Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C Nanorods as a Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
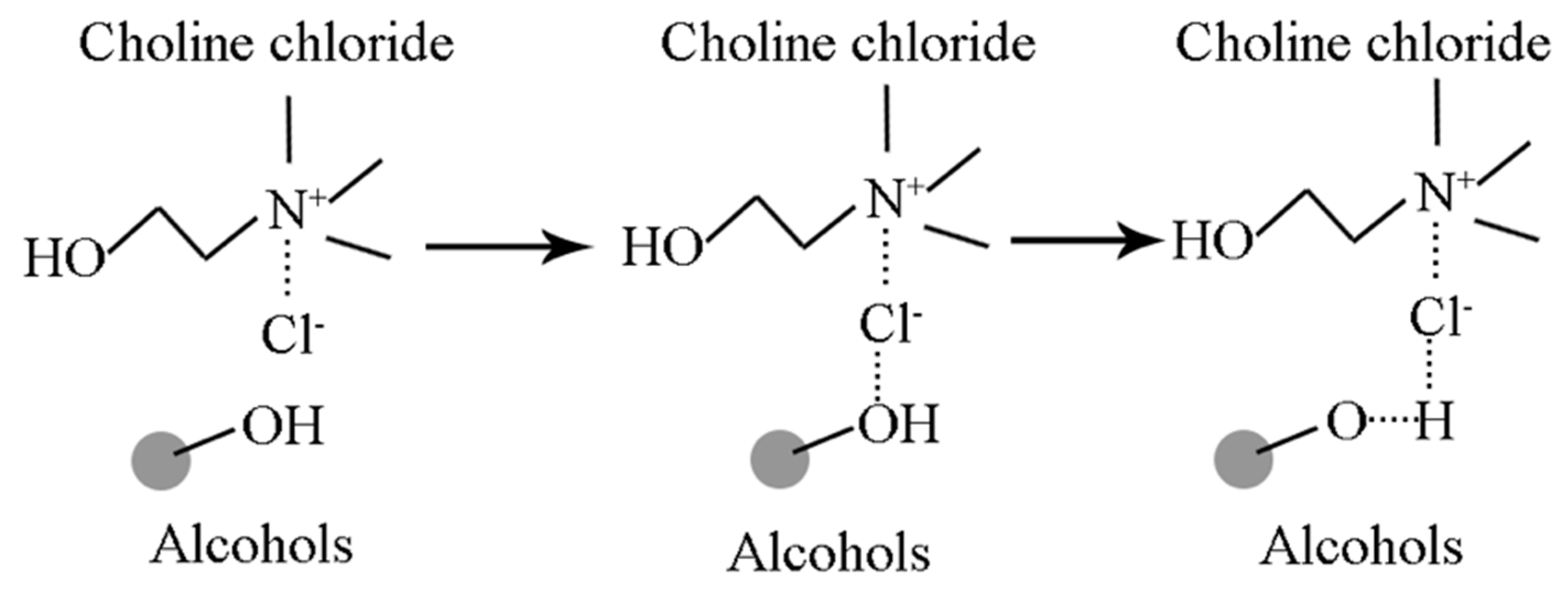
2.1. Sample Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
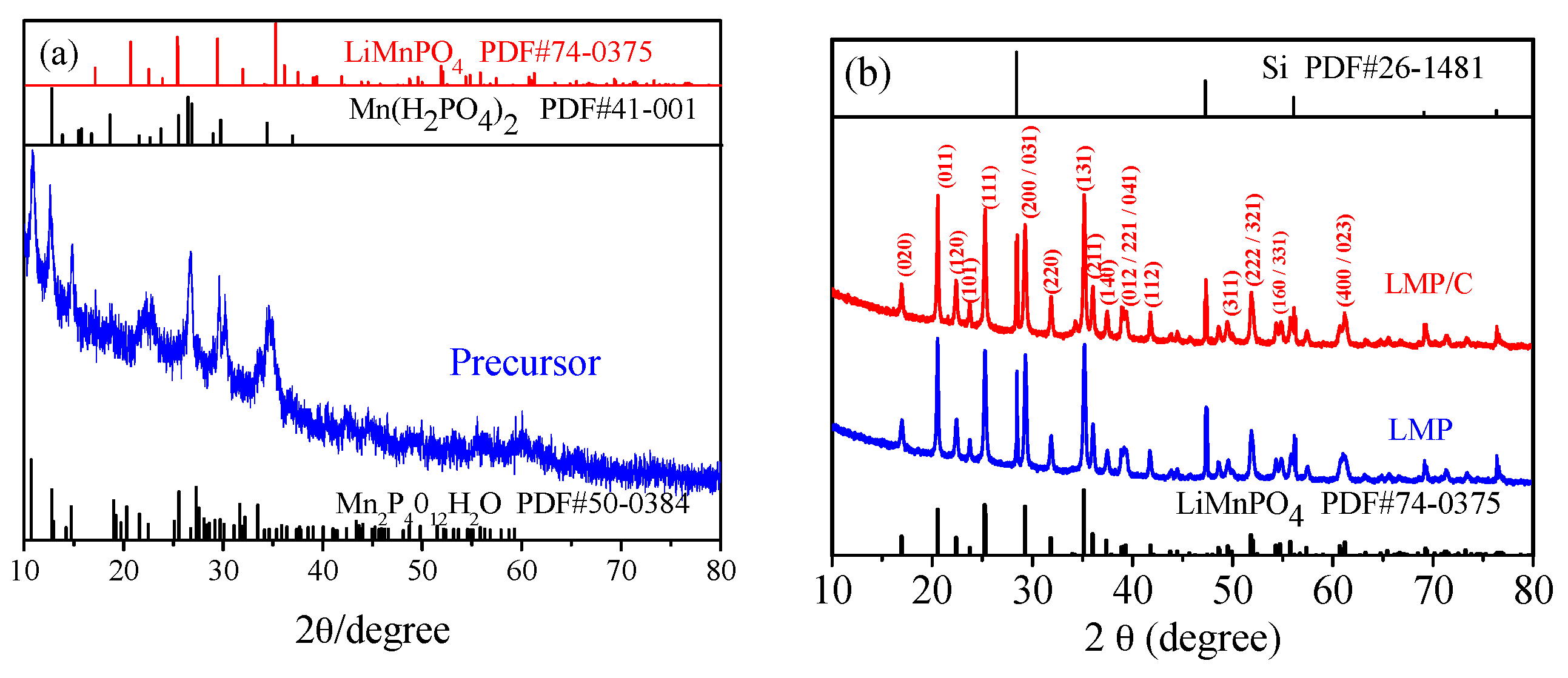
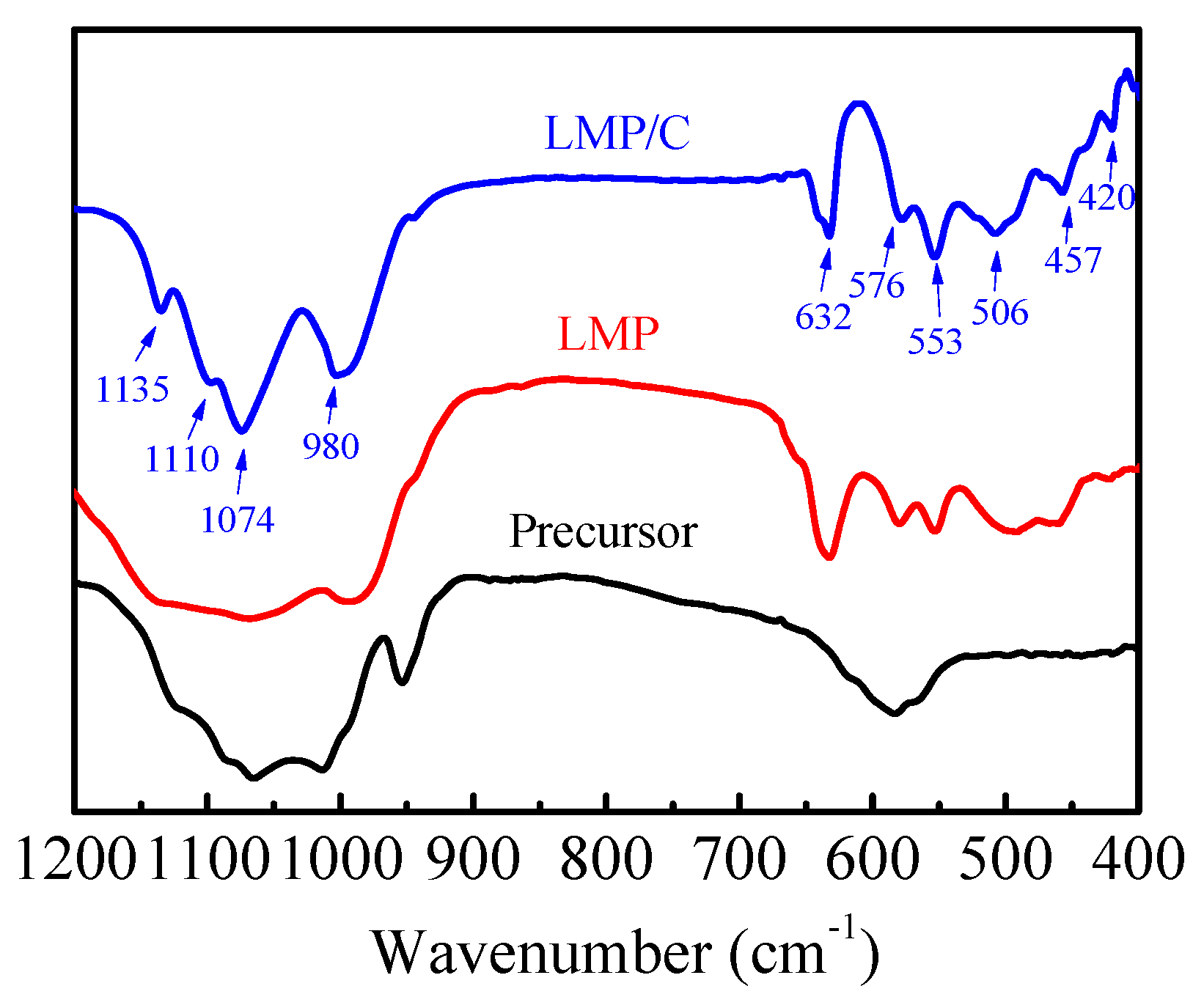
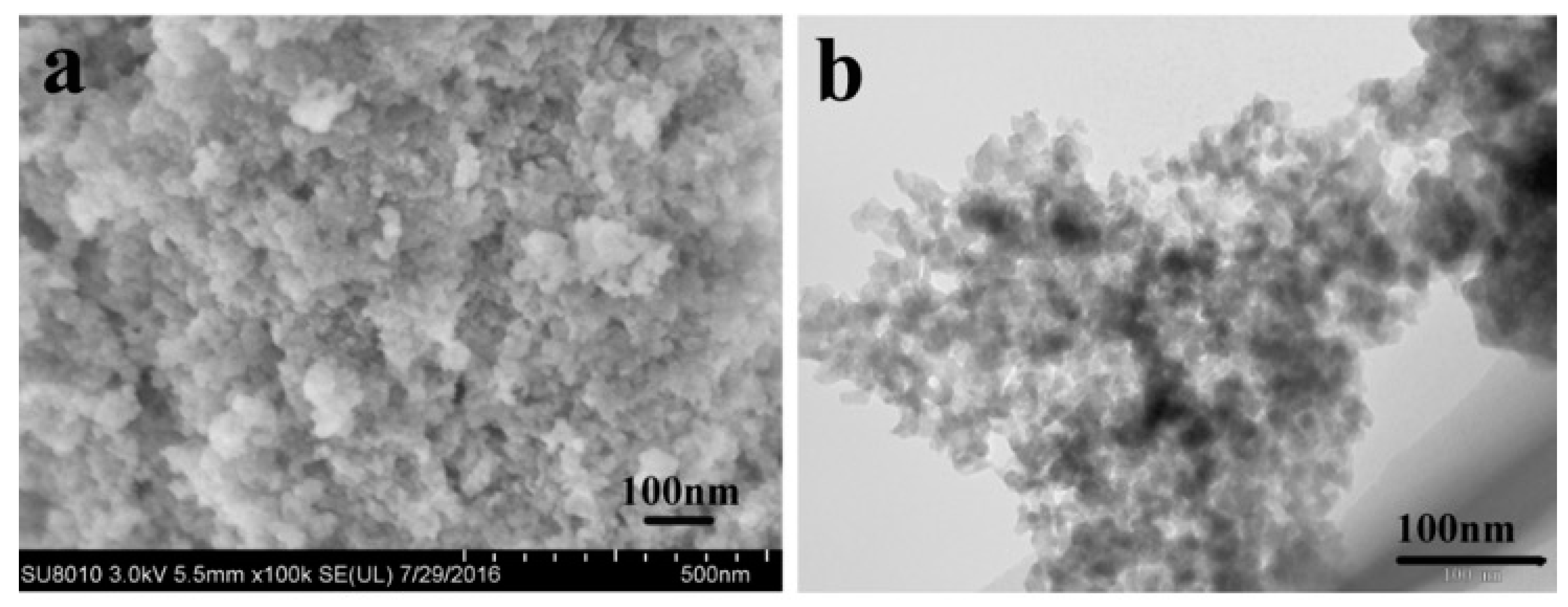
3.1. Material Identification
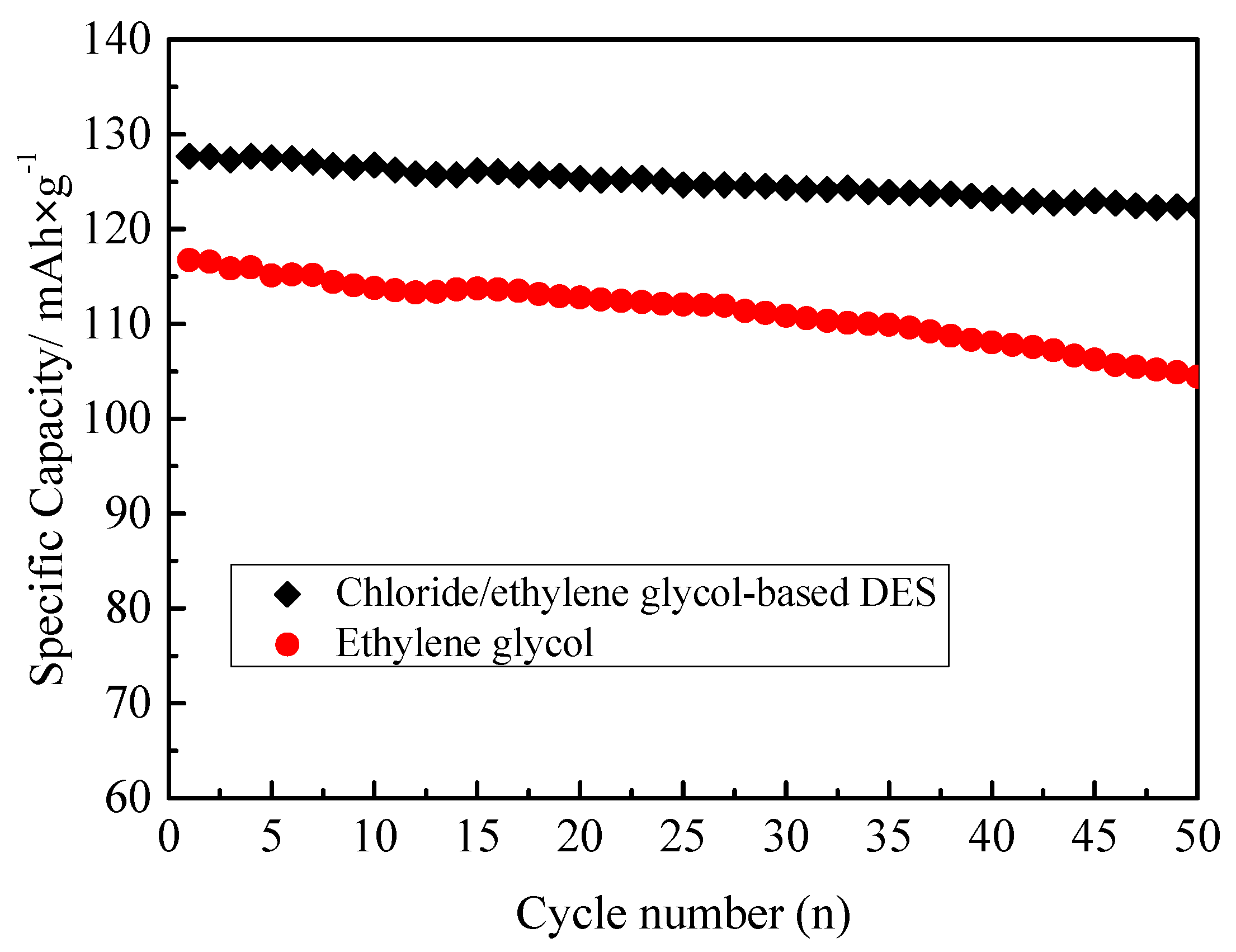
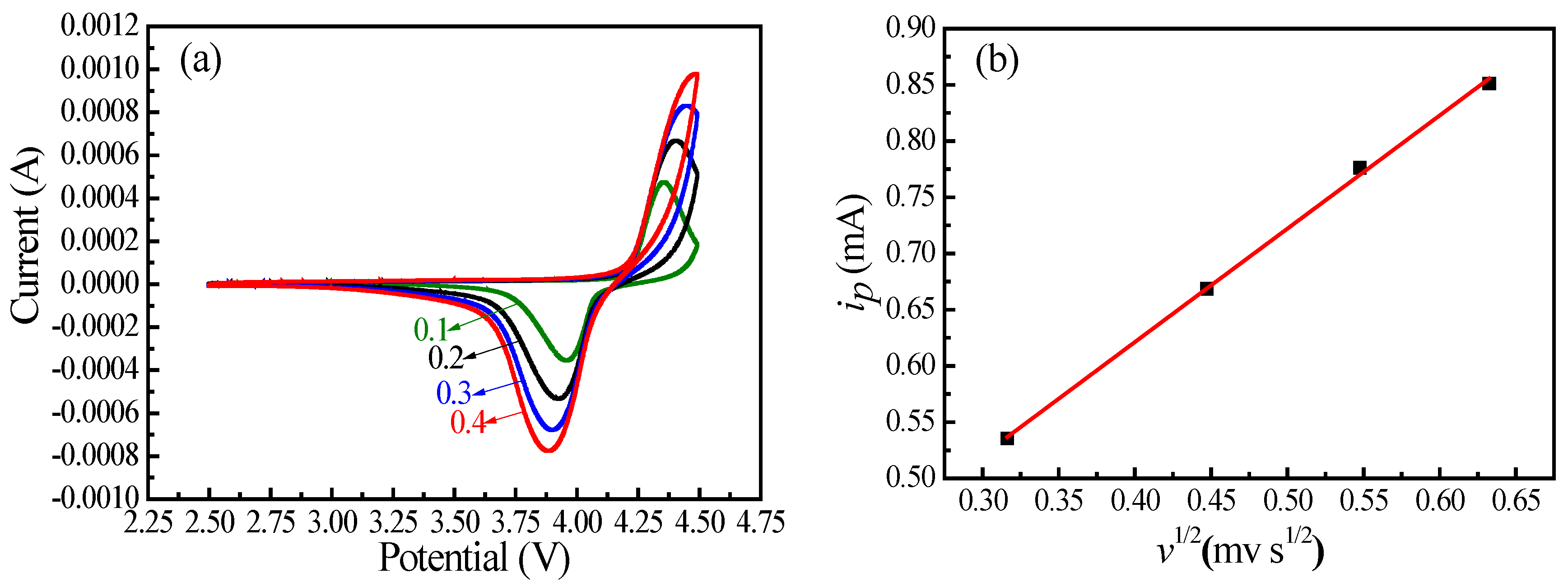
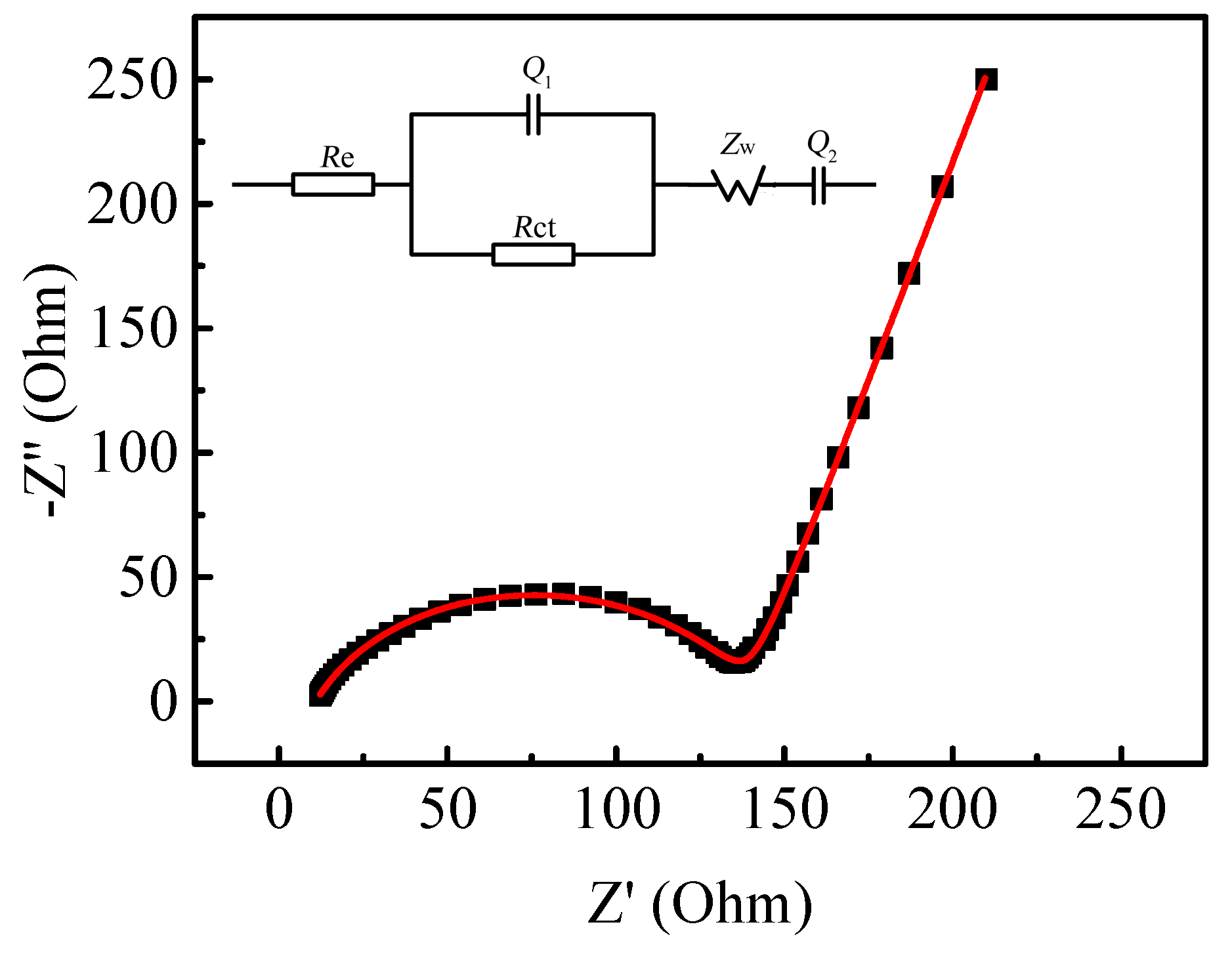
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, L.; Jing, Y.; Zhou, Z. Li ion battery materials with core-shell nanostructures. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3967–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraju, M.; Honma, I. Hydrothermal and solvothermal process towards development of LiMPO4 (M = Fe, Mn) nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.; Park, K. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; He, W.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Ma, J. Recent progress in hybrid cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 2984–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Wu, T.; Wang, Z. Sheet-like Li3V2(PO4)3 nanocomposite coated by SiO2 + C with better electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, A.K.; Nanjundaswamy, K.S.; Goodenough, J.B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 144, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimesso, L.; Forster, C.; Jaegermann, W.; Khanderi, J.P.; Tempel, H.; Popp, A.; Engstler, J.; Schneider, J.J.; Sarapulova, A.; Mikhailova, D.; et al. Developments in nanostructured LiMPO4 (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Mn) composites based on three dimensional carbon architecture. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5068–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Qiao, S.; Lu, G.M.; Munroe, P.; Ahn, H. Mesoporous LiFePO4/C nanocomposite cathode materials for high power lithium ion batteries with superior performance. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4944–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.K.; Oh, S.M.; Park, H.K.; Scrosati, B. Micrometer-sized, nanoporous, high-volumetric-capacity LiMn(0.85)Fe(0.15)PO(4) cathode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5050–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Xu, G.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Shen, G.; Han, G.; Zhou, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of stamen-like LiMnPO4 nanostructures self-assembled with [001]-oriented nanorods and their application in Li-ion batteries. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Azuma, H.; Tohda, M. LiMnPO4 as the cathode for lithium batteries. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2002, 5, A135–A137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Xia, Y.; Qiu, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Synthesis and electrochemical performances of (1 − x)LiMnPO4·xLi3V2(PO4)3/C composite cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masao, Y.; Atsuo, Y.; Yuki, T.; Noriyuki, S.; Ryoji, K. Comparative kinetic study of olivine LixMPO4 (M = Fe, Mn). J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A1352–A1356. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Zuo, P.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; Ma, Y.; Du, C.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Yin, G. High-performance carbon-coated LiMnPO4 nanocomposites by facile two-step solid-state synthesis for lithium-ion battery. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.X.; Ouyang, C.Y.; Chen, J.Z.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Du, Y.L.; Liu, D.S.; Shi, S.Q.; Lei, M.S. First principles study of Jahn-Teller effects in LixMnPO4. Solid State Commun. 2010, 150, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Wang, D.; Bae, I.T.; Xiao, J.; Nie, Z.; Wang, W.; Viswanathan, V.V.; Lee, Y.J.; Zhang, J.G.; Graff, G.L.; et al. LiMnPO4 nanoplate grown via solid-state reaction in molten hydrocarbon for Li-ion battery cathode. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drezen, T.; Kwon, N.; Bowen, P.; Teerlinck, I.; Isono, M.; Exnar, I. Effect of particle size on LiMnPO4 cathodes. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, H.; Mho, S.; Yeo, I.; Kang, Y.; Kim, D. Superior high rate capability of size-controlled LiMnPO4/C nanosheets with preferential orientation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100709–100714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Xu, Q.; Ge, H.; Zhou, G.; Xie, J. Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C for lithium-ion batteries with two kinds of carbon sources. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 1736–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wu, C.