Fabrication Approaches to Interconnect Based Devices for Stretchable Electronics: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Concept of Stretchable Electronics
1.2. Basic Concepts
1.2.1. Adjusted Patterning of Intrinsically Stiff Conductive Materials
1.2.2. Dispersion of Stiff Conductive Fillers in an Elastomeric Matrix
1.2.3. Intrinsically Stretchable Conductive Materials
1.3. Fabrication Routes for Stretchable Electronics
1.4. Methods of Validation
1.5. Contribution of This Review Paper
2. Insightful Geometric Patterning
2.1. Underlying Principle
2.2. Introduction of in Plane Tortuosity through Serpentines
2.3. Alternative Serpentine Shapes
2.4. Substrate Influence
2.5. Out of Plane Tortuosity with Buckling
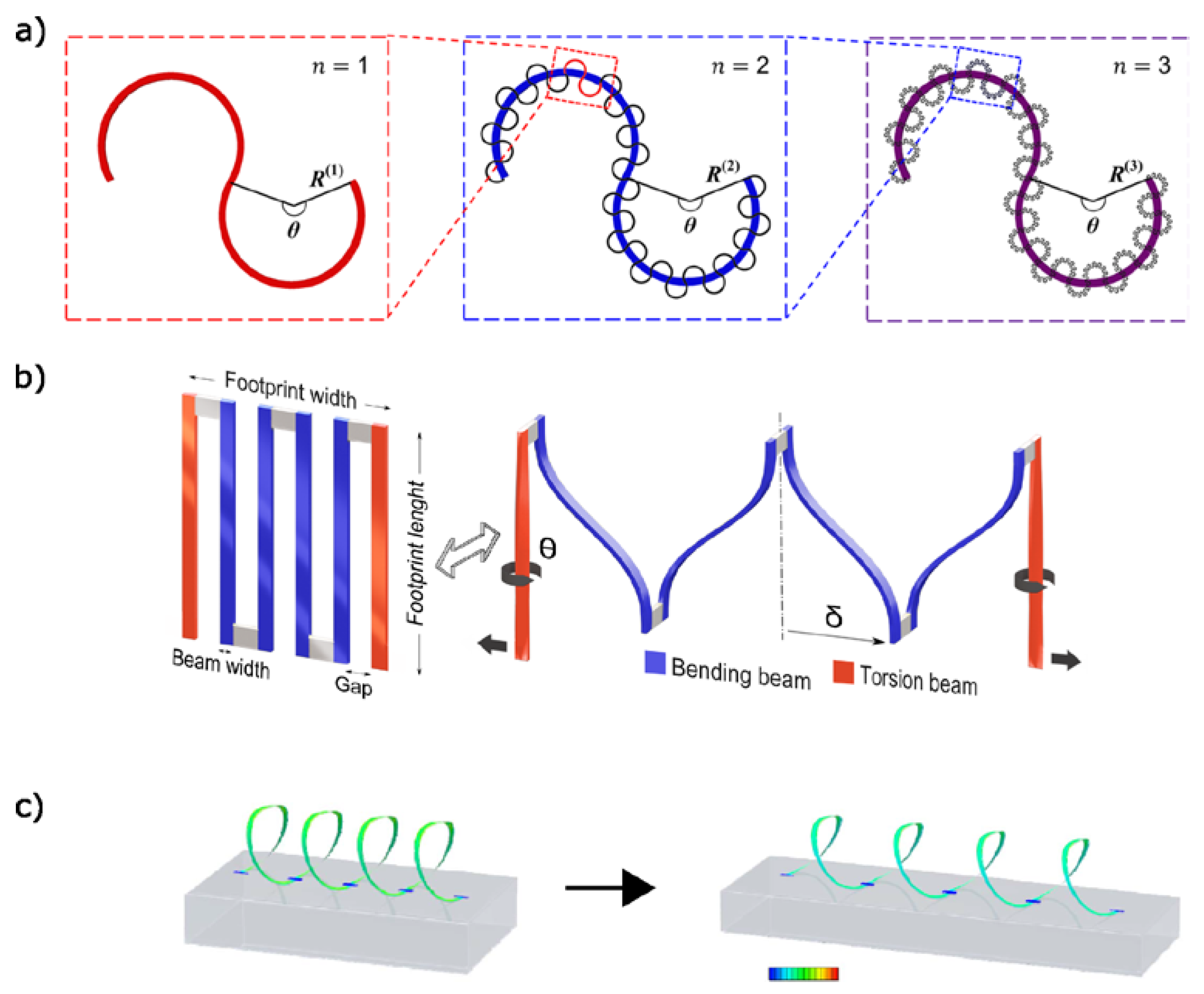
2.6. 3D Tortuosiy
2.7. Transition to Circuits
2.8. Examples of Devices
3. Conductive Filler Doped Elastomers
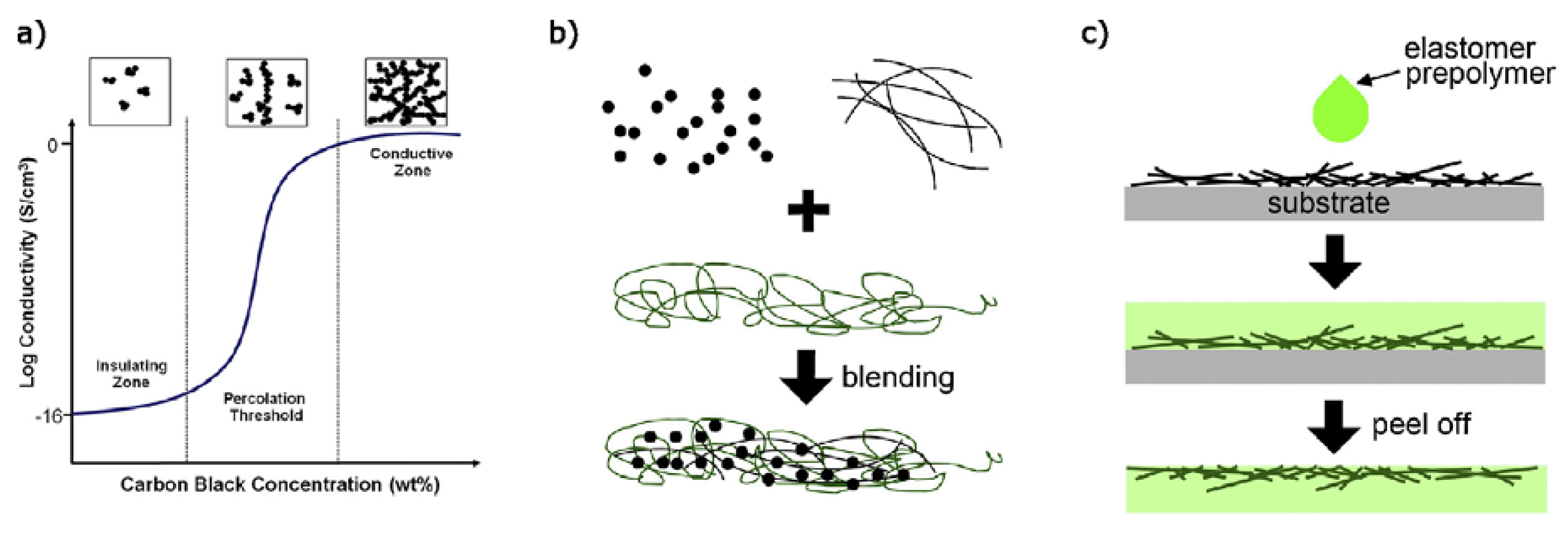
3.1. Concept of Percolation
3.2. Conductivity-Elasticity Balance
3.3. Conductive Fillers
3.4. Ways to Determine Bulk Conductivity of Solid Powders
3.5. Main Ways of Dispersion
3.6. Patterning Methods
3.7. Achieved Strains
3.8. Device Examples
4. Intrinsically Stretchable Conductors
4.1. Conductive Polymers
4.2. Liquid Metal (LM)
4.3. LM Properties
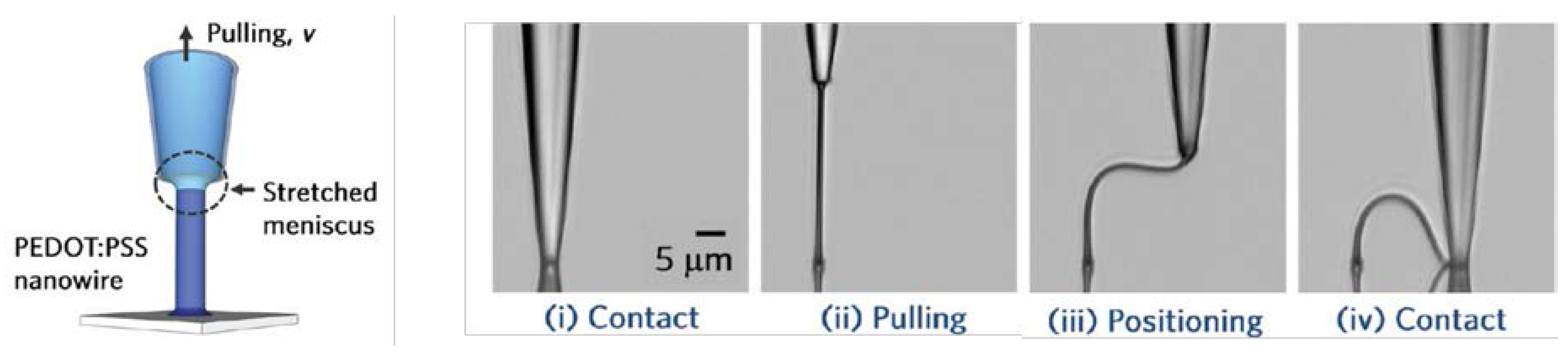
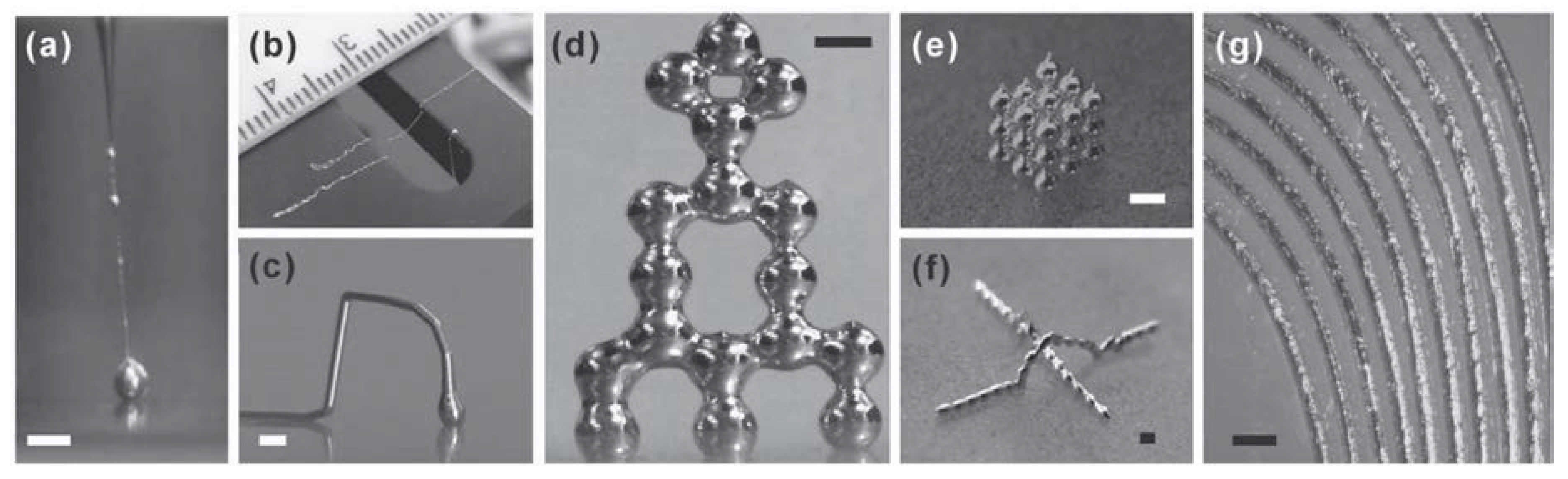
4.4. Patterning of LM
4.5. Demonstrated Devices
5. Standard Tests
5.1. Need
5.2. Tensile Tests
5.3. Resistance Measurements
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickey, M.D. Stretchable and Soft Electronics using Liquid Metals. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Kim, D.-H. Flexible and Stretchable Electronics Paving the Way for Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2013, 1, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Nicholls, B.; Sup Lee, D.; Chen, Y.; Chun, Y.; Siang Ang, C.; Yeo, W.-H. Soft Electronics Enabled Ergonomic Human-Computer Interaction for Swallowing Training. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, M.; Nittala, A.S.; Olwal, A.; Steimle, J. SkinMarks: Enabling Interactions on Body Landmarks Using Conformal Skin Electronics. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ’17), Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 3095–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.; Lyu, F.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, H. An Empirical Study on the Interaction Capability of Arm Stretching. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2017, 33, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Manco, M.; Moyal, D.; Huppert, G.; Araki, H.; Banks, A.; Joshi, H.; McKenzie, R.; Seewald, A.; Griffin, G.; et al. Soft, stretchable, epidermal sensor with integrated electronics and photochemistry for measuring personal UV exposures. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerratt, A.P.; Michaud, H.O.; Lacour, S.P. Elastomeric Electronic Skin for Prosthetic Tactile Sensation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Santos, V.J.; Posner, J.D. Bioinspired flexible microfluidic shear force sensor skin. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2017, 264, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Axisa, F.; Bulcke, M.V.; Brosteaux, D.; Vandevelde, B.; Vanfleteren, J. Design of Metal Interconnects for Stretchable Electronic Circuits using Finite Element Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation Experiments in Microelectronics and Micro-Systems (EuroSime 2007), London, UK, 16–18 April 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tamai, T. Electrical Properties of Conductive Elastomer as Electrical Contact Material. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1982, 5, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, M.D.; Chiechi, R.C.; Larsen, R.J.; Weiss, E.A.; Weitz, D.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Eutectic Gallium-Indium (EGaIn): A Liquid Metal Alloy for the Formation of Stable Structures in Microchannels at Room Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, S.; Myny, K.; Schols, S.; Vicca, P.; Smout, S.; Tripathi, A.; van der Putten, B.; van der Steen, J.-L.; van Neer, M.; Schütze, F.; et al. Design and realization of a flexible QQVGA AMOLED display with organic TFTs. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, C.; Johnson, R.W.; Zhang, T.; Hou, Z.; Charles, H.K. Flip Chip Assembly of Thinned Silicon Die on Flex Substrates. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2008, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, Z.; Korochkina, T.; Govindarajan, S.; Thomas, D.J.; O’Mahony, J.; Kettle, J.; Claypole, T.C.; Gethin, D.T. Ultra-thin flexible screen printed rechargeable polymer battery for wearable electronic applications. Org. Electron. 2015, 26, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.R.; Kim, E.H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, L.S. Flexible OLED encapsulated with gas barrier film and adhesive gasket. Synth. Met. 2014, 193, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-H.; Kwon, O.E.; Park, Y.-S.; Yu, B.G.; Lee, J.; Moon, J.; Cho, H.; Lee, H.; Cho, N.S. Flexible integrated OLED substrates prepared by printing and plating process. Org. Electron. 2017, 50, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.; Peele, B.; Li, S.; Robinson, S.; Totaro, M.; Beccai, L.; Mazzolai, B.; Shepherd, R. Highly stretchable electroluminescent skin for optical signaling and tactile sensing. Science 2016, 351, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Shin, J.; Yin, L.; You, J.-M.; Meng, Y.S.; Wang, J. All-Printed, Stretchable Zn-Ag2O Rechargeable Battery via Hyperelastic Binder for Self-Powering Wearable Electronics. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, N. On tortuosity and the tortuosity factor in flow and diffusion through porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.S.; Tien, J.; Chen, C.S. High-Conductivity Elastomeric Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y. Mechanics of Fractal-Inspired Horseshoe Microstructures for Applications in Stretchable Electronics. J. Appl. Mech. 2016, 83, 111008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazos Sepulveda, A.C.; Diaz Cordero, M.S.; Carreño, A.A.A.; Nassar, J.M.; Hussain, M.M. Stretchable and foldable silicon-based electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 134103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafqat, S.; Hoefnagels, J.P.M.; Savov, A.; Joshi, S.; Dekker, R.; Geers, M.G.D. Ultra-Stretchable Interconnects for High-Density Stretchable Electronics. Micromachines 2017, 8, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachicouras, N.; Tringides, C.M.; Campiche, P.B.; Lacour, S.P. Engineering reversible elasticity in ductile and brittle thin films supported by a plastic foil. