Forecast-Aided Converter-Based Control for Optimal Microgrid Operation in Industrial Energy Management System (EMS): A Case Study in Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Analysis
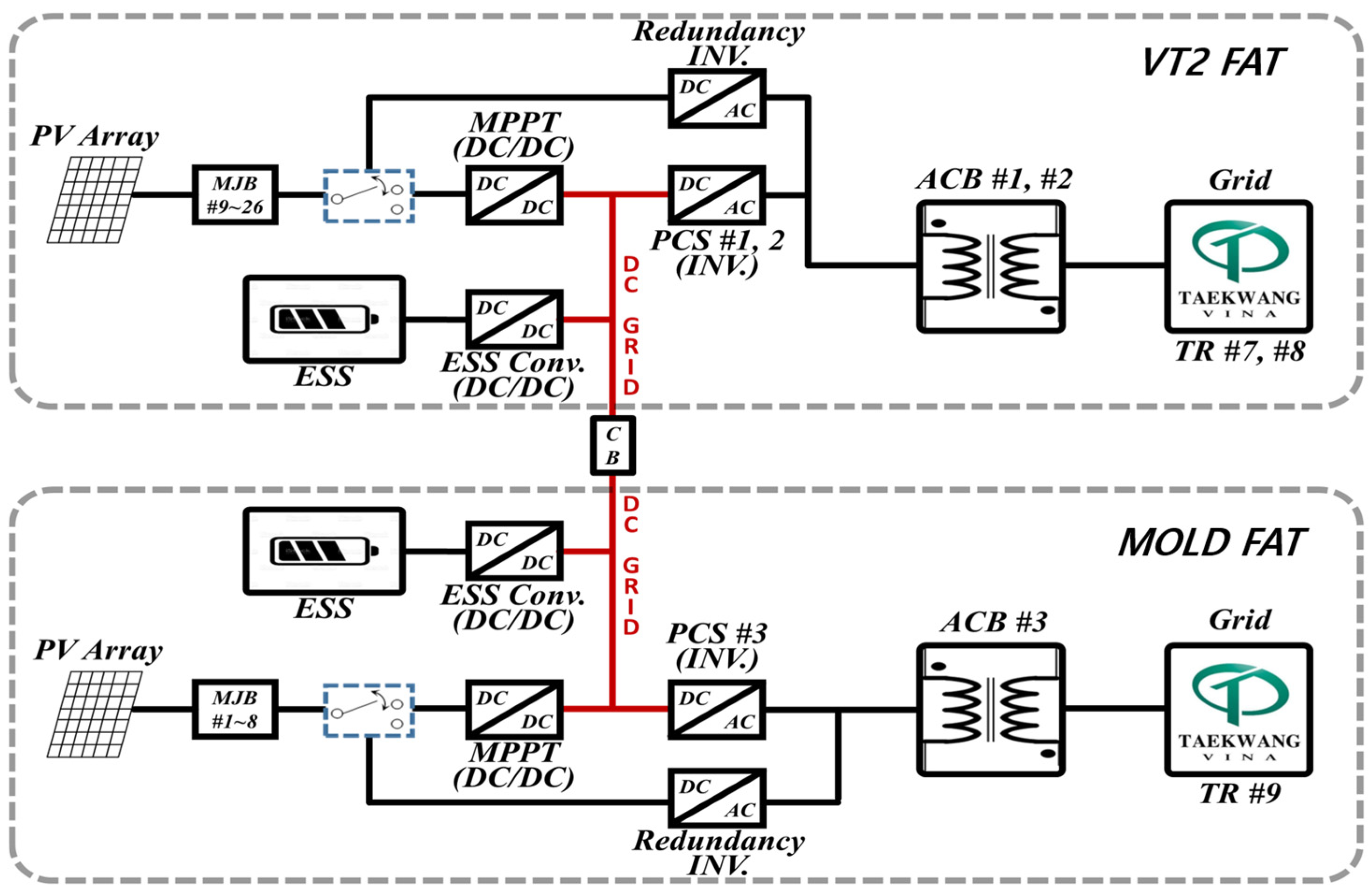
2.1. Overview of the Vietnam Demonstration Site
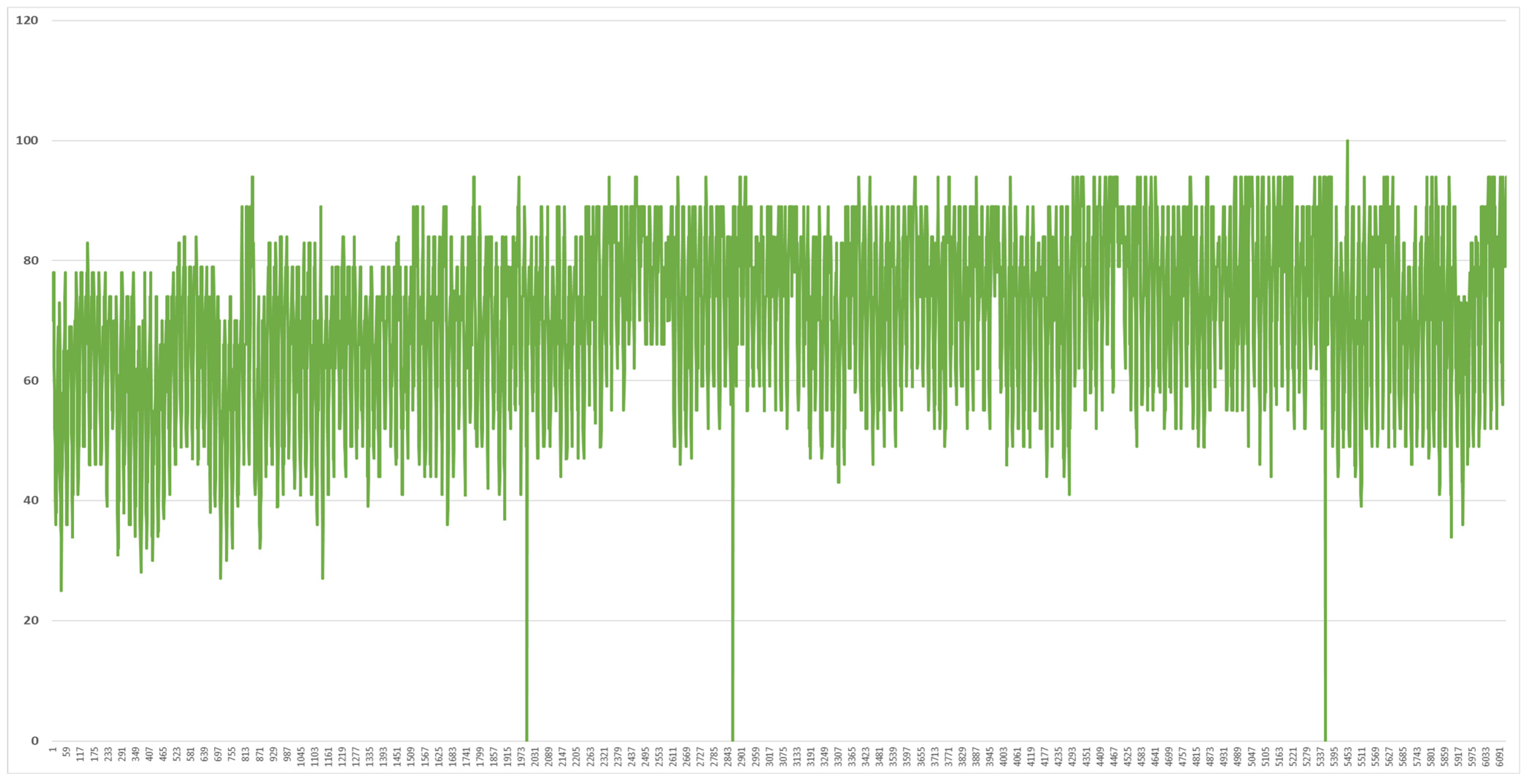
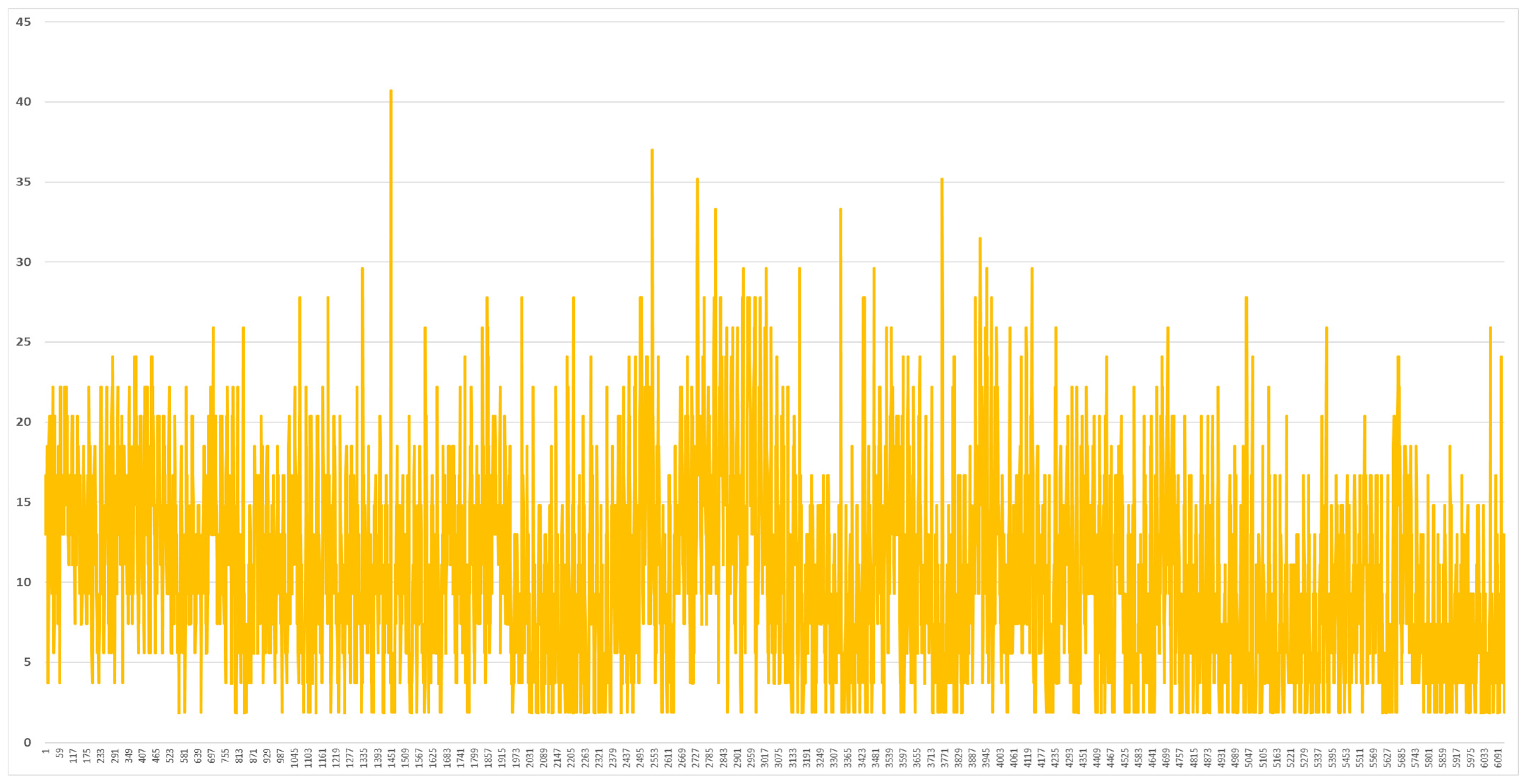
2.2. Analysis of Meteorological Data in Vietnam
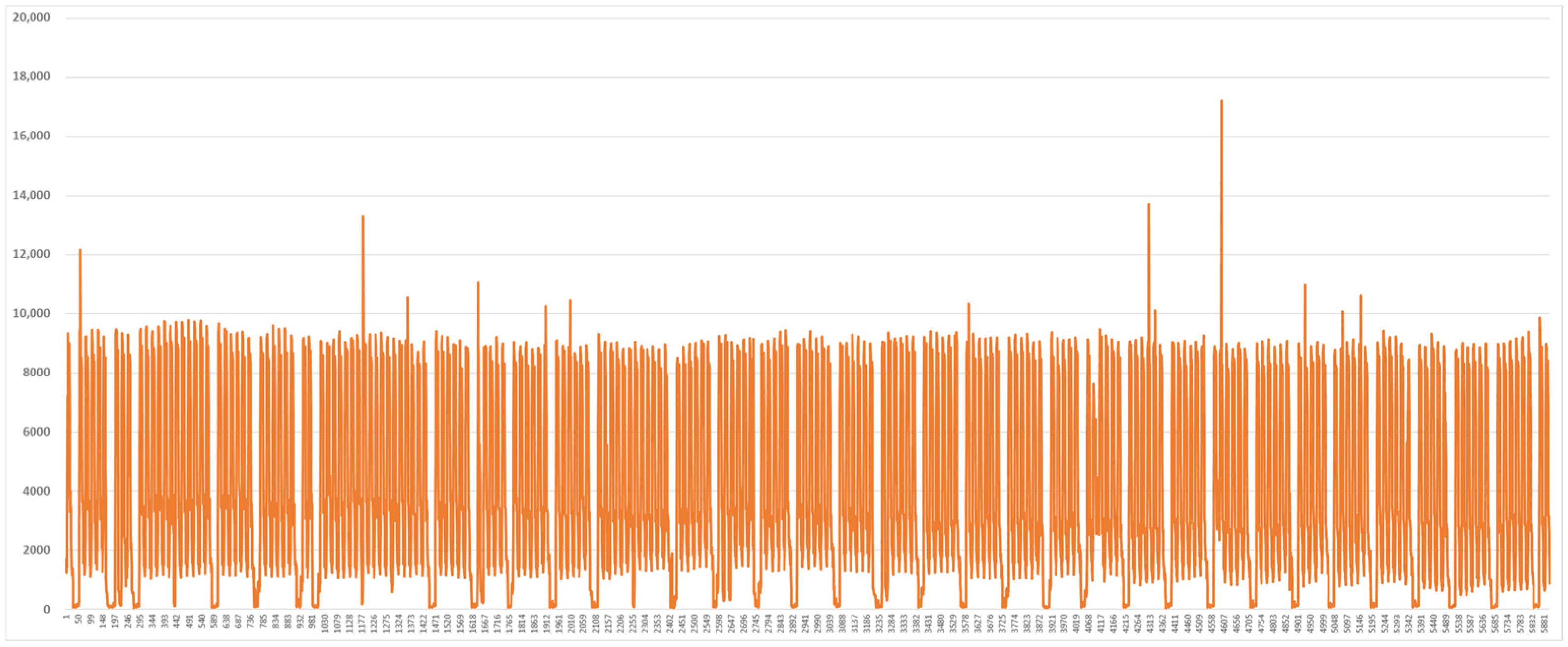
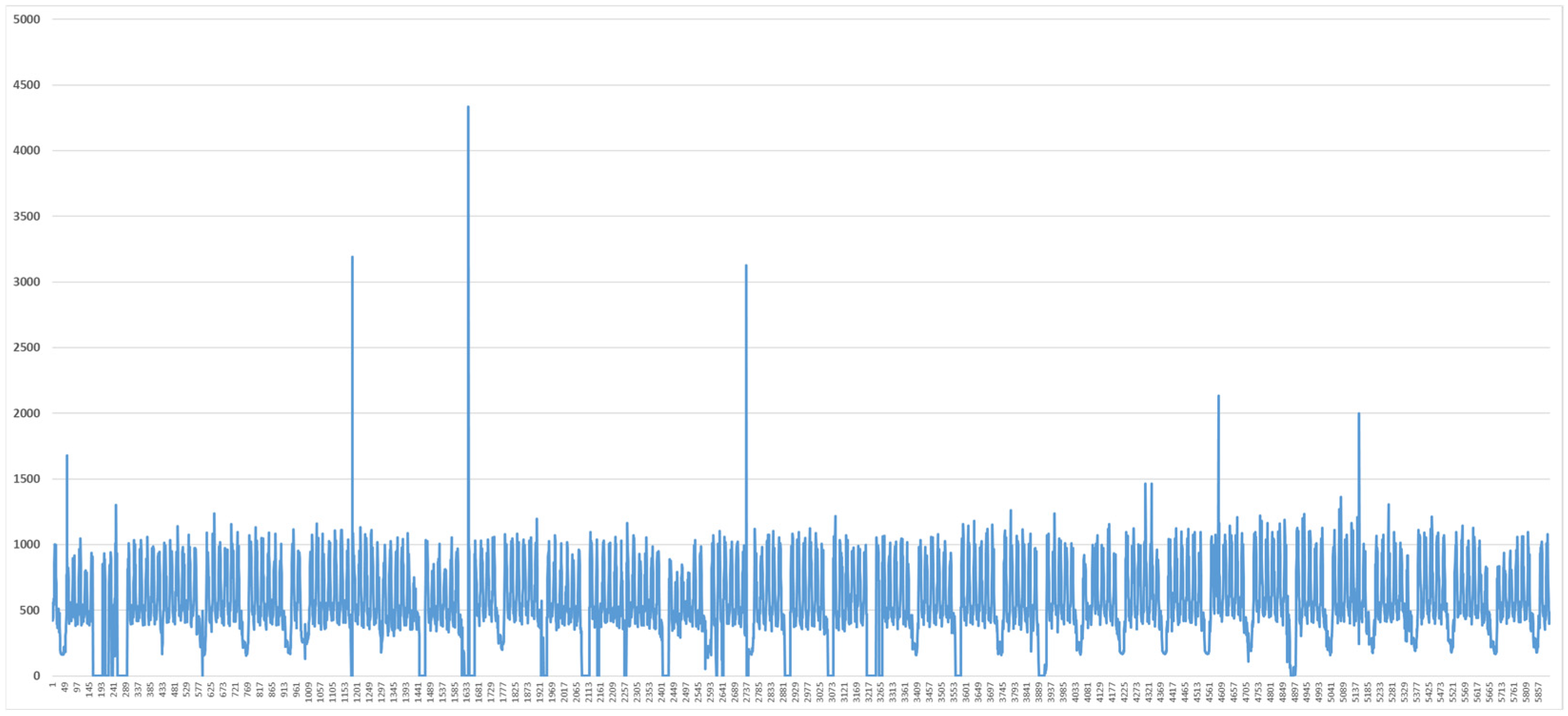
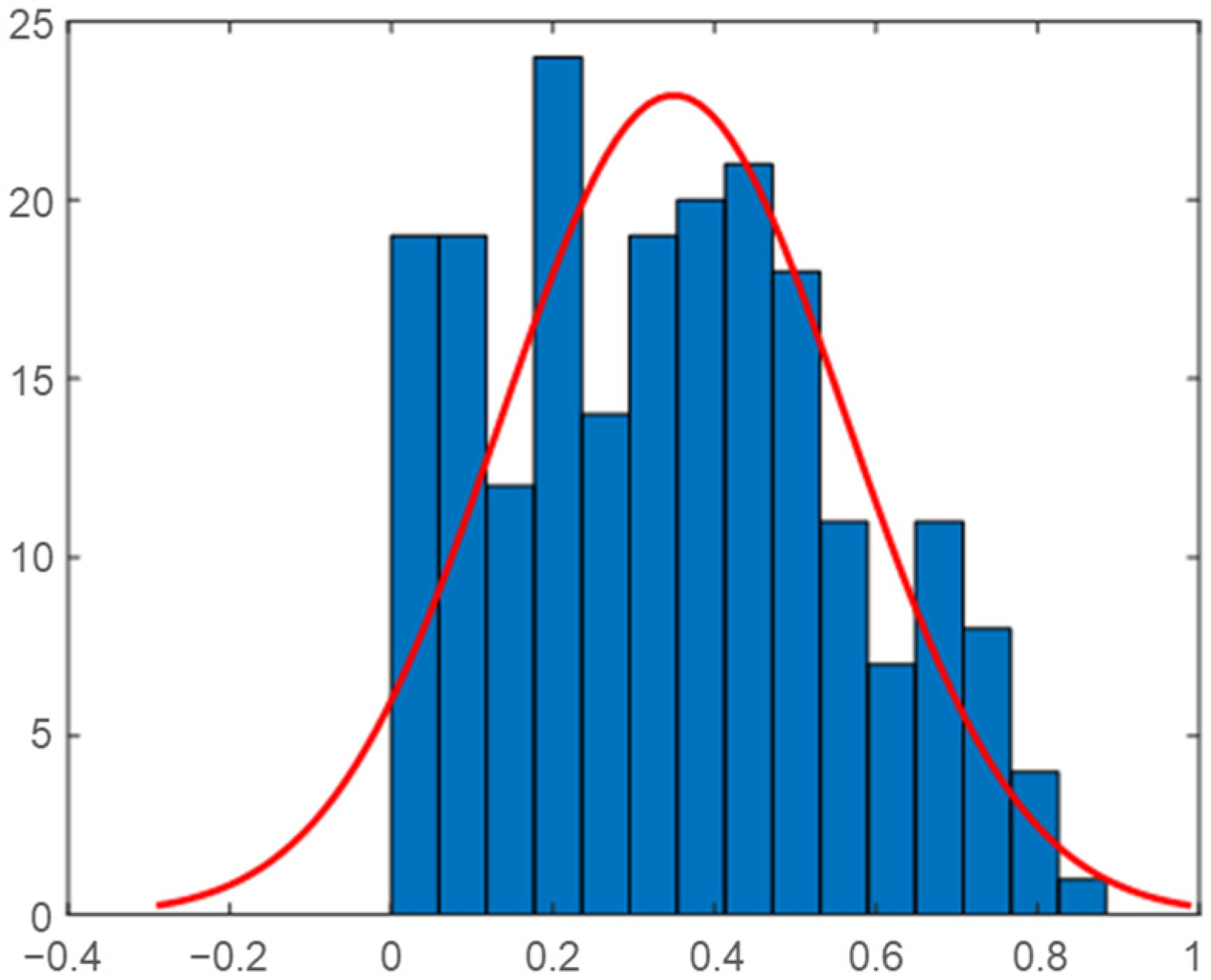
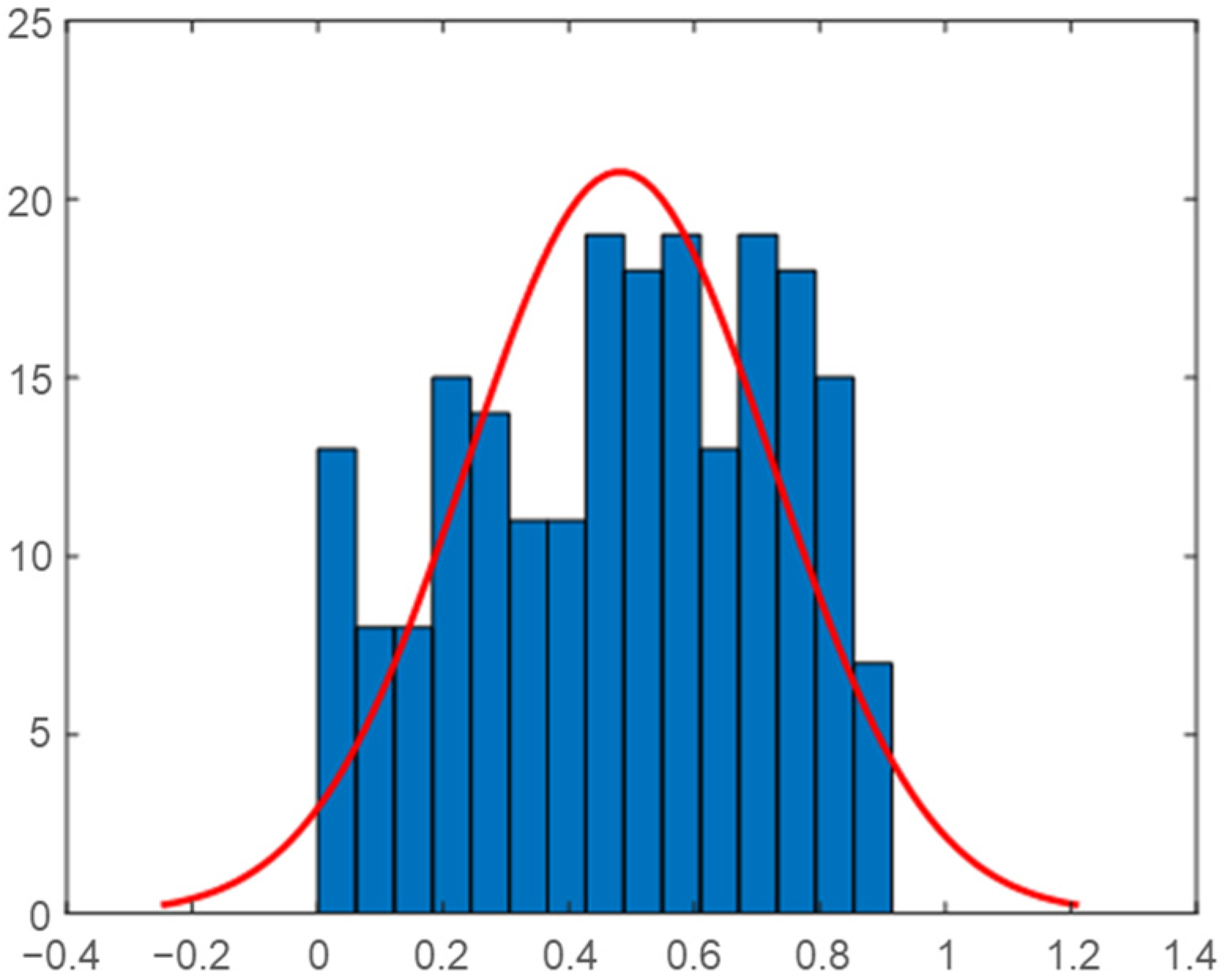
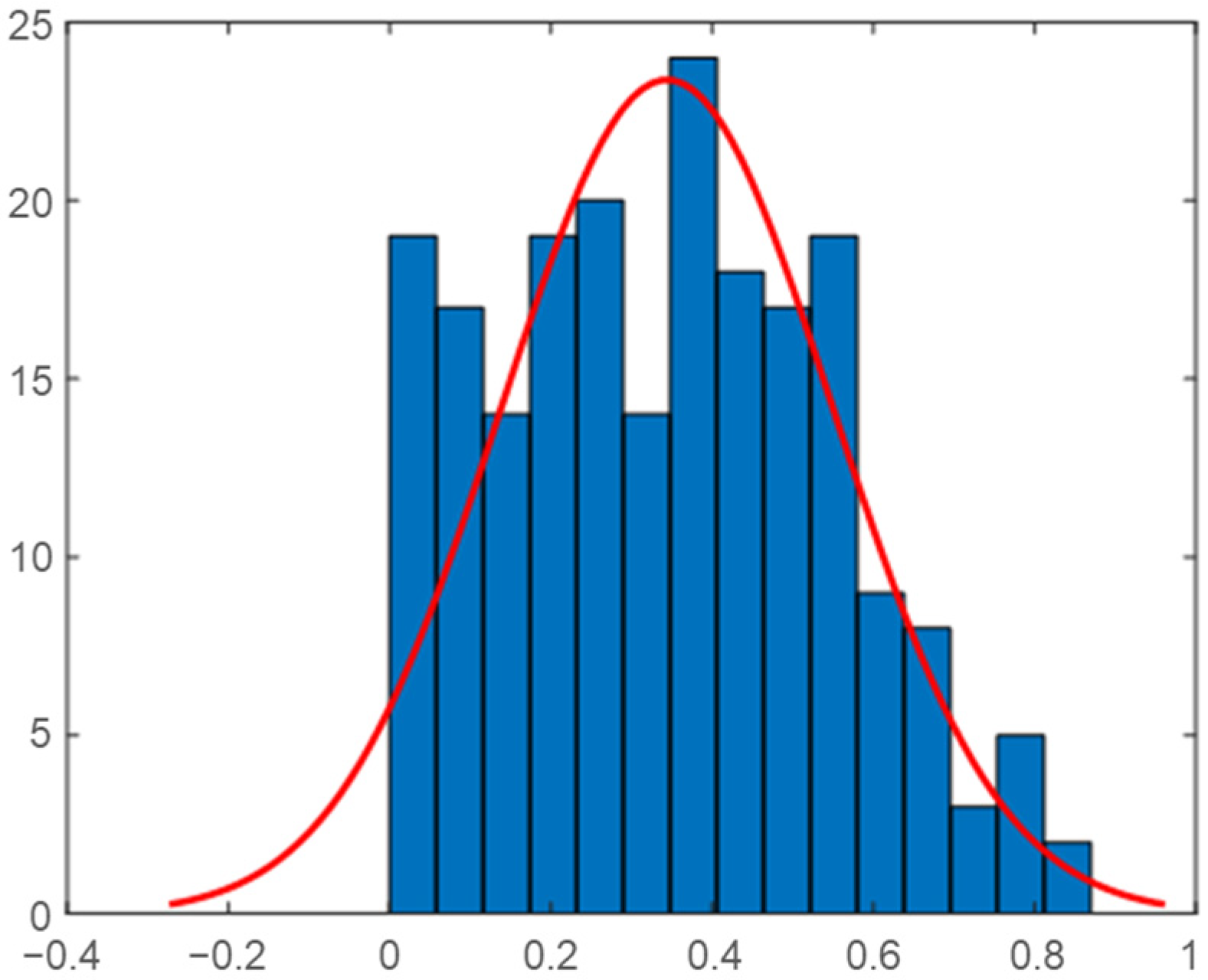
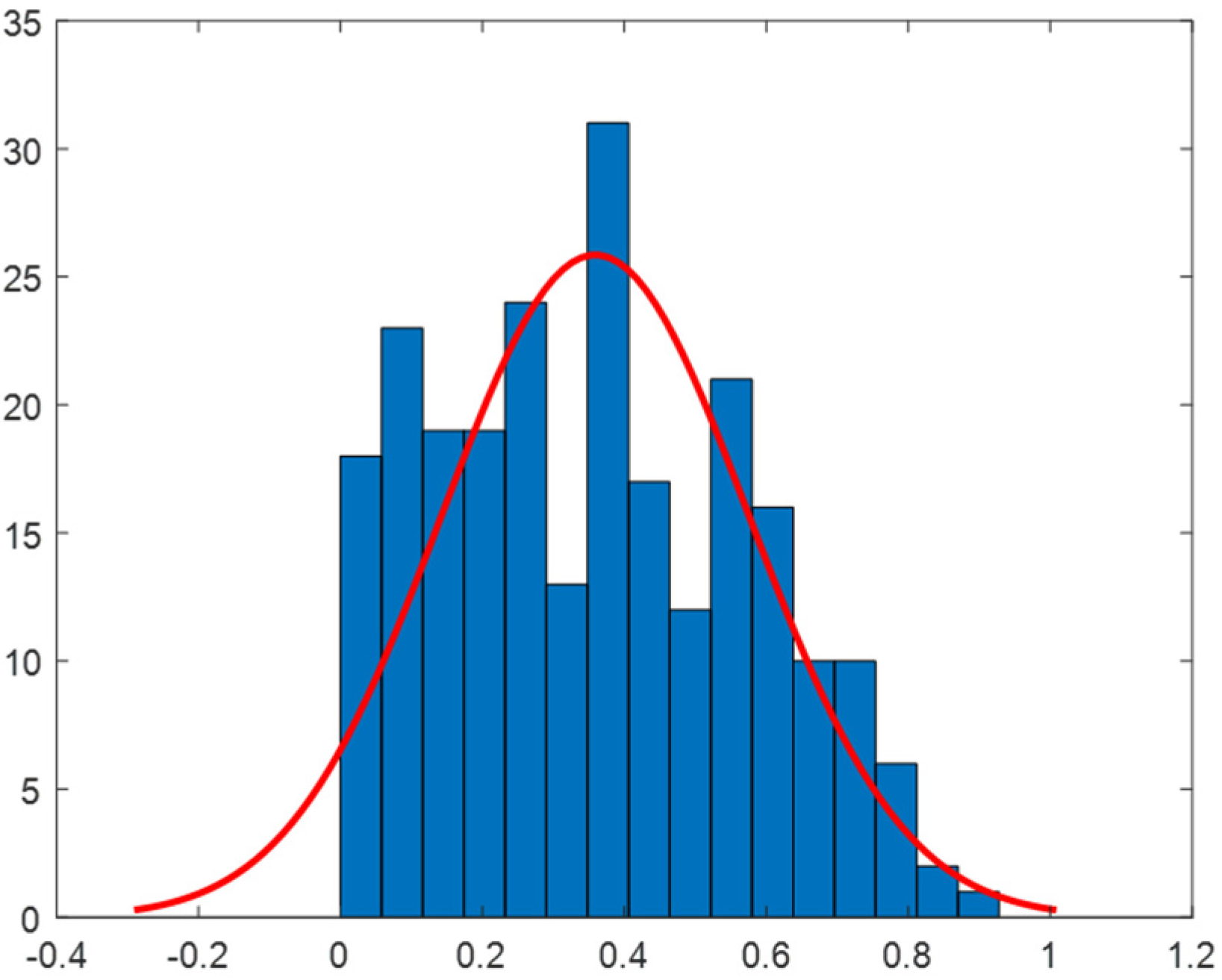
2.3. Analysis of Load Data in the Vietnam Demonstration Site
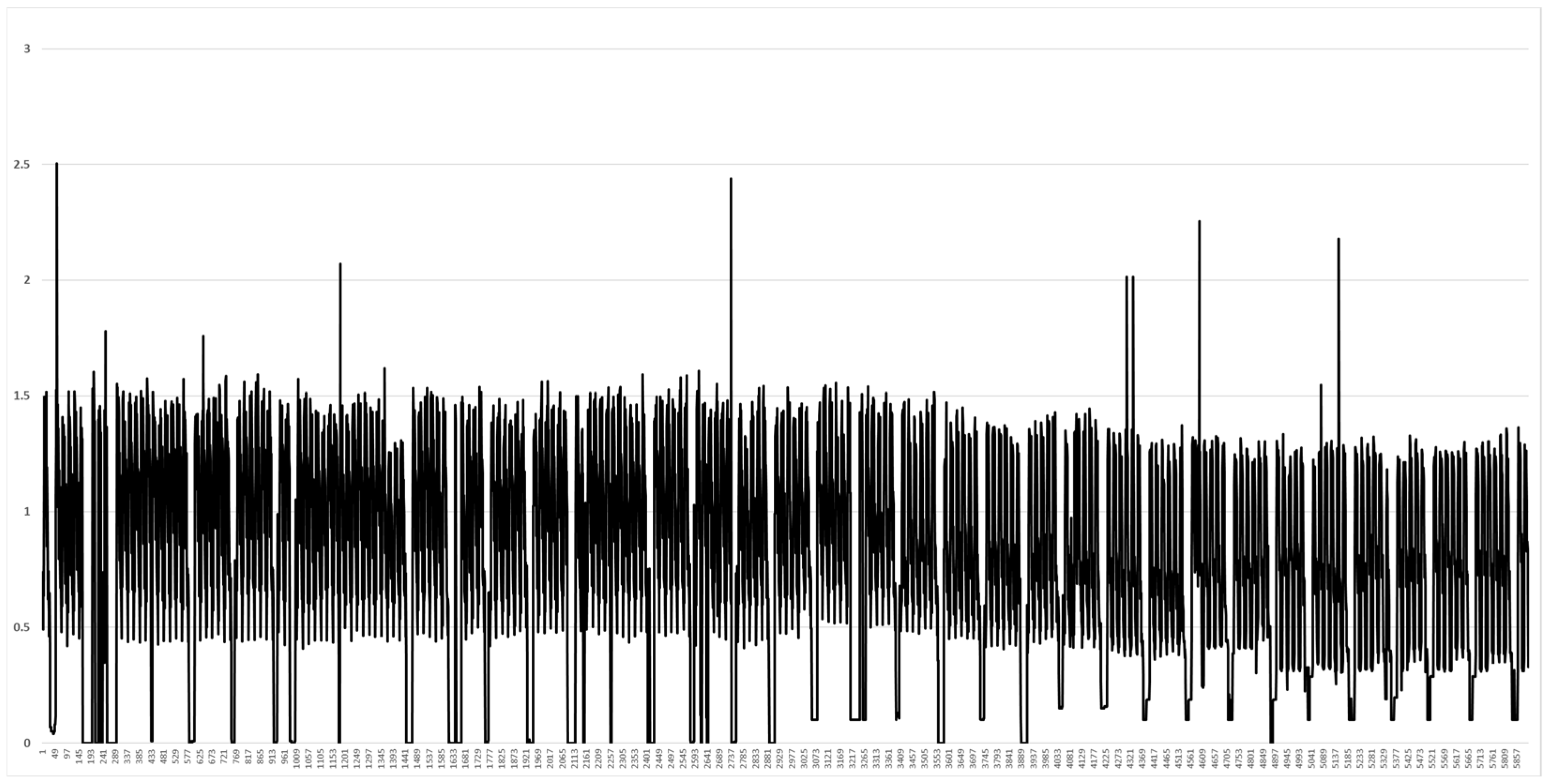
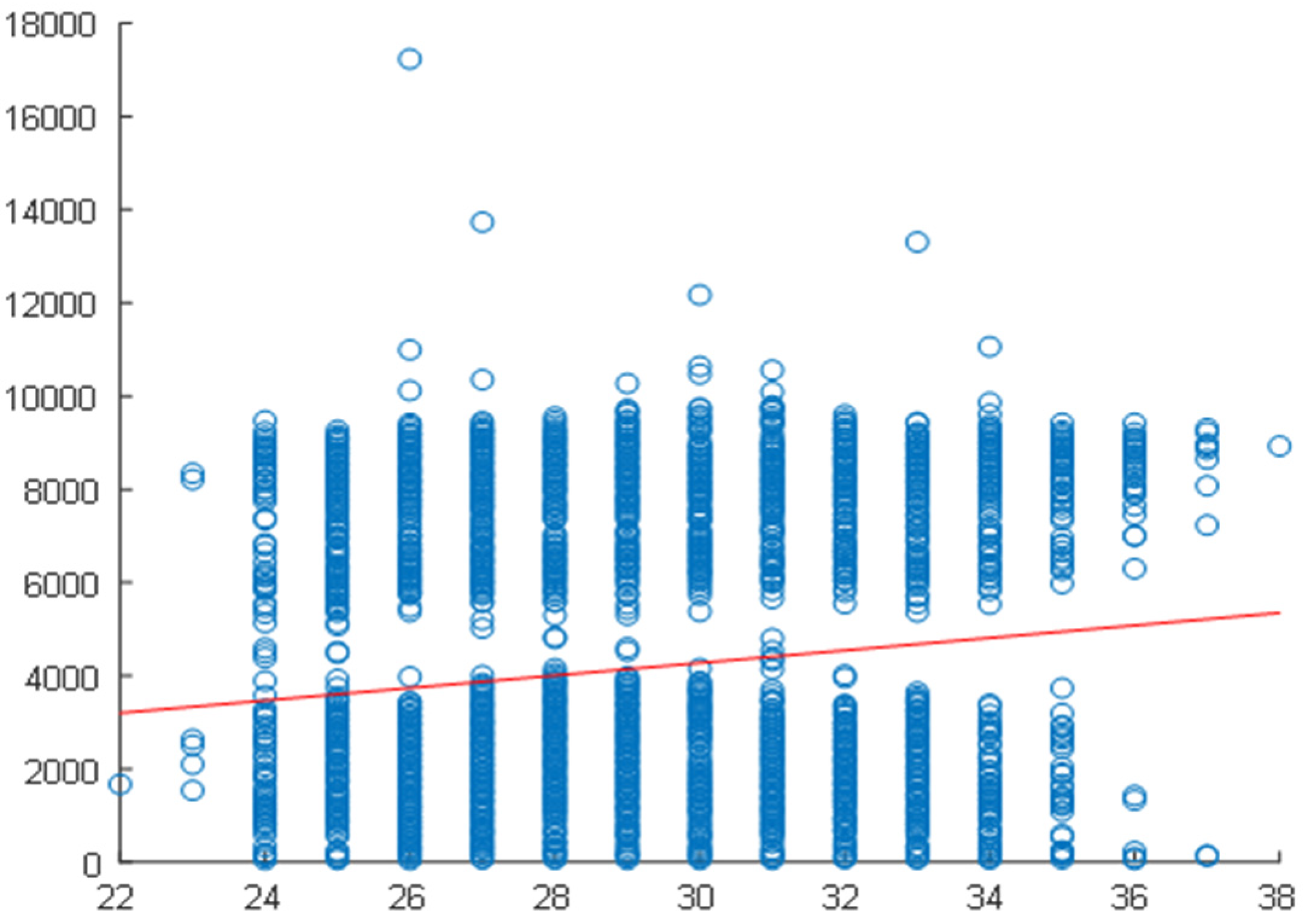
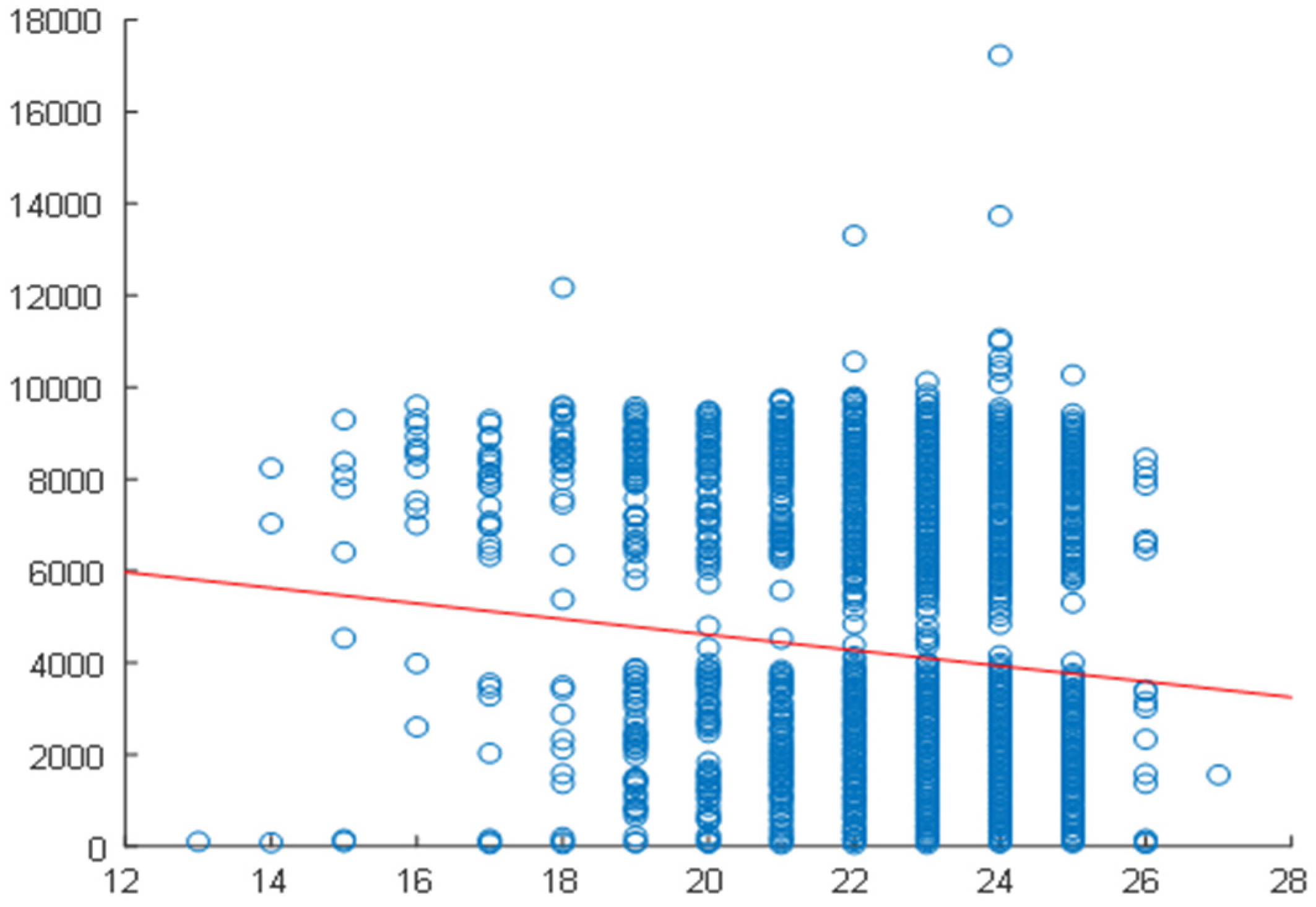
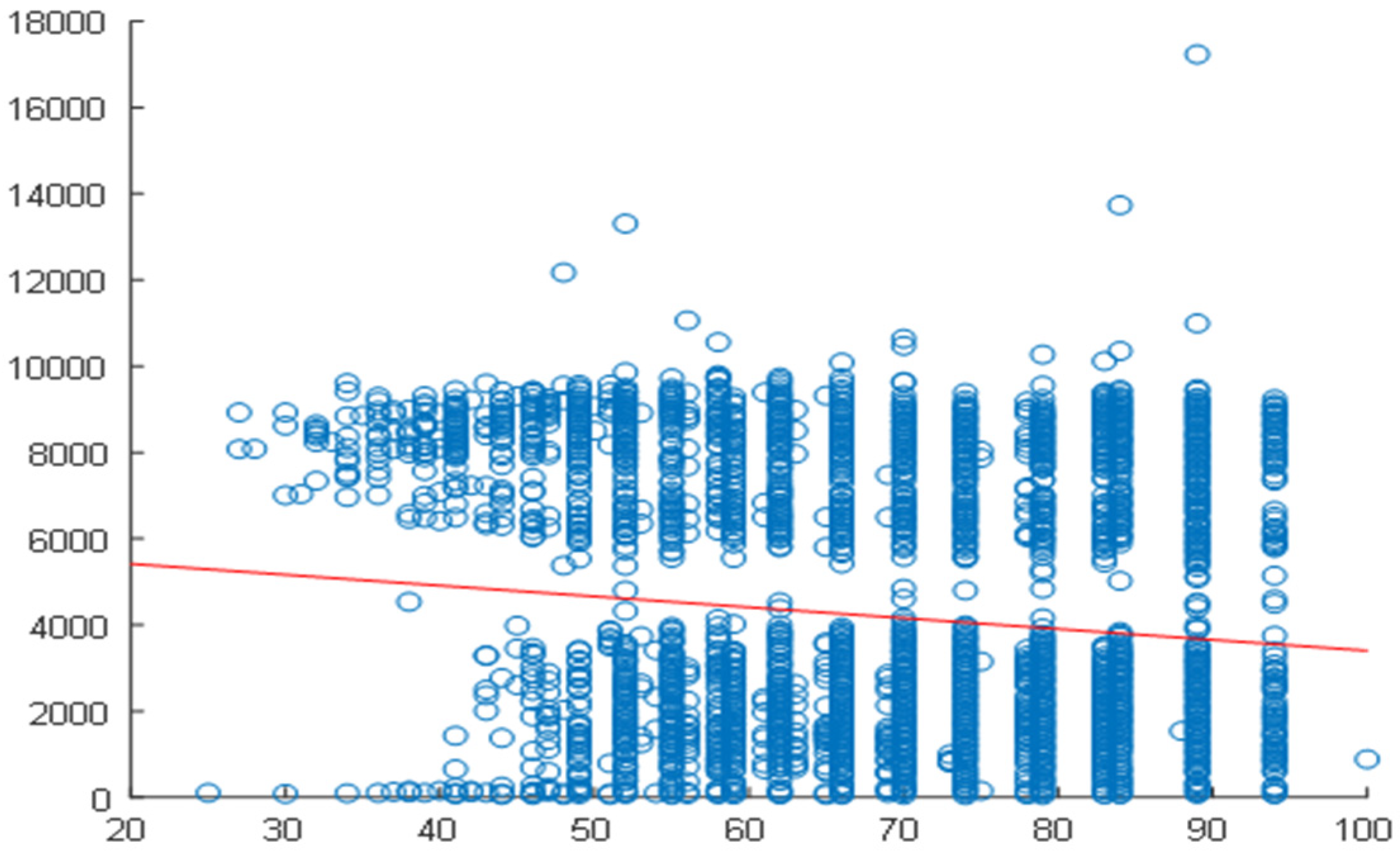
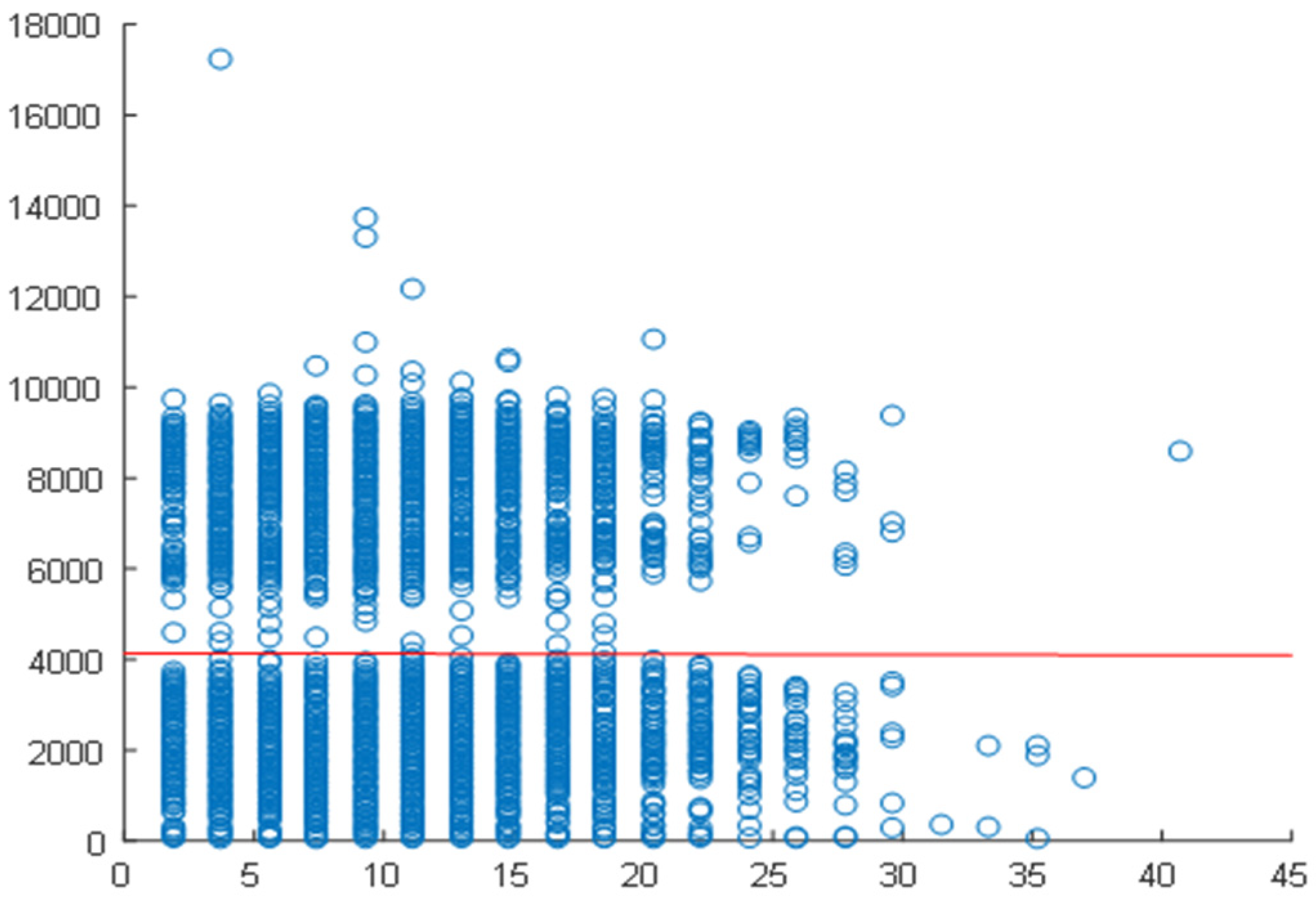
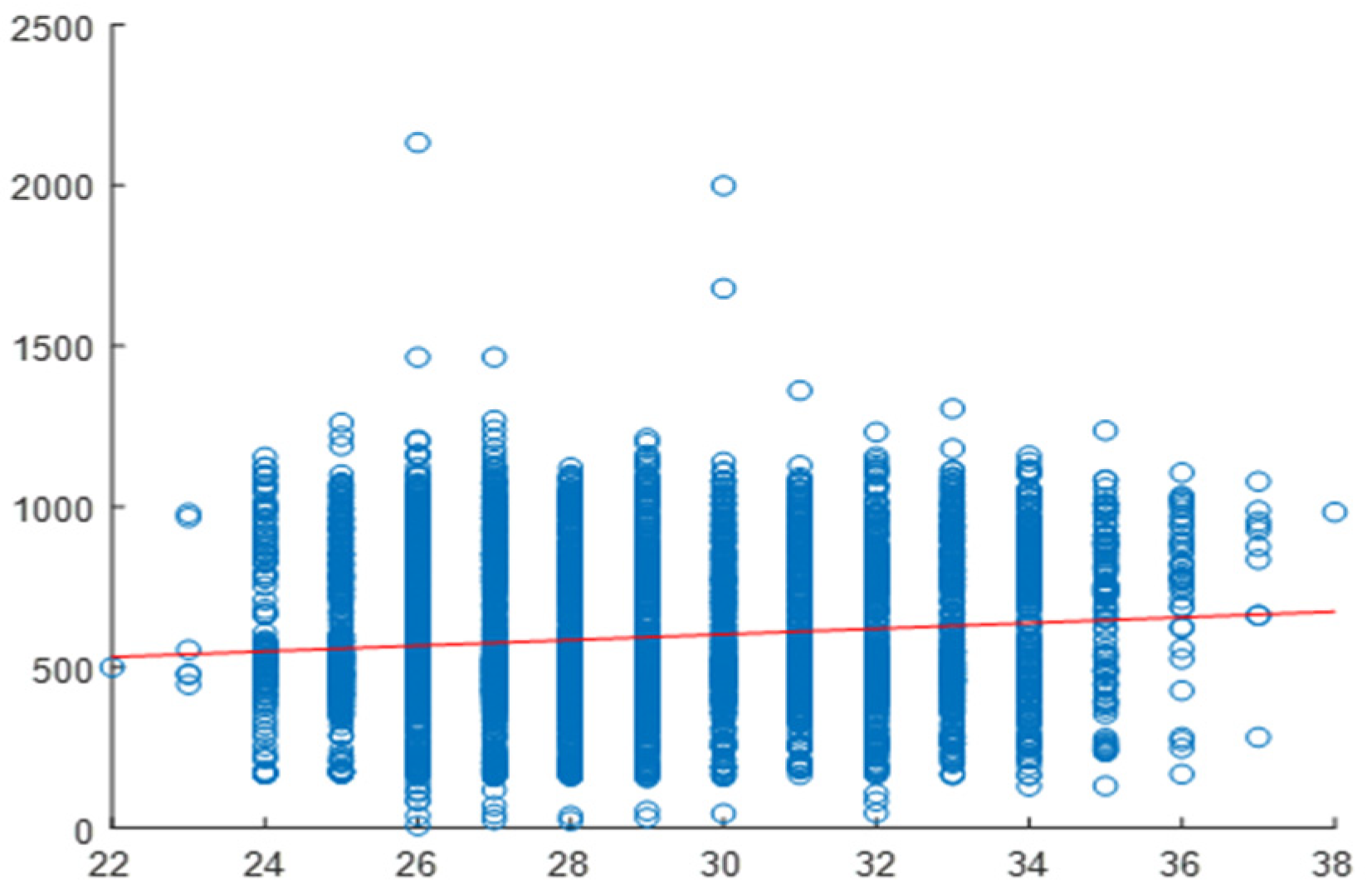
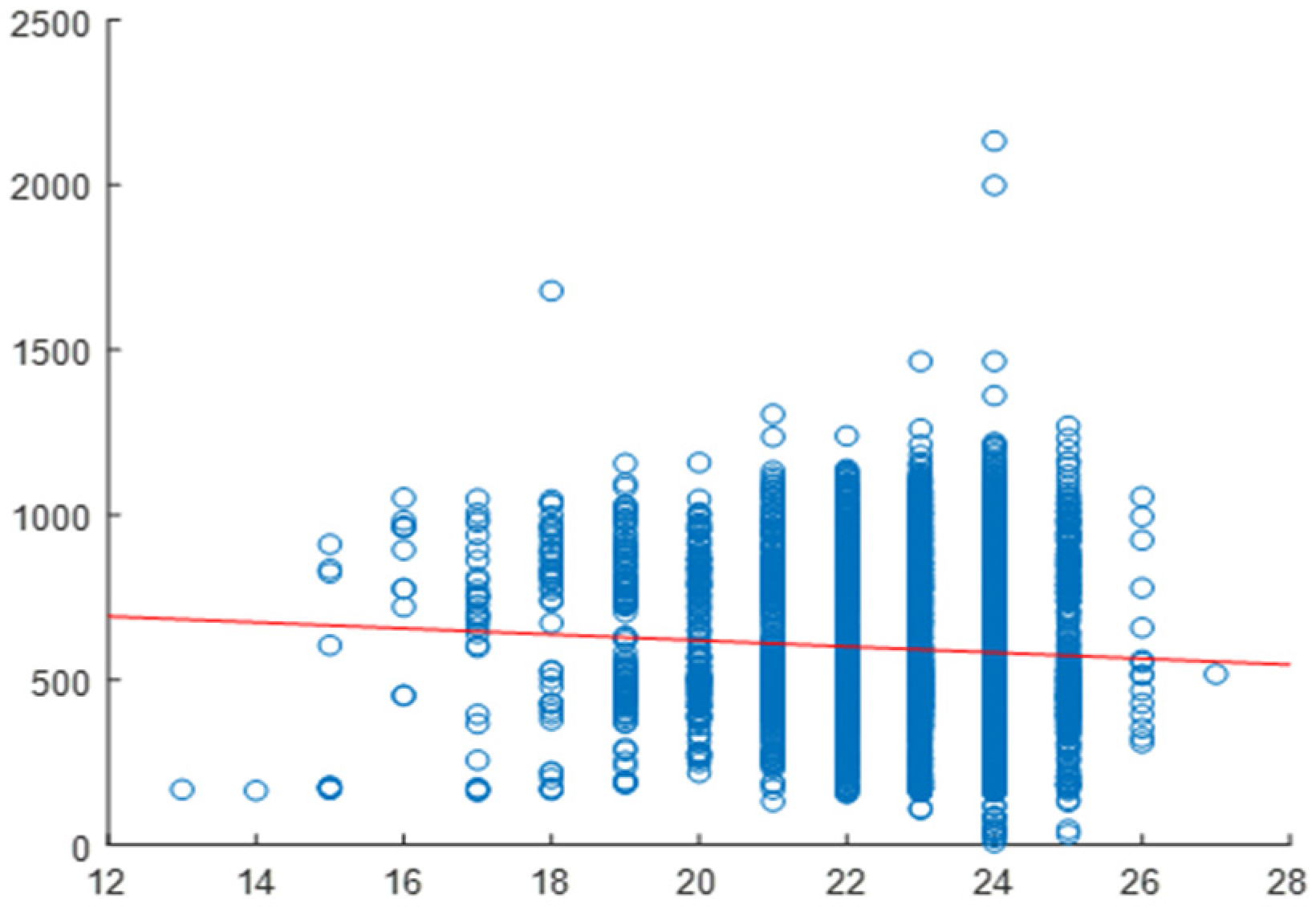
2.4. Correlation Analysis
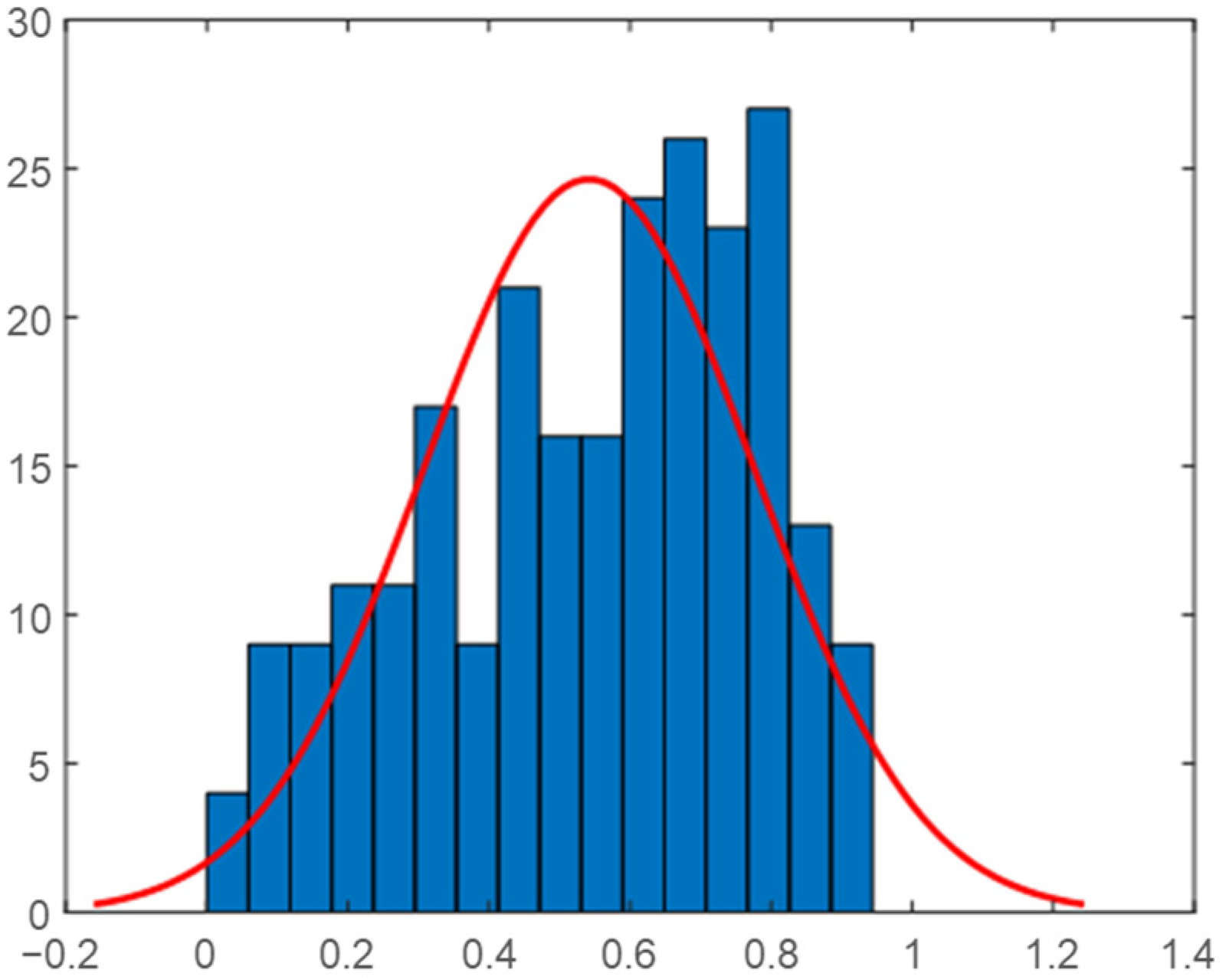
