Effective Degradation of Rh 6G Using Montmorillonite-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron under Microwave Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of nZVI/MMT
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Rh 6G Removal Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
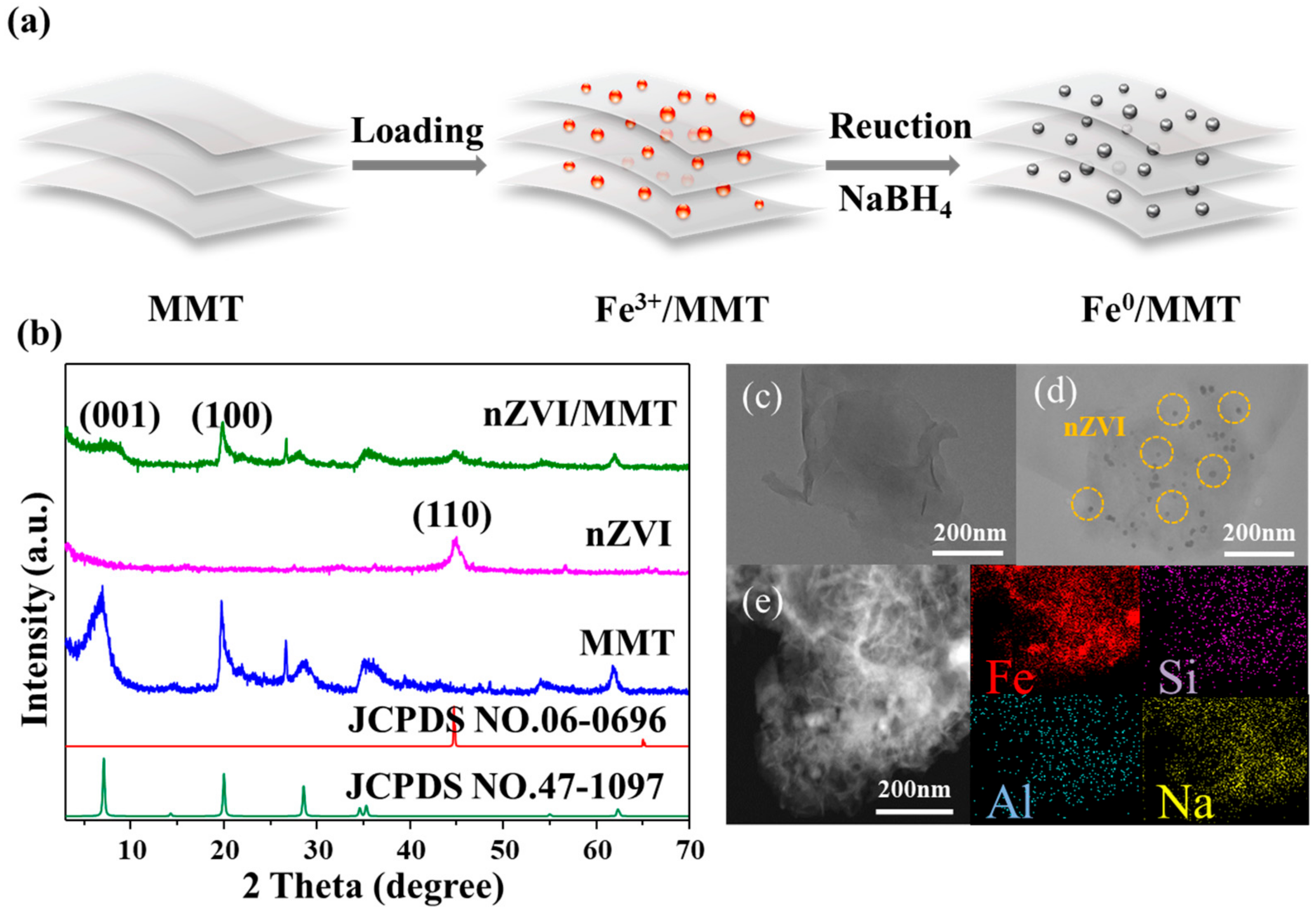
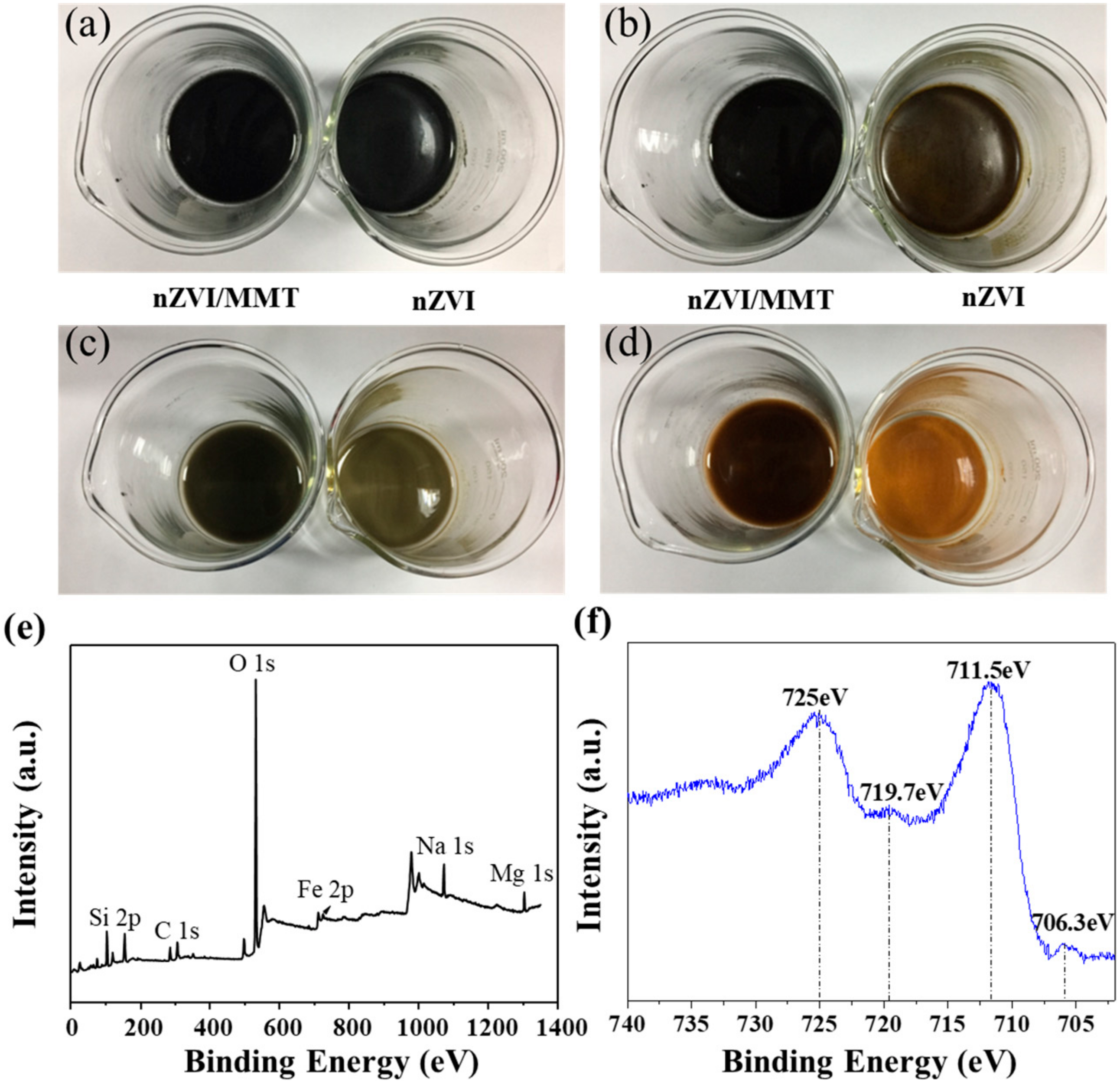
3.1. Crystallization, Morphology and Valence States of nZVI/MMT
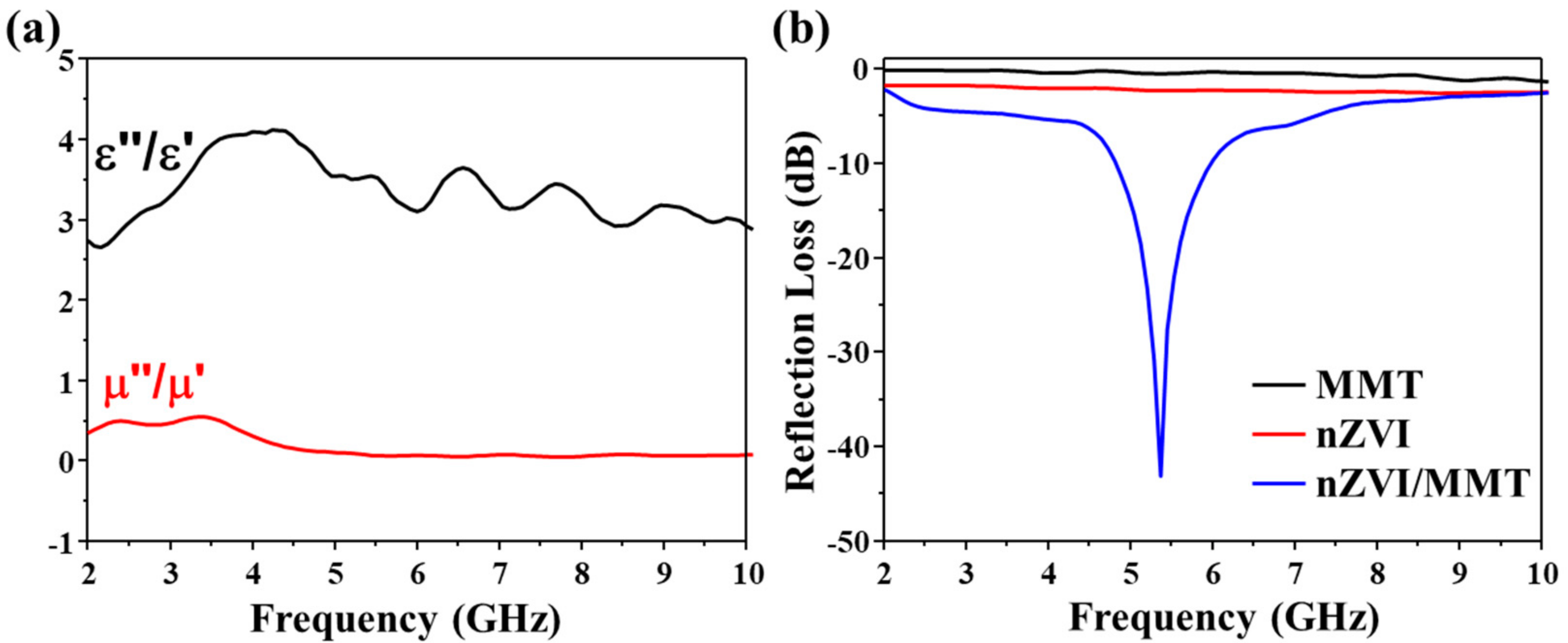
3.2. Microwave Absorption Properties of nZVI/MMT
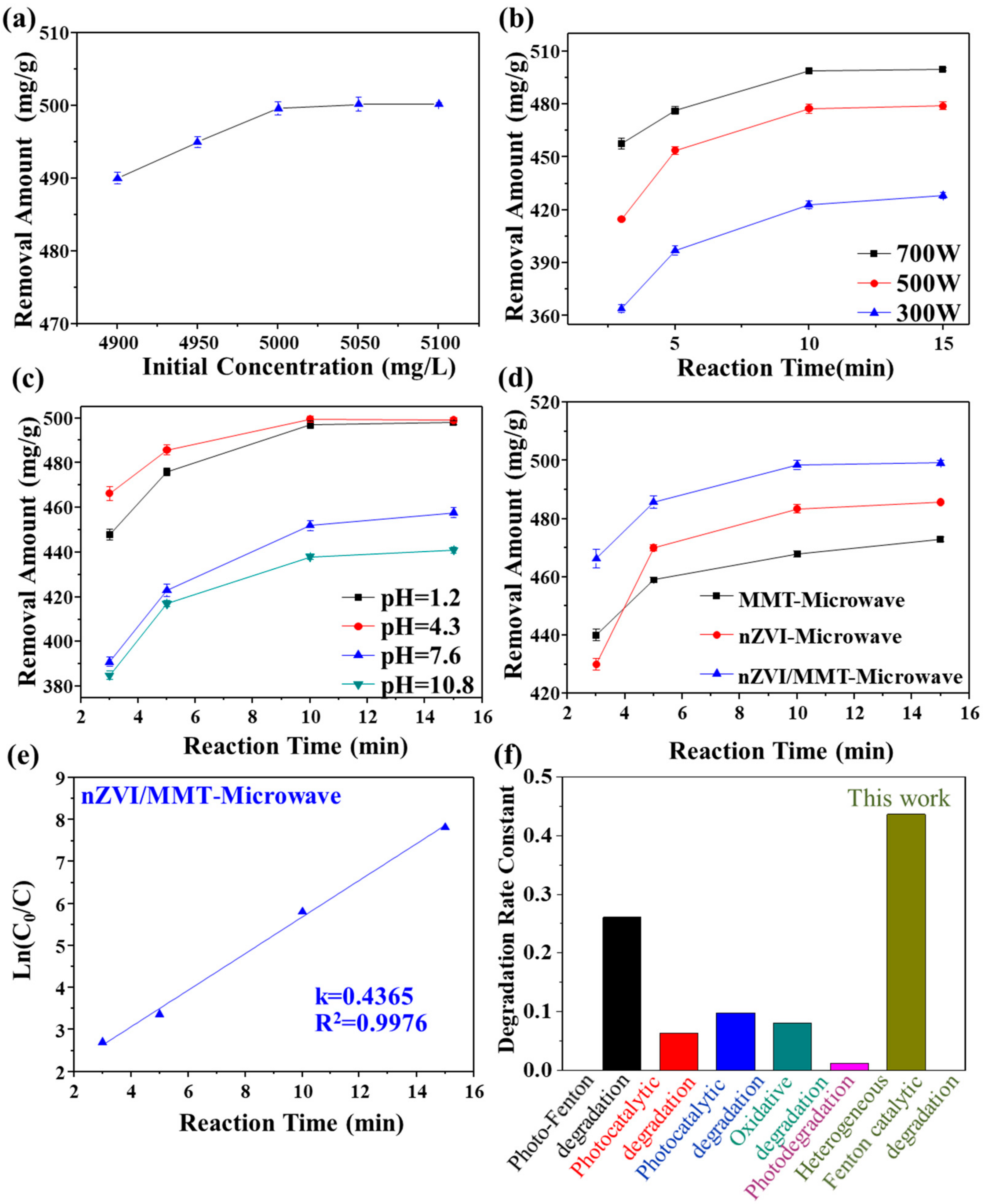
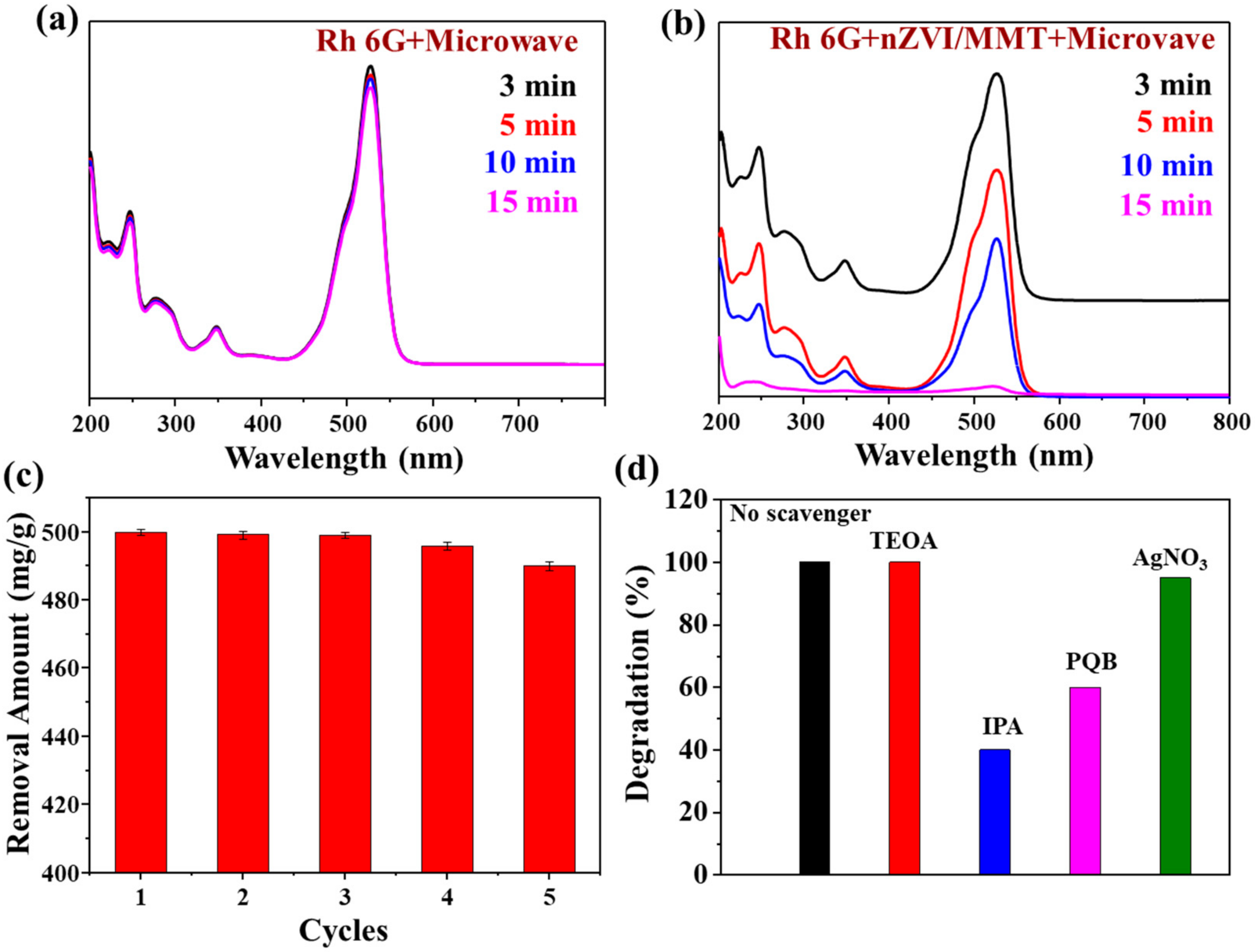
3.3. Degradation of Rh 6G Using nZVI/MMT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, T.; Mcmullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, T.M. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by ZnGa2O4 thin films. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, F.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, L.J.; Jiang, X.Q.; Yang, J.C.; Shi, W. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as sorbent for recovery of endocrine disrupting compound-bisphenol F from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Kong, H.; Liu, T.; Xia, M. Performance of combined process of anoxic baffled reactor-biological contact oxidation treating printing and dyeing wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.T. The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dyes. Pigm. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, D.; Kim, J.G. Oxidation of various reactive dyes with in situ electro-generated active chlorine for textile dyeing industry wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Sun, D. Advances in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater by physical and chemical processes. Ind. Water Treat. 2010, 72, 227–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, H.L.; Wu, H.F. A rapid determination method of chemical oxygen demand in printing and dyeing wastewater using ultraviolet spectroscopy. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Li, A.G.; Zheng, Y.C.; Jiao, Z. Study on Cleaning Methods of Membrane in Printing and Dyeing Wastewater by MBR. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 781–784, 1937–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, J.N.; Meng, G.H.; Guo, X.H.; Liu, Z.Y. A novel strategy for preparation of an effective and stable heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for the degradation of dye. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 136, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Hua, T. Removal of Organic Matter from Landfill Leachate by Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2010, 2010, 270532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, C.S.; Ollis, D.F. Photocatalytic degradation of organic water contaminants: Mechanisms involving hydroxyl radical attack. J. Catal. 1990, 122, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, C.; Ma, C.; Ren, W.; Cheng, H. Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, H.; Kaczala, F.; Marques, M.; Hogland, W. Photo-Fenton and Fenton Oxidation of Recalcitrant Industrial Wastewater Using Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Int. J. Photog. 2012, 2012, 515–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Huang, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, A.B.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.G. Microwave enhanced Fenton process for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.J.; Chen, T.C.; Young, W.L. Competitive Removal of Two Contaminants in a Goethite-Catalyzed Fenton Process at Neutral pH. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, J. Degradation of 4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol by a Heterogeneous Fenton-Like Reaction Using Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Catalysts. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.M.; Dong, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Y.J.; Hou, K.J.; Zhang, L.H.; Fan, C.Z. Nanoscale zero-valent iron/biochar composite as an activator for Fenton-like removal of sulfamethazine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 202, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, S.M.; Darab, J.G.; Mallouk, T.E. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) Aqueous Solutions Using Supported, Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2564–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.F.; Chen, H.W.; Cheng, W.P.; Lin, Y.J.; Huang, C.L. Monitoring of ORP, pH and DO in heterogeneous Fenton oxidation using nZVI as a catalyst for the treatment of azo-dye textile wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, Y.Q. Remediation of arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions using improved nanoscale zero-valent iron on pumice. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.P.; Ye, Z.F.; Xie, W.M.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.C.; Yao, M.S. Rapid magnetic removal of aqueous heavy metals and their relevant mechanisms using nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) particles. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4050–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aduseigyamfi, J.; Acha, V. Carriers for nano zerovalent iron (nZVI): Synthesis, application and efficiency. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 91025–91044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Misra, V.; Singh, R.P. Remediation of γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane contaminated soil using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Bionanoscience 2011, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, R.; Zhou, Y.X.; Wang, J. Influence of operating temperature on the reduction of high concentration p-nitrophenol (PNP) by zero valent iron (ZVI). Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 249, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Temsah, Y.S.; Joner, E.J. Effects of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on DDT degradation in soil and its toxicity to collembola and ostracods. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojeong, K.; Hong, H.J.; Juri, J.; Seonghye, K.; Yang, J.W. Degradation of trichloroethylene (TCE) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) immobilized in alginate bead. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Guler, U.A. Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron and functional pumice modified nanoscale zero valent iron. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 25, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.F. The dispersity-dependent interaction between montmorillonite supported nZVI and Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Jia, H.; Li, H.; Teppen, B.J.; Boyd, S.A. Synthesis of Highly Reactive Subnano-Sized Zero-Valent Iron Using Smectite Clay Templates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 4258–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chang, P.H.; Jean, J.S.; Jiang, W.T.; Hong, H. Mechanism of chlorpheniramine adsorption on Ca-montmorillonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 385, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luptáková, V.; Horváth, I.; Perjéssy, A.; Putyera, K. IR Spectroscopic Study on Host-Guest Interaction of Montmorillonite with Benzothiazolium Compounds. Chem. Pap. 1992, 46, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gemeay, A.H. Adsorption Characteristics and the Kinetics of the Cation Exchange of Rhodamine-6G with Na+-Montmorillonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 251, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Su, H.L.; Hung, T.J. Stably-Dispersing Composite of Metal Nanoparticle and Inorganic Clay and Method for Producing the Same. US Application. US20090148484A1, 7 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.D.; Zhang, G.K. Fabrication of AgFeO2/g-C3N4 nanocatalyst with enhanced and stable photocatalytic performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 391, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhu, R.L. Sulfur-mediated synthesis of N-doped carbon supported cobalt catalysts derived from cobalt porphyrin for ethylbenzene oxidation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 19482–19491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Znad, H.T.; Kawase, Y. Decolorization of dark brown colored coffee effluent by solar photo-Fenton reaction: Effect of solar light dose on decolorization kinetics. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4665–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Xu, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J. Synergetic Effect of Ultrasound, the Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction and Photocatalysis by TiO2 Loaded on Nickel Foam on the Degradation of Pollutants. Materials 2016, 9, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Hu, X.M.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.M. Study on Coupled Oxidation and Microwave Process in Treating Urban Landfill Leachate by Fenton and Fenton-like Reaction. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 393–395, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.; Baek, Y.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, Y.C. Oxidative coupling of methane with microwave and RF plasma catalytic reaction over transitional metals loaded on ZSM-5. Catal. Today 2002, 74, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, L.; Hourquebie, P.; Jousse, F. Microwave absorbing materials based on conducting polymers. Adv. Mater. 1993, 5, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saines, P.J.; Paddison, J.A.M.; Thygesen, P.M.M.; Tucker, M.G. Searching Beyond Gd for Magnetocaloric Frameworks: Magnetic Properties and Interactions of the Ln(HCO2)3 Series. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xue, S.; Song, Y.T.; Shen, M.