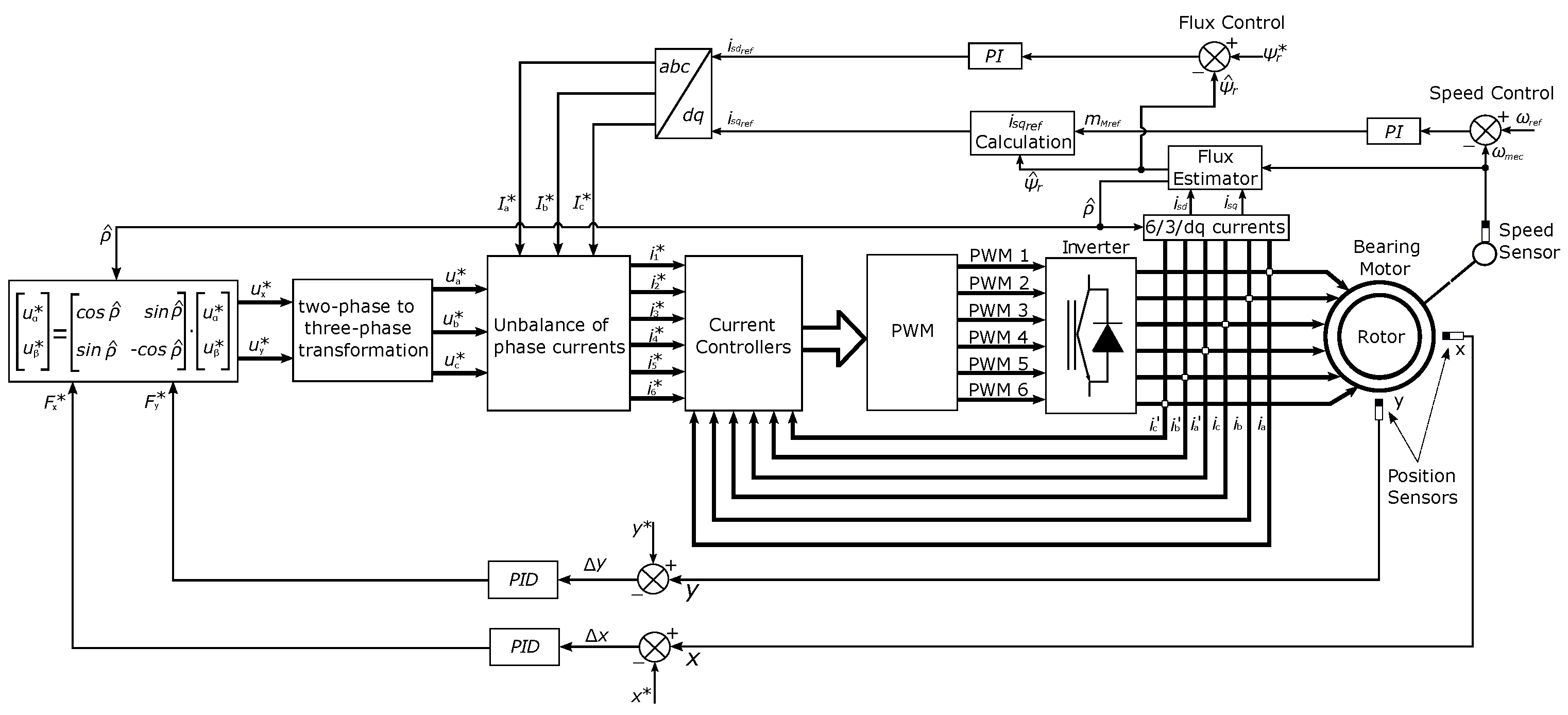
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the proposed simulated system.
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the proposed simulated system.
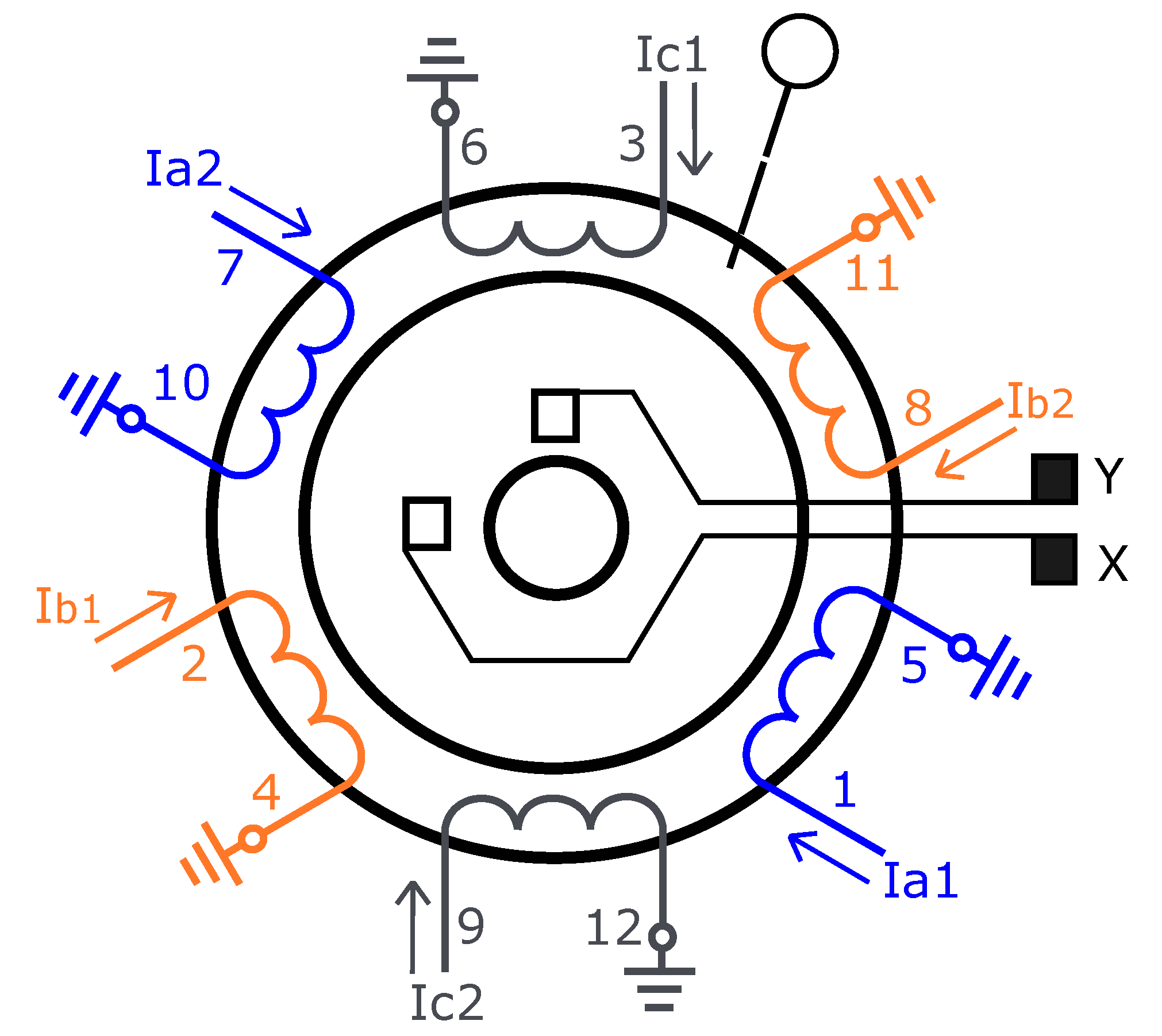
Figure 2.
Stator coil layout.
Figure 2.
Stator coil layout.
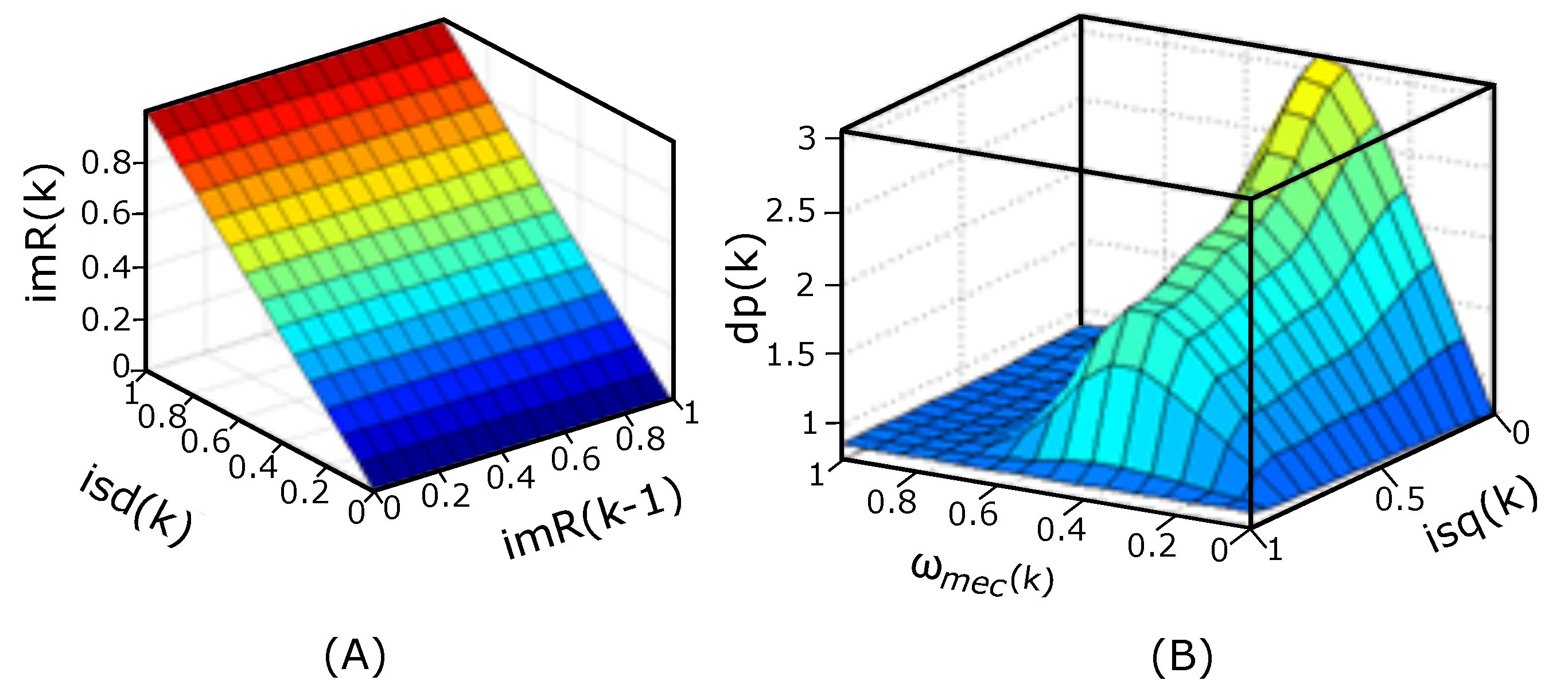
Figure 3.
(A)—Fuzzy Sugeno Surface—ANFIS 1 and (B)—ANFIS 2.
Figure 3.
(A)—Fuzzy Sugeno Surface—ANFIS 1 and (B)—ANFIS 2.
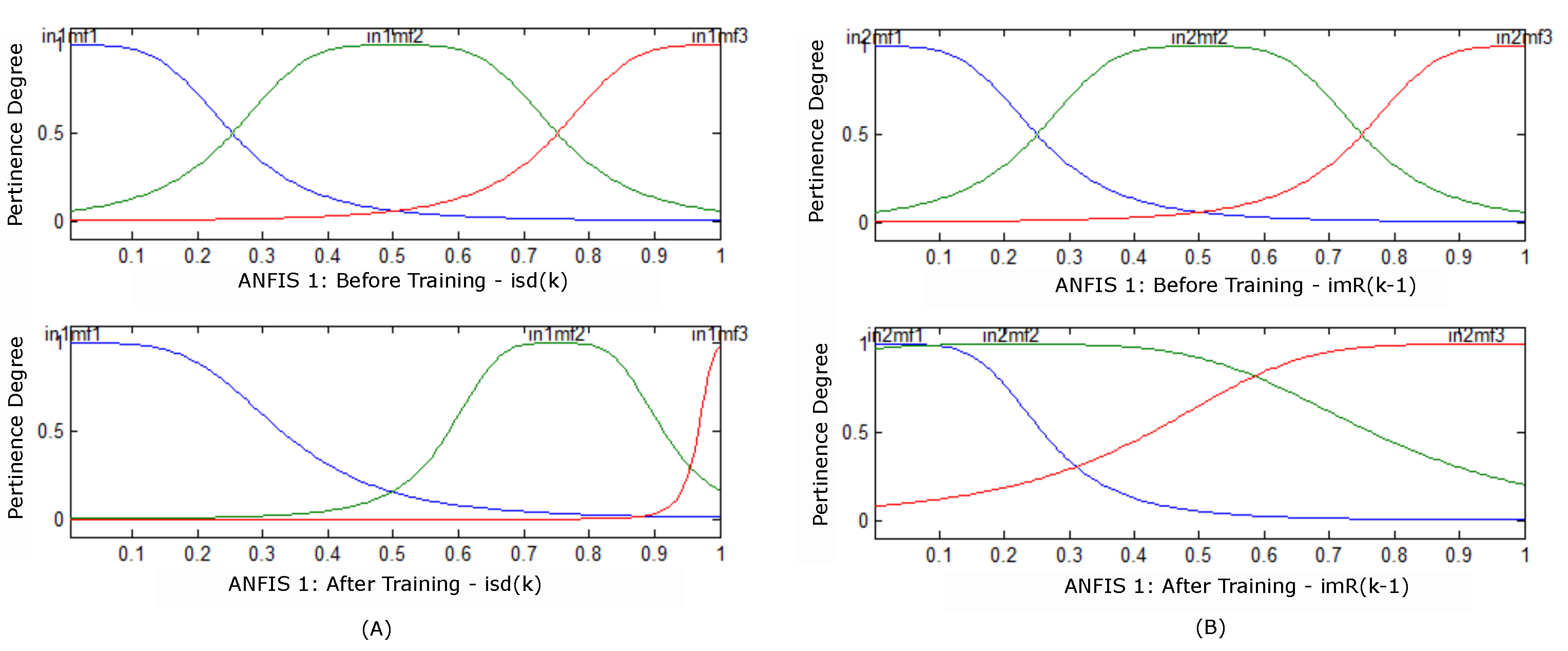
Figure 4.
(A) Pertinences before training and after –; (B) Pertinences before training and after .
Figure 4.
(A) Pertinences before training and after –; (B) Pertinences before training and after .
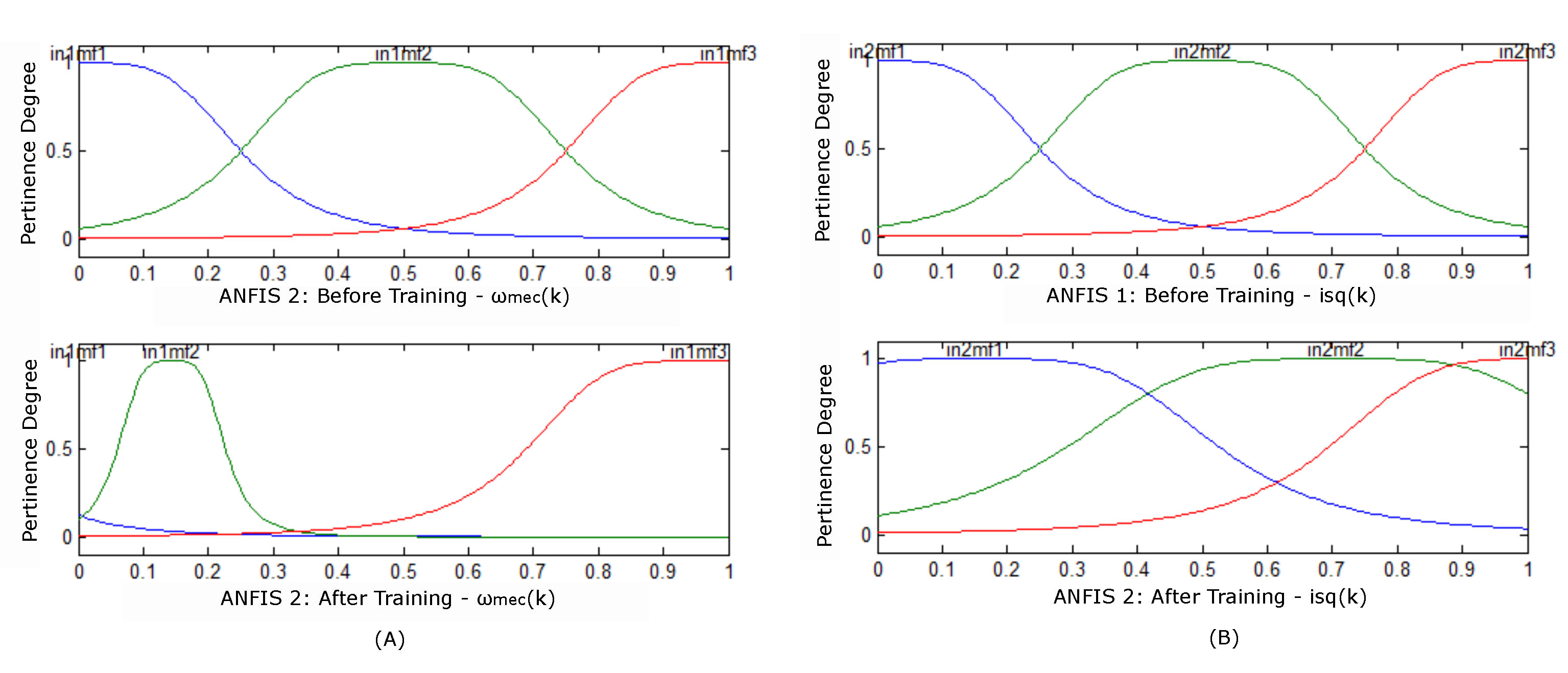
Figure 5.
