Assessment of Energy Self-Sufficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants—A Case Study from Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Energy Utilization and Energy Self-Sufficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants
2.1. Energy Consumption Assessment of WWTPs
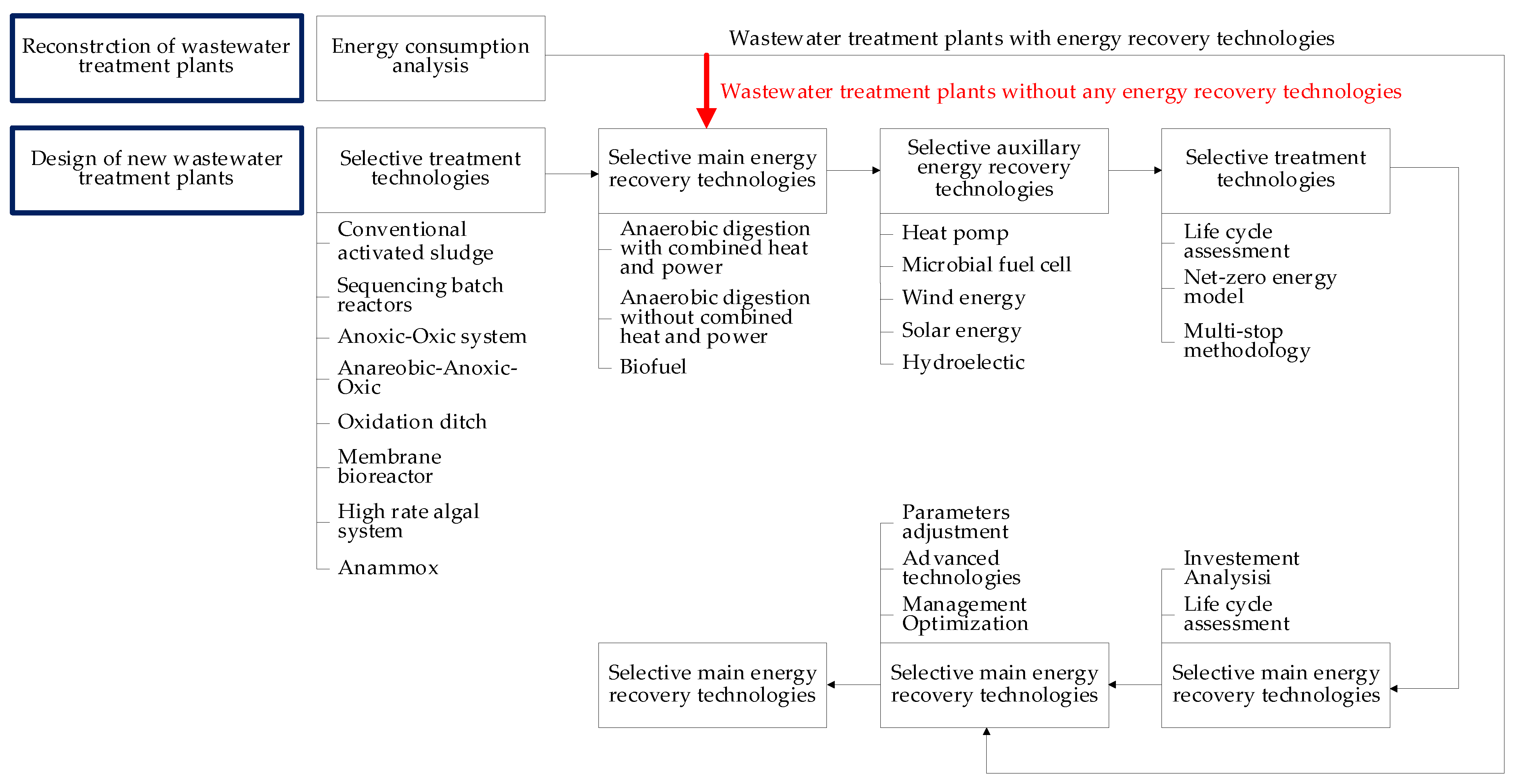
