State-of-the-Art and Recent Advances in the Abatement of Gaseous Pollutants from Waste-to-Energy
Abstract
1. Introduction
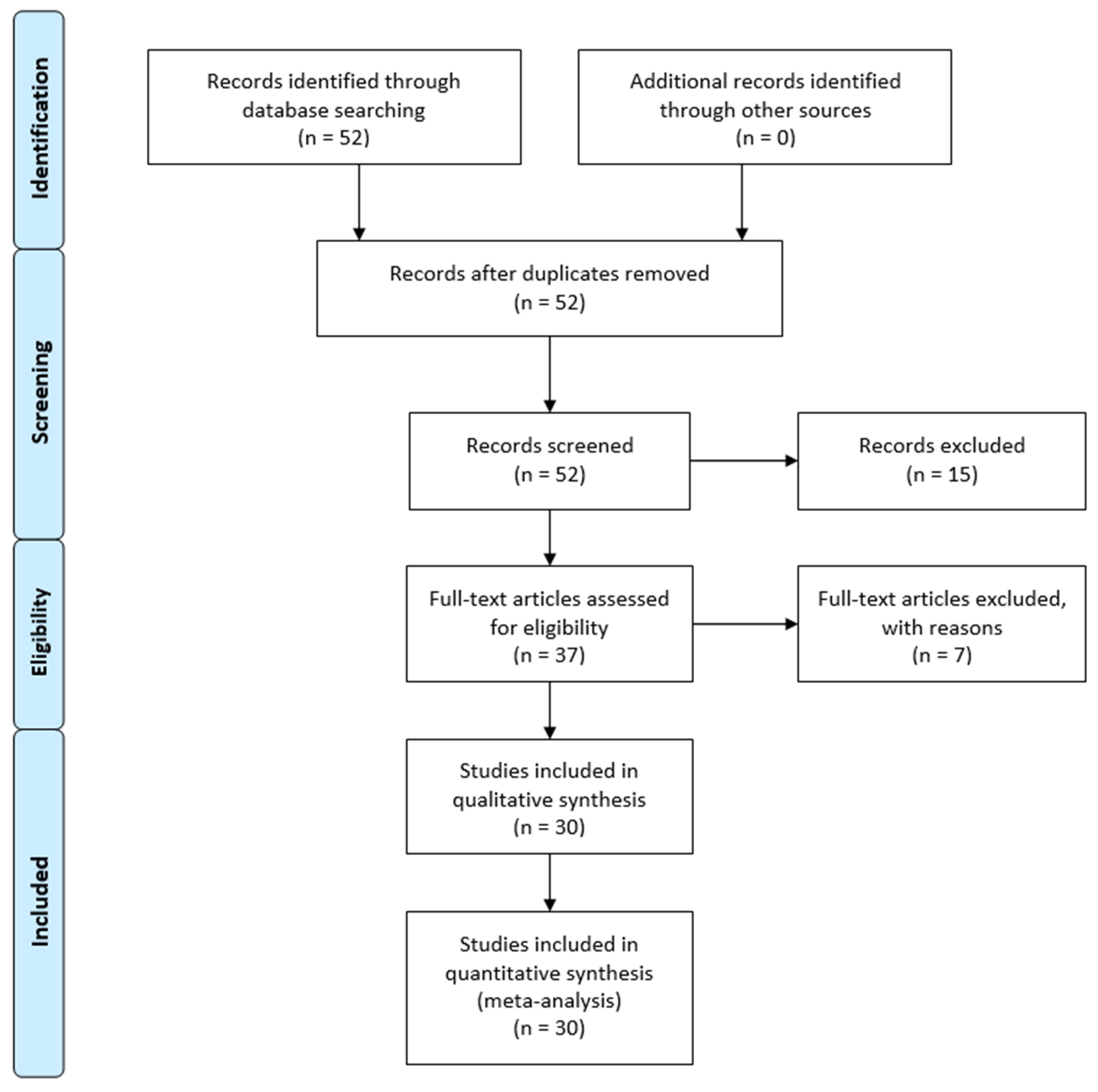
2. Materials and Methods
- waste AND incineration AND (air pollution control) AND NOx;
- waste AND incineration AND (air pollution control) AND ((acid gases) OR (HCl) OR (HF) OR (SO2) OR (SOx));
- waste AND incineration AND (air pollution control) AND VOCs, respectively, for the research on the removal of NOx, acid gases, and VOCs.