(A) Pertinences before training and after –; (B) Pertinences before training and after .
Figure 5.
(A) Pertinences before training and after –; (B) Pertinences before training and after .
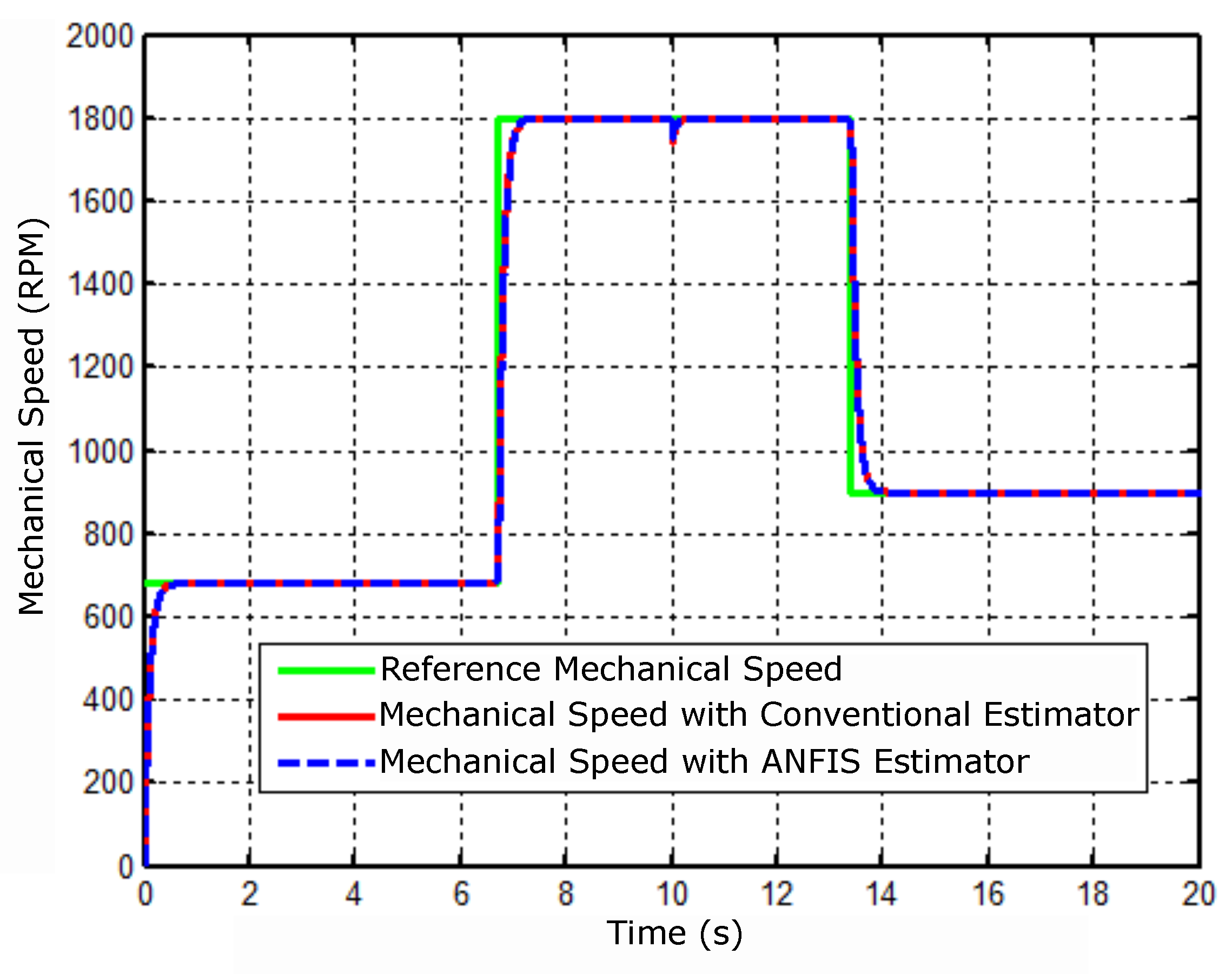
Figure 6.
Comparative result of mechanical speed with estimators.
Figure 6.
Comparative result of mechanical speed with estimators.
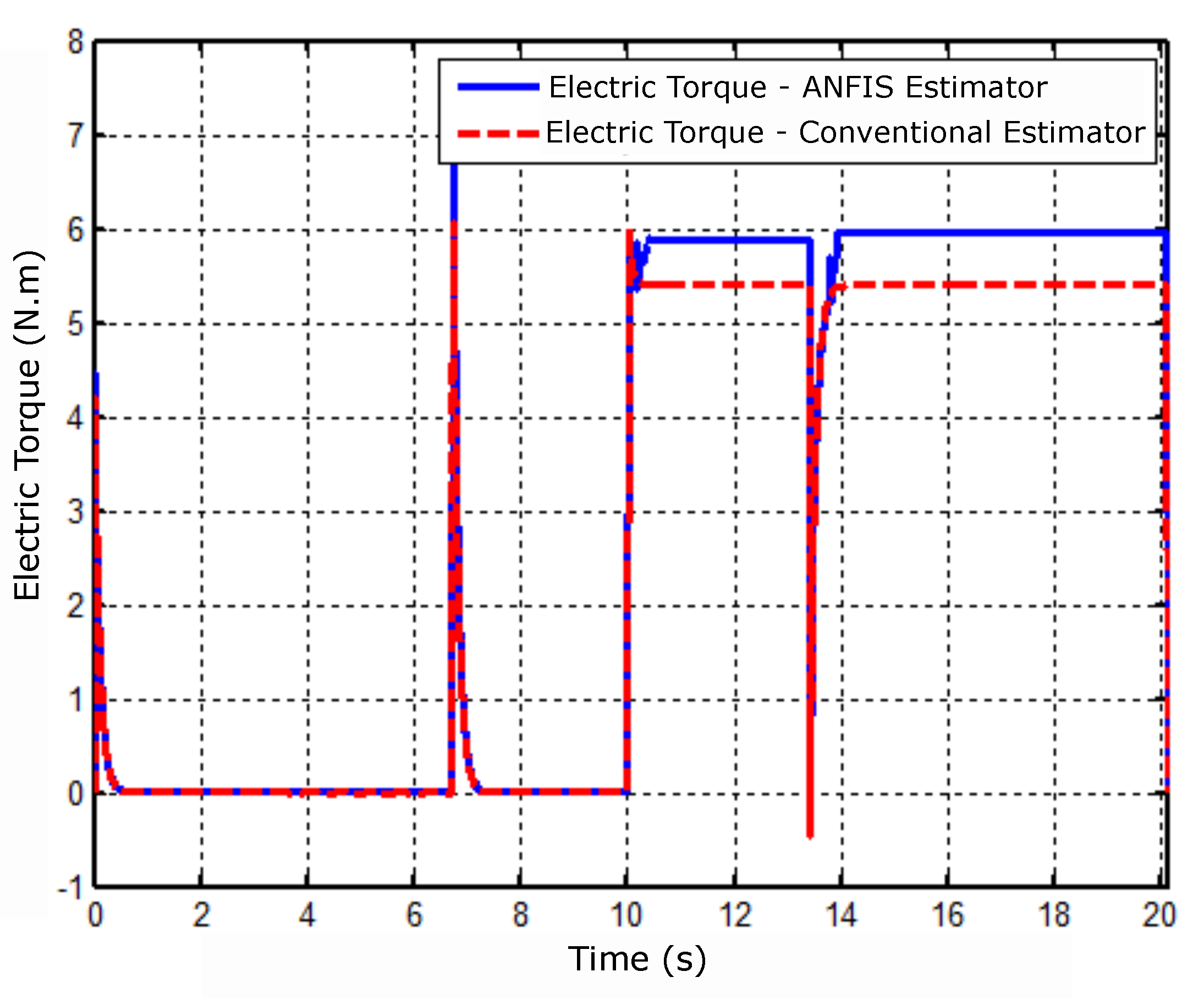
Figure 7.
Electrical torque response operating under simulation conditions.
Figure 7.
Electrical torque response operating under simulation conditions.
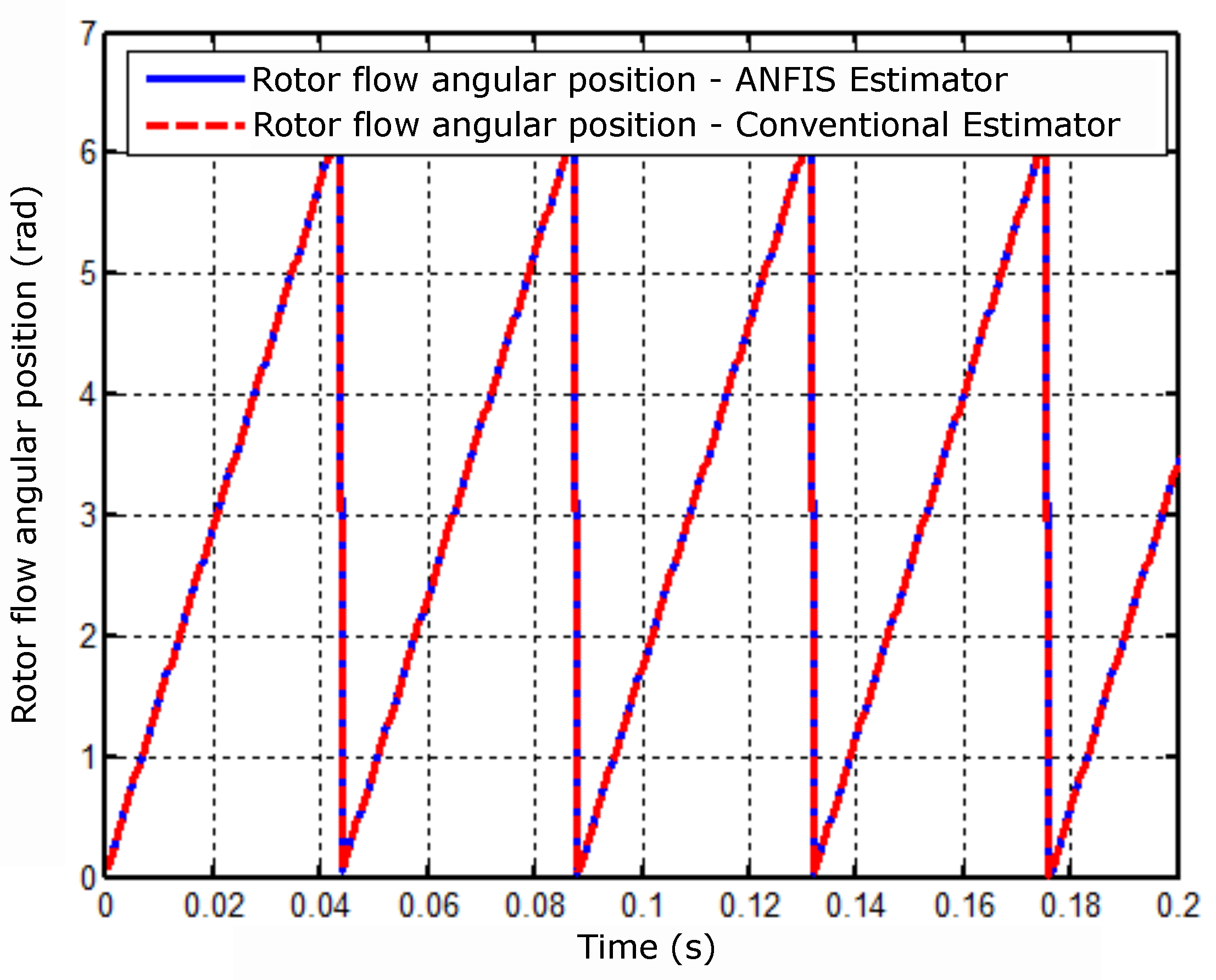
Figure 8.
Angular position result of the rotor flux.
Figure 8.
Angular position result of the rotor flux.
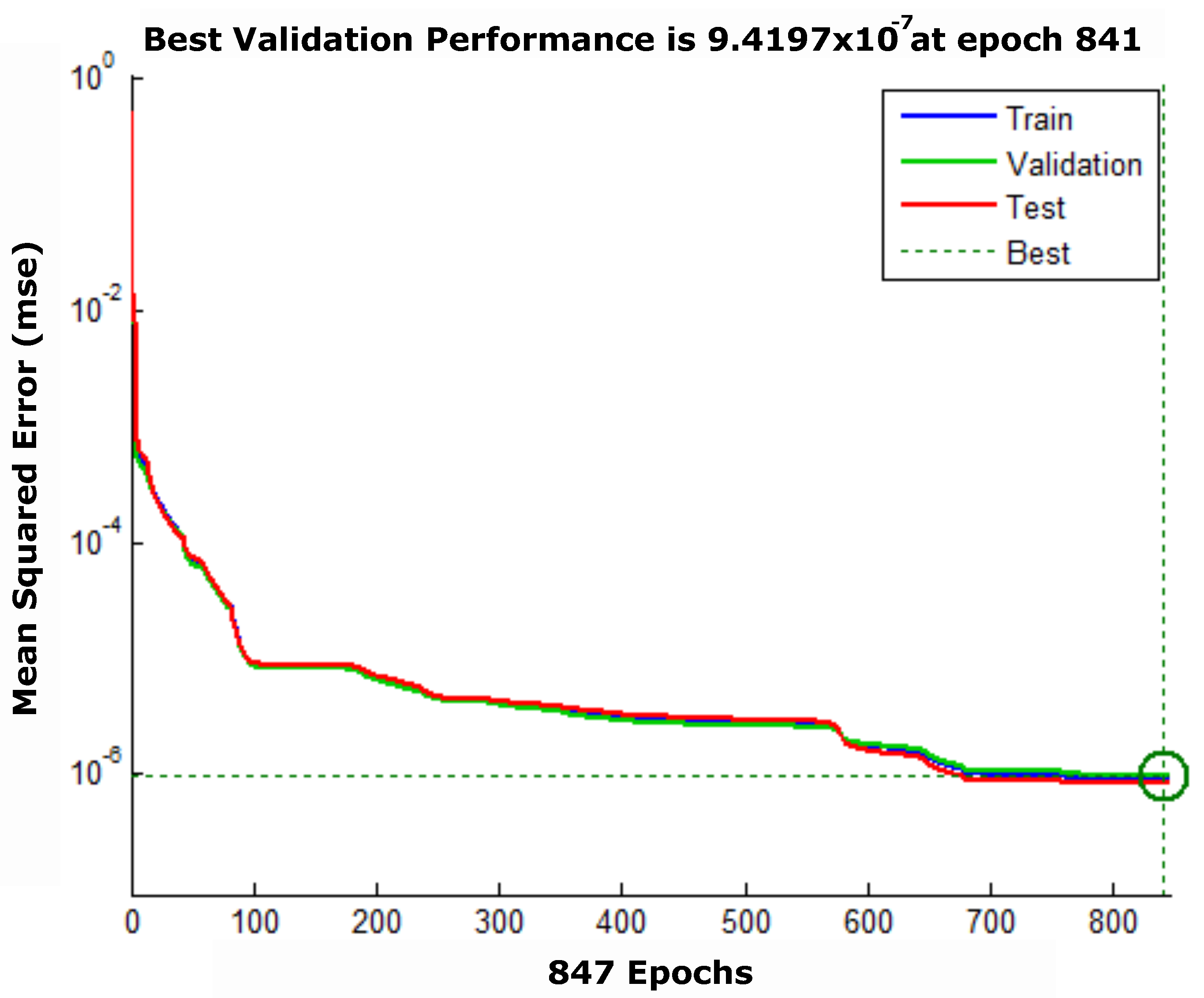
Figure 9.
Mean squared error for training () with 847 epochs.
