Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
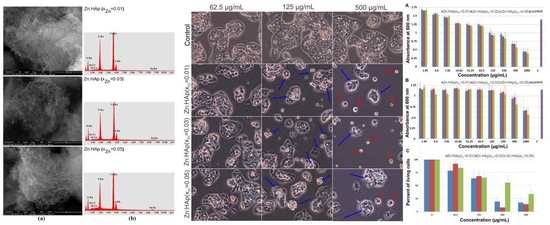
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.1.1. Materials
3.1.2. Zinc Doped Hydroxyapatite (Zn:HAp) Nanoparticles
3.2. Characterization Methods
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
3.3.1. Antimicrobial Assays on Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli Strain
3.3.2. HepG2 Cell Viability Assays
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.; Chappell, H.F.; Dove, M.T.; Reeder, R.J.; Lee, Y.J. Zinc incorporation into hydroxylapatite. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predoi, D.; Popa, C.L.; Predoi, M.V. Ultrasound studies on magnetic fluids based on maghemite nanoparticles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glimcher, M.J. Bone: Nature of the calcium phosphate crystals and cellular, structural, and physical chemical mechanisms in their formation. In Medical Mineralogy and Geochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry; Sahai, N., Schoonen, M.A.A., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 64, pp. 223–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hing, K.A.; Wilson, L.F.; Buckland, T. Comparative performance of three ceramic bone graft substitutes. Spine J. 2007, 7, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallot, E.; Nedelec, J.M.; Grimault, A.S.; Chassot, E.; Grandjean-Laquerriere, A.; Laquerriere, P.; Laurent-Maquin, D. STEM and EDXS characterisation of physico-chemical reactions at the periphery of sol–gel derived Zn-substituted hydroxyapatites during interactions with biological fluids. Colloid Surf. B 2005, 42, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legeros, R.Z.; Daculsi, G. Handbook of Bioactive Ceramics; Yamamuro, T., Hench, L.L., Wilson, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, E.; Ohkubo, M.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A.; Kawabata, K.; Bonhomme, C.; Babonneau, F. Selective protein adsorption property and characterization of nano-crystalline zinc-containing hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutley, L.S.; Gowan, J.; Milhaund, G. Calcium metabolism in manganese-deficient and zinc-deficient rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1969, 130, 856–860. [Google Scholar]