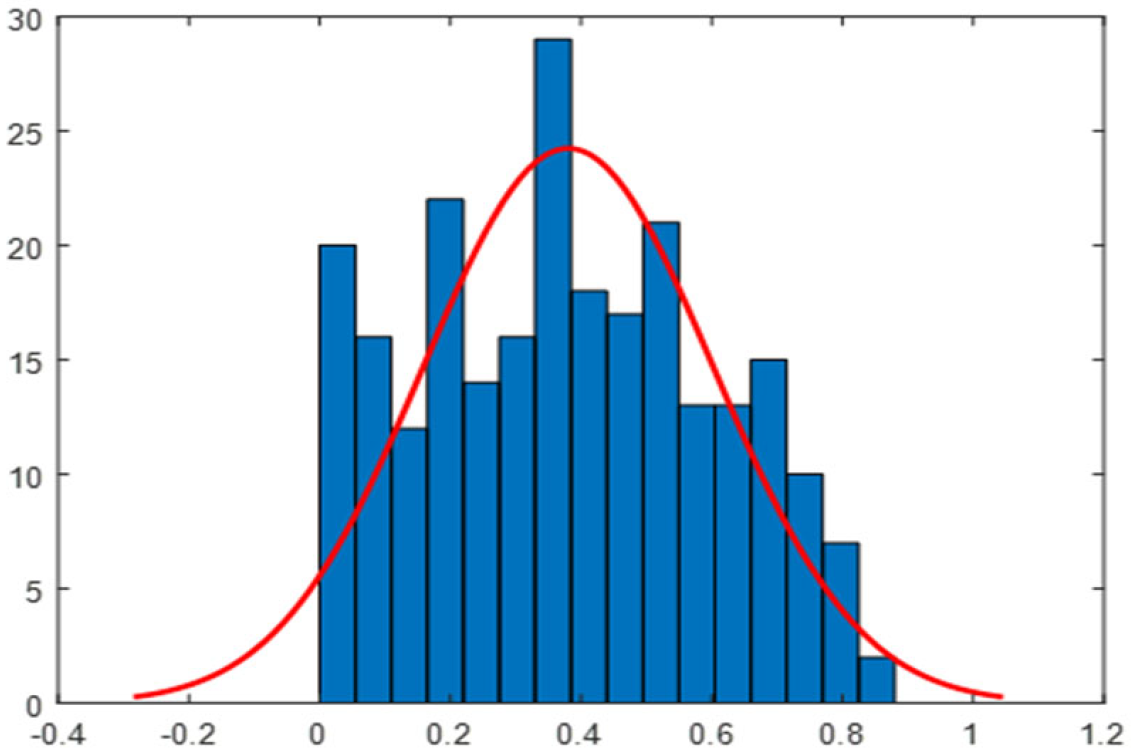
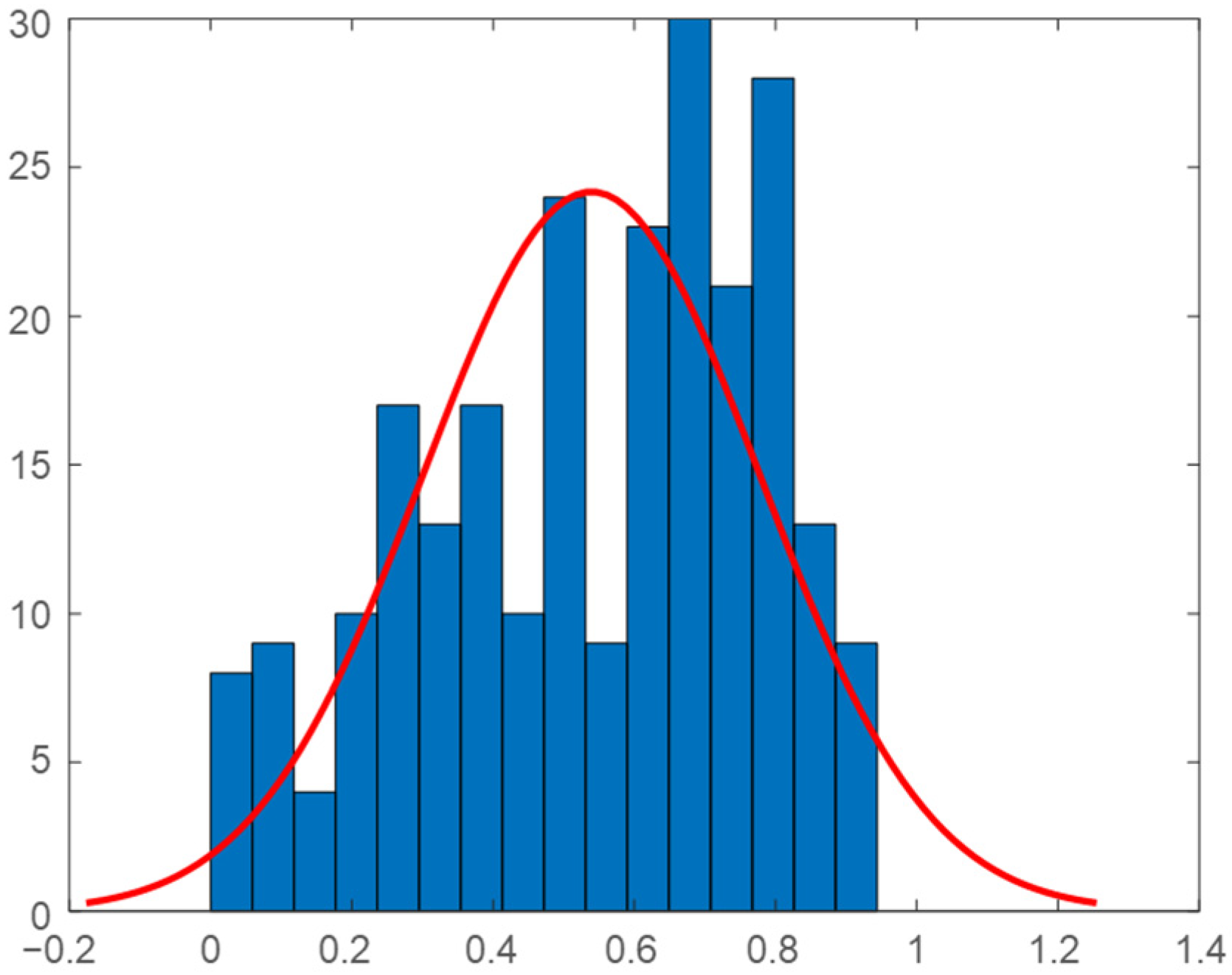
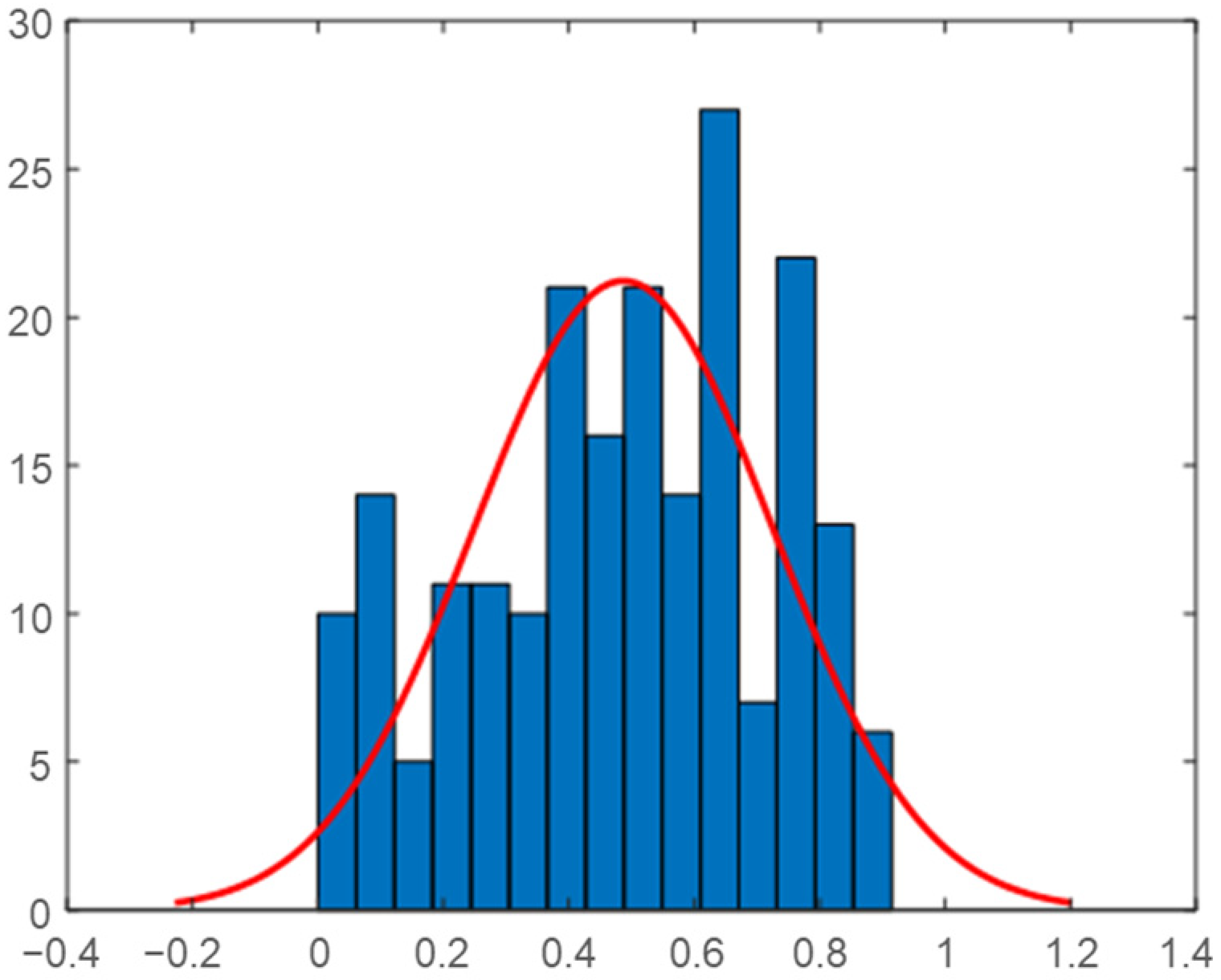
2.5. Daily Correlation Trend Analysis
3. Methodology
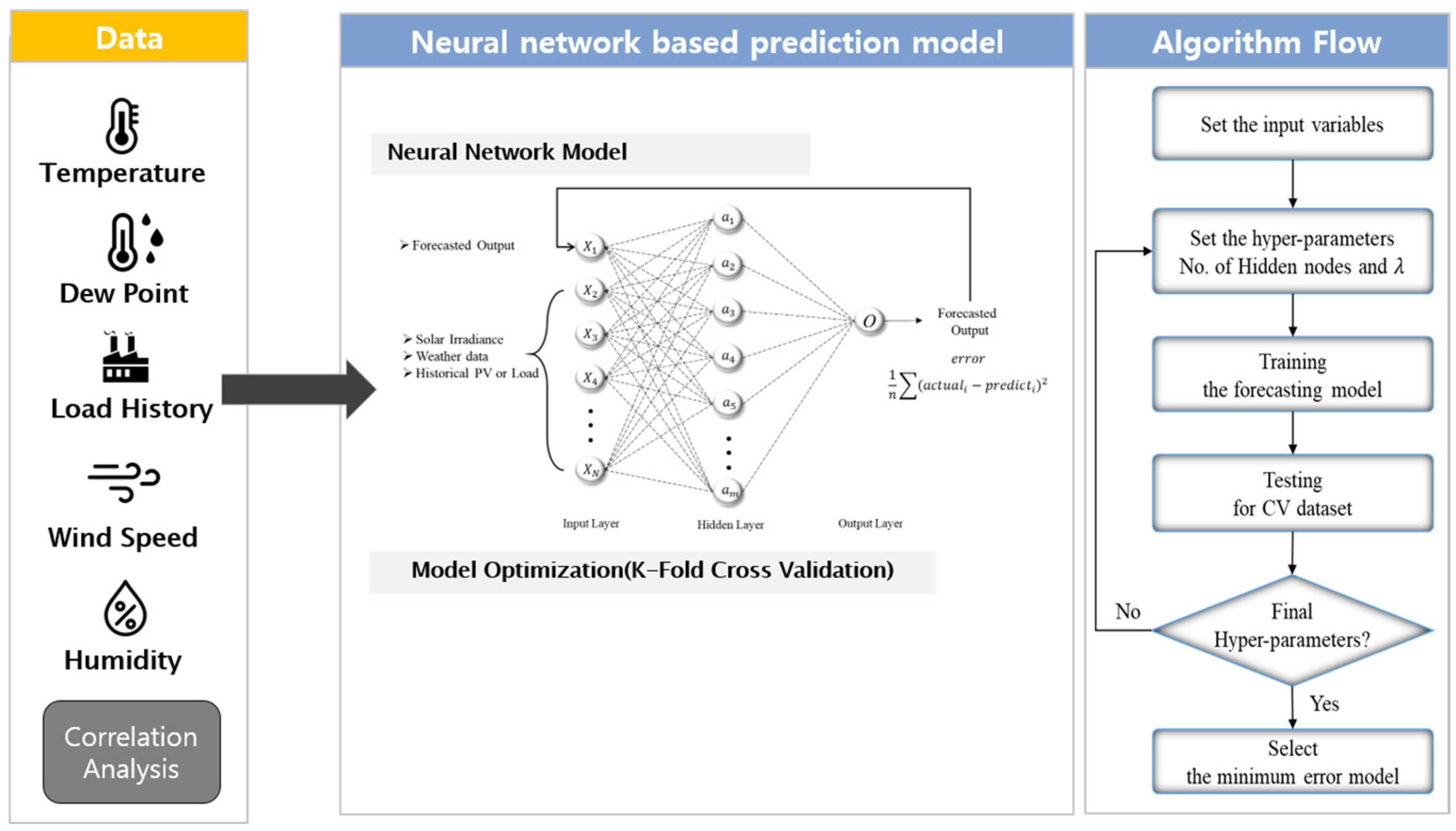
3.1. ANN Model Design
3.2. Model Training and Evaluation
3.3. Forecasting Approach
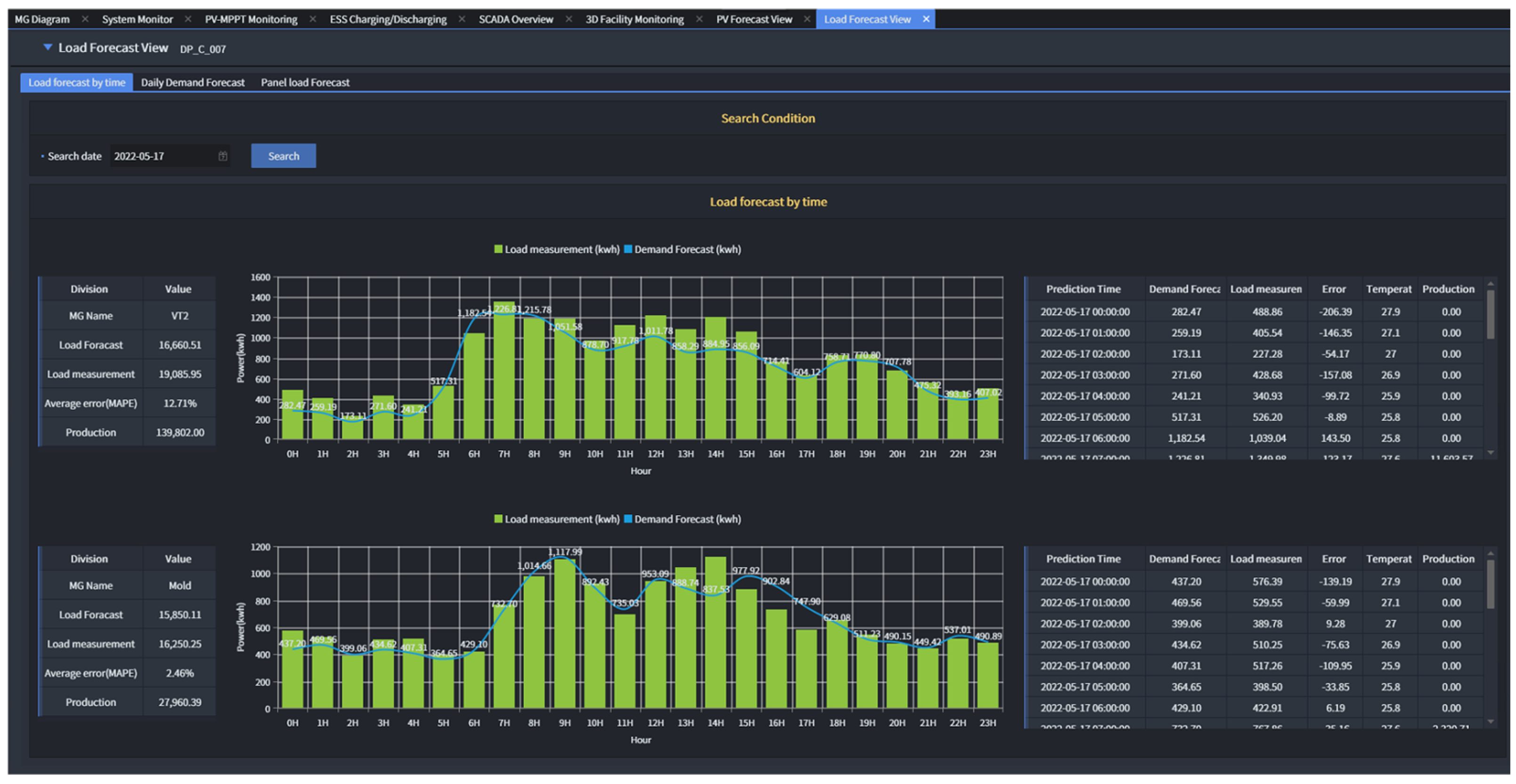
4. Results and Performance Evaluation
5. EMS Operation Strategy Based on Load Forecasting
5.1. Forecast-Aided Load Scheduling
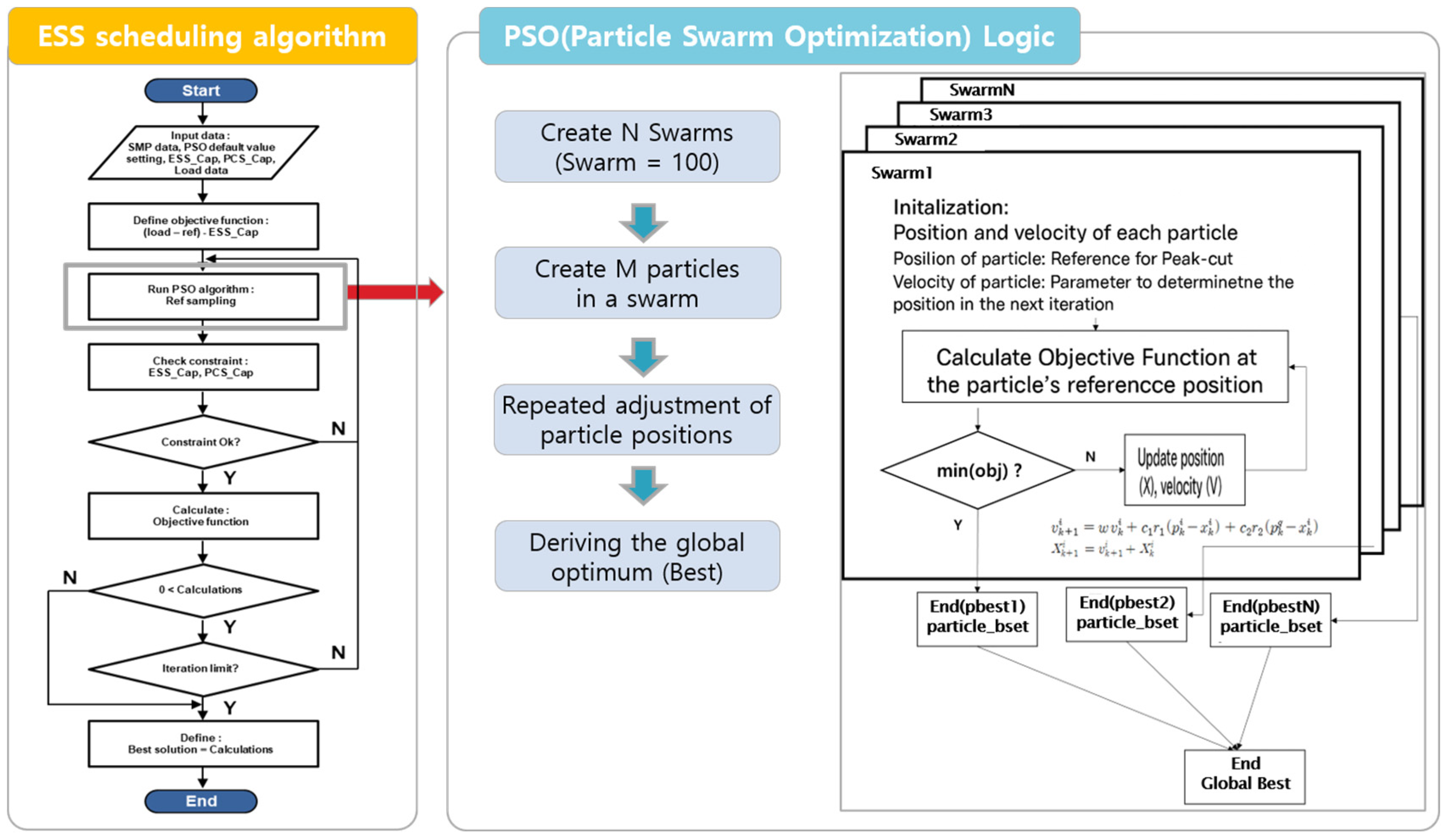
5.2. Economic Operation with PSO Algorithm
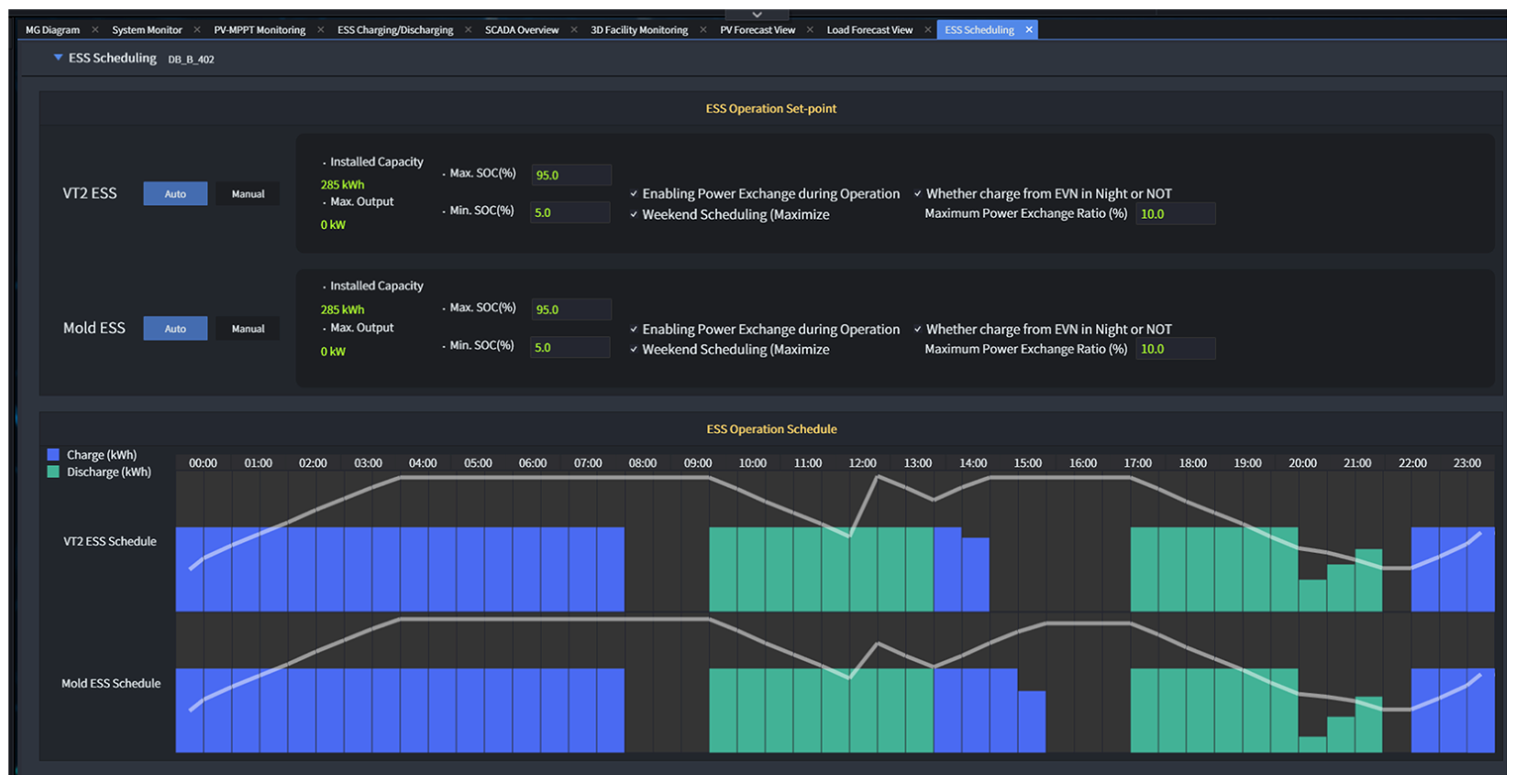
5.2.1. PSO Algorithm for ESS Scheduling
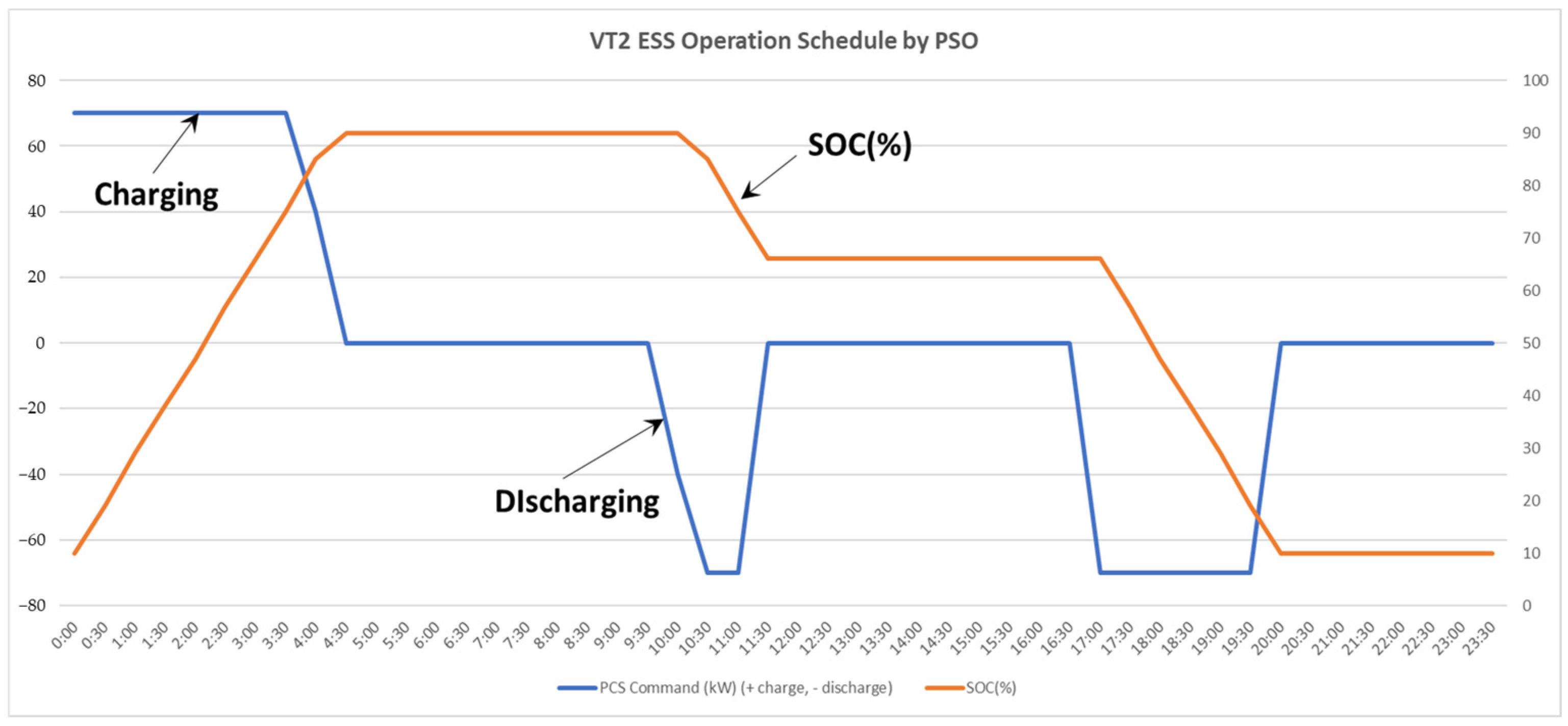
5.2.2. VT2 ESS Operation Results
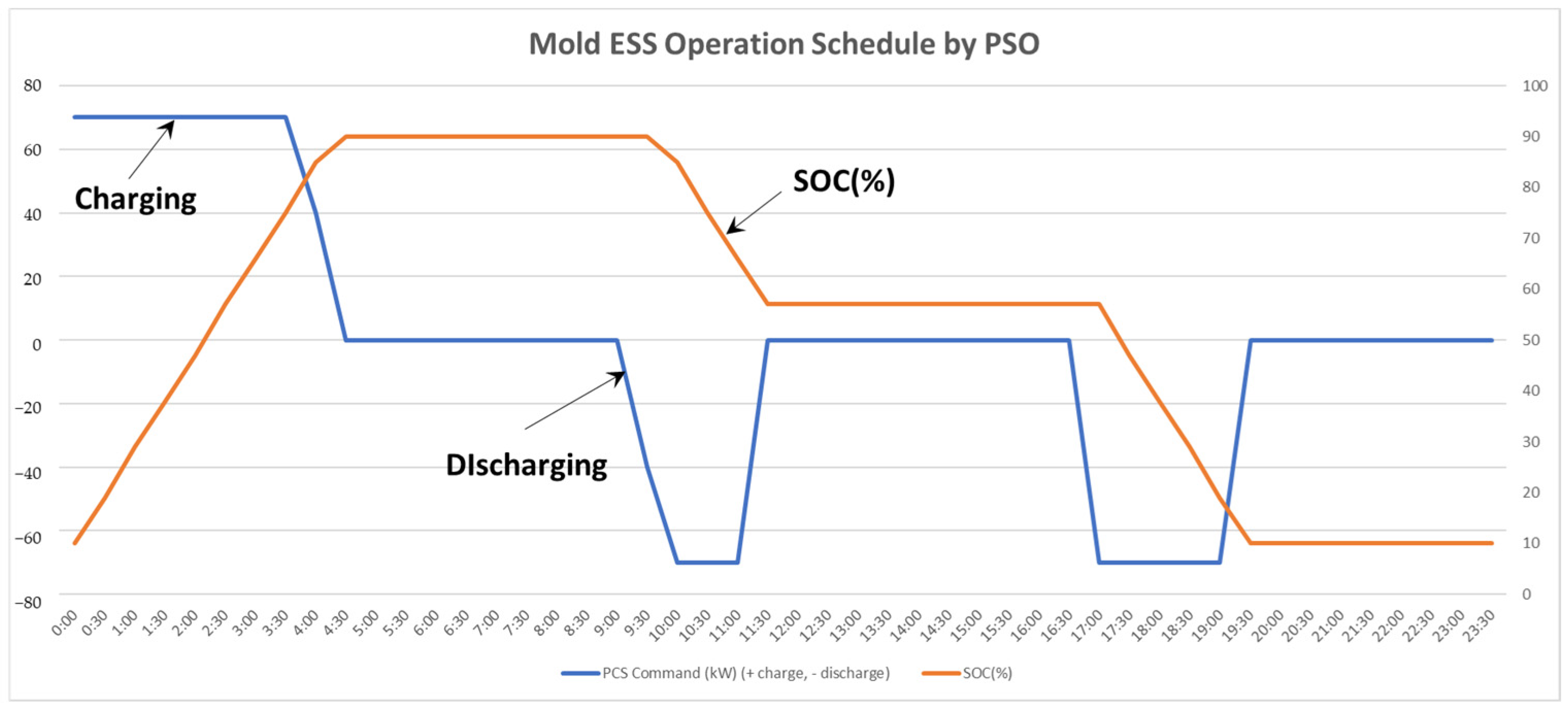
5.2.3. Mold ESS Operation Results
5.3. Multi-Microgrid Flexibility and Fault Resilience
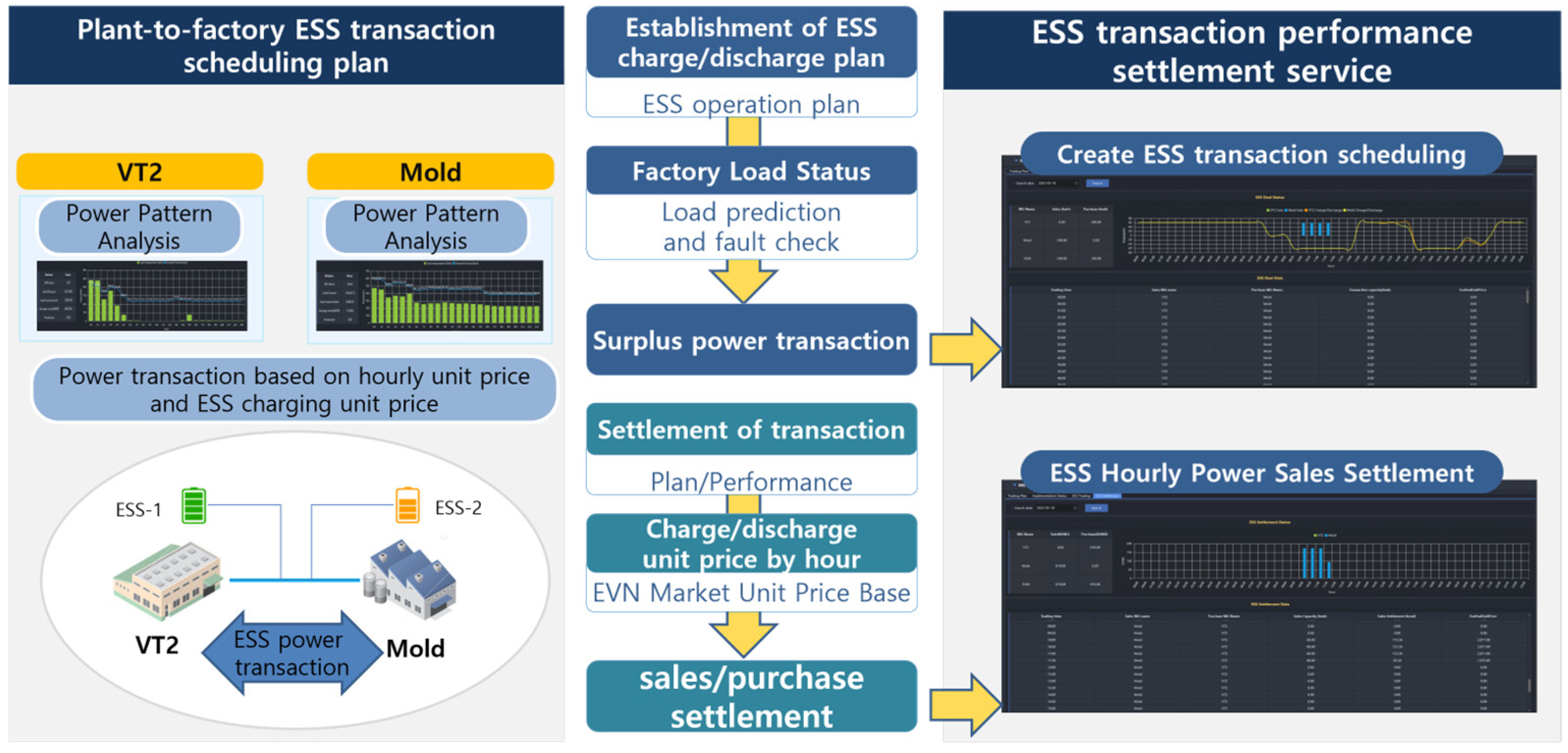
5.4. ESS Power Transaction and Settlement