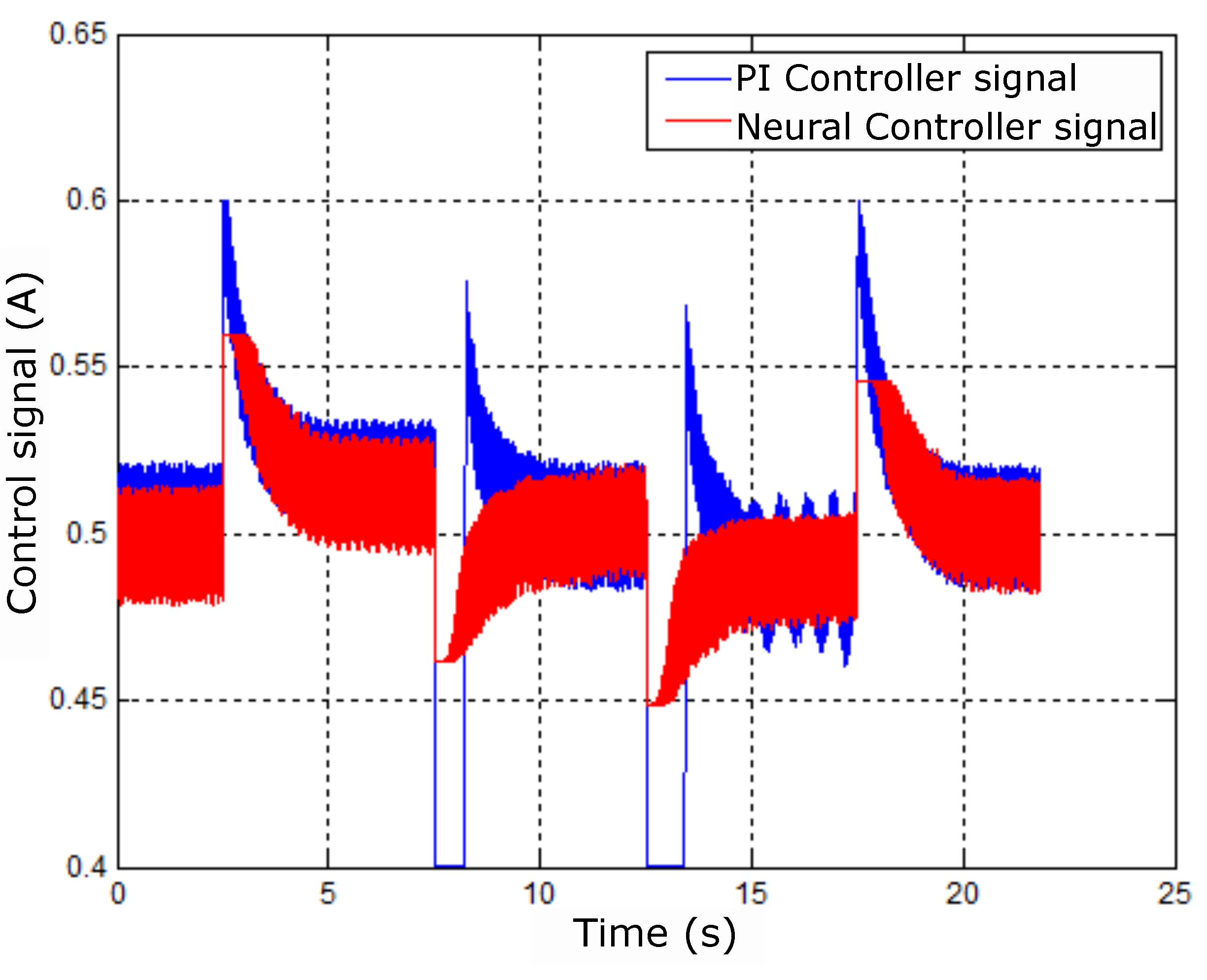
Figure 9.
Mean squared error for training () with 847 epochs.
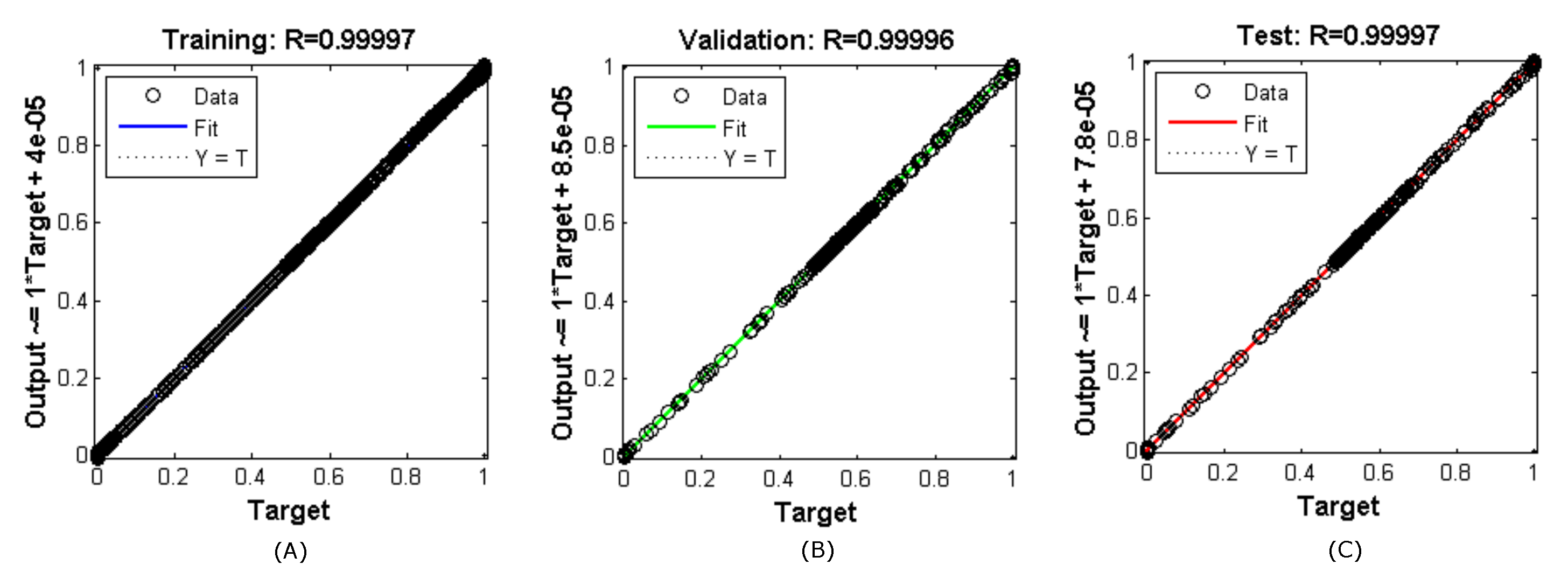
Figure 10.
Results of training (A); validation (B); and Neural Network tests (C).
Figure 10.
Results of training (A); validation (B); and Neural Network tests (C).
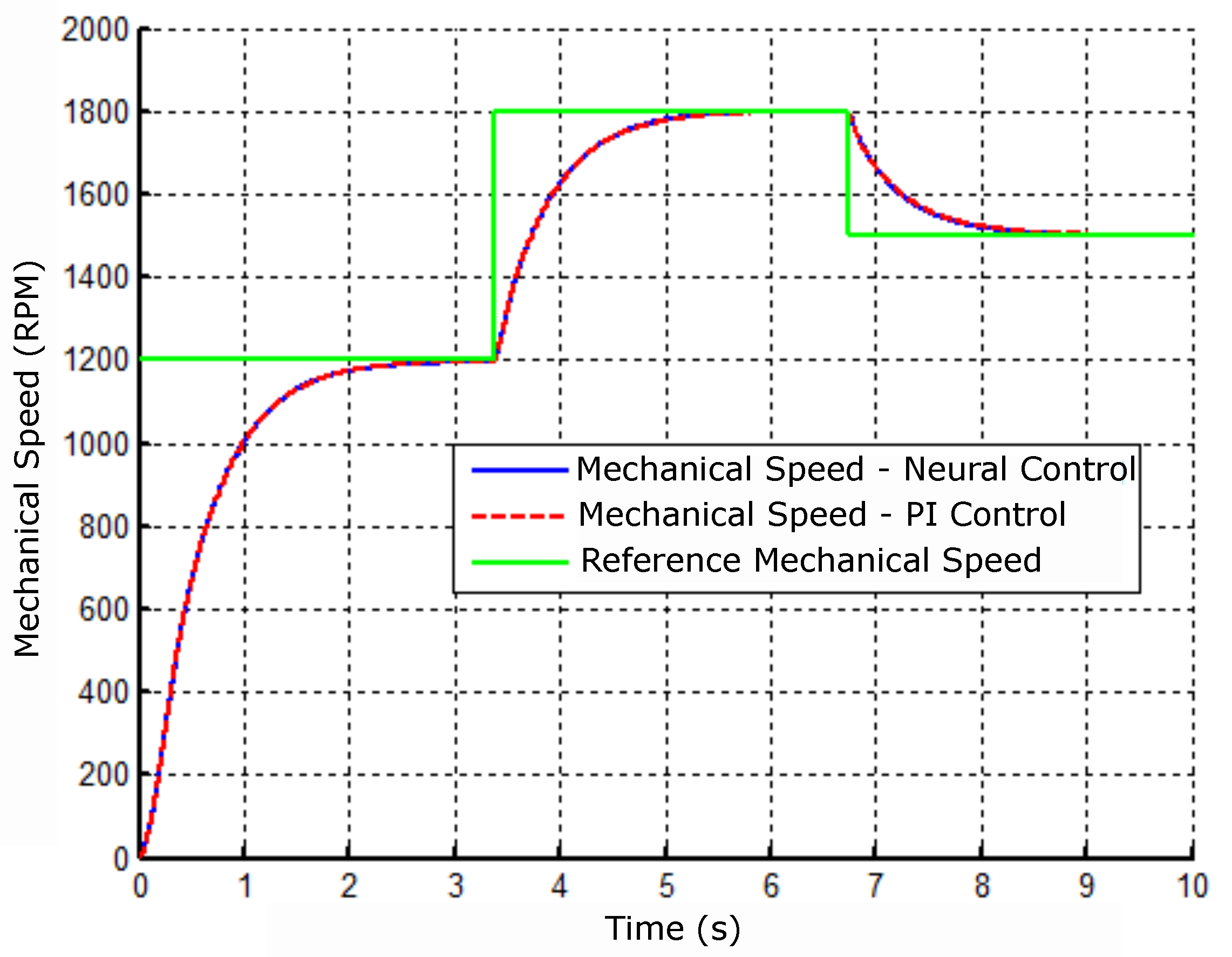
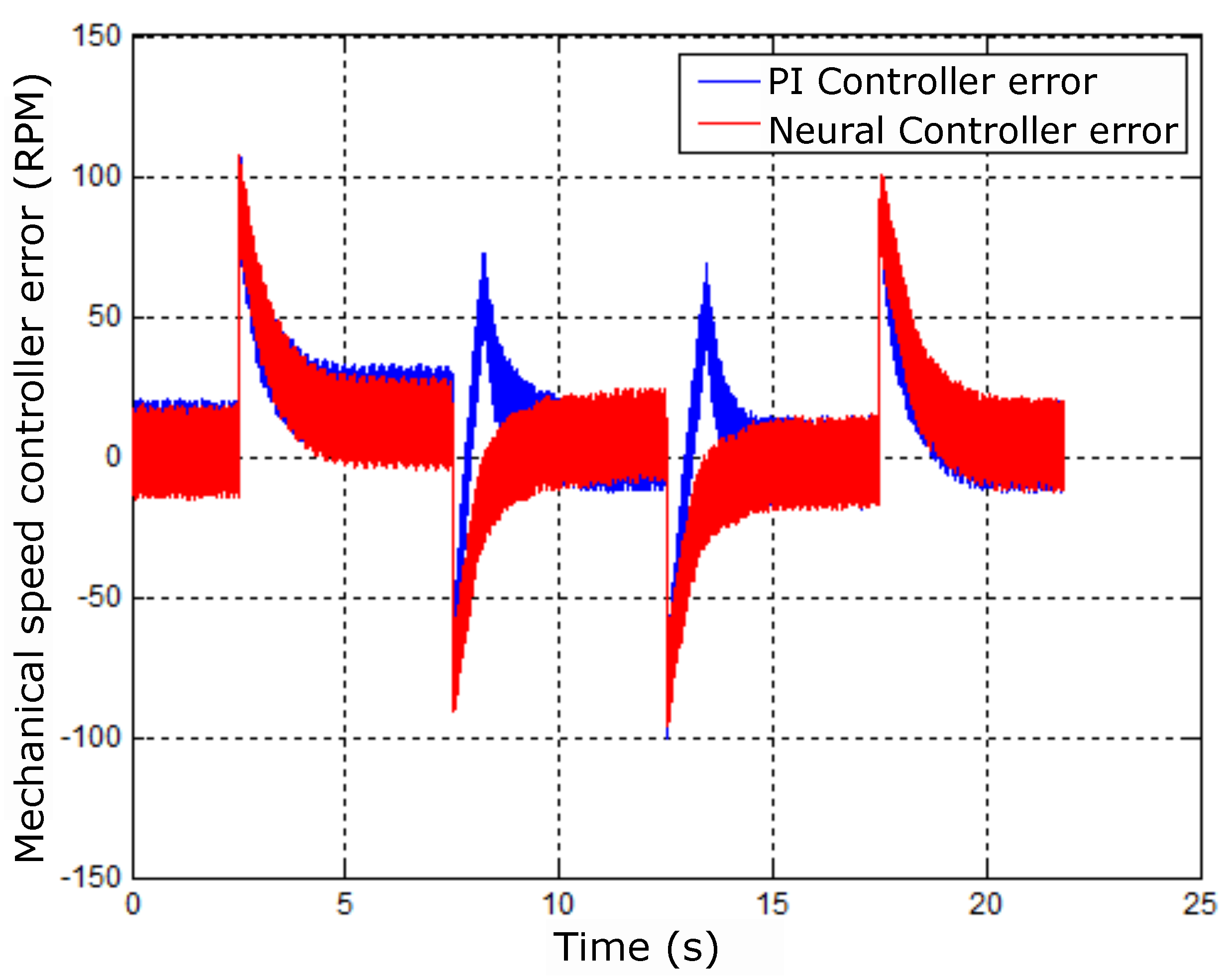
Figure 11.
Comparative result of the mechanical speed with the controllers: neural and PI.
Figure 11.
Comparative result of the mechanical speed with the controllers: neural and PI.