- Oner, G.; Bhaumick, B.; Bala, R.M. Effect of zinc deficiency on serum somatomedin levels and skeletal growth in young rats. Endocrinology 1984, 114, 1860–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molokwu, C.O.; Li, Y.V. Zinc Homeostasis and Bone Mineral Density; Ohio Research and Clinical Review: Athens, OH, USA, 2006; Volume 15, pp. 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, L.S.; Cosens, G.; Theriault, L.L.L.L. Magnesium, calcium and zinc levels of maternal and fetal tissues in magnesium deficient rats. J. Nutr. 1976, 106, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Dell, B.L.; Becker, J.K.; Emery, M.P.; Browning, J.D. Production and reversal of the neuromuscular pathology and related signs of zinc deficiency in guinea pigs. J. Nutr. 1989, 119, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frederickson, C.J.; Koh, J.Y.; Bush, A.I. The neurobiology of zinc in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambidge, M. Human zinc deficiency. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1344S–1349S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, C.S.; Massuyeau, F.; Constantin, L.V.; Predoi, D. Structural and physical properties of antibacterial Ag-doped nano-hydroxyapatite synthesized at 100 °C. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 3, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, C.S.; Iconaru, S.L.; Popa, C.L.; Motelica-Heino, M.; Predoi, D. Evaluation of Samarium Doped Hydroxyapatite, Ceramics for Medical Application: Antimicrobial Activity. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 849216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuillel, M.; Chevallet, M.; Charbonnier, P.; Fauquant, C.; Pignot-Paintrand, I.; Arnaud, J.; Cassio, D.; Michaud-Soret, I.; Mintz, E. Interference of CuO nanoparticles with metal homeostasis in hepatocytes under sub-toxic conditions. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaji, F.; Kono, Y.; Suyama, Y. Formation and structure of zinc-substituted calcium hydroxyapatite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Foresti, E.; Gandolfi, M.; Gazzano, M.; Roveri, N. Inhibiting effect of zinc on hydroxylapatite crystallization. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1995, 58, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, K.P.; Sharma, P.; Kanchan, D.K.; Joshi, M.J. FTIR, powder XRD, TEM and dielectric studies of pure and zinc doped nano-hydroxyapatite. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2011, 46, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsopoulos, S. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite crystals: A review study on the analytical methods. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 15, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, B.O. Infrared studies of apatites. I. Vibrational assignments for calcium, strontium, and barium hydroxyapatites utilizing isotopic substitution. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.S.; Iconaru, S.L.; Chifriuc, M.C.; Costescu, A.; Le Coustumer, P.; Predoi, D. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 916218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, C.S.; Iconaru, S.L.; Le Coustumer, P.; Constantin, L.V. Predoi, D. Antibacterial activity of silver-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima, I.R.; Costa, A.M.; Bastos, I.N.; Granjeiro, J.M.; de Almeida Soares, G. Development and Characterization of 5% mol Zn Bioceramic in Granular Form. Mater. Res. 2006, 9, 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Xie, J.; Chittur, K.; Riley, C. Transformation of modified brushite to hydroxyapatite in aqueous solution: Effects of potassium substitution. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoch, A.; Jastrzebski, W.; Brozek, A.; Stoch, J.; Szaraniec, J.; Trybalska, B.; Kmita, G. FTIR absorption-reflection study of biomimetic growth of phosphates on titanium implants. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 555, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzadeh, A. Fluorescence bands in the FT-Raman spectra of some calcium minerals. Spectrochim. Acta A 1997, 53, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, J.P. A Kinetic Study of the Formation of Calcium Phosphate