Effects of Grinding Passes and Direction on Material Removal Behaviours in the Rail Grinding Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
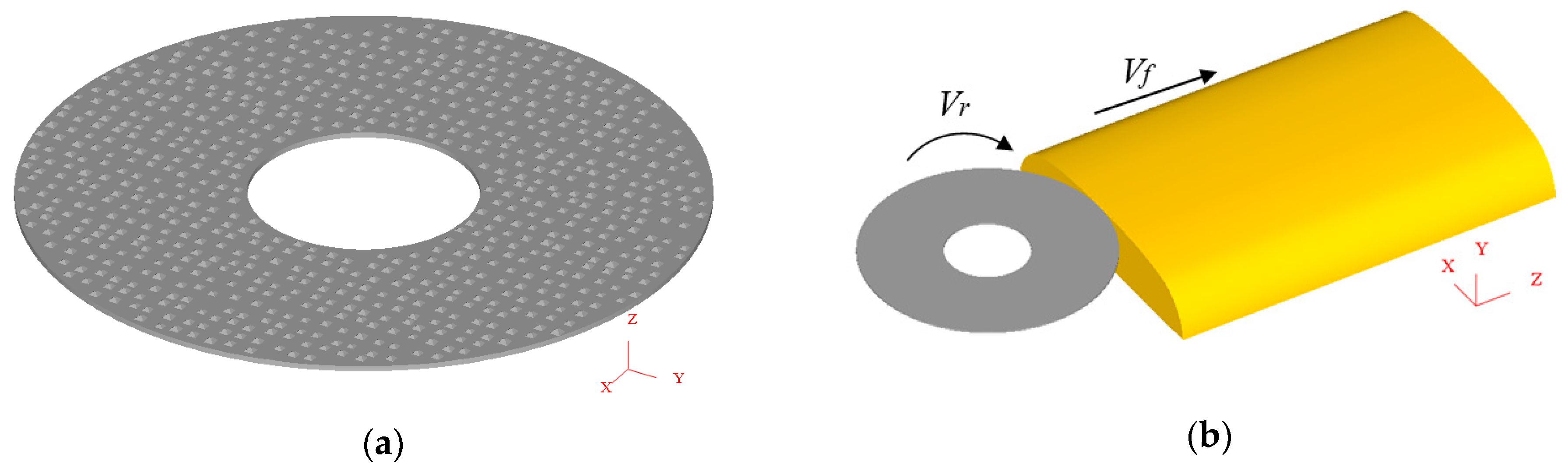
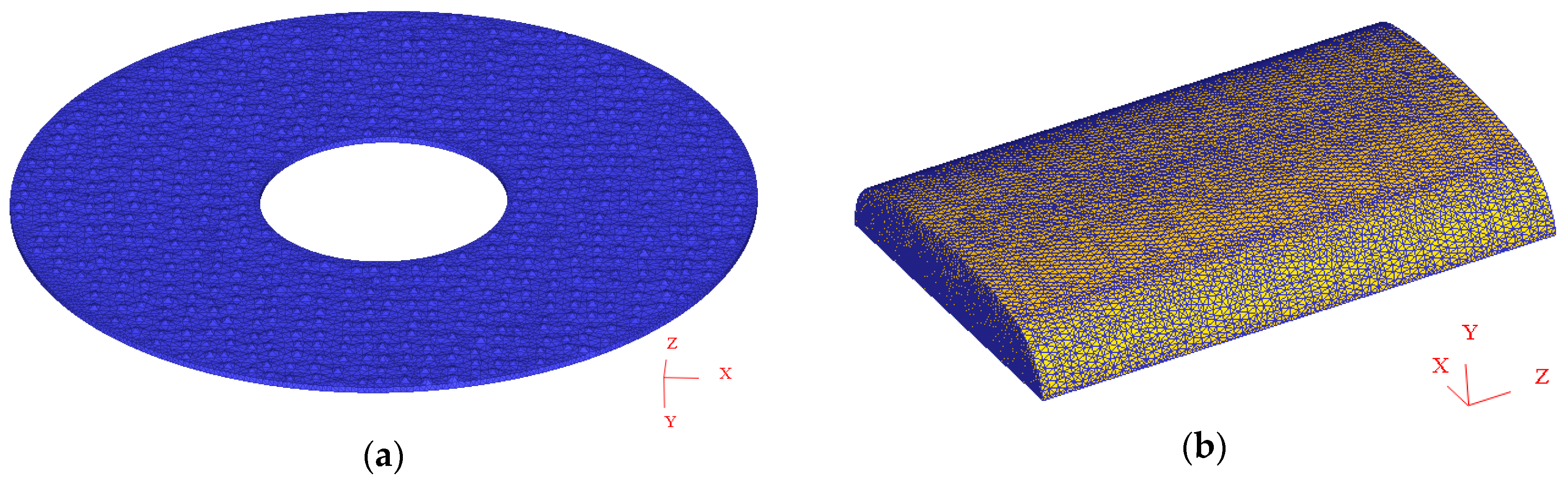
2. Simulation Details
2.1. Simulaiton Model
2.2. Simulation and Material Parameters
3. Results
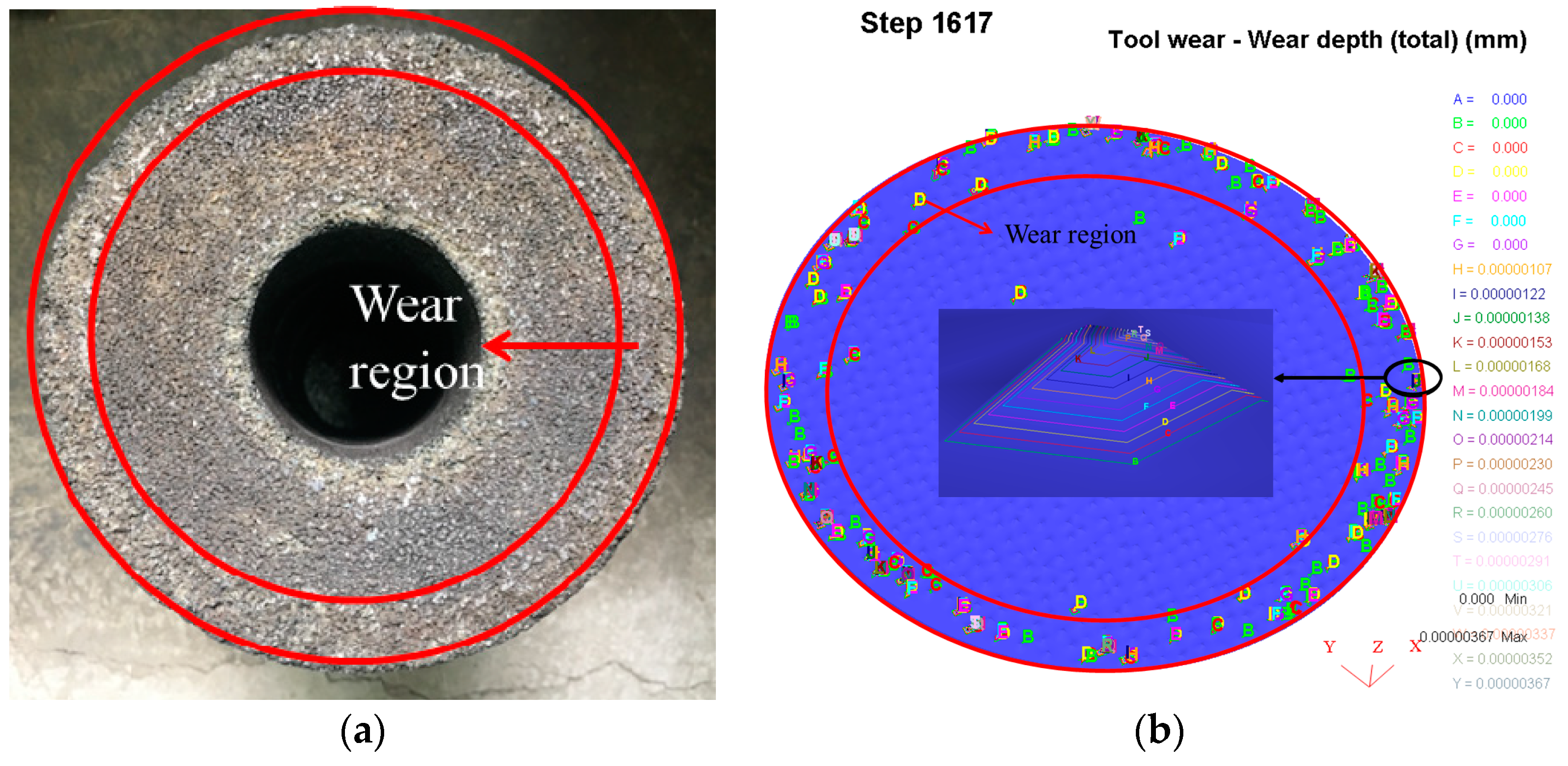
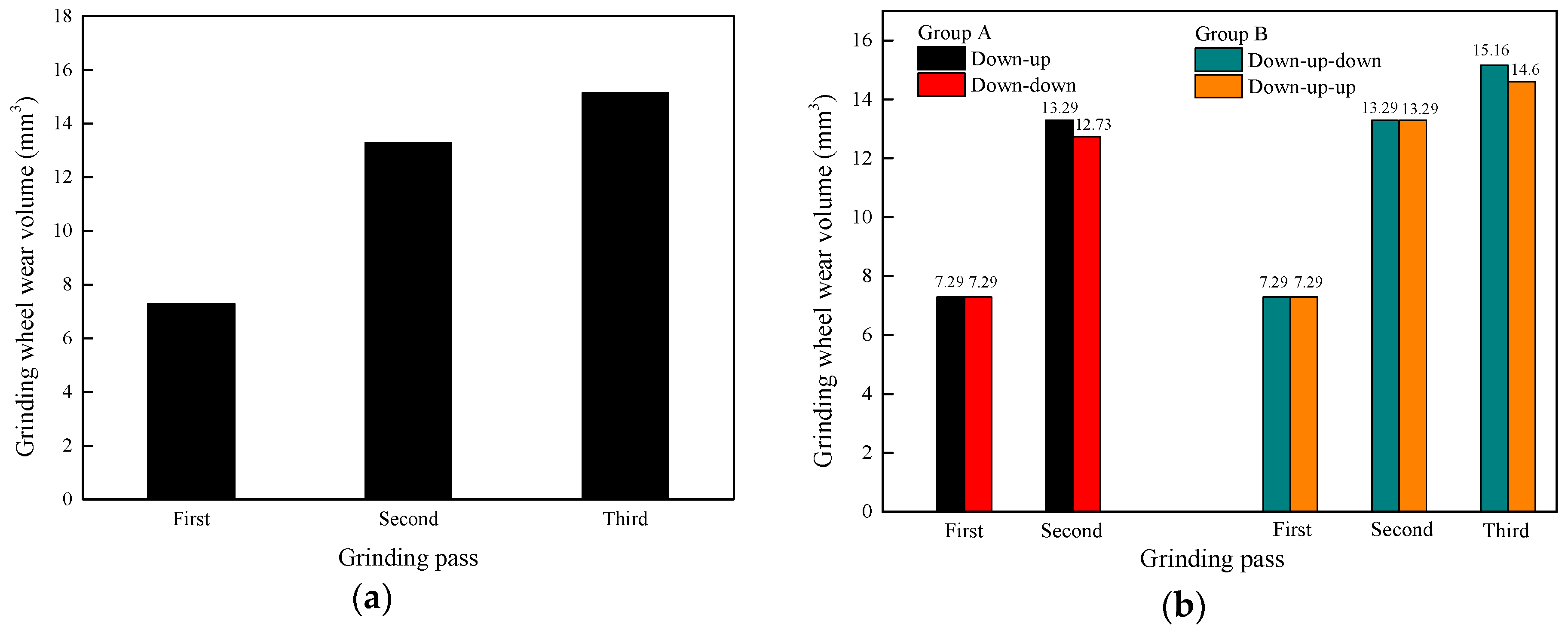
3.1. Wear Amount for the Grinding Wheel
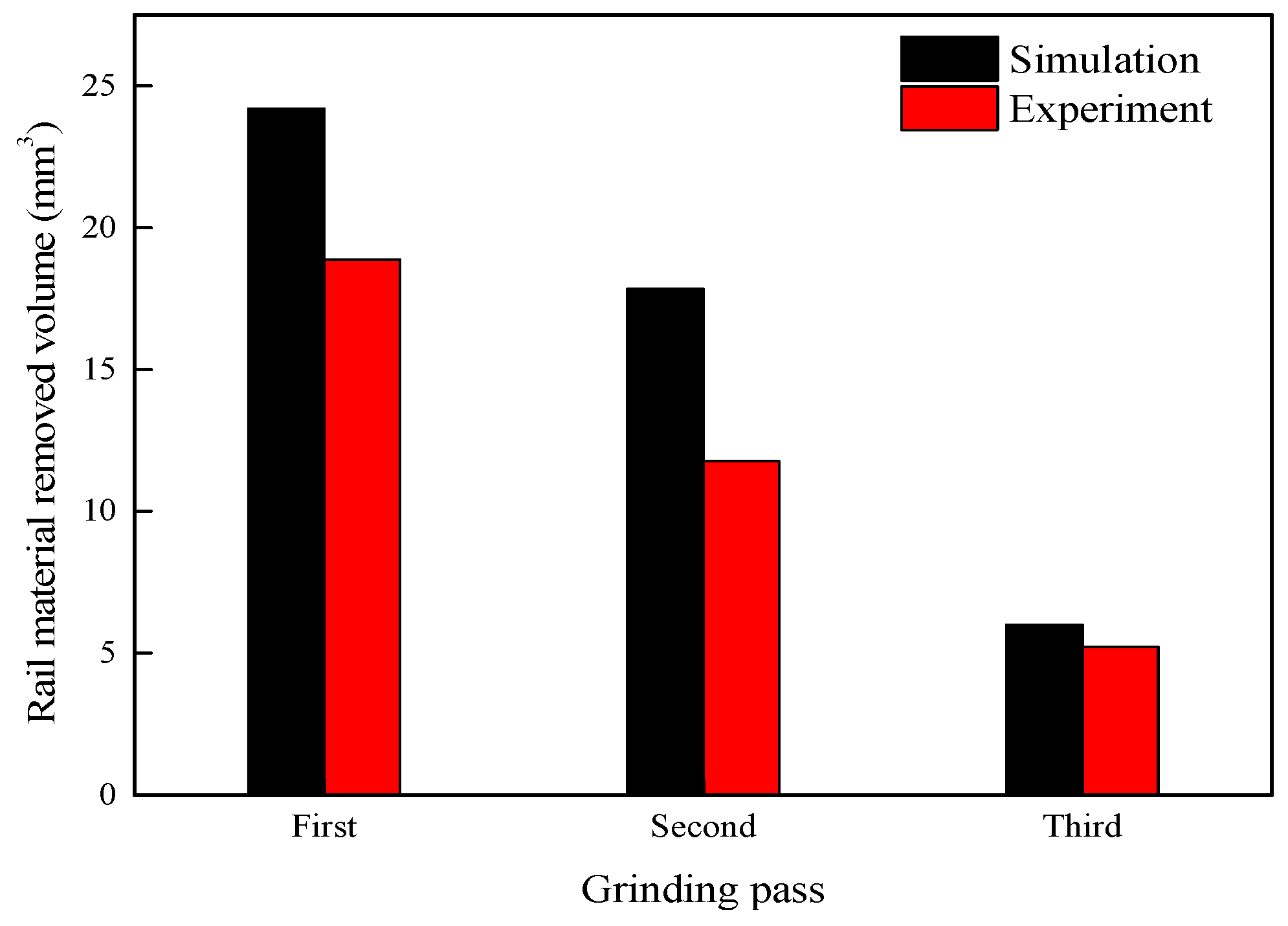
3.2. Volume of Removed Rail Material
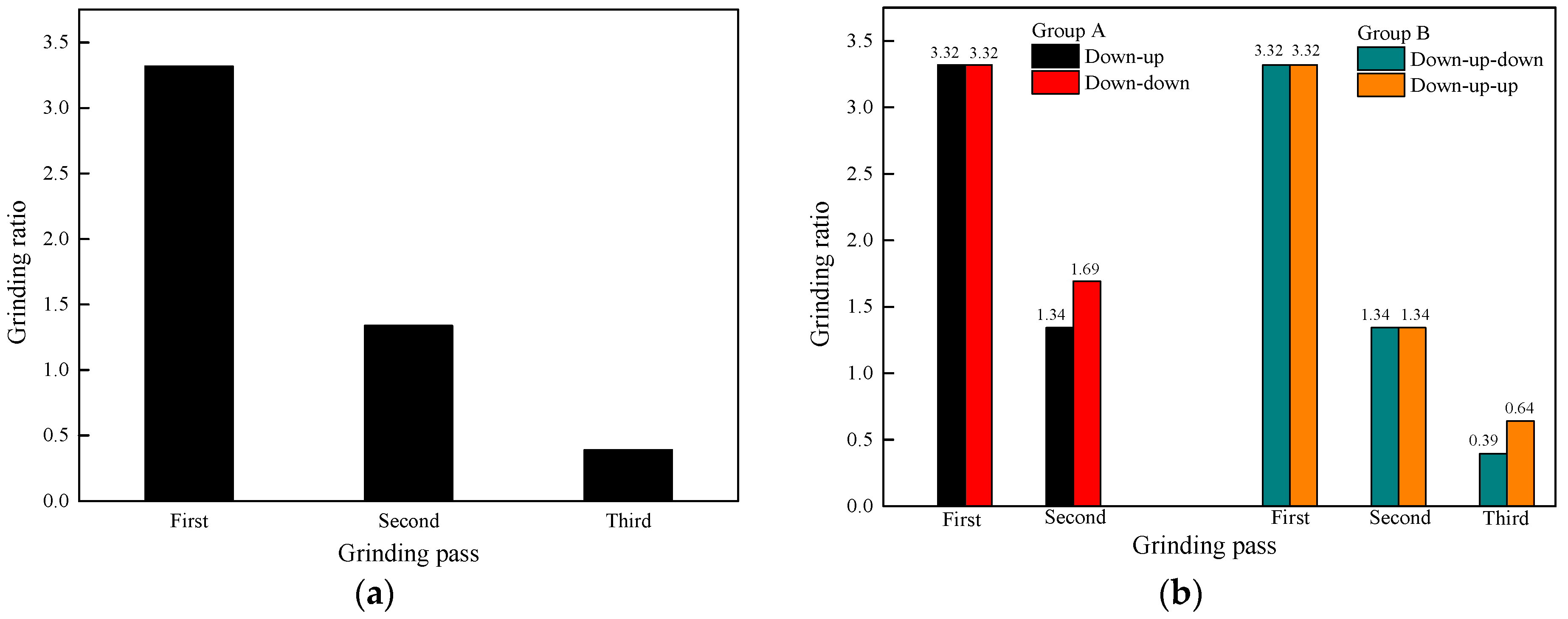
3.3. Grinding Ratio
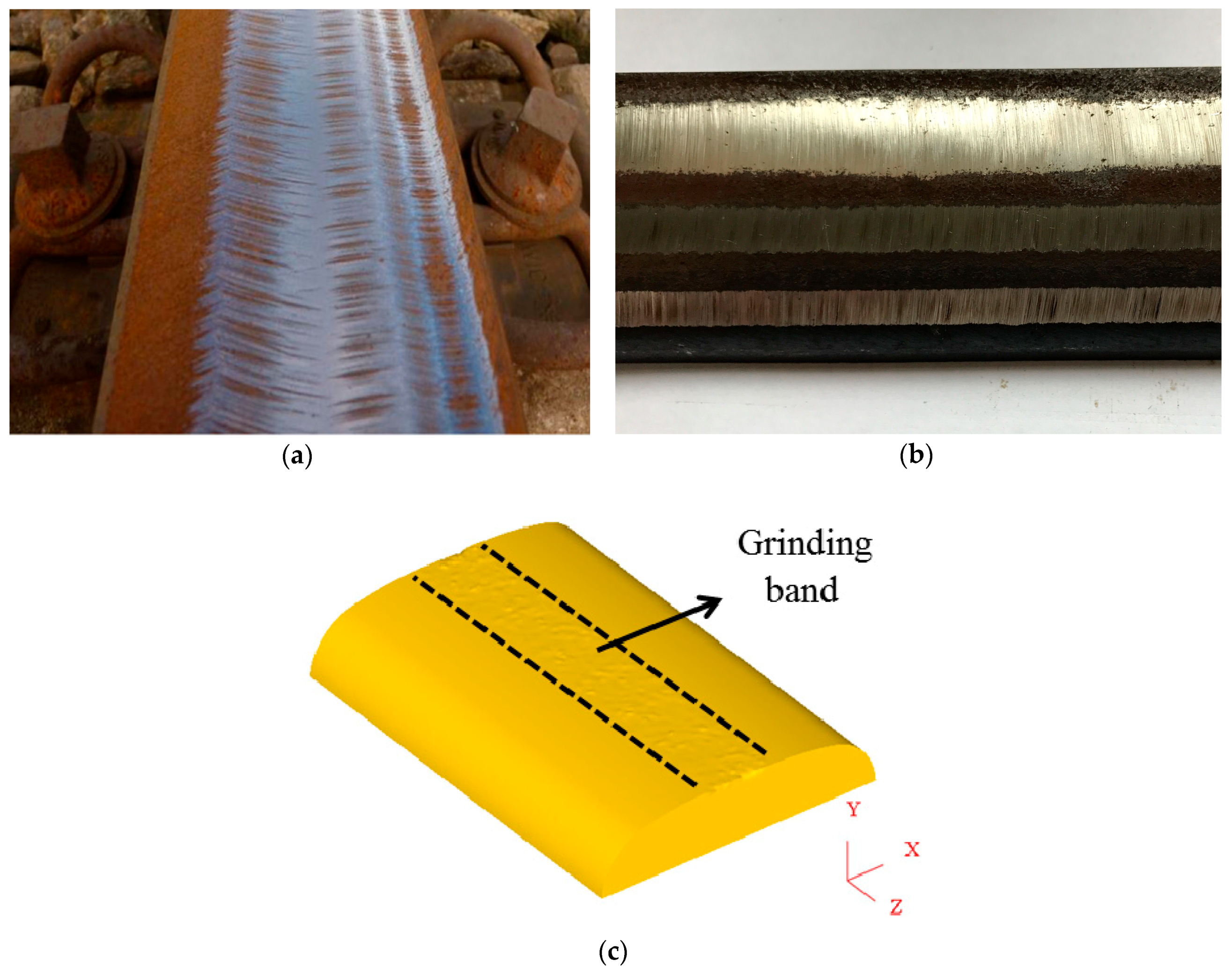
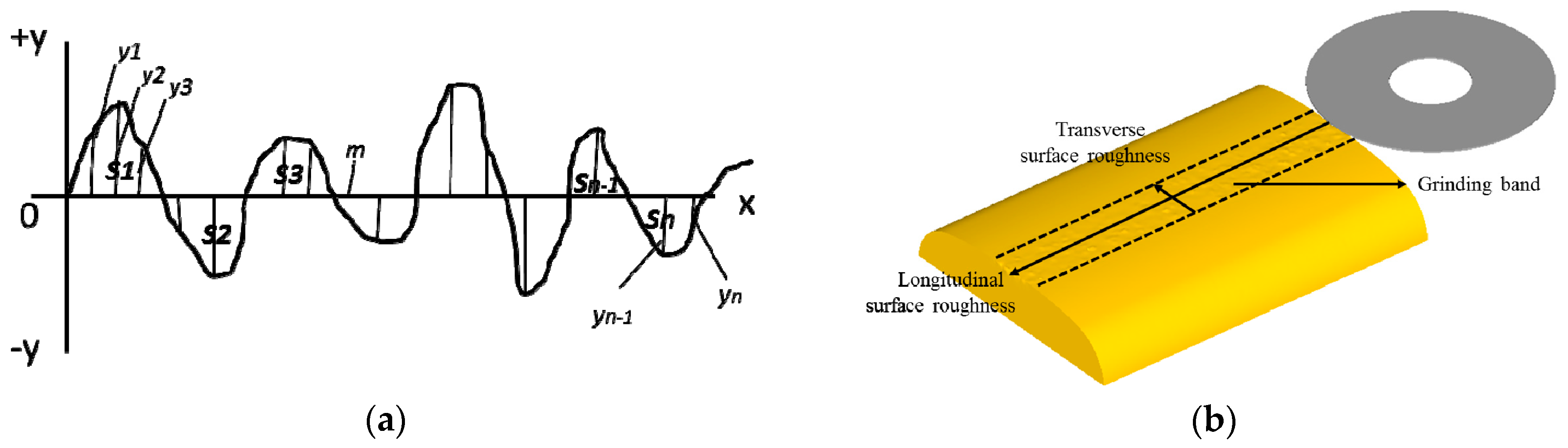
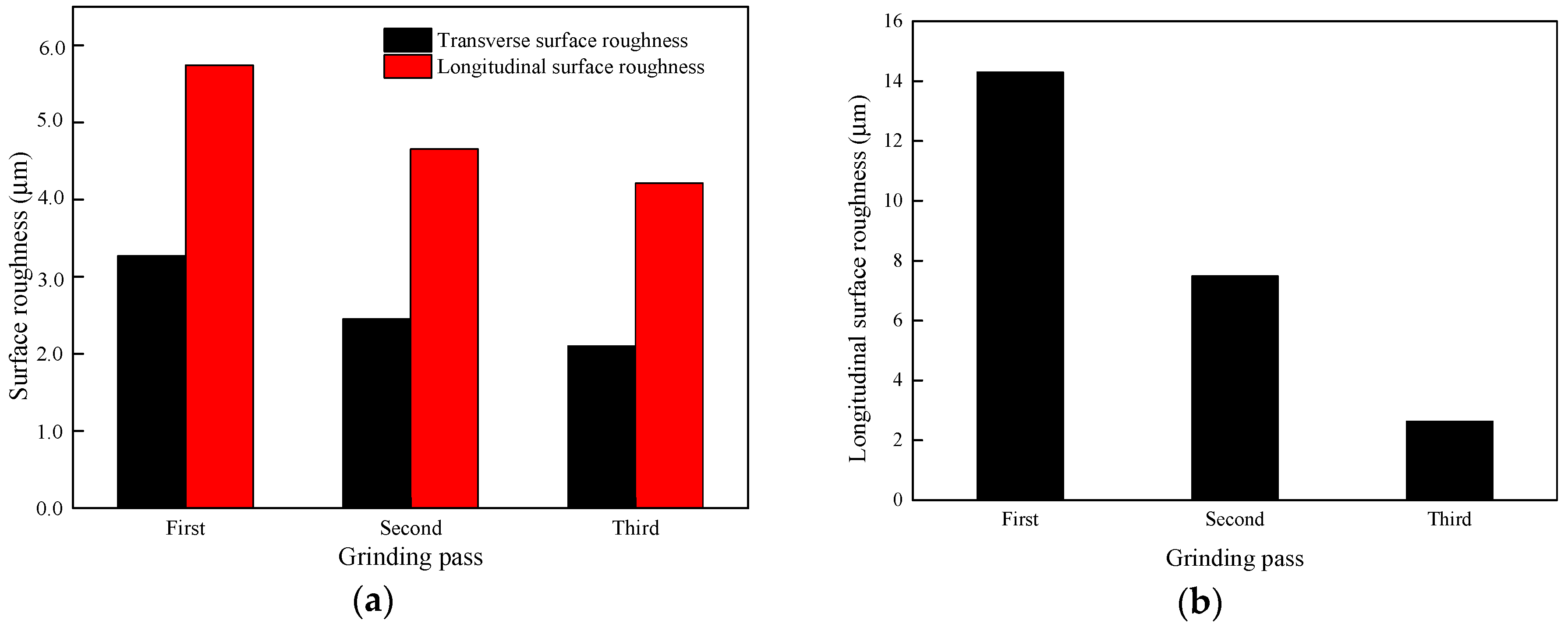
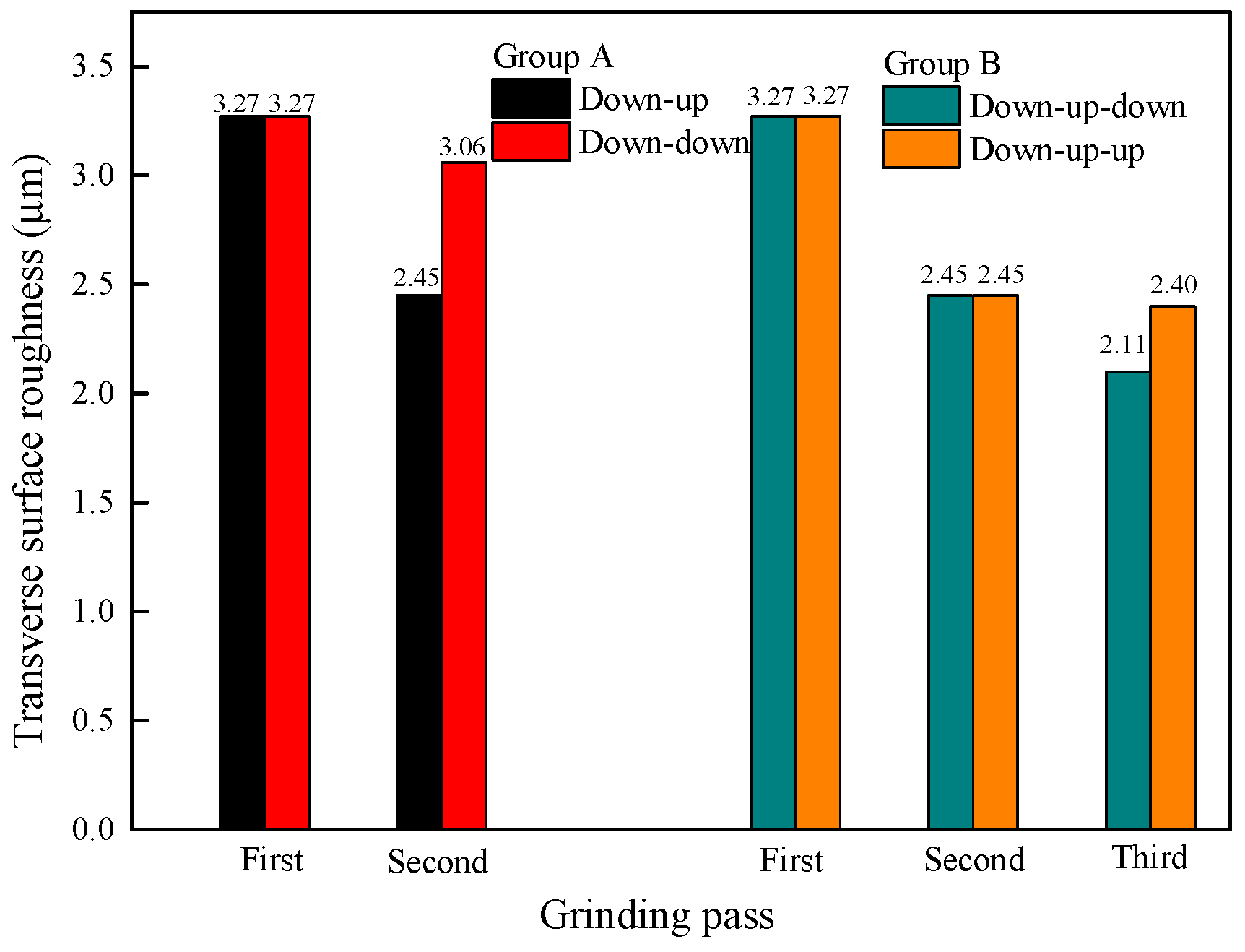
3.4. Surface Roughness of the Grinding Rail
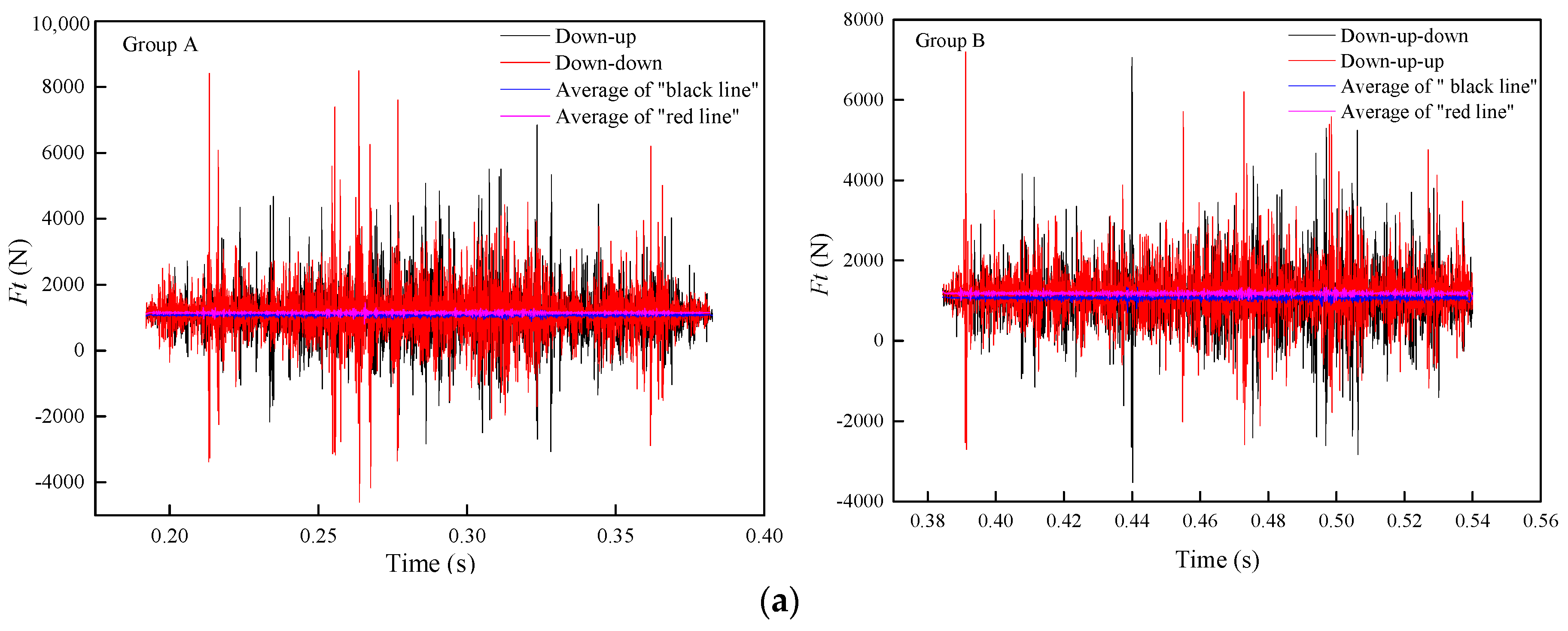
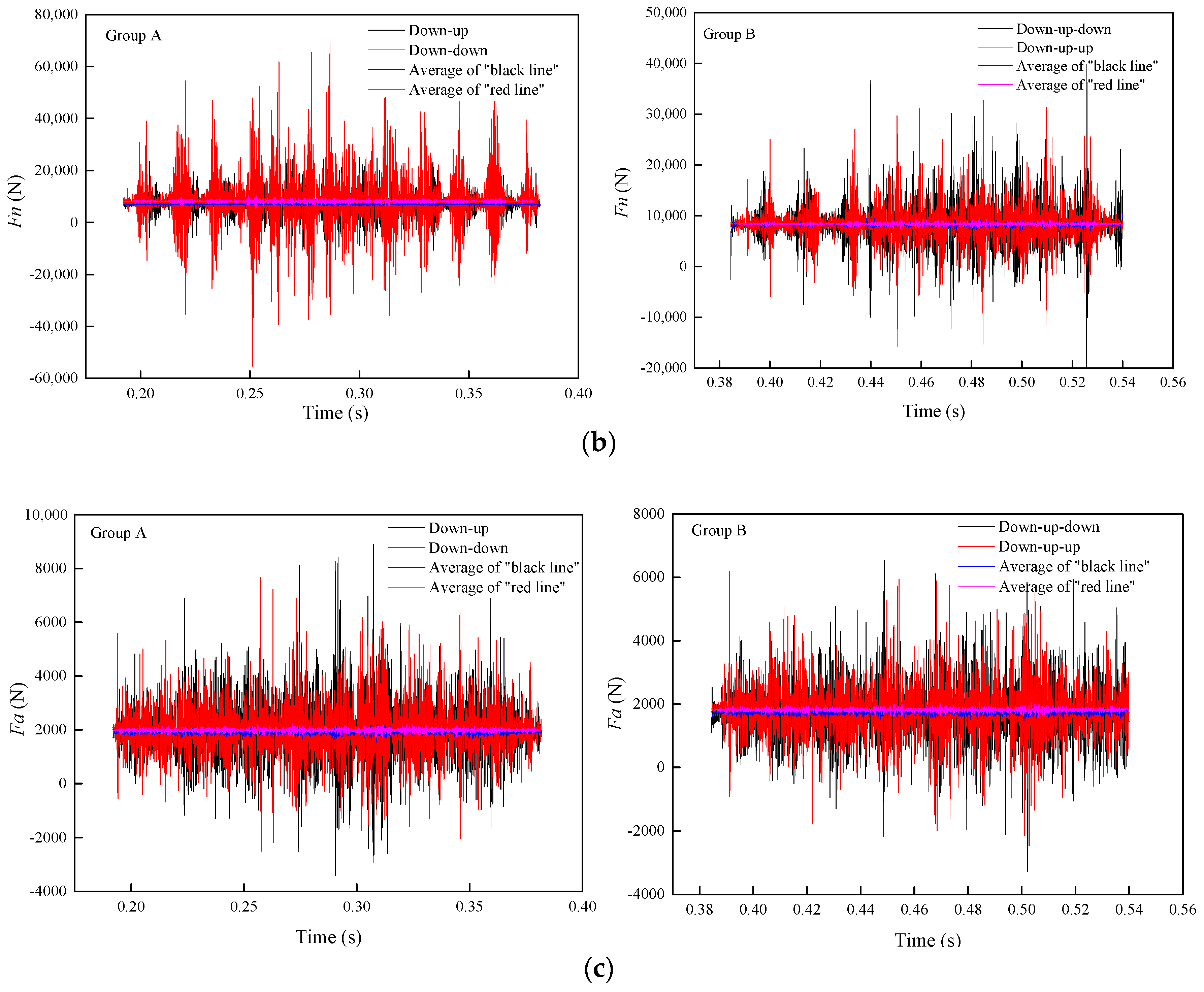
3.5. Grinding Force
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.M.; Yang, T.Y.; He, Z.; Li, J.Y. Analytical modeling of grinding process in rail profile correction considering grinding pattern. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.D.; Li, J.Y.; Zarembski, A.M. Predictive modeling of the rail grinding process using a distributed cutting grain approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. F–J. Rail Rapid Transit 2016, 230, 1540–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Gu, K.K.; Zhou, K.; Cai, Z.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q. Influence of granularity of grinding stone on grinding force and material removal in the rail grinding process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J–J Eng. Tribol. 2018. (In press) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q. Optimal design of rail grinding patterns based on a rail grinding target profile. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. F–J. Rail Rapid Transit 2018, 232, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magel, E.E.; Kalousek, J. The application of contact mechanics to rail profile design and rail grinding. Wear 2002, 253, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippeth, D.; Kalousek, J.; Simmons, J. A case study of the effect of lubrication and profile grinding on low rail roll-over derailments at CSX transportation. Wear 1996, 191, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Shang, W.; Ding, H.H.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, W.J. Thermal model and temperature field in rail grinding process based on a moving heat source. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 106, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wu, Y.; Vargheseb, V.; Malkin, S. Temperatures and energy partition for grinding with vitrified CBN wheels. CIRP. Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gao, L.; Hao, J.F. Dynamics simulation on asymmetrical rail grinding in railway curve. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Transportation Engineering, Chengdu, China, 22–24 July 2007; pp. 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Lin, Q.; Wang, W.J.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q. Study on dynamic behaviour of rail grinding vehicle considering the grinding process. J. China Railw. Soc. 2016, 38, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.F.; Zhao, H.H.; Cai, G.Q.; Jin, T. Study on the mechanism of high speed single abrasive grinding. J. Northeast Univ. 2002, 23, 470–473. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rasim, M.; Mattfeld, P.; Klocke, F. Analysis of the grain shape influence on the chip formation in grinding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 226, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Wang, W.J.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q. Simulation of single grain grinding in rail grinding based on SPH method. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2016, 36, 54–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.K.; Lin, Q.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, M. Analysis on the effect of rotational speed of grinding stone on removal behaviour of rail material. Wear 2015, 342, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; Lypovka, P.; Hochschild, L.; Schröer, N. Influence of rail grinding process parameters on rail surface roughness and surface layer hardness. Wear 2016, 366, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J. Research on the Effect of Rail Grinding Parameters on Grinding Quantity and Grinding Mode. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yossifon, S.; Rubenstein, C. Wheel wear when grinding workpieces exhibiting high adhesion. Int. J. Mach. Tool Des. Res. 1982, 22, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Rao, P.V. Experimental investigation of surface/subsurface damage formation and material removal mechanisms in SiC grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2008, 48, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Kuo, C.P.; Wang, F.C. Vibration analysis of rail grinding using a twin-wheel grinder. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksoud, T.M.A.; Atia, M.R.; Koura, M.M. Application of artificial intelligence to grinding operations via neural network. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2003, 7, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.C. Simulation and Experimental Study on the Influence Factors of Grinding Force Based on Rail Grinding Experiment. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, R.; Lin, K.; Shao, M. Mechanisms and FEM simulation of chip formation in orthogonal cutting in-situ TiB₂/7050Al MMC. Materials 2018, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Guo, B. Research on the single grit scratching process of oxygen-free copper (OFC). Materials 2018, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, W.; Liu, G. Analysis of surface-erosion mechanism due to impacts of freely rotating angular particles using smoothed particle hydrodynamics erosion model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J-J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Dynamic simulation of single abrasive grain cutting TC4 based on SPH method. J. Syst. Simul. 2015, 27, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, E.; Kitagawa, T.; Shirakashi, T. Analytical prediction of three dimensional cutting process—Part 3: Cutting temperature and crater wear of carbide tool. J. Eng. Ind. 1978, 100, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, M. Rolling contact fatigue in relation to rail grinding. Wear 2016, 356, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Normal Force (N) | Rotational Speed (r/min) | Feed Speed (mm/min) | Grinding Angle (°) | Grinding Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | 3600 | 83.33 | 2 | down-up-down |
| Grinding Pass | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width (mm) | Average | 12 | 13.66 | 14.3 |
| Deviation | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.35 | |
| Depth (mm) | Average | 0.06 | 0.01776 | 0.007456 |
| Deviation | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.175 | |
| Rail Material | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Thermal Conductivity (N·s−1·°C−1) | Heat Capacity (N·mm−2·°C−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U71Mn | 2.06754 × 105 | 0.3 | Change with temperature | |
| Grinding Wheel Material | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Density (kg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 3.7 × 105 | 0.22 | 3960 |
| A (MPa) | B (MPa) | n | C | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 792 | 510 | 0.26 | 0.014 | 1.03 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhou, K.; Ding, H.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W. Effects of Grinding Passes and Direction on Material Removal Behaviours in the Rail Grinding Process. Materials 2018, 11, 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112293
Zhang S, Zhou K, Ding H, Guo J, Liu Q, Wang W. Effects of Grinding Passes and Direction on Material Removal Behaviours in the Rail Grinding Process. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112293
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuyue, Kun Zhou, Haohao Ding, Jun Guo, Qiyue Liu, and Wenjian Wang. 2018. "Effects of Grinding Passes and Direction on Material Removal Behaviours in the Rail Grinding Process" Materials 11, no. 11: 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112293
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhou, K., Ding, H., Guo, J., Liu, Q., & Wang, W. (2018). Effects of Grinding Passes and Direction on Material Removal Behaviours in the Rail Grinding Process. Materials, 11(11), 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112293