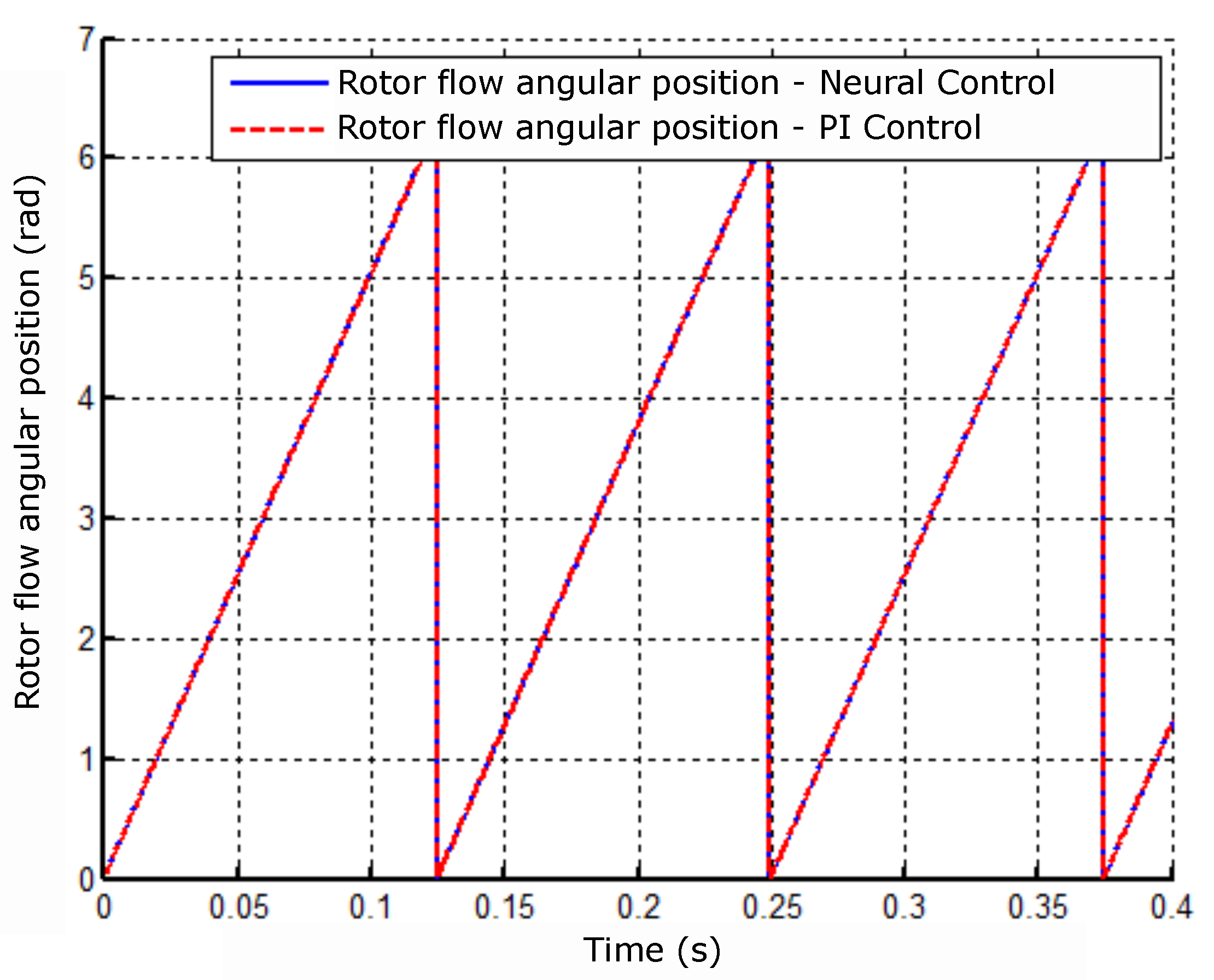
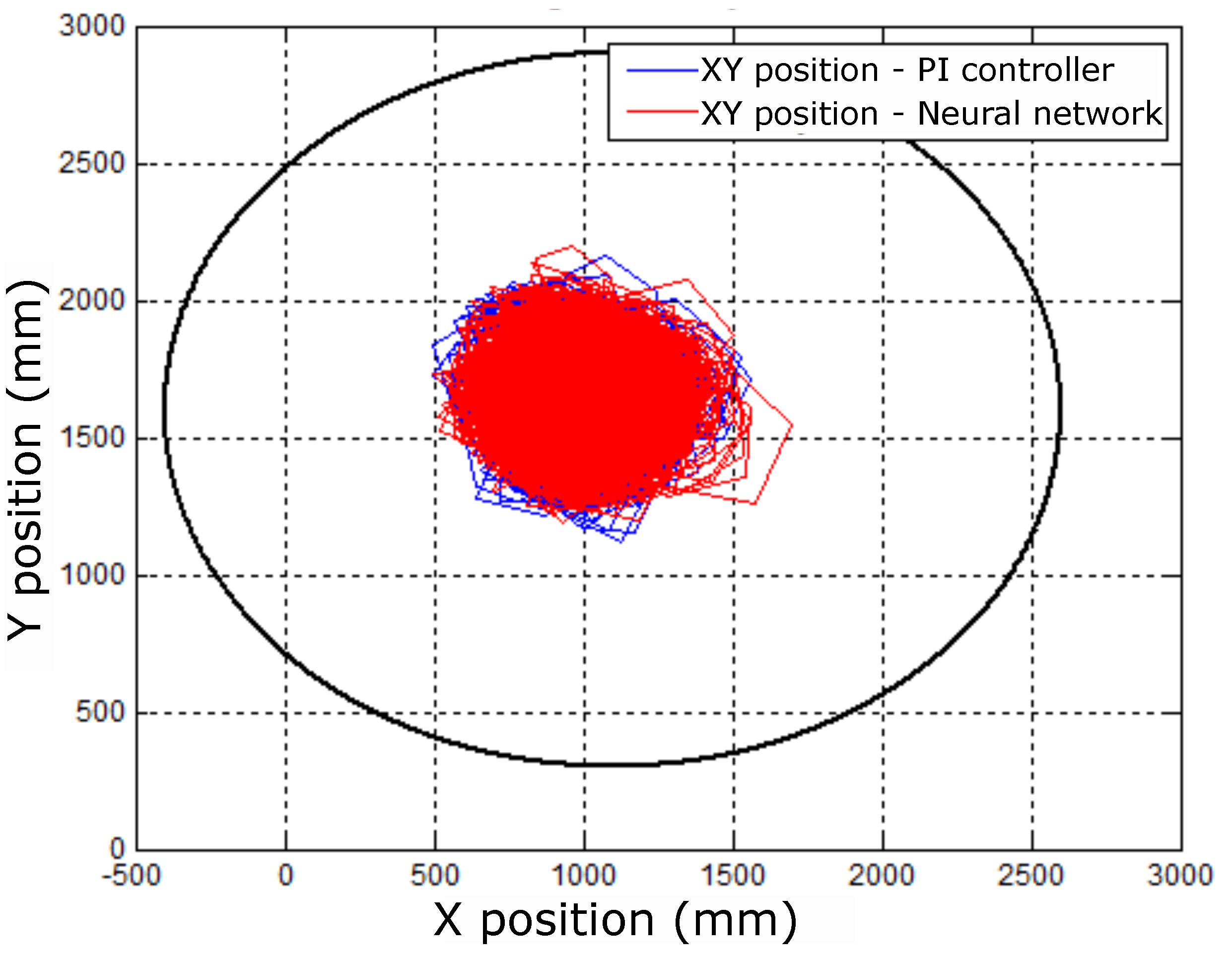
Figure 12.
Angular position result of the rotor flux with the neural controller and PI of velocity.
Figure 12.
Angular position result of the rotor flux with the neural controller and PI of velocity.
Figure 13.
Motor-bearing shaft eccentricities.
Figure 13.
Motor-bearing shaft eccentricities.
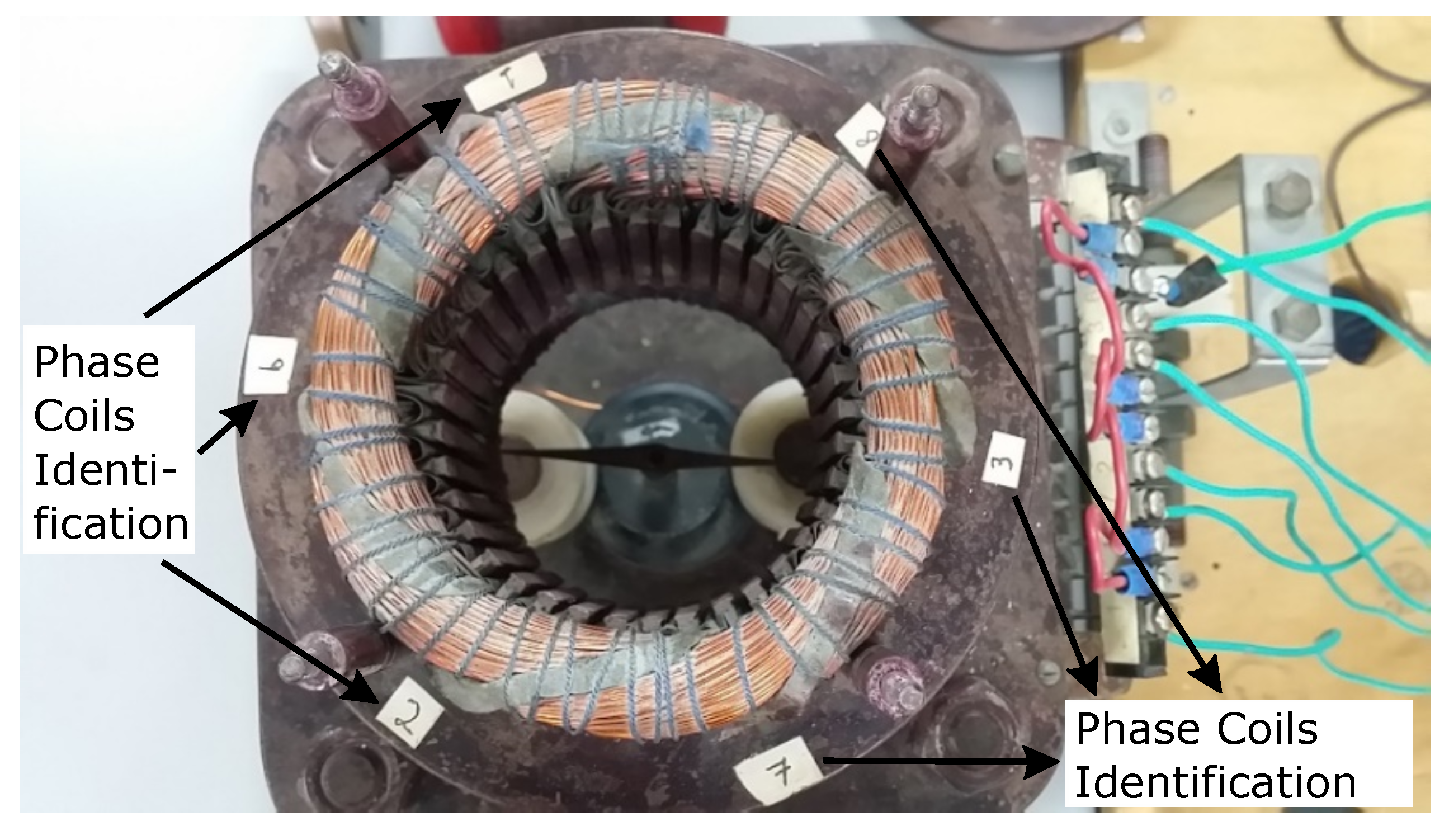
Figure 14.
Coverless bearing motor with identification of the coil groups.
Figure 14.
Coverless bearing motor with identification of the coil groups.
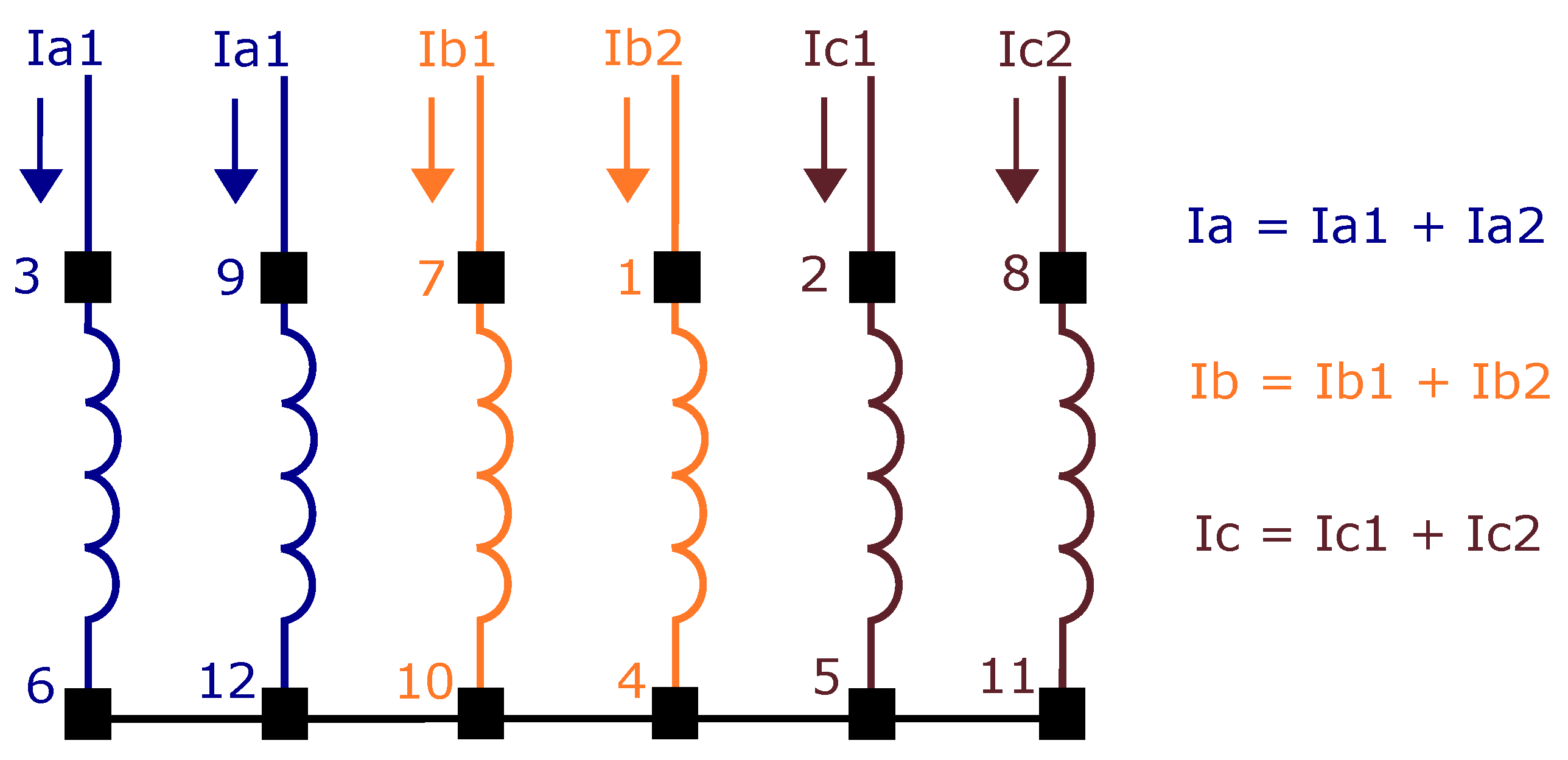
Figure 15.
Motor-bearing winding connection arrangement.
Figure 15.
Motor-bearing winding connection arrangement.
Figure 16.
Bearing motor winding connection arrangement. The result identified each coil group according to the sequence of
Figure 15.
Figure 16.
Bearing motor winding connection arrangement. The result identified each coil group according to the sequence of
Figure 15.
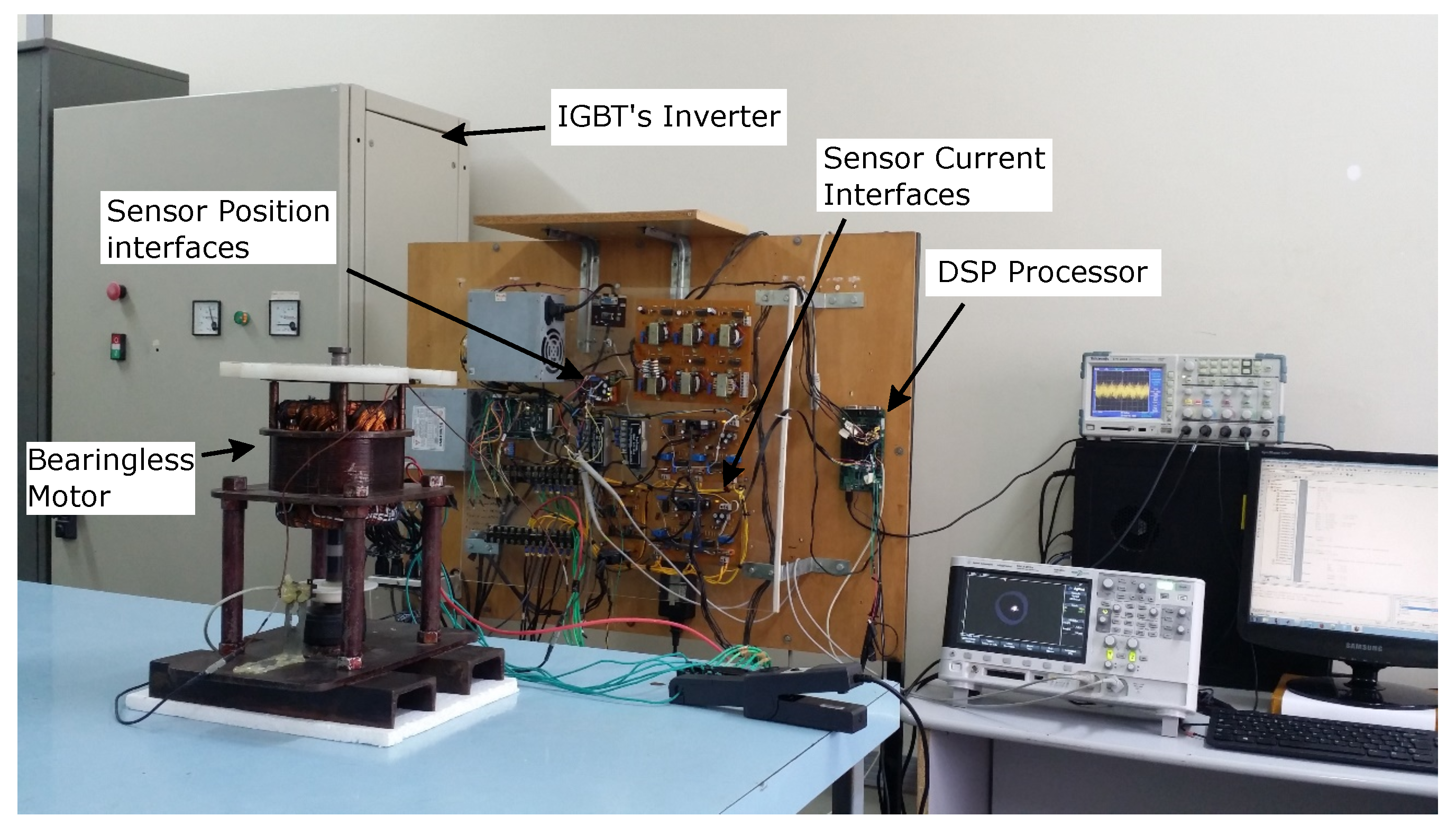
Figure 17.
