Hyperspectral-Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy for Single and Collective Nanoparticle Characterization in Biological Environments
Abstract
:1. Hyperspectral-Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy (HEDFM)
1.1. Dark Field Microscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging—A Brief Introduction
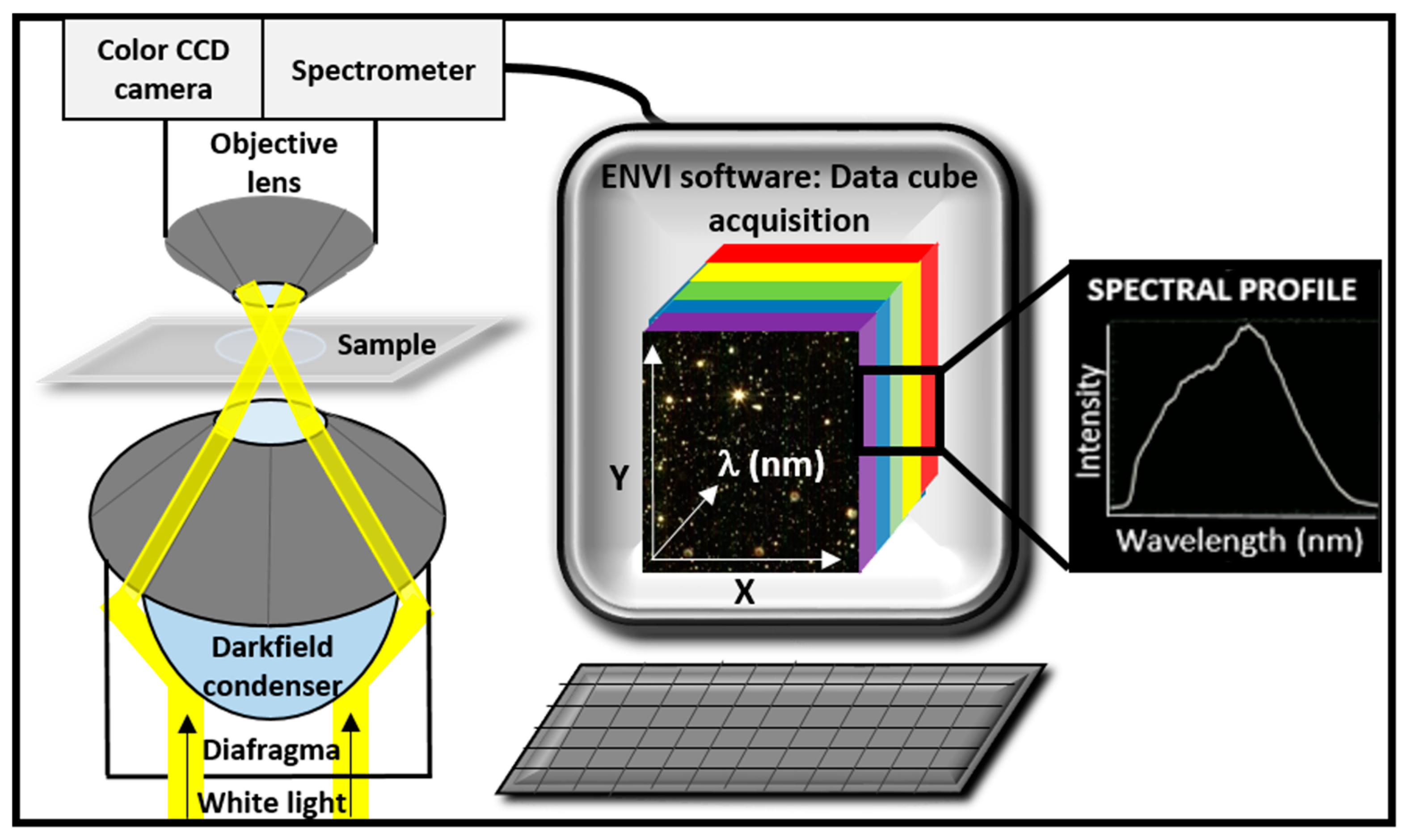
1.2. Instrumentation and Advantages
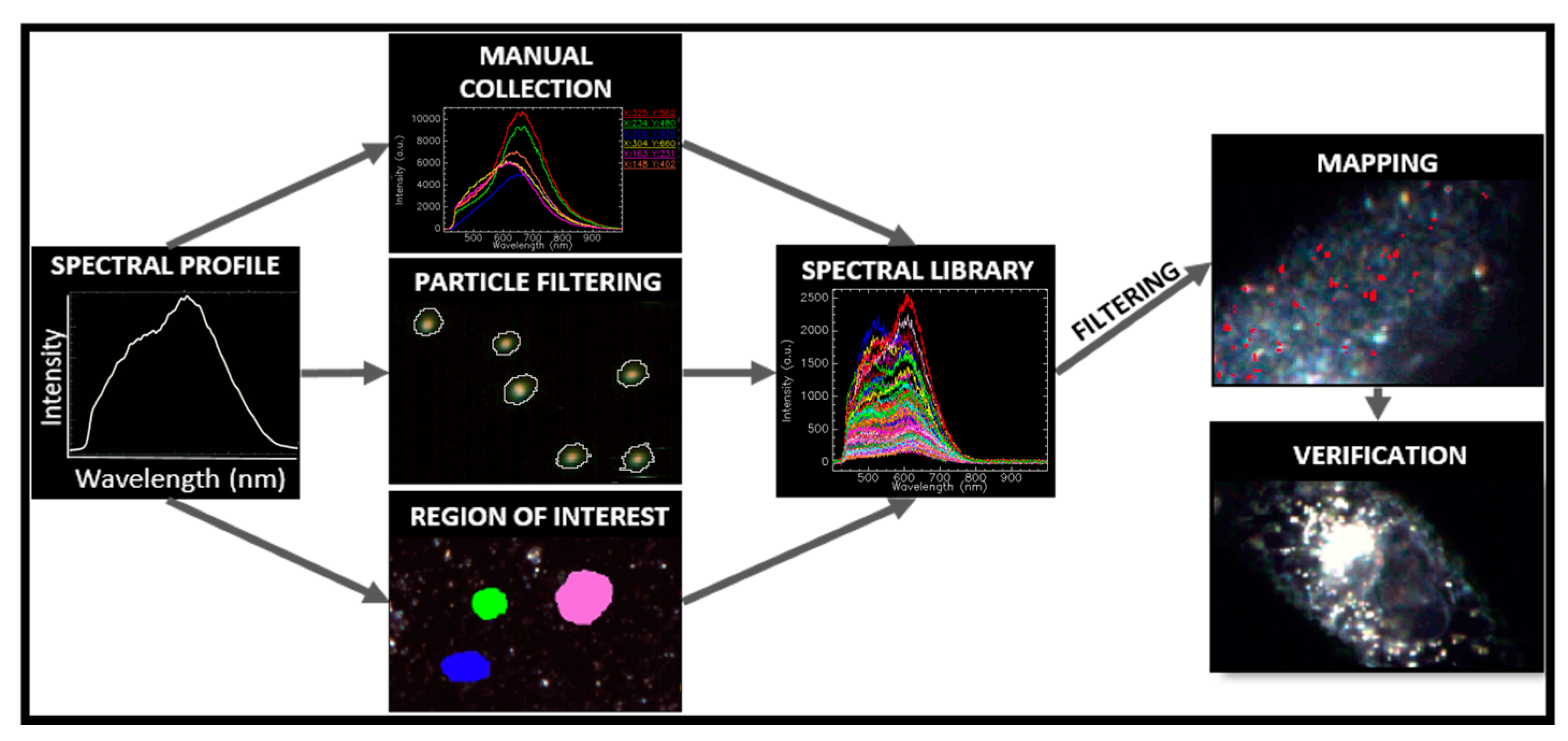
1.3. Image Acquisition and Hypercube Analysis
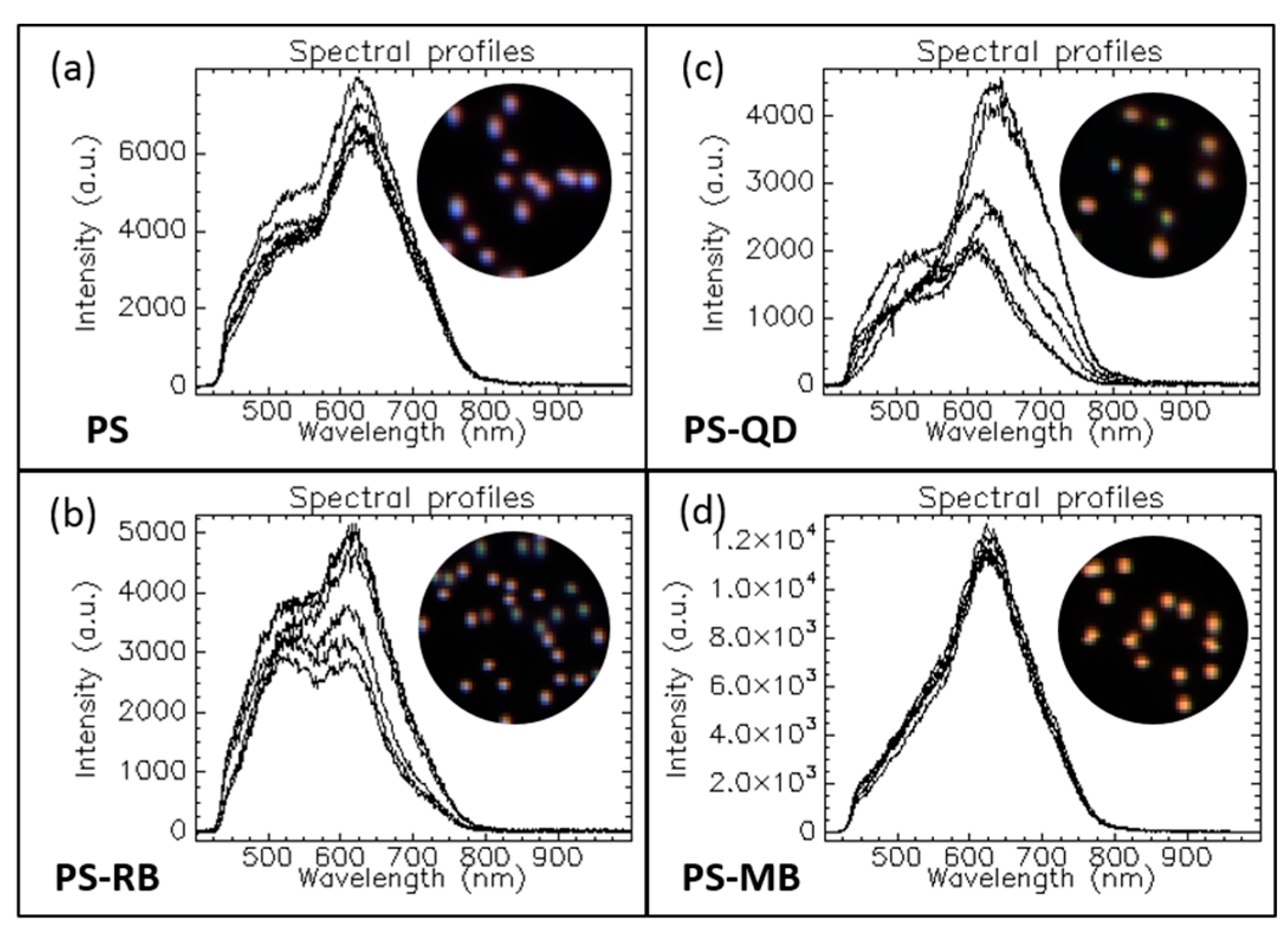
1.3.1. Optical Response of Multicomposite Nanoparticles
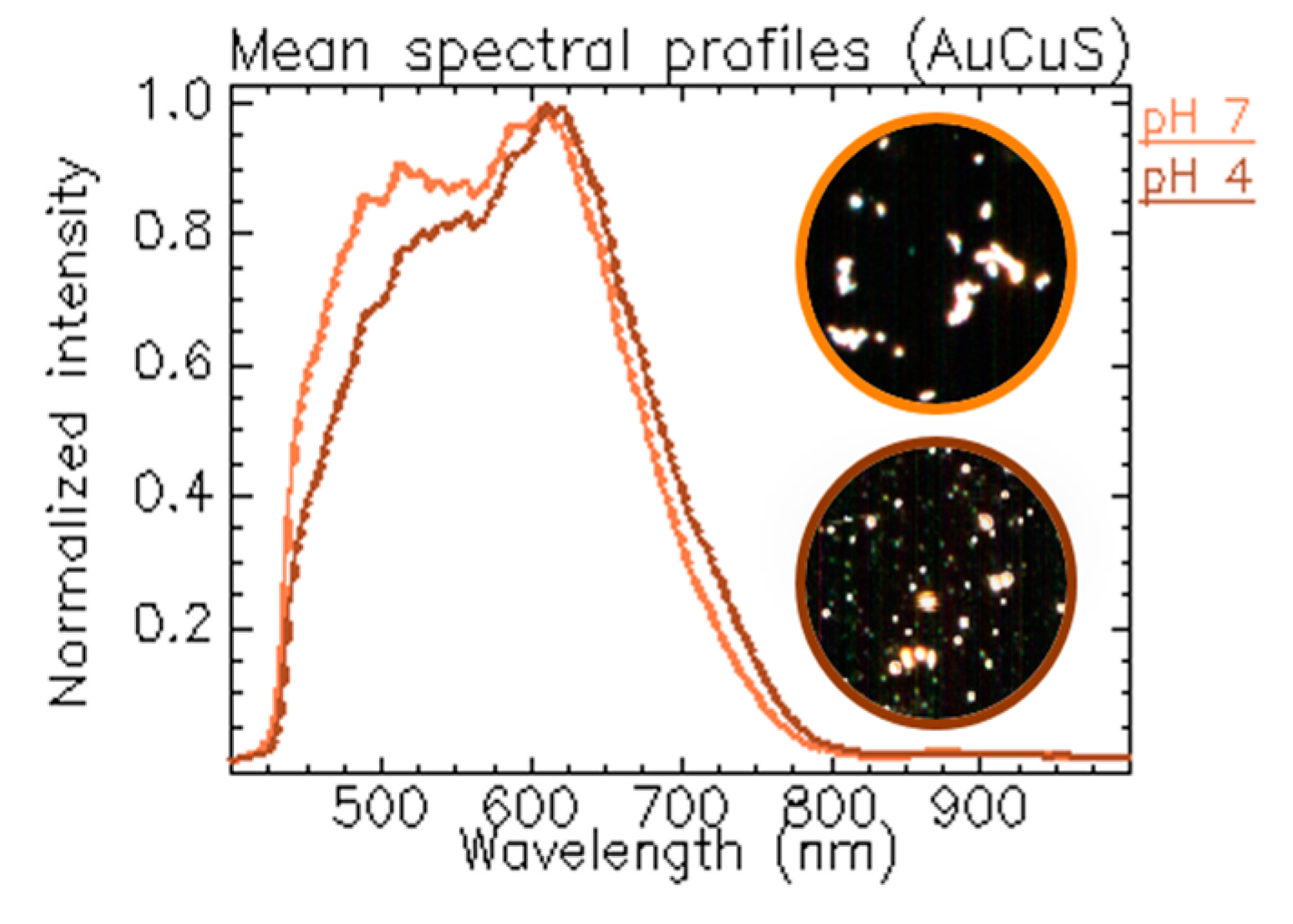
1.3.2. Tracking NPs’ Evolution at Different pH Values
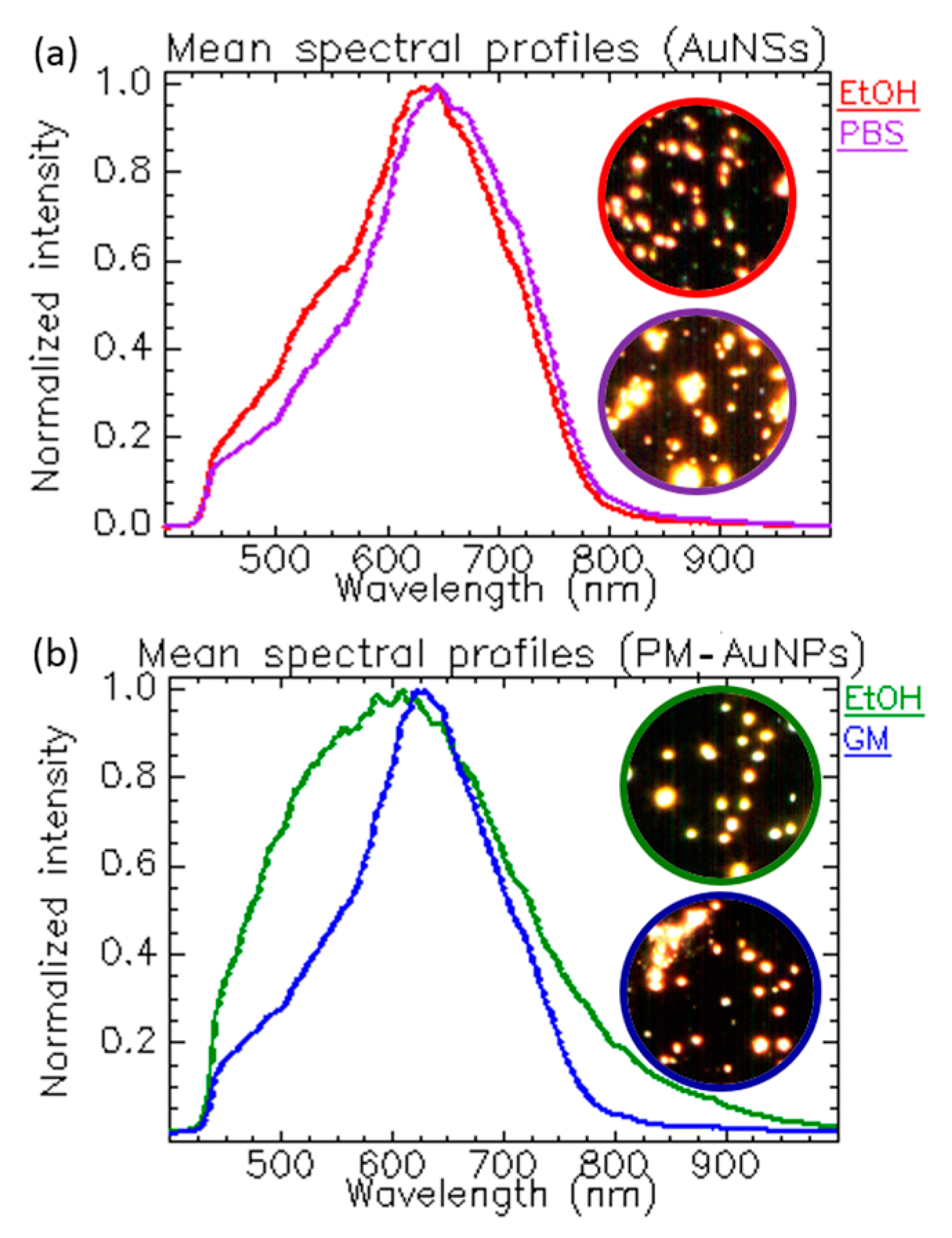
1.3.3. Tracking NPs’ Changes Induced by the Solvent’s Ionic Strength and Composition
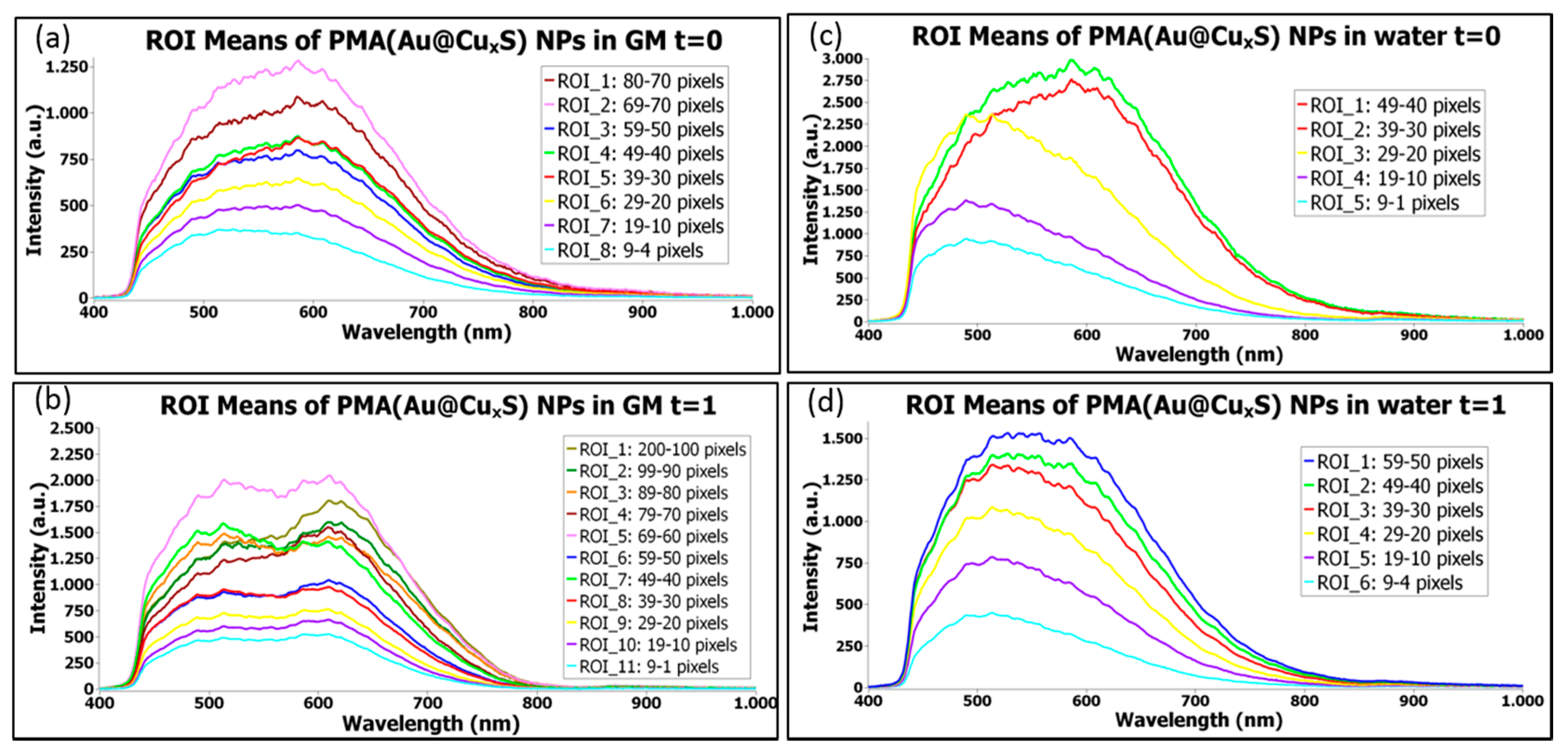
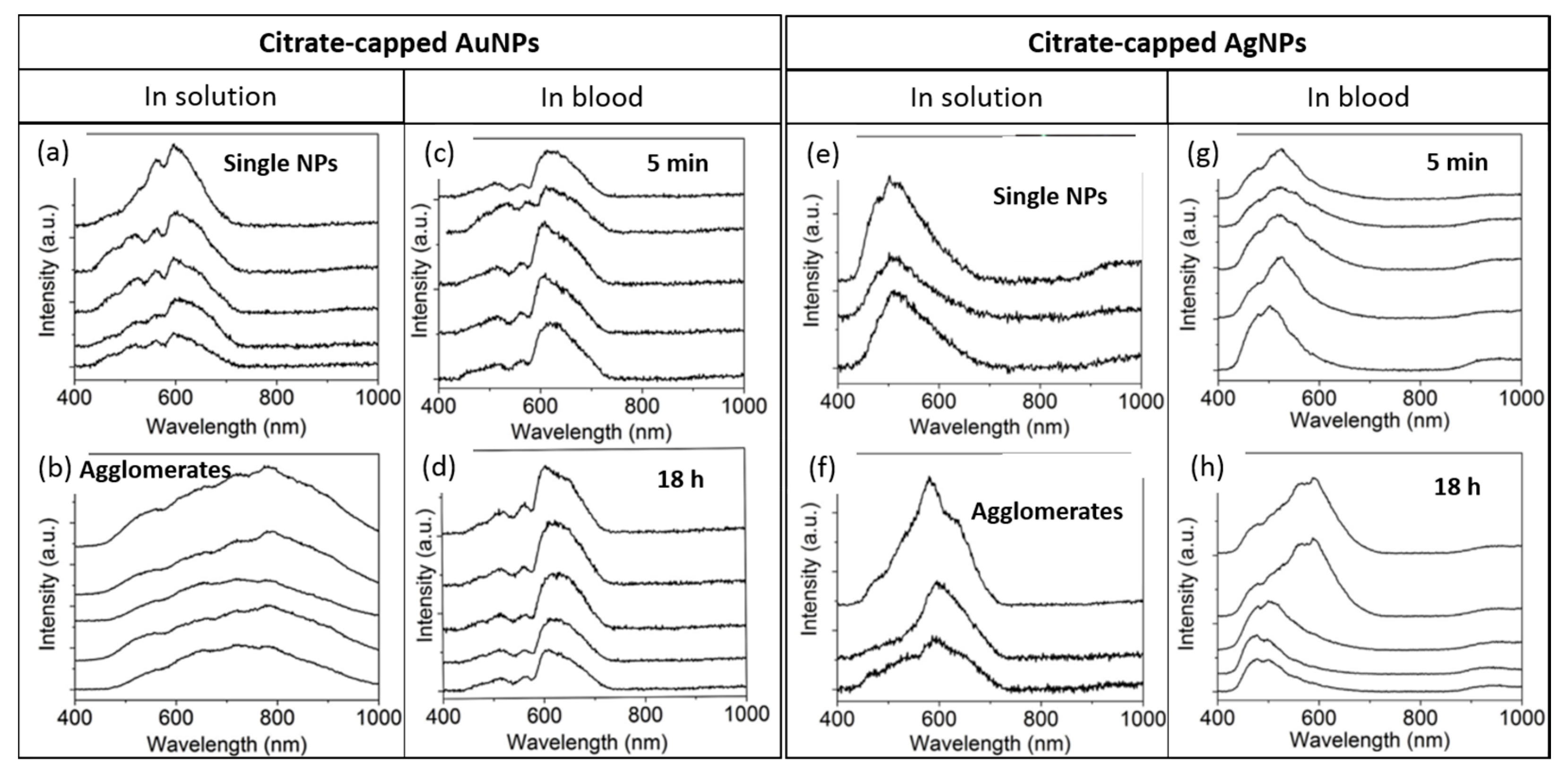
1.3.4. Time Evolution of NPs Stored in Water or in a Biological Medium