Minerals. Ph.D. Thesis, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, F.; Knobel, R.M. Distribution of fluorine in hydroxyapatite studied by infrared spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1977, 11, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.S.; Popa, C.L.; Predoi, D. Sm:HAp Nanopowders Present Antibacterial Activity against Enterococcus faecalis. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 780686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Christoffersen, J.; Christoffersen, M.R.; Eckert, H.; Fowler, B.O.; Heughebaert, J.C.; Nancollas, G.H.; Yesinowski, J.P.; Zawacki, S.J. A calcium hydroxyapatite precipitated from an aqueous solution; an international multimethod analysis. J. Crystal Growth 1987, 84, 512–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costescu, A.; Pasuk, I.; Ungureanu, F.; Dinischiotu, A.; Costache, M.; Huneau, F.; Galaup, S.; Le Coustumer, P.; Predoi, D. Chemical Properties of Nano-Sized Hexagonal Hydroxyapatite Powder Synthesized By Sol-Gel. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2010, 5, 989–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.I.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy—A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data; Chastain, J., King, R.C., Jr., Eds.; Physical Electronics, Inc.: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya, J.R.; Arul, K.T.; Elayaraja, K.; Kalkura, S.N. Physicochemical and biological properties of iron and zinc ions co-doped nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite, synthesized by ultrasonication. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16707–16717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, S.M.; Darwish, A.S.; Kamal, S.M. Ceria-containing uncoated and coated hydroxyapatite-based galantamine nanocomposites for formidable treatment of Alzheimer’s disease in ovariectomized albino-rat model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 65, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D. The synthesis of hierarchical porous iron oxide with wood templates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 85, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Lenihan, H.S.; Cherr, G.; Cardinale, B.J.; Miller, R.; Ji, Z. Stability