Mechatronic system with interfaces and the bearing motor.
Figure 17.
Mechatronic system with interfaces and the bearing motor.
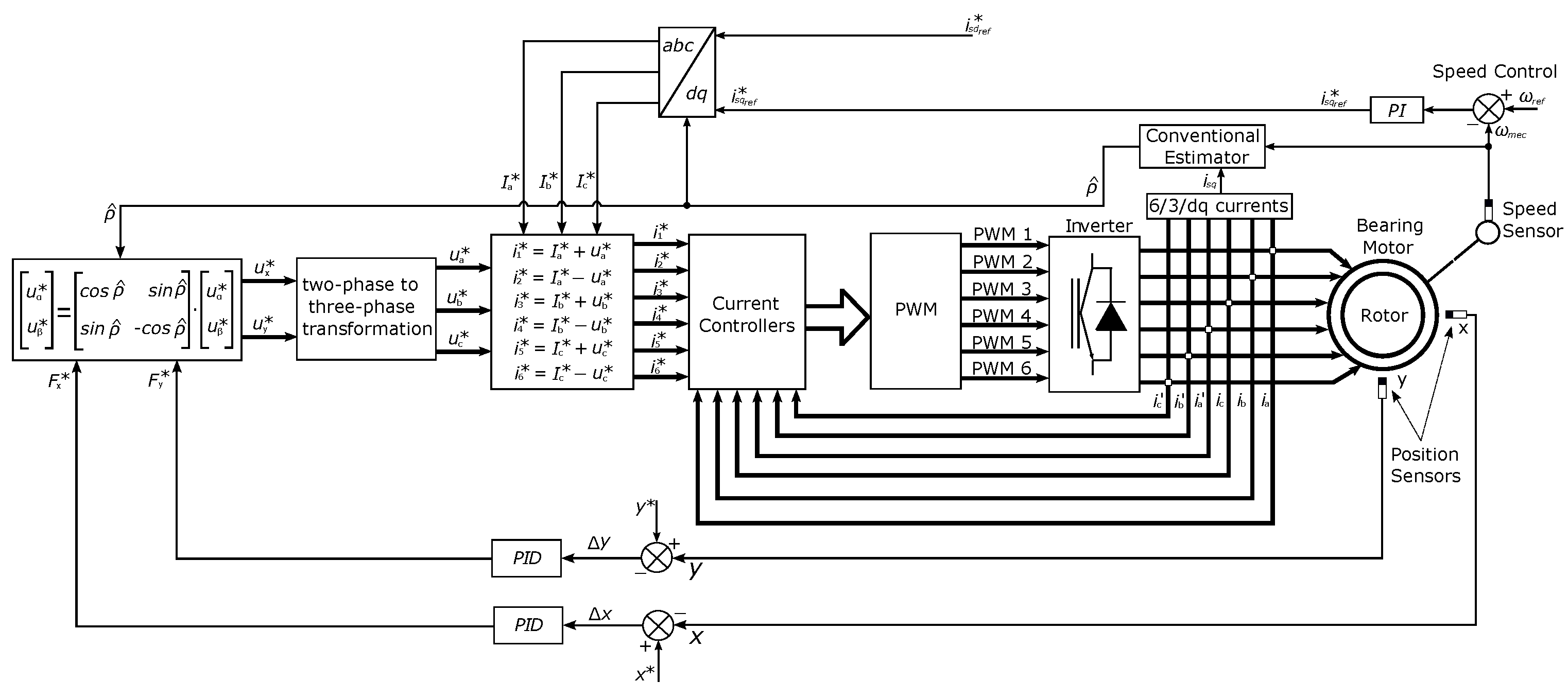
Figure 18.
Control structure with flux estimator.
Figure 18.
Control structure with flux estimator.
Figure 19.
Bearing motor cascade control diagram.
Figure 19.
Bearing motor cascade control diagram.
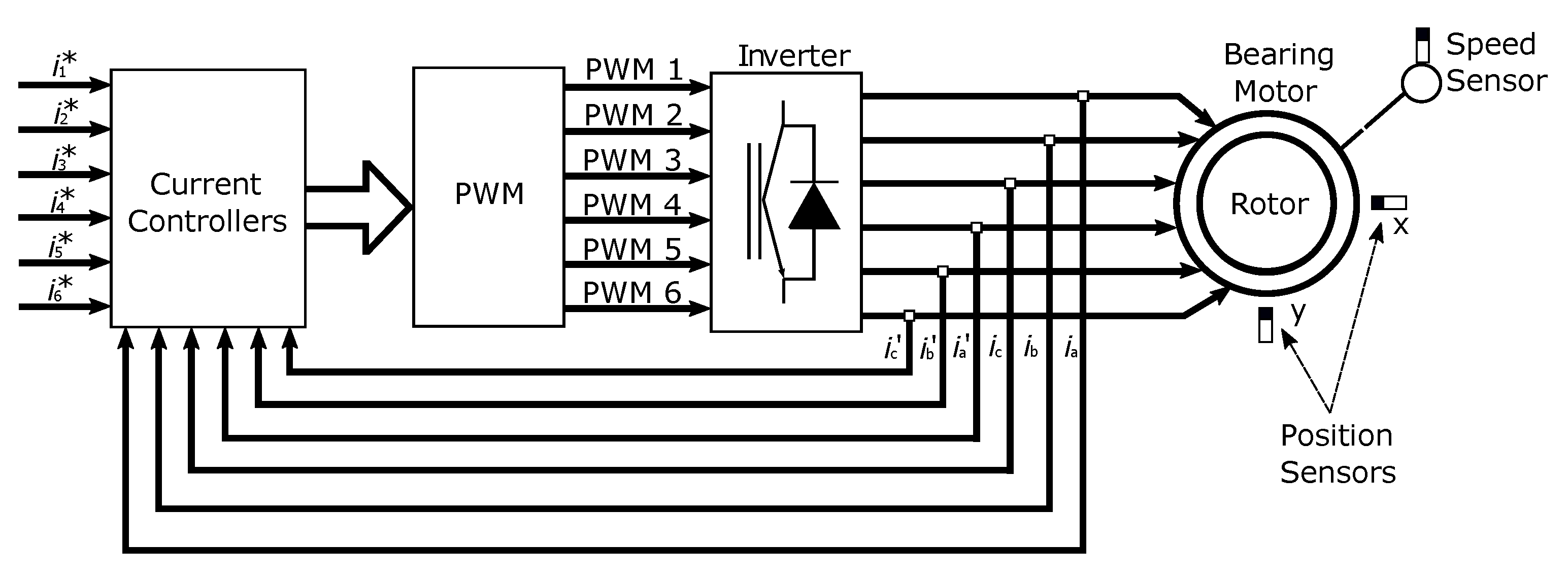
Figure 20.
Motor-bearing current control.
Figure 20.
Motor-bearing current control.
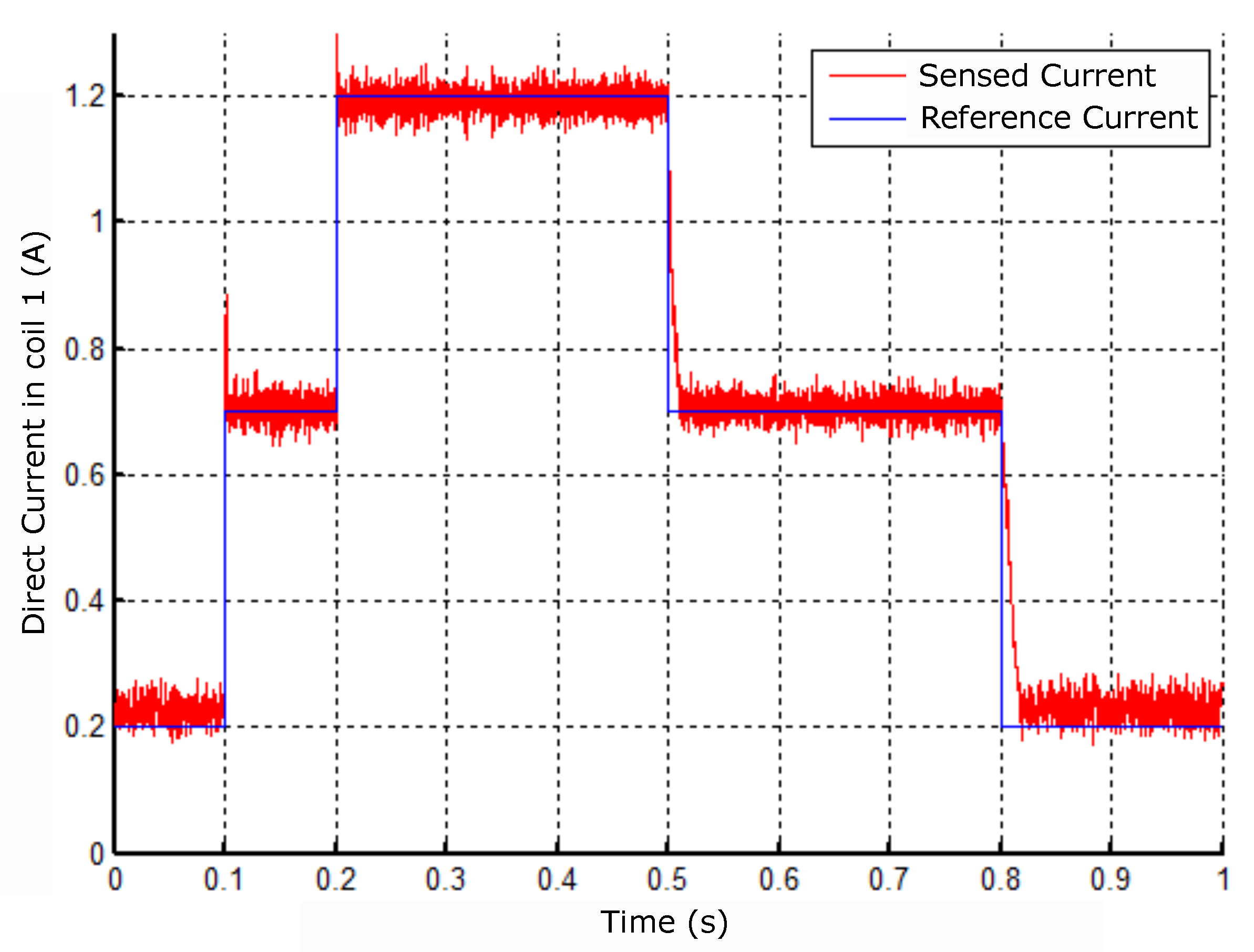
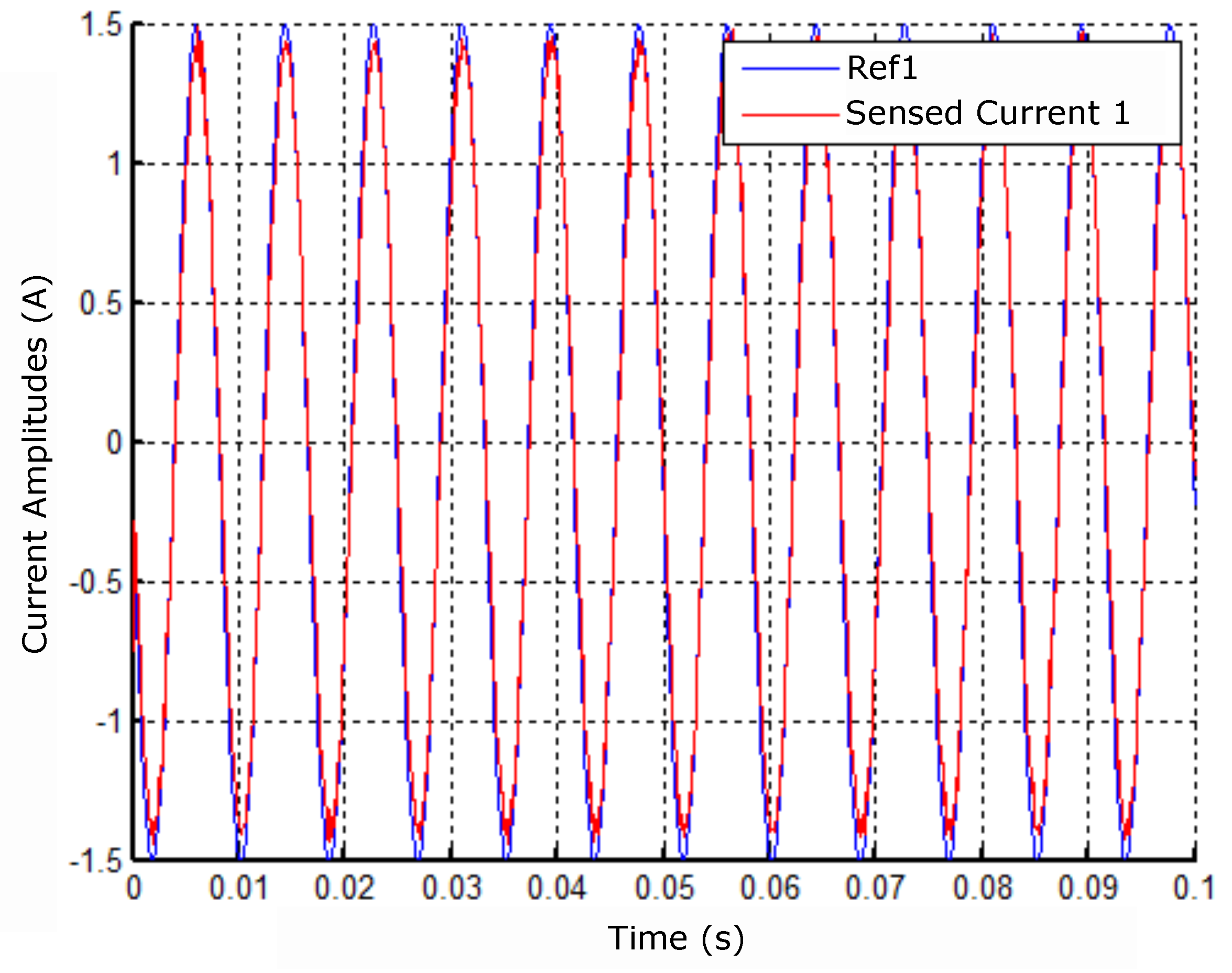
Figure 21.
Response to the reference change in coil 1.
Figure 21.
Response to the reference change in coil 1.
Figure 22.
Response to sinusoidal reference in coil 1.
Figure 22.
Response to sinusoidal reference in coil 1.
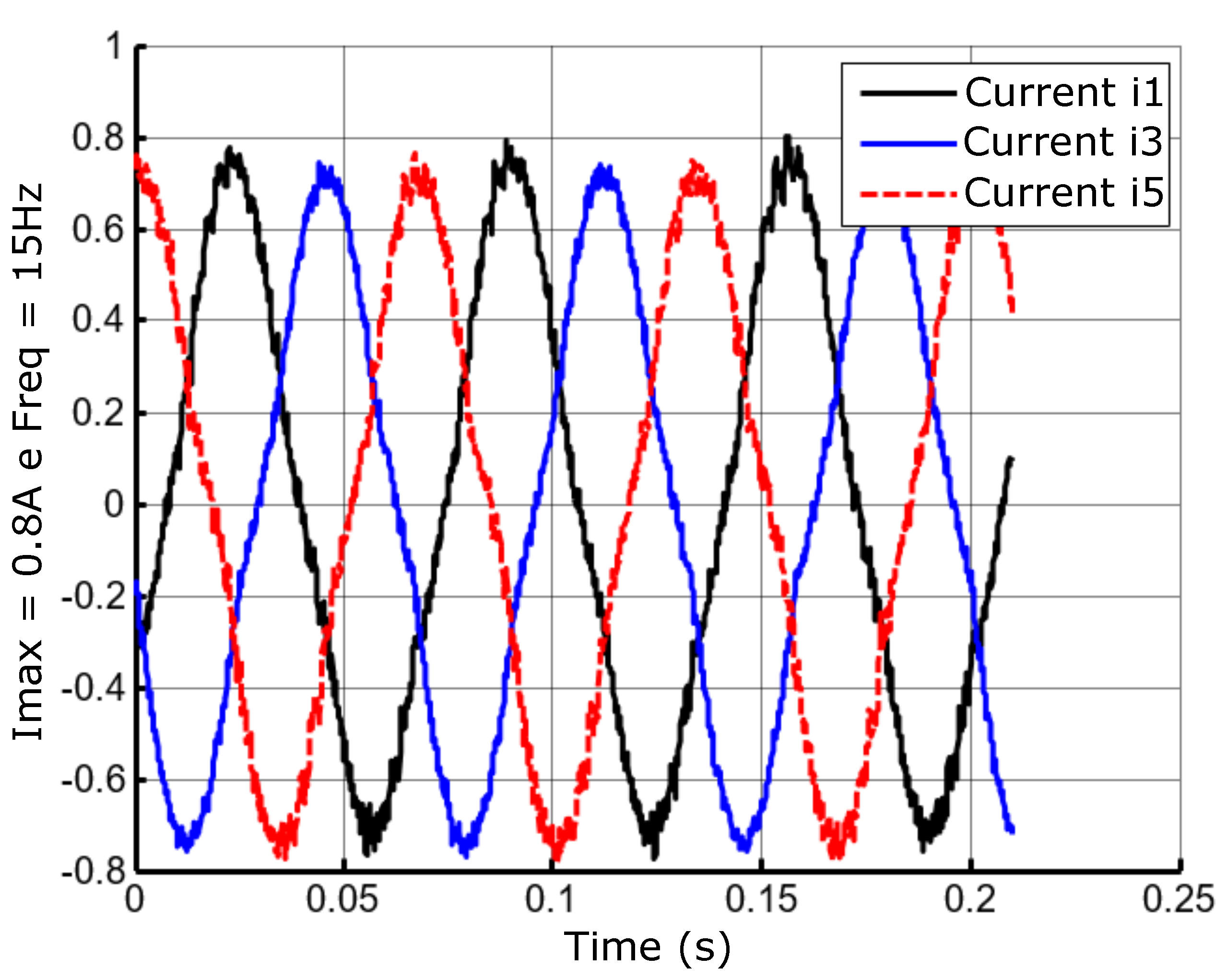
Figure 23.
