Synthesis and Properties of Magnetic Aryl-Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Dual Brønsted/Lewis Acidity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. General Procedure for Synthesis of Target FeCl4 Anion Salts (5a–5d)
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Acidity Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
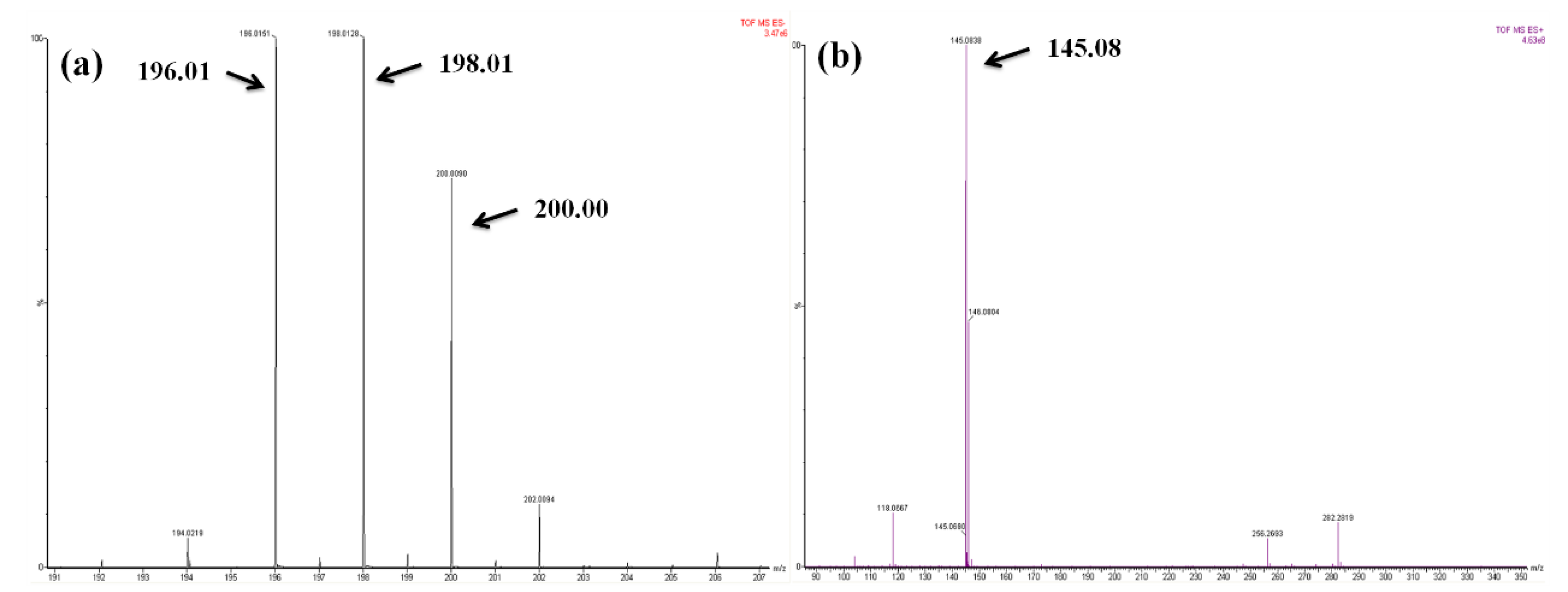
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of B-L MILs
3.2. Solubility of B-L MILs
3.3. Thermal Stability of B-L MILs
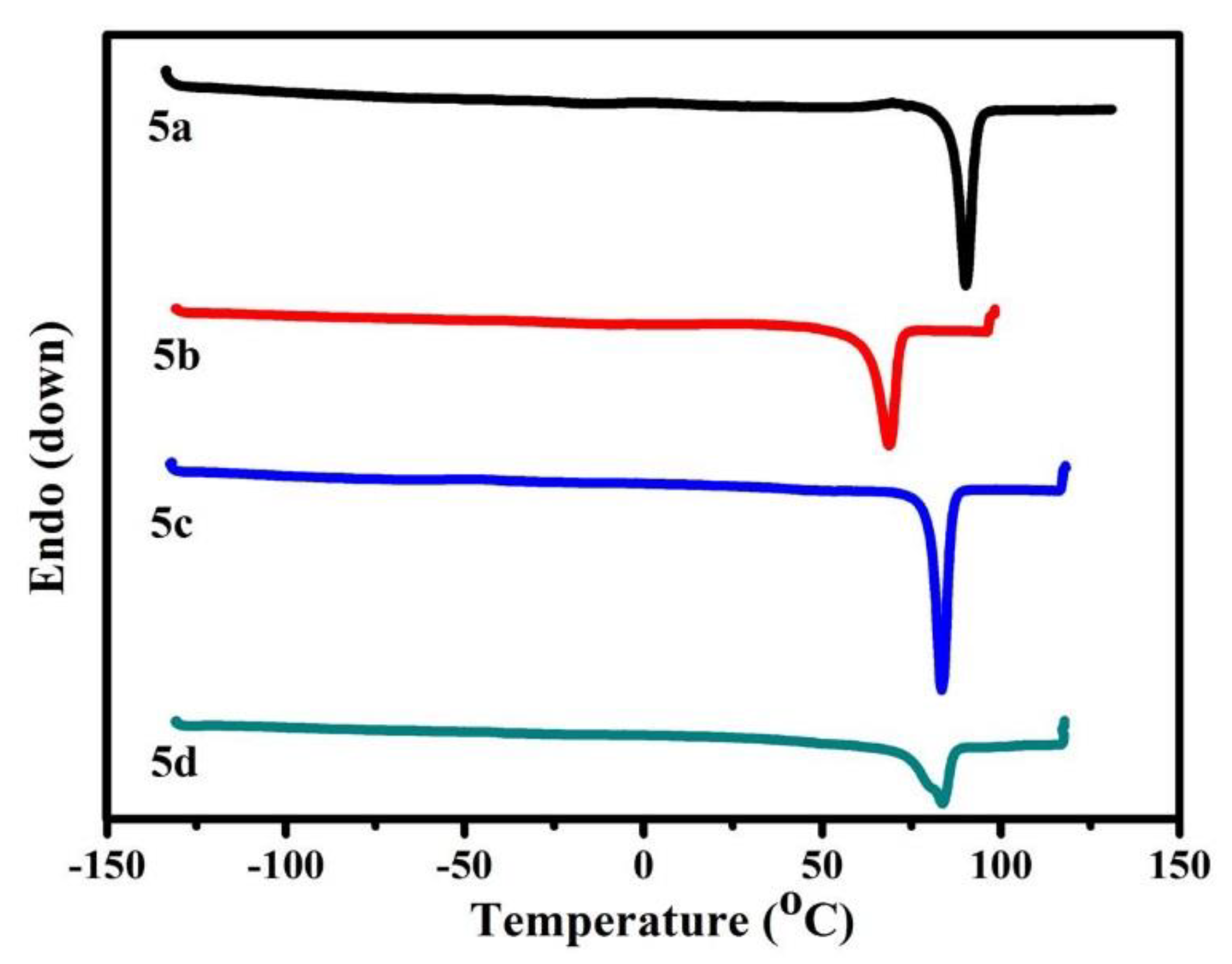
3.4. Melting Point Properties of B-L MILs
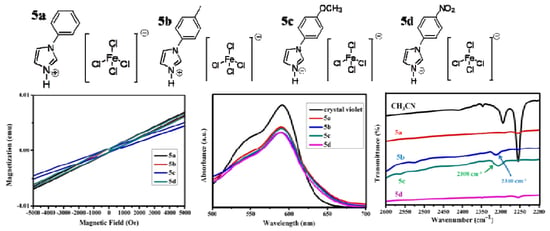
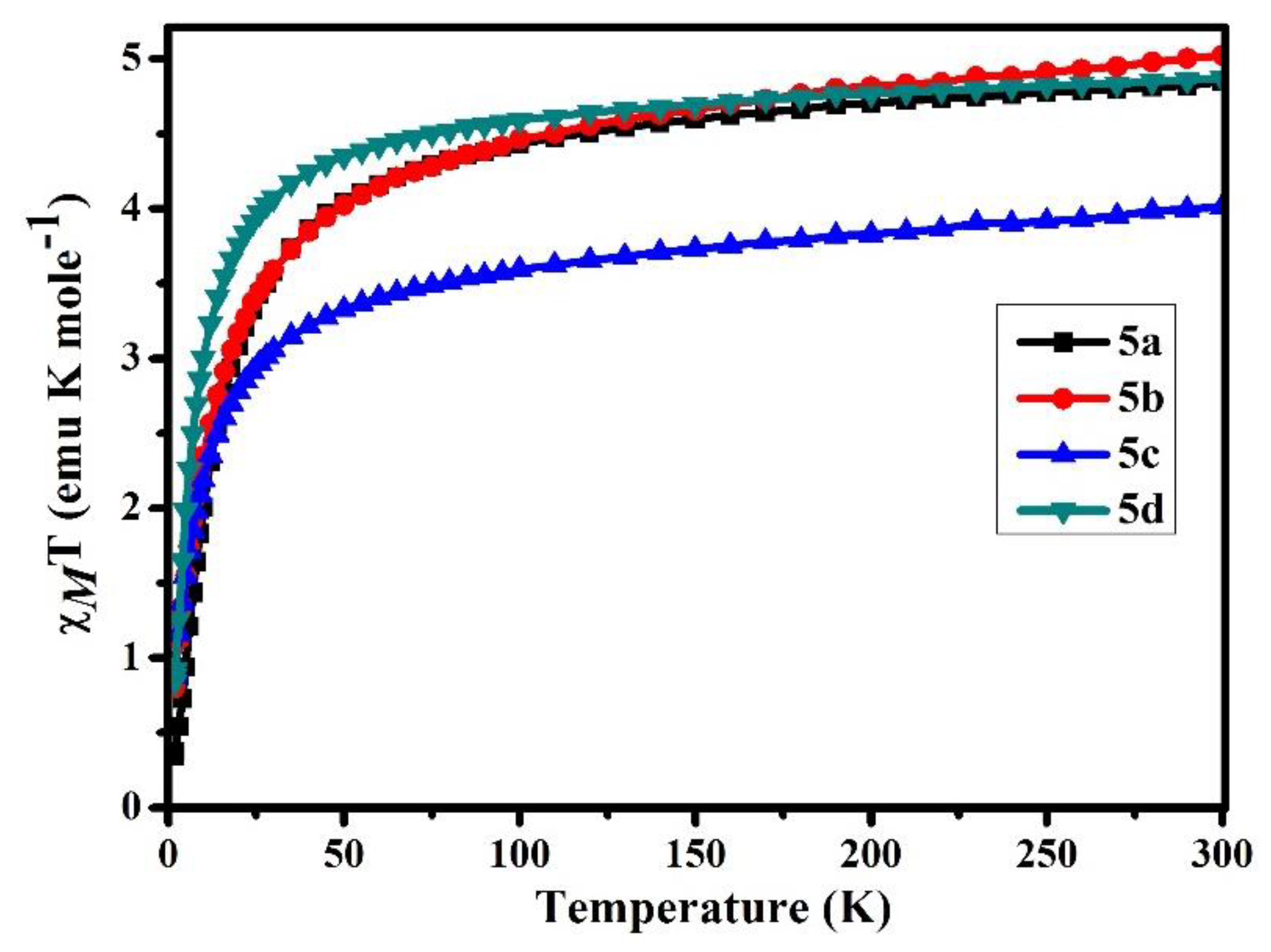
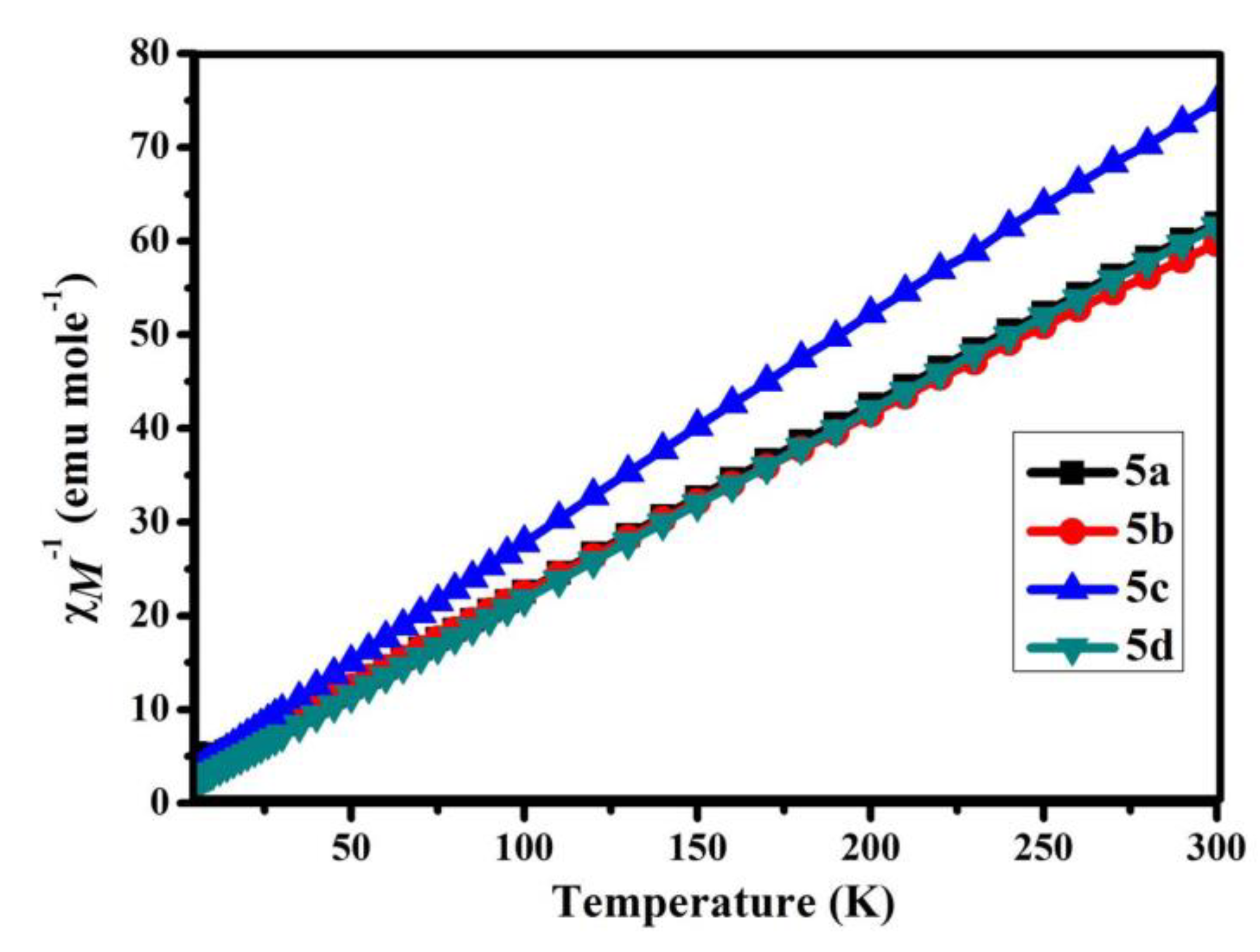
3.5. Magnetic Properties of B-L MILs
3.6. Brønsted Acidity Properties of B-L MILs
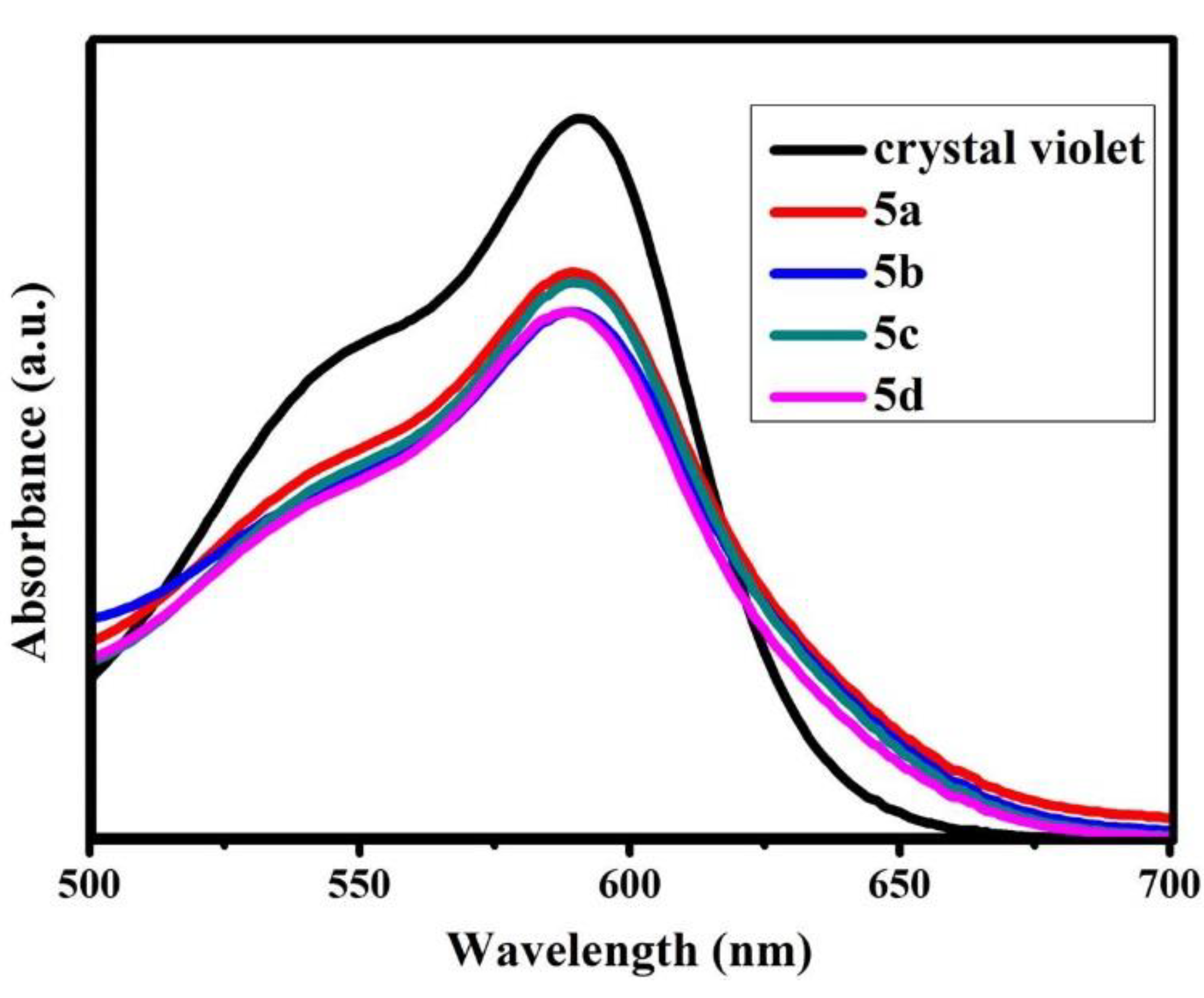
3.7. Lewis Acidity Properties of B-L MILs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Qin, L.; Mu, T.; Xue, Z.; Gao, G. Are ionic liquids chemically stable. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7113–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodius, D.; Mudring, A.-V. Rare earth metal-containing ionic liquids. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 363, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T. Ionic liquids as tool to improve enzymatic organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10567–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafaeezadeh, M.; Alinezhad, H. Brønsted acidic ionic liquids: Green catalysts for essential organic reactions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Huang, C.-W.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Teng, H. Electric double layer capacitors of high volumetric energy based on ionic liquids and hierarchical-pore carbon. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14963–14972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Yen, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-C.; Su, C.-W.; Chang, P.-Y.; Sun, I.-W.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Lee, Y.