Photometric and Colorimetric Assessment of LED Chip Scale Packages by Using a Step-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test (SSADT) Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Test Samples and Experiments
2.1. Test Sample Preparation
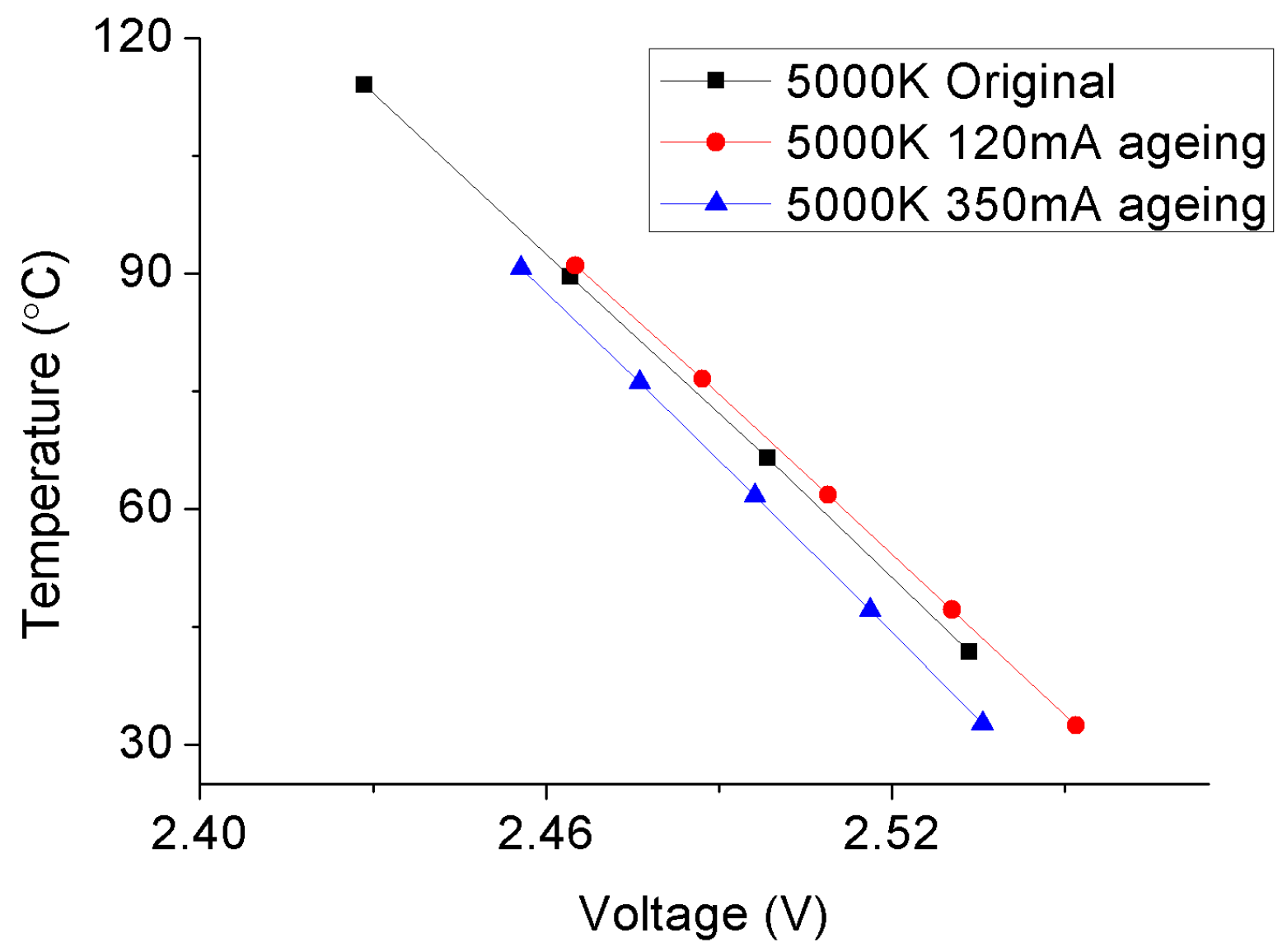
2.2. Junction Temperature Measurements
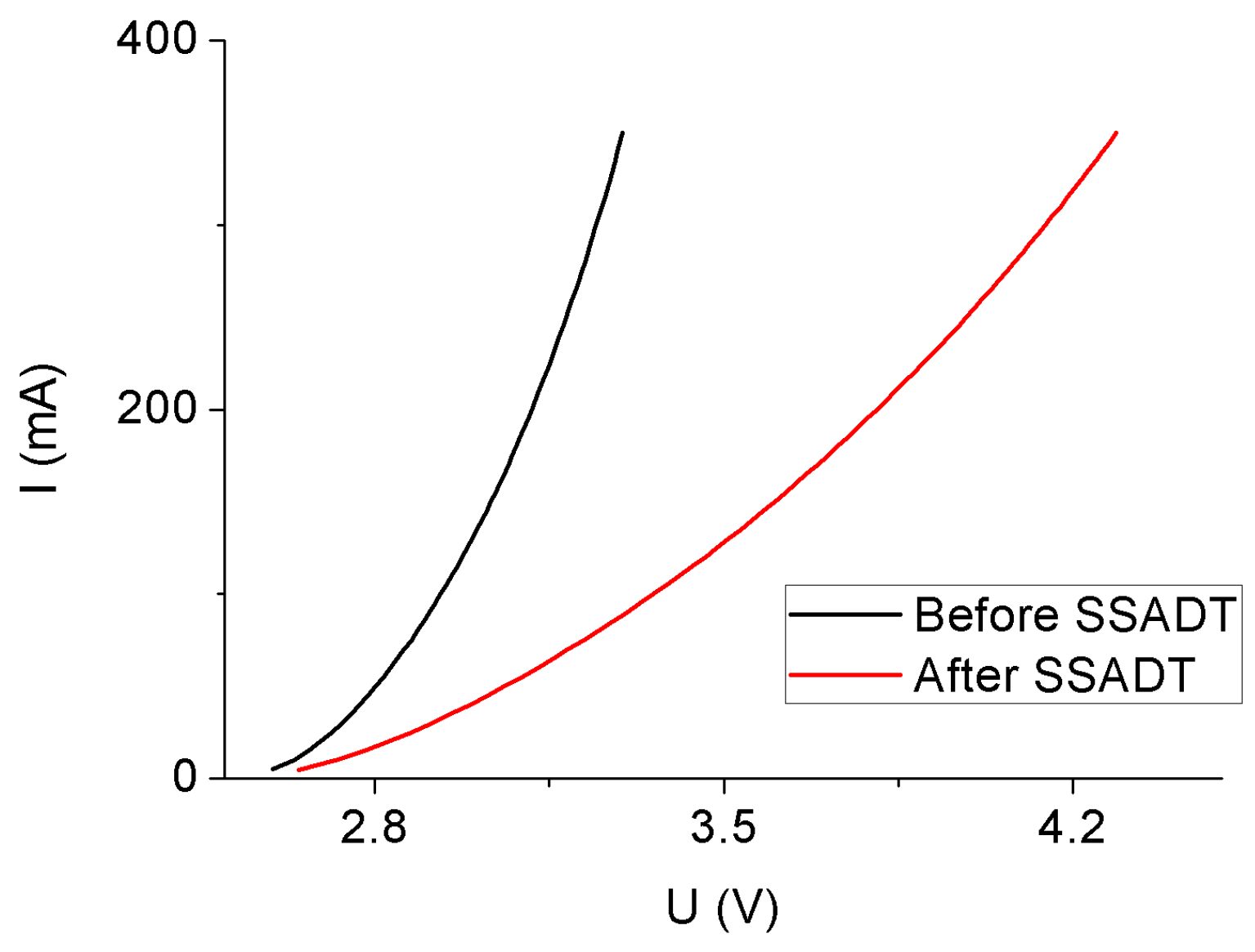
2.3. Step Stress Accelerated Degradation Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Analysis
