Microgrids’ Control Strategies and Real-Time Monitoring Systems: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An overview discussion of MGs’ elements is one of the study’s main outputs.
- MGs’ distribution network modes—AC, DC, and hybrid—as well as their advantages and disadvantages, are thoroughly examined.
- A comprehensive analysis of MGs’ advancements in control strategies and their impact on future microgrid developments is conducted.
- An in-depth examination is provided of how technology is transforming management operations at MGs through new developments in IoT real-time monitoring, including its difficulties and potential future paths.
2. Elements of Microgrid Systems
2.1. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
2.2. Power Generation Units
2.3. Power Conversion and Conditioning Equipment
2.4. Energy Management System (EMS)
2.5. Distribution Networks and Loads
3. Microgrid Operation/Distribution Network Modes
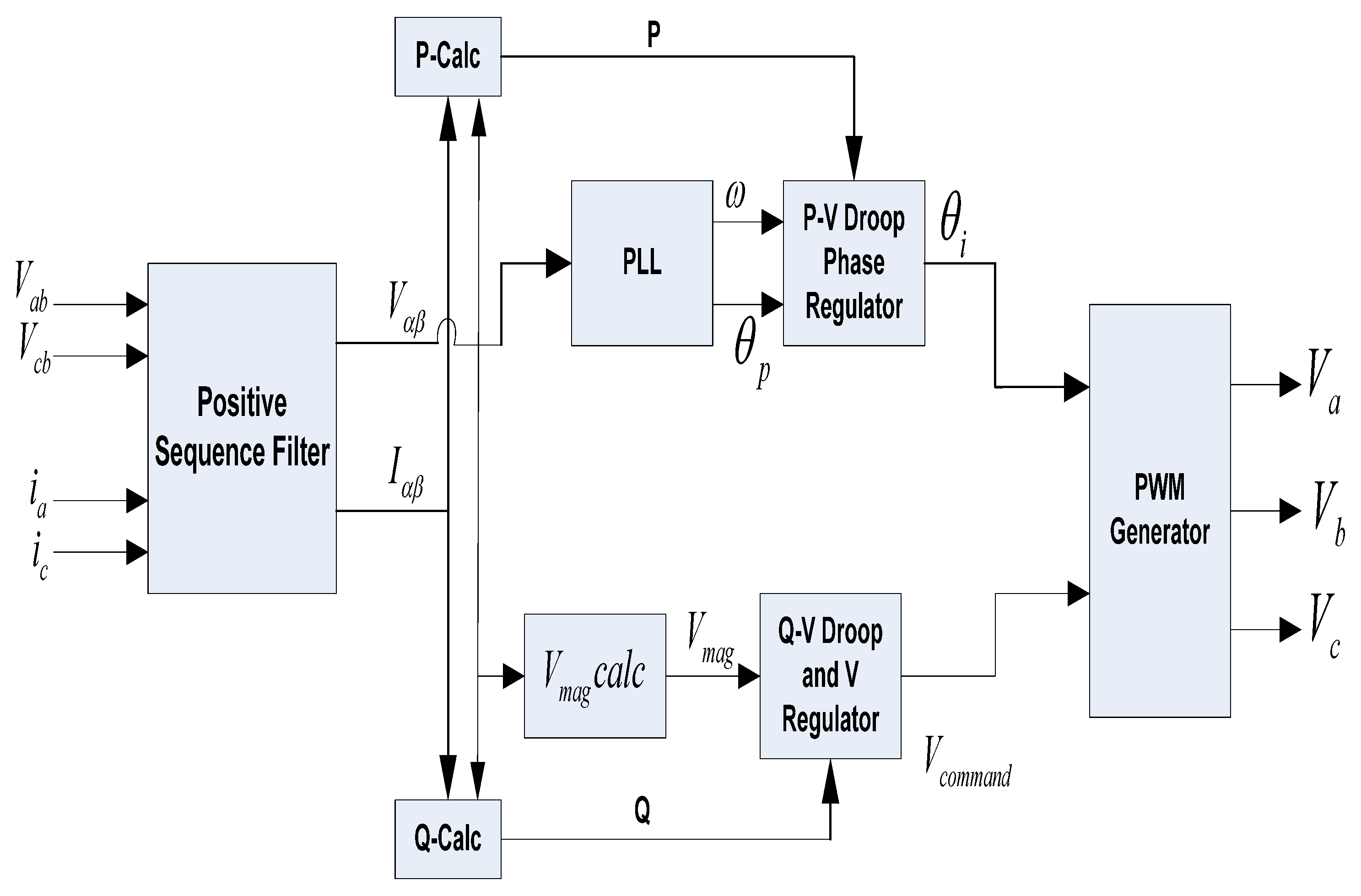
3.1. AC Microgrid Systems
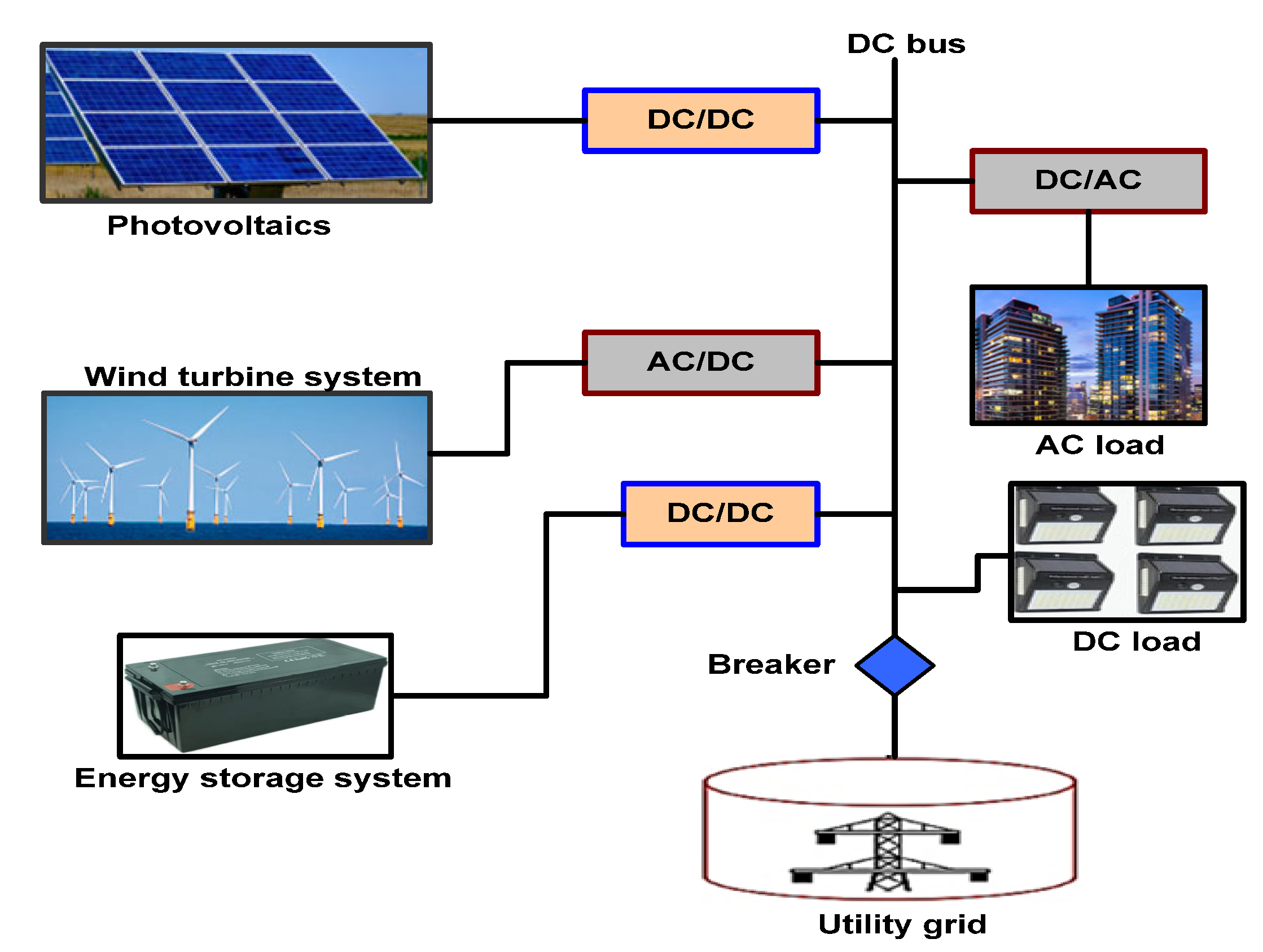
3.2. DC Microgrid Systems
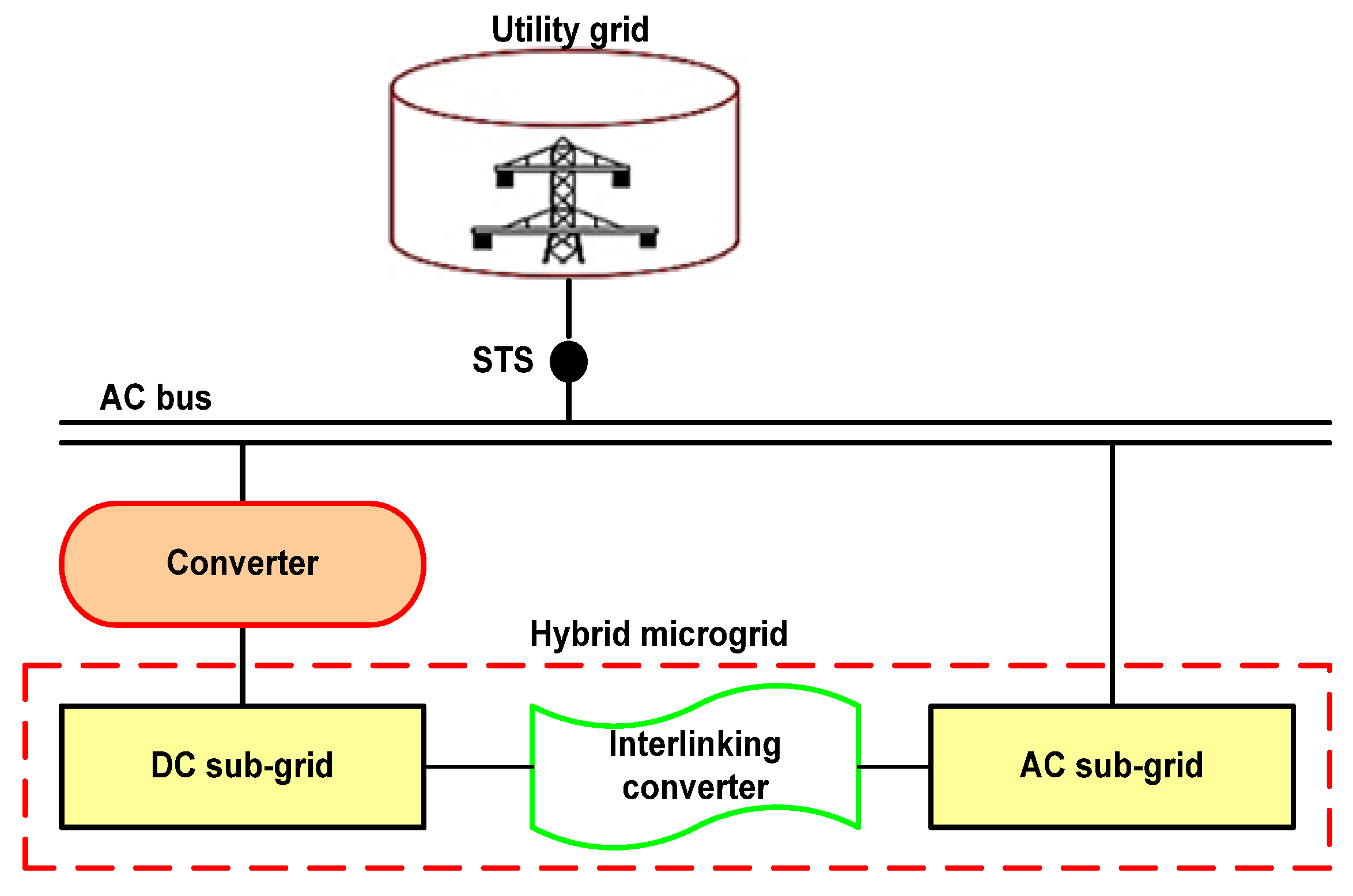
3.3. Hybrid (AC/DC) Microgrid Systems
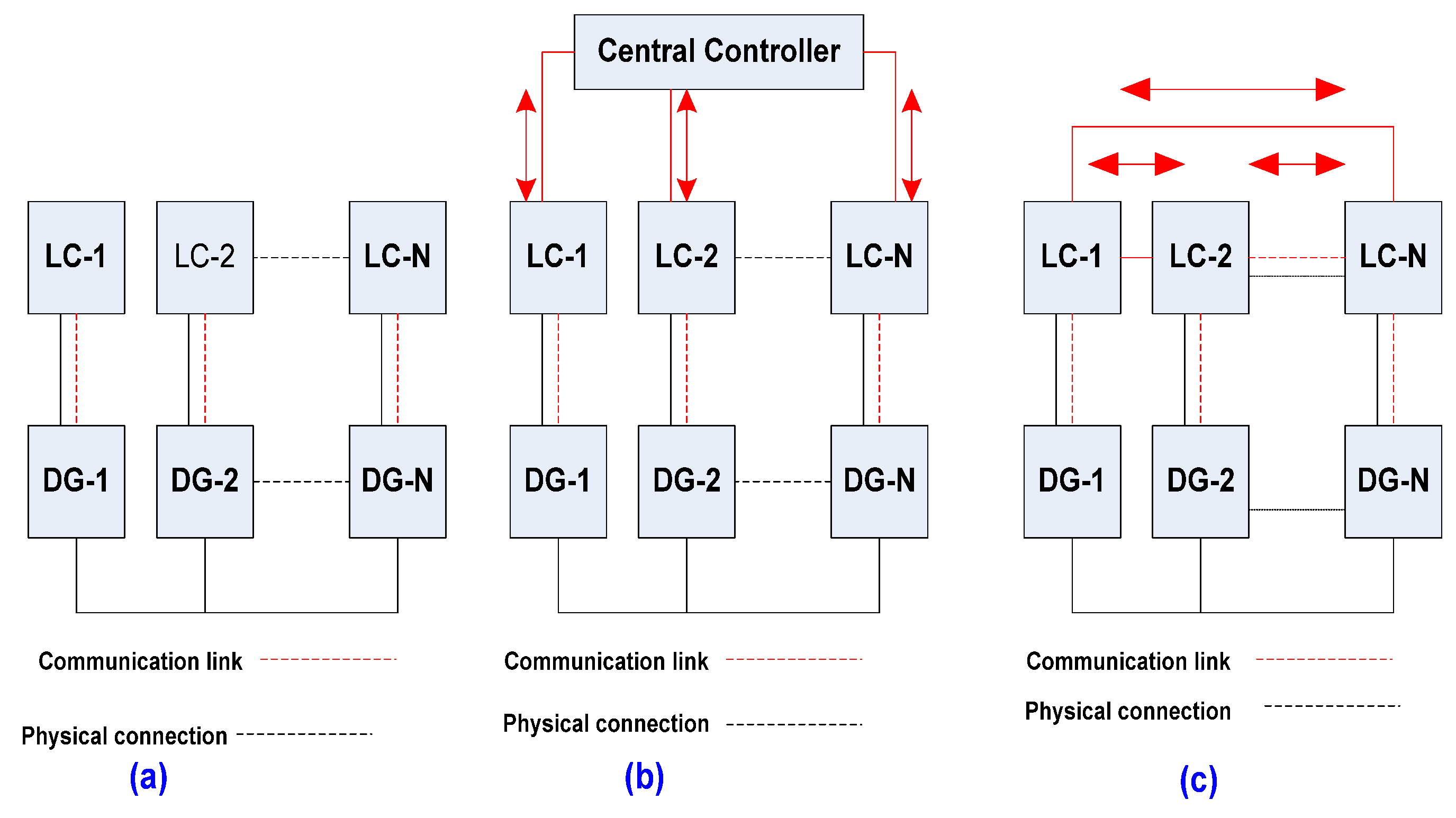
4. Microgrid Control Architectures
5. Advanced Control Techniques
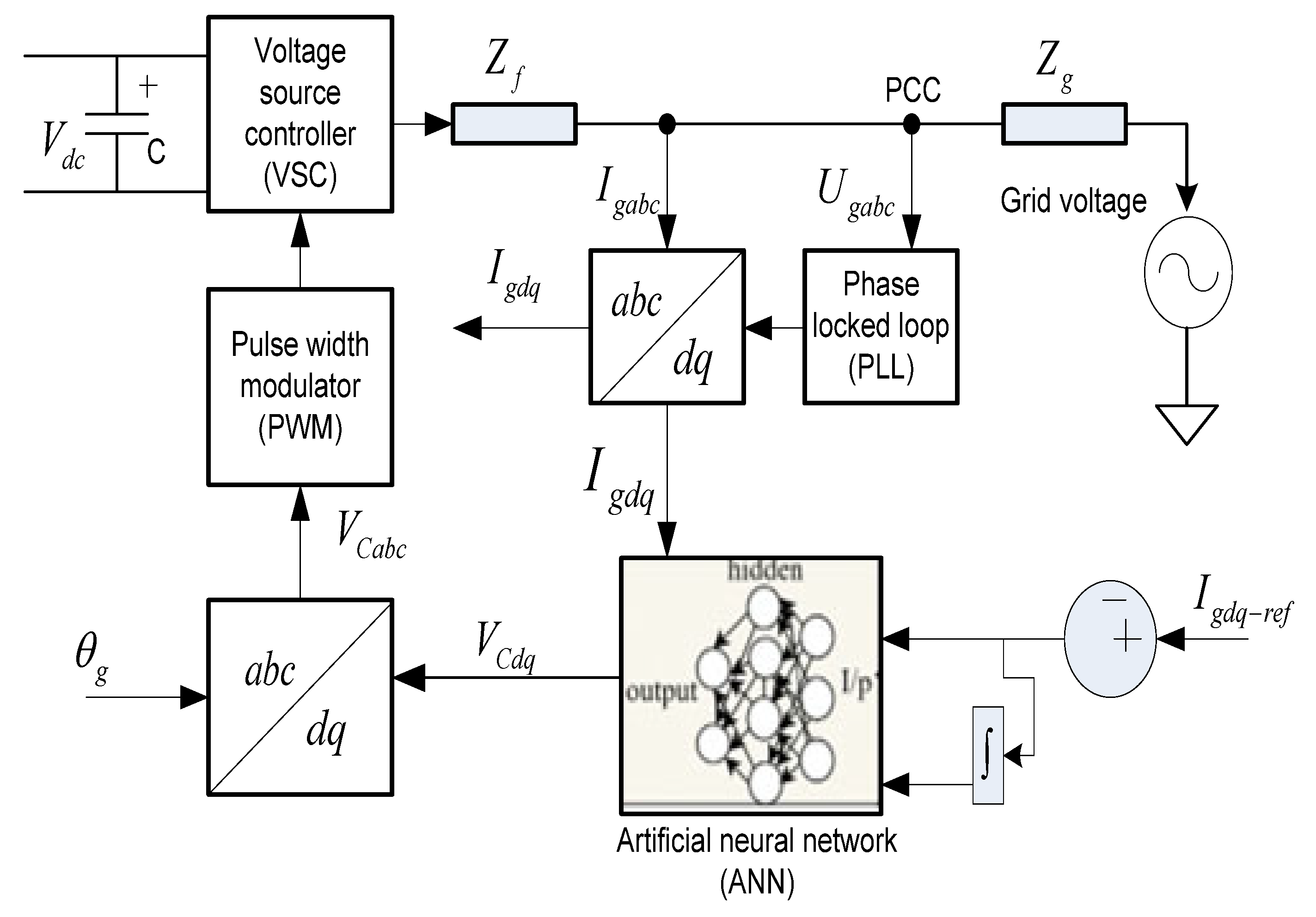
5.1. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
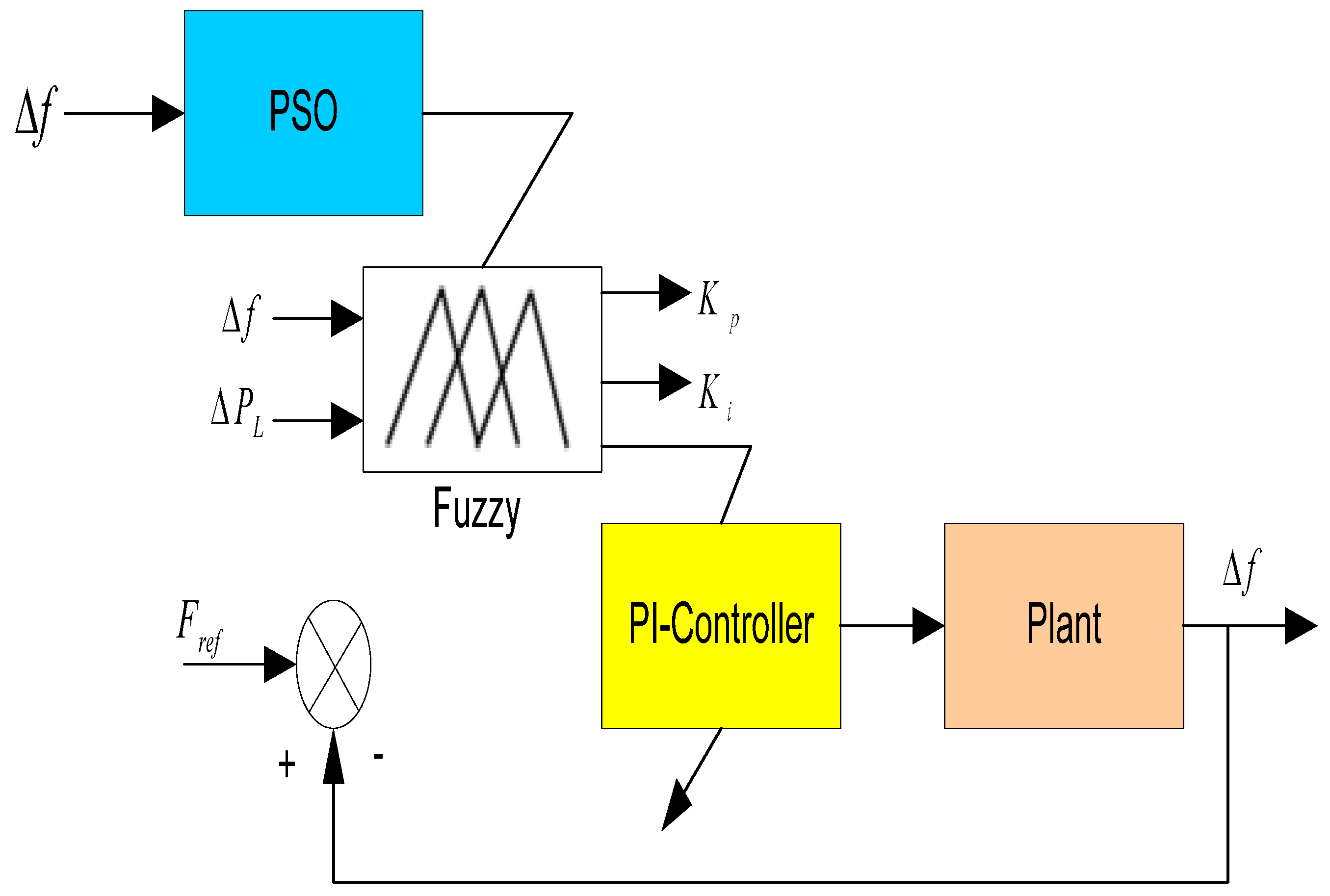
5.2. Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC)
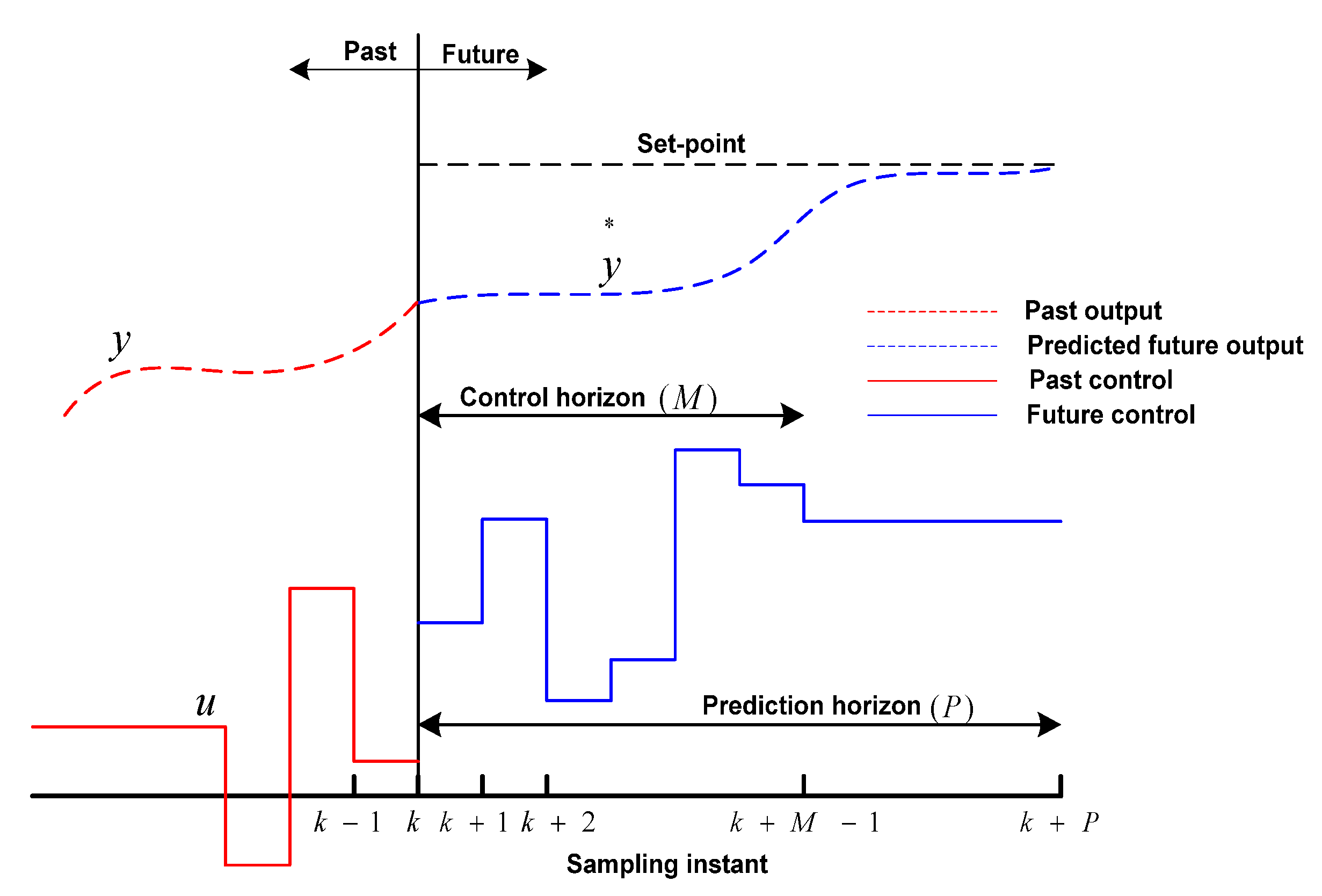
