Design of a Novel Nine-Phase Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine with Skewed Stator Slots
Abstract
1. Introduction
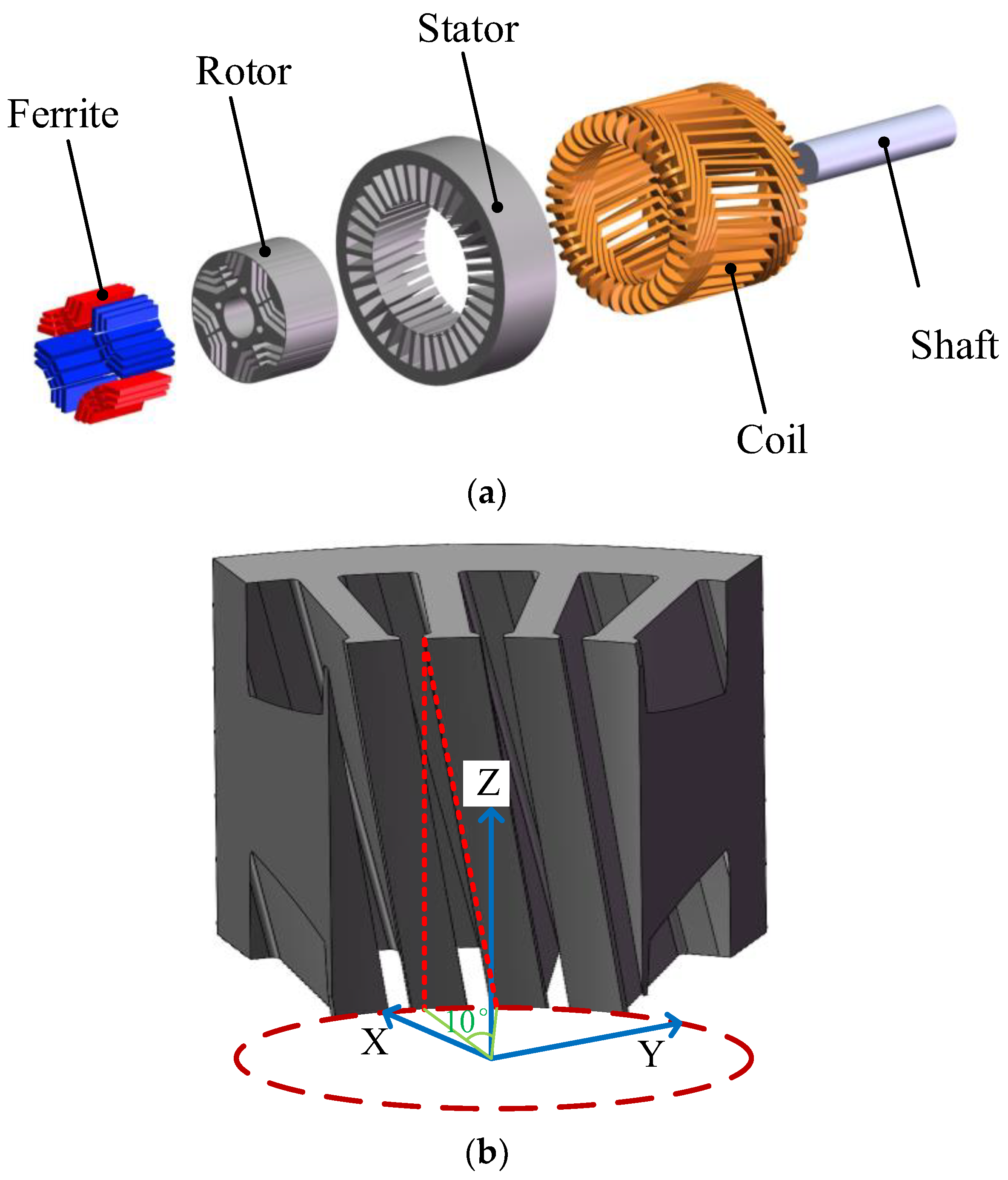
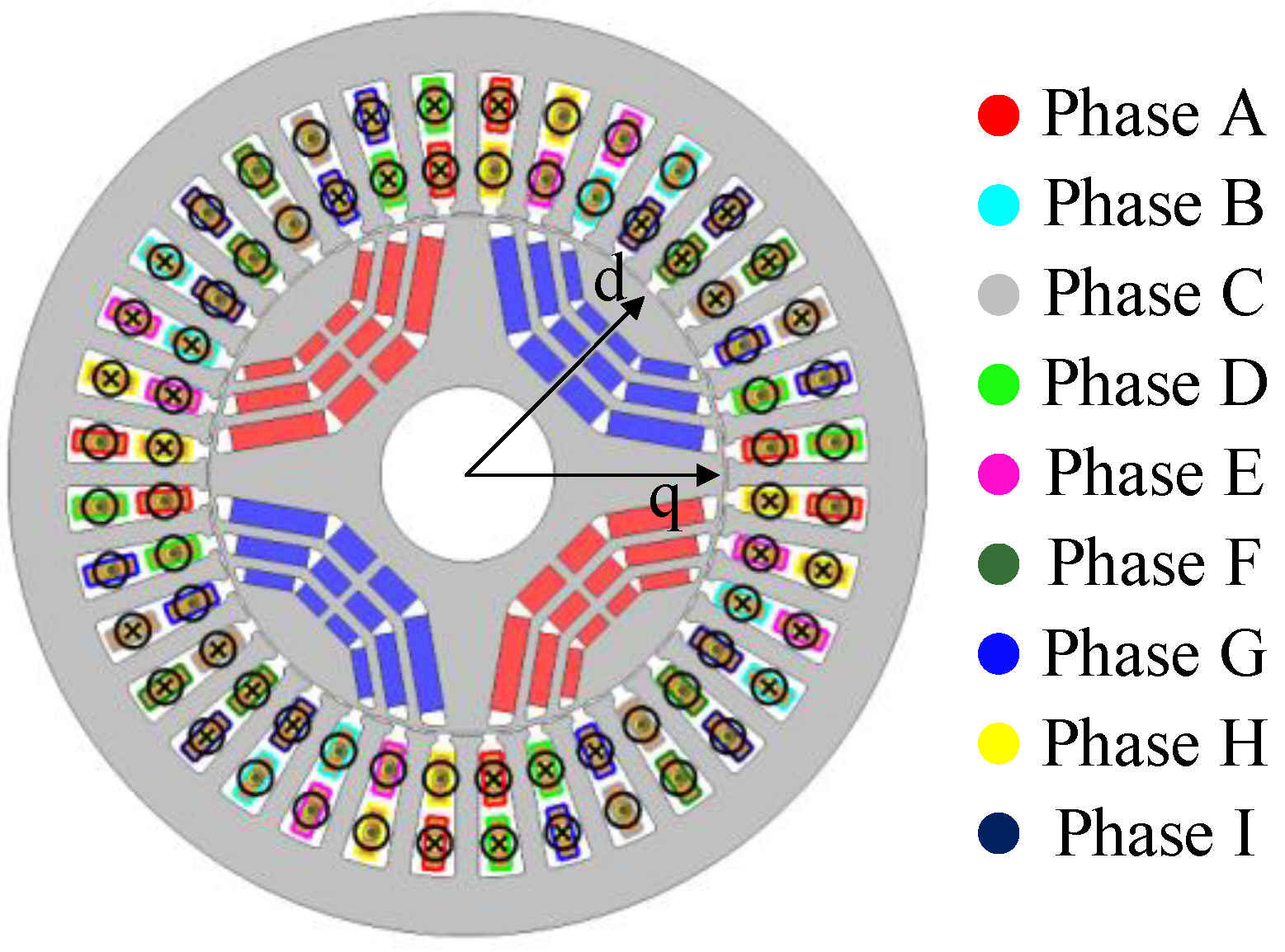
2. Machine Topology and Working Principle
2.1. Machine Topology
2.2. Working Principle
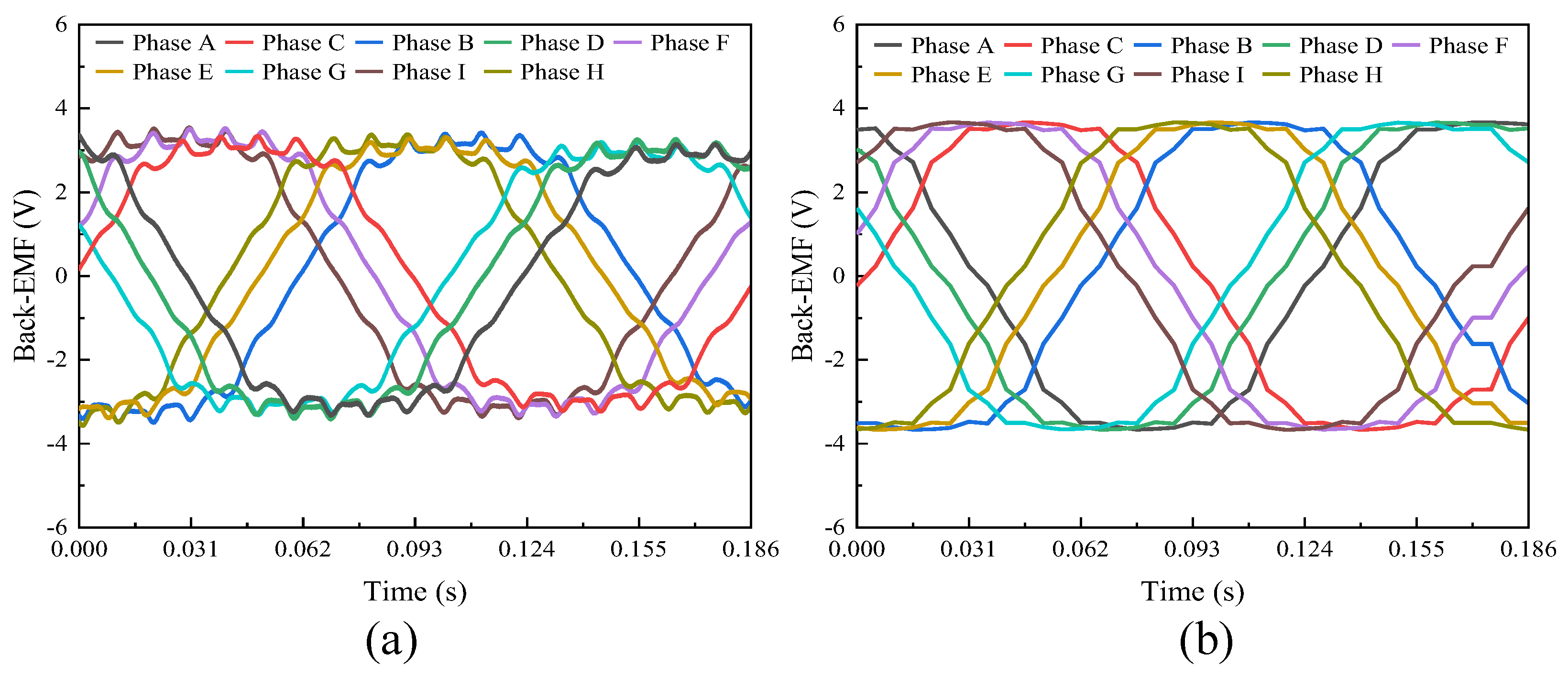
3. Finite Element Analysis
- The coils are independent of each other, and mutual inductance between windings is ignored.