-L.; Teng, H. An ether bridge between cations to extend the applicability of ionic liquids in electric double layer capacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 19160–19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Tuning environmental friendly chelate-based ionic liquids for highly efficient and reversible SO2 chemisorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15292–15300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Lv, X. Supported absorption of CO2 by tetrabutylphosphonium amino acid ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiglak, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Lu, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids for energy, materials, and medicine. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9228–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.A.; Zhang, C.; Devasurendra, A.M.; Tillekeratne, L.M.V.; Anderson, J.L.; Kirchhoff, J.R. Conductive polymeric ionic liquids for electroanalysis and solid-phase microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 910, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devasurendra, A.M.; Zhang, C.; Young, J.A.; Tillekeratne, L.M.V.; Anderson, J.L.; Kirchhoff, J.R. Electropolymerized pyrrole-based conductive polymeric ionic liquids and their application for solid-phase microextraction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24955–24963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Huang, P.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H.; Bao, C.; Gao, G.; He, R.; Cui, D. Dual phase-controlled synthesis of uniform lanthanide-doped NaGdF4 upconversion nanocrystals via an OA/ionic liquid two-phase system for in vivo dual-modality imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4470–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, R.; Yao, Y.; Tsuda, T.; Torimoto, T.; Kuwabata, S. Oxygen reduction electrocatalysts sophisticated by using Pt nanoparticle-dispersed ionic liquids with electropolymerizable additives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 11853–11862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, M.; Patil, R.A.; Armstrong, D.W. Physicochemical properties of branched-chain dicationic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payagala, T.; Huang, J.; Breitbach, Z.S.; Sharma, P.S.; Armstrong, D.W. Unsymmetrical dicationic ionic liquids: Manipulation of physicochemical properties using specific structural architectures. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5848–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Yang, B. Design, synthesis, and analysis of thermophysical properties for imidazolium-based geminal dicationic ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumene, T.; Belarbi, E.H.; Haddad, B.; Villemin, D.; Abbas, O.; Khelifa, B.; Bresson, S. Study of imidazolium dicationic ionic liquids by Raman and FTIR spectroscopies: The effect of the nature of the anion. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1083, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindri, I.M.; Siddiqui, D.A.; Bhardwaj, P.; Rodriguez, L.C.; Palmer, K.L.; Frizzo, C.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Rodrigues, D.C. Dicationic imidazolium-based ionic liquids: A new strategy for non-toxic and antimicrobial materials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62594–62602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.D.; Emaus, M.N.; Varona, M.; Bowers, A.N.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids: Solvents and sorbents in sample preparation. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.D.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids as tunable materials in (bio) analytical chemistry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4565–4566. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; DeRooy, S.L.; Bwambok, D.K.; El-Zahab, B.; DiTusa, J.F.; Warner, I.M. Magnetic chiral ionic liquids derived from amino acids. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6922–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, A.; Branco, L.C.; Pina, F. Electrochromic and magnetic ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2300–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Butts, C.P.; Eastoe, J.; Hernandez, E.P.; Machadob, F.L.; de Oliveira, R.J. Dication magnetic ionic liquids with tuneable heteroanions. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2765–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.D.; Nacham, O.; Purslow, J.A.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.C.; Hogg, J.M.; Swadzba-Kwasny, M. Lewis acidic ionic liquids. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 78–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasekara, A.S. Acidic ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6133–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoda-Földes, R. The use of supported acidic ionic liquids in organic synthesis. Molecules 2014, 19, 8840–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Magnetic ionic liquids: Synthesis, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40008–40018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Mahajan, R.K. Influence of various additives on the physicochemical properties of imidazolium based ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 748–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, S.; Peritz, A.; Strassner, T. Tunable aryl alkyl ionic liquids (TAAILs): The next generation of ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7908–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, S.; Schulz, T.; Cho, C.-W.; Arning, J.; Strassner, T. Synthesis, toxicity, and biodegradation of tunable aryl alkyl ionic liquids (TAAILs). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, B.; Rimaz, M. An investigation on the physicochemical properties of the nanostructured [(4-X)PMAT][N(CN)2] ion pairs as energetic and tunable aryl alkyl amino tetrazolium based ionic liquids. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1137, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, M.C.; Özgün, B. Tunable aryl alkyl ionic liquids (TAAILs) based on 1-aryl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazoles. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, F.; Lerch, S.; Kaliner, M.; Strassner, T. Cobalt-catalyzed hydroarylations and hydroaminations of alkenes in tunable aryl alkyl ionic liquids. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6215–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage-Estebanez, I.; del Olmo, L.; López, R.; de la Vega, J.M.G. Molecular modeling and physicochemical properties of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-FeX4 and -Fe2X7 (X = Cl and Br) magnetic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Saito, G. Influence of structural variations in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cation and tetrahalogenoferrate (III) anion on the physical properties of the paramagnetic ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, H. Discovery of a magnetic ionic liquid [bmim]FeCl4. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1590–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesto, R.E.D.; McCleskey, T.M.; Burrell, A.K.; Baker, G.A.; Thompson, J.D.; Scott, B.L.; Wilkes, J.S.; Williams, P. Structure and magnetic behavior of transition metal based ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2008, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Gaertner, P. An iron-containing ionic liquid as recyclable catalyst for aryl grignard cross-coupling of alkyl halides. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyahi, S.; Azin, A.; Saghanezhad, S.J. Synthesis and characterization of a novel paramagnetic functionalized ionic liquid as a highly efficient catalyst in one-pot synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphtols. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 198, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, R.; Song, X.; Liu, F.; Yu, S.; Liu, S.; Ge, X. Lewis acidic ionic liquid [Bmim]FeCl4 as a high efficient catalyst for methanolysis of poly (lactic acid). Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, A.R.; Rafiee, F. Acidic Bronsted ionic liquids. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2010, 42, 285–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomons, G.; Fryhle, C.; Snyder, S. Organic Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Obuchi, A.; Oi-Uchisawa, J.; Nanbab, T.; Kushiyama, S. Synergistic catalysis of carbon black oxidation by Pt with MoO3 or V2O5. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 30, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Hansen, P.E.; Le, T.N. An efficient and green method for regio- and chemo-selective Friedel–Crafts acylations using a deep eutectic solvent ([CholineCl][ZnCl2]3). RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 37031–37038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunagariya, J.; Dhar, A.; Vekariya, R.L. Efficient esterification of n-butanol with acetic acid catalyzed by the Bronsted acidic ionic liquids: Influence of acidity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5412–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Abdeltawab, A.A.; Guan, Y.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yu, G.; Yu, L. Brønsted−lewis acidic ionic liquids and application in oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2998–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Liu, F.; Song, Z. Brønsted-lewis acidic ionic liquid for the “one-pot” synthesis of biodiesel from waste oil. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2013, 5, 023111–023116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomazeau, C.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Magna, L.; Luts, S.; Gilbert, B. Determination of an acidic scale in room temperature ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5264–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, H.; Lu, X.; Yuan, Y. Brønsted acidic ionic liquid as an efficient and recyclable promoter for hydroesterification of olefins catalyzed by a triphenylphosphine-palladium complex. Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihichuk, L.M.; Driver, G.W.; Johnson, K.E. Brønsted acidity and the medium: Fundamentals with a focus on ionic liquids. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Kou, Y. Determination of the lewis acidity of ionic liquids by means of an IR spectroscopic probe. Chem. Commun. 2004, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouwer, P.H.J.; Swager, T.M. Synthesis and mesomorphic properties of rigid-core ionic liquid crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14042–14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Pan, P. A spectrophotometric study of Fe(II)-chloride complexes in aqueous solutions from 10 to 100 °C. Can. J. Chem. 2001, 79, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Saha, S.; Hamaguchi, H. A new class of magnetic fluids: Bmim[FeCl4] and nbmim[FeCl4] ionic liquids. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitze, M.S.; Schreiter, E.R.; Patterson, E.V.; Freeman, R.G. Ionic liquids based on FeCl3 and FeCl2. Raman scattering and ab initio calculations. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Sharpe, A.G. Inorganic Chemistry; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Crosthwaite, J.M.; Muldoon, M.J.; Dixon, J.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Brennecke, J.F. Phase transition and decomposition temperatures, heat capacities and viscosities of pyridinium ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2005, 37, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Armstrong, D.W. High-stability ionic liquids. A new class of stationary phases for gas chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4851–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; DeVos, N.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, K.J.; Deacon, G.B.