Loss and Thermal Analysis of a High-Power-Density Permanent Magnet Starter/Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
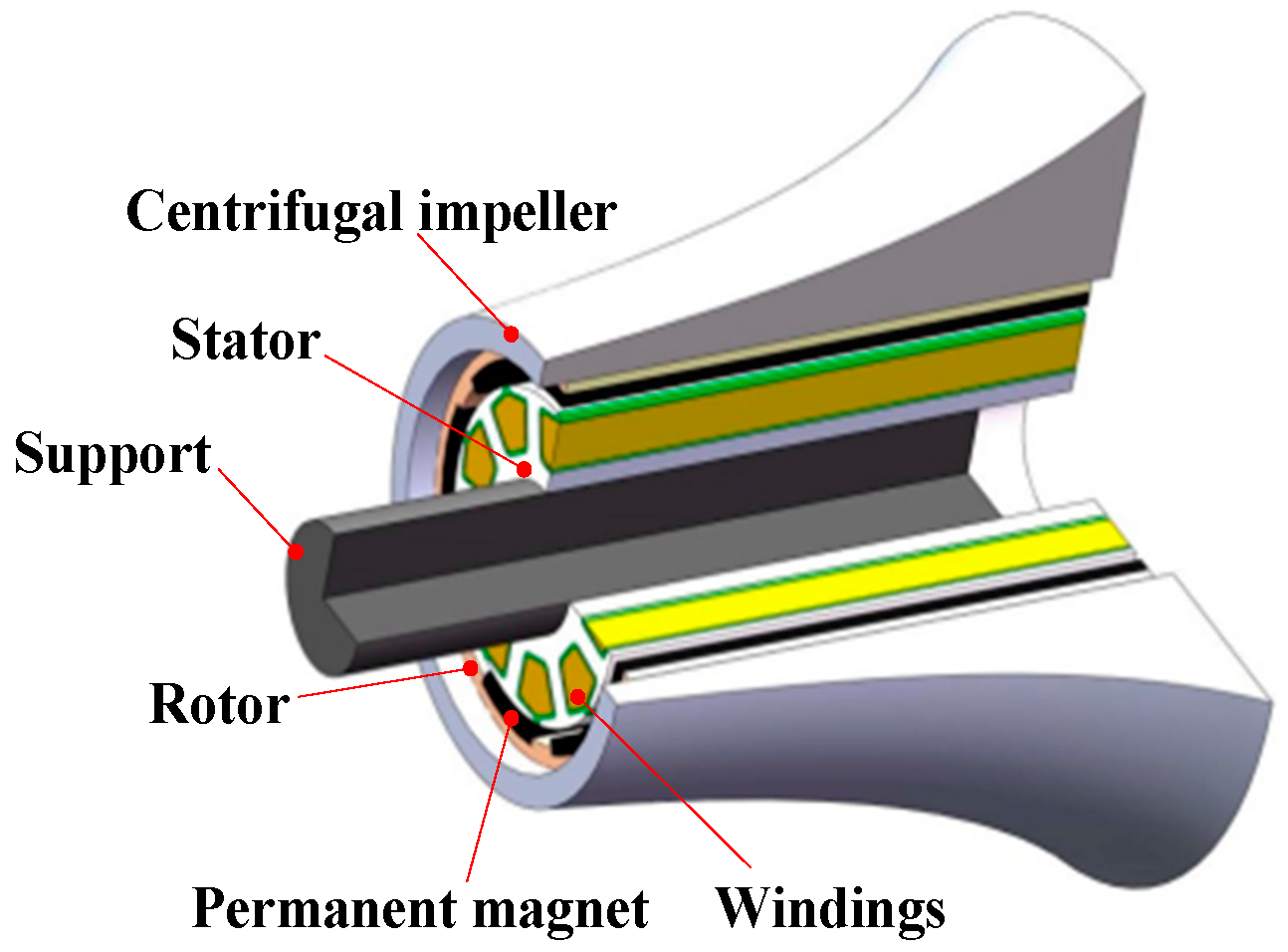