2.2. Solutions to Improve the Energy Self-Sufficiency Characterizing Wastewater Treatment Plants
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Site
3.2. Methodology for Calculating Individual Parameters
- –
- EI—electricity consumption indicator [kWh per m3 wastewater],
- –
- EIR—electric energy recovery indicator [kWh per m3 wastewater].
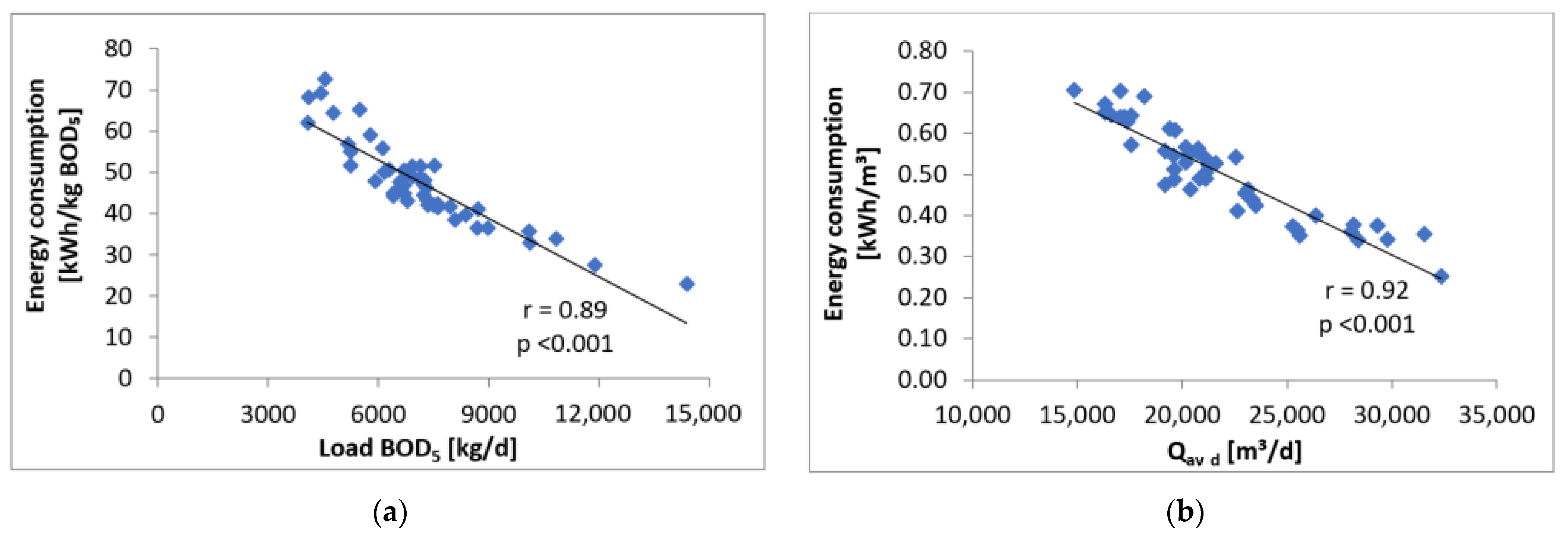
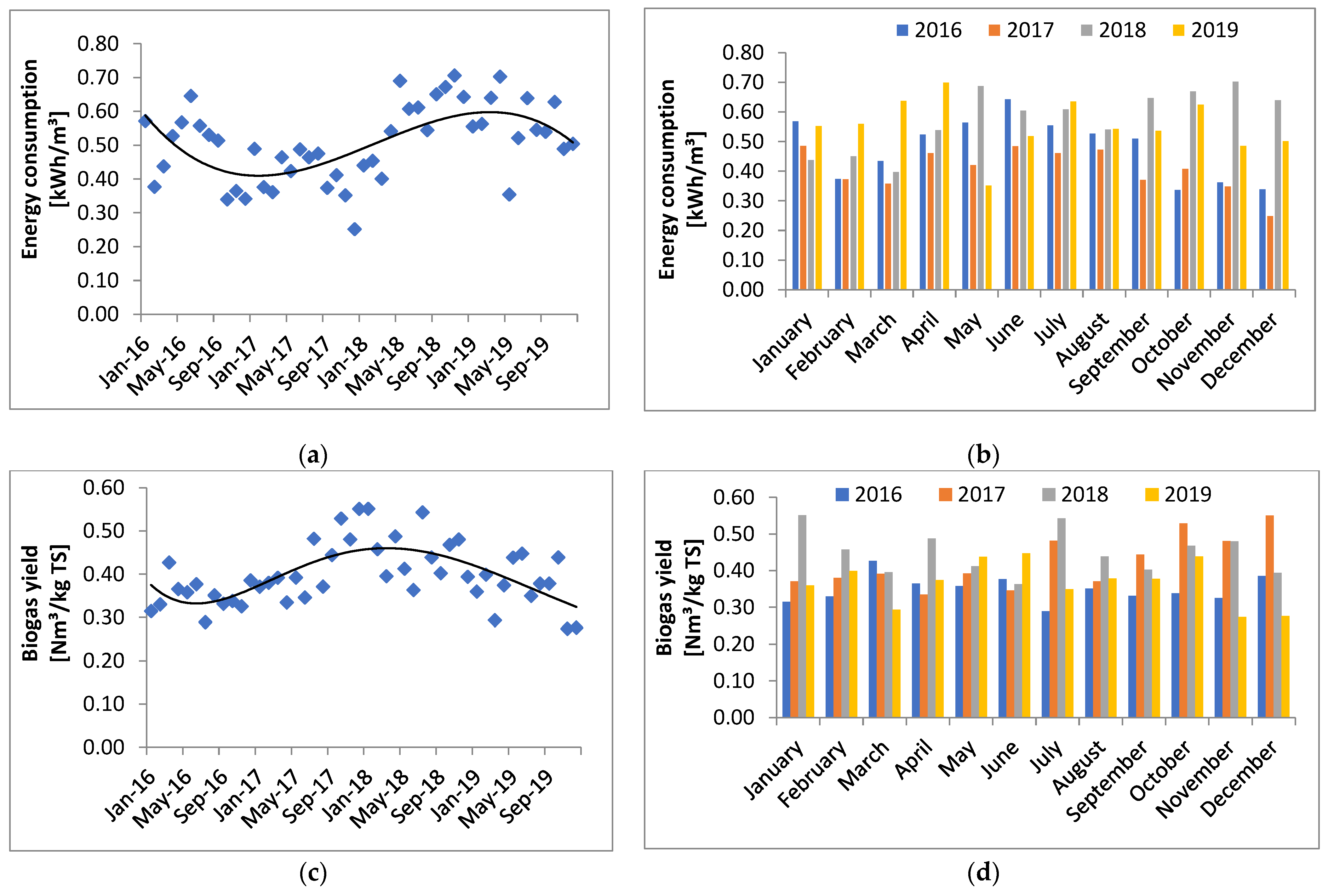
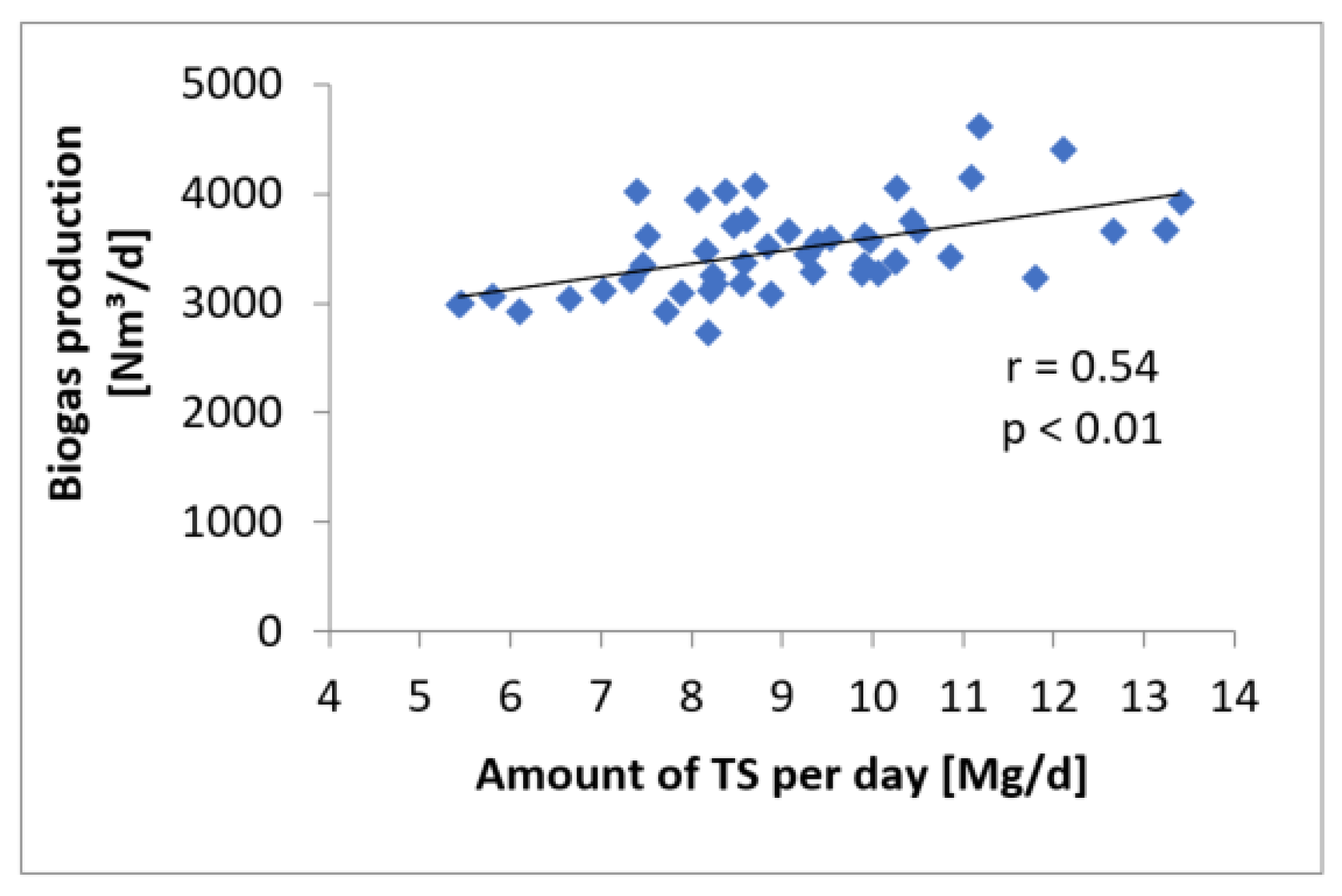
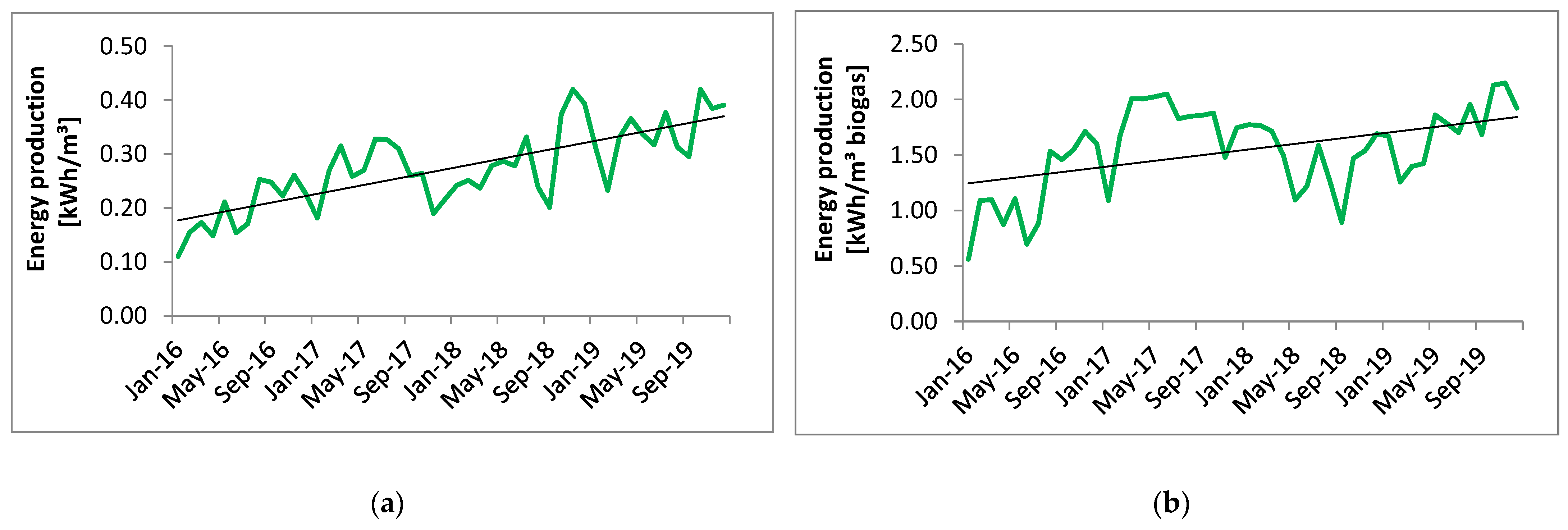
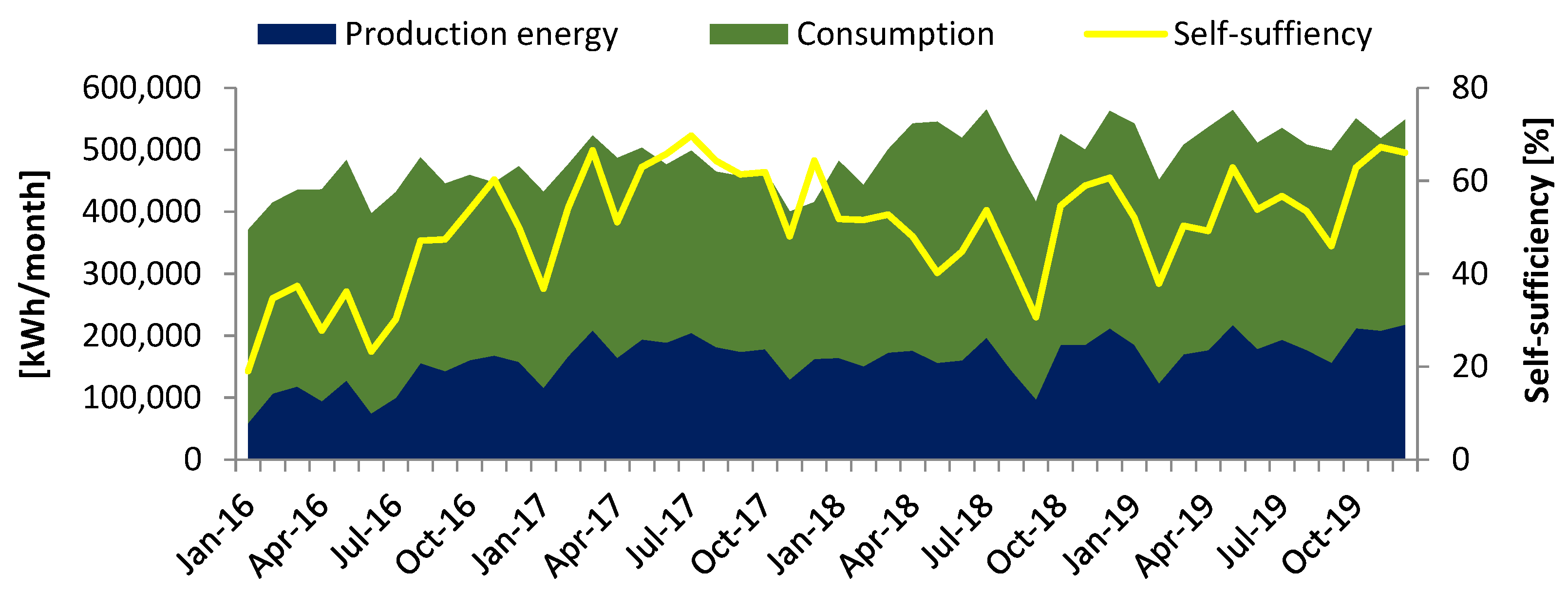
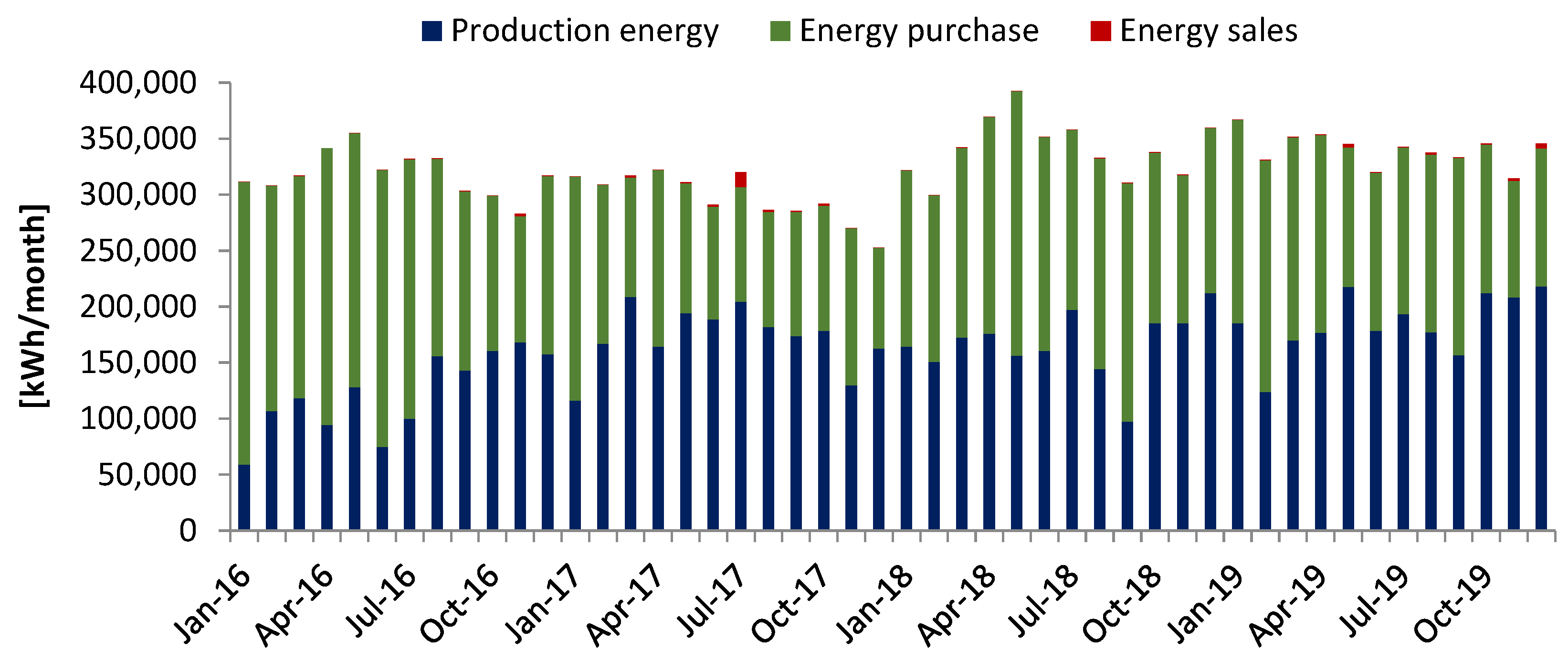
4. Results and Discussion
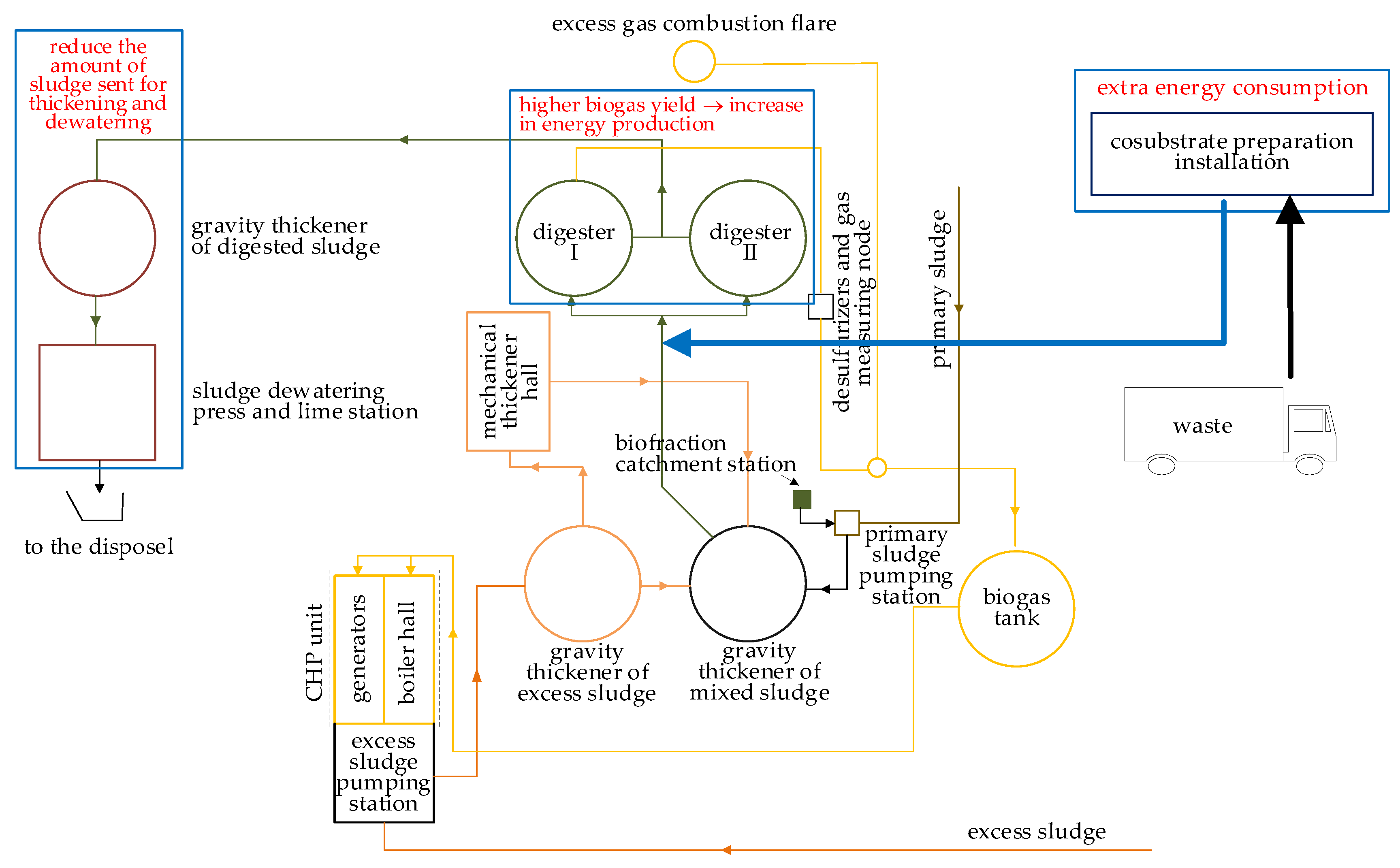
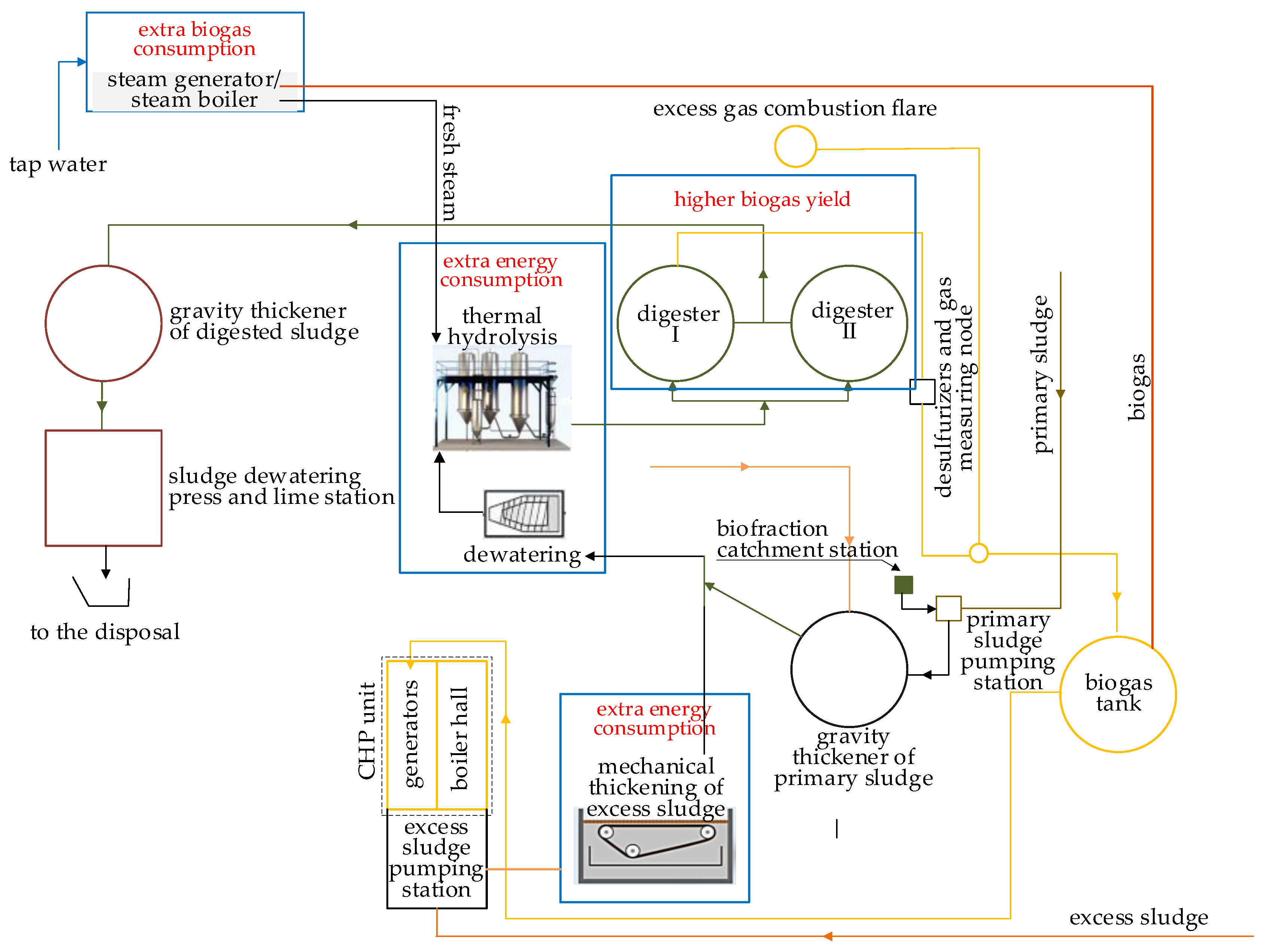
5. Concepts for Increasing the Self-Sufficiency of the WWTP in Krosno
6. Conclusions
- Currently, in the employed technological system, achieving 100% self-sufficiency of the WWTP in terms of electricity is not possible; however, the WWTP allowed for covering the demand for electricity by 50.5%.
- The implementation of the anaerobic digestion process enabled the production of 7.76 GWh of electricity in 2016–2019 and reduced its purchase by about 50.2%.
- The achievement of the self-sufficiency of the WWTP in Krosno is possible through the improvement of the anaerobic digestion process. The co-digestion strategy may be considered as the easiest to implement in existing digesters.