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2017, 15, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.-I.; Li, K.; Chung, H.U.; Xu, S.; Jung, H.N.; Yang, Y.; Kwak, J.W.; Jung, H.H.; Song, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Self-assembled three dimensional network designs for soft electronics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Mathewson, K.E.; Jang, K.-I.; Kim, J.; Fu, H.; Huang, X.; Chava, P.; Wang, R.; et al. Soft Microfluidic Assemblies of Sensors, Circuits, and Radios for the Skin. Science 2014, 344, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, F.; Vervust, T.; Vanfleteren, J. Stretchable Electronics Technology for Large Area Applications: Fabrication and Mechanical Characterization. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 3, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Pharr, M.; Ma, Y.; Ning, R.; Yan, Z.; Xu, R.; Feng, X.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Serpentine Interconnects on Ultrathin Elastomers for Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Ping, X.; Yu, K.J.; Lee, J.W.; Fan, J.A.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Harburg, D.V.; Huang, Y.; et al. In-Plane Deformation Mechanics for Highly Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khang, D.-Y.; Rogers, J.A.; Lee, H.H. Mechanical Buckling: Mechanics, Metrology, and Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drack, M.; Graz, I.; Sekitani, T.; Someya, T.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Bauer, S. An Imperceptible Plastic Electronic Wrap. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Bao, S.; Vinnikova, S.; Ghanta, P.; Wang, S. Buckling analysis in stretchable electronics. Npj Flex. Electron. 2017, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Choi, W.M.; Jiang, H.; Huang, Y.Y.; Rogers, J.A. Controlled buckling of semiconductor nanoribbons for stretchable electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2006, 1, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokoro, K.; Onoue, M.; Kojima, K.; Chikama, K.; Ushijima, H. Fabrication of copper wiring by micro-contact printing method and electroless plating and electroplating. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 05HC02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-S.; Jung, K.-H.; Jung, S.-B. Design and fabrication of screen-printed silver circuits for stretchable electronics. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 120, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, S.P.; Wagner, S.; Narayan, R.J.; Li, T.; Suo, Z. Stiff subcircuit islands of diamondlike carbon for stretchable electronics. J. Appl. Phys. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, M.; Yoon, J.; Park, S.-I.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Stretchable GaAs Photovoltaics with Designs That Enable High Areal Coverage. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, M.D.; Markvicka, E.J.; Majidi, C. Rapid Fabrication of Soft, Multilayered Electronics for Wearable Biomonitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8496–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Norton, J.J.S.; Qazi, R.; Zou, Z.; Ammann, K.R.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Tran, P.L.; Jang, K.-I.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Epidermal mechano-acoustic sensing electronics for cardiovascular diagnostics and human-machine interfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamarayeva, A.M.; Ostfeld, A.E.; Wang, M.; Duey, J.K.; Deckman, I.; Lechêne, B.P.; Davies, G.; Steingart, D.A.; Arias, A.C. Flexible and stretchable power sources for wearable electronics. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Park, J.; Ji, S.; Shin, S.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-U. Fully-integrated, bezel-less transistor arrays using reversibly foldable interconnects and stretchable origami substrates. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 9504–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Park, J.; Jeong, U. Design of conductive composite elastomers for stretchable electronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigandi, P.J.; Cogen, J.M.; Pearson, R.A. Electrically conductive multiphase polymer blend carbon-based composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.Z.; Peng, S.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Wen, W.J.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and Patterning of PDMS-Based Conducting Composites. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothon, R. (Ed.) Fillers for Polymer Applications; Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-28116-2. [Google Scholar]
- Amjadi, M.; Yoon, Y.J.; Park, I. Ultra-stretchable and skin-mountable strain sensors using carbon nanotubes-Ecoflex nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 375501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Pichitpajongkit, A.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensor Based on Silver Nanowire–Elastomer Nanocomposite. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5154–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, B.; Ghislandi, M.; Tkalya, E.; Koning, C.E.; de With, G. Electrical conductivity of compacts of graphene, multi-wall carbon nanotubes, carbon black, and graphite powder. Powder Technol. 2012, 221, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Rocha, R.; Osorio, L.; Almeida, M.; de Almeida, A.; Ramachandran, V.; Tabatabai, A.; Lu, T.; Majidi, C. Carbon doped PDMS: Conductance stability over time and implications for additive manufacturing of stretchable electronics. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, A.D.; Busbee, T.A.; Boley, J.W.; Raney, J.R.; Chortos, A.; Kotikian, A.; Berrigan, J.D.; Durstock, M.F.; Lewis, J.A. Hybrid 3D Printing of Soft Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.-H.; Park, Y.-B.; Yoon, K.H.; Bang, D.S. Smart Materials and Structures Based on Carbon Nanotube Composites. In Carbon Nanotubes-Synthesis, Characterization, Applications; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Han, F.; Zhang, G.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Highly electrically conductive and stretchable copper nanowires-based composite for flexible and printable electronics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 146, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, P.C.; Chow, W.S.; To, C.K.; Tang, B.Z.; Kim, J.