5.3. Model Predictive Control (MPC)
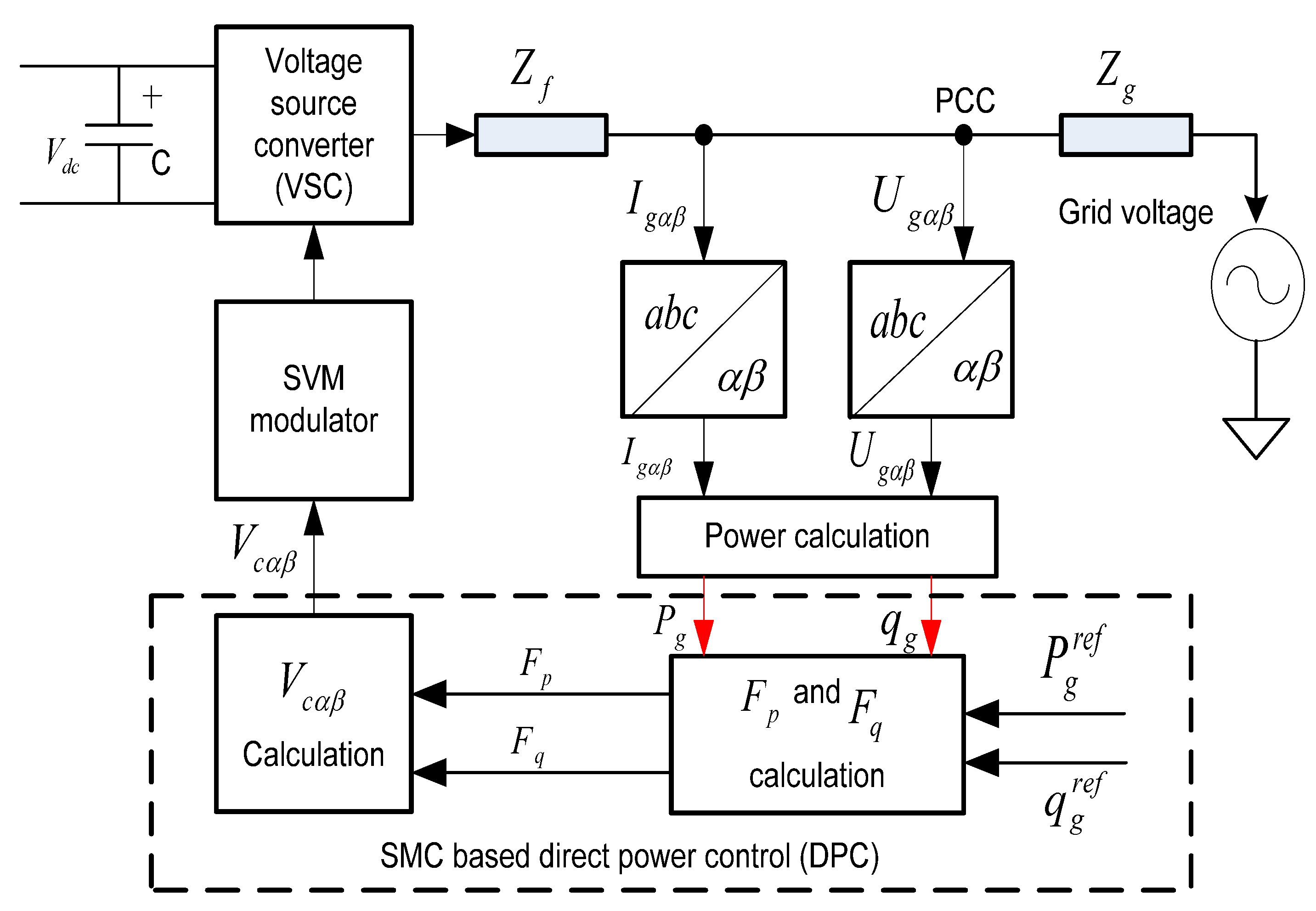
5.4. Sliding Mode Control
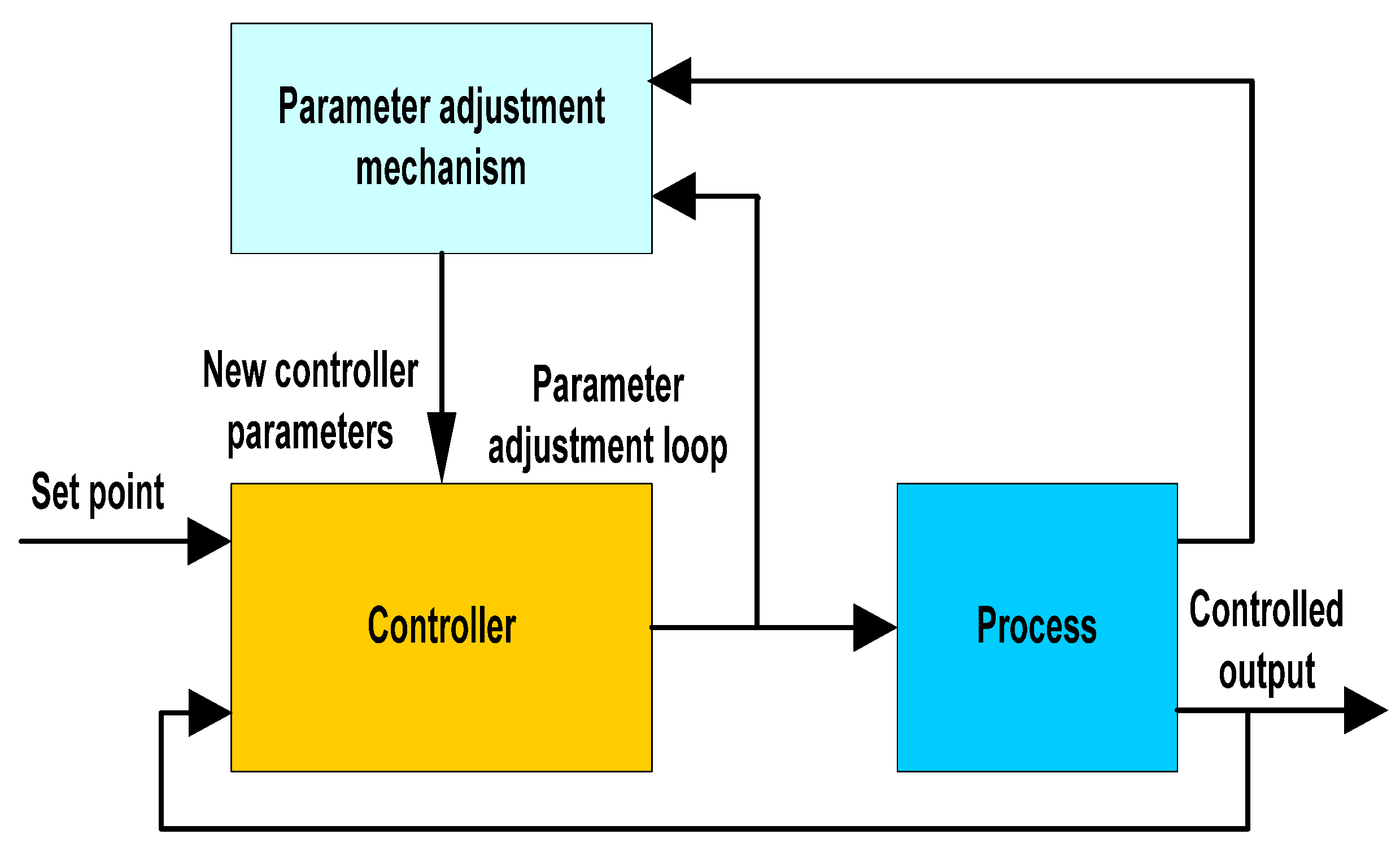
5.5. Adaptive Control
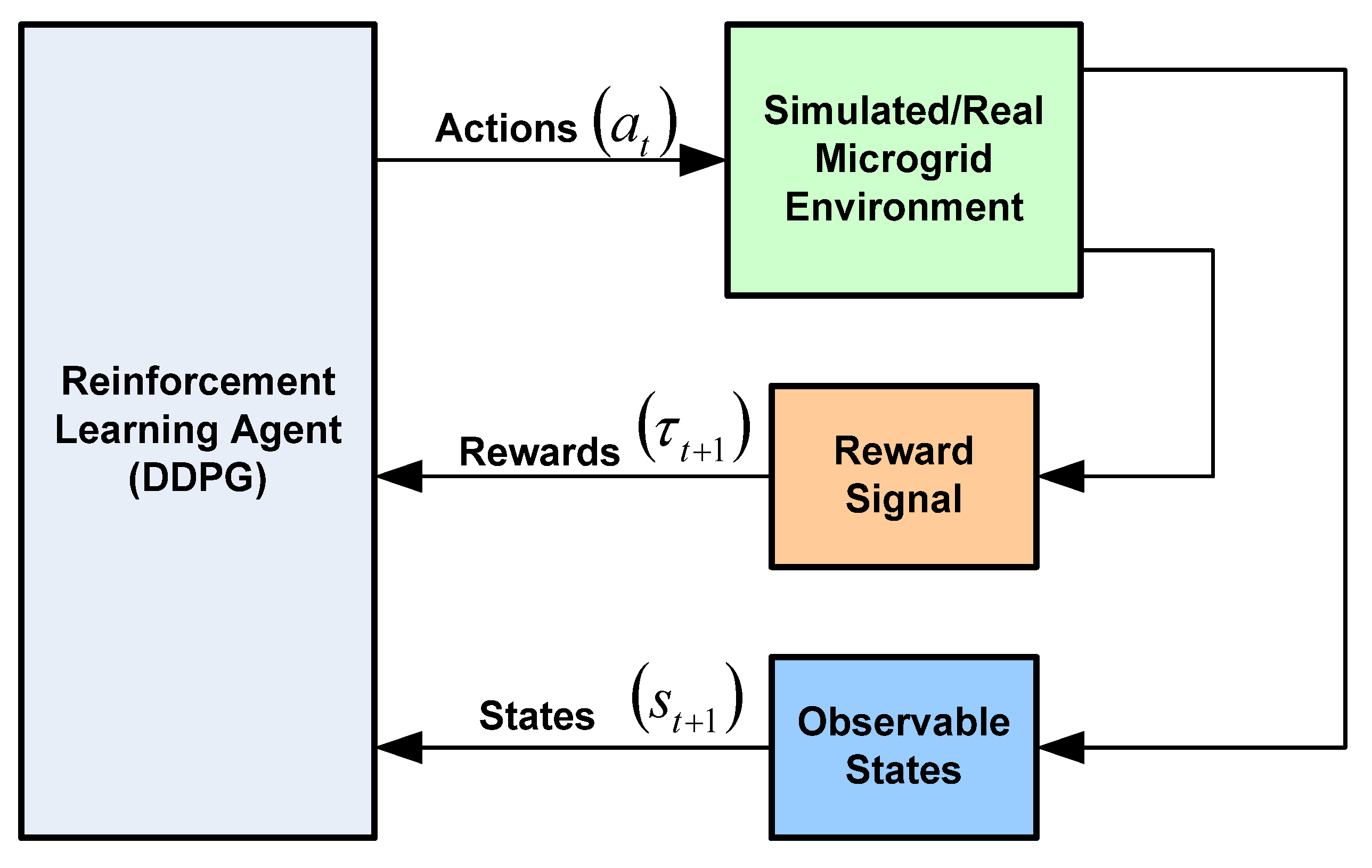
5.6. Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)
5.7. Impact of Control Strategies on Future Microgrid Developments
6. Microgrids’-Based IoT Monitoring Systems
6.1. Challenges of IoT Standardization
- Platform: this component covers the product’s form and design (UI/UX), analytics tools for handling the huge data streaming from all products in a secure manner, and scalability, which necessitates the widespread usage of protocols like IPv6 in all horizontal and vertical markets.