3. Air Pollution Control Technologies
3.1. BATs
- scientific and technical literature;
- more than 300 questionnaires from operators of waste incineration and incineration bottom ash treatment plants;
- additional information from the technical working group (TWG) members;
- about 2900 comments on Draft 1 of the revised BREF;
- information gathered from site visits;
- outcomes of workshops and webinars.
3.1.1. BATs for Acid Gas Reduction
- jet scrubbers;
- rotation scrubbers;
- venturi scrubbers;
- spray scrubbers;
- packed tower scrubbers.
- Techniques for injecting sorbent into the boiler: This approach involves introducing a dry sorbent into the combustion chamber or adding calcium- or magnesium-based sorbents to the bed of a fluidized bed boiler. The sorbent particles react with the acid gas present in the boiler effluents. Often, this technique is combined with a particulate emission control system;
- Circulating fluidized bed (CFB) dry purifier: the gaseous effluents coming from the air pre-heater in the boiler enter the lower part of the purifier and rise vertically through a venturi section, where a solid absorbent and water are injected separately. Also, in this case, this solution is usually associated with a technique for reducing suspended particles;
- Inline sorbent injection (DSI): This technique involves dispersing a dry powdered sorbent into the flue gas stream. The sorbent reacts with acid gases to form a solid, which is subsequently removed through particulate emission control systems. Usually, the use of bag filters is preferred;
- Atomizer, spray dryer absorber (SDA): a suspension or solution of alkaline reagent is introduced and dispersed in the flue gas flow. The material in contact with the gaseous contaminant reacts to form a solid, which is subsequently removed downstream through a particulate emission control system.
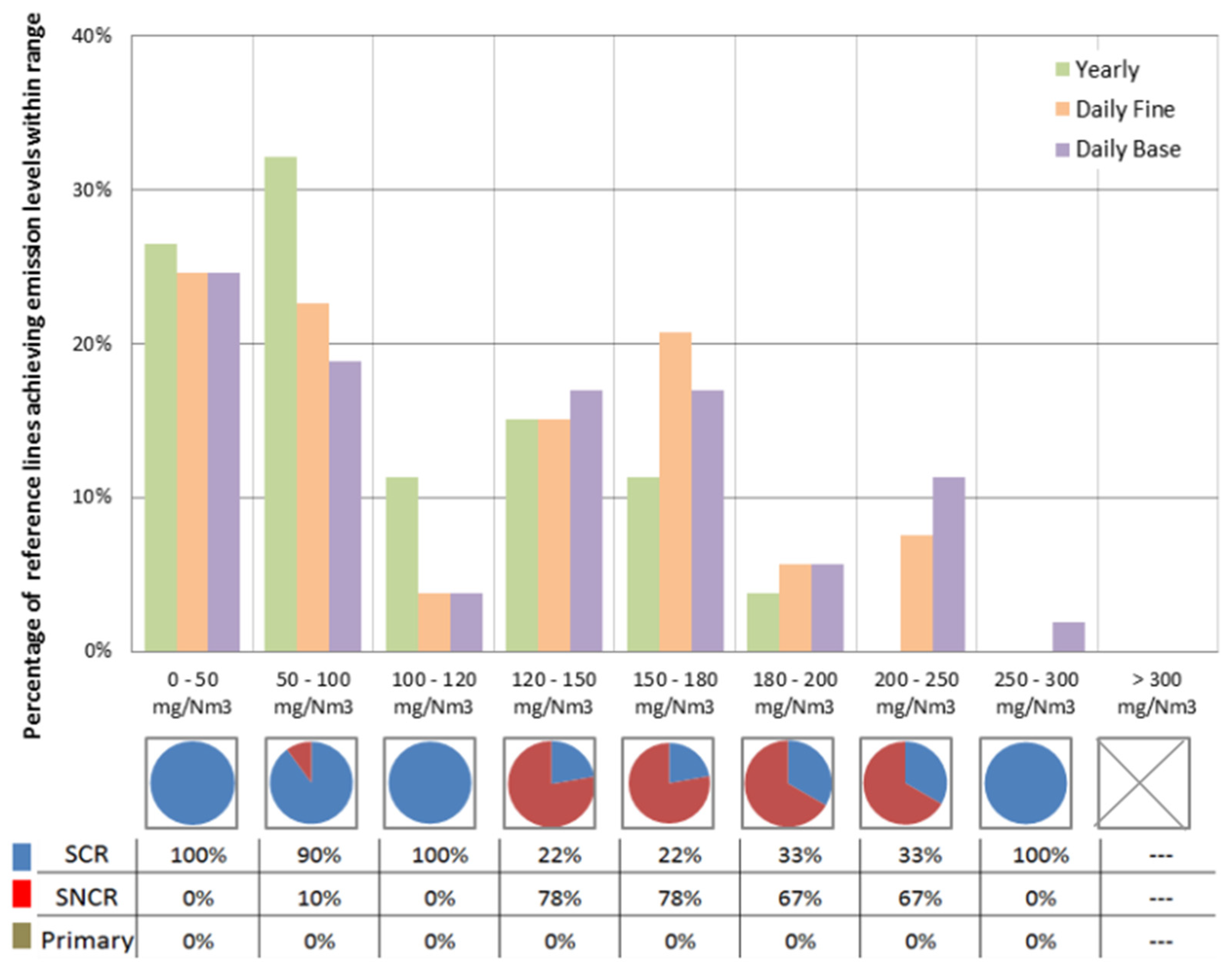
3.1.2. BATs for NOx Reduction
- Thermal NOx: generated during combustion due to the oxidation of nitrogen contained in the air. This reaction is significantly triggered at temperatures above 1300 °C, and the rate of conversion depends exponentially on the temperature.
- Fuel NOx: part of the nitrogen contained in the burning waste is oxidized to nitrogen oxides.
- Prompt NOx: formation of NOx via radical reaction; although this reaction cannot be stopped or mitigated, this mechanism has minor importance in waste incineration.
3.1.3. BATs for the Removal of Organic Pollutants
3.1.4. Recommendations for Future Work
- More information and technology assessments of gasification, plasma, and pyrolysis plants incinerating waste should be included;
- More information on the incineration process of hazardous waste or sewage sludge should be collected, in particular for the characterization of the boiler efficiency and its variation depending, for example, on the use of auxiliary fuels or on the type and extent of sludge pretreatment in the case of the incineration of sewage sludge;
- With regard to the monitoring method for PCDD/F emissions, more information on PCDD/F emissions measured on the basis of short-term versus long-term sampling should be collected.
3.2. Novel Options for APC
3.2.1. Acid Gas Removal
3.2.2. NOx Removal
3.2.3. VOC Removal
3.3. Suggested Configurations for an APC System, including Novel Removal Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| APC | Air pollution control | MgO | Magnesium oxide |
| BATs | Best available techniques | MSW | Municipal solid waste |
| BAT-AELs | BAT-associated emission limits | Na2CO3 | Sodium carbonate |
| BREFs | BAT Reference Documents | NaClO2 | Sodium chlorite |
| BTX | Benzene, toluene, and xylene | NaHCO3 | Sodium bicarbonate |
| CaCO3 | Limestone | NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| Ca(OH)2 | Calcium hydroxide | NH3 | Ammonia |
| CFB | Circulating fluidized bed | NO | Nitrogen oxide |
| CH4 | Methane | NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| CHP | Combined heat and power | NOx | Nitrogen oxides |
| CO | Carbon monoxide | PAHs | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide | PCBs | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