- The material permeability and conductivity of the core are assumed to be homogeneous and isotropic.
- The ferrite properties, such as remanence and coercivity, remain constant and are not affected by temperature or demagnetization.
- Thermal effects on the resistivity of windings are not considered.
- The air gap is assumed to be perfectly uniform.
- The ferrite PM losses are assumed to be negligible compared with the iron loss.
3.1. Comparison with Non-Skewed Stator Slots
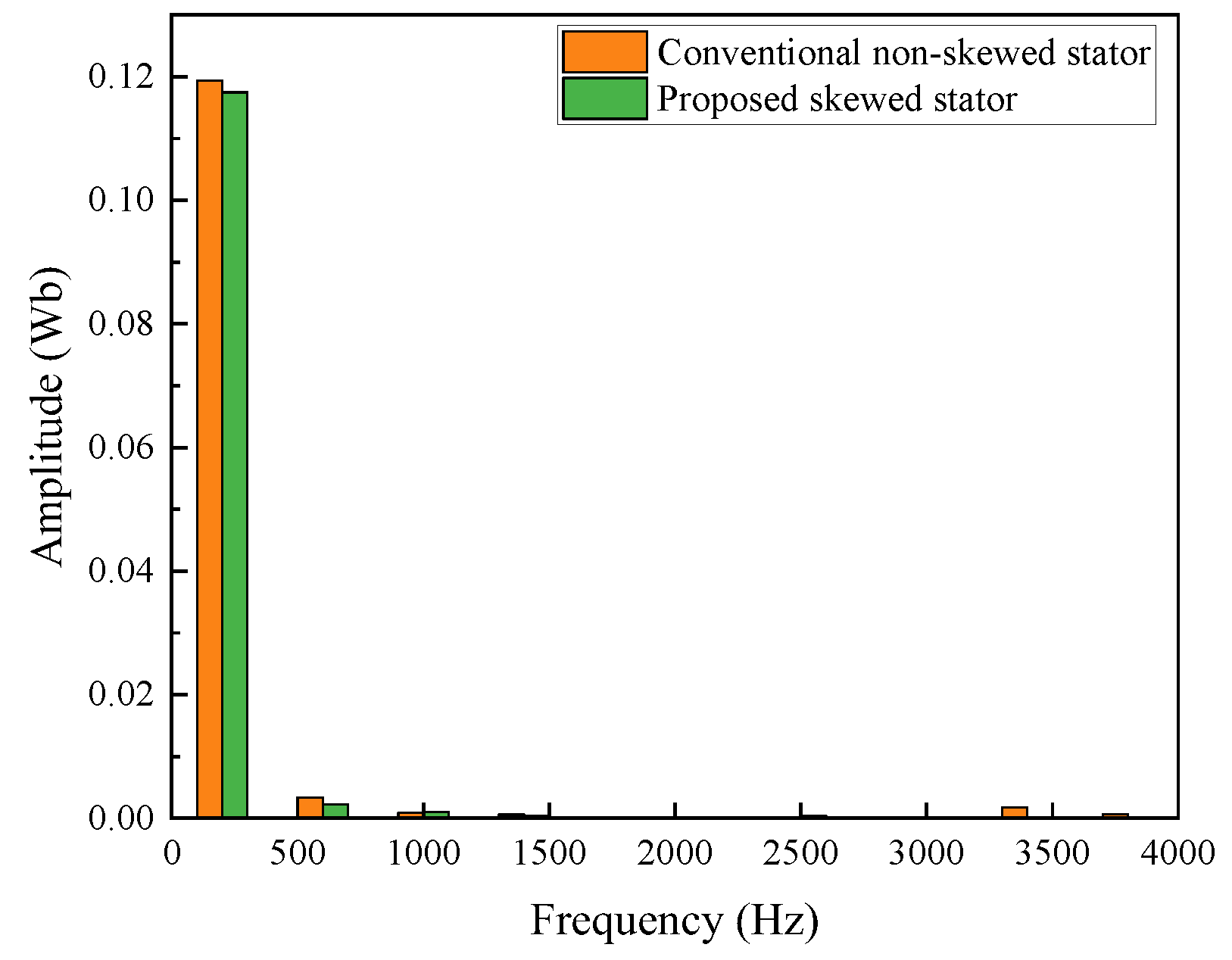
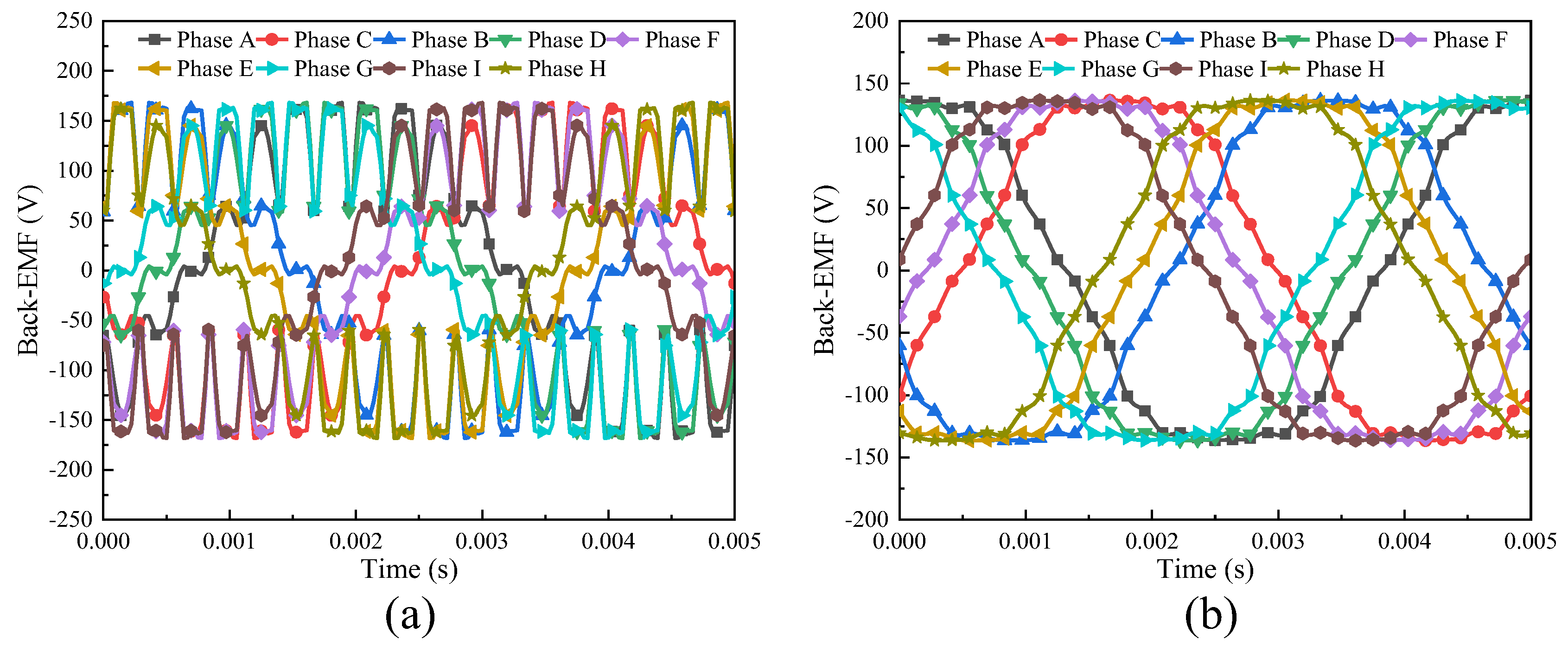
3.1.1. No-Load Analysis Between the Skewed and Non-Skewed Stator Designs
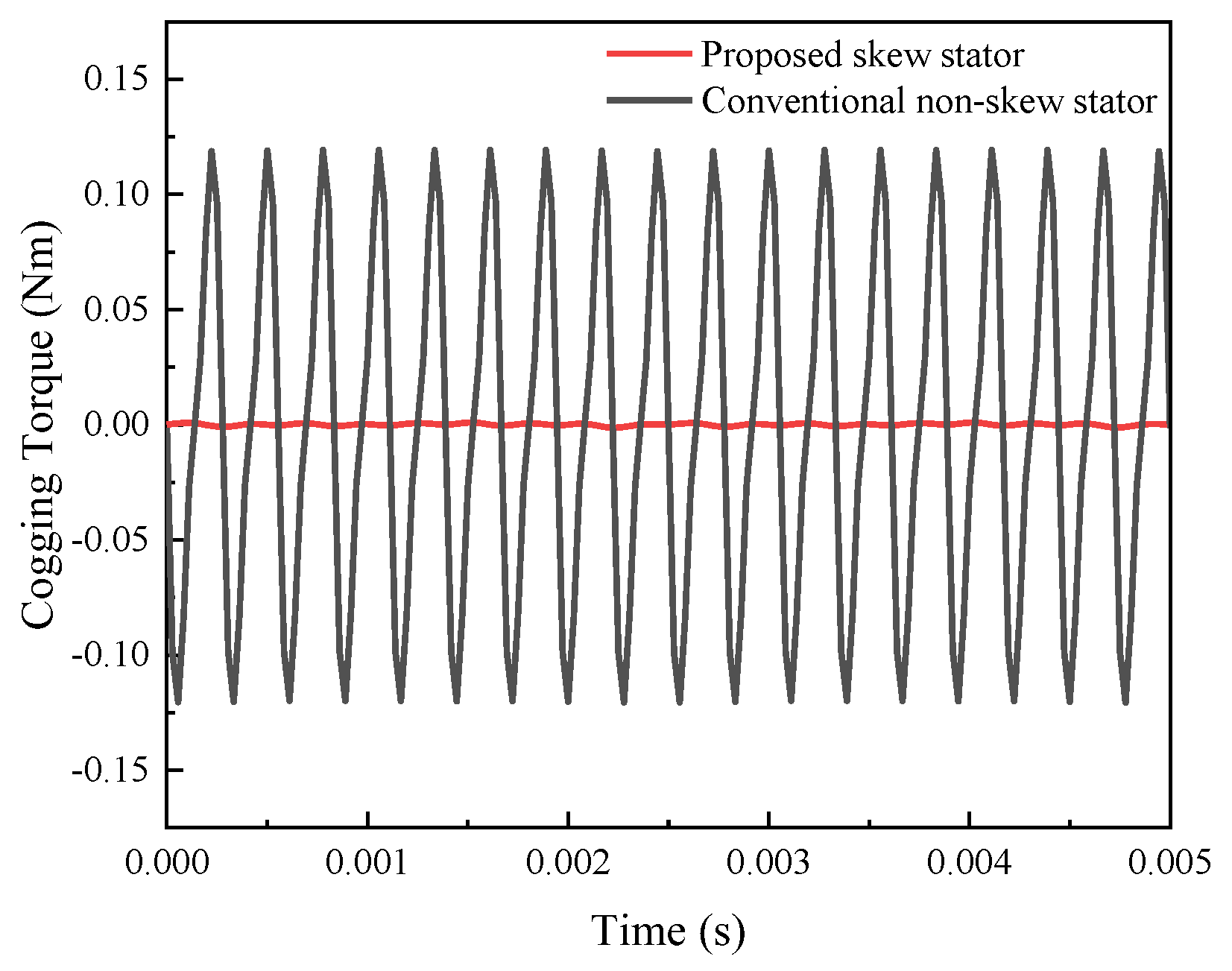
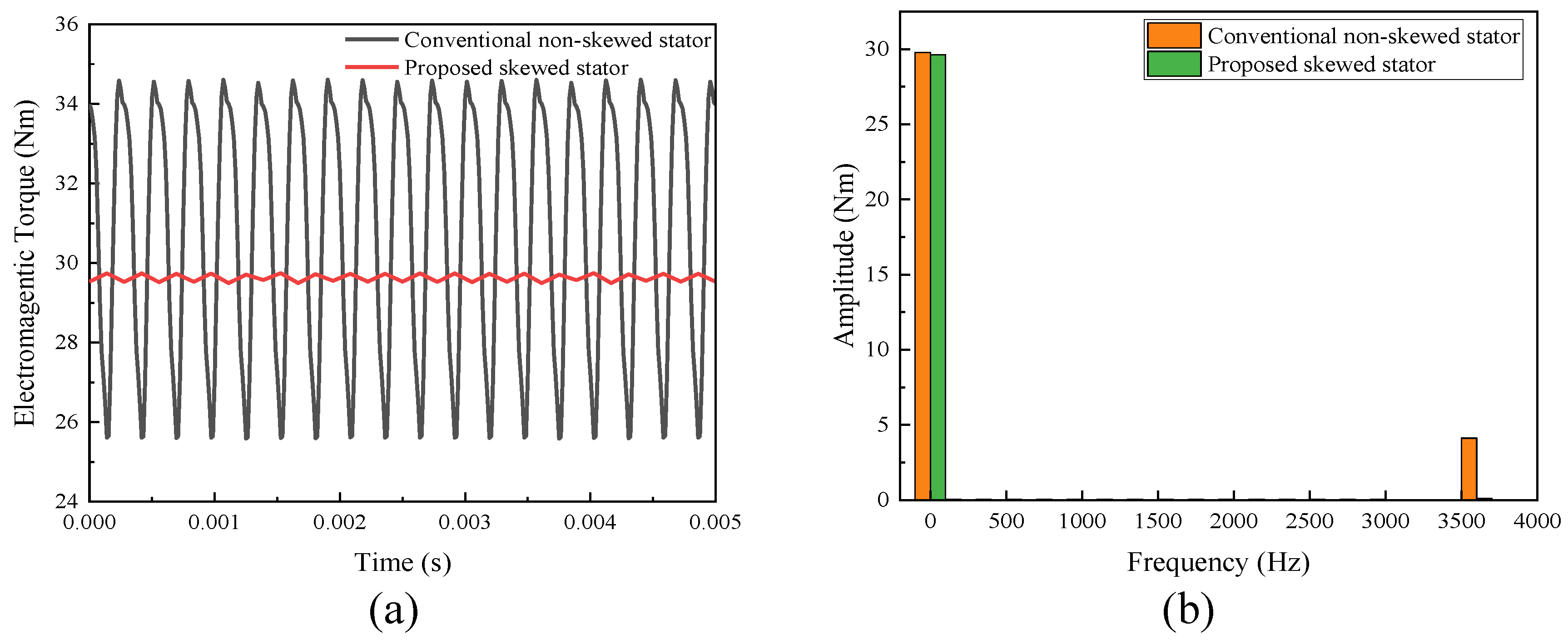