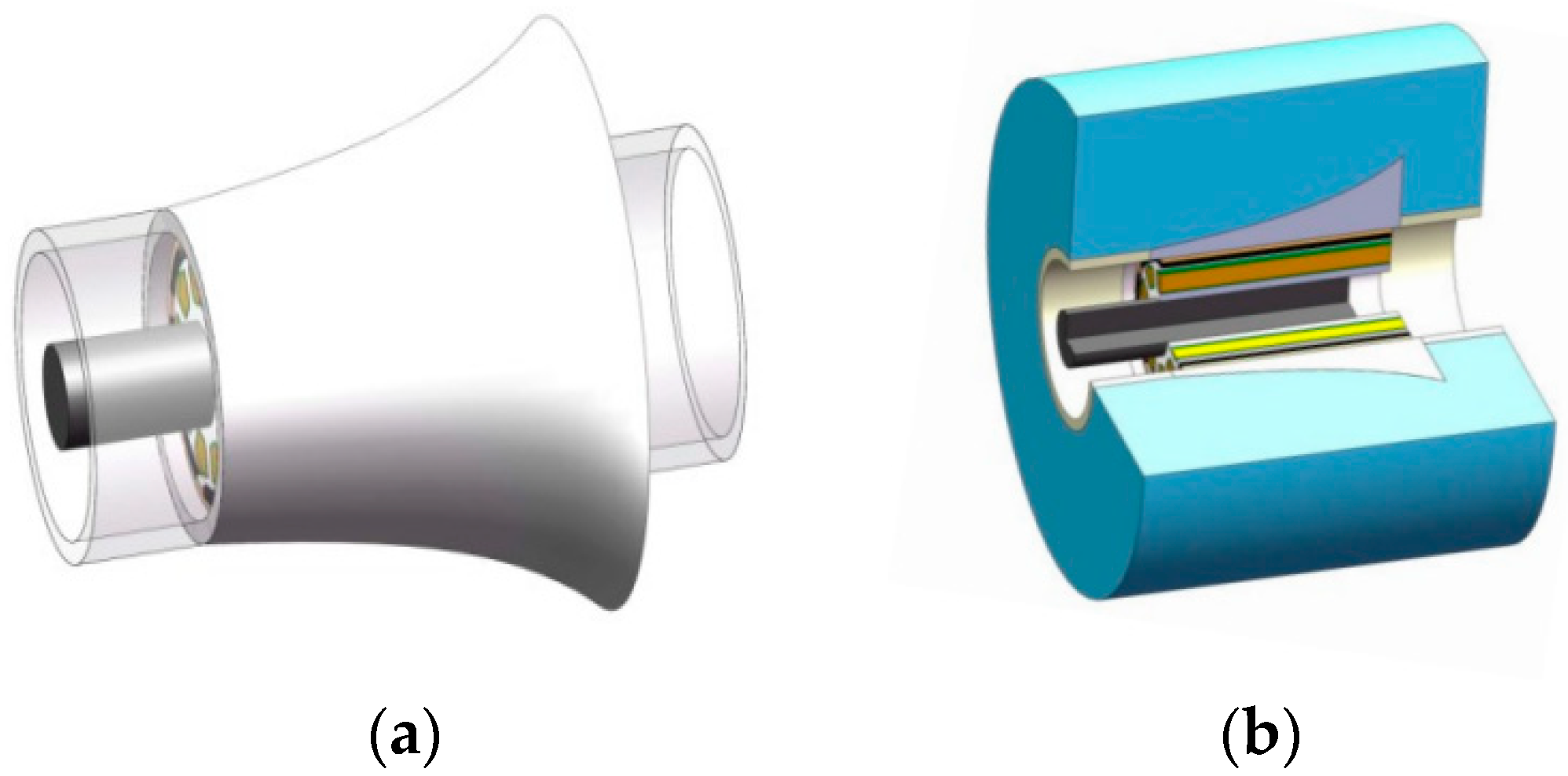
2. System Composition of the SG Motor
3. Loss Calculation and Analysis
3.1. Magnetic Field
3.2. Iron Loss
3.3. Copper Loss
3.4. Wind Friction Loss