| DSI | Duct sorbent injection | PCDD/Fs | Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans |
| ESP | Electrostatic precipitator | PM | Particulate matter |
| FGC | Flue gas control | SCR | Selective catalytic reduction |
| FGD | Flue gas desulfurization | SDA | Spray dryer absorber |
| FGR | Flue gas recirculation | SNCR | Selective noncatalytic reduction |
| H2SO4 | Sulfuric acid | SO2 | Sulfur dioxide |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid | SOx | Sulfur oxides |
| HF | Hydrofluoric acid | VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
| IED | Industrial Emission Directive | WtE | Waste-to-energy |
| IPPC | Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control |
References
- García, F.; Barbería, E.; Torralba, P.; Landin, I.; Laguna, C.; Marquès, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Decreasing Temporal Trends of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins and Dibenzofurans in Adipose Tissue from Residents near a Hazardous Waste Incinerator. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achillas, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Banias, G.; Kafetzopoulos, G.; Karagiannidis, A. Social Acceptance for the Development of a Waste-to-Energy Plant in an Urban Area. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, G.; Rada, E.C.; Ragazzi, M.; Mărculescu, C.; Badea, A.; Apostol, T. Integrated Municipal Solid Waste Scenario Model Using Advanced Pretreatment and Waste to Energy Processes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, D.; Aldás, C.; López, G.; Kaparaju, P. Municipal Solid Waste as a Valuable Renewable Energy Resource: A Worldwide Opportunity of Energy Recovery by Using Waste-To-Energy Technologies. Energy Procedia 2017, 134, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive (EU) 2018/850 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 Amending Directive 1999/31/EC on the Landfill of Waste. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32018L0850&from=EN (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- UK Environment Agency. Guidance for the Incineration of Waste and Fuel Manufactured from or Including Waste. Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control (IPPC); Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adami, L.; Schiavon, M.; Ferrai, M.; Dallago, L.; Rada, E.C.; Tubino, M.; Ragazzi, M. Perspectives of Stack and Environmental Monitoring in the Surroundings of a Waste-to-Energy Plant. In Proceedings of the Air Pollution 2019, Aveiro, Portugal, 4 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavon, M.; Adami, L.; Torretta, V.; Tubino, M. Environmental balance of an innovative waste-to-energy plant: The role of secondary emissions. Int. J. Environ. Impacts 2020, 3, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orach, J.; Rider, C.F.; Carlsten, C. Concentration-Dependent Health Effects of Air Pollution in Controlled Human Exposures. Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, E.; Cocozza, C.; Chirici, G.; Rizzi, A.; Sitzia, T. Preserving Air Pollution Forest Archives Accessible through Dendrochemistry. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, I.; Panepinto, D.; Zanetti, M. Environmental Impacts of Electricity from Incineration and Gasification: How the LCA Approach Can Affect the Results. Sustainability 2021, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raff, Z.; Meyer, A.; Walter, J.M. Political Differences in Air Pollution Abatement under the Clean Air Act. J. Public Econ. 2022, 212, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panepinto, D.; Ravina, M.; Zanetti, M. An Overview of Thermal Treatment Emissions with a Particular Focus on CO2 Parameter. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanga, K.; Cuib, J.; Zhoub, Y.; Chenc, A.Y.; Ouyangd, C.; Palocz-Andresene, M.; Lou, Z. GHG emissions reduction patterns from waste sectors after forced source separation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 180, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unegga, M.C.; Steiningerb, K.W.; Ramsauera, C.; Rivera-Aguilarb, M. Assessing the environmental impact of waste management: A comparative study of CO2 emissions with a focus on recycling and incineration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, A.; Mykhaylova, N.; Evans, G.J.; Lee, C.J.; Karney, B.; Brook, J.R. The Expanding Scope of Air Pollution Monitoring Can Facilitate Sustainable Development. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panepinto, D.; Zanetti, M.C. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Plant: A Multi-Step Approach to the Evaluation of an Energy-Recovery Configuration. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konga, R.; Lia, W.; Wanga, H.; Ren, Q. Energy efficiency analysis and optimization of a pressurized oxy-fuel circulating fluidized bed combustion system. Energy 2024, 286, 129613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ren, G.; Xue, Y.; Liu, K. How does green innovation affect air pollution? An analysis of 282 Chinese cities. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ju, Y.; Ni, W. Does the air pollution level information matter in public perception? Insights from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sha, Z.; Tang, A.; Goulding, K.; Liu, X. The application of machine learning to air pollution research: A bibliometric analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Chen, X.; Geng, Y.; Yang, K. Does regional collaborative governance reduce air pollution? Quasi-experimental evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for Waste Incineration. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/075477b7-329a-11ea-ba6e-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 November 2010 on Industrial Emissions (Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32010L0075 (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Council Directive 96/61/EC of 24 September 1996 Concerning Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:1996L0061:20060224:en:PDF (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- EIPPCB The European IPPC Bureau. Available online: https://eippcb.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Commission Implementing Decision of 10 February 2012 Laying down Rules Concerning Guidance on the Collection of Data and on the Drawing up of BAT Reference Documents and on Their Quality Assurance Referred to in Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on Industrial Emissions. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32012D0119&rid=1 (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Dijkmans, R. Methodology for Selection of Best Available Techniques (BAT) at the Sector Level. J. Clean. Prod. 2000, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylot, A.; Hochar, A.; Michel, P.; Descat, M.; Ménard, Y.; Villeneuve, J. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration in France: An Overview of Air Pollution Control Techniques, Emissions, and Energy Efficiency. J. Ind. Ecol. 2018, 22, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A. Prediction of SO2 and NOx emissions for low-grade Turkish lignites in CFB combustors. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 146, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Tan, Y.; Anthony, E.J. Emissions of SO2 and NOx during Oxy-Fuel CFB Combustion Tests in a Mini-Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Reactor. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellise, M.; Villot, J.; Gaucher, R.; Amardeil, A.; Laforest, V. Challenges in Assessing Best Available Techniques (BATs) Compliance in the Absence of Industrial Sectoral Reference. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Jana, S.K. Advances in Absorbents and Techniques Used in Wet and Dry FGD: A Critical Review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 843–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina, M.; Marotta, E.; Cerutti, A.; Zanetti, G.; Ruffino, B.; Panepinto, D.; Zanetti, M. Evaluation of Ca-Based Sorbents for Gaseous HCl Emissions Adsorption. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Su, W.; Chen, J.