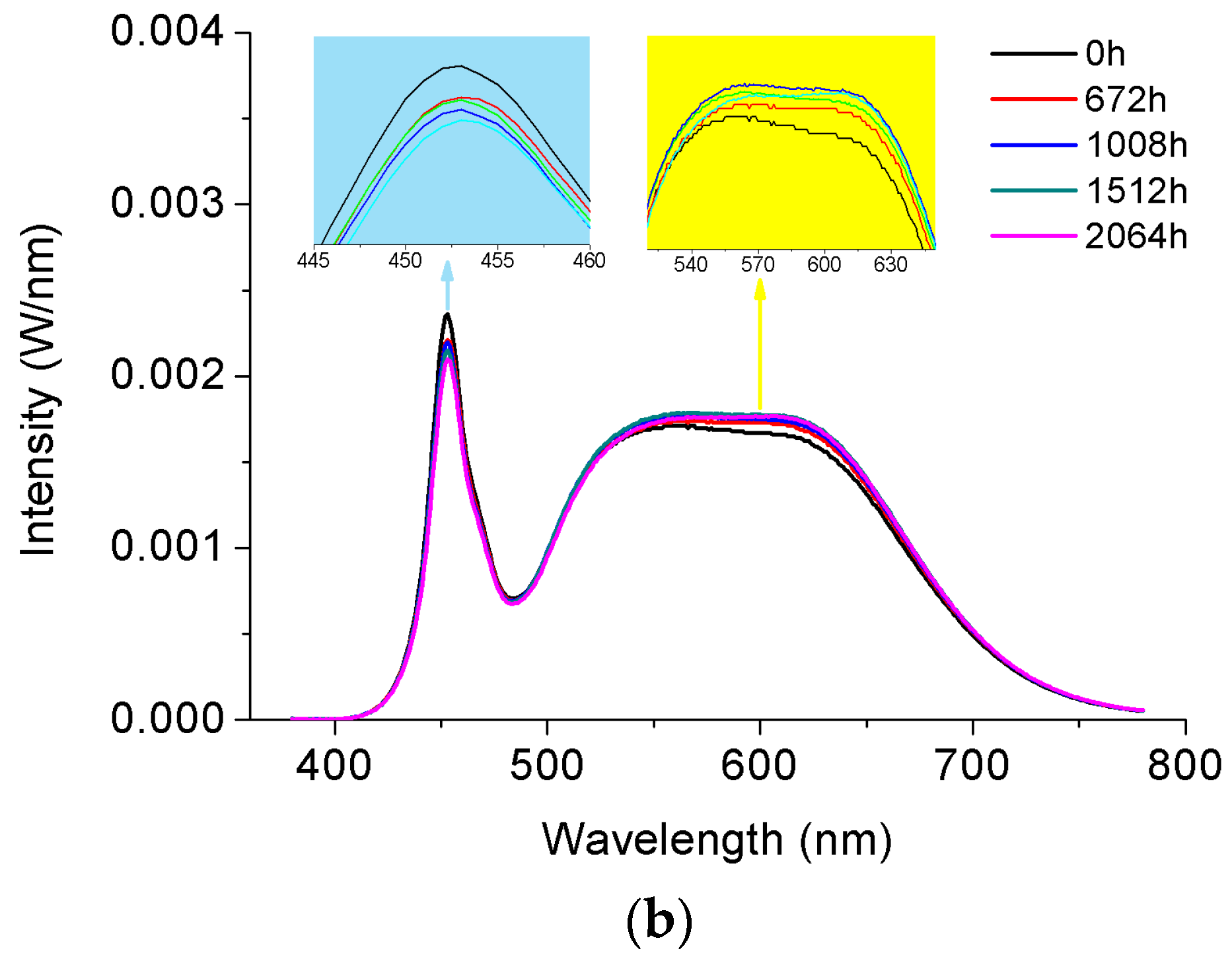
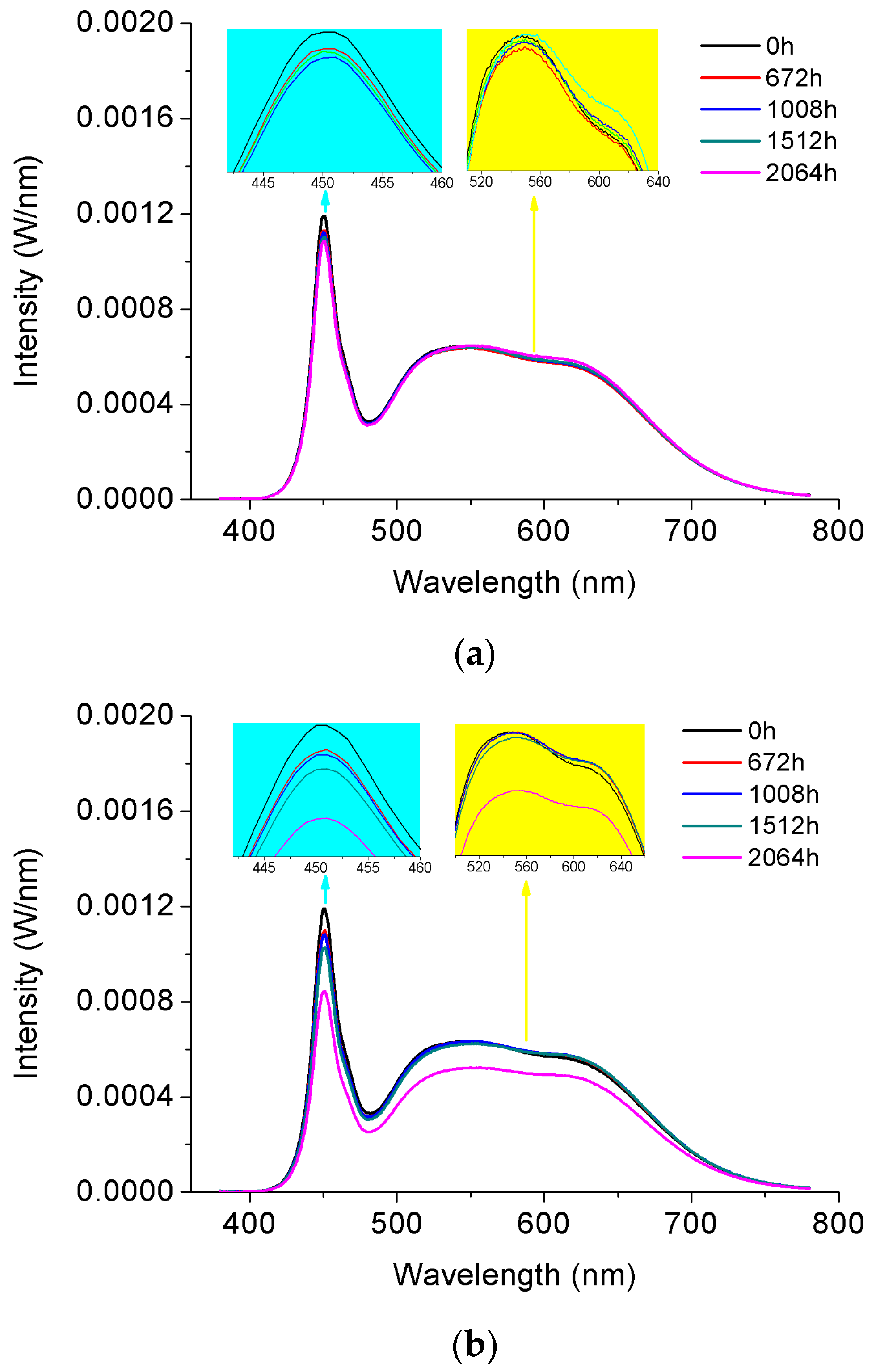
3.2. Spectral Power Distribution Attenuation
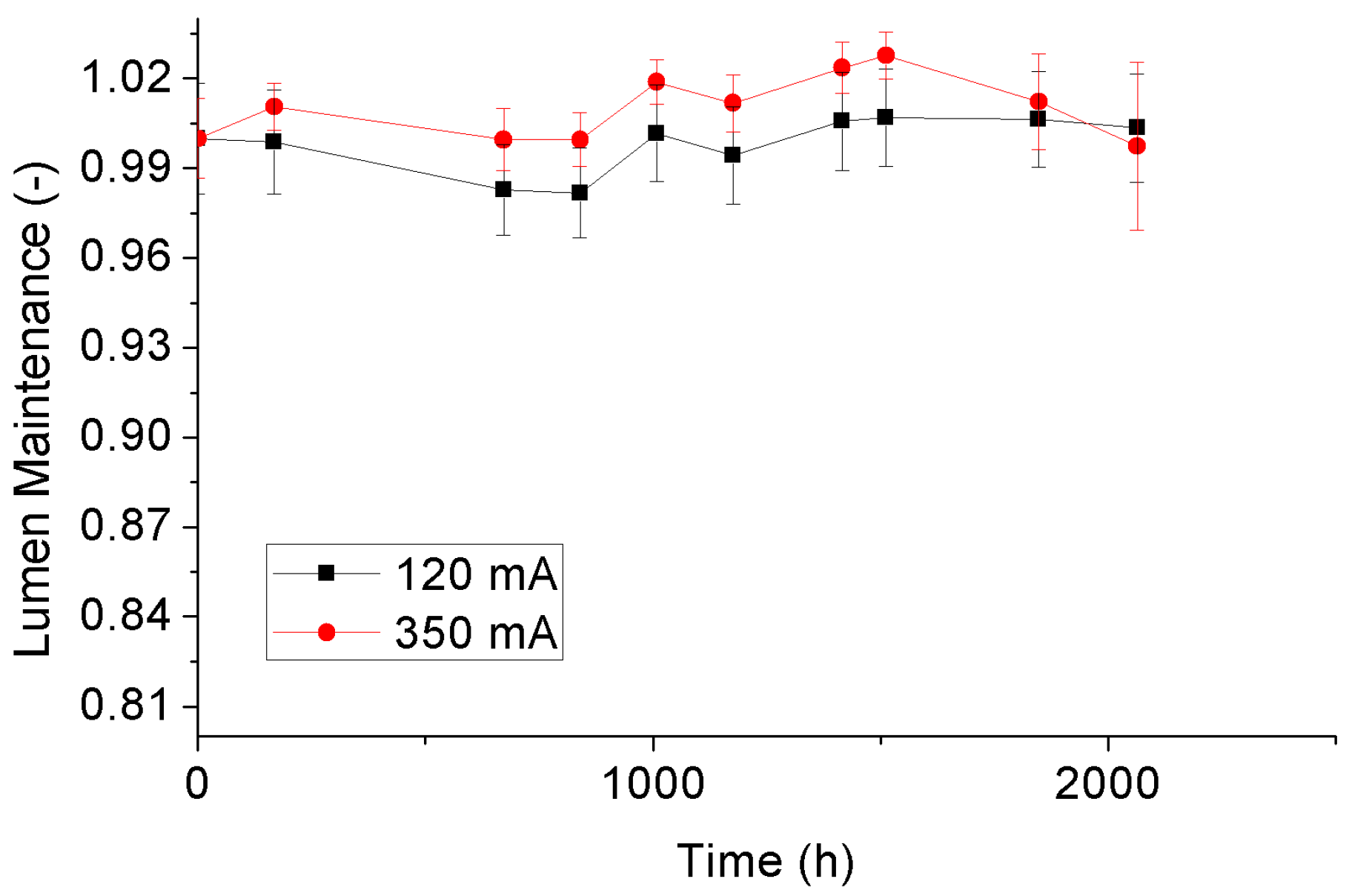
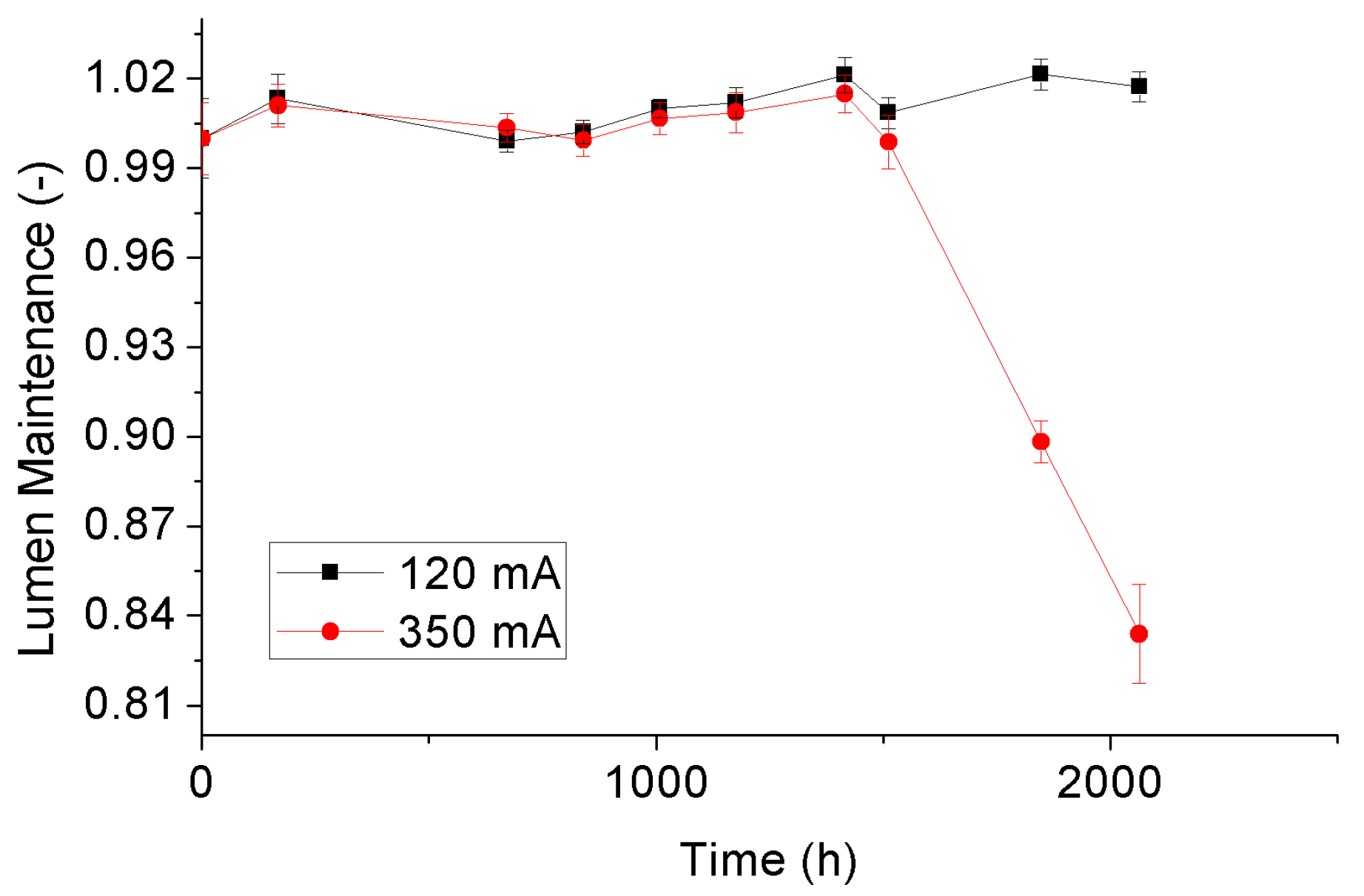
3.3. Lumen Maintenance Depreciation
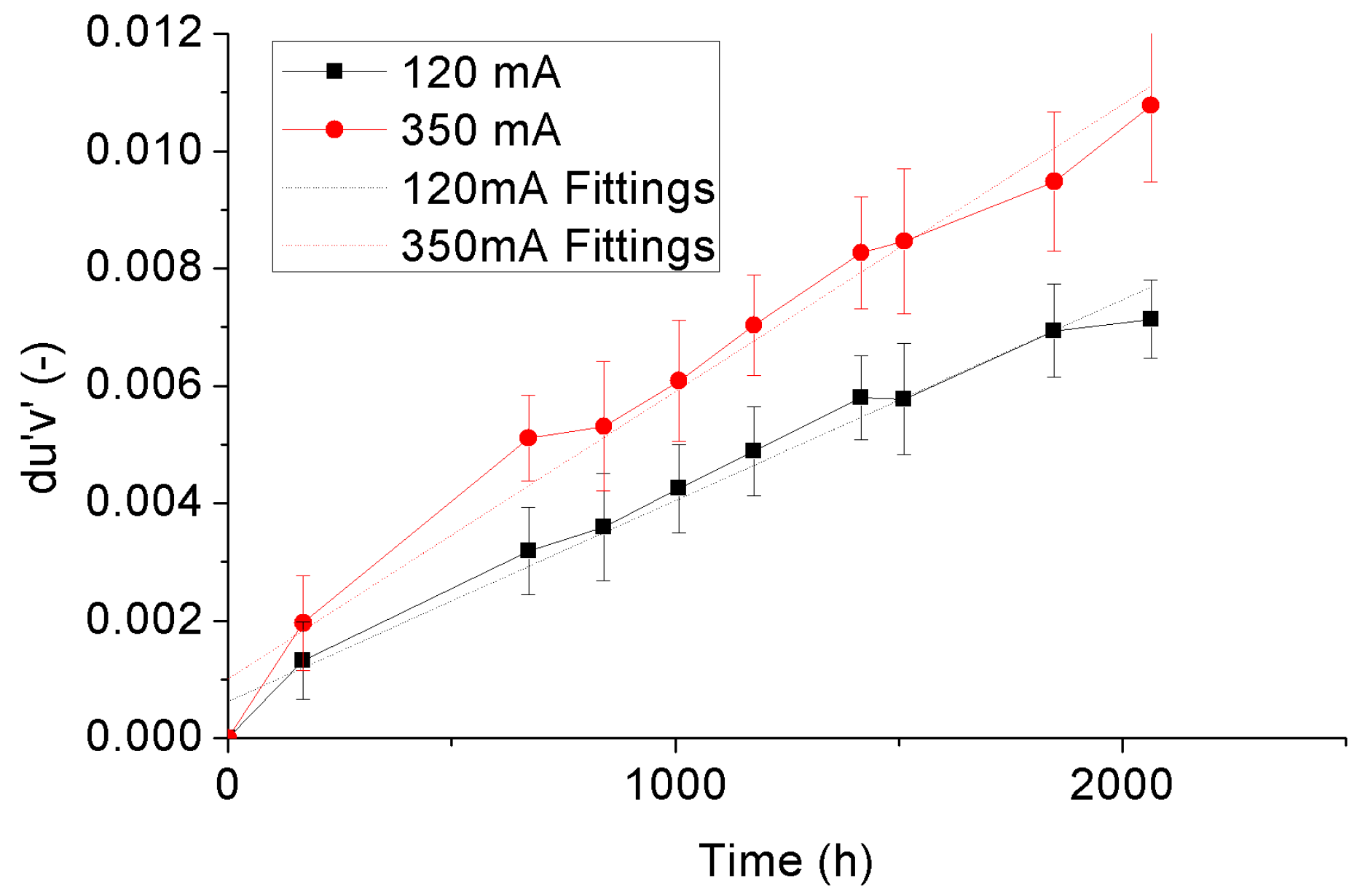
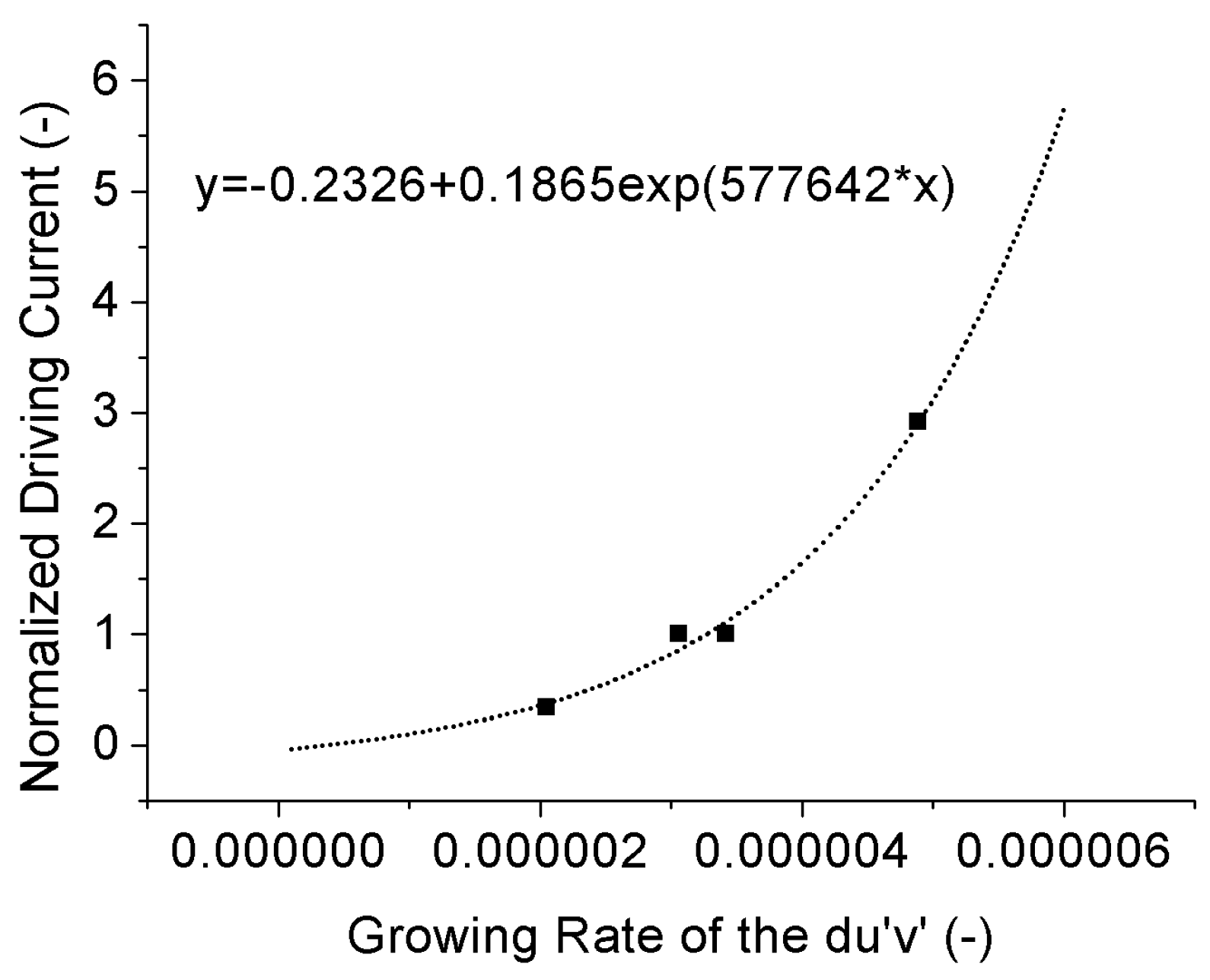
3.4. Color Shift
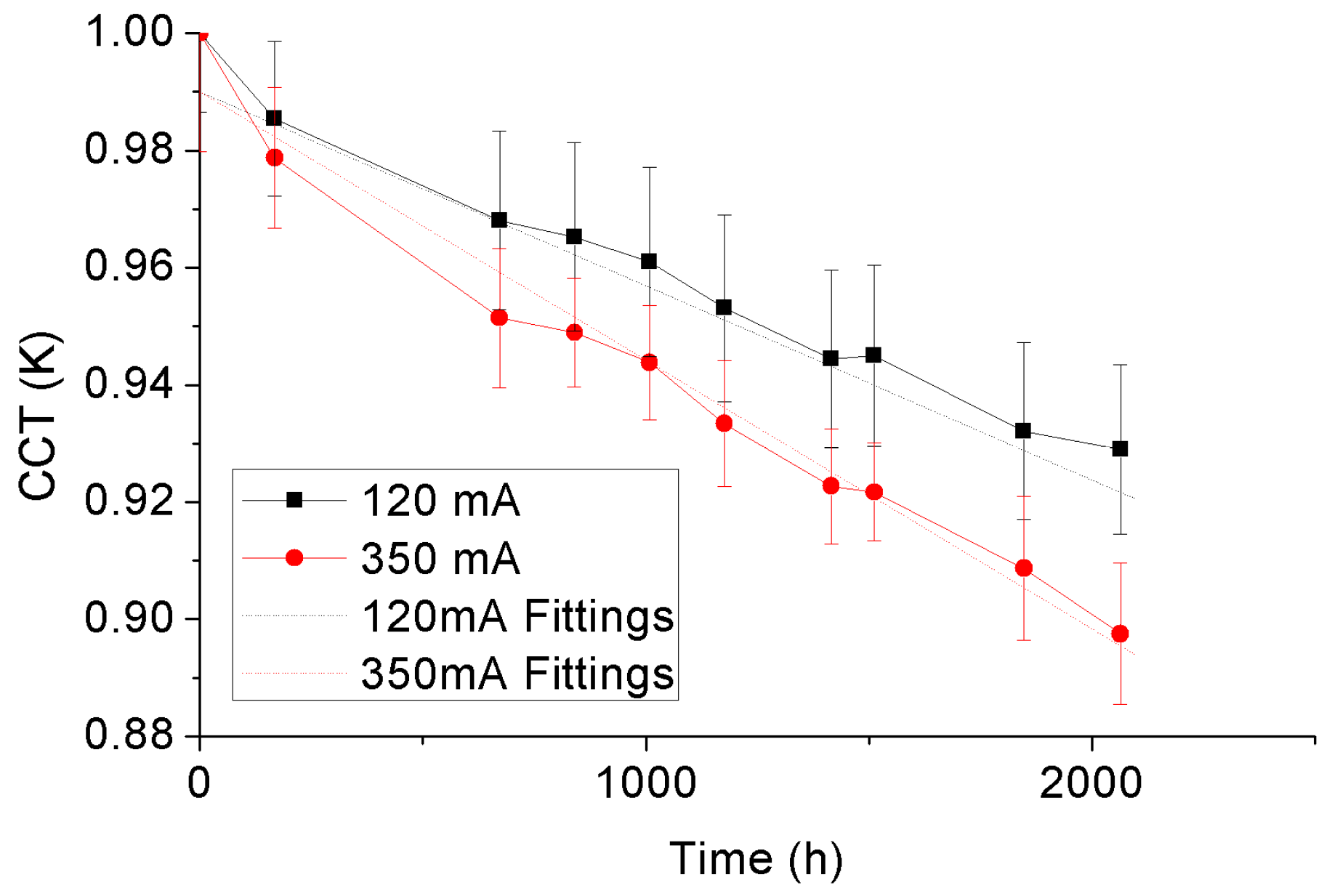
3.5. CCT Depreciation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCT | Correlated Color Temperature |
| CSP | Chip Scale Package |
| CSADT | Constant-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test |
| LED | Light-emitting Diode |
| SPD | Spectral Power Distribution |
| SSADT | Step-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test |
| WLCSP | Wafer Level Chip Scale Packaging |
References
- Wang, F.K.; Lu, Y.C. Useful lifetime analysis for high-power white LEDs. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jiang, X.; Yung, K.-C.; Fan, J.; Pecht, M. A review of prognostics techniques for high-power white LEDs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 6338–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driel, W.D.; Fan, X.J. Solid State Lighting Reliability: Components to Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- IES-LM-80-08. Approved Method for Lumen Maintenance Testing of LED Light Source; Illuminating Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- IES-TM-21-11. Projecting Long Term Lumen Maintenance of LED Light Sources; Illuminating Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ENERGY STAR® Program Requirements for Solid State Lighting Luminaires Eligibility Criteria—Version 1.2. Available online: https://www.energystar.gov/ia/partners/product_specs/program_reqs/SSL_prog_req.pdf?d519-671a (accessed on 12 October 2017).