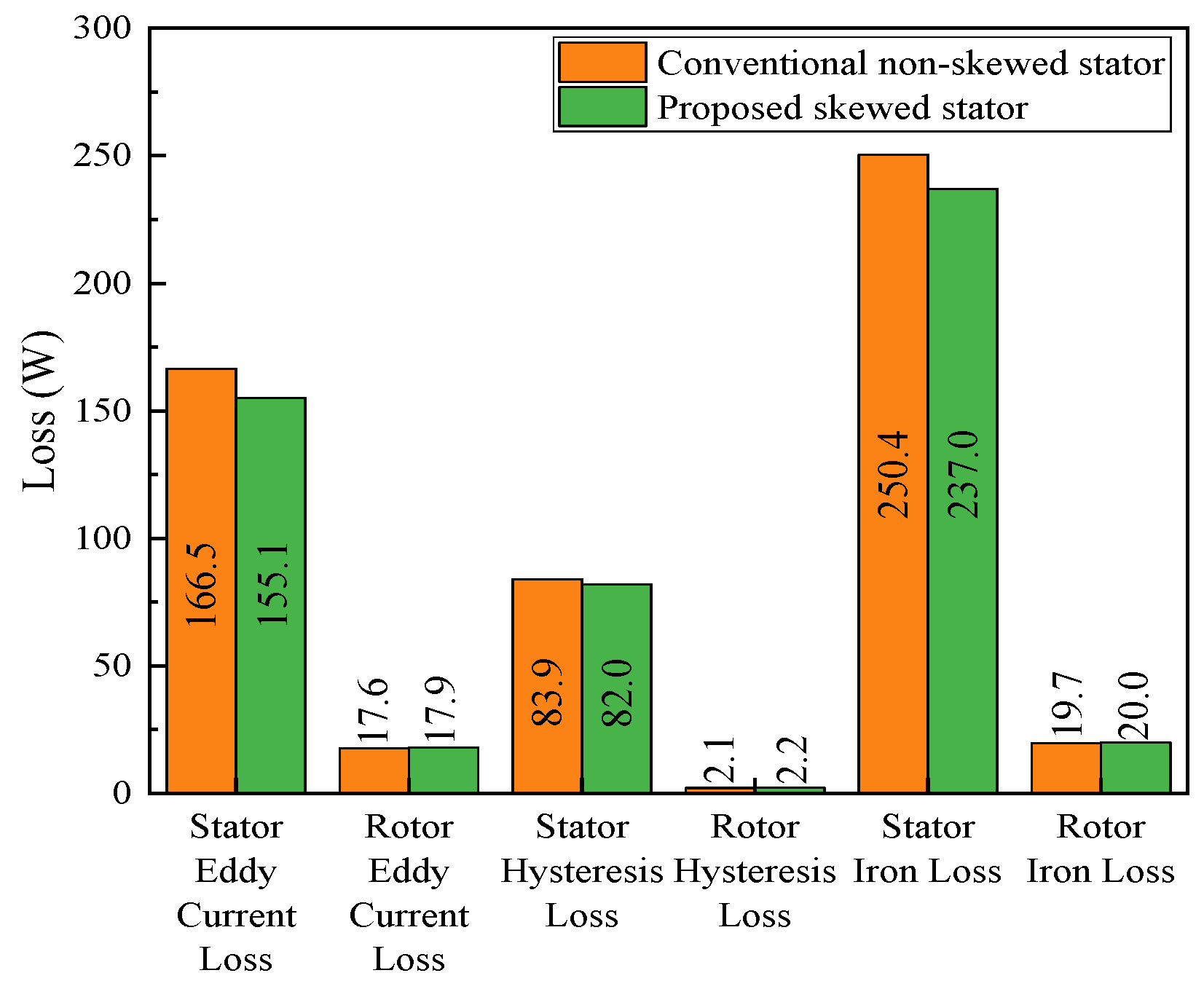
3.1.2. On-Load Analysis Between the Skewed and Non-Skewed Stator Designs
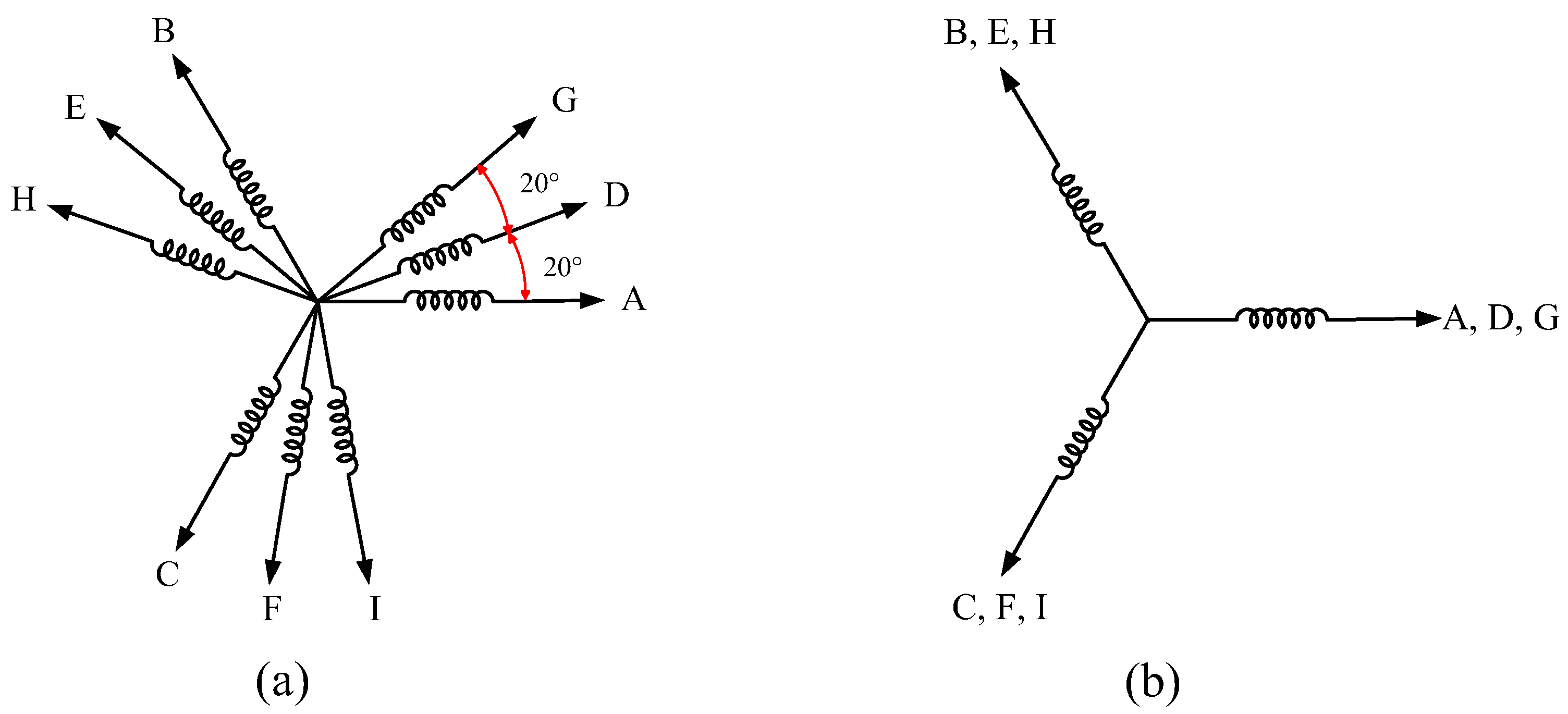
3.2. Comparative Study with Three-Phase Configuration
3.2.1. Theoretical Analysis
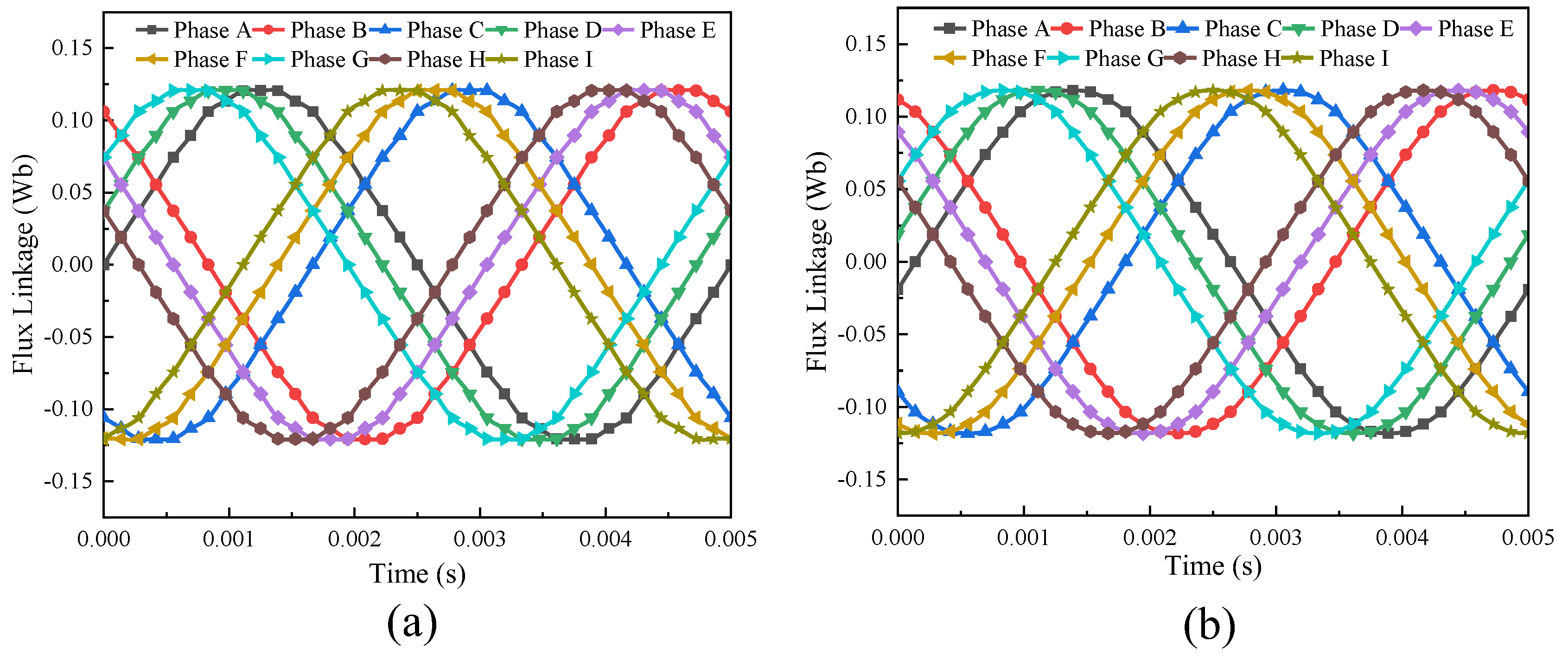
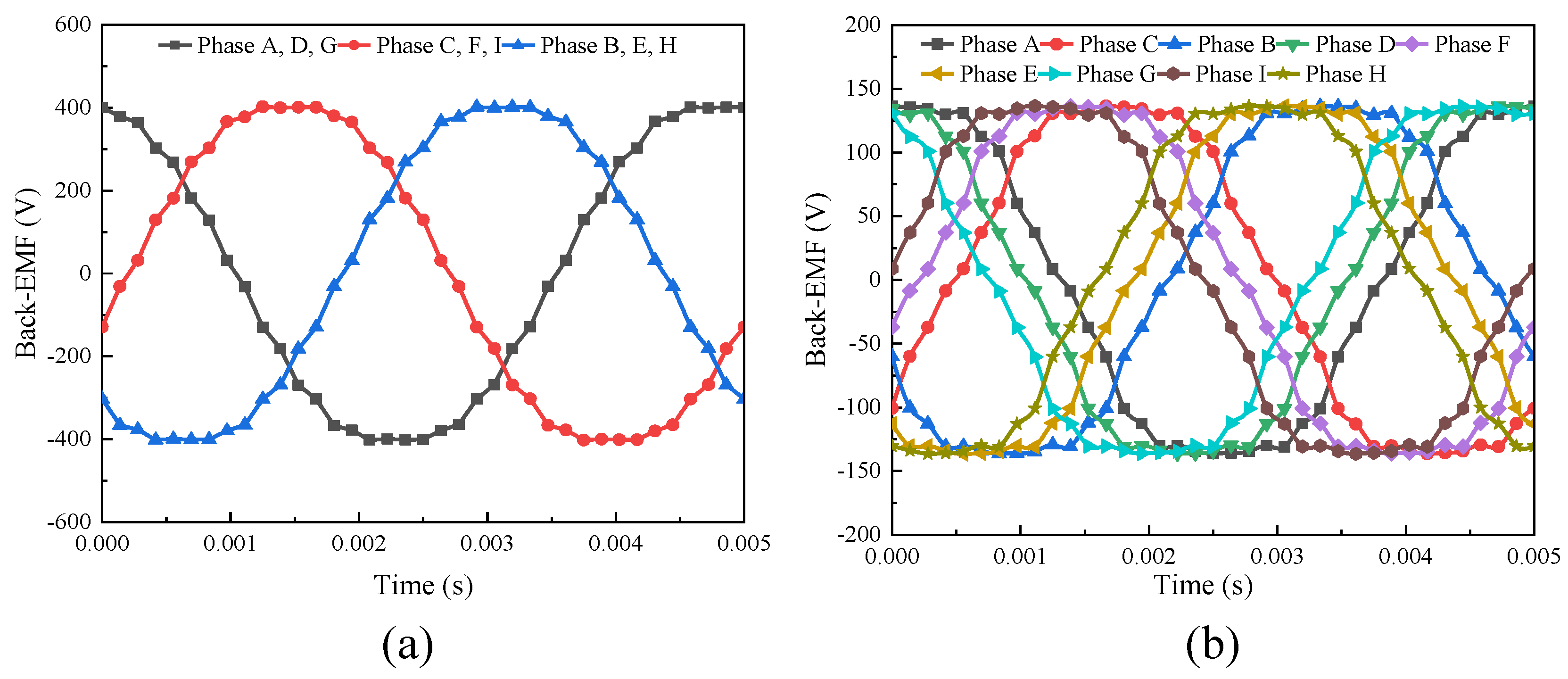
3.2.2. No-Load Analysis
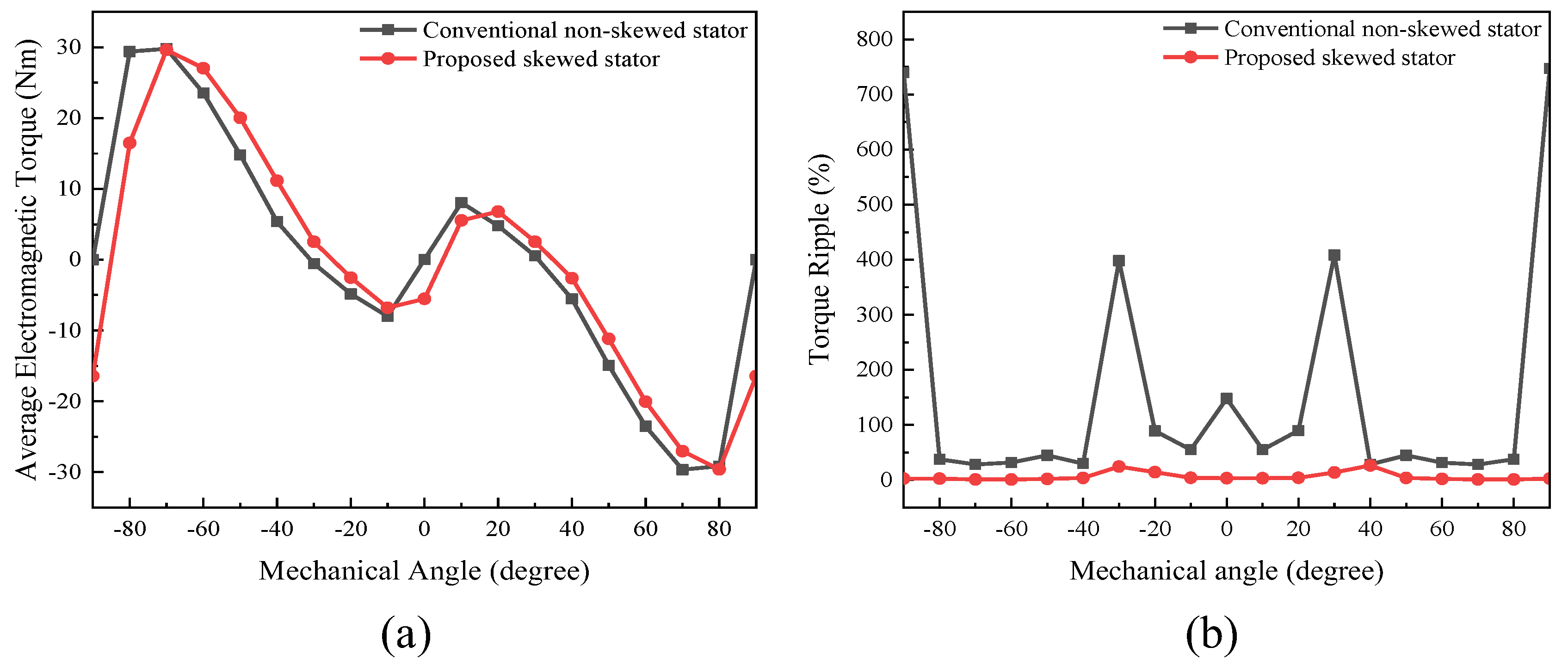