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qian, D. A Review of Hydrogen Chloride Removal from Calcium- and Sodium-Based Sorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 73116–73136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pozzo, A.; Antonioni, G.; Guglielmi, D.; Stramigioli, C.; Cozzani, V. Comparison of Alternative Flue Gas Dry Treatment Technologies in Waste-to-Energy Processes. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, A.; Morishita, Y.; Shibata, E.; Takatoh, C.; Cho, H. Basic Study of the Reaction of Calcium Hydroxide with Hydrogen Chloride Using Single Crystals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 9699–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koech, L.; Rutto, H.; Lerotholi, L.; Everson, R.C.; Neomagus, H.; Branken, D.; Moganelwa, A. Spray Drying Absorption for Desulphurization: A Review of Recent Developments. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 1665–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczyk, M.; Mikus, M.; Dziedzic, K. Flue gas cleaning in municipal waste-to-energy plants—Part II. Infrastrukt. Ekol. Teren. Wiej. 2016, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehlow, J. Air Pollution Control Systems in WtE Units: An Overview. Waste Manag. 2015, 37, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, B. Purification Technologies for NOx Removal from Flue Gas: A Review. Separations 2022, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohse-Höinghaus, K. Combustion, Chemistry, and Carbon Neutrality. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 5139–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogaume, T.; Auzanneau, M.; Jabouille, F.; Goudeau, J.C.; Torero, J.L. The Effects of Different Airflows on the Formation of Pollutants during Waste Incineration. Fuel 2002, 81, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldner, M.H.; Halter, R.; Sigg, A.; Brosch, B.; Gehrmann, H.J.; Keunecke, M. Energy from Waste—Clean, Efficient, Renewable: Transitions in Combustion Efficiency and NOx Control. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Kang, G.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Gao, S. Research on the Influence of Combustion Methods on NOx Emissions from Co-Combustion of Various Tannery Wastes. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4110–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Hu, C.; Zhao, J. The Abatement of Major Pollutants in Air and Water by Environmental Catalysis. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Tozaki, M. SNCR deNOx Process by Urea Decomposition System and Evaluation of CO2 Reduction. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Grift, C.J.G.; Woldhuis, A.F.; Maaskant, O.L. The Shell DENOX System for Low Temperature NOx Removal. Catal. Today 1996, 27, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Bian, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Yuan, P.; Shen, B. A Review of Synergistic Catalytic Removal of Nitrogen Oxides and Chlorobenzene from Waste Incinerators. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Česká Společnost Chemického Inženýrství. Summaries/17th International Congress of Chemical and Process Engineering, CHISA 2006, 27–31 August 2006, Praha, Czech Republic; Czech Society of Chemical Engineering, Ed.; EFCE event; Process Engineering Publ.: Prague, Czech Republic, 2006; ISBN 978-80-86059-45-7. [Google Scholar]
- Themba, N.; Sibali, L.L.; Chokwe, T.B. A Review on the Formation and Remediations of Polychlorinated Dibenzo P-Dioxins and Dibenzo-Furans (PCDD/Fs) during Thermal Processes with a Focus on MSW Process. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 2115–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Hu, X.; Lu, J. Analysis and Discussion on Formation and Control of Dioxins Generated from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Process. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2022, 72, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Yin, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, H.; An, T. Adsorption and Desorption Mechanism of Aromatic VOCs onto Porous Carbon Adsorbents for Emission Control and Resource Recovery: Recent Progress and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, D.; Feng, P.; Hao, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S. Municipal Sewage Sludge Incineration and Its Air Pollution Control. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Elwardany, A.E.; Ookawara, S.; Ahmed, M.; El-Sharkawy, I.I. Integrated Adsorption-Based Multigeneration Systems: A Critical Review and Future Trends. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 116, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Douthwaite, M.; Pattisson, S.; Hao, Z. Recent Advances in the Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review Based on Pollutant Sorts and Sources. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4471–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.; Sewell, M. Utilizing Dry Sorbent Injection Technology to Improve Acid Gas Control. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Thermal Treatment Technologies & Hazardous Waste Combustors, Houston, TX, USA, 20–22 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.-W.; Choi, S.; Park, D.-W. Simultaneous Treatment of NO and SO2 with Aqueous NaClO2 Solution in a Wet Scrubber Combined with a Plasma Electrostatic Precipitator. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ru, J.; Gao, S.; Li, C. The simultaneous removal of NOx and SO2 from flue gas by direct injection of sorbents in furnace of waste incinerator. Fuel 2023, 333, 126464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, C. Desulfurization and Denitrification Technologiesof Coal-Fired Flue Gas. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chang, L.; Liu, W.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Advances in Mercury Removal from Coal-Fired Flue Gas by Mineral Adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-D.; Jeon, S.-M.; Hasolli, N.; Lee, K.-S.; Lee, J.-R.; Han, J.-W.; Kim, H.T.; Park, Y.-O. HCl Removal Characteristics of Calcium Hydroxide at the Dry-Type Sorbent Reaction Accelerator Using Municipal Waste Incinerator Flue Gas at a Real Site. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davini, P. Investigation into the Desulphurization Properties of By-Products of the Manufacture of White Marbles of Northern Tuscany. Fuel 2000, 79, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiliyannis, C.A. Flue Gas Recirculation and Enhanced Performance of Waste Incinerators under Waste Uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8051–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiliyannis, C.A. Enhanced Waste to Energy Operability under Feedstock Uncertainty by Synergistic Flue Gas Recirculation and Heat Recuperation. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Song, G.; Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Ji, Z.; Lyu, Q.; Zhang, X. Application of Post-Combustion Ultra-Low NOx Emissions Technology on Coal Slime Solid Waste Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yan, M.; Dai, A.; Zhan, M.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Lu, S.; Buekens, A.; Yan, J. Simultaneous Suppression of PCDD/F and NOx during Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. Chemosphere 2015, 126, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Jing, J. Enhanced Catalytic Activity for Simultaneous Removal of PCDD/Fs and NO over Carbon Nanotubes Modified MnOx-CeO2/TiO2 Catalyst at Low Temperature. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, H.; Jin, J. Interaction Mechanism Study on Simultaneous Removal of 1,2-Dichlorobenzene and NO over MnOx−CeO2/TiO2 Catalysts at Low Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4820–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Lai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W. Integration of Dedusting and Denitration in V2O5-WO3/TiO2/PTFE-Based Catalytic Bag-Filter Materials: Lab- and Pilot-Scale Testing and Development of SCR Models. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 407, 137122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Porous TiO2 Aerogel-Modified SiC Ceramic Membrane Supported MnOx Catalyst for Simultaneous Removal of NO and Dust. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zeng, Y.; Ju, S.; Feng, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Flowerlike FeOx–MnOx Amorphous Oxides Anchored on PTFE/PPS Membrane for Efficient Dust Filtration and Low-Temperature NO Reduction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 5816–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, Q.; Chen, M.