Lagged currents at 15 Hz frequency and A amplitude.
Figure 23.
Lagged currents at 15 Hz frequency and A amplitude.
Figure 24.
Cascade position control with motor-bearing current control.
Figure 24.
Cascade position control with motor-bearing current control.
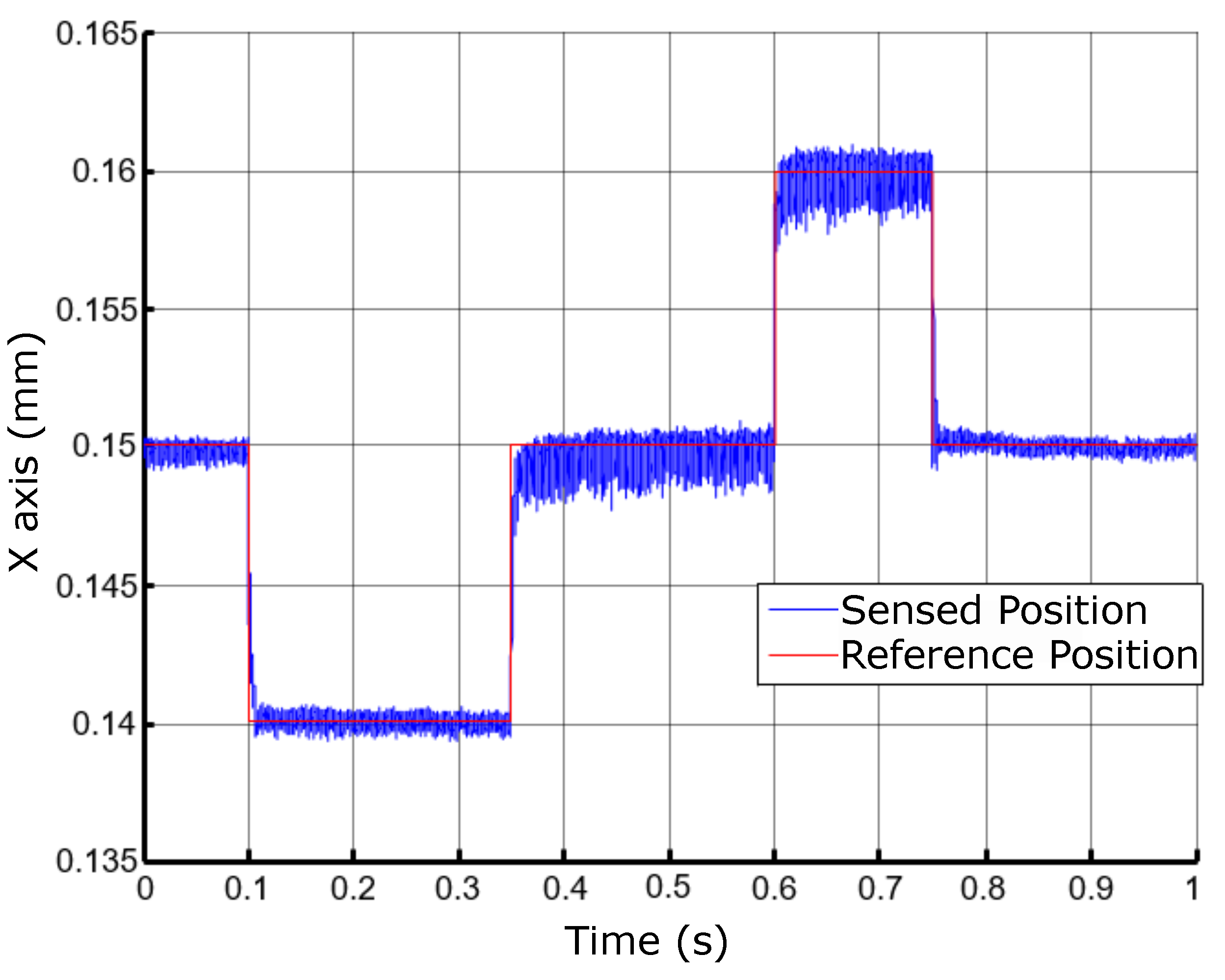
Figure 25.
Position control results for the X axis.
Figure 25.
Position control results for the X axis.
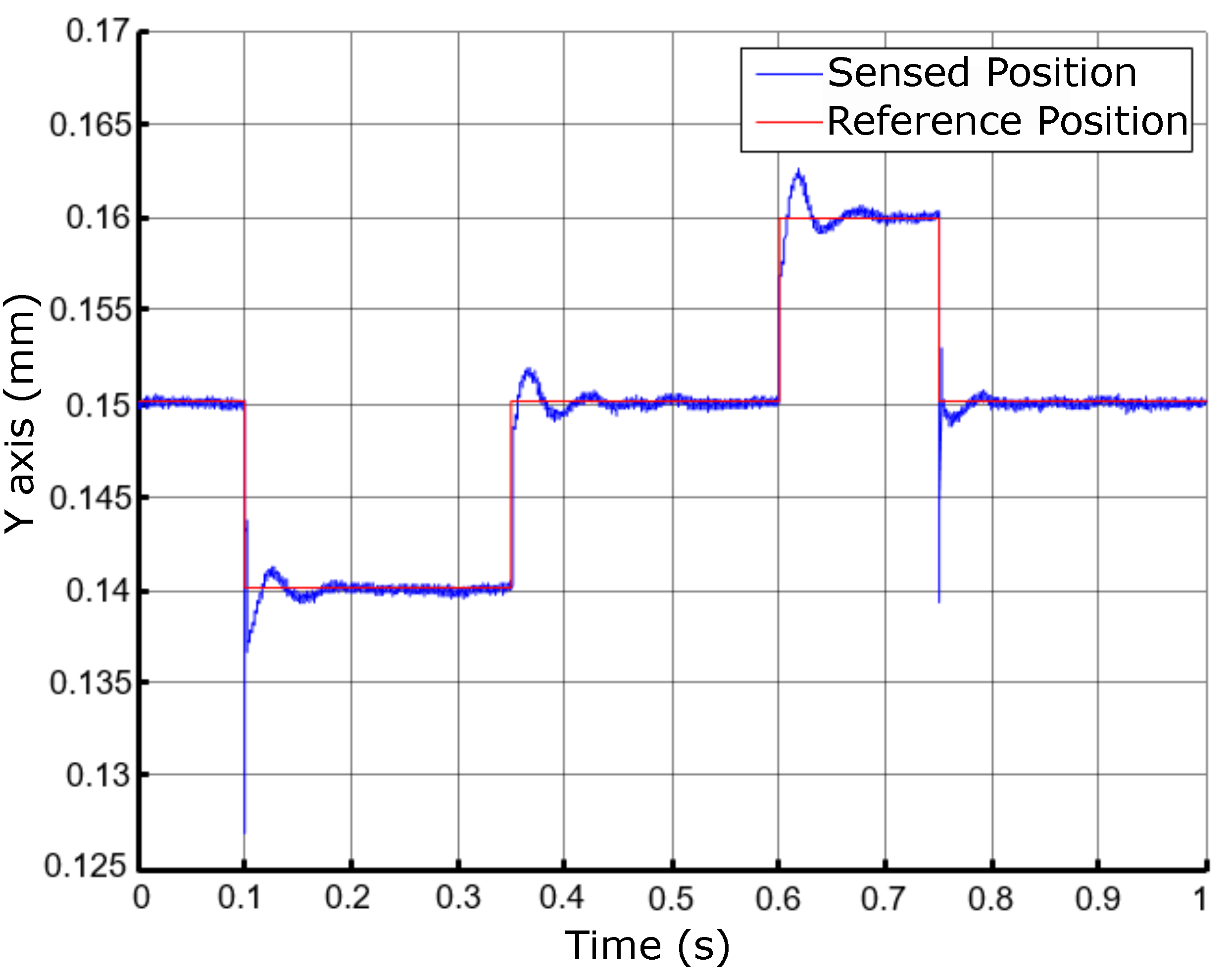
Figure 26.
Position control results for the Y axis.
Figure 26.
Position control results for the Y axis.
Figure 27.
Position control results with a rotor scatter area for activation at 60 Hz.
Figure 27.
Position control results with a rotor scatter area for activation at 60 Hz.
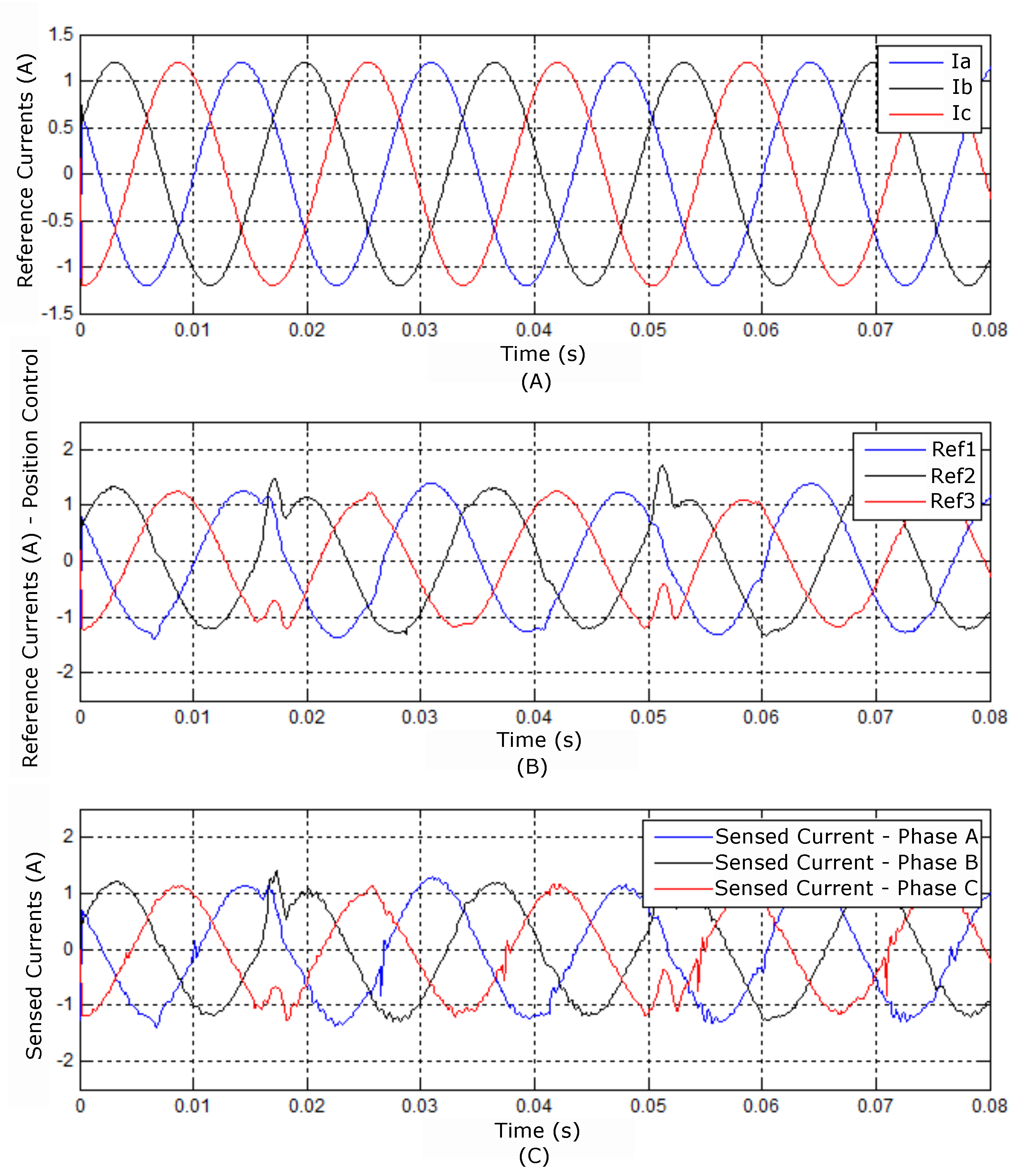
Figure 28.
Results referring to (A) imposed, (B) controlled, and (C) sensed currents.
Figure 28.
Results referring to (A) imposed, (B) controlled, and (C) sensed currents.
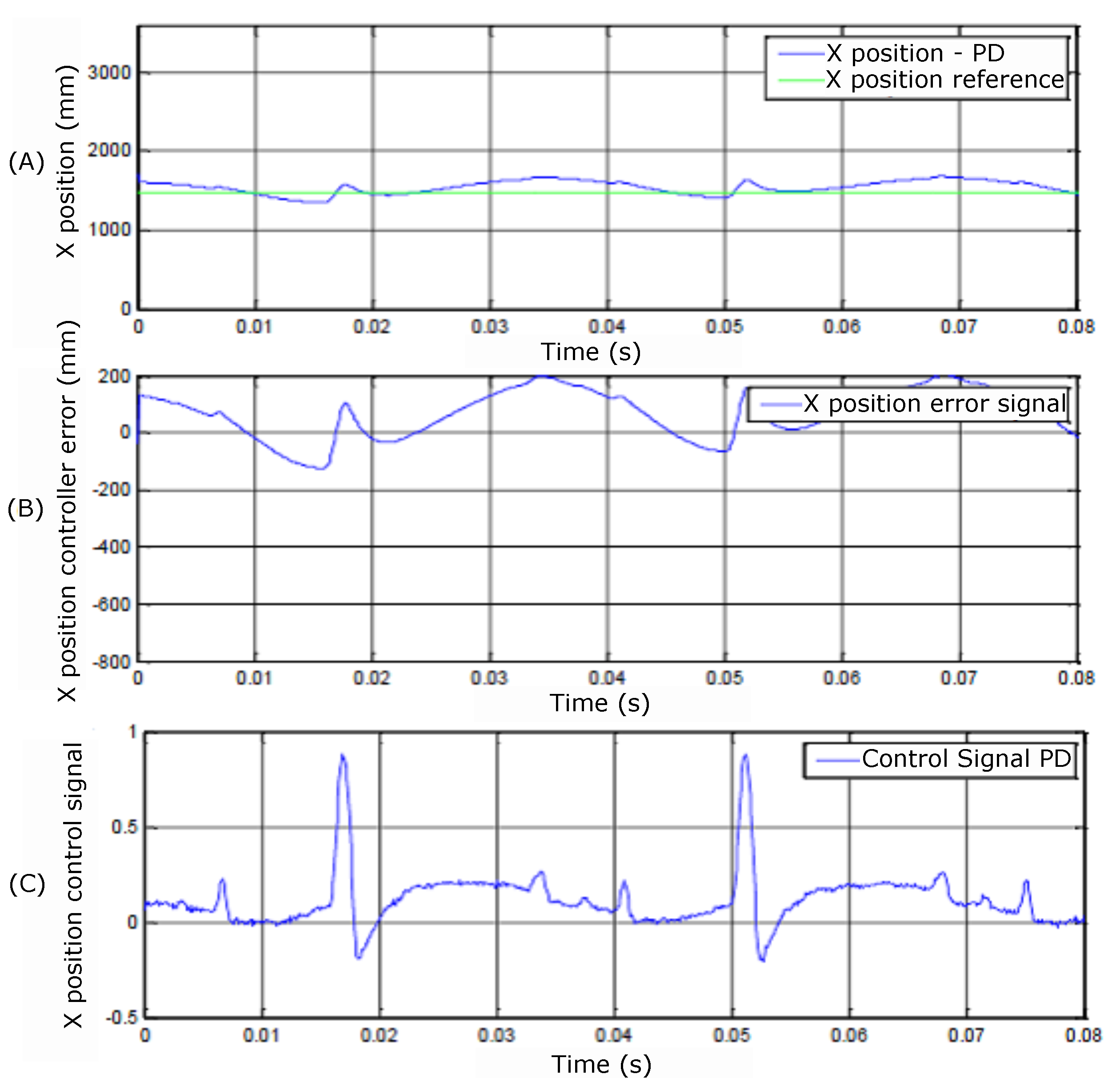
Figure 29.