-K. Correlations between Percolation Threshold, Dispersion State, and Aspect Ratio of Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Hjort, K.; Wu, Z. Tape Transfer Atomization Patterning of Liquid Alloys for Microfluidic Stretchable Wireless Power Transfer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suikkola, J.; Björninen, T.; Mosallaei, M.; Kankkunen, T.; Iso-Ketola, P.; Ukkonen, L.; Vanhala, J.; Mäntysalo, M. Screen-Printing Fabrication and Characterization of Stretchable Electronics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, D.P.; Ladd, C.; Panich, L.; Moussa, K.; Dickey, M.D. 3D printing of liquid metals as fugitive inks for fabrication of 3D microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuhisa, N.; Inoue, D.; Zalar, P.; Jin, H.; Matsuba, Y.; Itoh, A.; Yokota, T.; Hashizume, D.; Someya, T. Printable elastic conductors by in situ formation of silver nanoparticles from silver flakes. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, E.; Hwang, B.-U.; Kim, D.; Kim, B.-Y.; Lee, N.-E. Stretchable, Transparent, Ultrasensitive, and Patchable Strain Sensor for Human–Machine Interfaces Comprising a Nanohybrid of Carbon Nanotubes and Conductive Elastomers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6252–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, K.; Ji, S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Park, J.; Na, K.; Bae, K.-H.; Kyun Kim, H.; et al. Wearable smart sensor systems integrated on soft contact lenses for wireless ocular diagnostics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.-H.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, H. Electrical and Electrochemical Properties of Conducting Polymers. Polymers 2017, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, J. Scientific Importance of Water-Processable PEDOT–PSS and Preparation, Challenge and New Application in Sensors of Its Film Electrode: A Review. J. Polym. Sci. Part Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 1121–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, M.Y.; Kim, N.; Kee, S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, G.; Hong, S.; Jung, S.; Lee, K. Highly Stretchable and Highly Conductive PEDOT:PSS/Ionic Liquid Composite Transparent Electrodes for Solution-Processed Stretchable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Bao, Z. Stretchable Organic Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, W.; Yue, Z.; Too, C.O.; Wallace, G.G. Buckled, Stretchable Polypyrrole Electrodes for Battery Applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3580–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Pyo, J.; Rho, J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Je, J.H.; Margaritondo, G. Three-Dimensional Writing of Highly Stretchable Organic Nanowires. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.W.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Stretchable conductive fabric for electrotherapy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Meng, W.; Liu, C.; Pei, Z.; Hao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhi, C. From Industrially Weavable and Knittable Highly Conductive Yarns to Large Wearable Energy Storage Textiles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, R.J. The measurement of volume changes in human limbs. J. Physiol. 