- The introduction of a sewage sludge pretreatment strategy might be a positive course of action, while bearing in mind that it is an energy-intensive activity; thus, it will be necessary to carefully analyze the profitability of such a solution. The use of ultrasonication might improve the biogas production even to the level of 40–50%.
- Another way might be improving the energy efficiency of equipment (blowers, mixers, and pumps) and implementing intelligent monitoring as well as a control for the WWTP operation. Such solutions might contribute to reducing energy consumption by approximately 30%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | anaerobic digestion process |
| BOD5 | biochemical oxygen demand |
| CHP | combined heat and power |
| THP | temperature hydrolysis process |
| TS | total solids content |
| WWTP | wastewater treatment plant |
| VS | volatile solids |
References
- Panepinto, D.; Fiore, S.; Zappone, M.; Genon, G.; Meucci, L. Evaluation of the energy efficiency of a large wastewater treatment plant in Italy. Appl. Energy 2016, 161, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziotis, A.; Sala-Garrido, R.; Mocholi-Arce, M.; Molinos-Senante, M. A comprehensive assessment of energy efficiency of wastewater treatment plants: An efficiency analysis tree approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.L.; Williams, A.P.; Styles, D. Pitfalls in international benchmarking of energy intensity across wastewater treatment utilities. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.J.; Rodrigues, E.; Gaspar, A.R.; Gomes, Á. Energy performance factors in wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, P.; Wang, H.; Robinson, Z.P.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, F. The feasibility and challenges of energy self-sufficient wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Energy 2017, 204, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapote, A.; Albaladejo, A.; Simón, P. Energy consumption in an urban wastewater treatment plant: The case of Murcia Region (Spain). Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2014, 31, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siatou, A.; Manali, A.; Gikas, P. Energy consumption and internal distribution in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants of Greece. Water 2020, 12, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maktabifard, M.; Zaborowska, E.; Makinia, J. Achieving energy neutrality in wastewater treatment plants through energy savings and enhancing renewable energy production. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 655–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, N.; Mobini, S.; Zhang, X.N. Appendix E. Mass and Energy Balances at the Gaobeidian Wastewater Treatment Plant in Beijing, China. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/43133293/appendix-e-mass-and-energy-balances-at-the-gaobeidian- (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Trojanowicz, K. Energetyczna utylizacja biogazu jako element gospodarki osadowej w oczyszczalni ścieków w Krośnie. Forum Eksploatatora 2016, 4, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Üstün, G.E.; Solmaz, S.K.A.; Çiner, F.; Bažkaya, H.S. Tertiary treatment of a secondary effluent by the coupling of coagulation-flocculation-disinfection for irrigation reuse. Desalination 2011, 277, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.M.; de Guzmán, I.; Elosegi, A.; Larrañaga, A. Tertiary wastewater treatment combined with high dilution rates fails to eliminate impacts on receiving stream invertebrate assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; d’Antoni, B.M.; Bongards, M.; Chaparro, A.; Cronrath, A.; Fatone, F.; Lema, J.M.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M.; Soares, A.; Hospido, A. Monitoring and diagnosis of energy consumption in wastewater treatment plants. A state of the art and proposals for improvement. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 1251–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatkowska, B.; Neczej, E. Analiza Ścieżek Odzysku Energii i Poprawy Efektywności w Komunalnych Oczyszczalniach Ścieków; ETV4Water Consortium: Oslo, NOR, 2017; Available online: https://etv.ietu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/ETV4Water_WP1_Report.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Krzeminski, P.; Van Der Graaf, J.H.J.M.; Van Lier, J.B. Specific energy consumption of membrane bioreactor (MBR) for sewage treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, E.; Giuliano, S.; Ranieri, A.C. Energy consumption in anaerobic and aerobic based wastewater treatment plants in Italy. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, M.; Foladori, P.; Nembrini, S.; Vitali, F. Benchmarking of energy consumption in municipal wastewater treatment plants—A survey of over 200 plants in Italy. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y. Efficiency assessment of urban wastewater treatment plants in China: Considering greenhouse gas emissions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Su, J.; Gin, K.; Lev, O.; Shen, G.; Hu, S. State of the art of tertiary treatment technologies for controlling antibiotic resistance in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Rosa, M.J. Energy performance indicators of wastewater treatment: A field study with 17 Portuguese plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svardal, K.; Kroiss, H. Energy requirements for waste water treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, F. Energy Self-sufficient Wastewater Treatment Plants: Feasibilities and Challenges. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llácer-Iglesias, R.M.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Energy self-sufficiency aiming for sustainable wastewater systems: Are all options being explored? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakkasunchi, S.; Hewitt, N.J.; Zoppi, C.; Brandoni, C. A review of energy optimization modelling tools for the decarbonisation of wastewater treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, A.B.L.; Velázquez, F.D.C.; del Riquelme, M.L.P. Methodology for energy optimization in wastewater treatment plants. Phase I: Control of the best operating conditions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Elsayed, N.; Rezaei, N.; Guo, T.; Mohebbi, S.; Zhang, Q. Wastewater-based resource recovery technologies across scale: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rodríguez, S.; Oulego, P.; Rodríguez, E.; Singh, D.N.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J. Towards the implementation of circular economy in the wastewater sector: Challenges and opportunities. Water 2020, 12, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Pan, H.; Xiao, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y. The comparison of performances of a sewage treatment system before and after implementing the cleaner production measure. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandiglio, M.; Lanzini, A.; Soto, A.; Leone, P.; Santarelli, M. Enhancing the energy efficiency of wastewater treatment plants through co-digestion and fuel cell systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, U.; Viccione, G.; Coppola, S.; Landi, A.; Meda, A.; Gualtieri, C. Analysis of anaerobic digester mixing: Comparison of long shafted paddle mixing vs gas mixing. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, P.M.V.; D’ Silva, T.C.; Adlak, K.; Kumar, S.; Chandra, R.; Vijay, V.K. Anaerobic digestion as a sustainable technology for efficiently utilizing biomass in the context of carbon neutrality and circular economy. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.Y. Mass Flow and Energy Efficiency of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 9781780400907. [Google Scholar]