(A) X position, (B) controller error, and (C) control signals.
Figure 29.
(A) X position, (B) controller error, and (C) control signals.
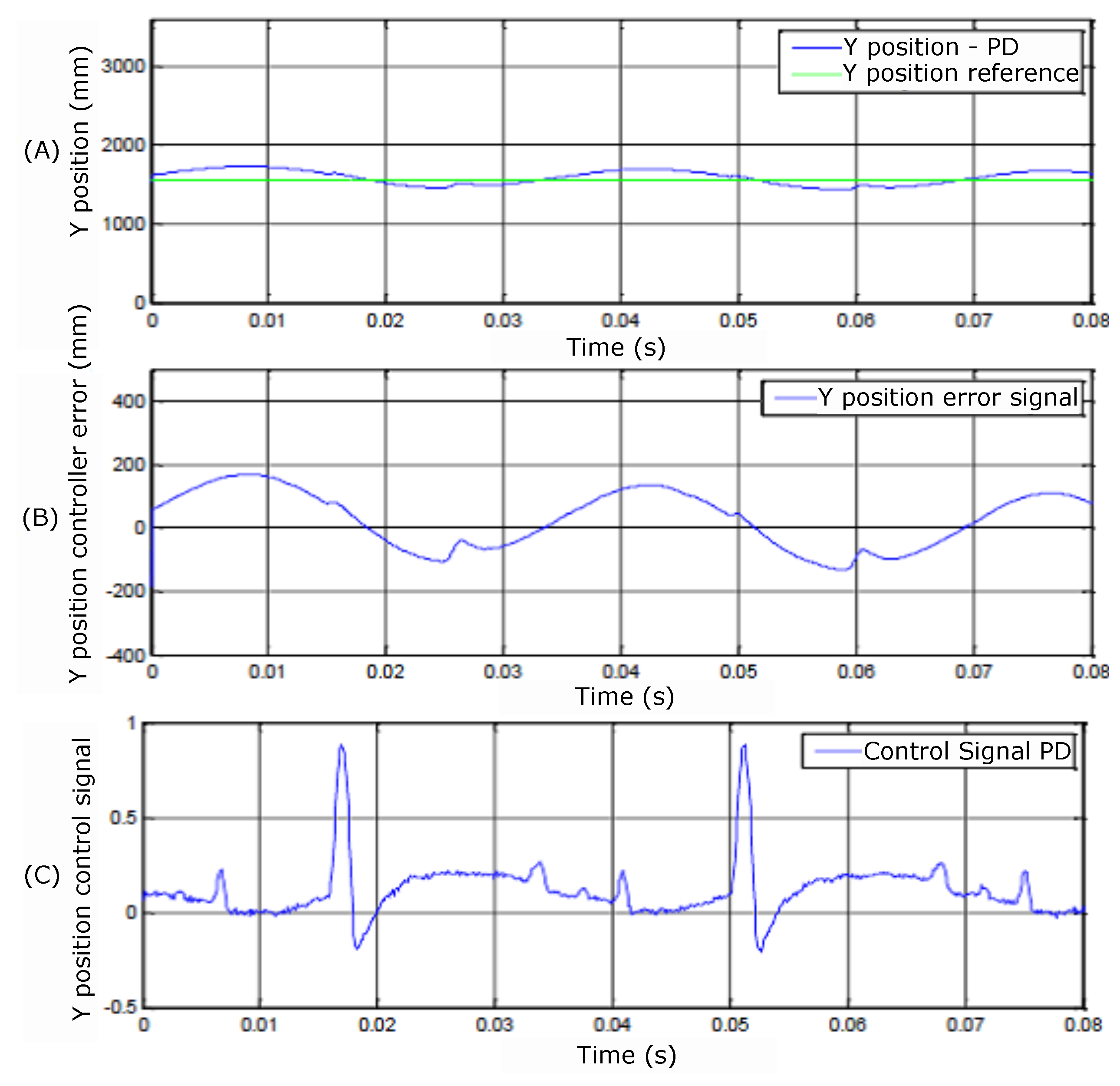
Figure 30.
(A) Y position; (B) controller error; and (C) control signals.
Figure 30.
(A) Y position; (B) controller error; and (C) control signals.
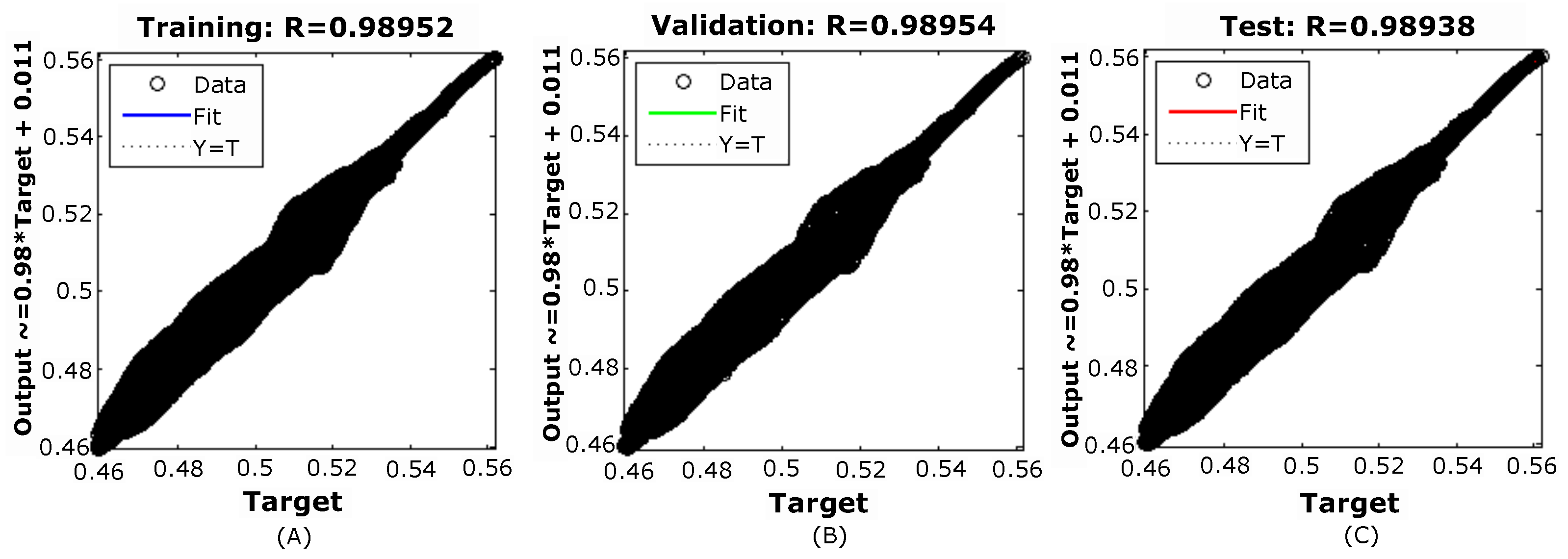
Figure 31.
Result of training, validation, and testing of the Neural Network.
Figure 31.
Result of training, validation, and testing of the Neural Network.
Figure 32.
Mean squared error for training () with 104 epochs.
Figure 32.
Mean squared error for training () with 104 epochs.
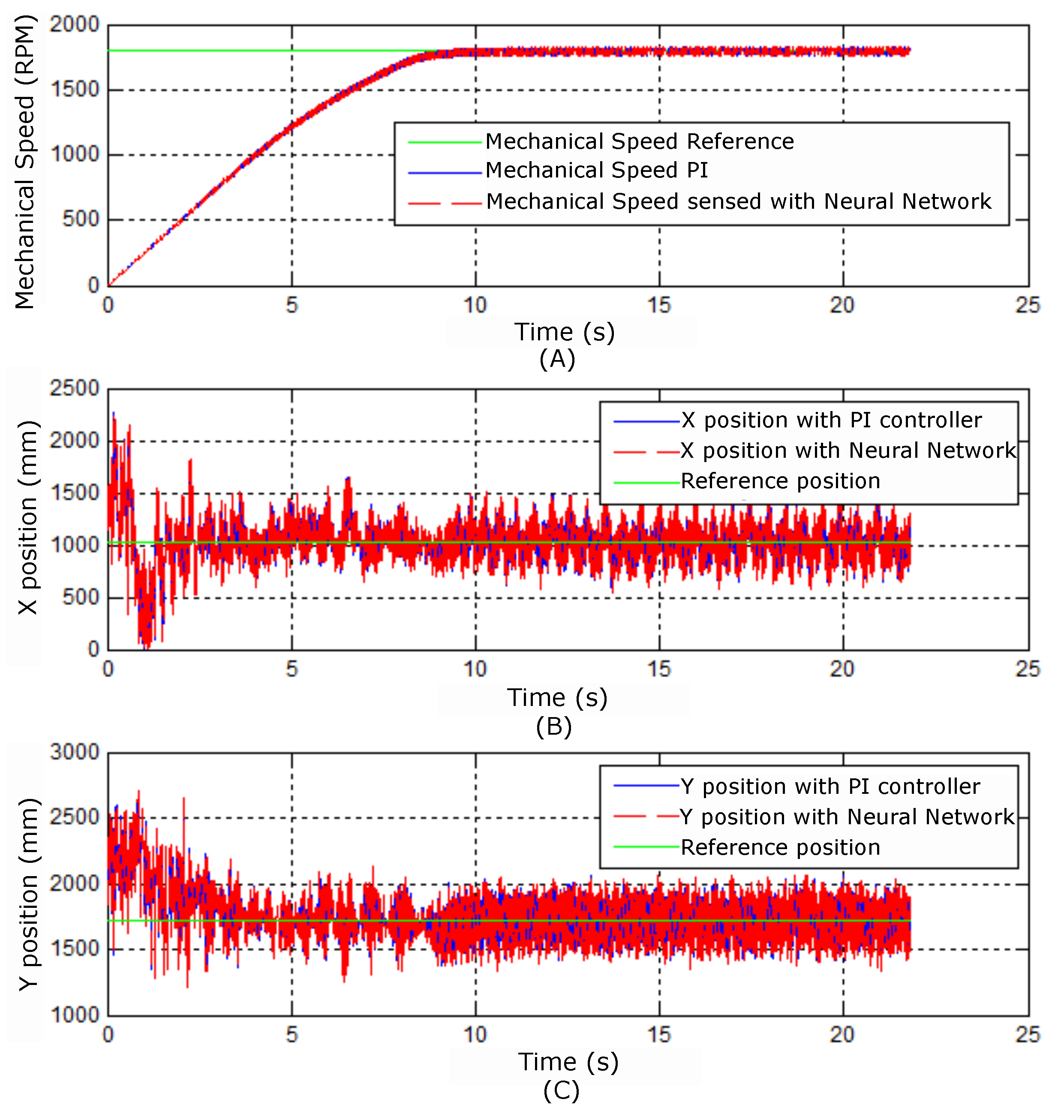
Figure 33.
Mechanical speeds and X and Y positions for step speed reference constant.
Figure 33.
Mechanical speeds and X and Y positions for step speed reference constant.
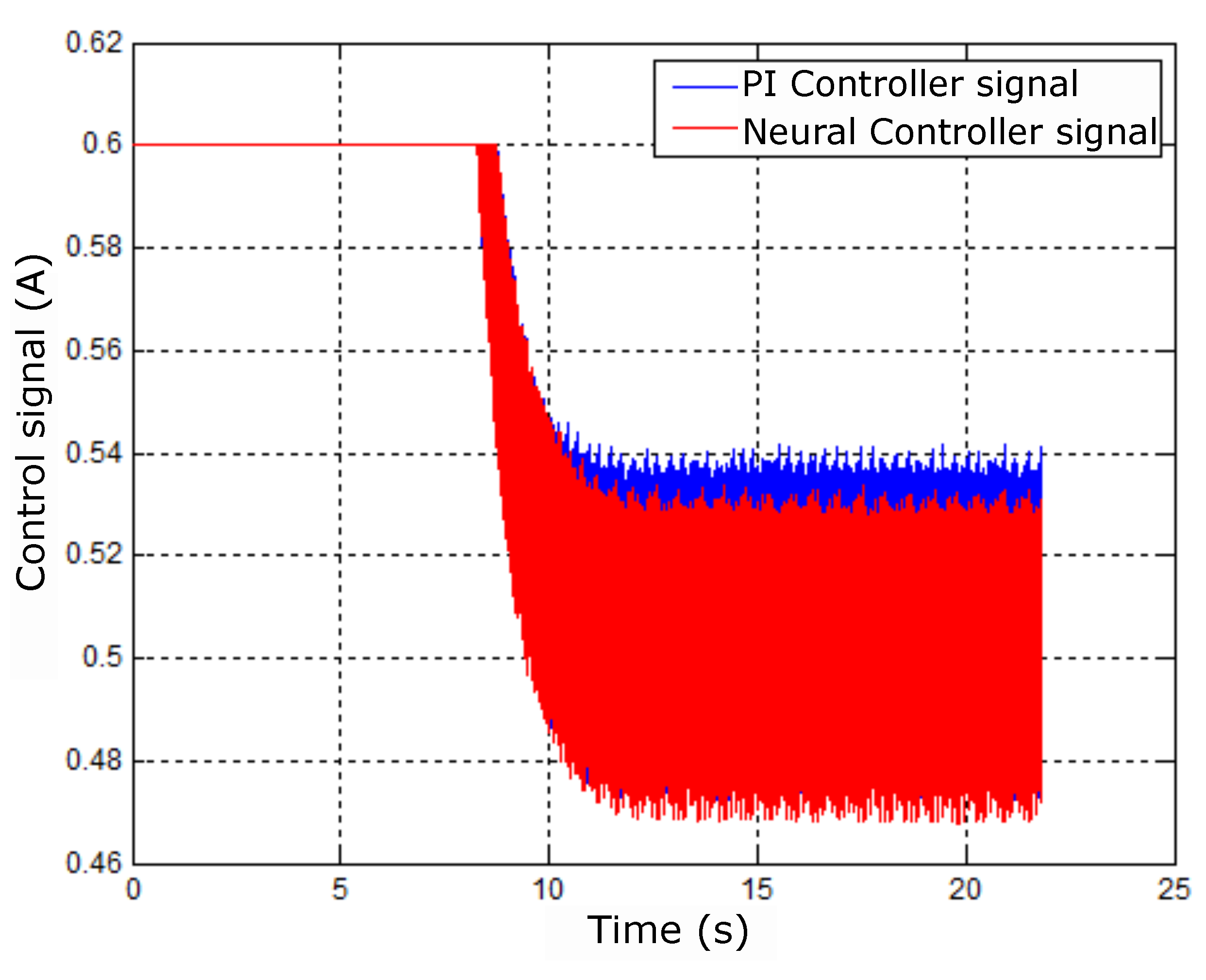
Figure 34.
PI and neural control signals for step speed reference.
Figure 34.
PI and neural control signals for step speed reference.
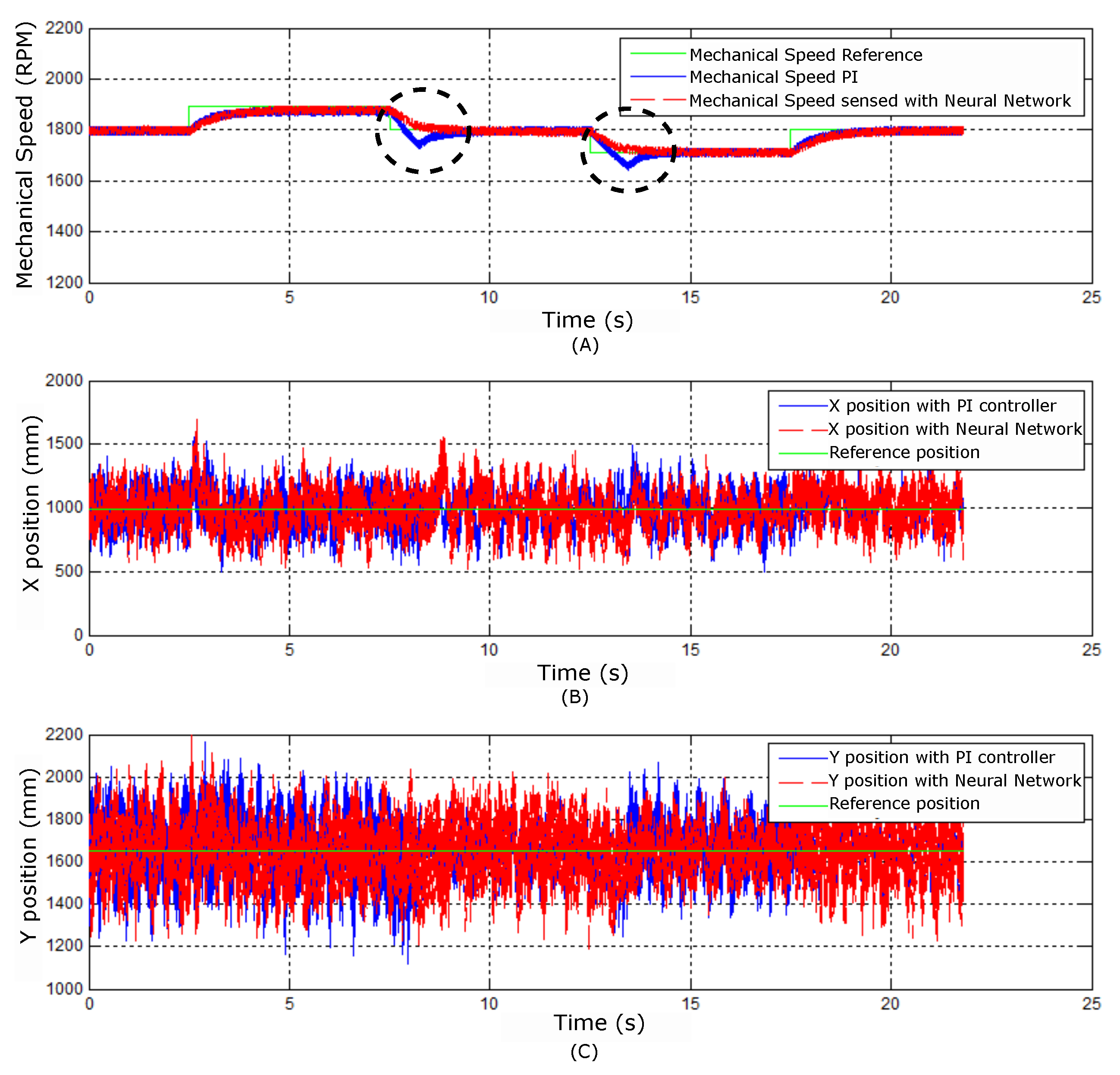
Figure 35.