- ENERGY STAR® Program Requirements for Lamps (Light Bulbs) Eligibility Criteria—Version 1.1. Available online: https://www.energystar.gov/sites/default/files/ENERGY%20STAR%20Lamps%20V1%201_Specification.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2017).
- IEC/PAS 62612. Self-Ballasted LED-Lamps for General Lighting Services—Performance Requirements; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- IES-TM-28-14. Projecting Long-Term Luminous Flux Maintenance of LED Lamps and Luminaires; Illuminating Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.J.; Yung, K.C.; Pecht, M. Lifetime estimation of high-power white LED using degradation-data-driven method. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2012, 12, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Golubović, D.S.; Koh, S.; Yang, D.G.; Li, X.P.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, G.Q. Degradation modeling of mid-power white-light LEDs by using Wiener process. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A966–A978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.T.; Peng, C.Y. Stochastic diffusion modeling of degradation data. J. Data Sci. 2007, 5, 315–333. [Google Scholar]
- Van Driel, W.D.; Schuld, M.; Jacobs, B.; Commissaris, F.; van der Eyden, J.; Hamon, B. Lumen maintenance predictions for LED packages using LM80 data. In Proceedings of the 2015 16th International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems (EuroSimE 2015), Budapest, Hungary, 19–22 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tarashioon, S.; Baiano, A.; Van Zeijl, H.; Guo, C.; Koh, S.W.; Van Driel, W.D.; Zhang, G.Q. An approach to “Design for Reliability” in solid state lighting systems at high temperatures. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, B.; Driel, W.D.V. LED degradation: From component to system. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 64, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, L.A.; Meeker, W.Q. A review of accelerated test models. Stat. Sci. 2006, 21, 552–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Fane, X.J.; Fanb, J.J.; Yuan, C.A.; Zhang, G.Q. An accelerated test method of luminous flux depreciation for LED luminaires and lamps. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 147, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, B.; Liu, S. Effects of moist environments on LED module reliability. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2010, 10, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.; Hong, W.; Kim, K.; Yoon, Y.; Han, J.; Jang, J.S. Accelerated life test of high power white light emitting diodes based on package failure mechanisms. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Golubović, D.S.; Koh, S.; Yang, D.G.; Li, X.P.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, G.Q. Rapid degradation of mid-power white-light LEDs in saturated moisture conditions. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2015, 15, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghini, M.; Trevisanello, L.R.; Meneghesso, G.; Zanoni, E. A review on the reliability of GaN-based LEDs. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2008, 8, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Golubović, D.S.; Koh, S.; Yang, D.G.; Li, X.P.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, G.Q. Degradation mechanisms of mid-power white-light LEDs under high temperature-humidity conditions. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2015, 15, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.T.; Wen, Z.C. Step-stress accelerated degradation analysis for highly reliable products. J. Qual. Technol. 2000, 32, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, S.T.; Balakrishnan, N.; Tsai, C.C. Optimal step-stress accelerated degradation test plan for Gamma process. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2009, 58, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D. Time and cost constrained optimal designs of constant-stress and step-stress accelerated life tests. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 140, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Tang, J. Optimum step-stress accelerated degradation test for Wiener degradation process under constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 241, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Golubovic, D.S.; Koh, S.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G.Q. Lumen degradation modeling of white-light LEDs in step stress accelerated degradation test. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 154, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Yang, D.; Tian, K.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Step-stress accelerated testing of high-power LED lamps based on subsystem isolation method. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yu, C.; Qian, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G. Thermal/luminescence characterization and degradation mechanism analysis on phosphor-converted white LED chip scale packages. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 74, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Chen, K.J.; Tsai, M.T.; Shih, M.H.; Sun, C.W.; Lee, W.I.; Lin, C.C.; Kuo, H.C. High-efficiency and low assembly-dependent chip-scale package for white light-emitting diodes. J. Photonics Energy 2015, 5, 057606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.; Cognetti, C.; Tiziani, R. Designing with thermal impedance. In Proceedings of the IEEE Semiconductor Thermal & Temperature Measurement Symposium, Reprint from “Semi-Thermal Proceedings”, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 February 1988; pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Shin, M.W. Mechanism and thermal effect of delamination in light-emitting diode packages. Microelectron. J. 2007, 38, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.M.; Kudryk, Y.Y.; Shynkarenko, V.V.; Kudryk, R.Y.; Sai, P.O. Degradation processes in LED modules. Semicond. Phys. Quantum Electron. Optoelectron. 2016, 19, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.J.; Li, Y.Q.; Hirosaki, N.; Yamamoto, H. Nitride Phosphors and Solid-State Lighting; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- CIE TN 001:2014. Chromaticity Difference Specification for Light Source; Central Bureau of the CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- CIE 15:2004. Colorimetry, 3rd ed.; Central Bureau of the CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- CIE 121:1996. The Photometry and Goniophotometry of Luminaires; Central Bureau of the CIE: Vienna, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- CIE 127:2007. Measurements of LEDs, 2nd ed.; Central Bureau of the CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Mohamed, M.G.; Qian, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G.; Pecht, M. Color shift failure prediction for phosphor-converted white LEDs by modeling features of spectral power distribution with a nonlinear filter approach. Materials 2017, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lall, P.; Sakalaukus, P.; Wei, J.; Davis, L. SSL and LED life prediction and assessment of CCT shift. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE ITHERM Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; pp. 1179–1185. [Google Scholar]
