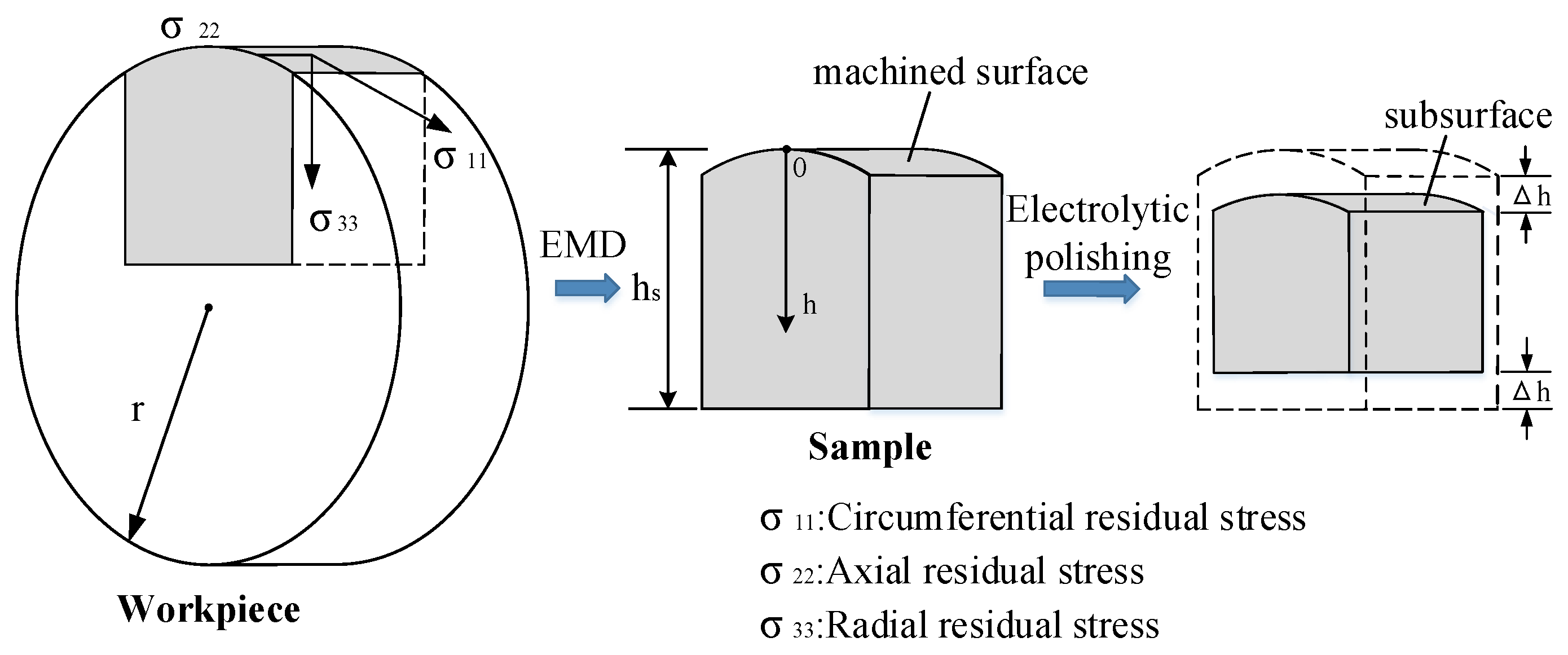
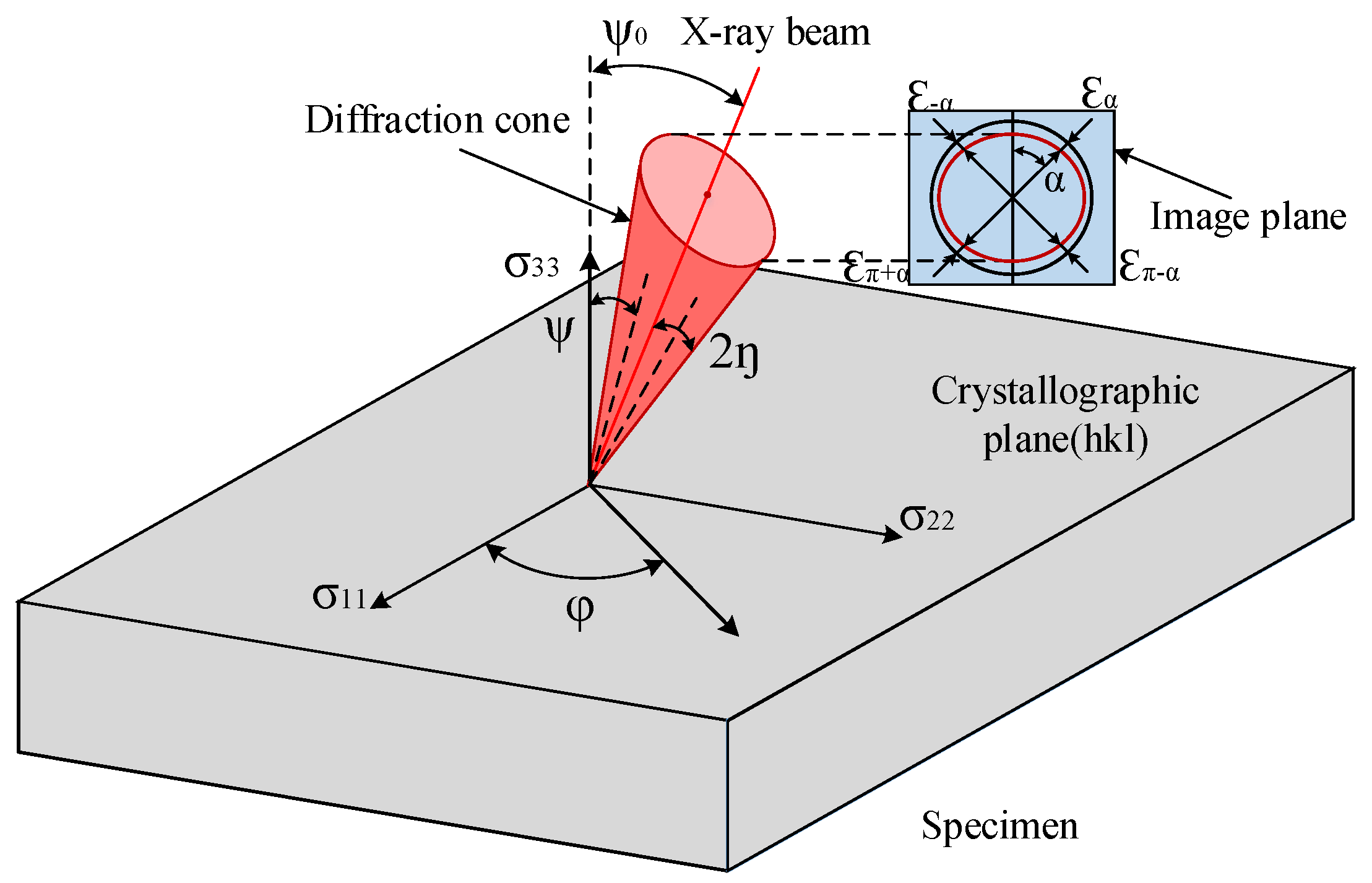
3. Orthogonal Experiments and Measurements of Residual Stress
4. Numerical Modeling
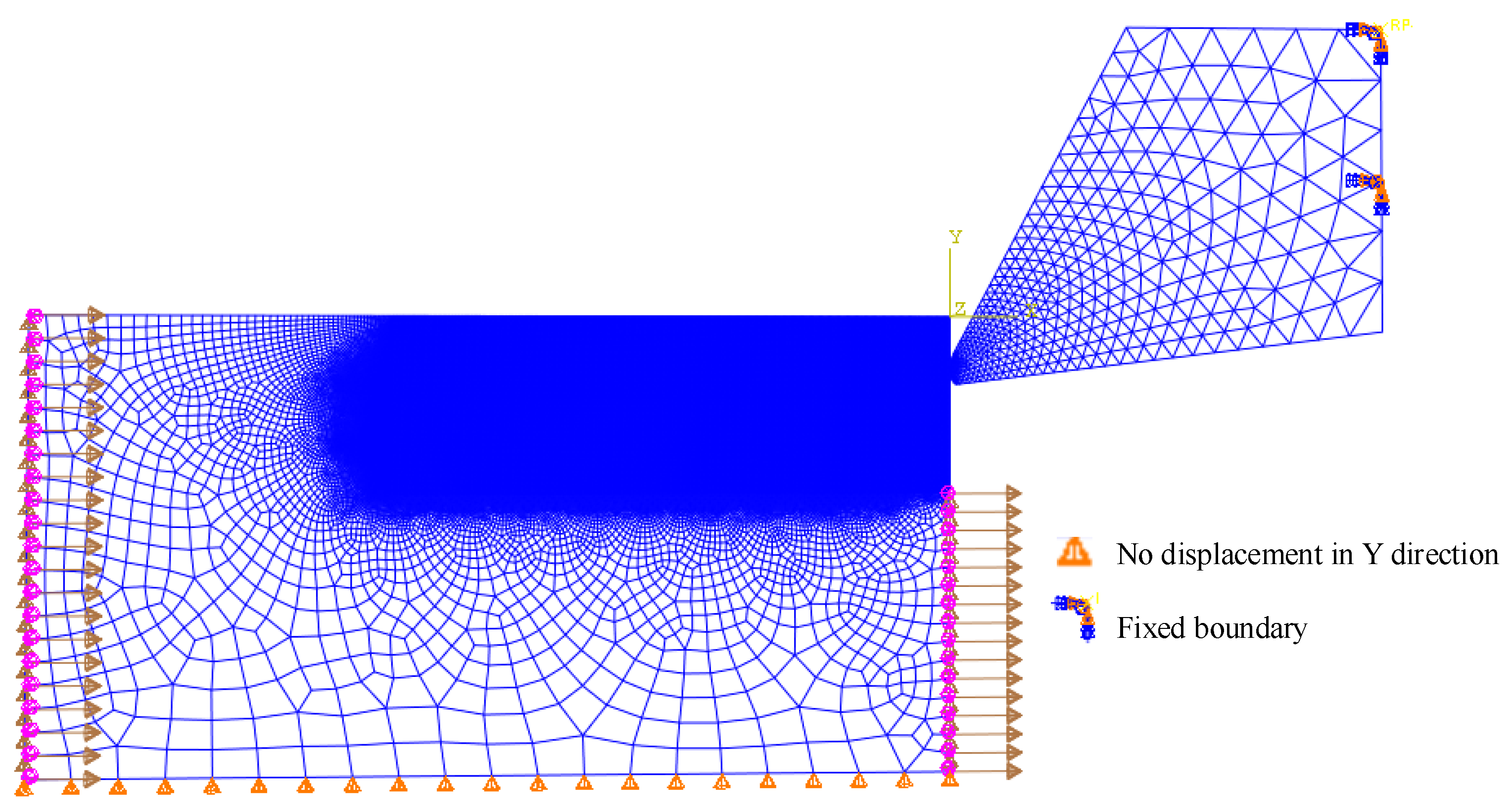
4.1. Geometry Modeling and Mesh Controlling
4.2. Initial Conditions
5. Results and Discussions
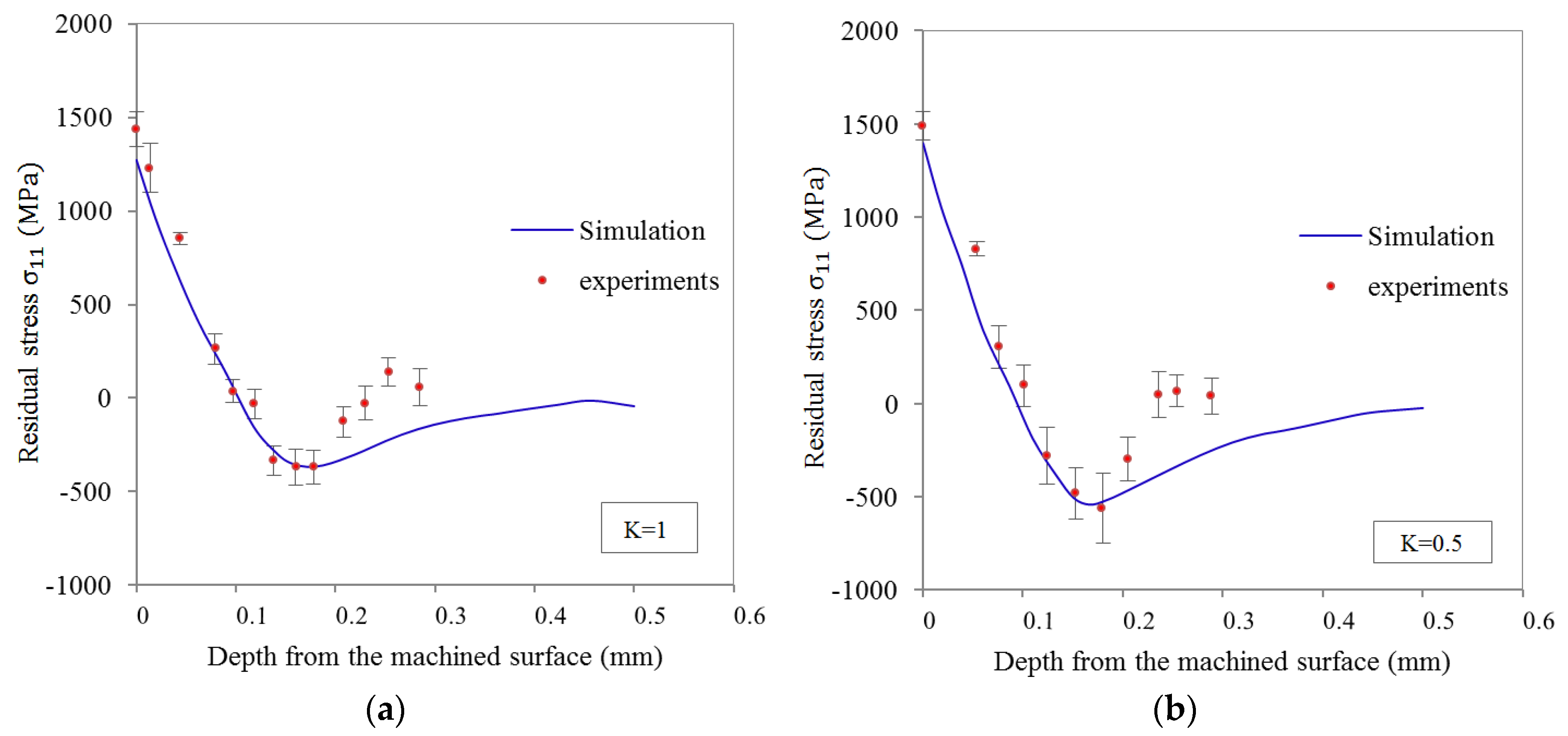
5.1. Validation of FE Model
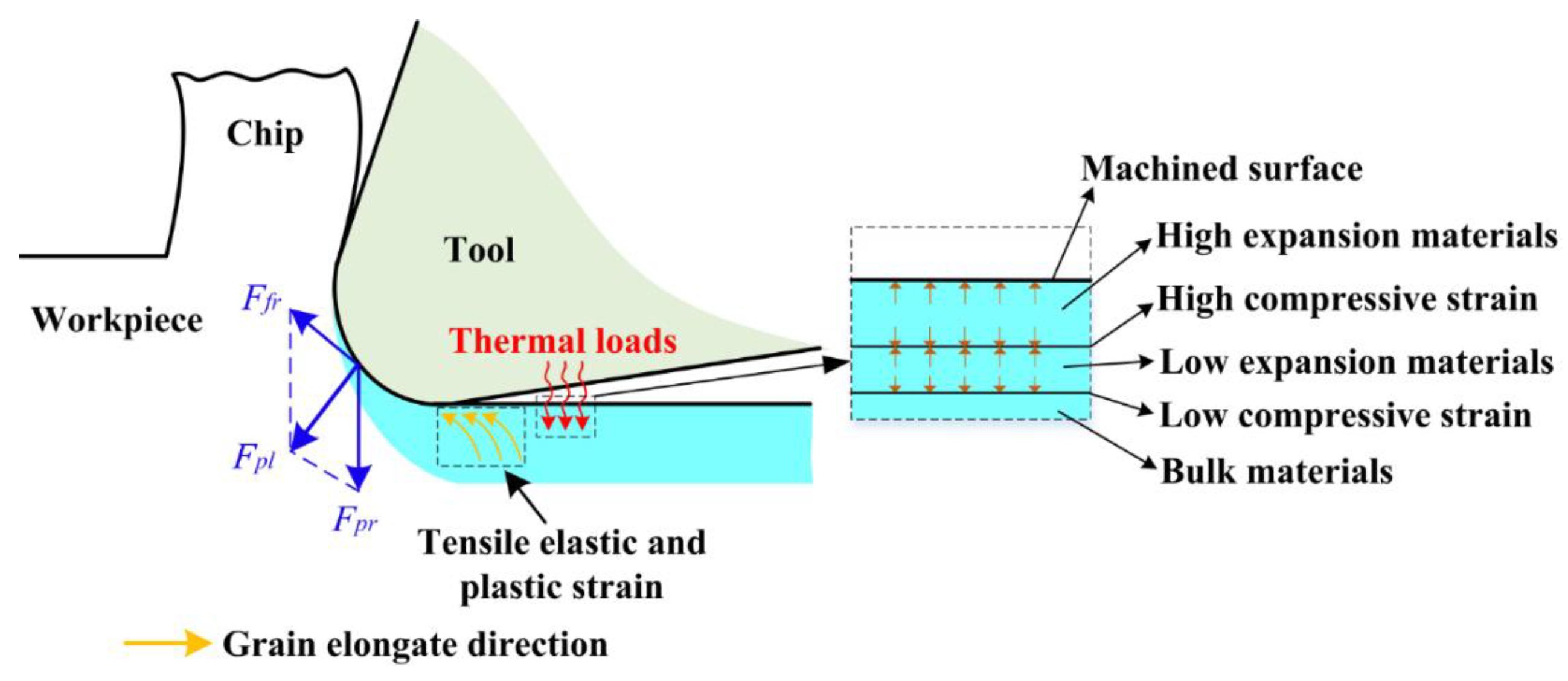
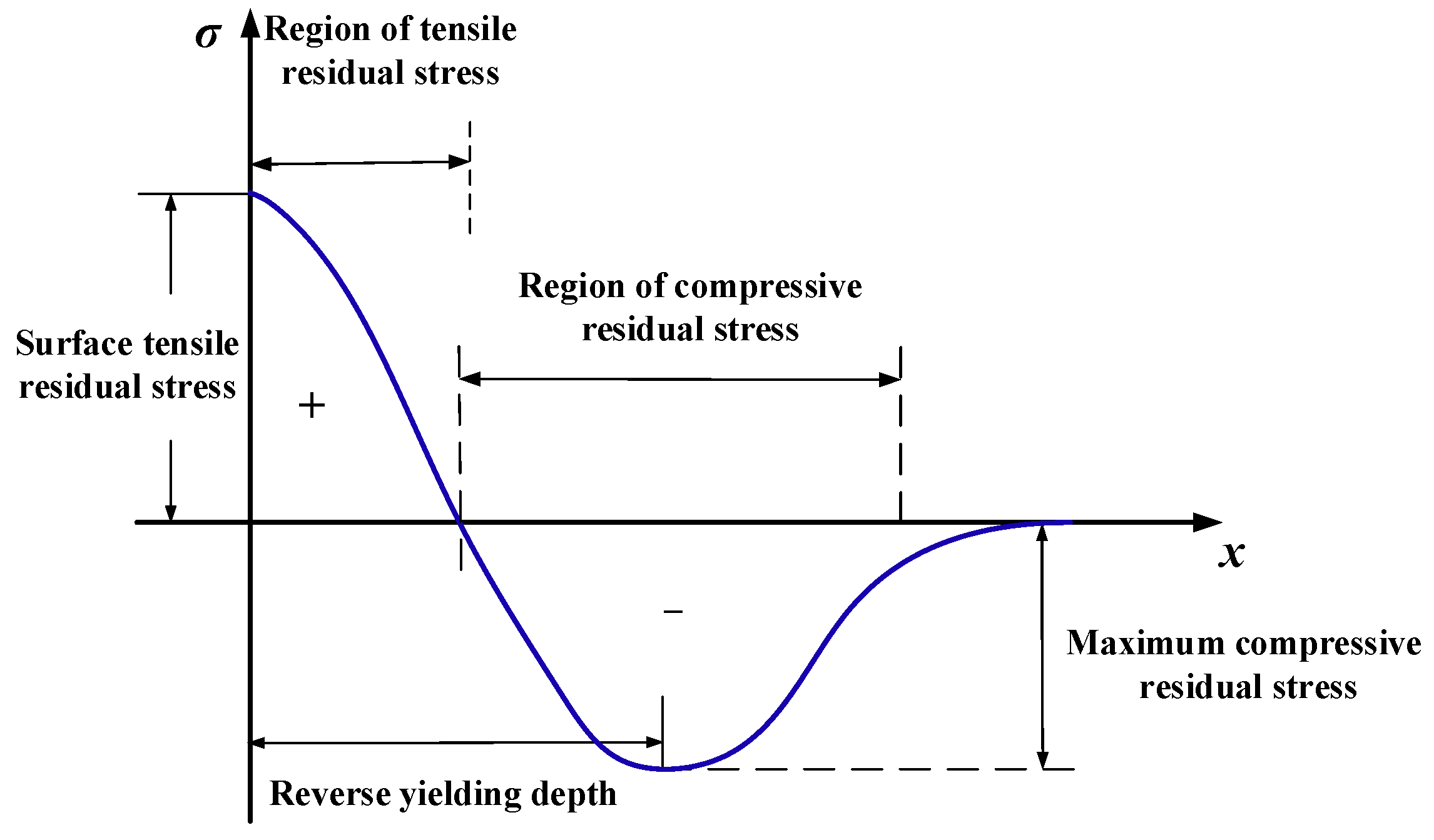
5.2. Formation Mechanism of Residual Stress
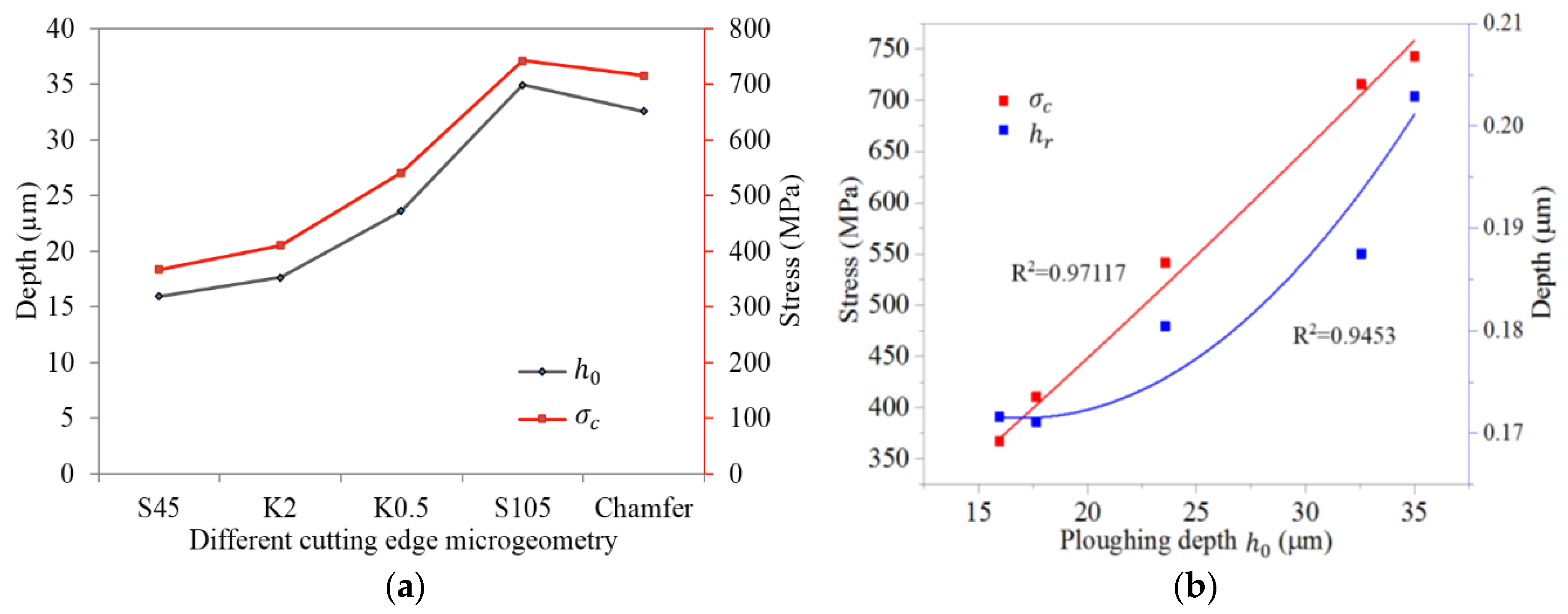
5.3. Effects of Cutting Edge Microgeometry on the Variation of Residual Stress
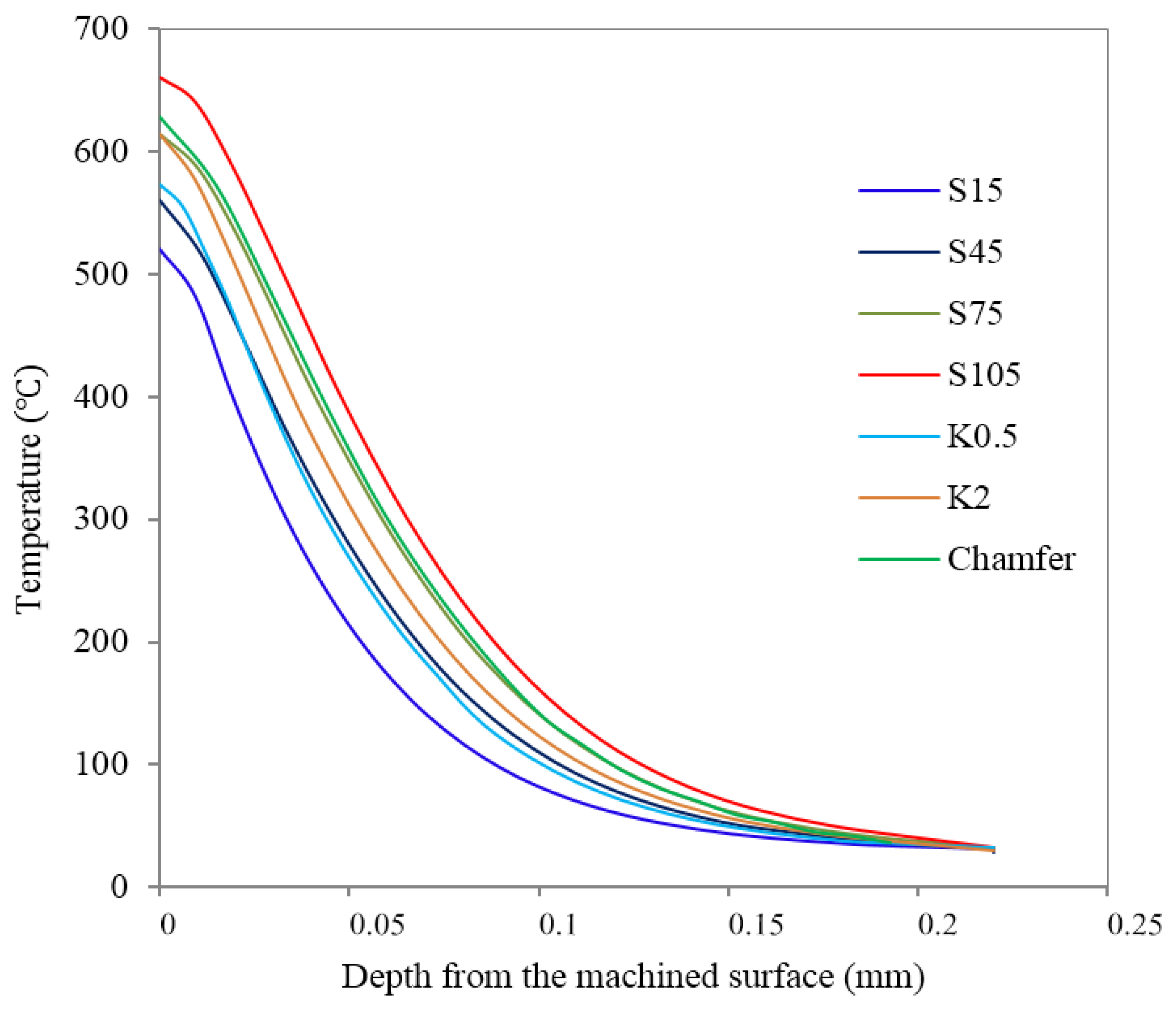
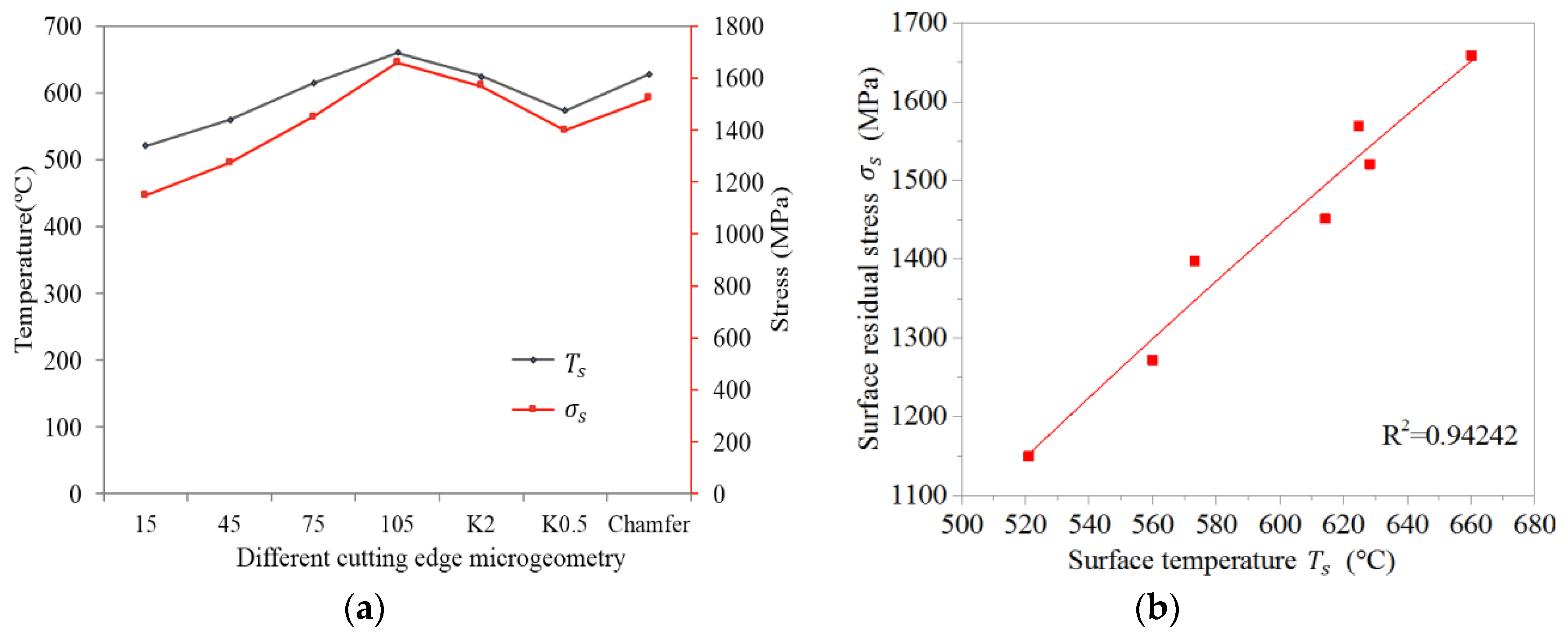
5.4. Temperature Distribution and Tensile Residual Stress
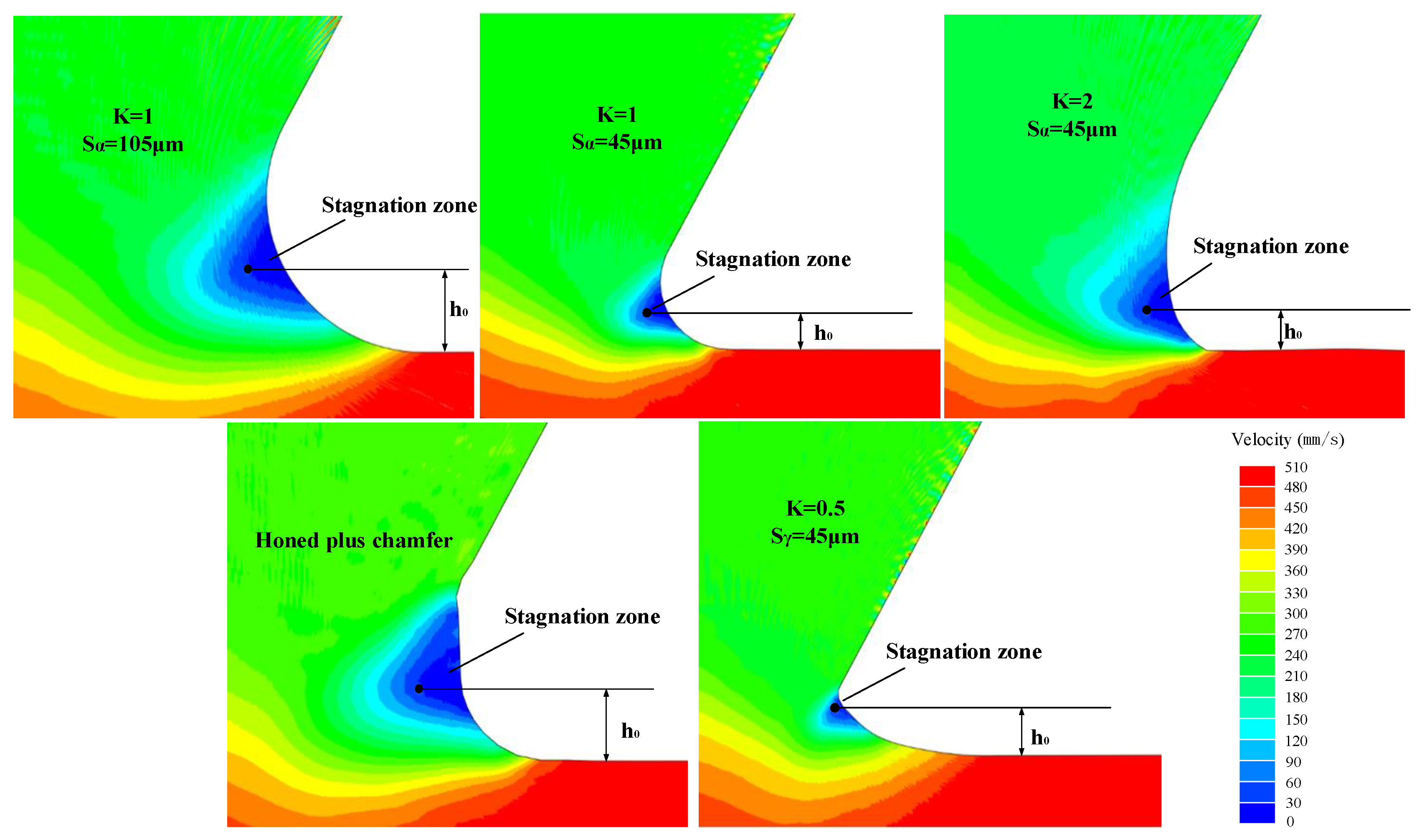
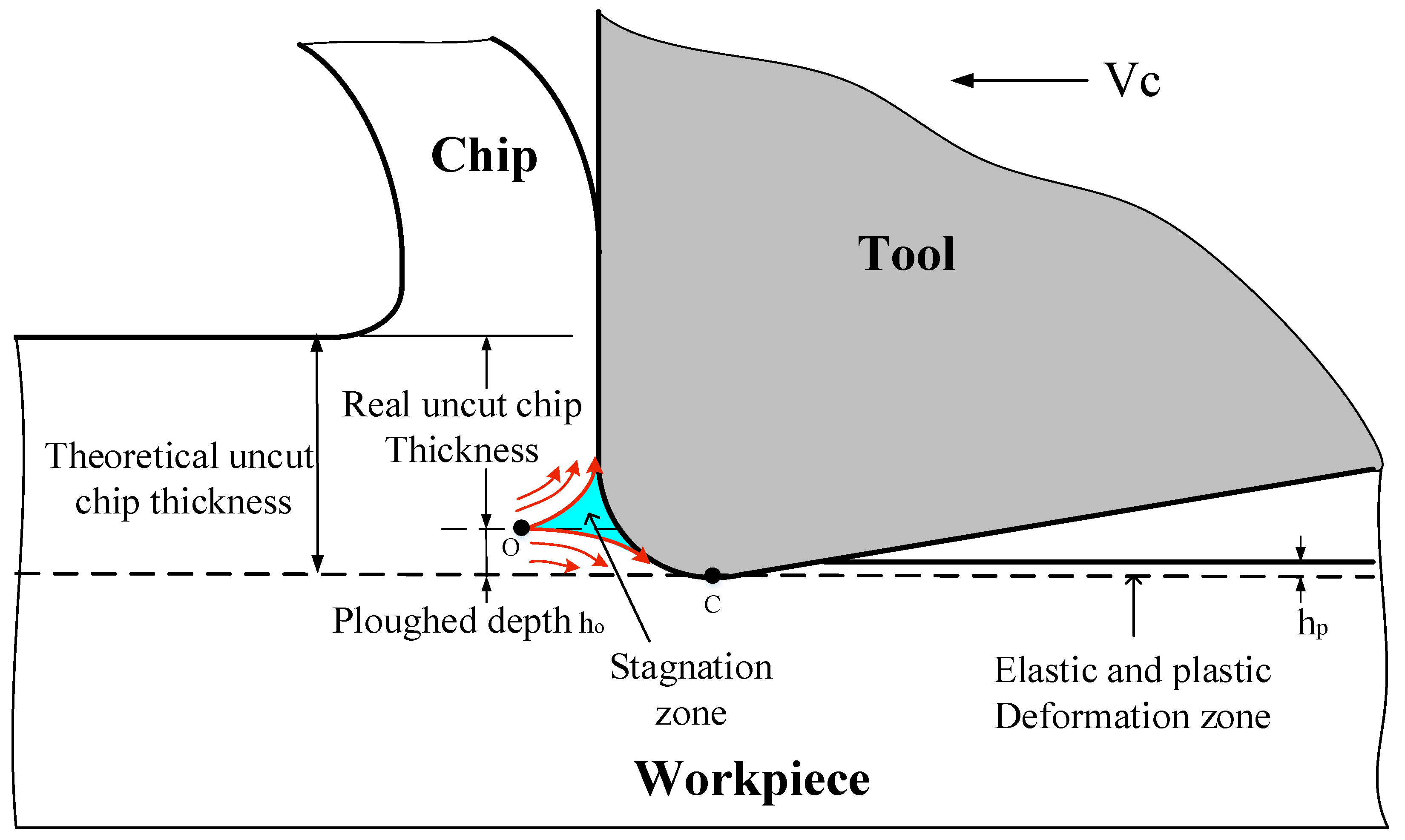
5.5. Stagnation Zone and Compressive Residual Stress
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.; Cong, W.L.; Zhang, H.-C.; Liu, Z.C. Laser engineered net shaping of nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 powders onto AISI 4140 alloy steel substrates: Interface bond and fracture failure mechanism. Materials 