Mechanical speed and X and Y positions for step speed reference.
Figure 35.
Mechanical speed and X and Y positions for step speed reference.
Figure 36.
Control signals for step speed reference.
Figure 36.
Control signals for step speed reference.
Figure 37.
Control error signals for step speed reference.
Figure 37.
Control error signals for step speed reference.
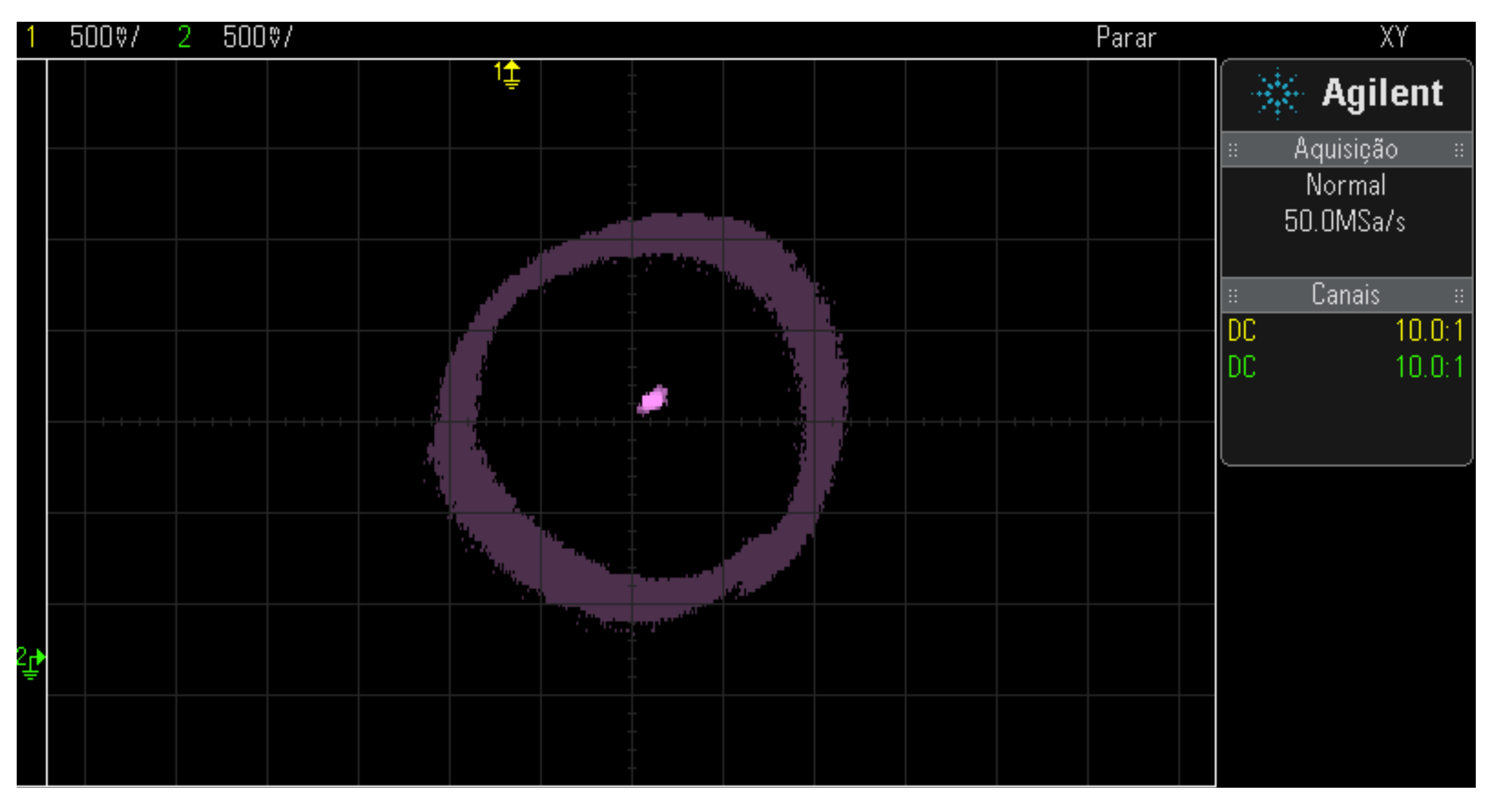
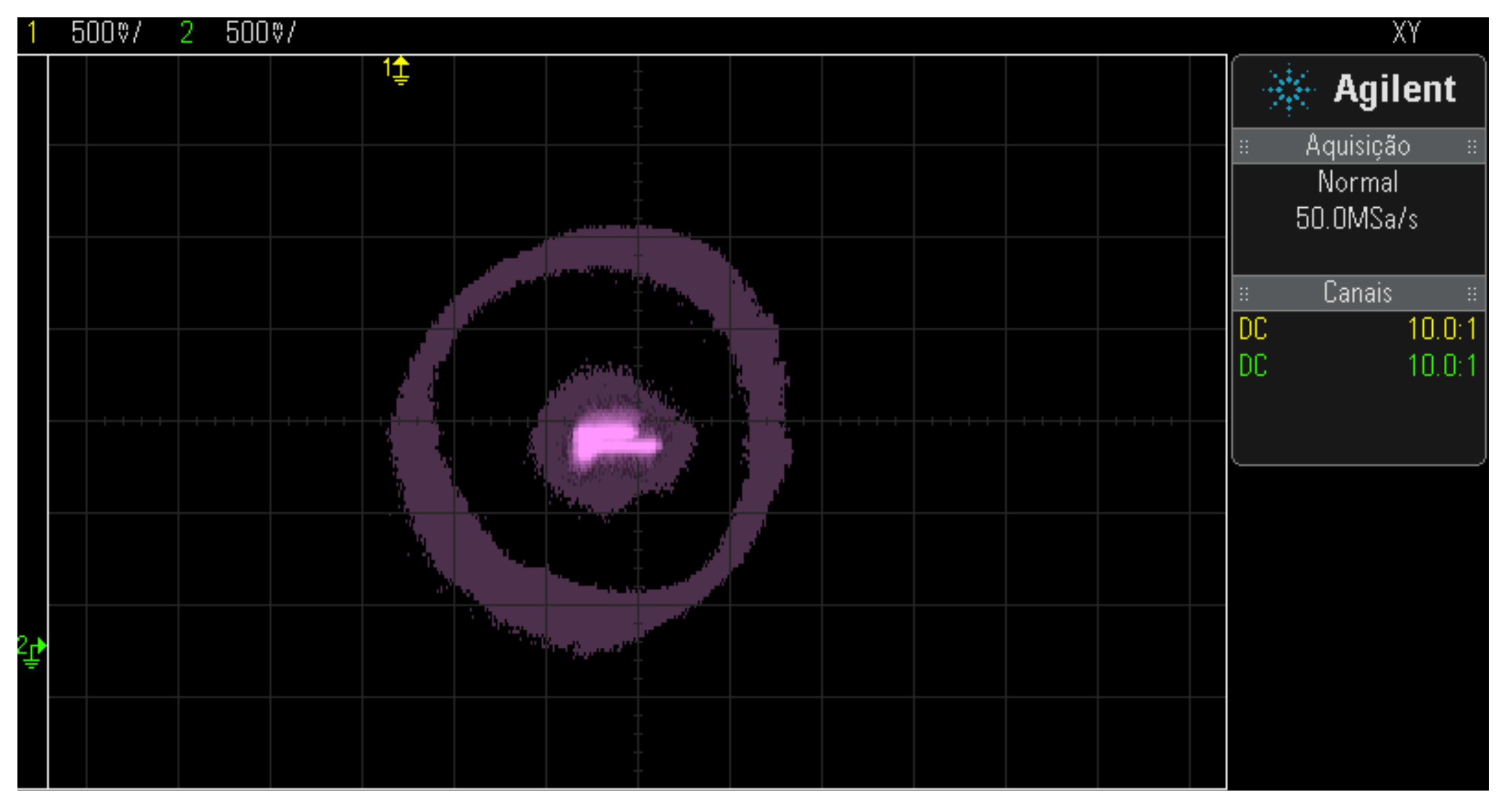
Figure 38.
Radial positioning diagrams for step speed reference.
Figure 38.
Radial positioning diagrams for step speed reference.
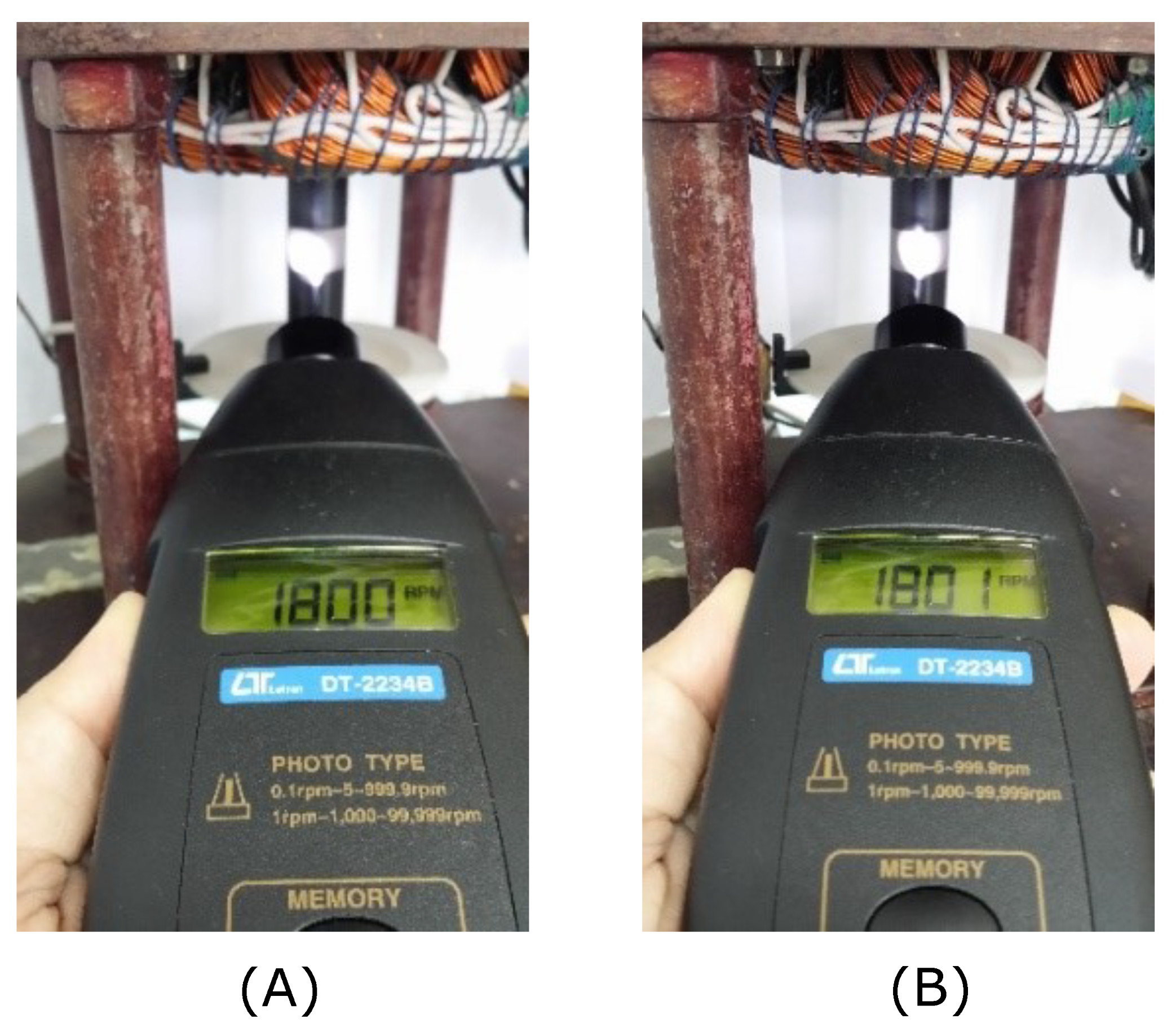
Figure 39.
Mechanical velocity measurement (A) PI control and (B) neural control.
Figure 39.
Mechanical velocity measurement (A) PI control and (B) neural control.
Table 1.
Motor Parameters and Characteristics.
Table 1.
Motor Parameters and Characteristics.
| Symbols | Description | Values |
|---|
| Pnom | Rated power | 3.70 kW |
| Wmec | Rated Speed | 1715 RPM |
| Tnom | Rated voltage | 380 V |
| Np | Pole Pair Number | 2 |
| R1 | Stator Resistance | 1.182 |
| R2 | Rotor Resistance | 1.42 |
| J | Inertia moment | 0.00995 kg·m2 |
| Ls | Stator Inductance | 6.56 mH |
| Lr | Rotor Inductance | 6.56 mH |
| Lm | Magnetization Inductance | 0.14 H |
| Core loss | 891.2 |
| Gap size | 0.25 mm |
Table 2.
ANFIS 1 Parameters.
Table 2.
ANFIS 1 Parameters.
| Pertinence Functions | Epoach | Training Error | Validation Error |
|---|
| 2 | 50 | 0.0558002 | 0.00813261 |
| 3 | 150 | 0.0488926 | 0.00815185 |
| 3 | 300 | 0.0409925 | 0.01109080 |
| 5 | 500 | 0.00175787 | 0.00781050 |
Table 3.
ANFIS 2 Parameters.
Table 3.
ANFIS 2 Parameters.
| Pertinence Functions | Epoach | Training Error | Validation Error |
|---|
| 2 | 50 | 0.00406290 | 0.00489893 |
| 3 | 150 | 0.00533958 | 0.7491140 |
| 3 | 300 | 0.00448118 | 0.3522810 |
| 5 | 400 | 0.00359959 | 0.3302490 |
Table 4.
Neural Network Parameters.
Table 4.
Neural Network Parameters.
| Network Architecture | Multilayer Perceptron |
|---|
| Training type | Supervised-offline |
| Layers number | 3 |
| Input layer neurons | 3 |
| 1st hidden layer neurons | 10 |
| Output layer neurons | 1 |
| Training algorithm | Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation |
| Learning rate | |
| Epochs number | 841 |
| Training error | |
| Hidden layer activation function | Hyperbolic tangent |
| Output layer activation function | Linear |
Table 5.
Motor prototype parameters.
Table 5.
Motor prototype parameters.
| Parameters | Values |
|---|
| Rated power | 1 Hp |
| Frequency | 60 Hz |
| Poles numbers | 4 |
| Rated voltage | 220/380 V |
| Rated current | 3.02/1.75 A |
| Empty current | 1.90 A |
| No load power | 160.00 W |
| Resistance | 7.38 Ohms |
| Stator Resistance per Phase | 0.73 Ohms |
Table 6.
New Neural Network Parameters.
Table 6.
New Neural Network Parameters.
| New Network Architecture | New Multilayer Perceptron |
|---|
| Type of training | Supervised-offline |
| Number of layers | 3 |
| Input layer neurons | 2 |
| 1st hidden layer neurons | 10 |
| Output layer neurons | 1 |
| Training algorithm | Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation |
| Learning rate | |
| Epoch number | 104 |
| Training error | |
| Hidden layer activation function | Hyperbolic tangent |
| Output layer activation function | Linear |