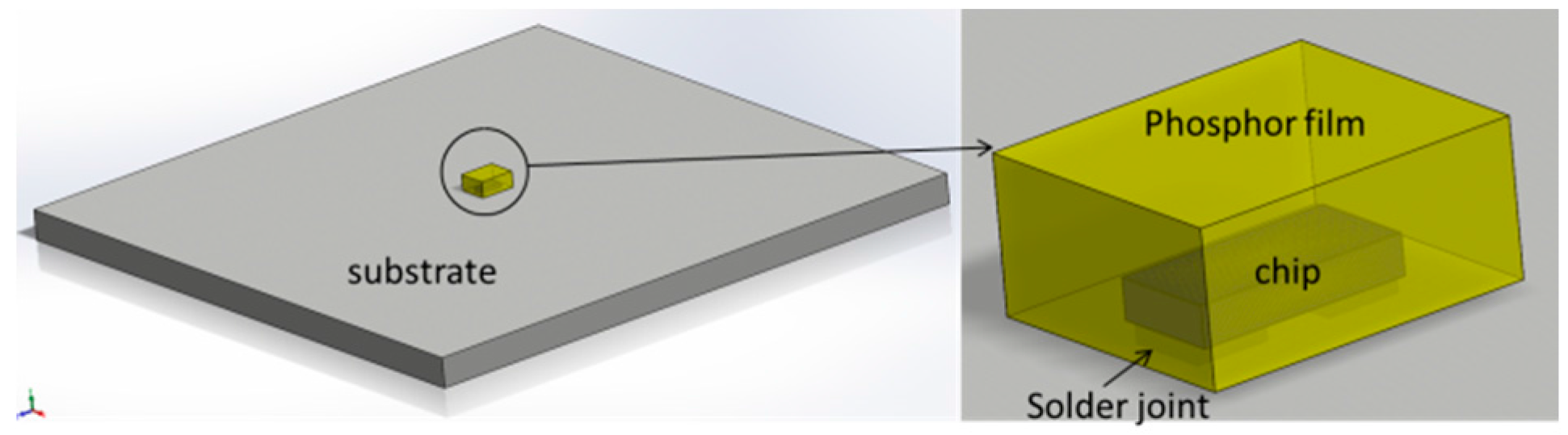

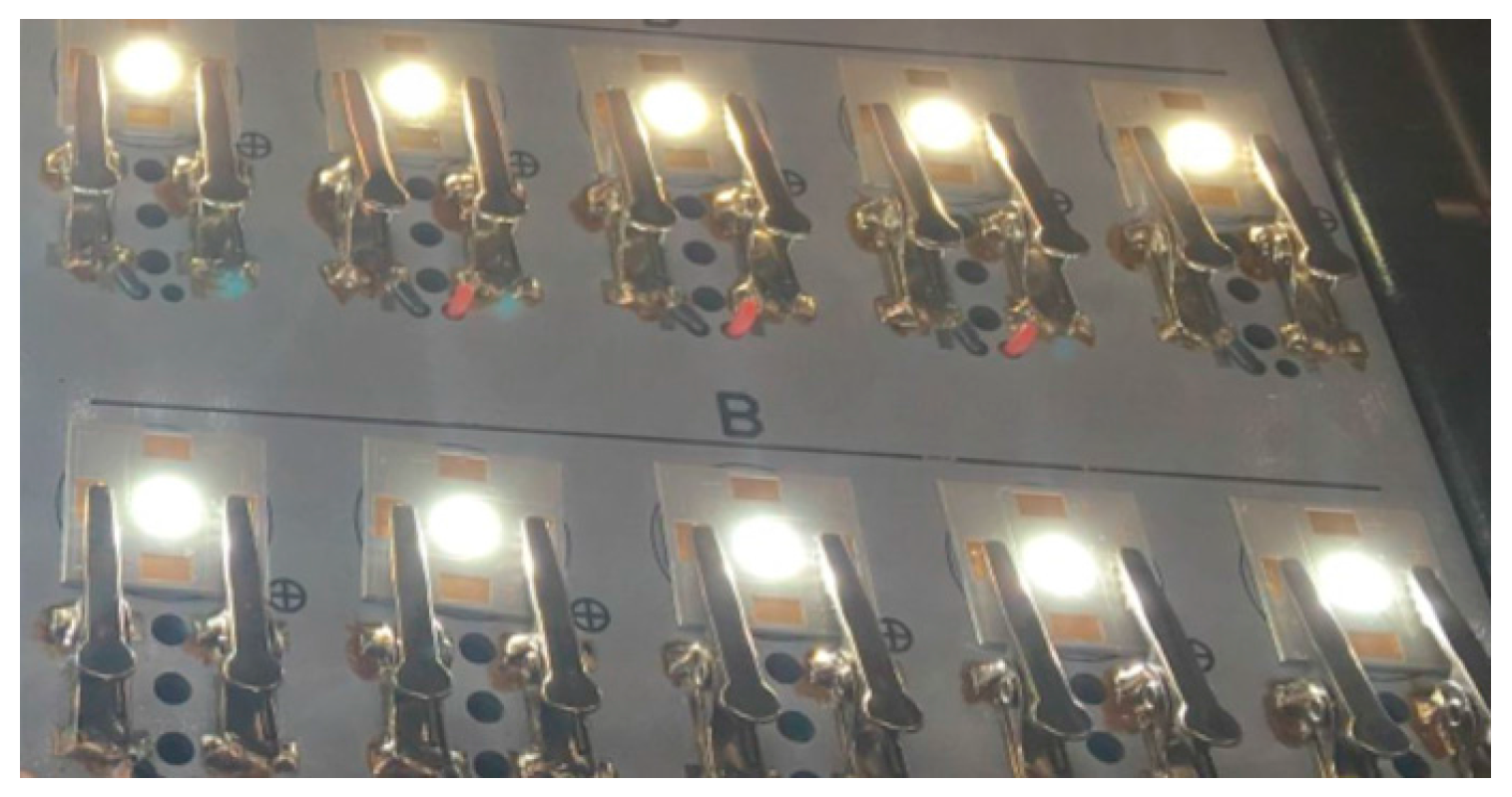
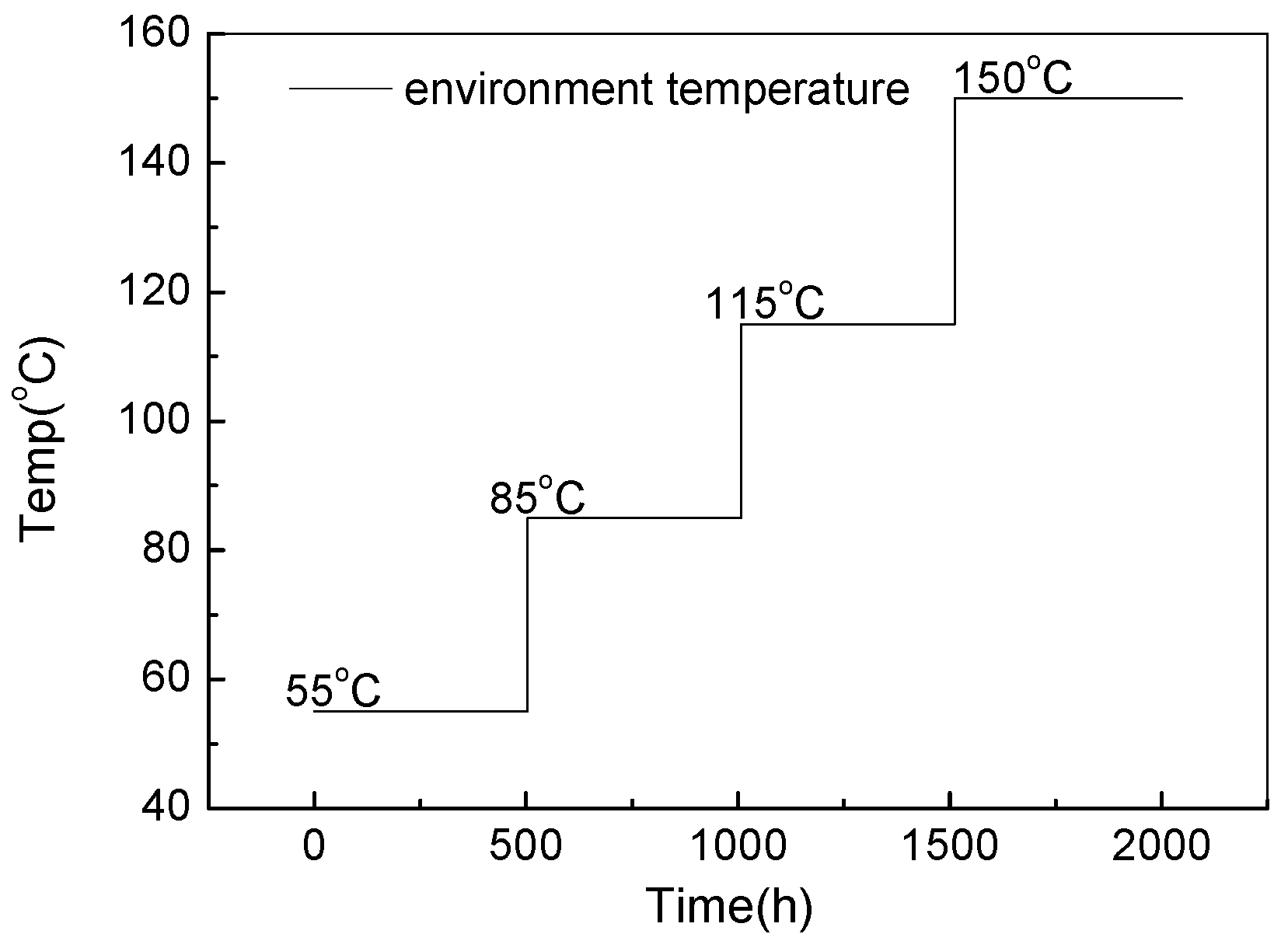
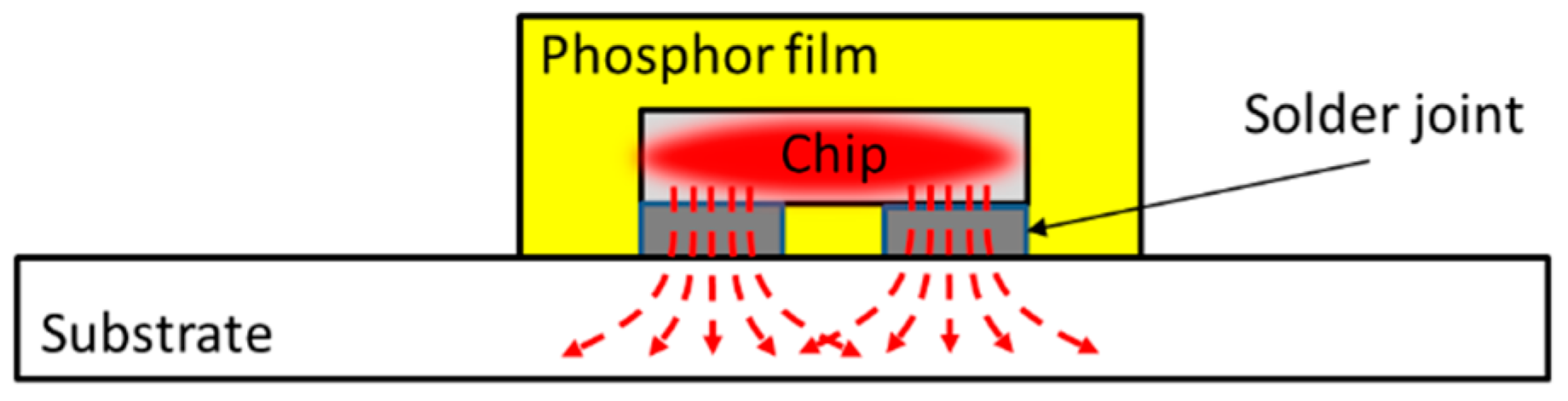




| Target CCTs | Phosphor Weight Ratio % | Phosphor Composition (YAG04: GM537H5: RH650D) | Sample Dimension (L × W × H) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4000 °K | 18.5 | 3.2:12.6:4.8 | 0.97 mm × 0.97 mm × 0.15 mm |
| 5000 °K | 18.5 | 0:3.38:1 | 0.78 mm × 0.38 mm × 0.14 mm |
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | LEETs Lighting Shanghai |
| Rated voltage | 220 V 50/60 Hz |
| Operational current | <0.5 A |
| Junction temperature measurement current | 1 mA/5 mA ± 0.2% |
| Temperature tolerance of K coefficient | ±0.5 °C |
| Sampling pulse width | 5 ms |
| Junction temperature measurement error | ±1 °C |
| Driving Conditions | 4000 °K Sample | 5000 °K Sample | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tj (°C) | Tp (°C) | Pth (W) | Rth (°C/W) | Tj (°C) | Tp (°C) | Pth (W) | Rth (°C/W) | |
| Original | 75.52 | 48.08 | 0.710 | 38.63 | 54.01 | 34.37 | 0.219 | 89.84 |
| After test under 120 mA | 84.38 | 58.59 | 0.744 | 34.65 | 59.78 | 44.66 | 0.212 | 71.39 |
| After test under 350 mA | 89.41 | 69.01 | 0.745 | 27.37 | 51.27 | 41.99 | 0.297 | 31.24 |
| Driving Conditions | Parameters | 4000 °K Sample | 5000 °K Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving by 120 mA | C1,120 mA | 2.05 × 10−6 | 3.42 × 10−6 |
| C2,120 mA | 1.94 × 10−4 | 6.28 × 10−4 | |
| Driving by 350 mA | C1,350 mA | 3.06 × 10−6 | 4.89 × 10−6 |
| C2,350 mA | 7.03 × 10−4 | 1.02 × 10−3 | |
| AFdu’v’ | 1.49 | 1.43 | |
| Driving Conditions | Parameters | 4000 °K Sample | 5000 °K Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving by 120 mA | D1120 mA | −2.05 × 10−5 | −3.05 × 10−5 |
| D2120 mA | 1.002 | 0.990 | |
| Driving by 350 mA | D1350 mA | −2.35 × 10−5 | −4.14 × 10−5 |
| D2350 mA | 0.990 | 0.983 | |
| AFCCT | 1.15 | 1.36 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, C.; Fan, J.; Fang, J.; Yu, C.; Ren, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G. Photometric and Colorimetric Assessment of LED Chip Scale Packages by Using a Step-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test (SSADT) Method. Materials 2017, 10, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101181
Qian C, Fan J, Fang J, Yu C, Ren Y, Fan X, Zhang G. Photometric and Colorimetric Assessment of LED Chip Scale Packages by Using a Step-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test (SSADT) Method. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101181
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Cheng, Jiajie Fan, Jiayi Fang, Chaohua Yu, Yi Ren, Xuejun Fan, and Guoqi Zhang. 2017. "Photometric and Colorimetric Assessment of LED Chip Scale Packages by Using a Step-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test (SSADT) Method" Materials 10, no. 10: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101181
APA StyleQian, C., Fan, J., Fang, J., Yu, C., Ren, Y., Fan, X., & Zhang, G. (2017). Photometric and Colorimetric Assessment of LED Chip Scale Packages by Using a Step-Stress Accelerated Degradation Test (SSADT) Method. Materials, 10(10), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101181