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Pringle, J.M.; Scott, J.L. Thermal degradation of ionic liquids at elevated temperatures. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, T.; Ahrens, S.; Meyer, D.; Allolio, C.; Peritz, A.; Strassner, T. Electronic effects of para-substitution on the melting points of TAAILs. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, D.; Strassner, T. 1,2,4-Triazole-based tunable aryl/alkyl ionic liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, O. Molecular Magnetism; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.-C.; Ho, W.-Y.; Sun, I.-W.; Chou, Y.-K.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Wu, T.-Y.; Liang, S.-S. Synthesis and properties of new (μ-oxo)bis[trichloroferrate(III)] dianion salts. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-C.; Ho, W.-Y.; Sun, I.-W.; Chou, Y.-K.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Wu, T.-Y. Synthesis and properties of new tetrachlorocobaltate (II) and tetrachloromanganate (II) anion salts with dicationic counterions. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, J.J.; Jimenez-Sanchez, A.; Cano, F.H.; Saez-Puche, R.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, E. Preparation and characterization of tetrachlorocobaltates(II) of α,ω-alkylenediammonium. Magnetic and thermal properties. Crystal structure of [NH3(CH2)5NH3]CoCl4. Acta Crystallogr. B 1999, 55, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, B.M.; Lee, H.Y.; Emge, T.J.; Wishart, J.F.; Castner, E.W., Jr. Ionic liquids and solids with paramagnetic anions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 8919–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

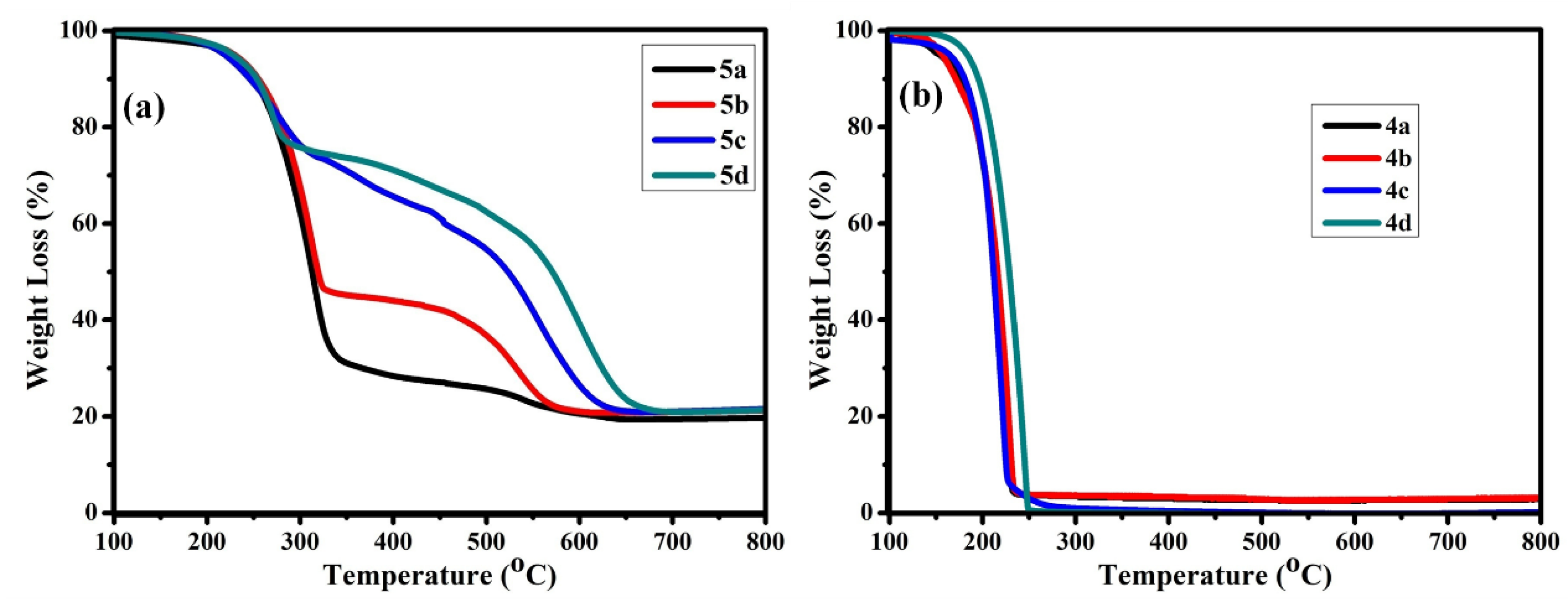
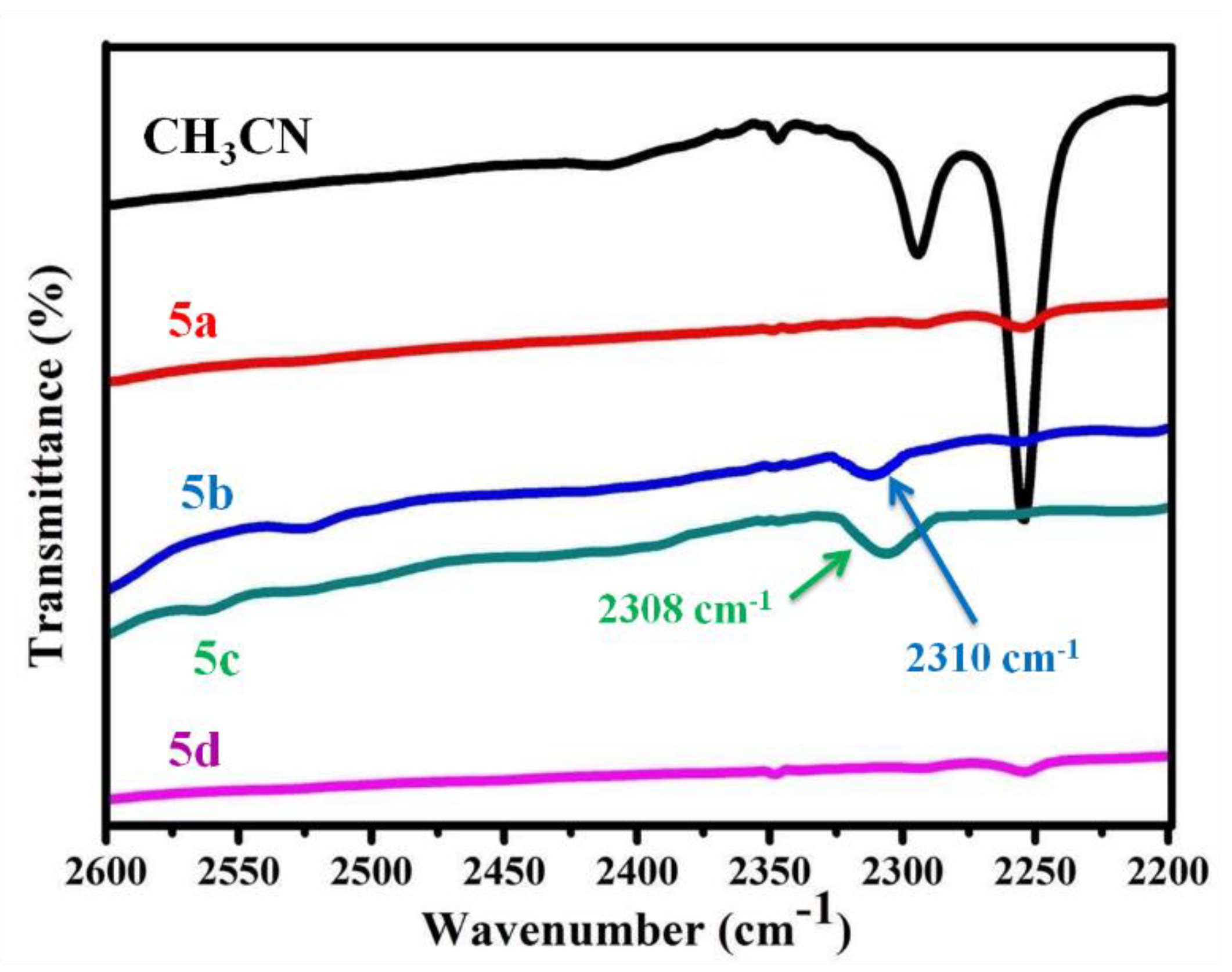
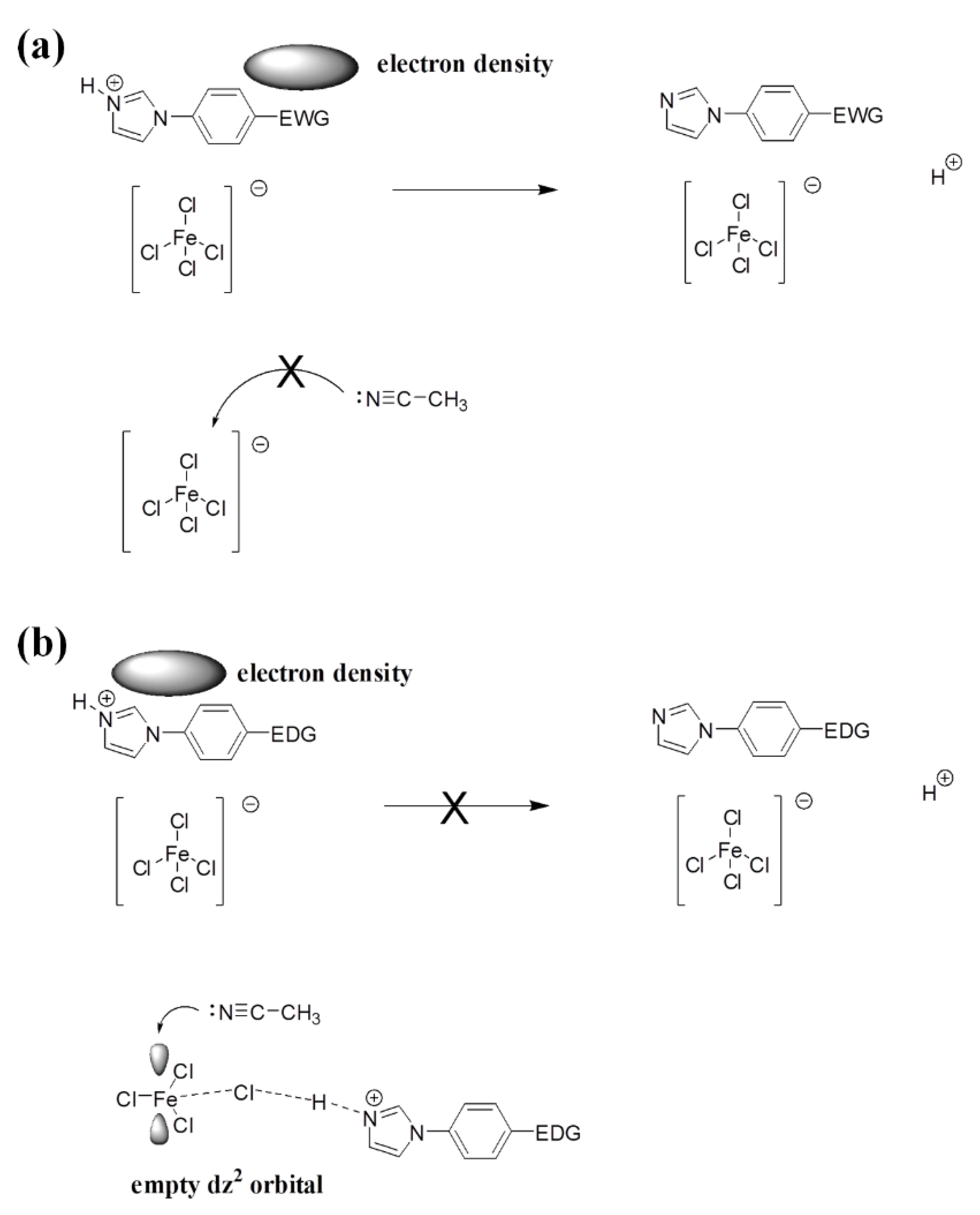
| Compound | Td (°C) a | Td (°C) b | Td (°C) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 106 | 153 | 176 |
| 4b | 129 | 157 | 170 |
| 4c | 127 | 165 | 181 |
| 4d | 157 | 182 | 195 |
| 5a | 205 | 224 | 250 |
| 5b | 207 | 228 | 255 |
| 5c | 192 | 219 | 246 |
| 5d | 213 | 228 | 253 |
| Compound | DMSO | H2O | ACN | MeOH | EtOH | Acetone | EA | DCM | Et2O | Hex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε a | 46.7 | 80.1 | 37.5 | 32.7 | 24.5 | 20.7 | 6.02 | 8.93 | 4.33 | 1.88 |
| 5a | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ± | − |