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heldeweg, M.A.; Séverine, S. Renewable energy communities as ‘socio-legal institutions’: A normative frame for energy decentralization? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urishev, B. Decentralized Energy Systems, Based on Renewable Energy Sources. Appl. Sol. Energy 2019, 55, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoot, M.; Diwan, P.; Kandpal, T.C. Review of barriers to the dissemination of decentralized renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; So, S.M.; Kim, J.-T.; Cho, J.-W.; Park, H.-J.; Jufri, F.H.; Jung, J. Microgrids platform: A design and implementation ofcommon platform for seamless microgrids operation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 167, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, M.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C. Short-Term Net Load Forecasting for Regions with Distributed Photovoltaic Systems Based on Feature Reconstruction. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Dong, Z.Y.; Jia, Y.; Hill, D.J.; Zhang, Y. A Review of Deep Learning Methods for Short-Term Load Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Smart Grid and Electrical Automation (ICSGEA 2021), Kunming, China, 29–30 May 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, G.; Li, Y.; Yin, S. Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Outlier Correction, Decomposition, and Ensemble Reinforcement Learning. Energies 2023, 16, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Raihani, A.; Bouattane, O. Sustainable Intelligent Energy Management System for Microgrid Using Multi-Agent Systems: A Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Oliva, D.; Colmenar-Santos, A.; Rosales-Asensio, E. A Review of the State of the Art of Industrial Microgrids Based on Renewable Energy. Electronics 2022, 11, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg-Ganz, E.; Segev, I.; Balabanov, A.; Segev, E.; Kaully Naveh, S.; Machlev, R.; Belikov, J.; Katzir, L.; Keren, S.; Levron, Y. Reinforcement Learning Model-Based and Model-Free Paradigms for Optimal Control Problems in Power Systems: Comprehensive Review and Future Directions. Energies 2024, 17, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gupta, B.B.; Tian, Z. An Edge-AI Based Forecasting Approach for Improving Smart Microgrid Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform 2022, 18, 7946–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W.; McSharry, P.E.; de Menezes, L.M. A Comparison of Univariate Methods for Forecasting Electricity Demand up to a Day Ahead. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, H.B. Modeling and Forecasting Electricity Consumption of Residential Consumers by Using the ARIMA and Hybrid Models. Energy 2017, 124, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Load Forecasting with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S. Short-Term Load Forecasting for Microgrids Based on LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Wen, Y.; Ma, C. Short-Term Load Forecasting Using a Deep Neural Network. Energies 2020, 13, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, I.; Payman, A.; Camara, M.-B.; Dakyo, B. Energy Management in a Renewable-Based Microgrid Using a Model Predictive Control Method for Electrical Energy Storage Devices. Electronics 2024, 13, 4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cen, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Lin, K.; Yang, D. Distributed Optimization of Multi-Microgrid Integrated Energy System with Coordinated Control of Energy Storage and Carbon Emissions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, A.; Al-Durra, A.; El Fouly, T.; El-Saadany, E.F. Multifunctional energy management system for optimized network of microgrids considering battery degradation and load adjustment. J. Energy Storage 2024, 100, 113709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, C.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Lee, S.E.; Shah, K.K. A Review on Time Series Forecasting Techniques for Building Energy Consumption. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 902–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.-h. High-Definition Dynamic Voltage Restorer Systems Using Equivalent Time Sampling Techniques and Circular Structural Memory Filters. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