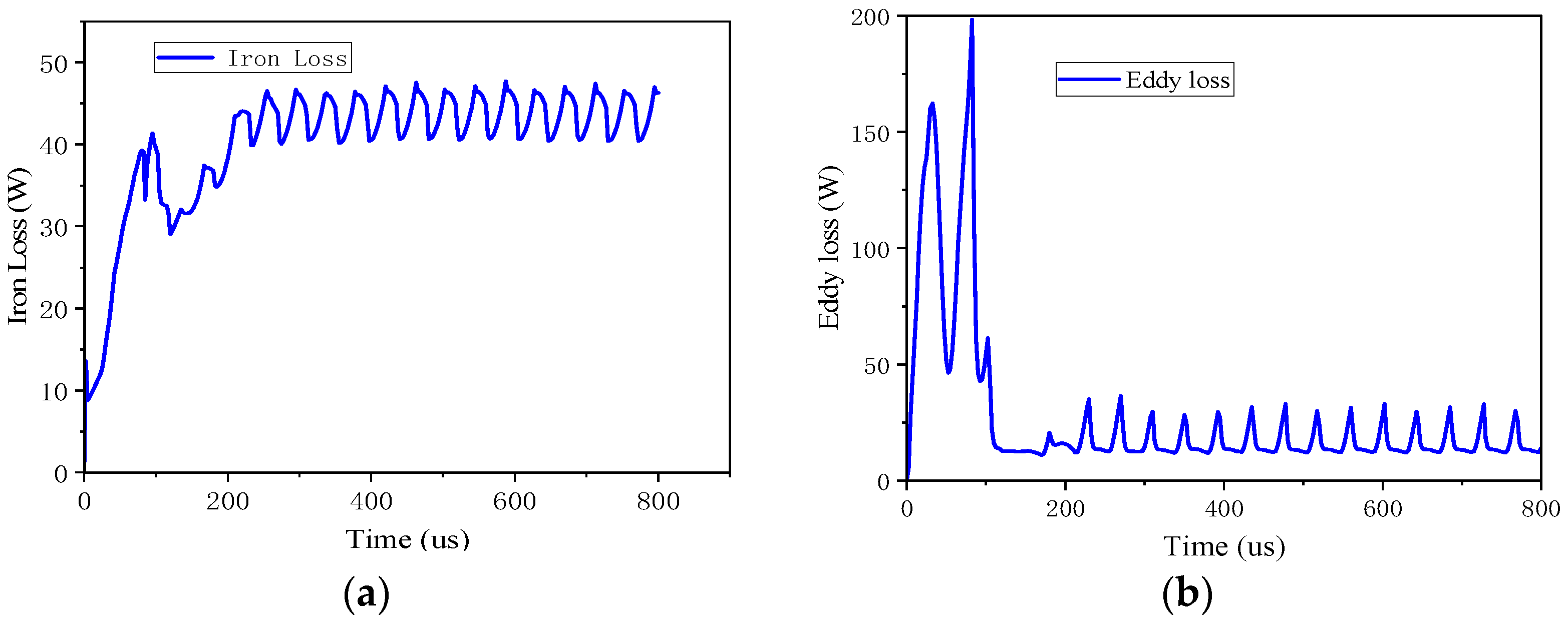
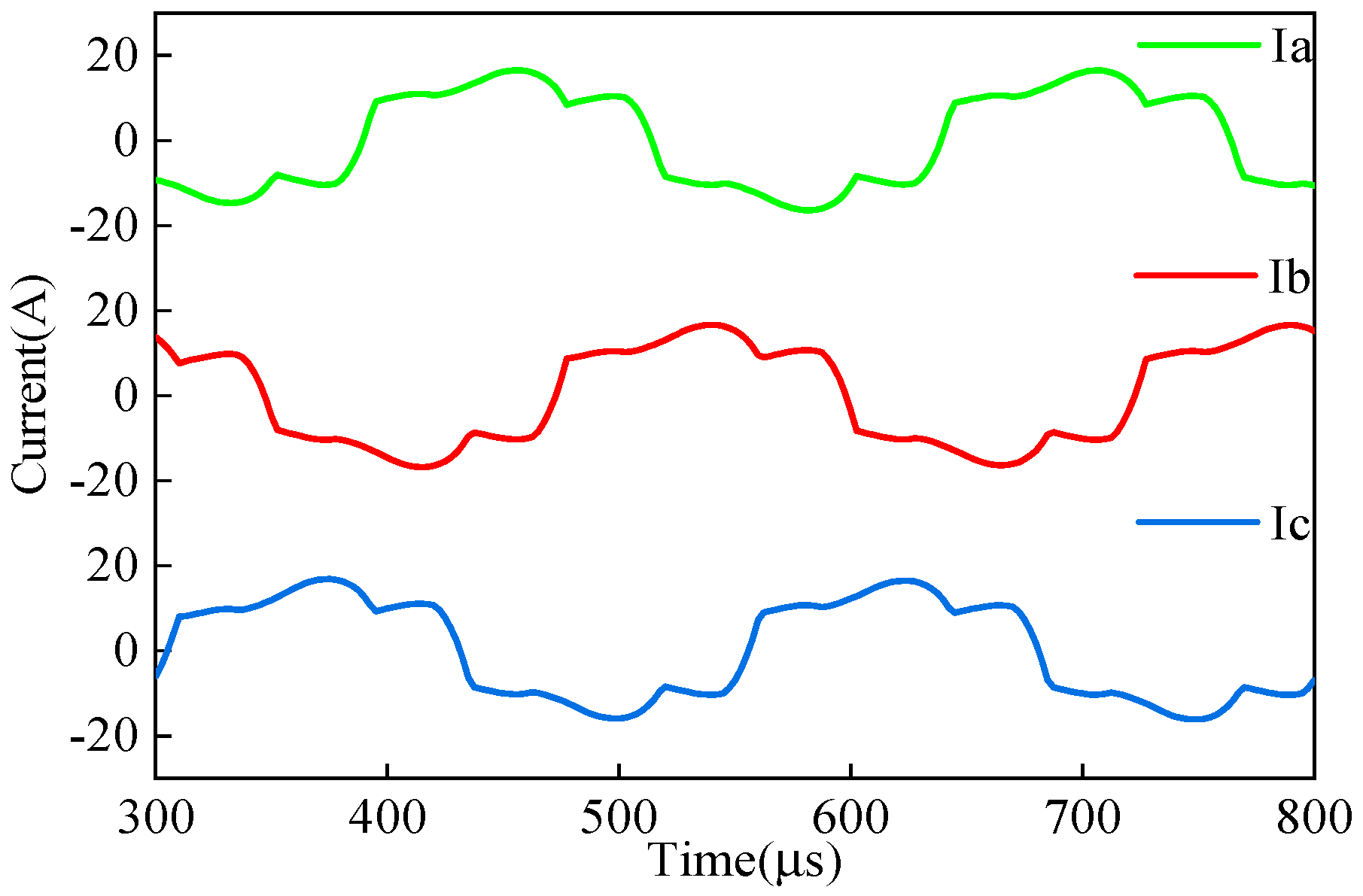
3.5. Loss Calculation with FEM
4. Temperature Field Analysis