- Connectivity: this stage covers every aspect of the consumer’s day and nightly routine, including the use of wearable technology, smart cars, smart houses, smart grids, and, ultimately, smart cities. From a business standpoint, M2M communications are the dominant field, and we have connectivity through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
- Business model: IoT ventures must have a solid business plan to be successful and long-lasting. Without it, the sector could degenerate into yet another unsustainable bubble. The approach needs to handle major legal and regulatory obstacles while serving all e-commerce types, including consumer, vertical, and horizontal markets.
- Killer applications: three functions are required in this category to have killer applications: “things” control, “data collection,” and “data analysis”. In order to drive the business model with a unified platform, IoT requires killer applications.
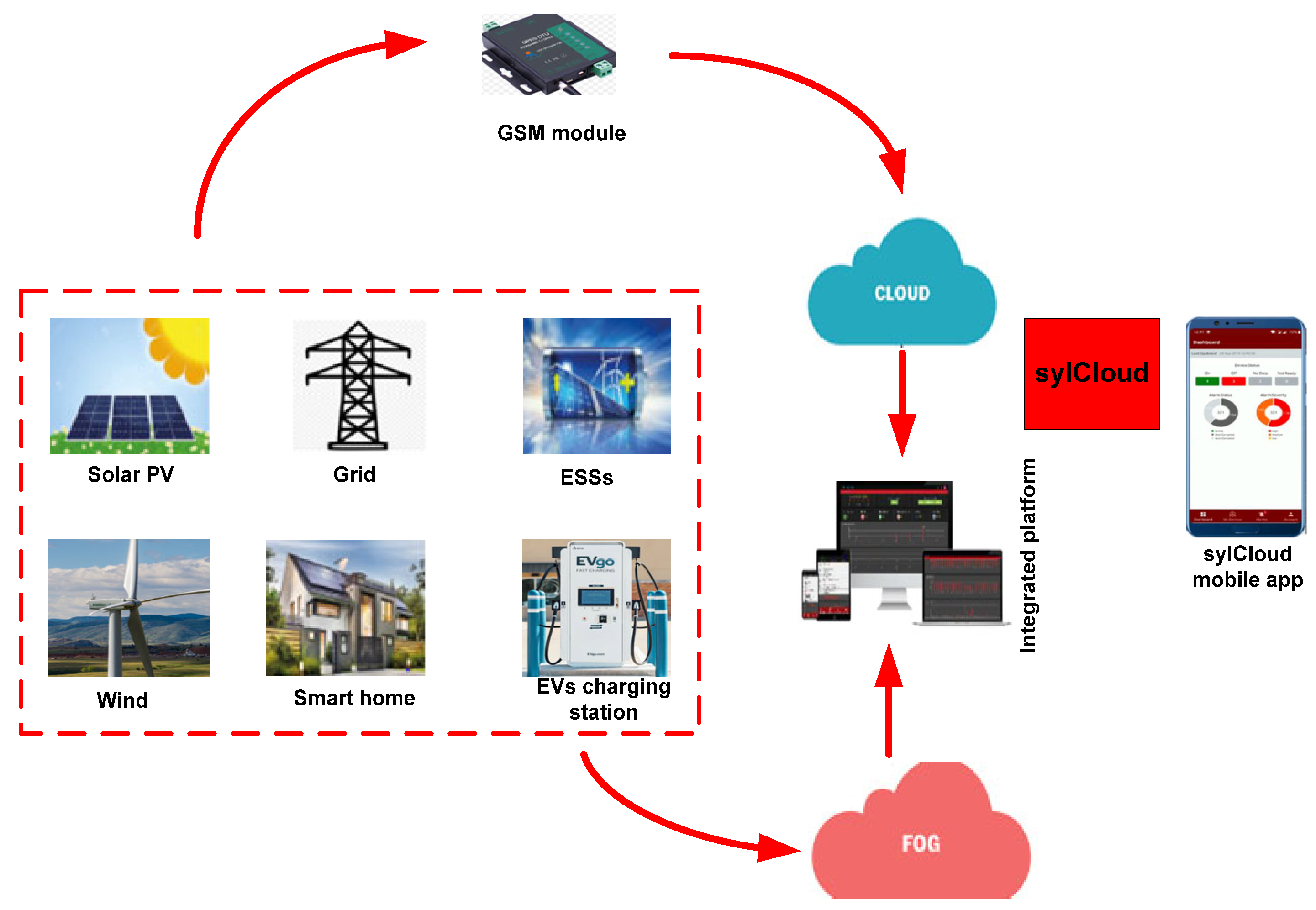
6.2. Emerging Technologies: Cloud, Fog Computing, and Smart Meter Systems
6.3. Microgrid Systems: Cyberattacks and Cybersecurity Issues
6.4. Microgrid Systems: Cybersecurity Standardization Protocols
6.5. Impact of Blockchain in Cybersecurity
7. Challenges and Future Direction of Microgrids
- Future research should focus on creating strong, AI-driven optimization that can quickly detect and halt aggressive campaigns, create peer-to-peer energy markets, and use blockchain technology to encrypt transactions and protect private data.