and Aggregation of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Natural Aqueous Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berne, B.J.; Pecora, R. Dynamic Light Scattering: With Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Deming, L.; Deming, W.; Teller, E.J. On a Theory of the van der Waals Adsorption of Gases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, J.H.; Lippens, B.C. Studies on pore systems in catalysts II. The shapes of pores in aluminum oxide systems. J. Catal. 1964, 3, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emri, E.; Miko, E.; Bai, P.; Boros, G.; Nagy, G.; Rozsa, D.; Juhasz, T.; Hegedus, C.; Horkay, I.; Remenyik, E.; et al. Effects of non-toxic zinc exposure on human epidermal keratinocytes. Metallomics 2015, 7, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, N.; Katzenberger, N.; Martin, F.; Schmidtke, K.U.; Kupper, J.H. Generation of cytochrome P450 3A4-overexpressing HepG2 cell clones for standardization of hepatocellular testosterone 6β-hydroxylation activity. J. Cell. Biotechnol. 2015, 1, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepins, A.; Nowicky, J.W.; Bustamante, J.O.; Lam, E. Induction of bimodal programmed cell death in malignant cells by the derivative Ukrain (NSC-631570). Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1996, 22, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tank, K.P.; Chudasama, K.S.; Thaker, V.S.; Joshi, M.J. Pure and zinc doped nano-hydroxyapatite: Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and hemolyticstudies. J. Cryst. Growth 2014, 401, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Akbar, S.; Sadiqa, A.; Kazmi, M. Novel continuous flow synthesis, characterization and antibacterial studies of nanoscale zinc substituted hydroxyapatite bioceramics. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 453, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanića, V.; Dimitrijević, S.; Antić-Stanković, J.; Mitrić, M.; Jokić, B.; Plećaš, I.B.; Raičević, S. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of copper and zinc-doped hydroxyapatite nanopowders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 6083–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, A.; Furtos, G.; Rapuntean, S.; Horovitz, O.; Flore, C.; Garbo, C.; Danisteanu, A.; Rapuntean, G.; Prejmerean, C.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M. Synthesis; characterization and antimicrobial effects of composites based on multi-substituted hydroxyapatite and silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 298, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.N.; Feng, Q.L.; Kim, J.O.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.C.; Cui, F.Z. Antimicrobial effects of metal ions (Ag+, Cu2+, Zn2+) in hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzengue, Y.; Candéias, S.M.; Sauvaigo, S.; Douki, T.; Favier, A.; Rachidi, W.; Guiraud, P. The toxicity redox mechanisms of cadmium alone or together with copper and zinc homeostasis alteration: Its redox biomarkers. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2011, 25, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.S.; Beck, F.W.; Endre, L.; Handschu, W.; Kukuruga, M.; Kamar, G. Zinc deficiency affects cell cycle and deoxythymidine kinase gene expression in HUT-78 cells. J. Clin. Med. 1996, 128, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.; Mailloux, R.; Appanna, V.D. Zinc toxicity alters mitochondrial metabolism and leads to decrease ATP production in hepatocytes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesters, J.K.; Petrie, L.; Vint, H. Specificity and timing of the Zn2+ requirement for DNA synthesis by 3T3 cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 1989, 184, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.M.; Sun, X.M.; Snowden, R.T.; Dinsdale, D.; Skilleter, D.N. Key morphological features of apoptosis may occur in the absence of internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Biochem. J. 1992, 286, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Kawamura, H.; Otsuka, M.; Ikeuchi, M.; Ohgushi, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Onuma, K.; Kanzaki, N.; Sogo, Y.; Ichinose, N. Zinc-releasing Calcium Phosphate for Stimulating Bone Formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 22, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parat, M.O.; Richard, M.J.; Beani, J.C.; Favier, A. Involvement of zinc in intracellular oxidant/antioxidant balance. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1997, 60, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, A.; Anderson, M.E. Glutathione. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1983, 52, 711–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Kuboa, J.; Yoshioka, T.; Sakuma, S.; Takeguchi, T.; Ueda, W. Reaction of ethanol over hydroxyapatite affected by Ca/P ratio of catalyst. J. Catal. 2008, 259, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Campbell, C.T.; Graham, D.J.; Ratner, B.D. Surface Characterization of Hydroxyapatite and Related Calcium Phosphates by XPS and TOF-SIMS. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-López, J.R.; Pomés, R.; DellaVédova, C.O.; Viña, R.; Punte, G. Influence of nickel on hydroxyapatite crystallization. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2001, 32, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.G.A.; Williamson, B.E. Low-temperature laser Raman spectroscopy of synthetic carbonated apatites and dental enamel. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.C.; Gibsond, I.; Barbosa, M.A. The uptake of titanium ions by hydroxyapatite particles—Structural changes and possible mechanisms. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeGeros, R.Z. Ultrastructural properties of human enamel apatite. In Handbook of Experimental Aspects of Oral Biochemistry; Lazzari, E.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1983; pp. 159–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small 2008, 4, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Neuss, S.; Leifert, A.; Fischler, M.; Wen, F.; Simon, U.; Schmid, G.; Brandau, W.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. Small 2007, 3, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Yin, L.H.; Tang, M.; Pu, Y.P. ZnO, TiO2, SiO2, and Al2O3 nanoparticles-induced toxic effects on human fetal lung fibroblasts. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Xi, Z. Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: the role of particle size, shape and composition. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