- Enebe, N.L.; Chigor, C.B.; Obileke, K.; Lawal, M.S.; Enebe, M.C. Biogas and Syngas Production from Sewage Sludge: A Sustainable Source of Energy Generation. Methane 2023, 2, 192–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmasoumi, S.; Ebrahimi, S.; Saray, R.K. Enhancement of biogas production from sewage sludge in a wastewater treatment plant: Evaluation of pretreatment techniques and co-digestion under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Energy 2018, 157, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, F.; Neugebauer, G.; Stoeglehner, G.; Ertl, T. Participation as a key aspect for establishing wastewater as a source of renewable energy. Energies 2018, 11, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Chuenchart, W.; Surendra, K.C.; Shrestha, S.; Raskin, L.; Sung, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Kumar Khanal, S. Anaerobic co-digestion: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linville, J.L.; Shen, Y.; Schoene, R.P.; Nguyen, M.; Urgun-Demirtas, M.; Snyder, S.W. Impact of trace element additives on anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge with in-situ carbon dioxide sequestration. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, M.J.; Vinardell, S.; Astals, S.; Koch, K. Opportunities and challenges of micronutrients supplementation and its bioavailability in anaerobic digestion: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 186, 113689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; He, S.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Yang, C. Functional biochar in enhanced anaerobic digestion: Synthesis, performances, and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambini, M.; Vellini, M.; Stilo, T.; Manno, M.; Bellocchi, S. High-efficiency cogeneration systems: The case of the paper industry in Italy. Energies 2019, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacchei, E.; Colacicco, A. Direct Method to Design Solar Photovoltaics to Reduce Energy Consumption of Aeration Tanks in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabaş Baş, G.; Aydinalp Koksal, M. Environmental and Techno-Economic Analysis of the Integration of Biogas and Solar Power Systems to Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Snyder, S.W.; Kim, H.; Lei, Z.; Pan, S.Y. Pathways to a net-zero-carbon water sector through energy-extracting wastewater technologies. Npj Clean Water 2022, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, V.; Choo, K.-H.; Cornel, P. Water-Energy Interactions in Water Reuse; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarova, V.; Choo, K.-H.; Cornel, P. Meeting the challenges of the water-energy nexus: The role of reuse and wastewater treatment. Water21 2012, 14, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Spriet, J.; McNabola, A.; Neugebauer, G.; Stoeglehner, G.; Ertl, T.; Kretschmer, F. Spatial and temporal considerations in the performance of wastewater heat recovery systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żaba, T. Energetycznie pasywna oczyszczalnia ścieków—Innowacja czy konieczność? Kierun. Wod-Kan 2022, 3, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, L. Ultra-low energy consumption process (PN+Anammox) for enhanced nitrogen removal from decentralized sewage. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mąkinia, J.; Zaborowska, E.; Ramm, K. Jakie będą oczyszczalnie’jutra”? Kierun. Wod. Kan 2022, 3, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Koul, Y.; Devda, V.; Varjani, S.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Chang, J.S.; Wong, J.W.C.; Bilal, M.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Microbial electrolysis: A promising approach for treatment and resource recovery from industrial wastewater. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8115–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, G.; Pipitone, G.; Pirone, R.; Bensaid, S. Aqueous phase reforming process for the valorization of wastewater streams: Application to different industrial scenarios. Catal. Today 2022, 387, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Municipal Utilities Company located in Krosno—Krośnieński Holding Komunalny (Krosno, Podkarpackie Province, Poland), Personal Communication. 2023.
- Masłoń, A. Analysis of energy consumption at the Rzeszów Wastewater Treatment Plant. E3S Web Conf. 2017, 22, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłoń, A. Energy Consumption of Selected Wastewater Treatment Plants Located in South-Eastern Poland. Eng. Prot. Environ. 2017, 20, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.; Zou, W.; Zhou, G. Assessment of energy consumption of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, F.; Nouri, A.S.; Mehrani, M.-J.; Thennadil, S. Prediction of energy consumption and evaluation of affecting factors in a full-scale WWTP using a machine learning approach. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 154, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, Z.; Ramocki, W. Energochłonność miejskich oczyszczalni ścieków. Forum Eksploatatora 2009, 5, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Szczyrba, P.; Masłoń, A.; Czarnota, J.; Olszewski, K. Analysis of sewage sludge and biogas-energy management at the opole wastewater treatment plant; [Analiza gospodarki osadowej i biogazowoenergetycznej w oczyszczalni ścieków w opolu]. Inz. Ekol. 2020, 21, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłoń, A.; Czarnota, J.; Szaja, A.; Szulżyk-Cieplak, J.; Łagód, G. The Enhancement of Energy Efficiency in a Wastewater Treatment Plant through Sustainable Biogas Use: Case Study from Poland. Energies 2020, 13, 6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłoń, A.; Tendera, K. Gospodarka odpadami ściekowymi w oczyszczalni ścieków Rzeszów. Forum Eksploatatora 2017, 1, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, K.; Wu, J.; Qi, L.; Niu, Q. Energy intensity of wastewater treatment plants and influencing factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Keller, A.A.; Li, X.; Feng, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, F. Comparative analysis of energy intensity and carbon emissions in wastewater treatment in USA, Germany, China and South Africa. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłoń, A. An Analysis of Sewage Sludge and Biogas Production at the Zamość WWTP. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 47, pp. 291–298. ISBN 9783030270117. [Google Scholar]