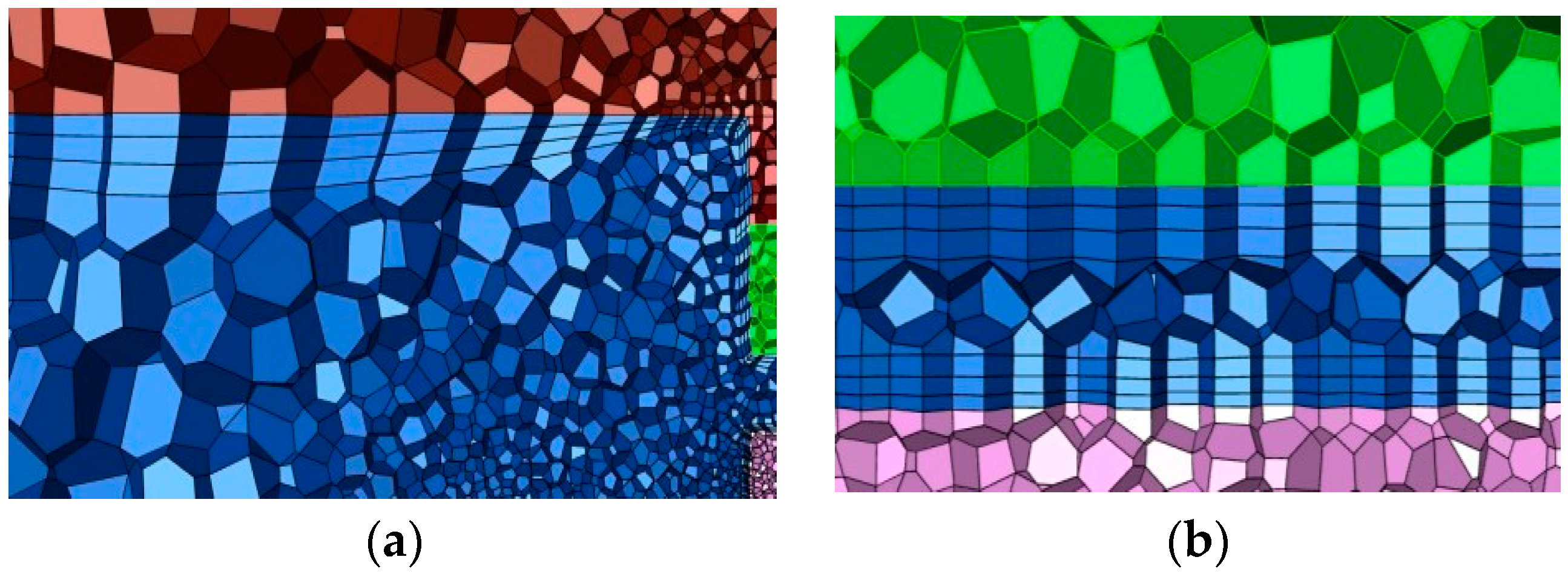
4.1. Construction of Thermal Analysis Model
- (1)
- Fluid domains of simulation model
- (2)
- Boundary meshing
- (3)
- Heat Source Setting