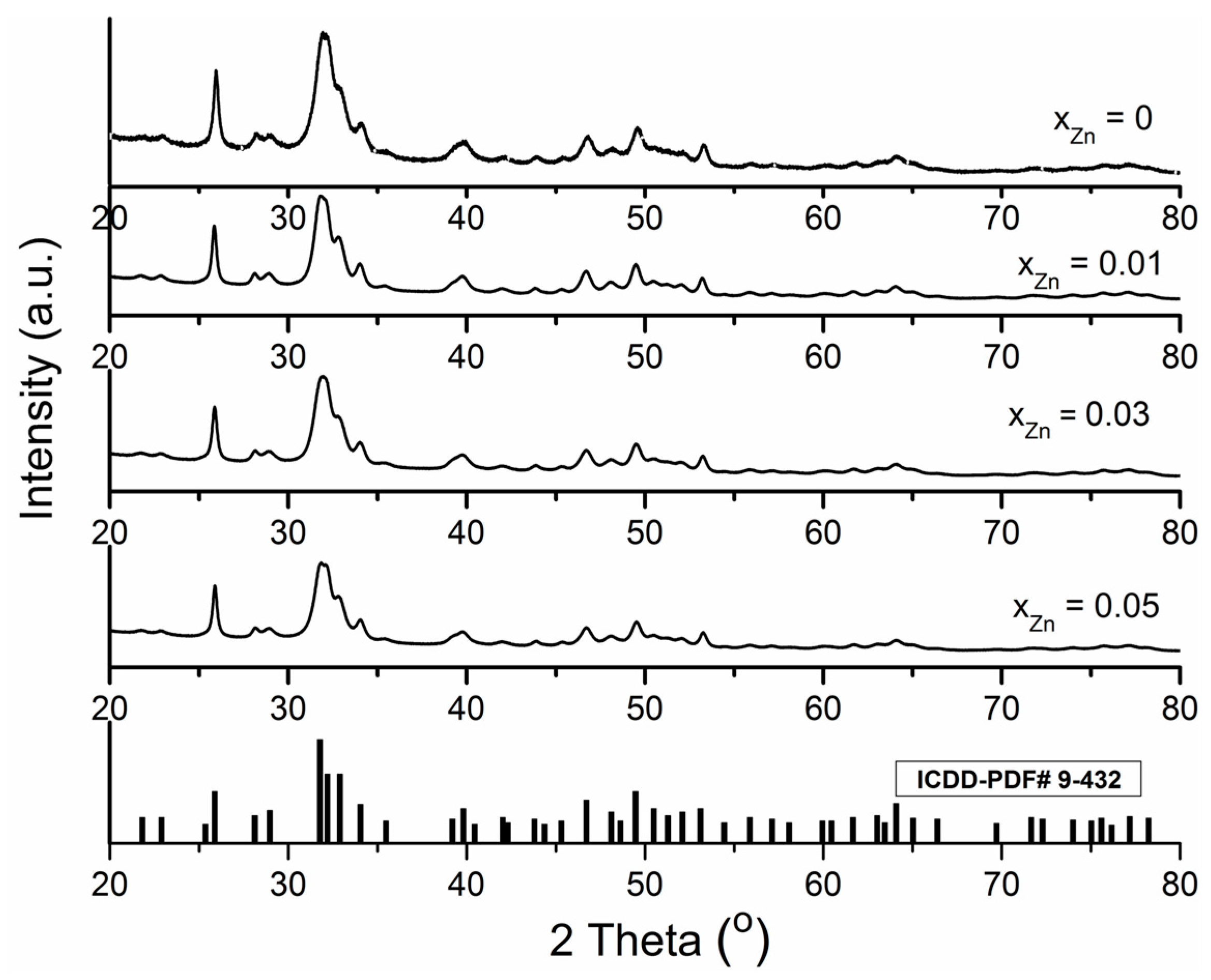

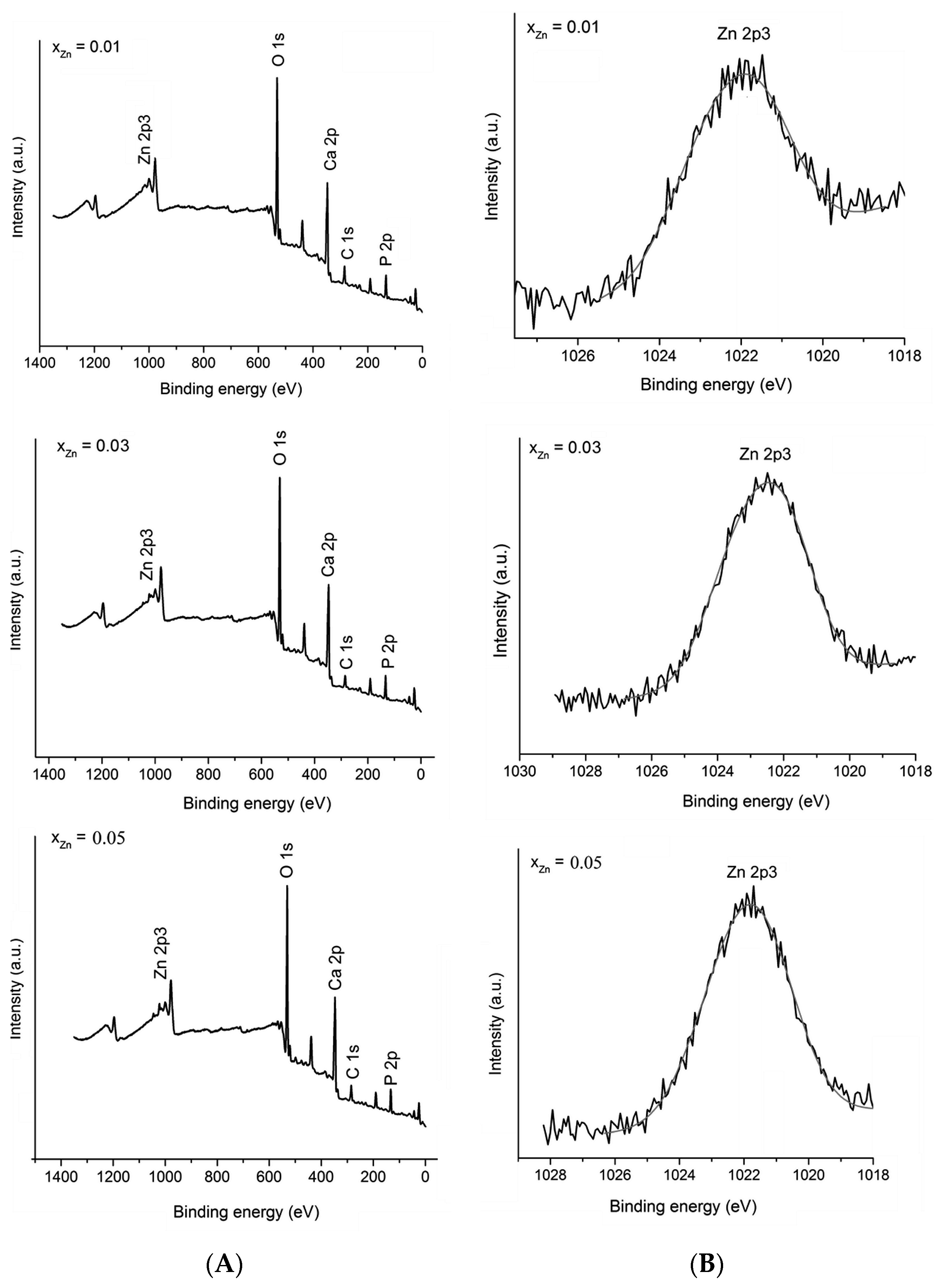
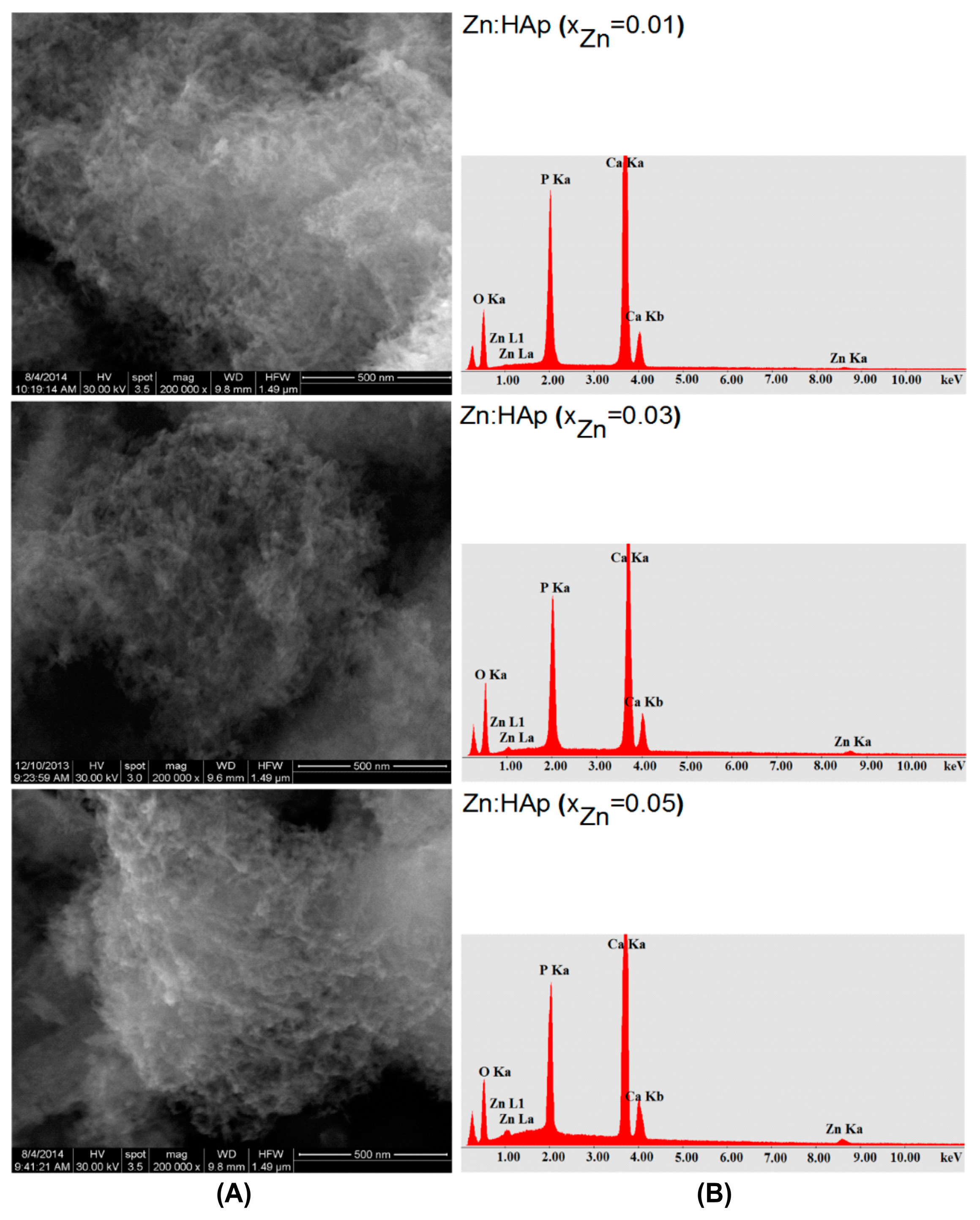
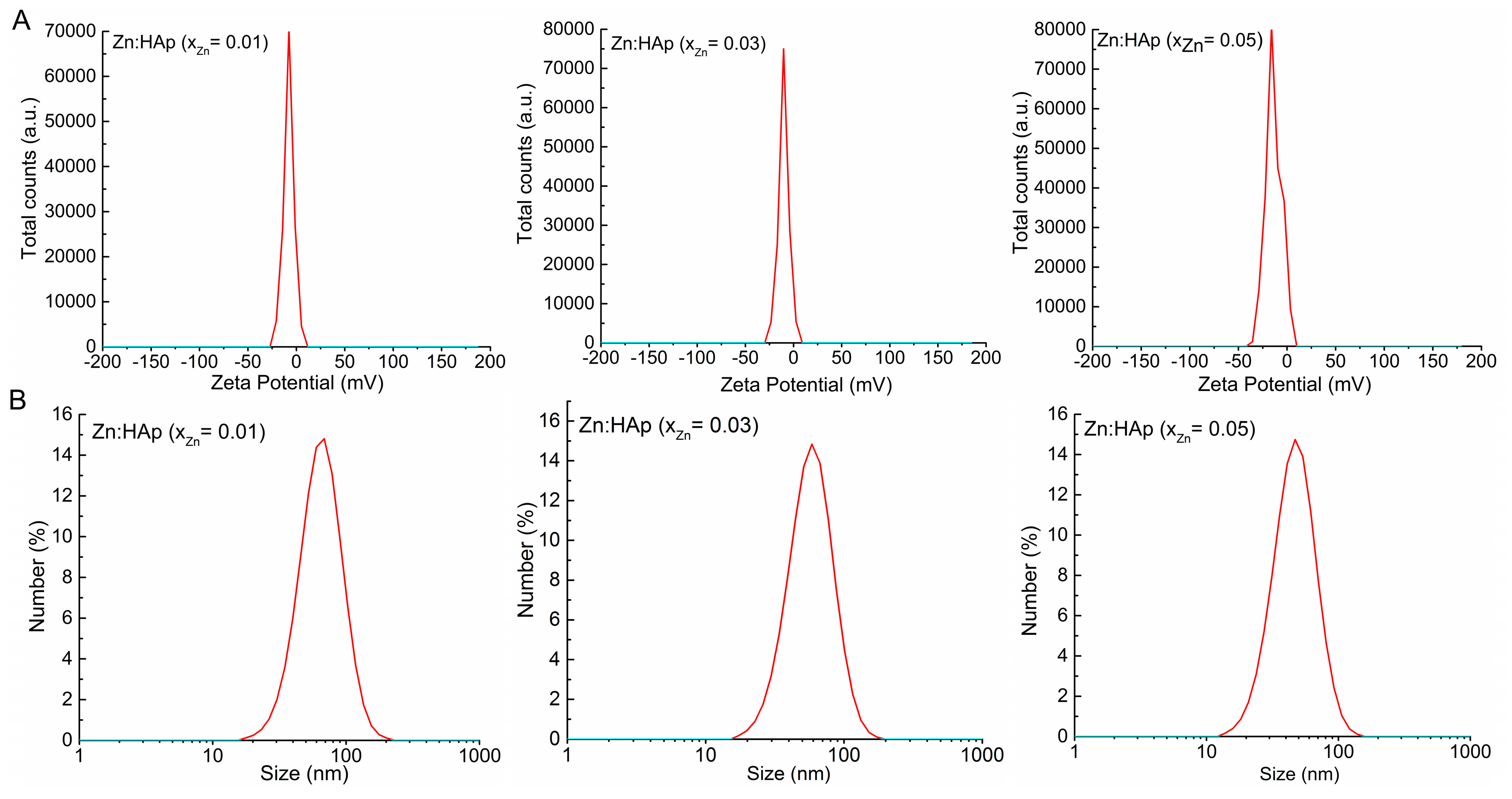
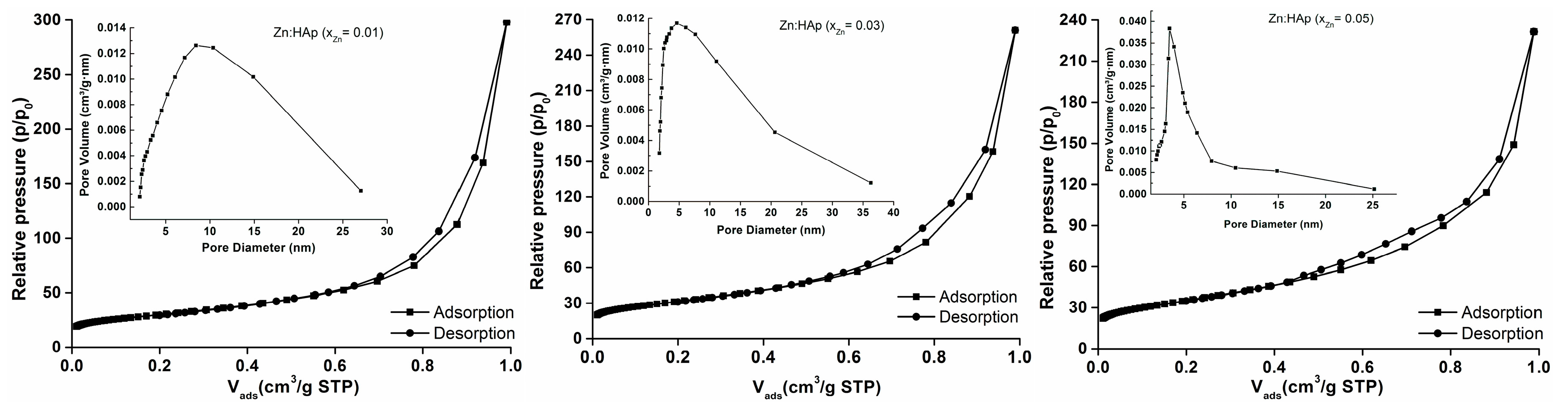
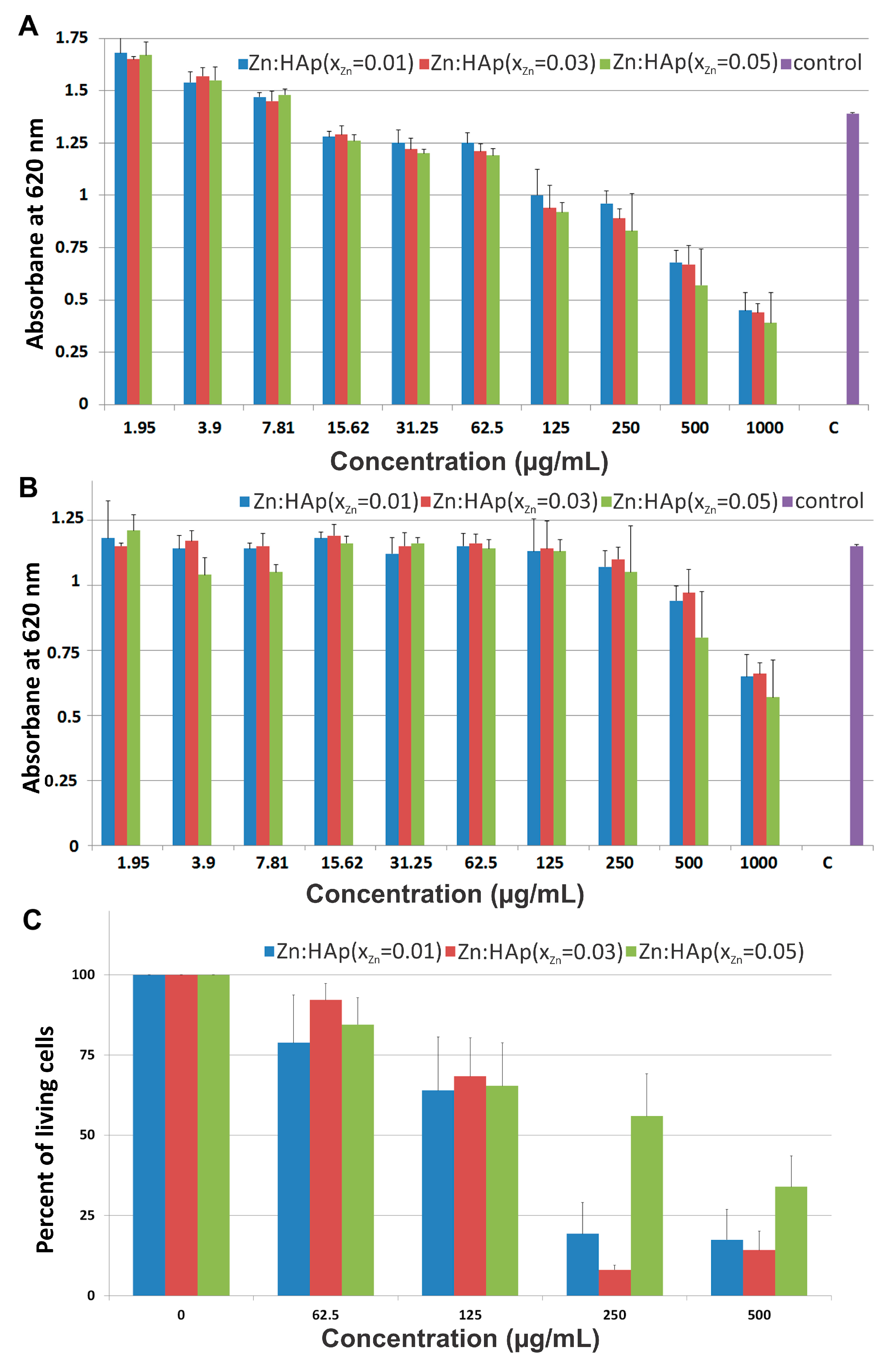
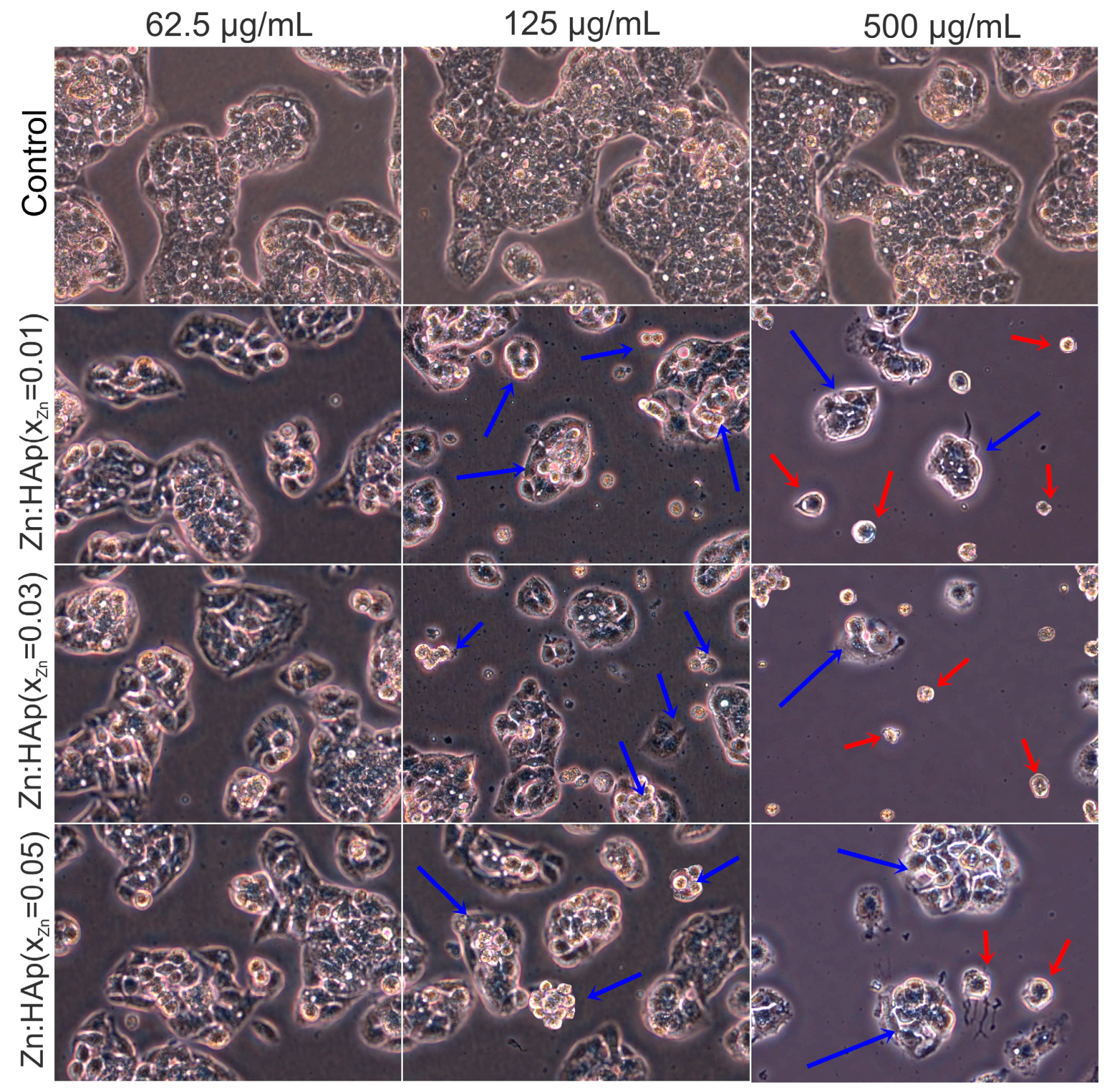
| Sample | Cell Parameters | Crystallite Sizes (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a = b/Deviation (Å) | c/Deviation (Å) | ||
| ICDD-PDF#9-432 | 9.418 | 6.884 | - |
| xZn = 0 | 9.4320/0.001 | 6.8838/0.001 | 231.879 ± 1.000 |
| xzn = 0.01 | 9.4325/0.001 | 6.8828/0.001 | 230.797 ± 1.000 |
| xzn = 0.03 | 9.4348/0.001 | 6.8818/0.001 | 224.182 ± 1.000 |
| xzn = 0.04 | 9.4365/0.001 | 6.8808/0.002 | 201.651 ± 1.000 |
| Sample | BET Nitrogen Adsorption/Desorption | BJH Nitrogen Adsorption/Desorption | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | Vm (cm3) | C | Pore Size (nm) | Pore Volume (m3/g) | |
| xZn = 0.01 | 99.481 | 22.852 | 386.660 | 18.533 | 0.461 |
| xZn = 0.03 | 104.285 | 23.956 | 383.430 | 15.485 | 0.404 |
| xZn = 0.05 | 115.421 | 26.514 | 393.876 | 12.408 | 0.358 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Predoi, D.; Iconaru, S.L.; Deniaud, A.; Chevallet, M.; Michaud-Soret, I.; Buton, N.; Prodan, A.M. Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations. Materials 2017, 10, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030229
Predoi D, Iconaru SL, Deniaud A, Chevallet M, Michaud-Soret I, Buton N, Prodan AM. Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations. Materials. 2017; 10(3):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030229
Chicago/Turabian StylePredoi, Daniela, Simona Liliana Iconaru, Aurélien Deniaud, Mireille Chevallet, Isabelle Michaud-Soret, Nicolas Buton, and Alina Mihaela Prodan. 2017. "Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations" Materials 10, no. 3: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030229
APA StylePredoi, D., Iconaru, S. L., Deniaud, A., Chevallet, M., Michaud-Soret, I., Buton, N., & Prodan, A. M. (2017). Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations. Materials, 10(3), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030229