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Cao, G.; Zhao, X. Controllable synthesis of high-performance LiMnPO4 nanocrystals by a facile one-spot solvothermal process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10581–10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y. Graphene oxide assisted solvothermal synthesis of LiMnPO4 naonplates cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 146, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q. Nonaqueous synthesis of nano-sized LiMnPO4/C as cathode material for high performance lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 194, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zong, J.; Ding, F.; Lu, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, X. Effects of Fe2+ ion doping on LiMnPO4 nanomaterial for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27164–27169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerman, D.G.; Chukalkin, Y.G.; Medvedeva, N.L.; Gorshkov, V.S.; Semenova, A.S. Effect of vanadium doping on the magnetic properties of LiMnPO4. Phys. Status Solidi 2016, 253, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajammal, K.; Sivakumar, D.; Duraisamy, N.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Structural and electrochemical characterizations of LiMn1−xAl0.5xCu0.5xPO4 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2) cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 2016, 173, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Qiu, B.; Xia, Y.; Qin, Z.; Qin, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Solvothermal synthesis of Fe-doping LiMnPO4 nanomaterials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Quan, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Controllable synthesis of LiMnPO4 nanocrystals: Morphology evolution and their size-dependent electrochemical properties. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 8769–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroslavtsev, A.B.; Kulova, T.L.; Skundin, A.M. Electrode nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2015, 84, 826–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meethong, N.; Huang, H.; Speakman, S.; Carter, W.; Chiang, Y. Strain accommodation during phase transformationsin olivine-based cathodes as a materials selection criterionfor high-power rechargeable batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, T.; Yu, A. Synthesis of nano-sized LiMnPO4 and in situ carbon coating using a solvothermal method. J. Power Sources 2013, 229, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Cao, G.; Zhao, X. Facile synthesis of nanostructured LiMnPO4 as a high-performance cathode material with long cycle life and superior rate capability. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 99632–99639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xia, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z. Morphology controlled synthesis and modification of high-performance LiMnPO4 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Math. Chem. 2012, 22, 21144–21153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chang, K.; Li, B.; Tang, H.; Fu, X.; Chang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H. Glucose-assisted synthesis of highly dispersed LiMnPO4 nanoparticles at a low temperature for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 189, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Shen, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X. Flower-like LiMnPO4 hierarchical microstructures assembled from single-crystalline nanosheets for lithium-ion batteries. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 4284–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, S.; Quan, W.; Zhang, Z. High-performance LiMnPO4 nanorods synthesized via a facile EG-assisted solvothermal approach. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10267–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Xu, C.; Hong, D.; Fang, H.; Zhen, L. Hydrothermal synthesis of well-dispersed LiMnPO4 plates for lithium ion batteries cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.; Zong, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, S.; Shen, G.; Han, G. Hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like LiMnPO4 nanostructures self-assembled with (010) nanosheets and their application in Li-ion batteries. CrystEngComm. 2015, 17, 6399–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Bao, L.; Li, X.; Shen, G.; Han, G. Ethylene glycol (EG) solvothermal synthesis of flower-like LiMnPO4 nanostructures self-assembled with (010) nanobelts for Li-ion battery positive cathodes. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Chu, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of 3D-hierarchical hemoglobin-like LiMnPO4 microspheres as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2015, 274, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Pan, X.; Li, H.; Xie, S.; Yi, R.; Jin, W. Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical properties of dispersed LiMnPO4 wedges. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 7808–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voepel, P.; Suchomski, C.; Hofmann, A.; Gross, S.; Dolcet, P.; Smarsly, B.M. In-depth mesocrystal formation analysis of microwave-assisted synthesis of LiMnPO4 nanostructures in organic solution. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, Z.; Luan, Y.; Mu, T. Ionic liquids for synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Chen, M.; Li, G.; Teng, Y.; Xu, T.; Mho, S.