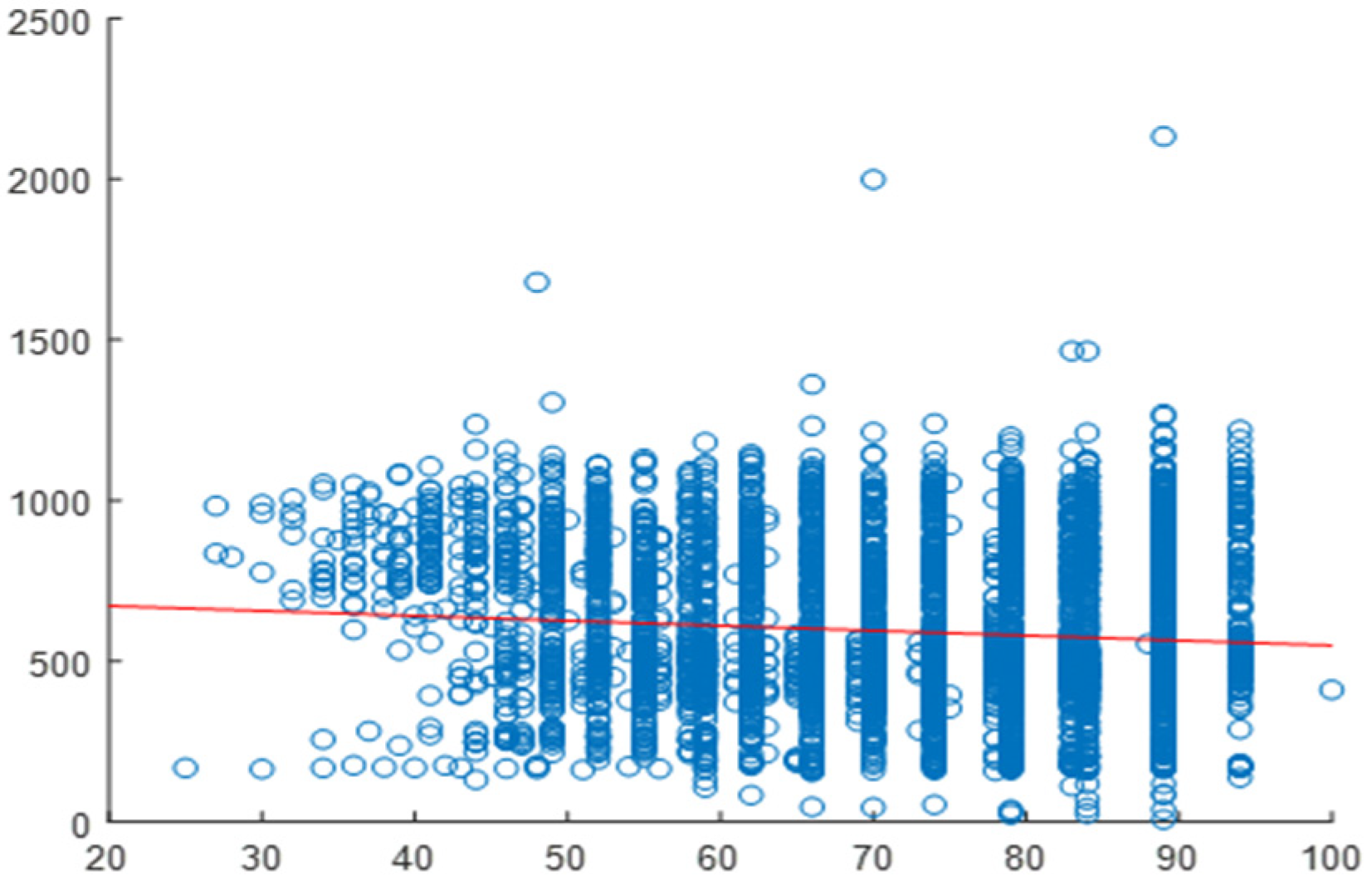
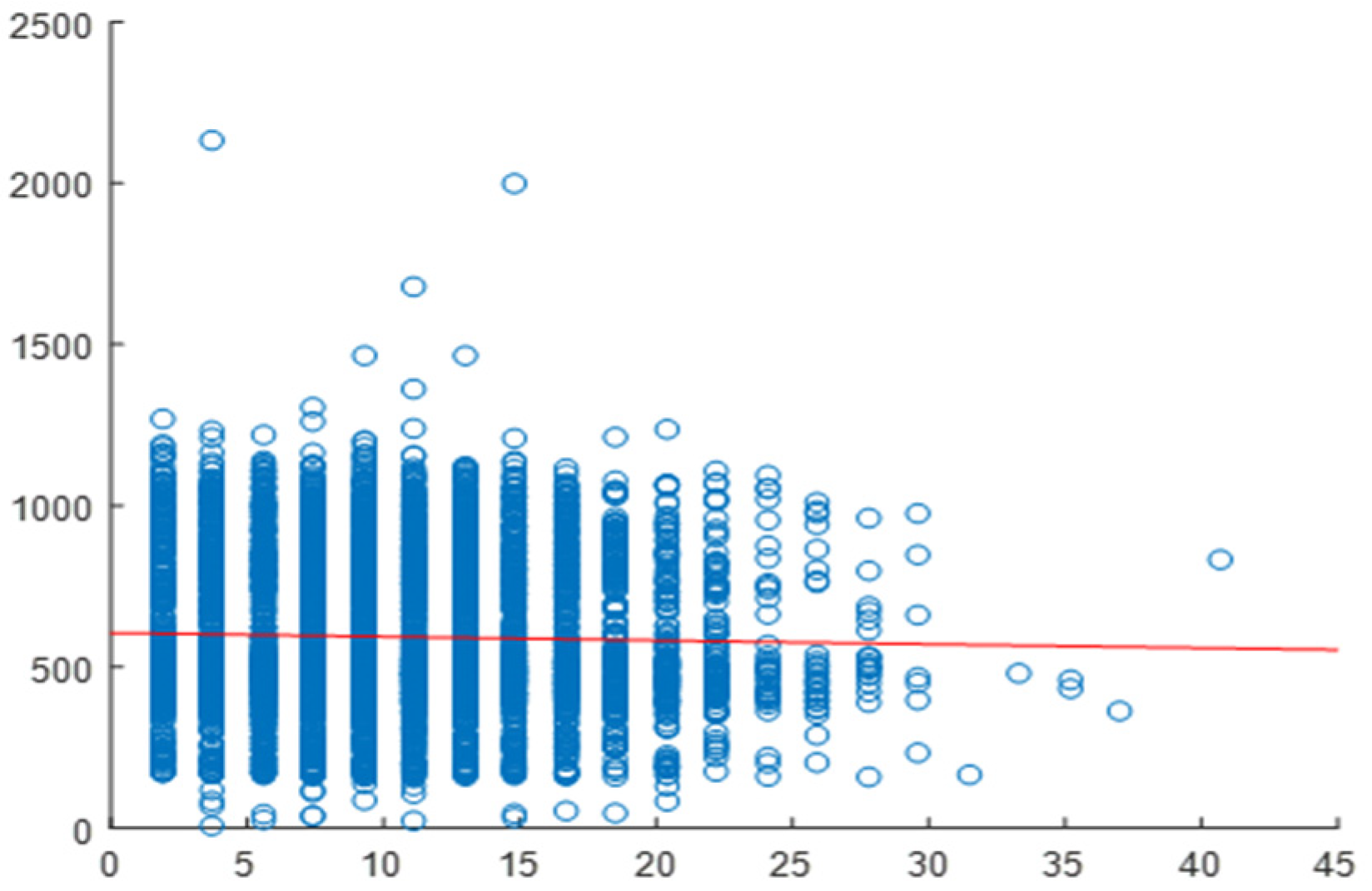
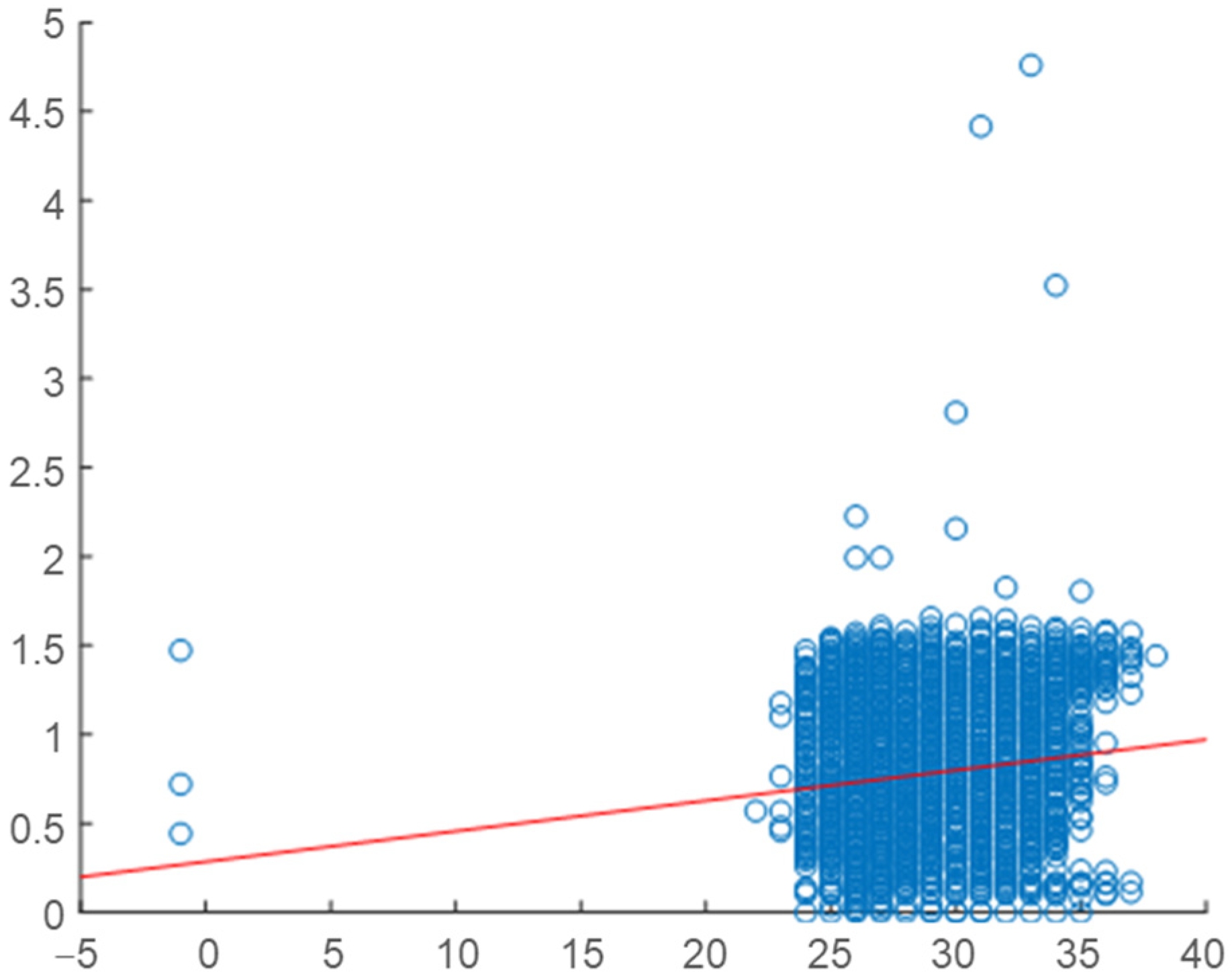
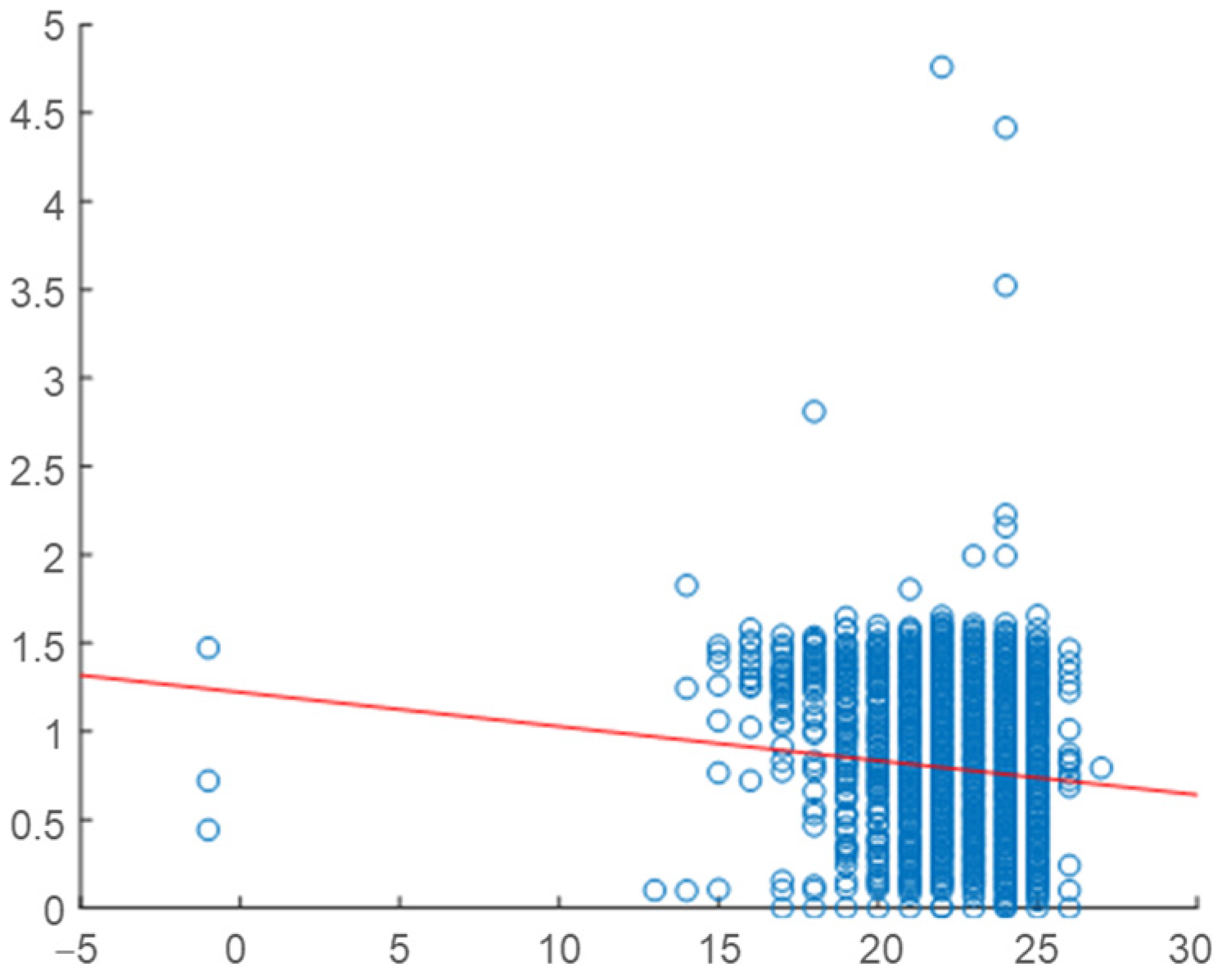













| Building | Variable | Overall Correlation | Daily Correlation Range | Strength of Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VT2 | Temperature | 0.1194 | 0.6–0.8 | Strong |
| Dew Point | −0.0828 | 0.3–0.5 | Moderate | |
| Humidity | −0.1077 | 0.6–0.8 | Strong | |
| Wind Speed | −0.002 | 0–0.4 | Weak | |
| Mold | Temperature | 0.1073 | 0.4–0.6 | Moderate |
| Dew Point | −0.0598 | 0.3–0.5 | Moderate | |
| Humidity | −0.0906 | 0.6–0.8 | Strong | |
| Wind Speed | −0.0279 | 0–0.4 | Weak | |
| Kindergarten | Temperature | 0.1149 | 0.4–0.8 | Moderate to Strong |
| Dew Point | −0.0729 | 0.2–0.5 | Weak to Moderate | |
| Humidity | −0.1104 | 0.6–0.8 | Strong | |
| Wind Speed | 0.0548 | 0–0.4 | Weak |
| Building | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|
| VT2 | 10.2 |
| Mold | 8.8 |
| Kindergarten | 10.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, Y.-N.; Ko, J.-h. Forecast-Aided Converter-Based Control for Optimal Microgrid Operation in Industrial Energy Management System (EMS): A Case Study in Vietnam. Energies 2025, 18, 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123202
Jeon Y-N, Ko J-h. Forecast-Aided Converter-Based Control for Optimal Microgrid Operation in Industrial Energy Management System (EMS): A Case Study in Vietnam. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123202
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Yeong-Nam, and Jae-ha Ko. 2025. "Forecast-Aided Converter-Based Control for Optimal Microgrid Operation in Industrial Energy Management System (EMS): A Case Study in Vietnam" Energies 18, no. 12: 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123202
APA StyleJeon, Y.-N., & Ko, J.-h. (2025). Forecast-Aided Converter-Based Control for Optimal Microgrid Operation in Industrial Energy Management System (EMS): A Case Study in Vietnam. Energies, 18(12), 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123202