1953, 121, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, S.J.; Saunders, D.J.; Ingle, G.W. The System Gallium-Indium. J. Phys. Chem. 1937, 42, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; So, J.-H.; Mays, R.; Desai, S.; Barnes, W.R.; Pourdeyhimi, B.; Dickey, M.D. Ultrastretchable Fibers with Metallic Conductivity Using a Liquid Metal Alloy Core. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, M.D. Emerging Applications of Liquid Metals Featuring Surface Oxides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18369–18379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladd, C.; So, J.-H.; Muth, J.; Dickey, M.D. 3D Printing of Free Standing Liquid Metal Microstructures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5081–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J. Direct writing of electronics based on alloy and metal (DREAM) ink: A newly emerging area and its impact on energy, environment and health sciences. Front. Energy 2012, 6, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshipura, I.D.; Ayers, H.R.; Majidi, C.; Dickey, M.D. Methods to pattern liquid metals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3834–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sheng, L.; Jin, C.; Liu, J. Liquid Metal as Connecting or Functional Recovery Channel for the Transected Sciatic Nerve. 2014; preprint at ArXiv:1404.5931. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, J. Surface tension of liquid metal: Role, mechanism and application. Front. Energy 2017, 11, 535–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaker, C.B.; Khan, M.R.; Dickey, M.D. A Method to Manipulate Surface Tension of a Liquid Metal via Surface Oxidation and Reduction. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2016, e53567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Wu, Z. Microfluidic stretchable RF electronics. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Gordon, O.; Khan, M.R.; Vasquez, N.; Genzer, J.; Dickey, M.D. Vacuum filling of complex microchannels with liquid metal. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3043–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhen, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Deng, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Liu, L. Liquid metal fiber composed of a tubular channel as a high-performance strain sensor. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 12483–12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, D.; He, C.; Liu, Y.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Liquid metal sponges for mechanically durable, all-soft, electrical conductors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Finkenauer, L.; Wissman, J.; Majidi, C. Rapid Prototyping for Soft-Matter Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3351–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Markvicka, E.J.; Jin, Y.; Majidi, C. Soft-Matter Printed Circuit Board with UV Laser Micropatterning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22055–22062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, W. Micropatterning of Liquid Metal by Dewetting. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J. Pervasive liquid metal direct writing electronics with roller-ball pen. AIP Adv. 2013, 3, 112117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozen, B.A.; Tabatabai, A.; Ozdoganlar, O.B.; Majidi, C. High-Density Soft-Matter Electronics with Micron-Scale Line Width. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5211–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassler, A.; Majidi, C. Liquid-Phase Metal Inclusions for a Conductive Polymer Composite. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, B.; Liu, J. A Personal Desktop Liquid-Metal Printer as a Pervasive Electronics Manufacturing Tool for Society in the Near Future. Engineering 2015, 1, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, Z.-Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, J. Personal electronics printing via tapping mode composite liquid metal ink delivery and adhesion mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wu, X.; Lee, D.-W. A galinstan-based inkjet printing system for highly stretchable electronics with self-healing capability. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lear, T.R.; Hyun, S.-H.; Boley, J.W.; White, E.L.; Thompson, D.H.; Kramer, R.K. Liquid metal particle popping: Macroscale to nanoscale. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2017, 13, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.G.; Kramer, R. All-Printed Flexible and Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boley, J.W.; White, E.L.; Kramer, R.K. Mechanically Sintered Gallium–Indium Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, W.; Yeo, J.C.; Yu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lim, C.T. Ultrathin and Wearable Microtubular Epidermal Sensor for Real-Time Physiological Pulse Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Ro, K.; Kim, S.; Bae, J. A Soft Sensor-Based Three-Dimensional (3-D) Finger Motion Measurement System. Sensors 2017, 17, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.C.; Yap, H.K.; Xi, W.; Wang, Z.; Yeow, C.-H.; Lim, C.T. Flexible and Stretchable Strain Sensing Actuator for Wearable Soft Robotic Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.B.; Arutselvan, K.; Liu, Y.; Armstrong, D.; Lin, Y.; Khan, M.R.; Genzer, J.; Dickey, M.D. Stretchable Capacitive Sensors of Torsion, Strain, and Touch Using Double Helix Liquid Metal Fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Chao, M.; Gao, Y.; Wu, E.; Tai, L.-C.; Chen, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Iwai, K.; Fahad, H.M.; Gao, W.; et al. 3D Printed “Earable” Smart Devices for Real-Time Detection of Core Body Temperature. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Li, X.; Kim, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Wiley, B.J.; Ham, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Stretchable Microfluidic Radiofrequency Antennas. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2749–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.W.; Park, J.; Hong, S.Y.; Park, H.; Jeong, Y.R.; Park, J.; Lee, S.-S.; Ha, J.S. Stretchable Loudspeaker using Liquid Metal Microchannel. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Sivan, V.; Petersen, P.