-I.; Hua, X. Synergism of ionic liquid and surfactant molecules in the growth of LiFePO4 nanorods and the electrochemical performances. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barpanda, P.; Recham, N.; Djellab, K.; Boulineau, A.; Armand, M. Ionothermal synthesis and electrochemical characterization of nanostructured lithium manganese phosphates. ECS Trans. 2010, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kareem, M.; Mjalli, F.; Hashim, M.; Alnashef, I. Phosphonium-based ionic liquids analogues and their physical properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep eutectic solvents: Sustainable media for nanoscale and functional materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheed, R.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheed, R. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Power Sources 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.D.O.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, N.; Dezfooli, S.; Khajeh, M.; Hashemi, M.M. Efficient deep eutectic solvents catalyzed synthesis of pyran and benzopyran derivatives. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 186, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; McKenzie, K.J.; Obi, S.U. Solubility of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbeck, C.; Lehmann, J.; Lovelock, K.; Cremer, T.; Paape, N. Density and surface tension of ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 17025–17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-based ionic liquids with metal-containing anions and cations. Chemistry 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Fan, Y.J.; Tian, N.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhao, X.Q.; Mao, B.W.; Sun, S.G. Electrochemically shape-controlled synthesis in deep eutectic solvents-a new oute to prepare Pt nanocrystals enclosed by high-index facets with high catalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 2040–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Leron, R.B.; Caparanga, A.R.; Li, M. Henry’s constant of carbon dioxide-aqueous deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride/ethylene glycol, choline chloride/glycerol, choline chloride/malonic acid) systems. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 68, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, D.; de la Fuente Revenga, M.; Widersten, M. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are viable cosolvents for enzyme-catalyzed epoxide hydrolysis. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 147, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhong, H.R.; Wong, D.S.H.; Wan, C.