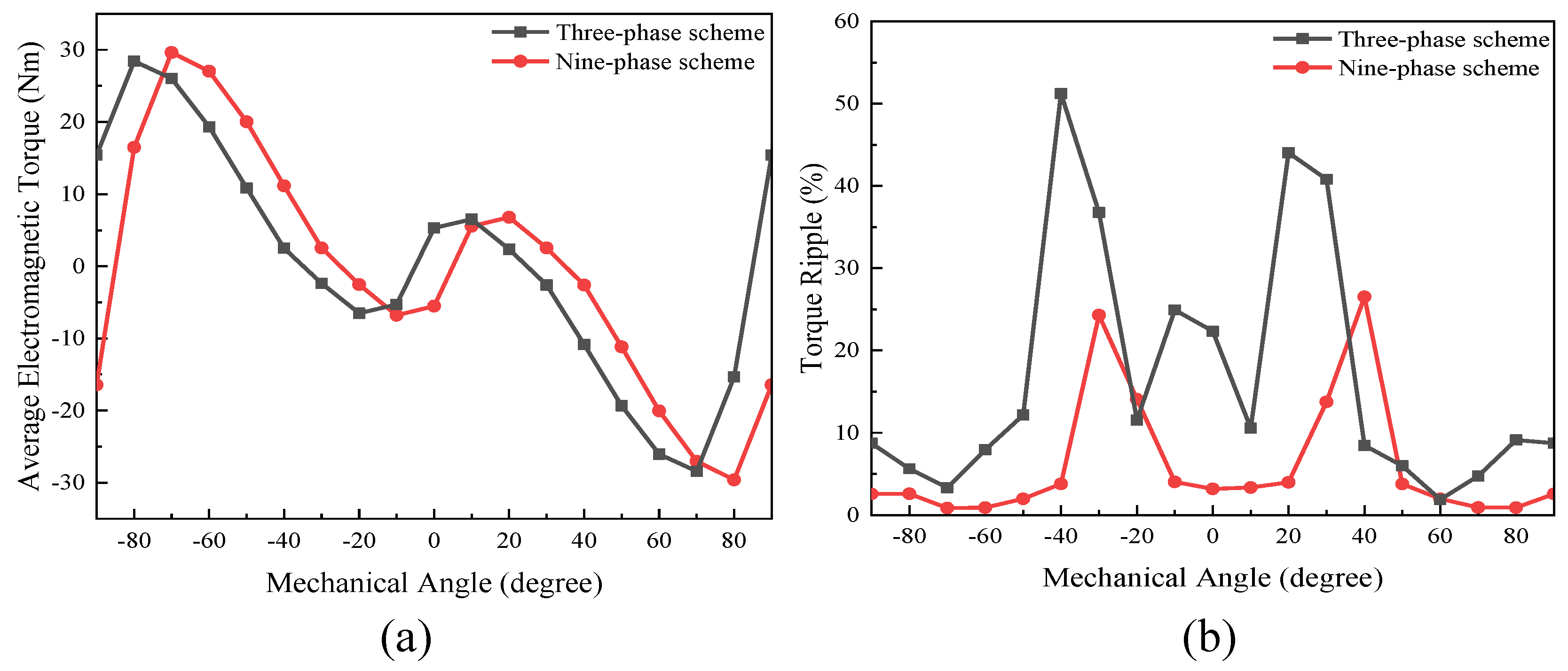
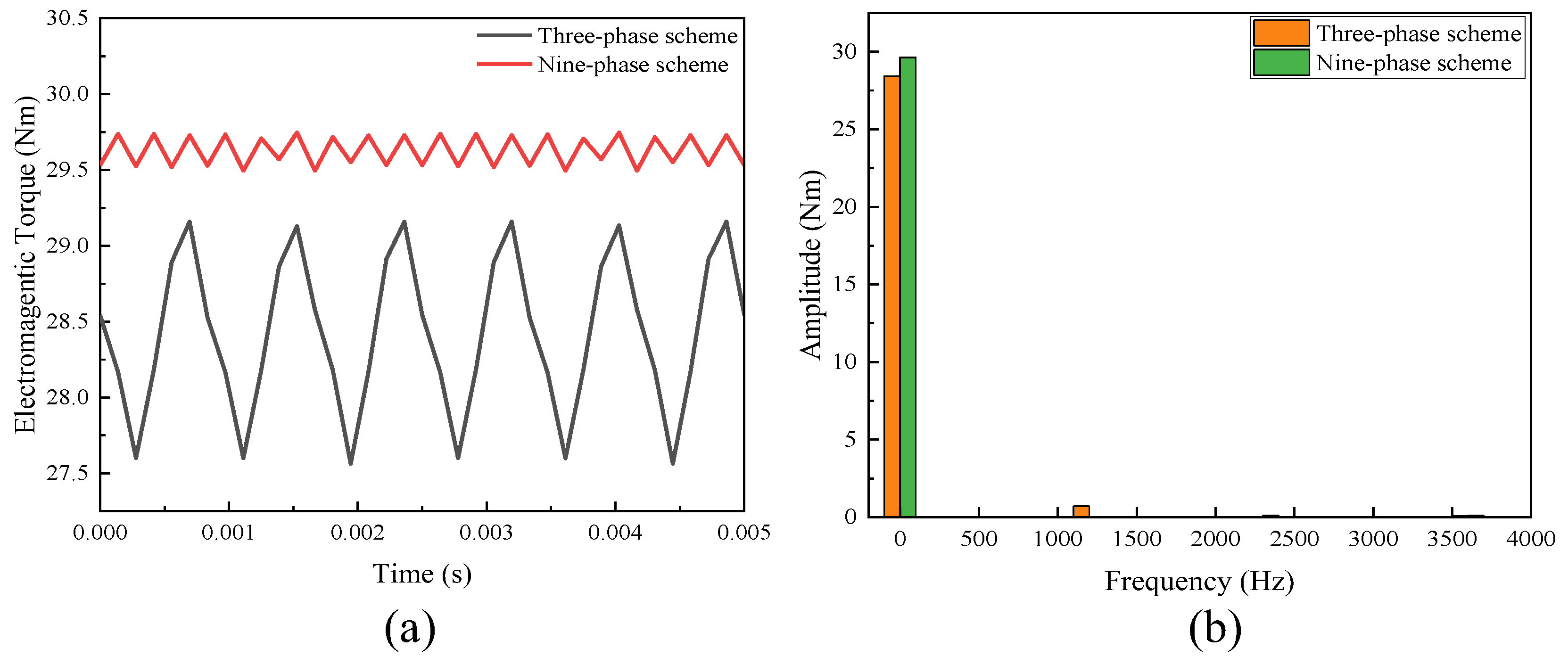
3.2.3. On-Load Analysis
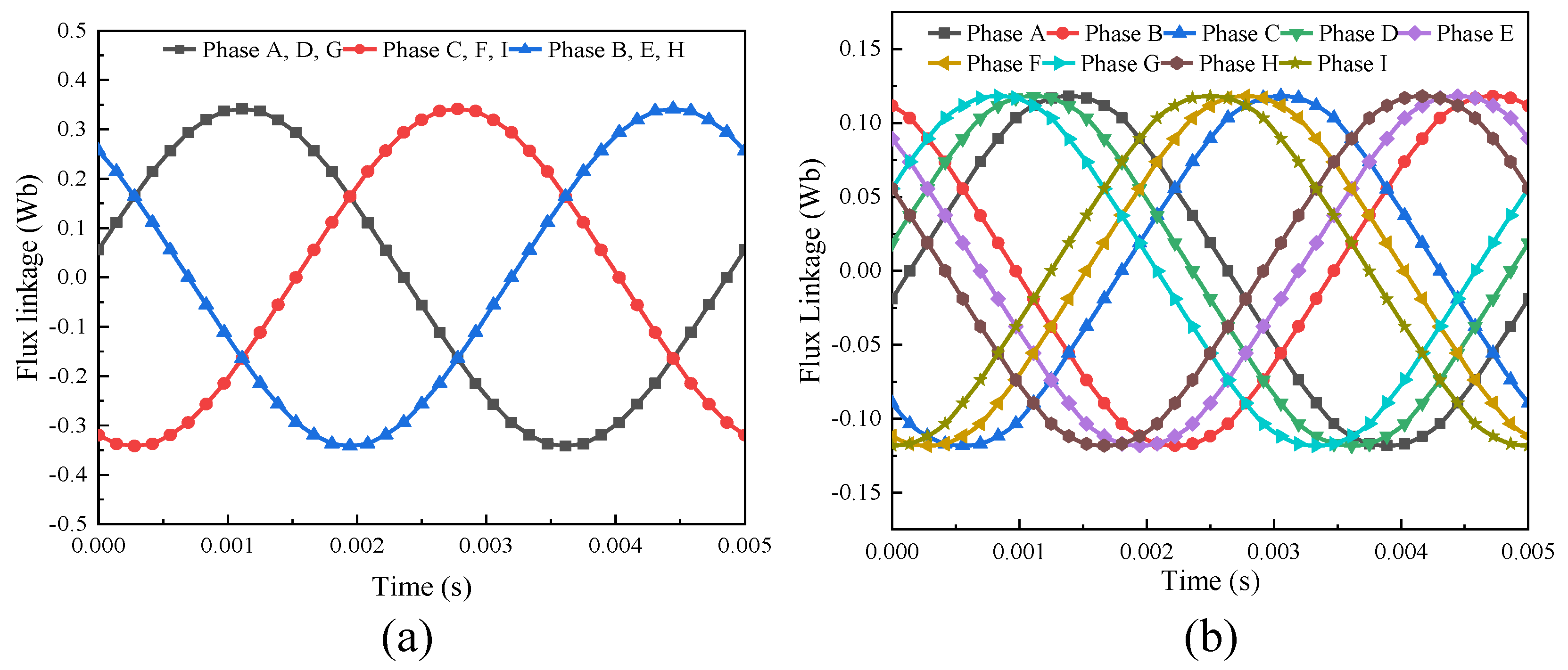
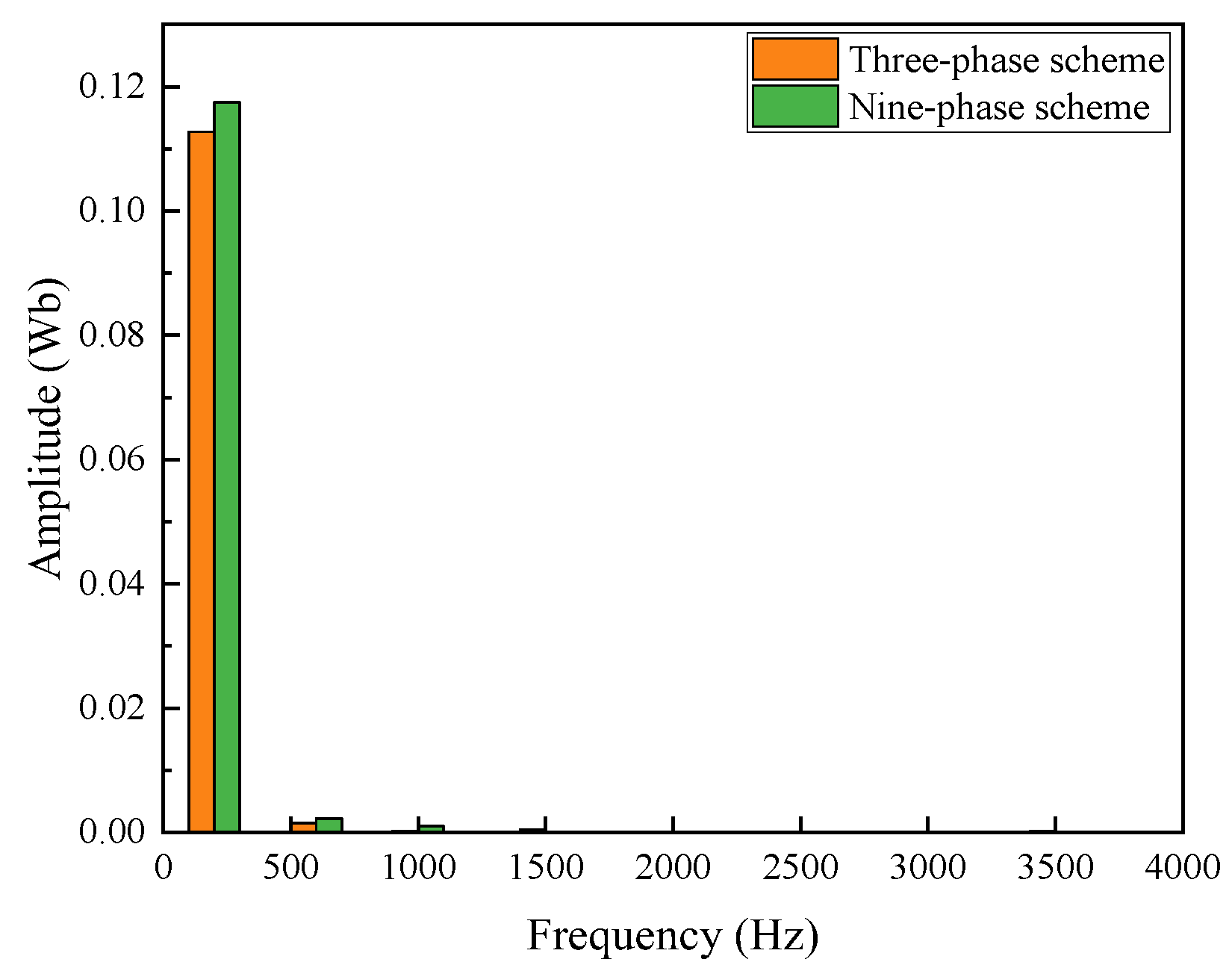
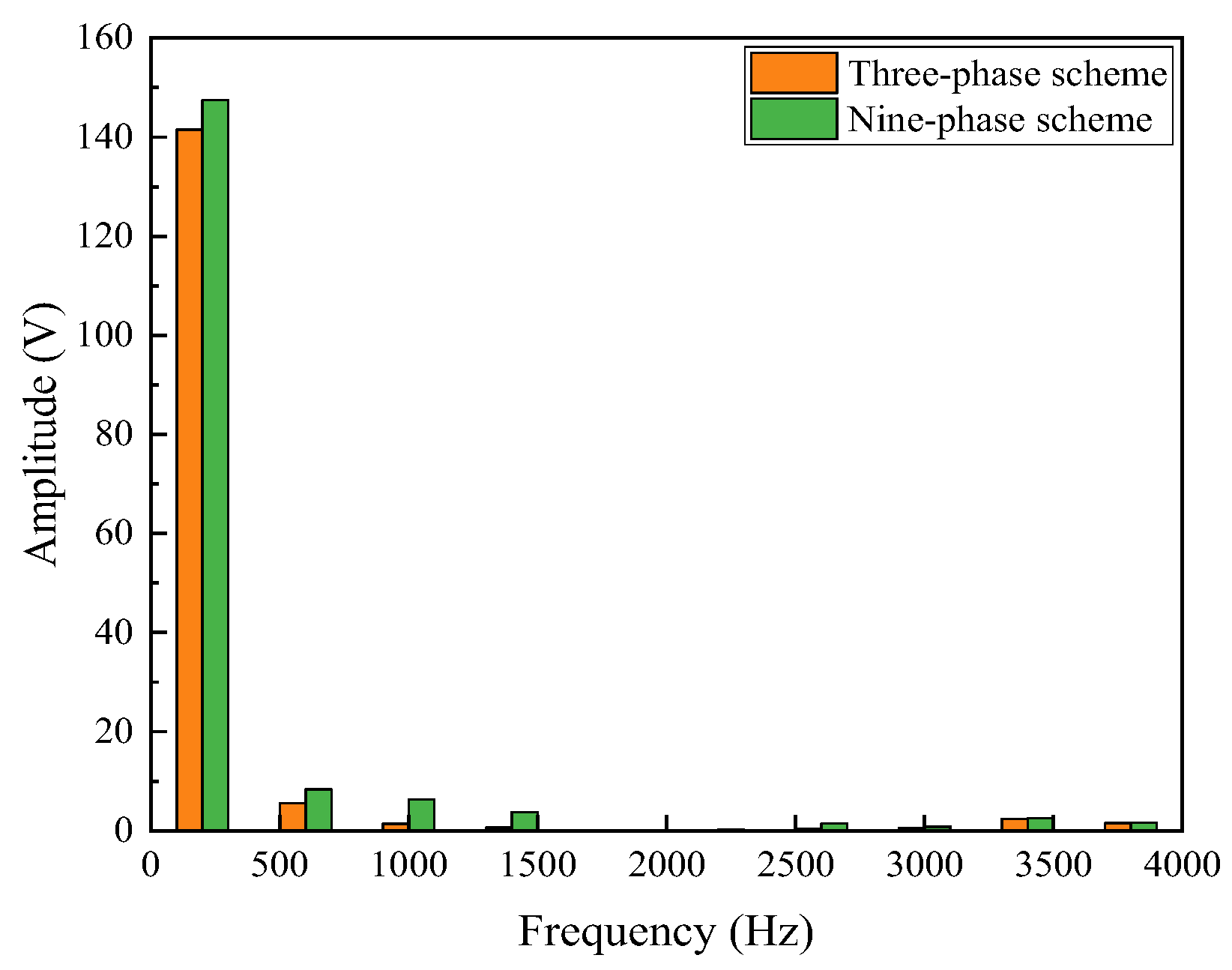
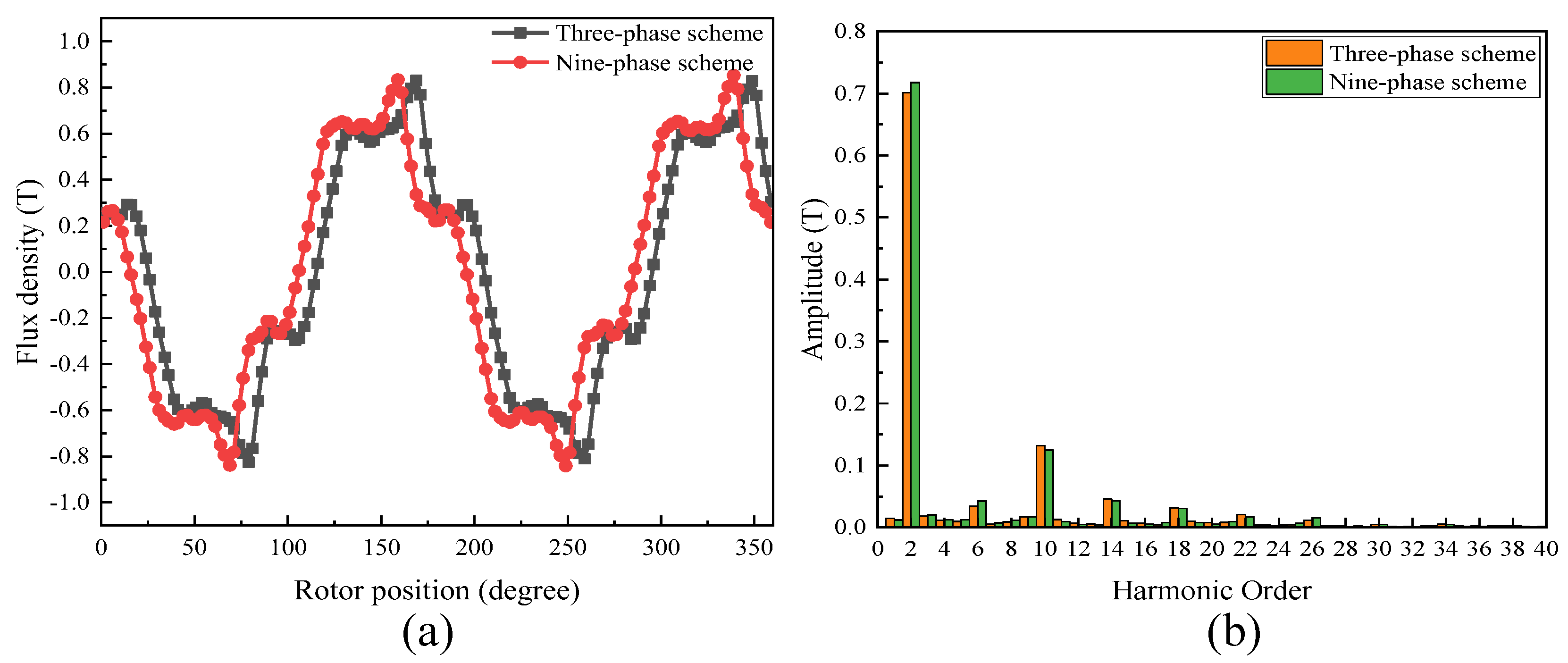
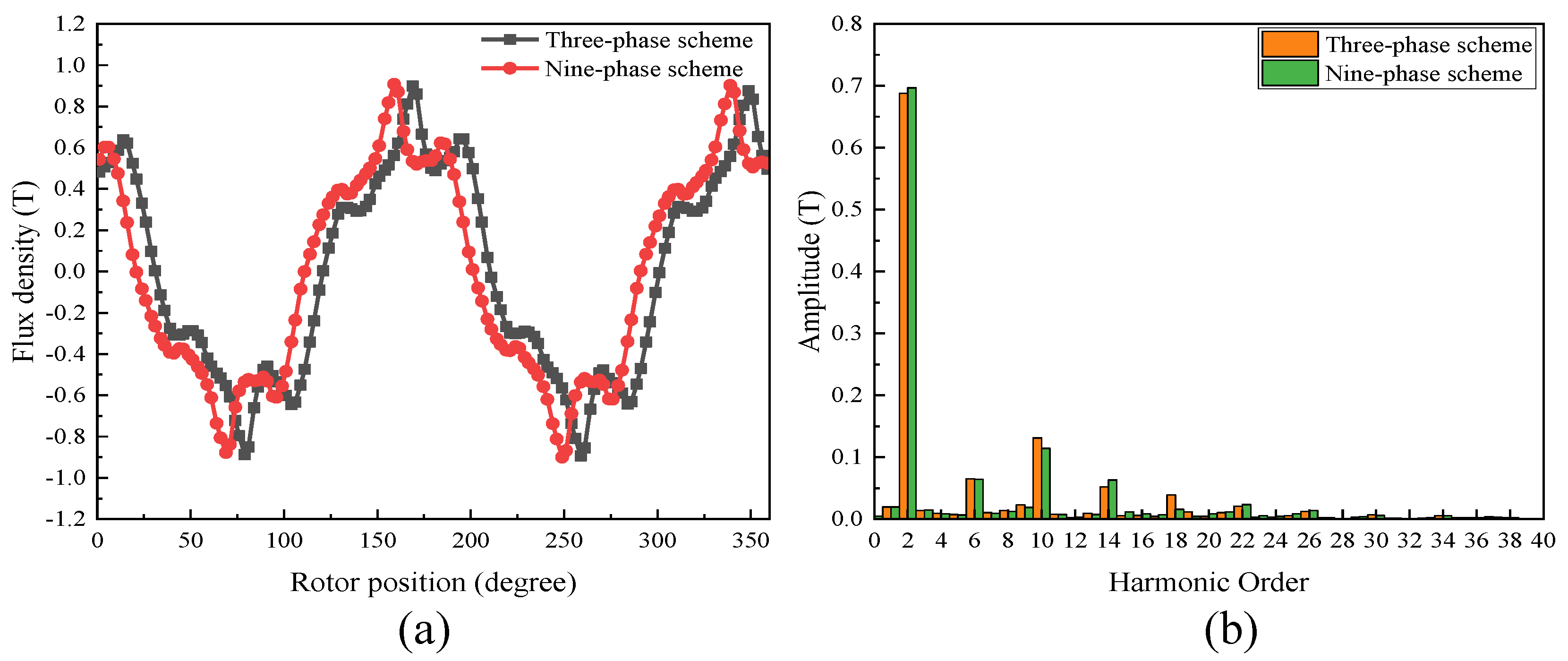
3.2.4. Air-Gap Flux Analysis