- To accomplish dynamic changes in energy flow, fewer GHG emissions, and better control for microgrid systems, future research should focus on the application of AI-powered algorithms, based on the careful analysis of large data, rather than traditional and mathematical methods.
- To guarantee the security of energy transactions and DER operations in MGs, future research should employ blockchains and smart contracts.
- For MGs, next-generation ESSs are essential, particularly for those running unreliable RESs. Making storage solutions that are more cost-effective, long-lasting, and efficient without compromising quality should be the main goal of future research.
- Coordination and communication amongst MGs become more important as their numbers increase. The creation of standard interoperability, blockchain-enabled energy trade, and collaboration control mechanisms is an important research area.
- Research into AI-assisted security frameworks, regulatory standards, and methods for expanding the scalability of smart microgrids for wider use should be the main areas of future study.
- Future MGs may be able to detect problems and fix them on their own, which might speed up recovery and restore more loads to the network.
- Pilot projects that involve collaboration are an effective means of proving the viability and offering a plan for implementing creative design. Future studies should concentrate on how governments, academic institutions, businesses, and communities must work together to promote microgrid technologies.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elmouatamid, A.; Ouladsine, R.; Bakhouya, M.; El Kamoun, N.; Khaidar, M.; Zine-Dine, K. Review of Control and Energy Management Approaches in Micro-Grid Systems. Energies 2020, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Zheng, Z.; Aillerie, M.; Sawicki, J.P.; Pera, M.C.; Hissel, D. A Review of DC Microgrid Energy Management Systems Dedicated to Residential Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhtadi, A.; Pandit, D.; Nguyen, N.; Mitra, J. Distributed Energy Resources-Based Microgrid: Review of Architecture, Control, and Reliability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 10, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boche, A.; Foucher, C.; Villa, L.F. Understanding microgrid sustainability: A systemic and comprehensive review. Energies 2022, 15, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, M.; Kajanova, M.; Bracinik, P. A review of advanced control strategies of microgrids with charging stations. Energies 2023, 16, 6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.R.; Kumar, R.S.; Bajaj, M.; Khadse, C.B.; Zaitsev, I. Machine learning-based energy management and power forecasting in grid-connected microgrids with multiple distributed energy sources. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elazab, R.; Dahab, A.A.; Adma, M.A.; Hassan, H.A. Reviewing the frontier: Modeling and energy management strategies for sustainable 100% renewable microgrids. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M. Smart grids and renewable energy systems: Perspectives and grid integration challenges. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 51, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y. Transitioning to sustainable energy: Opportunities, challenges, and the potential of blockchain technology. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1258044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakis, A.; Zafeiratou, I.; Lagos, D.T.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. The Evolution of Research in Microgrids Control. IEEE Open Access J. Power Energy 2020, 7, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S. A Comprehensive Review on Issues, Investigations, Control and Protection Trends, Technical Challenges and Future Directions for Microgrid Technology. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Bayhan, S.; Abu-Rub, H. AC Microgrid Control and Management Strategies: Evaluation and Review. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2019, 6, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, P.; Zangeneh, A.; Moradzadeh, M.; Ghafouri, A.; Parazdeh, M.A. Various Droop Control Strategies in Microgrids. In Microgrid Architectures, Control and Protection Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 527–554. [Google Scholar]
- Rokrok, E.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Catalão, J. Review of Primary Voltage and Frequency Control Methods for Inverter-Based Islanded Microgrids with Distributed Generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Kumar, V. Microgrid Control: A Comprehensive Survey. Annu. Rev. Control 2018, 45, 118–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosini, A.; Labella, A.; Bonfiglio, A.; Procopio, R.; Guerrero, J.M. A Review of Reactive Power Sharing Control Techniques for Islanded Microgrids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarakati, A.J.; Boujoudar, Y.; Azeroual, M.; Eliysaouy, L.; Kotb, H.; Aljarbouh, A.; Alkahtani, H.K.; Mostafa, S.M.; Tassaddiq, A.; Pupkov, A. Microgrid Energy Management and Monitoring Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 1097858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Matas, J.; De Vicuña, L.G.; Castilla, M. Hierarchical Control of Droop-Controlled AC and DC Microgrids—A General Approach Toward Standardization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 58, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, D.; Lu, T. A literature review of the control challenges of distributed energy resources based on microgrids: Past, present, and future. Energies 2022, 15, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, L.; Guo, F.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Guerrero, J.M. A Reactive Power-Voltage Control Strategy of an AC Microgrid Based on Adaptive Virtual Impedance. Energies 2019, 12, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, G.; Jamuna, K. Real-time implementation of sliding mode controller for standalone microgrid systems for voltage and frequency stabilization. Energies 2023, 10, 768–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaghian, M.S.; Saffari, M.; Heidari, A.; Shafie-khah, M.; Catalão, J.P.S. Tri-level optimization of industrial microgrids considering renewable energy sources, combined heat and power units, thermal and electrical storage systems. Energies 2019, 161, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Mifta, Z.; Atia, N.; Janefar, S.; Hossain, M.; Roy, P.; Chowdhury, N.; Farrok, O. A critical review on control mechanisms, supporting measures, and monitoring systems of microgrids considering large-scale integration of renewable energy sources. Energies 2023, 10, 4582–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, A.; Suleiman, H.O.; Dahiru, Y.; Bukar, B. The role of power electronic converters in microgrid technology: A review of challenges, solutions, and research directions. Eur. J. Theor. and Appl. Sci. 2024, 2, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evandro, M.; Junior, T.S.; Freitas, L.C.G. Power electronics for modern sustainable power systems: Distributed generation, microgrids and smart grids—A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, V.; Chaturvedi, P. Design, control, reliability, economic and energy management of microgrid: A review. e-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2023, 5, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, S.S.; Raman, R.; Singh, A.; Shiva, C.K.; Kumar, R.; Sadhu, P.K.; Collins, E.R.; Senjyu, T. DC microgrids: A propitious smart grid paradigm for smart cities. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1690–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassereddine, K.; Turzyński, M.; Strzelecki, R. Review and indication of key activities for energy management improvement in DC microgrids. In Proceedings of the IEEE 17th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG), Tallinn, Estonia, 14–16 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Eyimaya, S.E.; Altin, N. Review of energy management systems in microgrids. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Deng, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Blaabjerg, F. Microgrid energy management with energy storage systems: A review. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 483–504. [Google Scholar]
- Montano, J.; Guzmán-Rodríguez, J.P.; Palomeque, J.M.; González-Montoya, D. Comparison of different optimization techniques applied to optimal operation of energy storage systems in standalone and grid-connected direct current microgrids. J. Energy Storage 2024, 96, 112708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Tobar, A.; Massi Pavan, A.; Petrone, G.; Spagnuolo, G. A review of the optimization and control techniques in the presence of uncertainties for the energy management of microgrids. Energies 2022, 15, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Shahzad, M.; Abbas, F.; Muqeet, H.A.; Hussain, M.M.; Bin, L. Optimal energy management system of IoT-enabled large building considering electric vehicle scheduling, distributed resources, and demand response schemes. Sensors 2022, 22, 7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasali, F.; Saad, S.M.; Salah, A.; Itradat, A. Powering up microgrids: A comprehensive review of innovative and intelligent protection approaches for enhanced reliability. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 1899–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayeh, D.D.; Mahmud, F.F.; Moein, M.A.; Fei, D.P.W. Estimating participation abilities of industrial customers in demand response programs: A two-level decision-making tree analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/IAS 56th Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Technical Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 June–28 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hemanth, G.R.; Charles, R.S.; Nesamalar, J.D.; Kumar, J.S. Cost-effective energy consumption in a residential building by implementing demand side management in the presence of different classes of power loads. Adv. Build. Energy Res. 2020, 16, 145–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinos, E.I.E.; Trakas, D.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. Microgrids for power system resilience enhancement. Energies 2022, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, P.A.; Martínez, M.; Molina, M.G.; Mercado, P.E. Development of Control Techniques for AC Microgrids: A Critical Assessment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Study on Frequency Stability Control Strategies for Microgrid Based on Hybrid Renewable Energy. Emerg. Adv. Hybrid Renew. Energy Syst. Integr. 2024, 79, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Peng, Y.; He, M.; Deng, T.; Wang, G.; Cao, Q.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Yu, D. Research on Smooth Switching Control Technology between Grid-Connected Operation and Off-Grid Operation of Micro-Grid. In Proceedings of the Panda Forum on Power and Energy (PandaFPE), Chengdu, China, 27–30 April 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gaurav, S.; Nougain, V.; Panigrahi, B.K. Protection of low-voltage dc microgrid based on series RLC equivalent circuit utilizing local measurements. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 3877–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrao, I.; Toran, E.; González-Medina, R.; Mascarell, M.L.; Figueres, E. DC-Bus signaling control laws for the operation of DC-microgrids with renewable power sources. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2023, 5, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Deng, C.; Guiyuan, L. Control strategy of an interlinking converter in hybrid microgrid based on line impedance estimation. Energies 2022, 15, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Kang, L.; He, J.; Zheng, F.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y. Coordination control of hybrid AC/DC microgrid. Energies 2019, 16, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H. Arc voltage and current characteristics in low-voltage direct current. Energies 2018, 11, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallah, M.; Youssef, A.R.; Ali, A.; Mohamed, E.M. Advancements in microgrid technologies: A critical review. Energies 2024, 5, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Chandorkar, M.; Lee, T.-L.; Loh, P.C. Advanced Control Architectures for Intelligent Microgrids—Part I: Decentralized and Hierarchical Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altin, N.; Eyimaya, S.E. A Review of Microgrid Control Strategies. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA 2021), Istanbul, Turkey, 8–21 September 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Espina, E.; Llanos, J.; Burgos-Mellado, C.; Cárdenas-Dobson, R.; Martínez-Gómez, M.; Sáez, D. Distributed Control Strategies for Microgrids: An Overview. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193412–193448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennagi, A.; AlHousrya, O.; Cotfas, D.T.; Cotfas, P.A. Comprehensive study of the artificial intelligence applied in renewable energy. Energy Strat. Rev. 2024, 54, 101446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.E.; Martí, J.M.; Radivojevic, T.; Jonnalagadda, S.V.R.; Gentz, R.; Hillson, N.J.; Peisert, S.; Kim, J.; Simmons, B.A.; Petzold, C.J.; et al. Machine learning for metabolic engineering: A review. Metab. Eng. 2021, 63, 34–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhy, S.; Sahu, P.R.; Panda, S.; Padmanaban, S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Khan, B. Marine predator algorithm-based pd-(1+pi) controller for frequency regulation in the multi-microgrid system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, 16, 2136–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, E.K.; Akinremi, O.I.; Adeleke, A.H.; Adewale, O.A.; Ajibola, C.D.; Ogunkeyede, O.Y. An Optimal Placement of STATCOM Controller on 14-Bus IEEE Standard Test Transmission Network Using Particle Swarm Optimization. FUOYE J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, I.; Abido, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Savkin, A.V. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances in Smart Grids: A Sustainable Future with Renewable Energy Resources. Energies 2020, 13, 6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, N.; Ye, L.; Du, E.; Kang, C. Advances in Model Predictive Control for Large-Scale Wind Power Integration in Power Systems. Adv. Appl. Energy 2024, 14, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, M.; Boukhris, A.; Gasbaoui, B.; Sellami, A.; Mimouni, M.F.; Benbouzid, M.E.H. Design of Vector Control Strategies Based on Fuzzy Gain Scheduling PID Controllers for a Grid-Connected Wind Energy Conversion System: Hardware FPGA-in-the-Loop Verification. Electronics 2023, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmia, I.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Turci, L.D.O. Robust Data Predictive Control Framework for Smart Multi-Microgrid Energy Dispatch Considering Electricity Market Uncertainty. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32390–32404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Oshnoei, A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Hierarchical Control for Microgrids: A Survey on Classical and Machine Learning-Based Methods. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Yu, X.; Fu, Z. Sliding Mode Control of Networked Control Systems: An Auxiliary Matrices-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2021, 66, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, S.; Riggs, H.; Tariq, M.; Sarwat, A.I. Advancements and Challenges in Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review of Models, Libraries, Applications, and Algorithms. Electronics 2023, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi Satya Nagasri, D.; Marimuthu, R. Review on Advanced Control Techniques for Microgrids. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 3054–3072. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Andalib-Bin-Karim, C.; Li, W.; Mitolo, M.; Shabbir, M.N.S.K. Adaptive virtual impedance-based reactive power sharing in virtual synchronous generator controlled microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 57, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, J.; Liang, G.; Dong, Z.Y. Cooperative Wind Farm Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Knowledge-Assisted Learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 6912–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenoğlu, A.K.; Şengör, İ.; Erdinç, O.; Taşcıkaraoğlu, A.; Catalão, J.P.S. Optimal energy management system for microgrids considering energy storage, demand response and renewable power generation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 136, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, S.S.; Ur Rahman, A.; Ahmad, I. Fuzzy-Barrier Sliding Mode Control of Electric-Hydrogen Hybrid Energy Storage System in DC Microgrid: Modelling, Management and Experimental Investigation. Energy 2022, 239, 122260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, X.; Wang, W. Adaptive event triggered predictive control for finite time microgrid. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Basak, P. A comprehensive review on control techniques for stability improvement in microgrids. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, e12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Gholap, A.D.; Jetha, K.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Solanki, H.K.; Chavda, V.P. Artificial intelligence in pharmaceutical technology and drug delivery design. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awelewa, A.; Olajube, A.; Ojo, K.; Samuel, I.; Davies, H.; Akinola, O. ANN Based Load Forecasting Model for Short Term Planning: A Case Study of Ota Community in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Innovation and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing, and Technologies (3ICT), Sakheer, Bahrain, 22–23 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, E.; Al-Ghaili, A.M.; Kadir, D.H.; Gunasekaran, S.S.; Ahmed, A.N.; Jamil, N.; Deveci, M.; Razali, R.A. Meta-heuristics and deep learning for energy applications: Review and open research challenges (2018–2023). Energy Strateg. Rev. 2024, 53, 101409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Torres, F.; Baez-Gonzalez, P.; Tobajas, J.; Vazquez, F.; Nieto, E. Cooperative Optimization of Networked Microgrids for Supporting Grid Flexibility Services Using Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, U.R.; Costa-Castelló, R. A Model Predictive Control-Based Energy Management Scheme for Hybrid Storage System in Islanded Microgrids. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 97809–97822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konneh, K.V.; Adewuyi, O.B.; Lotfy, M.E.; Sun, Y.; Senjyu, T. Application strategies of model predictive control for the design and operations of renewable energy-based microgrid: A survey. Electronics 2022, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control Based on Disturbance Observer for Placement Pressure Control System. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, H. Distributed adaptive secondary control for microgrids with time delay and switching topology. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 210, 108117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakr, H.; Vasquez, J.C.; Mohamed, T.H.; Guerrero, J.M. The concept of direct adaptive control for improving voltage and frequency regulation loops in several power system applications. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 140, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasis, S. Controllable transient power-sharing of inverter-based droop controlled microgrid. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 155, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, A.; Mikhaylov, A.; Senjyu, T.; Eslami, M.; Hemeida, A.M.; Osheba, D.S.M. Modified Droop Control for Microgrid Power-Sharing Stability Improvement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Pou, J.; Konstantinou, G. Stability-Oriented Multi objective Control Design for Power Converters Assisted by Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 12394–12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Konstantinou, G.; Pou, J.; Zou, G.; Zhang, X. Multi-Objective Controller Design for Grid-Following Converters with Easy Transfer Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 6566–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, S.; Abbasi, M.A.; Ali, H.; Iqbal, M.; Munir, R.; Kilic, H. Possibilities, challenges, and future opportunities of microgrids: A review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Sustainable energy transition for renewable and low carbon grid electricity generation and supply. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 743114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality. Innovation 2021, 2, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakare, M.S.; Abdulkarim, A.; Zeeshan, M.; Shuaibu, A.N. A comprehensive overview on demand side energy management towards smart grids: Challenges, solutions, and future direction. Energy Inform. 2023, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Haider, Z.M.; Malik, F.H.; Almasoudi, F.M.; Alatawi, K.S.S.; Bhutta, M.S. A comprehensive review of microgrid energy management strategies considering electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and AI techniques. Processes 2024, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumick, D.; Deb, P.; Khan, M.M. Operation and control of microgrids using IoT (Internet of Things). J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 2021, 14, 418–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, P.K.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Kasinathan, P.; Yong, J.Y.; Pasupuleti, J.; Rajagopalan, A. Application and Assessment of Internet of Things toward the Sustainability of Energy Systems: Challenges and Issues. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedhom, B.E.; El-Saadawi, M.M.; El Moursi, M.S.; Hassan, M.A.; Eladl, A.A. IoT-Based optimal demand side management and control scheme for smart microgrid. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 127, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Choi, B.J. State-of-the-Art Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Distributed Smart Grids: A Review. Electronics 2020, 9, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Wang, Z.; Mehrandezh, M.; Jalilian, S.; Ghadimi, N. Evolution of Smart Grids towards the Internet of Energy: Concept and Essential Components for Deep Decarbonisation. IET Smart Grid 2022, 6, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, N.M.; Dai, L.V.; Tung, D.D.; Toan, N.A. An Advanced IoT System for Monitoring and Analysing Chosen Power Quality Parameters in Microgrid Solution. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2021, 70, 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, T.; Asim, M.; MacDermott, Á.; Iqbal, F.; Kamoun, F.; Shah, B.; Alfandi, O.; Hammoudeh, M. A secure fog-based platform for SCADA-based IoT critical infrastructure. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2020, 50, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-K. A Phase Tracking System for Three Phase Utility Interface Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2000, 15, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, L.; Silva, S.; Filho, B. PLL Structures for Utility Connected Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2001; pp. 2655–2660. [Google Scholar]