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, S. Mn-Ce-Nb-Ox/P84 Catalytic Filters Prepared by a Novel Method for Simultaneous Removal of Particulates and NO. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Di, J.; Liu, S.; Han, J.; Lee, J.C.K. Evaluation of Flue-Gas Treatment Technologies for Municipal Waste Incineration: A Case Study in Changzhou, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, E.C.; Schiavon, M.; Torretta, V. A Regulatory Strategy for the Emission Control of Hexavalent Chromium from Waste-to-Energy Plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbasson, V.; Castro-Vaquero, C.; Clifford, Z.; Shareefdeen, Z.; Elkamel, A. Advances in Hazardous Waste Treatment Methods. In Hazardous Waste Management; Shareefdeen, Z., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, G.; Fan, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, Z. Adsorption and Membrane Separation for Removal and Recovery of Volatile Organic Compounds. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, L.M.; Coller, G.; Schiavon, M.; Cernuto, A.; Ragazzi, M.; Dilecce, G.; Tosi, P. Non-Thermal Plasma in Waste Composting Facilities: From a Laboratory-Scale Experiment to a Scaled-up Economic Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Torretta, V.; Casazza, A.; Ragazzi, M. Non-Thermal Plasma as an Innovative Option for the Abatement of Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2017, 228, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, N.; Hou, L.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Pr-Modified Vanadia-Based Catalyst for Simultaneous Elimination of NO and Chlorobenzene. Mol. Catal. 2023, 548, 113430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, J.A.; González-Marcos, M.P.; Aranzabal, A.; González-Velasco, J.R. Effect of Interaction Degree between Mn and Ce of MnOX-CeO2 Formulation on NO Reduction and o-DCB Oxidation Performed Simultaneously. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, J. Review on NH3-SCR for Simultaneous Abating NOx and VOCs in Industrial Furnaces: Catalysts’ Composition, Mechanism, Deactivation and Regeneration. Fuel Process Technol. 2023, 247, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US National Research Council. Waste Incineration & Public Health. Committee on Health Effects of Waste Incineration; US National Research Council: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Cen, K. Formation, Measurement, and Control of Dioxins from the Incineration of Municipal Solid Wastes: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 13247–13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorishi, S.B.; Altwicker’, E.R. Rapid formation of polychlorinated dioxinslfurans during the heterogeneous combustion of l,2-dichlorobenzene and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Chemosphere 1996, 32, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielgosiński, G. The Reduction of Dioxin Emissions from the Processes of Heat and Power Generation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quina, M.J.; Bordado, J.; Quinta-Ferreira, R. Air Pollution Control in Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators. In The Impact of Air Pollution on Health, Economy, Environment and Agricultural Sources; Khallaf, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 331–358. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.I.; Kim, K.H.; Jang, H.N.; Seo, Y.C.; Seok, K.S.; Hong, J.H.; Jang, M. Particle size distribution of PM-10 and heavy metal emission with different temperature and HCl concentrations from incinerators. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C.; Ragazzi, M. State of the art and advances in the impact assessment of dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.H.; Chang, M.B.; Chang, S.H. Evaluation of PCDD/F Partitioning between Vapor and Solid Phases in MWI Flue Gases with Temperature Variation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFRA. Review of Environmental and Health Effects of Waste Management: Municipal Solid Waste and Similar Wastes; Enviros Consulting Ltd.: Southampton, UK; University of Birmingham with Risk and Policy Analysts Ltd.: Birmingham, UK; Open University and Maggie Thurgood: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, U. Process and Technological Aspects of Municipal Solid Waste Gasification. A Review. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Technology | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiler/Inline injection of sorbent (or duct sorbent injection, DSI) | A dry sorbent powder is dispersed by injecting it into the effluent gas stream (or combustion chamber). The sorbent reacts with the acid gas to form a solid, which is subsequently removed with dust suppression systems. | Simple technology; minimum amount of auxiliary equipment; low operating costs | Major consumption of sorbent; higher amount of residuals; possible dust pollution of heat exchange surfaces |
| Conditioned dry sorption | Separation of the pollutants is ameliorated by a hydrate shell, which is formed around the lime particles and results from the water contained in the flue gas. The separation is governed by the dissolution rate of the pollutants in aqueous solution. | Higher efficiency than no conditioned dry sorption | Flue gas must be conditioned to achieve higher relative humidity |
| Semi-dry scrubbing | A spray dryer is used to inject a suspension of lime and water (lime slurry) into the flue gas stream. When the suspension is injected into the flue gas stream, the water component evaporates, and only the solid lime particles remain in the flue gas. | 50% less water consumption than wet methods; dry residuals | Worse use of sorbent in comp. to wet methods; Higher investment costs comp. to dry method |
| Wet scrubbing | Makes use of a liquid such as water or an aqueous solution capable of absorbing the acidic compounds present in the gaseous effluent. | Low consumption of sorbents; low sensitivity to fluctuation in flows | Higher complexity; higher corrosion; drop in flue gas temperature; large area needed |
| Flue gas desulphurization (FGD) with seawater | Wet non-regenerative type that makes use of the natural alkalinity of seawater to absorb the acidic contaminants present in the gaseous effluent. | No waste is formed; no reagents or additional chemicals; lower capital and operating costs. | Low efficiency; wet residues. |
| Calcium Hydroxide | Sodium Bicarbonate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca(OH)2 ⇄ Ca2+ + 2OH− HCl → H+ + Cl− Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O | (1) | 2NaHCO3 → 2Na+ + HCO3− HCO3− ⇄ CO32− + 2H+ ⇄ CO2 + H2O 2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O | (4) |
| Ca(OH)2 ⇄ Ca2+ + 2OH− SO2 + 2OH− → SO42− + 2H+ Ca(OH)2 + SO2 + ½O2 → CaSO4 + H2O | (2) | Na2CO3 → 2Na+ + CO32− HCl → H+ + Cl− CO32− + 2H+ ⇄ CO2 + H2O Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + CO2 + H2O | (5) |
| Ca(OH)2 ⇄ Ca2+ + 2OH− CO2 + OH− → HCO3− ⇄ CO32− + H+ Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O | (3) | Na2CO3 → 2Na+ + CO32− SO2 + 2OH− → SO42− + 2H+ Na2CO3 + SO2 ½O2 → Na2SO4 + CO2 | (6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiavon, M.; Ravina, M.; Zanetti, M.; Panepinto, D. State-of-the-Art and Recent Advances in the Abatement of Gaseous Pollutants from Waste-to-Energy. Energies 2024, 17, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030552
Schiavon M, Ravina M, Zanetti M, Panepinto D. State-of-the-Art and Recent Advances in the Abatement of Gaseous Pollutants from Waste-to-Energy. Energies. 2024; 17(3):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030552
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiavon, Marco, Marco Ravina, Mariachiara Zanetti, and Deborah Panepinto. 2024. "State-of-the-Art and Recent Advances in the Abatement of Gaseous Pollutants from Waste-to-Energy" Energies 17, no. 3: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030552
APA StyleSchiavon, M., Ravina, M., Zanetti, M., & Panepinto, D. (2024). State-of-the-Art and Recent Advances in the Abatement of Gaseous Pollutants from Waste-to-Energy. Energies, 17(3), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030552