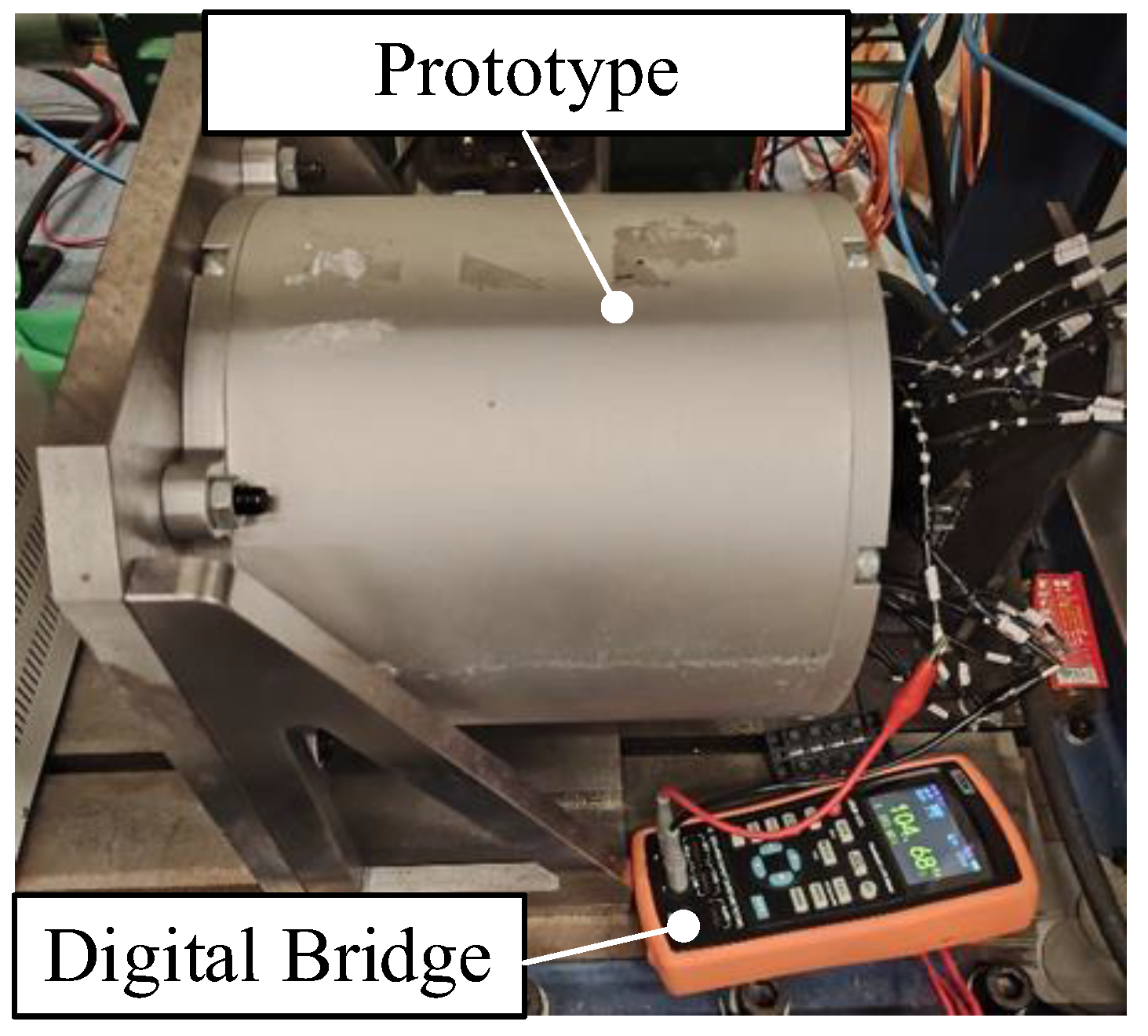
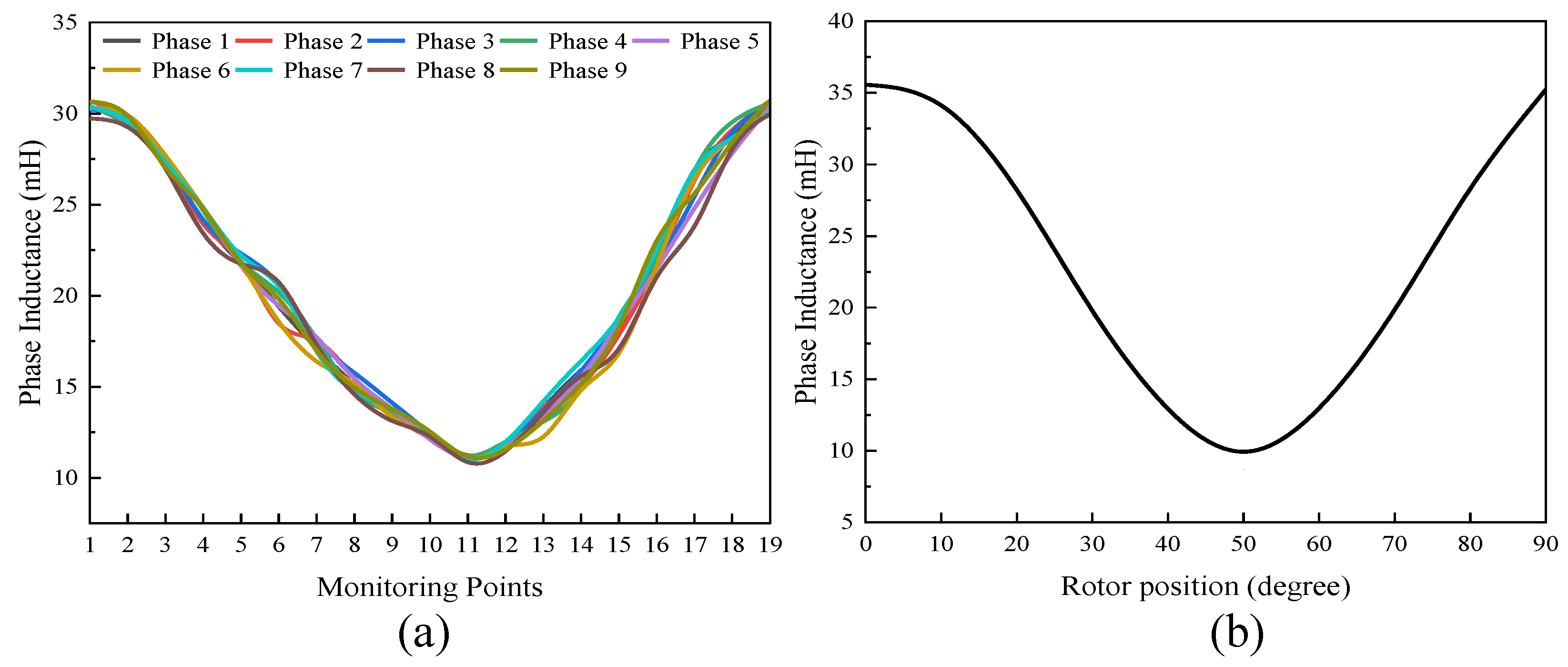
4. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- A 3D FEA model of the proposed FA-SynRM was established and compared with a reference FA-SynRM featuring non-skewed stator slots. The results revealed that the proposed design effectively suppressed harmonic components in the back-EMF, achieving a reduction in total harmonic distortion from 12.29% to 7.9%. Furthermore, at maximum on-load electromagnetic torque, the proposed design maintained a minimal torque ripple of 0.85%, significantly lower than the 28.27% observed in the non-skewed stator design. Additionally, the proposed machine exhibited lower stator losses, enhancing overall efficiency.