- Masłoń, A.; Pazdro, S.; Mroczek, W. Gospodarka osadowa w oczyszczalni ścieków w Mielcu. Forum Eksploatatora 2015, 4, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Masłoń, A.; Czarnota, J. Biogas production from sewage sludge as an energy balance element of the wastewater treatment plant. In Proceedings of the VI International Scientific and Technical Conference “Pure Water. Fundamental, Applied and Industrial Aspects”, Kiev, Ukraine, 14–15 November 2019; pp. 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gazda, M.; Adam, R.; Sudak, M. Research on cofermentation of sewage sludge with waste fats for the wastewater treatment plant in Brzeg. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2012, 3, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Torregrossa, D.; Castellet-Viciano, L.; Hernández-Sancho, F. A data analysis approach to evaluate the impact of the capacity utilization on the energy consumption of wastewater treatment plants. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaśkieicz, K. Oszczędności energetyczne i kosztowe. Nowoczesne mieszadła średnoobrotowe Wilo. Kierun. Wod-Kan 2022, 3, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Grosser, A.; Neczaj, E. Sewage sludge and fat rich materials co-digestion—Performance and energy potential. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, M. A-B Processes towards Energy Self-Sufficient Municipal Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, W.L.; Chong, S.; Lim, J.W.; Chan, Y.J.; Chong, M.F. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Wastewater Sludge: A Review of Potential Co-Substrates and Operating. Processes 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bień, B.; Bień, J.D. Conditioning of sewage sludge with physical, chemical and dual methods to improve sewage sludge dewatering. Energies 2021, 14, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budych-Gorzna, M.; Smoczynski, M.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P. Enhancement of biogas production at the municipal wastewater treatment plant by co-digestion with poultry industry waste. Appl. Energy 2016, 161, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, M.; Stachowicz, F. Influence of physical, chemical and dual sewage sludge conditioning methods on the dewatering efficiency. Powder Technol. 2019, 344, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawieja, I.; Włodarczyk, R.; Kowalczyk, M. Biogas generation from sonicated excess sludge. Water 2019, 11, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawieja, I. Effect of thermal and alkaline disintegration of excess sludge on biodegradation. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bień, B.; Bień, J.D. Dewatering of sewage sludge treated by the combination of ultrasonic field and chemical methods. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 199, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamizela, T.; Kowalczyk, M.; Zawieja, I. The use of chemical methods and magnetic field in conditioning and dewatering of digested sewage sludge. Water 2020, 12, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Koo, B.; Sun, X.; Yoon, J.Y. Investigation of sludge disintegration using rotor-stator type hydrodynamic cavitation reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Han, X.; Chen, H.; Yuan, R.; Wang, F.; Zhou, B. New insights into impact of thermal hydrolysis pretreatment temperature and time on sewage sludge: Structure and composition of sewage sludge from sewage treatment plant. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Kjørlaug, O.; Higgins, M.J.; Linjordet, R.; Horn, S.J. Post-anaerobic digestion thermal hydrolysis of sewage sludge and food waste: Effect on methane yields, dewaterability and solids reduction. Water Res. 2018, 132, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hu, C.; Dai, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, B.; Dai, X. Post-thermal hydrolysis and centrate recirculation for enhancing anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2019, 92, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukawa, J.; Pająk, T.; Rzepecki, T.; Banaś, M. Energy Potential of Biogas from Sewage Sludge after Thermal Hydrolysis and Digestion. Energies 2022, 15, 5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, F.; Mormede, S.; Clark, P.; Crane, M. Ultrasonic sludge treatment for enhanced anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borukało, K.; Kowal, L.; Milanowski, A. Ultradźwiękami w osad. Przegląd Komunaln. 2013, 2, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, C.M.; Marder, M.; Junges, E.; Konrad, O. Technologies for biogas desulfurization—An overview of recent studies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 159, 112205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłoń, A.; Wójcik, M.; Chmielowski, K. Efficient Use of Energy in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Energy Policy Stud. 2018, 1, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dąbrowska, S.; Masłoń, A. The Use of Biogas From the Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge To Improve the Energy Balance of Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Civ. Eng. Environ. Archit. 2020, 37, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Direction | Action | Literature |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing energy consumption of existing equipment |
| [23,24,25] |
| ||
| ||
| Implementing technologies allowing for recovery of energy from wastewater/sludge and production of renewable energy |
| [24,26,27] |
|
| Technical Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Electric power | [kW] | 192 |
| Thermal power | [kW] | 214 |
| Rotational speed | [rpm] | 1500 |
| Maximum water temperature at the inlet | [°C] | 70 |
| Maximum water temperature at the outlet | [°C] | 90 |
| Maximum electrical power demand for auxiliary drives | [kW] | 4 |
| Gas consumption (for 54% CH4) | [Nm3/h] | 90.7 |
| Hydraulic Load | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Average | SD | |
| Total amount of wastewater, m3/d | 14,858.0 | 32,351.6 | 21,743.6 | 4240.0 | |
| Physicochemical Parameters | |||||
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Average | SD | |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) | mg/L | 125.5 | 680.5 | 342.5 | 112.5 |
| kg/d | 4060.1 | 14,384.8 | 7150.1 | 1952.5 | |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg/L | 375.5 | 1295.0 | 794.4 | 211.1 |
| kg/d | 9556.2 | 23,780.9 | 16,613.0 | 2756.8 | |
| Total suspended solids (TSSs) | mg/L | 180.0 | 805.0 | 475.1 | 141.5 |
| kg/d | 3857.4 | 15,008.4 | 9991.1 | 2438.8 | |
| Total nitrogen (TN) | mg/L | 28.2 | 113.8 | 73.2 | 19.0 |
| kg/d | 913.9 | 2077.9 | 1514.8 | 224.3 | |
| Total phosphorous (TP) | mg/L | 3.4 | 26.2 | 13.5 | 4.8 |
| kg/d | 108.4 | 569.5 | 280.5 | 79.3 | |
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Average | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4, % v/v | 50.6 | 65.8 | 61.8 | 4.68 |
| CO2, % v/v | 29.2 | 44.5 | 35.4 | 3.8 |
| Other, % v/v | 0.01 | 5.25 | 1.75 | 3.83 |
| H2S, ppm | 6.2 | 207.0 | 95.2 | 67.2 |
| Year | Production | Energy Purchase | Energy Consumption | Energy Sales | Self-Sufficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [kWh] | [kWh] | [kWh] | [kWh] | [%] | |
| 2016 | 122,370.00 | 195,666.75 | 317,685.83 | 350.92 | 38.92 |
| 2017 | 172,639.67 | 123,266.12 | 293,985.33 | 1920.45 | 58.92 |
| 2018 | 166,937.17 | 173,977.65 | 340,262.15 | 67.92 | 49.16 |
| 2019 | 184,953.75 | 154,395.75 | 337,640.15 | 1164.02 | 54.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masłoń, A.; Czarnota, J.; Szczyrba, P.; Szaja, A.; Szulżyk-Cieplak, J.; Łagód, G. Assessment of Energy Self-Sufficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants—A Case Study from Poland. Energies 2024, 17, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051164
Masłoń A, Czarnota J, Szczyrba P, Szaja A, Szulżyk-Cieplak J, Łagód G. Assessment of Energy Self-Sufficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants—A Case Study from Poland. Energies. 2024; 17(5):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051164
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasłoń, Adam, Joanna Czarnota, Paulina Szczyrba, Aleksandra Szaja, Joanna Szulżyk-Cieplak, and Grzegorz Łagód. 2024. "Assessment of Energy Self-Sufficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants—A Case Study from Poland" Energies 17, no. 5: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051164
APA StyleMasłoń, A., Czarnota, J., Szczyrba, P., Szaja, A., Szulżyk-Cieplak, J., & Łagód, G. (2024). Assessment of Energy Self-Sufficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants—A Case Study from Poland. Energies, 17(5), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051164