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yuan, T.X.; Tian, F.Y.; Dionysiou, D.D. Microwave-induced carbon nanotubes catalytic degradation of organic pollutants in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Drew, M.G.B.; Liu, Y. A theoretical and practical clarification on the calculation of reflection loss for microwave absorbing materials. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Wang, G.S.; Cao, W.Q.; Wei, Y.Z.; Liang, J.F.; Guo, L.; Cao, M.S. Enhanced Microwave Absorption Property of Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO)-MnFe2O4 Nanocomposites and Polyvinylidene Fluoride. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7471–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, L.; Yao, H. Characteristics and mechanisms of 4A zeolite supported nanoparticulate zero-valent iron as Fenton-like catalyst to degrade methylene blue. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y. The role of nanoscale zerovalent iron particles in the biosorption and biodegradation of BDE-47 by Pseudomonas stutzeri, under aerobic conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradat. 2016, 112, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Novel low-cost Fenton-like layered Fe-titanate catalyst: Preparation, characterization and application for degradation of organic colorants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 422, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, T.S.; Bajaj, H.C.; Tayade, R.J. Palmyra tuber peel derived activated carbon and anatase TiO2 nanotube based nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic performance in rhodamine 6G dye degradation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Jiao, W.L.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.S.; Li, D.D.; Che, R.C. Two hybrid Au-ZnO aggregates with different hierarchical structures: A comparable study in photocatalysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 509, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Hu, W.; Niu, Y. Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles loaded on Fe/N-doped graphene as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for degradation of organic pollutants. Colloids Surf. A Physico. Chem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 518, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírezaparicio, J.; Sánchezmartínez, A.; Ramírezbon, R. Photodecolorization of rhodamine under sunlight irradiation driven by chabazite. Sol. Energy 2016, 129, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Yan, Y.; Da, Z.L.; Shi, W.D.; Ma, C.C.; Lv, P.; Tang, Y.F.; Yao, G.X.; Wu, Y.T.; Huo, P.W.; et al. Significantly enhanced photocatalytic performance of CdS coupled nanosheets and the mechanism study. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 241, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Khairou, K.S.; Mokhtar, M. Carbon nanotube/titanium nanotube composites loaded platinum nanoparticles as high performance photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 475, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, W.; Liu, H.; Lv, G.; Wang, D.; Liao, L. Effective Degradation of Rh 6G Using Montmorillonite-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron under Microwave Treatment. Materials 2018, 11, 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112212
Rao W, Liu H, Lv G, Wang D, Liao L. Effective Degradation of Rh 6G Using Montmorillonite-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron under Microwave Treatment. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112212
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Wenxiu, Hao Liu, Guocheng Lv, Danyu Wang, and Libing Liao. 2018. "Effective Degradation of Rh 6G Using Montmorillonite-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron under Microwave Treatment" Materials 11, no. 11: 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112212
APA StyleRao, W., Liu, H., Lv, G., Wang, D., & Liao, L. (2018). Effective Degradation of Rh 6G Using Montmorillonite-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron under Microwave Treatment. Materials, 11(11), 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112212