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wei, T.C. A novel deep eutectic solvent-based ionic liquid used as electrolyte for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauric, A.D.; Halalay, I.C.; Goward, G.R. Combined NMR and molecular dynamics modeling study of transport properties in sulfonamide based deep eutectic lithium electrolytes: LiTFSI based binary systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 6657–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, V.; Heuer, A.; Rad, B.R.; Winter, M.; Smiatek, J. Atomistic insights into deep eutectic electrolytes: The influence of urea on the electrolyte salt LiTFSI in view of electrochemical applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 28403–28408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Frisch, G.; Gurman, S.; Ryder, K.S.; Fernando Silva, A. Double layer effects on metal nucleation in deep eutectic solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 10224–10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, W.; Du, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Shan, Z. Reaction mechanism and influence of the experimental variables for solvothermal synthesized LiMnPO4 nanoplates. J. Power Sources 2015, 300, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barpanda, P.; Djellab, K.; Recham, N.; Armand, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Direct and modified ionothermal synthesis of LiMnPO4 with tunable morphology for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10143–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebresilassie Eshetu, G.; Armand, M.; Scrosati, B.; Passerini, S. Energy storage materials synthesized from ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13342–13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wu, C.; Liao, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, P.; Cao, G.; Zhao, X. Performance improvement of lithium manganese phosphate by controllable morphology tailoring with acid-engaged nano engineering. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Zhu, P.; Fu, X.; Chen, R.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.P. Comparative study of LiMnPO4 cathode materials synthesized by solvothermal methods using different manganese salts. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Singh, P.; Appadoo, D.; Martin, D.E. Synthesis and characterization of olivine LiNiPO4 for aqueous rechargeable battery. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 4356–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Jozwiak, P.; Garbarczyk, J.; Benkhouja, K.; Zaghib, K.; Gendron, F.; Julien, C. Local structure and redox energies of lithium phosphates with olivine and nasicon-like structures. J. Power Sources 2005, 140, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.N.; Li, W.C.; Cheng, F.; Lu, A.H. Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C with superior performance as Li-ion battery cathodes by a two-stage microwave solvothermal process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13920–13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Fu, Y.; Xu, N.; Li, G.; Wu, M.; Gao, X. High performance LiMnPO4/C prepared by a crystallite size control method. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 15070–15077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hu, Z.; Gao, H.; Feng, H.; Cheng, F.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J. Spindle-like LiMnPO4 assembled by nanorods with different crystallographic orientations as the cathode of lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2013, 5, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoma, Y.; Kim, J.M.; Abiko, K.; Naoaki, K. Optimization of electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C prepared by an aqueous solution method using sucrose. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.G.; Wickham, J.; Alivisatos, A.P. Kinetics of II–VI and III–V colloidal semiconductor nanocrystal growth: “Focusing” of size distributions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5343–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.J.; Rochford, L.A.; Ryan, M.P.; Jones, T.S.; Heutz, S. The influence of polar (0001) zinc oxide (ZnO) on the structure and morphology of vanadyl phthalocyanine (VOPc). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65949–65952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, H. Confined synthesis of hierarchical structured LiMnPO4/C granules by a facile surfactant-assisted solid-state method for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 2, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.R.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K.; Satyanarayana, N. Carbon coated LiMnPO4 nanorods for lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A227–A230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.R.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K.; Satyanarayana, N. Enhanced conductivity and electrical relaxation studies of carbon-coated LiMnPO4 nanorods. Ionics 2012, 19, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Yu, X.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Huang, X. Kinetic analysis on LiFePO4 thin films by CV, GITT, and EIS. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 4869–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced electrochemical properties of LiMnPO4/C composites by tailoring polydopamine-derived carbon coating. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Markovsky, B.; Salitra, G.; Markevich, E.; Talyossef, Y.; Koltypin, M.; Nazar, L.; Ellis, B.; Kovacheva, D. Review on electrode-electrolyte solution interactions, related to cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaberscek, M.; Dominko, R.; Jamnik, J. The meaning of impedance measurements of LiFePO4 cathodes: A linearity study. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B. A package for impedance/admittance data analysis. Solid State Ionics 1986, 18–19, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
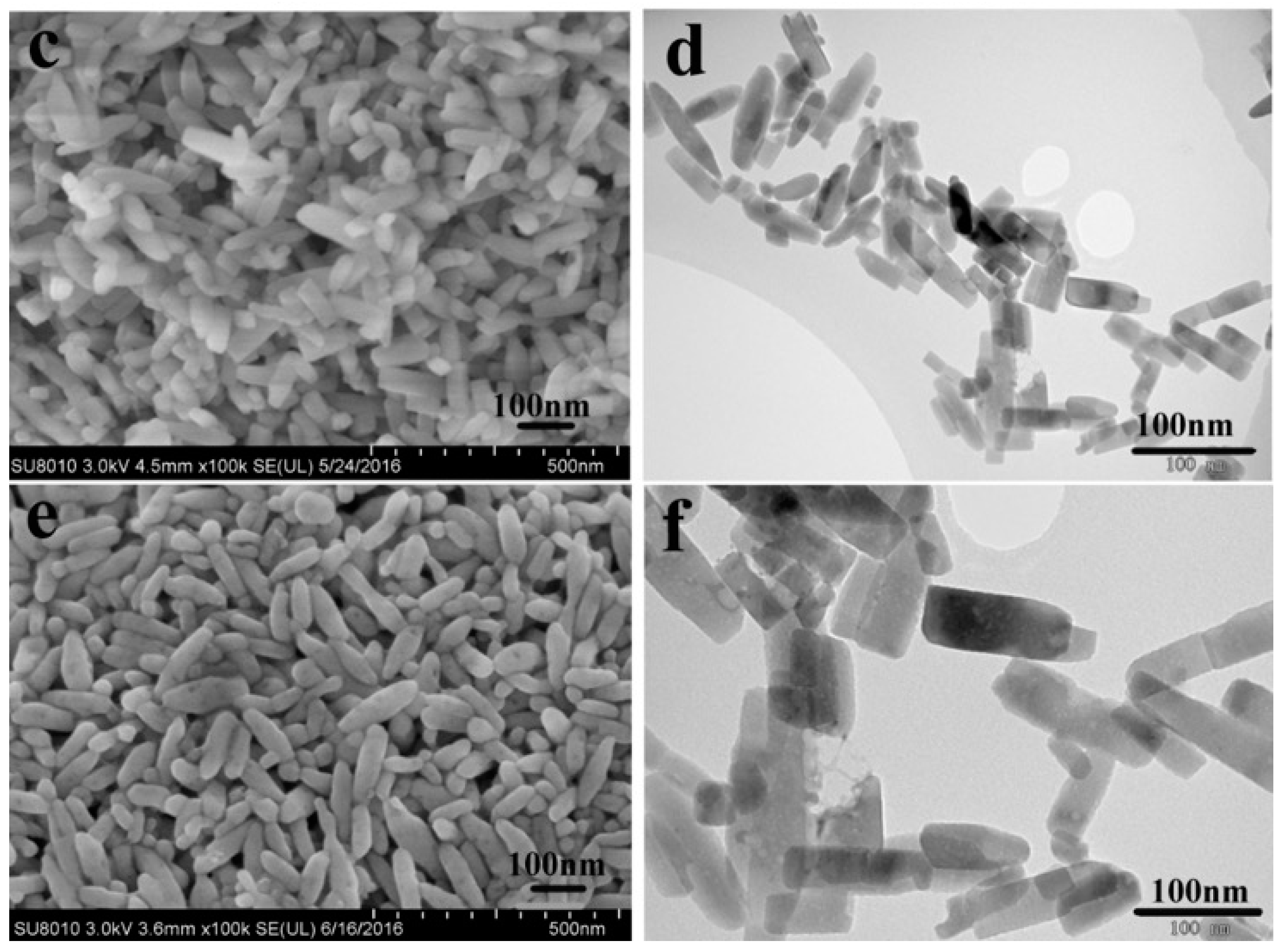
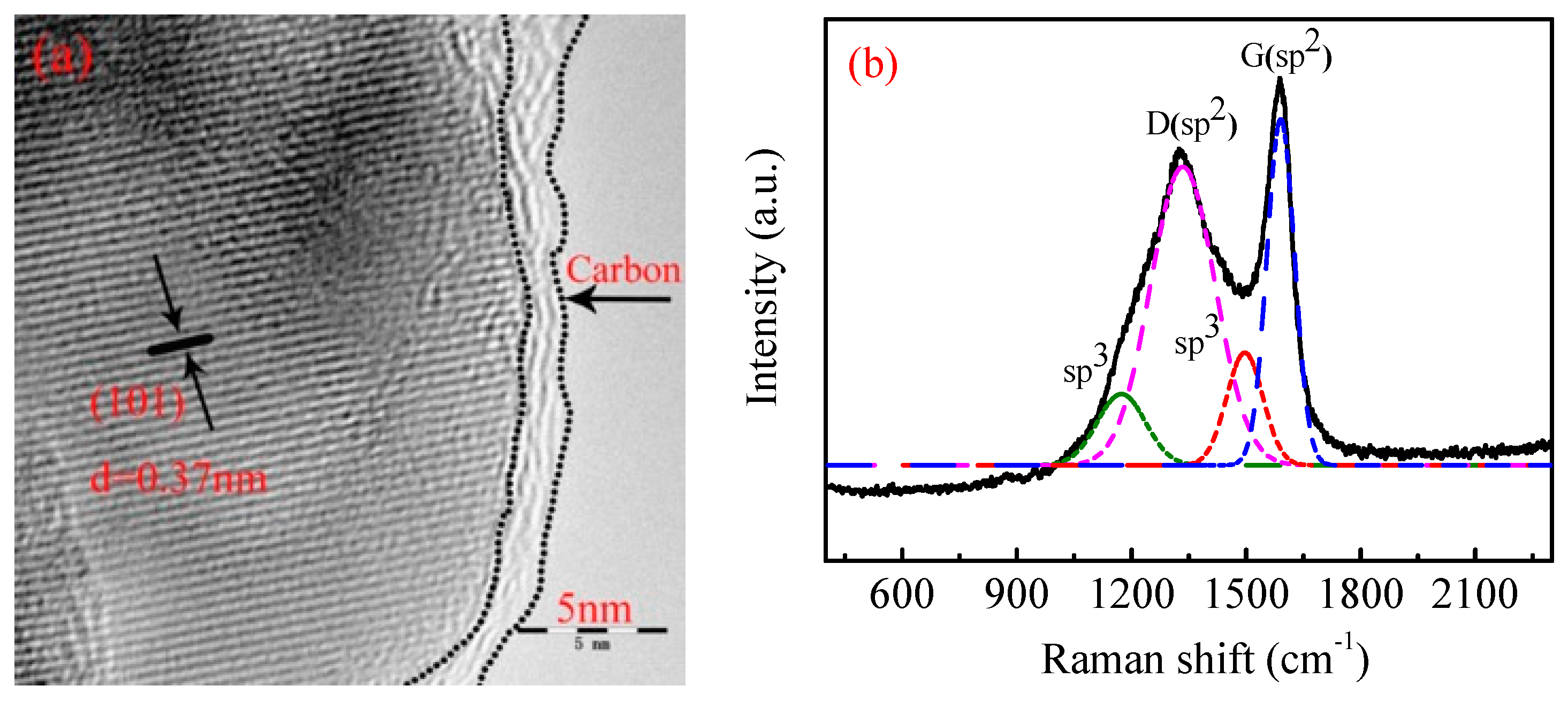
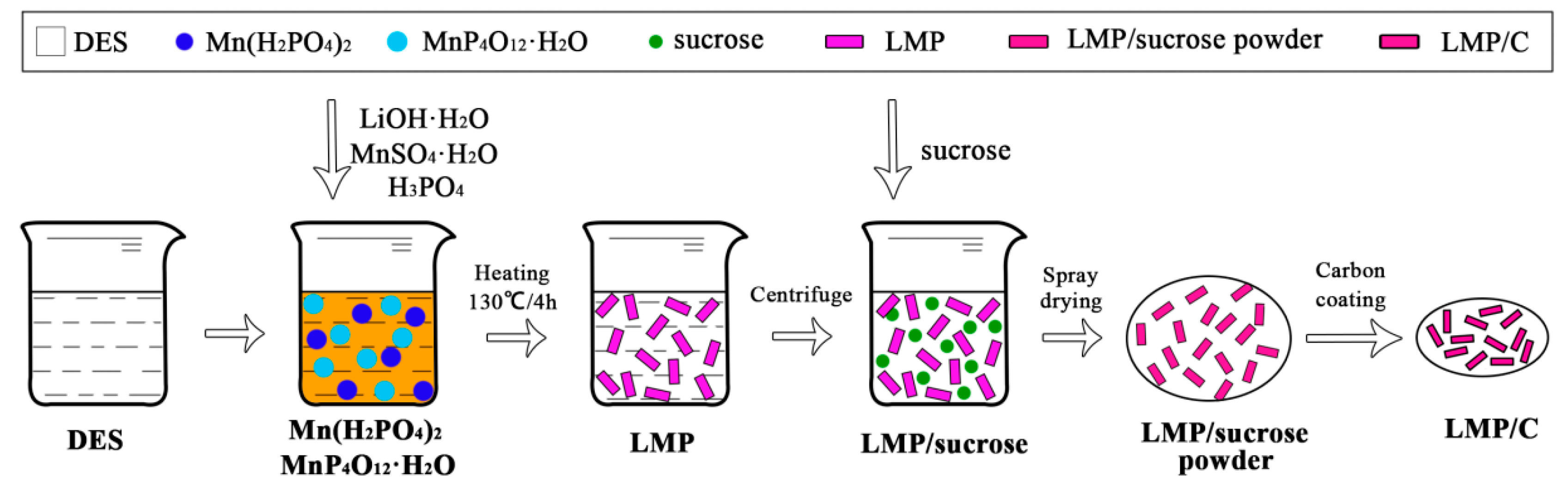
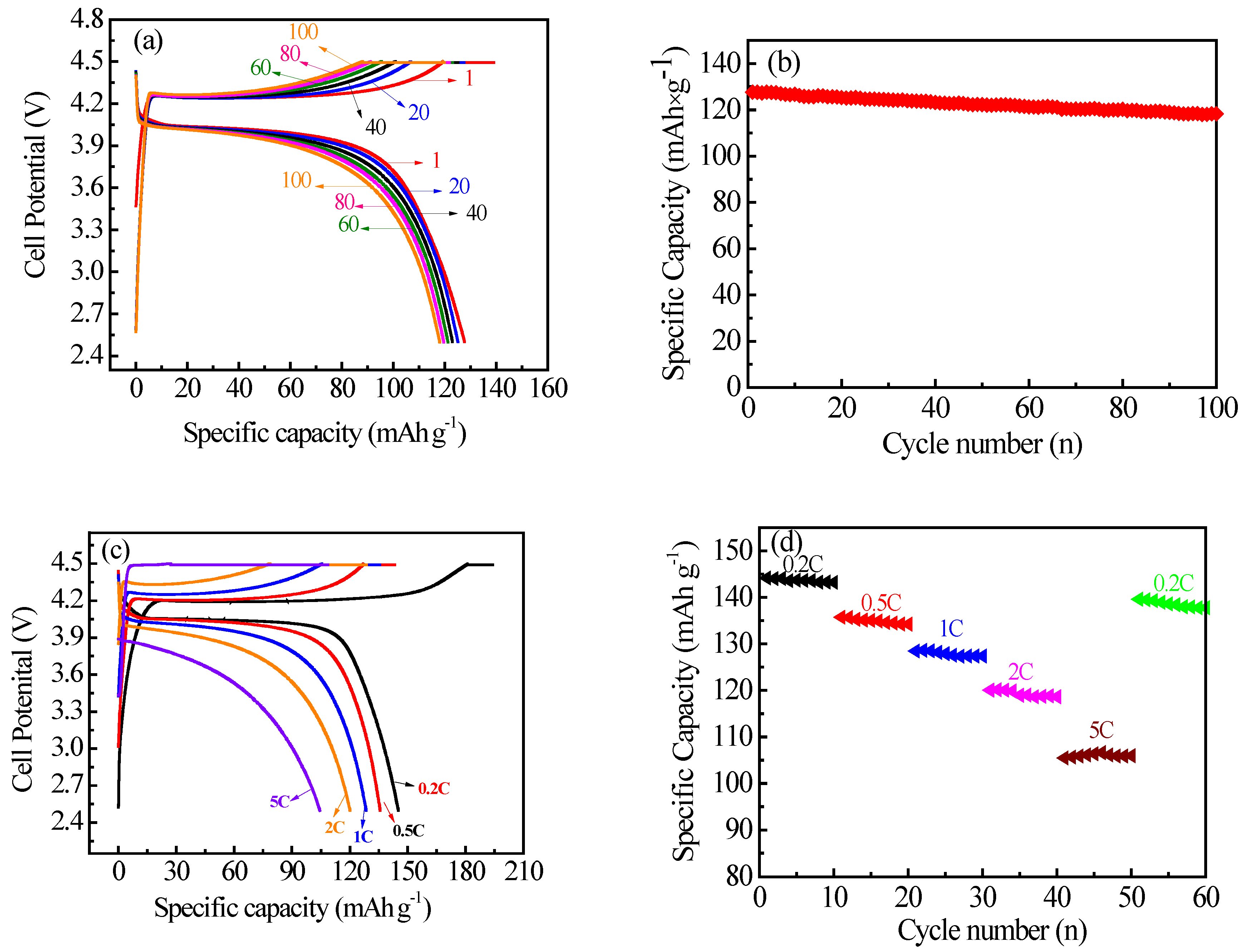
| Sample | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | V (Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMP | 10.4437 | 6.0980 | 4.7424 | 302.0 |
| LMP/C | 10.4439 | 6.1021 | 4.7430 | 302.3 |
| Element | Re (Ω) | Rct (Ω) | Q1 (F) | n1 | Q2 (F) | n2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 10.93 | 128.00 | 1.55 × 10−6 | 0.8 | 2.18 × 10-3 | 0.8 |
| Error (%) | 0.93 | 1.13 | 4.15 | 0.59 | 4.76 | 2.67 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Huang, R.-R.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.-C.; Lv, X.-Y.; Su, J.; Long, Y.-F.; Wen, Y.-X. Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C Nanorods as a Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. Materials 2017, 10, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020134
Wu Z, Huang R-R, Yu H, Xie Y-C, Lv X-Y, Su J, Long Y-F, Wen Y-X. Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C Nanorods as a Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. Materials. 2017; 10(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhi, Rong-Rong Huang, Hang Yu, Yong-Chun Xie, Xiao-Yan Lv, Jing Su, Yun-Fei Long, and Yan-Xuan Wen. 2017. "Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C Nanorods as a Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries" Materials 10, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020134
APA StyleWu, Z., Huang, R.-R., Yu, H., Xie, Y.-C., Lv, X.-Y., Su, J., Long, Y.-F., & Wen, Y.-X. (2017). Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C Nanorods as a Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. Materials, 10(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020134