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Abbott, D.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Liquid metal enabled pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3304–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, M.; Gui, L. A Liquid-Metal Based Spiral Magnetohydrodynamic Micropump. Micromachines 2017, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Liu, J. Self-propelled liquid metal motors steered by a magnetic or electrical field for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5349–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Kim, C.J.C. Microscale Liquid-Metal Switches—A Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissman, J.; Dickey, M.D.; Majidi, C. Field-Controlled Electrical Switch with Liquid Metal. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, J. Autonomous convergence and divergence of the self-powered soft liquid metal vehicles. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 10, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, J.-B.; Chung, S.K.; Kim, D. On-demand magnetic manipulation of liquid metal in microfluidic channels for electrical switching applications. Lab Chip 2016, 17, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, R.A.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Kramer, R.K. Liquid Metal Switches for Environmentally Responsive Electronics. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, M.D.; Kazem, N.; Powell-Palm, M.J.; Huang, X.; Sun, W.; Malen, J.A.; Majidi, C. High thermal conductivity in soft elastomers with elongated liquid metal inclusions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 37:2011. In Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Determination of Tensile Stress-Strain Properties; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2011.
- ASTM D412-06a. In Standard Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, 2006.
- ASTM D257-99. In Standard Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, 1999.
- ASTM D4496-87. In Standard Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, 1987.
- ASTM B193-02. In Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, 2002.
- Hirsch, A.; Michaud, H.O.; Gerratt, A.P.; de Mulatier, S.; Lacour, S.P. Biphasic Metal Films: Intrinsically Stretchable Biphasic (Solid–Liquid) Thin Metal Films (Adv. Mater. 22/2016). Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagels, S.; Deferme, W. Fabrication Approaches to Interconnect Based Devices for Stretchable Electronics: A Review. Materials 2018, 11, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030375
Nagels S, Deferme W. Fabrication Approaches to Interconnect Based Devices for Stretchable Electronics: A Review. Materials. 2018; 11(3):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030375
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagels, Steven, and Wim Deferme. 2018. "Fabrication Approaches to Interconnect Based Devices for Stretchable Electronics: A Review" Materials 11, no. 3: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030375
APA StyleNagels, S., & Deferme, W. (2018). Fabrication Approaches to Interconnect Based Devices for Stretchable Electronics: A Review. Materials, 11(3), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030375