2017, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Hou, X. Influences of Cutting Speed and Material Mechanical Properties on Chip Deformation and Fracture during High-Speed Cutting of Inconel 718. Materials 2018, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Valdivielso, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Urbikain, G. Detecting the key geometrical features and grades of carbide inserts for the turning of nickel-based alloys concerning surface integrity. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2016, 230, 3725–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, H. An enhanced analytical model of residual stress for peripheral milling. Procedia CIRP 2017, 58, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillez, A.; Coz, G.L.; Dominiak, S.; Dudzinski, D. Dry machining of inconel 718, workpiece surface integrity. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundrák, J.; Szabó, G.; Markopoulos, A.P. Numerical Investigation of the Influence of Tool Rake Angle on Residual Stresses in Precision Hard Turning. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 686, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsan, A.U.H.; Liu, Z.; Padhy, G.K. A review on the progress towards improvement in surface integrity of Inconel 718 under high pressure and flood cooling conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 91, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Liang, S.Y. The effects of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) on machining force, temperature, and residual stress. Int. J. Prescis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 18, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Y.; Ye, B.Y.; Wu, B. Investigation into influence of cutting fluid and liquid nitrogen on machined surface residual stress. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 566, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkena, B.; Köhler, J.; Mengesha, M.S. Influence of the cutting edge rounding on the chip formation process: Part 1. Investigation of material flow, process forces, and cutting temperature. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2012, 6, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, E.; Köhler, J.; Denkena, B. On the honed cutting edge and its side effects during orthogonal turning operations of AISI1045 with coated WC-Co inserts. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkena, B.; Biermann, D. Cutting edge geometries. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 63, 631–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, T.; Ulutan, D. Prediction of machining induced residual stresses in turning of titanium and nickel based alloys with experiments and finite element simulations. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, P.I.; Rakurty, C.S.; Balaji, A.K. Surface Integrity in Hard Machining of 300 M Steel: Effect of Cutting-edge Geometry on Machining Induced Residual Stresses. Procedia CIRP 2014, 13, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.N.A.; Ng, E.G.; Elbestawi, M.A. Modelling the effects of tool-edge radius on residual stresses when orthogonal cutting AISI 316L. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.E.; Breidenstein, B.; Denkena, B. Influence of customized cutting edge geometries on the workpiece residual stress in hard turning. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, V.; Autenrieth, H.; Deuchert, M.; Weule, H. Investigation of surface near residual stress states after micro-cutting by finite element simulation. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 59, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Hao, Z.P. Surface residual stress in high speed cutting of superalloy Inconel718 based on multiscale simulation. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 31, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkena, B.; Reichstein, M.; Brodehl, J.; Leon, G.L. Surface Preparation, Coating and Wear Performance of Geometrically Defined Cutting Edges. In Proceedings of the 8th CIRP Intternational Workshop on Modeling of Machining Operations, Chemnitz, Germany, 10–11 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Noyan, I.C.; Cohen, J.B. Residual Stress: Measurement by Diffraction and Interpretation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Grissa, R.; Zemzemi, F.; Fathallah, R. Three approaches for modeling residual stresses induced by orthogonal cutting of AISI316L. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 135, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmell, M.; Ahadi, A.; Stahl, J.E. A fully coupled thermomechanical two-dimensional simulation model for orthogonal cutting: Formulation and simulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 225, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; von der Schulenburg, M.G.; Zettier, R. Finite element modeling and cutting simulation of Inconel 718. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 56, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Abia, A.I.; Barreiro, J.; de Lacalle, L.N.L. Behavior of austenitic stainless steels at high speed turning using specific force coefficients. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 62, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, R.; Albizuri, J.; Rodríguez, A. Influence of low-plasticity ball burnishing on the high-cycle fatigue strength of medium carbon AISI 1045 steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 55, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Hashimoto, F.; Lahoti, G. Surface integrity generated by precision hard turning. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.B.; Warren, A.W.; Hashimoto, F. The basic relationships between residual stress, white layer, and fatigue life of hard turned and ground surfaces in rolling contact. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Saoubi, R.; Outeiro, J.C.; Changeux, B.; Lebrun, J.L.; Morão, D.A. Residual stress analysis in orthogonal machining of standard and resulfurized AISI 316l steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 96, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Shivpuri, R.; Cheng, X. Effect of feed rate, workpiece hardness and cutting edge on subsurface residual stress in the hard turning of bearing steel using chamfer + hone cutting edge geometry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 394, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmell, M.; Ahadi, A.; Gutnichenko, O.; Ståhl, J.E. The influence of tool micro-geometry on stress distribution in turning operations of AISI 4140 by FE analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 3109–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrolyte Composition | CH3OH/HNO3 | 200 mL/100 mL |
| Electrolytic Parameters | Voltage Current density | 10 V 0.5~0.7 A/cm2 |
| Environment | Room temperature (20 °C) | |
| A (MPa) | B (MPa) | C | n | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450 | 1700 | 0.017 | 0.65 | 1.3 |
| Properties | Density | Young’s Modulus | Poisson’s Ratio | Thermal Expansion | Conductivity | Specific Heat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool | 14,800 Kg/m3 | 640 GPa | 0.22 | 4.5 μm/mK | 50.24 W/mK | 220 J/kgK |
| Workpiece | 8250 Kg/m3 | 214.580 GPa | 0.305 | 14.8 μm/mK | 17.8 W/mK | 526.3 J/kgK |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Hua, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lv, W.; Mohsan, A.U.H. Effects of Cutting Edge Microgeometry on Residual Stress in Orthogonal Cutting of Inconel 718 by FEM. Materials 2018, 11, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061015
Shen Q, Liu Z, Hua Y, Zhao J, Lv W, Mohsan AUH. Effects of Cutting Edge Microgeometry on Residual Stress in Orthogonal Cutting of Inconel 718 by FEM. Materials. 2018; 11(6):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061015
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Qi, Zhanqiang Liu, Yang Hua, Jinfu Zhao, Woyun Lv, and Aziz Ul Hassan Mohsan. 2018. "Effects of Cutting Edge Microgeometry on Residual Stress in Orthogonal Cutting of Inconel 718 by FEM" Materials 11, no. 6: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061015
APA StyleShen, Q., Liu, Z., Hua, Y., Zhao, J., Lv, W., & Mohsan, A. U. H. (2018). Effects of Cutting Edge Microgeometry on Residual Stress in Orthogonal Cutting of Inconel 718 by FEM. Materials, 11(6), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061015