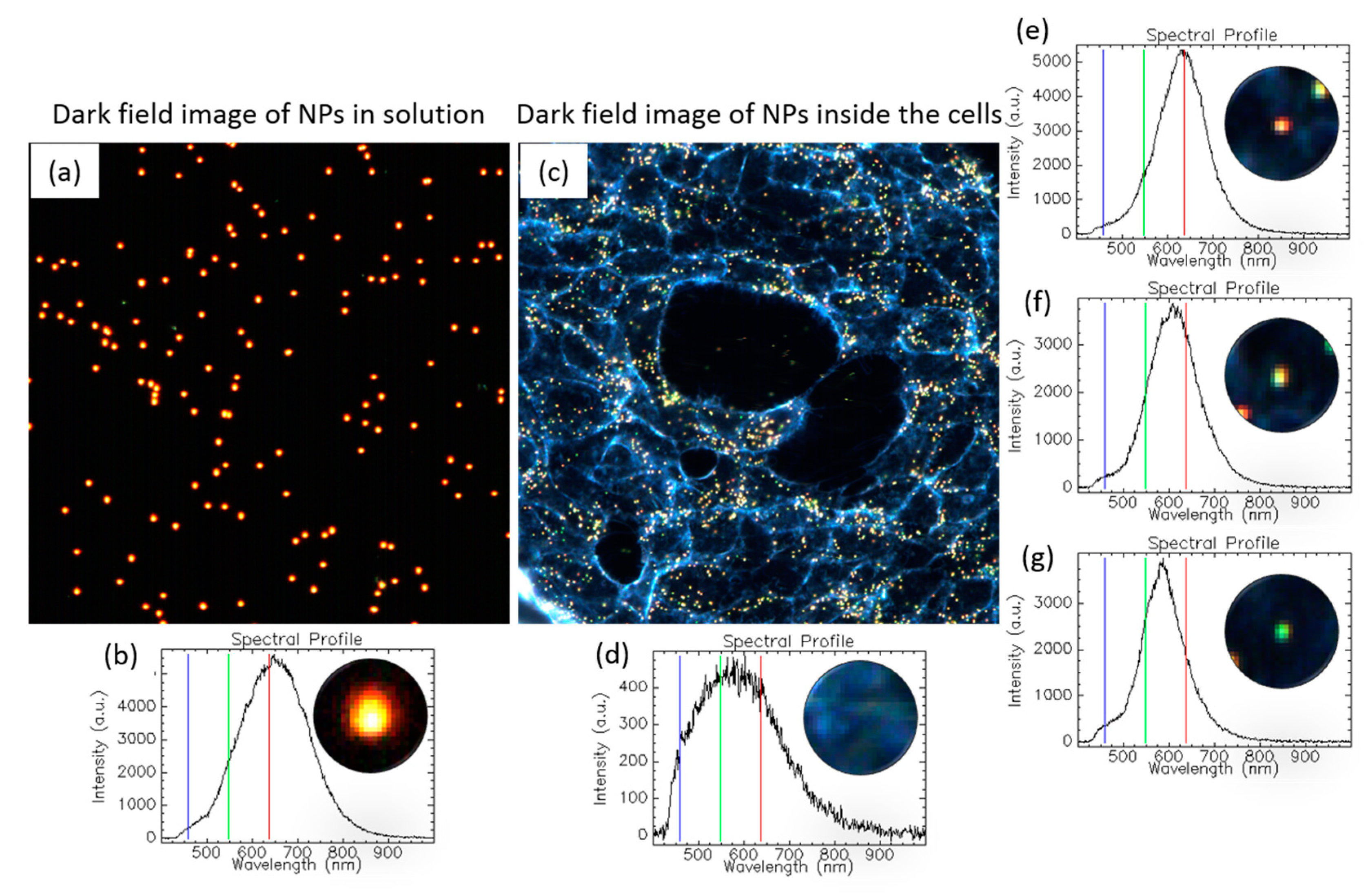
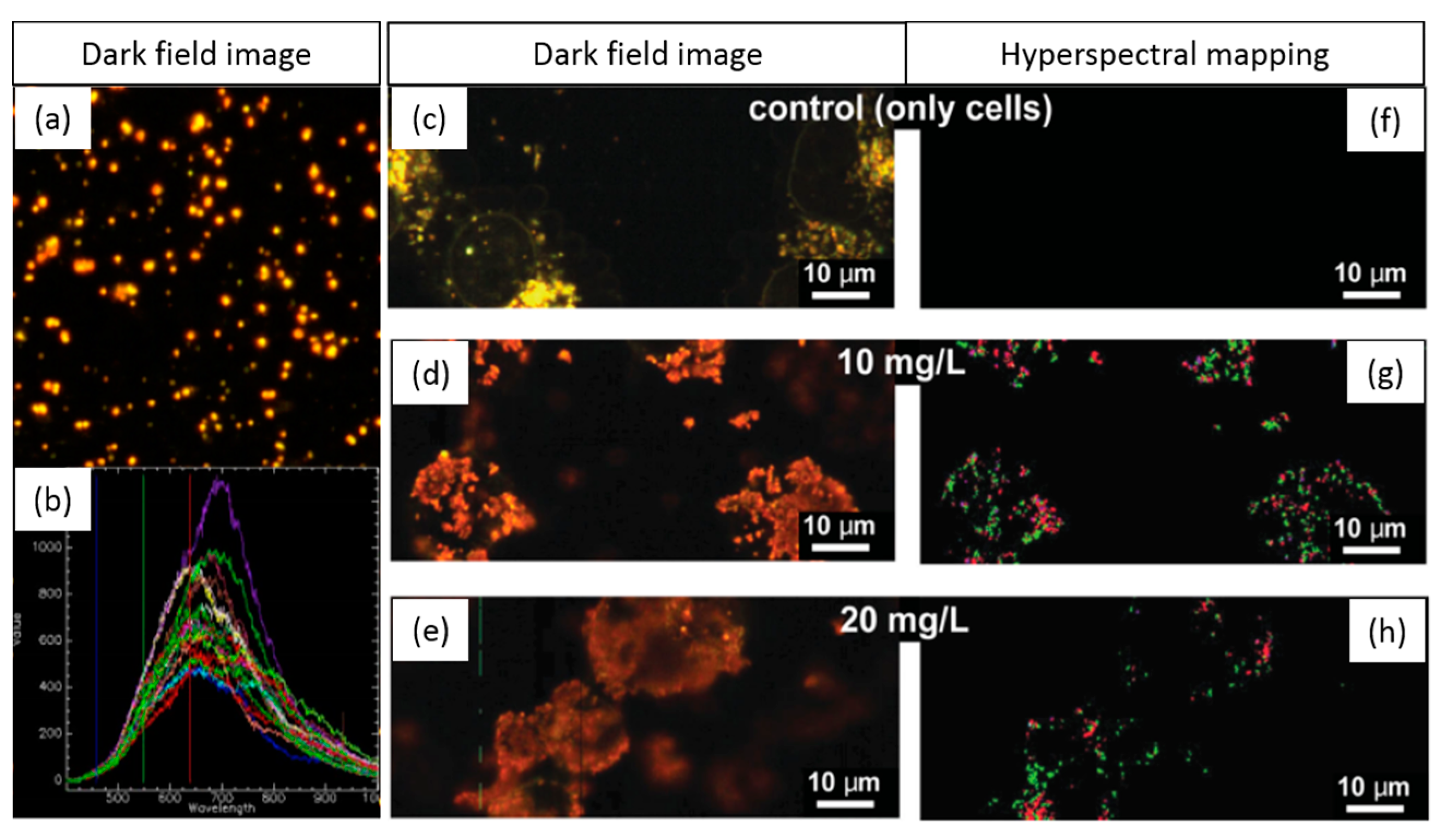
1.3.5. Tracking NPs’ Evolution in the Intracellular Milieu
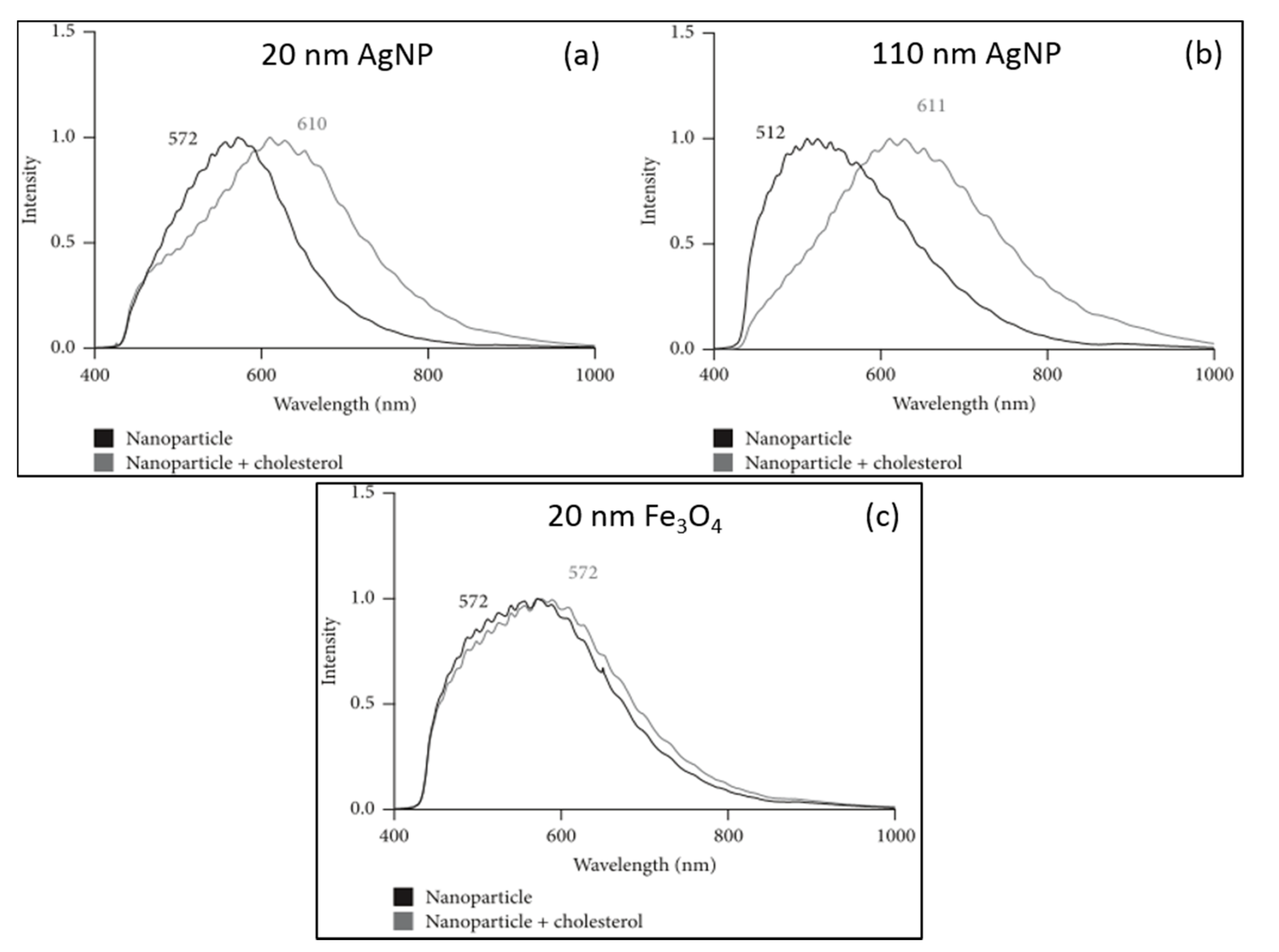
2. Biomedical Applications of HEDFM
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verebes, G.S.; Melchiorre, M.; Garcia-Leis, A.; Ferreri, C.; Marzetti, C.; Torreggiani, A. Hyperspectral enhanced dark field microscopy for imaging blood cells. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Yeung, E.S. Optical Imaging of individual plasmonic nanoparticles in biological samples. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairbairn, N.; Christofidou, A.; Kanaras, A.G.; Newman, T.A.; Muskens, O.L. Hyperspectral darkfield microscopy of single hollow gold nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4163–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z. Plasmonic dark field microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 113107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Smith, R.T. Optical hyperspectral imaging in microscopy and spectroscopy—A review of data acquisition. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théoret, T.; Wilkinson, K.J. Evaluation of enhanced darkfield microscopy and hyperspectral analysis to analyse the fate of silver nanoparticles in wastewaters. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3920–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainrub, A.; Pustovyy, O.; Vodyanoy, V. Resolution of 90 nm (λ/5) in an optical transmission microscope with an annular condenser. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2855–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Perez, P.; Pélaz, B.; Tsoutsi, D.; Parak, W.; Rivera Gil, P. Hyperspectral enhanced darkfield imaging of individual and collective hyperthermia-driven gold-copper sulfide nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Gowen, A.A.; Feng, Y.; Gaston, E.; Valdramidis, V. Recent applications of hyperspectral imaging in microbiology. Talanta 2015, 137, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patskovsky, S.; Bergeron, E.; Rioux, D.; Simard, M.; Meunier, M. Hyperspectral reflected light microscopy of plasmonic Au/Ag alloy nanoparticles incubated as multiplex chromatic biomarkers with cancer cells. Analyst 2014, 139, 5247–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patskovsky, S.; Bergeron, E.; Meunier, M. Hyperspectral darkfield microscopy of PEGylated gold nanoparticles targeting CD44-expressing cancer cells. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, M.; Gogos, A.; Bartolome, N.; Kahru, A.; Bucheli, T.D.; Slaveykova, V.I. Potential of hyperspectral imaging microscopy for semi-quantitative analysis of nanoparticle uptake by protozoa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8760–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera Gil, P.; Oberdörster, G.; Elder, A.; Puntes, V.; Parak, W.J. Correlating physico-chemical with toxicological properties of nanoparticles: The present and the future. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5227–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soenen, S.J.; Rivera-Gil, P.; Montenegro, J.M.; Parak, W.J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K. Cellular toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles: Common aspects and guidelines for improved nanotoxicity evaluation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Gil, P.; Jimenez De Aberasturi, D.; Wulf, V.; Pelaz, B.; Del Pino, P.; Zhao, Y.; De La Fuente, J.M.; Ruiz De Larramendi, I.; Rojo, T.; Liang, X.J.; et al. The challenge to relate the physicochemical properties of colloidal nanoparticles to their cytotoxicity. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 46, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannahan, J.H.; Sowrirajan, H.; Persaud, I.; Podila, R.; Brown, J.M. Impact of silver and iron nanoparticle exposure on cholesterol uptake by macrophages. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossari, A.A.; Shannahan, J.H.; Podila, R.; Brown, J.M. Influence of physicochemical properties of silver nanoparticles on mast cell activation and degranulation. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Starsich, F.; Dasargyri, A.; Wurnig, M.C.; Krumeich, F.; Boss, A.; Leroux, J.C.; Pratsinis, S.E. Photothermal killing of cancer cells by the controlled plasmonic coupling of silica-coated Au/Fe2O3 nanoaggregates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.V.; Qu, H.; Mudalige, T.; Ingle, T.M.; Wang, R.; Wang, F.; Howard, P.C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. Rapid determination of plasmonic nanoparticle agglomeration status in blood. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, D.; SoRelle, E.D.; Liba, O.; Dalal, R.; Paulus, Y.M.; Kim, T.-W.; Moshfeghi, D.M.; de la Zerda, A. High-resolution contrast-enhanced optical coherence tomography in mice retinae. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 066002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.J.; Zhang, L.W.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Yen, T.C.; Fang, J.Y. Theranostic liposomes loaded with quantum dots and apomorphine for brain targeting and bioimaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian Senthil, K.; Isabel, P.-S.; Benito, R.-G.; de Abajo, F.J.G.; Luis, M.L.-M. High-yield synthesis and optical response of gold nanostars. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 015606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanles-Sobrido, M.; Exner, W.; Rodrıguez-Lorenzo, L.; Rodrıguez-Gonzalez, B.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Design of SERS-encoded, submicron, hollow particles nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamora-Perez, P.; Tsoutsi, D.; Xu, R.; Rivera_Gil, P. Hyperspectral-Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy for Single and Collective Nanoparticle Characterization in Biological Environments. Materials 2018, 11, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020243
Zamora-Perez P, Tsoutsi D, Xu R, Rivera_Gil P. Hyperspectral-Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy for Single and Collective Nanoparticle Characterization in Biological Environments. Materials. 2018; 11(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamora-Perez, Paula, Dionysia Tsoutsi, Ruixue Xu, and Pilar Rivera_Gil. 2018. "Hyperspectral-Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy for Single and Collective Nanoparticle Characterization in Biological Environments" Materials 11, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020243
APA StyleZamora-Perez, P., Tsoutsi, D., Xu, R., & Rivera_Gil, P. (2018). Hyperspectral-Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy for Single and Collective Nanoparticle Characterization in Biological Environments. Materials, 11(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020243