| 5b | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ± | ± | − |
| 5c | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ± | − |
| 5d | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ± | ± | − |
| Compound | DSC (°C) | MP-S3 (°C) a |
|---|---|---|
| 5a | 90.2 | 88.5–90.4 |
| 5b | 68.6 | 64.5–67.8 |
| 5c | 83.4 | 83.2–84.1 |
| 5d | 83.7 | 82.3–83.4 |
| Compound | χMT (emu K mole−1) | μeff | Θ (K) g | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | 4.85 | 6.23 | −16.28 | This work |
| 5b | 5.02 | 6.34 | −13.14 | This work |
| 5c | 4.01 | 5.66 | −10.08 | This work |
| 5d | 4.87 | 6.24 | −7.34 | This work |
| [Bmim][FeCl4] a | 4.11 | 5.73 | nr h | [40] |
| [Nbmim][FeCl4] b | 4.38 | 5.91 | nr h | [58] |
| [N1444][FeCl4] c | 4.42 | 5.95 | nr h | [71] |
| [Pyrr14][FeCl4] d | 4.47 | 5.98 | nr h | [71] |
| [C10mim][FeCl4] e | 4.01 | 5.66 | −3.30 | [41] |
| [Emim][FeCl4] f | 4.03 | 5.67 | −2.50 | [39] |
| Compound | Amax | [I] | [IH+] | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 1.0874 | 100 | 0 | - |
| 5a | 0.8541 | 78.57 | 21.43 | 1.36 |
| 5b | 0.7934 | 73.12 | 26.88 | 1.23 |
| 5c | 0.8388 | 77.19 | 22.81 | 1.33 |
| 5d | 0.7899 | 72.59 | 27.05 | 1.23 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, J.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Sun, I.-W.; Ho, W.-Y.; Wu, T.-Y. Synthesis and Properties of Magnetic Aryl-Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Dual Brønsted/Lewis Acidity. Materials 2018, 11, 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122539
Chang J-C, Yang C-H, Sun I-W, Ho W-Y, Wu T-Y. Synthesis and Properties of Magnetic Aryl-Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Dual Brønsted/Lewis Acidity. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122539
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Jui-Cheng, Che-Hsuan Yang, I-Wen Sun, Wen-Yueh Ho, and Tzi-Yi Wu. 2018. "Synthesis and Properties of Magnetic Aryl-Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Dual Brønsted/Lewis Acidity" Materials 11, no. 12: 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122539
APA StyleChang, J.-C., Yang, C.-H., Sun, I.-W., Ho, W.-Y., & Wu, T.-Y. (2018). Synthesis and Properties of Magnetic Aryl-Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Dual Brønsted/Lewis Acidity. Materials, 11(12), 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122539