- Możdżyński, K.; Rafał, K.; Bobrowska-Rafał, M. Application of the Second Order Generalized Integrator in Digital Control Systems. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2014, 63, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y. A Novel Discretization Method for Multiple Second-Order Generalized Integrators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 10998–11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chambers, J.A. An Outlier Robust Kalman Filter with an Adaptive Selection of Elliptically Contoured Distributions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 994–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, I.D.; Antunes, M.P. Microgrid State and Frequency Estimation Using Kalman Filter: An Approach Considering an Augmented Measurement Jacobian Matrix. Electronics 2022, 104, 3523–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.; Mishra, K.N.; Singh, S.P. Securing data and preserving privacy in cloud IoT-based technologies: An analysis of assessing threats and developing effective safeguards. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Wan, J.; Lu, J.; Qiu, D. Security of the Internet of Things: Perspectives and Challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2014, 20, 2481–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Asim, M.; Tariq, N.; Baker, T.; Abbas, S. A Mechanism for Securing IoT-Enabled Applications at the Fog Layer. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2019, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, M.; Carnì, D.L.; Rotondo, S.; Paolillo, A.; Manzo, F.; Martirano, L. A Nearly Zero-Energy Microgrid Testbed Laboratory: Centralized Control Strategy Based on SCADA System. Energies 2020, 13, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.K.; Rastogi, V. Integration of Technology to Access the Manufacturing Plant via Remote Access System—A Part of Industry 4.0. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 56, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Asim, M.; Khan, F.A. Securing SCADA-based critical infrastructures: Challenges and open issues. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 155, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, T.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Jeslin, D.N.J. Design of IoT-Based Smart Compact Energy Meter for Monitoring and Controlling the Usage of Energy and Power Quality Issues with Demand-Side Management for a Commercial Building. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2021, 26, 100454. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, D.L.S.; Rabelo, R.A.L.; Veloso, A.F.S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; dos Reis Junior, J.V. An Adaptive data compression mechanism for smart meters considering a demand side management scenario. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, T.; Talpur, D.B.; Shloul, T.A.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Haq, I.; Ullah, I.; Ouahada, K.; Hamam, H. Analysis of IoT security challenges and its solutions using artificial intelligence. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Xiao, G.; Lu, R. Defending Against False Data Injection Attacks on Power System State Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.Q.; Hou, Y.; Li, V.O.K. Online False Data Injection Attack Detection with Wavelet Transform and Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mili, L.; Wang, M. A Generalized False Data Injection Attacks Against Power System Nonlinear State Estimator and Countermeasures. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 4868–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Mishra, S.; Peng, J.C.; Dragicevic, T. A Stealth Cyber Attack Detection Strategy for DC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8162–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, O.; Tivani, L.; Mbatha, L. A Review on Cybersecurity for Distributed Energy Resources: Opportunities for South Africa. J. Infrastruct. Policy Dev. 2024, 8, 8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabatkhah, F.; Li, Y.W.; Liang, H.; Reza Ahrabi, R. Cyber-Security of Smart Microgrids: A Survey. Energies 2021, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.; Long, D.; Reinhard, K. Visualizing NISTIR 7628, Guidelines for Smart Grid Cyber Security. In Proceedings of the 2014 Power and Energy Conference at Illinois (PECI), Champaign, IL, USA, 28 February–1 March 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.M.S.; Ustun, T.S.; Kalam, A. A Review of IEC 62351 Security Mechanisms for IEC 61850 Message Exchanges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 5643–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyna, R. Standards on Cyber Security Assessment of Smart Grid. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2018, 22, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.A.; Obeidat, S.; Holst, J.; Al Hayajneh, A.; Brown, J. A Comprehensive and Systematic Survey on the Internet of Things: Security and Privacy Challenges, Security Frameworks, Enabling Technologies, Threats, Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures. Computers 2020, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60870-5; Telecontrol Equipment and Systems—Transmission Protocols—Companion Standard for Basic Telecontrol Tasks. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- IEC 61850-5; Communication Networks and Systems for Power Utility Automation—Part 5: Communication Requirements for Functions and Device Models. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Tawalbeh, L.; Muheidat, F.; Tawalbeh, M.; Quwaider, M. IoT Privacy and Security: Challenges and Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weixiong, W. The role of blockchain technology in advancing sustainable energy with security settlement: Enhancing security and efficiency in China’s security market. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1271752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Teng, F.; Gan, W.; Yao, W.; Wen, J. Blockchain for secure decentralized energy management of multi-energy system using state machine replication. Appl. Energy 2023, 337, 120863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukaras, P.; Afentoulis, K.D.; Gkaidatzis, P.A.; Mystakidis, A.; Ioannidis, D.; Vagropoulos, S.I.; Tjortjis, C. Integrating blockchain in smart grids for enhanced demand response: Challenges, strategies, and future directions. Energies 2024, 17, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.G.; Deshmukh, S.M. Efficient Service-Centric Blockchain Data Security for Smart Grid Systems. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 540, 01035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ren, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, S. Edge Blockchain Assisted Lightweight Privacy-Preserving Data Aggregation for Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021, 18, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Ren, B.; Li, B.; Kong, Q. BBNP: A Blockchain-Based Novel Paradigm for Fair and Secure Smart Grid Communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 12984–12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Dong, M.; Miao, W.; Zhang, M.; Tang, H. A Data-Driven Approach for Blockchain-Based Smart Grid System. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 70061–70070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-D.; Li, J.-H.; Chen, T.-H. A Blockchain-Enabled Authentication and Conserved Data Aggregation Scheme for Secure Smart Grids. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 85202–85213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.P.; Gupta, K.; Chandavarkar, B.R. The Role of Cryptography in Cryptocurrency. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communications (ICSCCC), Jalandhar, India, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Almihat, M.G.M.; Munda, J.L. The Role of Smart Grid Technologies in Urban and Sustainable Energy Planning. Energies 2025, 18, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| AC Microgrid | |
| Benefits | Assessment |
| Grid compatibility |
|
| Use of standard equipment |
|
| Simple Interface Loads |
|
| Drawbacks | Assessment |
| Problems with power quality |
|
| Required synchronization |
|
| Limited efficiency |
|
| DC Microgrid | |
| Benefits | Assessment |
| Higher efficiency |
|
| Simplified control |
|
| Improved reliability |
|
| Drawbacks | Assessment |
| Minimal standardization |
|
| Complexity of protection |
|
| High-priced equipment |
|
| Hybrid (AC/DC) Microgrid | |
| Benefits | Assessment |
| Versatility and adaptability |
|
| Efficiency optimization |
|
| Seamless grid integration |
|
| Resiliency |
|
| Drawbacks | Assessment |
| Higher complexity |
|
| High-cost infrastructure |
|
| Complexity of maintenance |
|
| Ref. | Control Method | Types | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [53,54] | Droop Control | Traditional |
|
|
| [55] | Proportional–integral–derivative | Traditional |
|
|
| [56] | Multi-agent systems | Traditional |
|
|
| [57,58] | Fuzzy logic control | Advanced |
|
|
| [59,60] | Model predictive control | Advanced |
|
|
| [61,62] | Artificial neural networks | Advanced |
|
|
| [63,64] | Reinforcement learning | Advanced |
|
|
| [65,66] | Sliding mode control | Advanced |
|
|
| [67] | Virtual impedance control | Advanced |
|
|
| System | Functionality | Local Processing | Latency | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCADA systems | Supervisory control and data acquisition from field devices. | Centralized (control center) | Moderate | Limited |
| Smart Meters | Monitor energy usage, support billing, and load profiling. | Edge (device level) | Very low | Moderate |
| Cloud computing | Large-scale data storage, analytics, forecasting, and remote monitoring. | Remote/cloud data centers | High | High |
| Fog computing | Local data preprocessing, control coordination, and communication bridge. | Intermediate (between edge and cloud) | Low | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojo, K.E.; Saha, A.K.; Srivastava, V.M. Microgrids’ Control Strategies and Real-Time Monitoring Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2025, 18, 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133576
Ojo KE, Saha AK, Srivastava VM. Microgrids’ Control Strategies and Real-Time Monitoring Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Energies. 2025; 18(13):3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133576
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjo, Kayode Ebenezer, Akshay Kumar Saha, and Viranjay Mohan Srivastava. 2025. "Microgrids’ Control Strategies and Real-Time Monitoring Systems: A Comprehensive Review" Energies 18, no. 13: 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133576
APA StyleOjo, K. E., Saha, A. K., & Srivastava, V. M. (2025). Microgrids’ Control Strategies and Real-Time Monitoring Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Energies, 18(13), 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133576