- (2)
- The performance of the proposed FA-SynRM was evaluated under both a nine-phase winding scheme and a traditional three-phase winding scheme. The nine-phase configuration demonstrated superior performance, achieving higher average torque with lower ripple. It also produced a higher fundamental harmonic amplitude in the air-gap flux density while suppressing unwanted harmonics.
- (3)
- A prototype of the proposed FA-SynRM was constructed, and experimental results were consistent with the FEA predictions, validating the effectiveness of the proposed design.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, W.; Mecrow, B.C.; Atkinson, G.J.; Bennett, J.W.; Atkinson, D.J. Overview of Electric Motor Technologies Used for More Electric Aircraft (MEA). IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, R.R.; Magnussen, F.; Sadarangani, C. Theoretical and Experimental Reevaluation of Synchronous Reluctance Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamloo, A.M.; Ghaheri, A.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Sergeant, P. Principle of Torque-Axis Alignment in New Asymmetric PM Synchronous Reluctance Machines: Toward Less-Rare-Earth PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 6392–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wen, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C. A Novel Series Elastic Actuator with Variable Transmission Ratio Using Reconfigurable Epicyclic Gearing for Hip Exoskeletons. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Dong, Z.; Song, Z.; Liu, C. A Novel Counter-Rotating AFPM Machine Based on Magnetic-Field Modulation for Underwater Propulsion System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 2167–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri-Zarandi, R.; Karami-Shahnani, A.; Toulabi, M.S.; Tessarolo, A. Design and Experimental Performance Assessment of an Outer Rotor PM-Assisted SynRM for the Electric Bike Propulsion. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E. Multiphase Electric Machines for Variable-Speed Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, F.; Duran, M.J. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines—Part I. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.J.; Barrero, F. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines—Part II. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Investigation of Magnetic Isolation in a Double-Side Asynchronous Rotor-AFPM Machine Based on Harmonic Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Shrestha, A.; Halfmann, B.; Islam, M. Performance Evaluation of Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines Under Faults for Redundant Applications. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 10288–10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.; Tutelea, L.N.; Parsa, L.; Dorrell, D. Automotive Electric Propulsion Systems with Reduced or No Permanent Magnets: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5696–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trancho, E.; Ibarra, E.; Arias, A.; Kortabarria, I.; Jurgens, J.; Marengo, L.; Fricassè, A.; Gragger, J.V. PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine Flux Weakening Control for EV and HEV Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2986–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boazzo, B.; Vagati, A.; Pellegrino, G.; Armando, E.; Guglielmi, P. Multipolar Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines: A General Design Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Guan, B.; Xu, L. Low-Cost Ferrite PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5741–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, C. Improved PWM Control with Wide Speed Range for a Double-Side Asynchronous Rotor AFPMM Series-End Winding Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, Z.; Huang, R.; Liu, C. Reconfigurable Open-End Winding Motor Drive Topology for Inverter Short-Circuit Fault Tolerance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 3854–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwly, M.Y.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Hamad, M.S.; Ahmed, S.; Elmalhy, N.A. Multiphase Stator Winding: New Perspectives, Advanced Topologies, and Futuristic Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 103241–103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfiq, K.B.; Güleç, M.; Sergeant, P.; Zeineldin, H.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Al-Durra, A.; El-Saadany, E.F. A Comprehensive Study of Thermal and Performance Characteristics in Revamped Multiphase Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 4717–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gong, S.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Qu, R. Fault-Tolerant Reconfiguration Topology and Control Strategy for Symmetric Open-Winding Multiphase Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 8656–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, R.B.; Goltz, E.C.; Eckert, P.R.; Pereira, L.A. Torque Assessment of Multiphase AFPM Machines with Experimental Validation for YASA Topology. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Design and Performance Comparison of Nine-Phase Ferrite Spoke Interior Permanent Magnet Machines with Concentrated Windings for Traction Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 4282–4288. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, C. A Compact Wireless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor System with Precise Speed and Position Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 11852–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, W.; Goetz, S.M. Design and Control of Wireless Permanent-Magnet Brushless DC Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, P.; Tang, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, C. Multiphase Modular Fault-Tolerant Permanent-Magnet Machine with Hybrid Single/Double-Layer Fractional-Slot Concentrated Winding. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 7500506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfiq, K.B.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Refaie, A.M.E.; Sergeant, P. A Rewound Five-Phase Synchronous Reluctance Machine: Operating Voltage, Inductance Analysis and Comparison with Conventional Multiphase Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Lim, Y.C.; Kim, H.C. Acoustic Noise/Vibration Reduction of a Single-Phase SRM Using Skewed Stator and Rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 4292–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Yang, S.; Hu, Y.; Cao, W. Investigation of Skewing Effects on the Vibration Reduction of Three-Phase Switched Reluctance Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8203509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhulipati, H.; Mukundan, S.; Iyer, K.L.V.; Kar, N.C. Skewing of stator windings for reduction of spatial harmonics in concentrated wound PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Windsor, ON, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Permanent Magnet Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor with Asymmetric Rotor for High Torque Performance. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2023, 7, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, D.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.I. Performance Improvement of Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines Using Asymmetrical Rotor Configurations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8108504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Mirimani, S.M. Design of a Novel PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor Topology Using V-Shape Permanent Magnets for Improvement of Torque Characteristic. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Shao, J.; He, S.; Ye, B.; Yang, F.; Wang, L. Novel PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines Using Asymmetrical Rotor Configuration. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 79564–79573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xing, F.; Wang, X.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.i. Design and Analysis of a Novel PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine with Axially Integrated Magnets by the Finite-Element Method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Degano, M.; Fornasiero, E. Sensitivity Analysis of Torque Ripple Reduction of Synchronous Reluctance and Interior PM Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, O.; Nardo, M.D.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C. A Novel Flux Barrier Parametrization for Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M.; Inoue, Y. Performance Evaluation of a High-Power-Density PMASynRM with Ferrite Magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-ani, M.; Walker, A.; Vakil, G.; Gerada, D.; Gerada, C.; Paciura, K. Modifications to PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine to Achieve Rare-Earth Free Heavy-Duty Traction. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcaro, M.; Bianchi, N. Interior PM Machines Using Ferrite to Replace Rare-Earth Surface PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.X.; Lin, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.; Qin, X.F.; Wan, W.J.; Cai, S. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Reluctance Machines with Axially Combined Rotor Structure. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8103310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Outer stator radius | 100 mm |
| Inner stator radius | 56.6 mm |
| Outer rotor radius | 56.1 mm |
| Inner rotor radius | 19 mm |
| Air-gap length | 0.5 mm |
| Axial length | 60 mm |
| Number of coil turns | 35 |
| Rated current (rms) | 8 A |
| Rated speed | 6000 r/min |
| Ferrite remanence | 0.4 T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, H.; Song, Z.; Liu, C. Design of a Novel Nine-Phase Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine with Skewed Stator Slots. Energies 2025, 18, 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092323
Guo H, Wang T, Chen H, Song Z, Liu C. Design of a Novel Nine-Phase Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine with Skewed Stator Slots. Energies. 2025; 18(9):2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092323
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hongliang, Tianci Wang, Hongwu Chen, Zaixin Song, and Chunhua Liu. 2025. "Design of a Novel Nine-Phase Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine with Skewed Stator Slots" Energies 18, no. 9: 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092323
APA StyleGuo, H., Wang, T., Chen, H., Song, Z., & Liu, C. (2025). Design of a Novel Nine-Phase Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine with Skewed Stator Slots. Energies, 18(9), 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092323