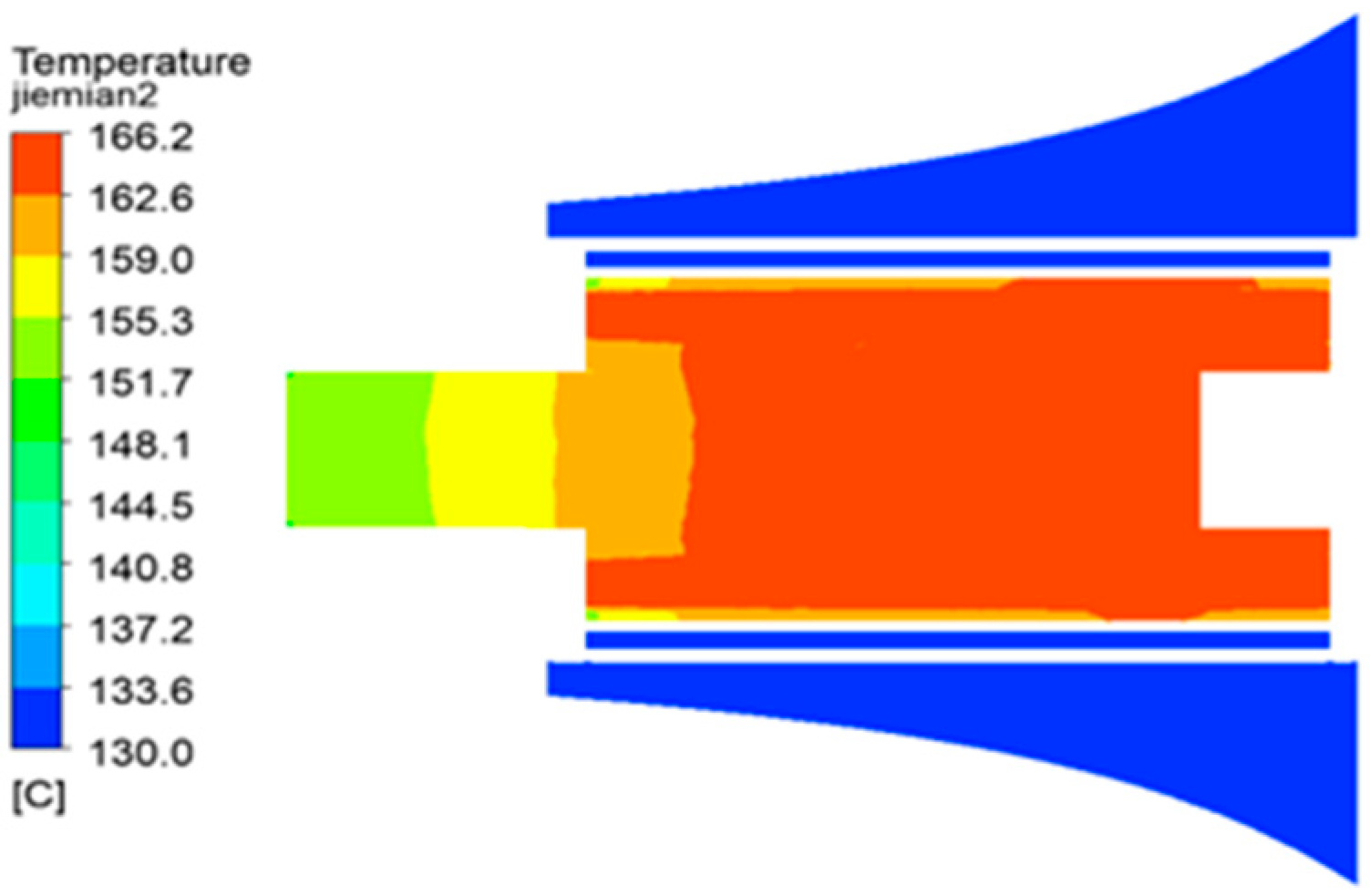
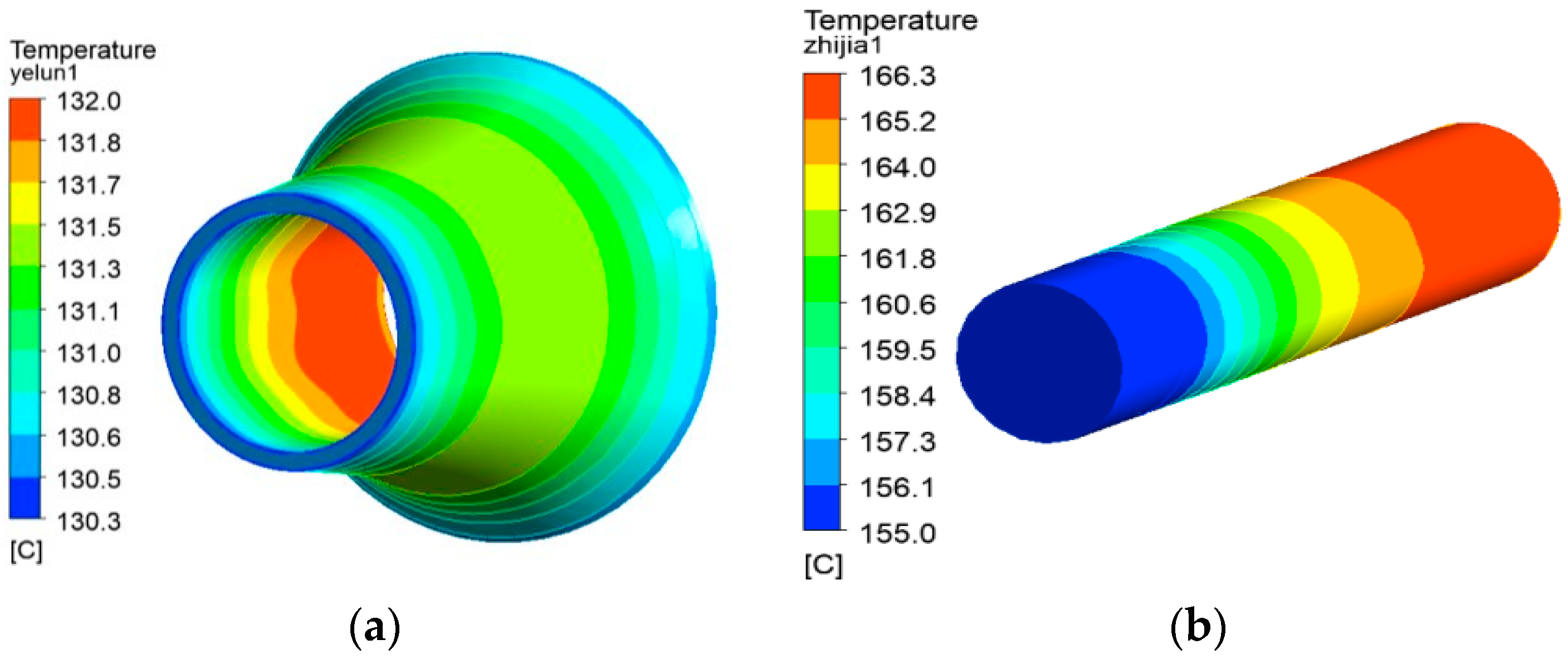
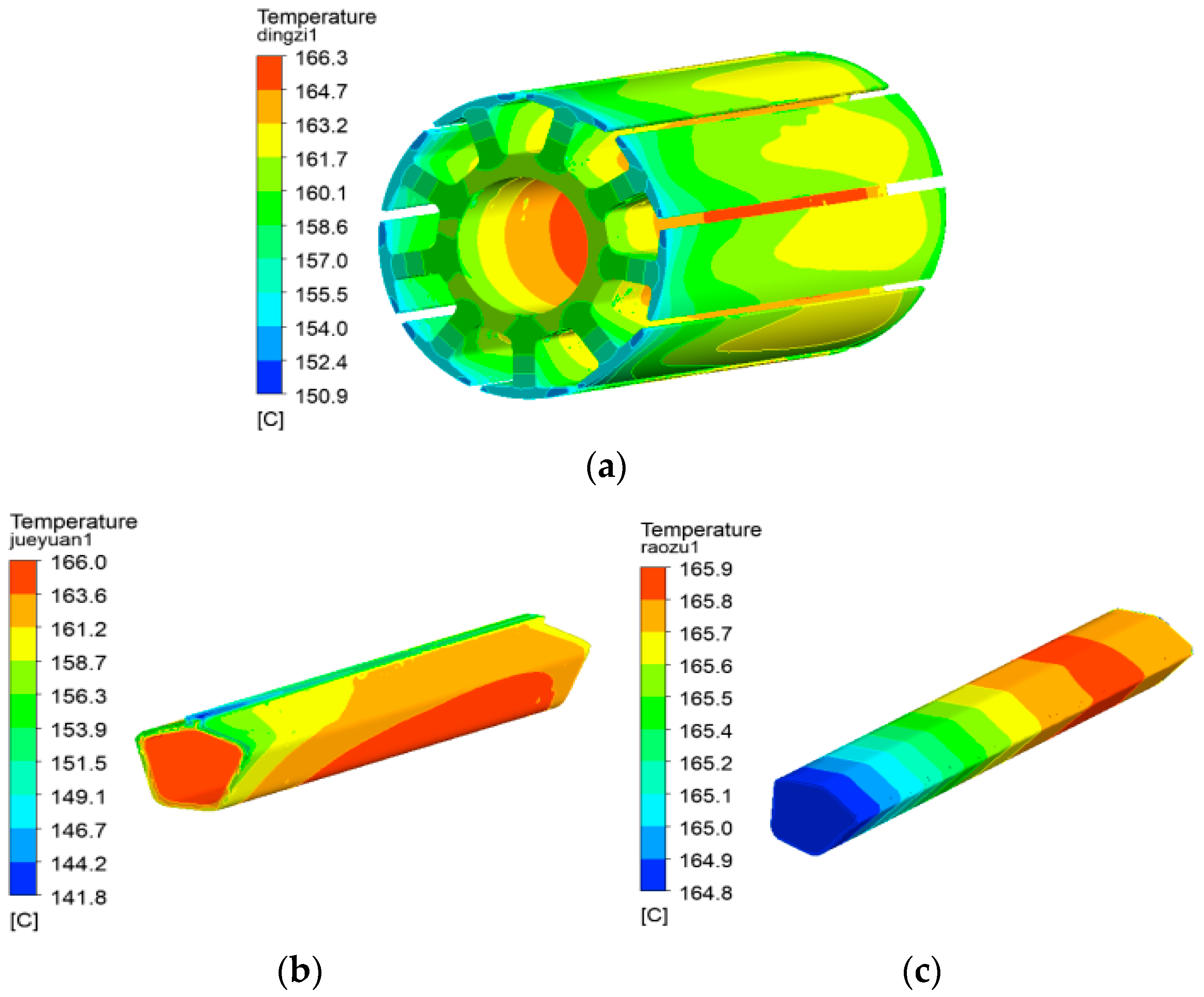
4.2. Temperature Field Calculation Results
- (1)
- Steady-state temperature field distribution
- (2)
- Temperature field of centrifugal impeller
- (3)
- Temperature field of the stator and winding
- (4)
- Temperature field of protective sleeve and PM
5. Enhanced Analysis of Air Cool
5.1. Effect of Cooling Air Flow on Temperature
5.2. Effect of Cooling Air Temperature
5.3. Effect of Speed on Motor Temperature
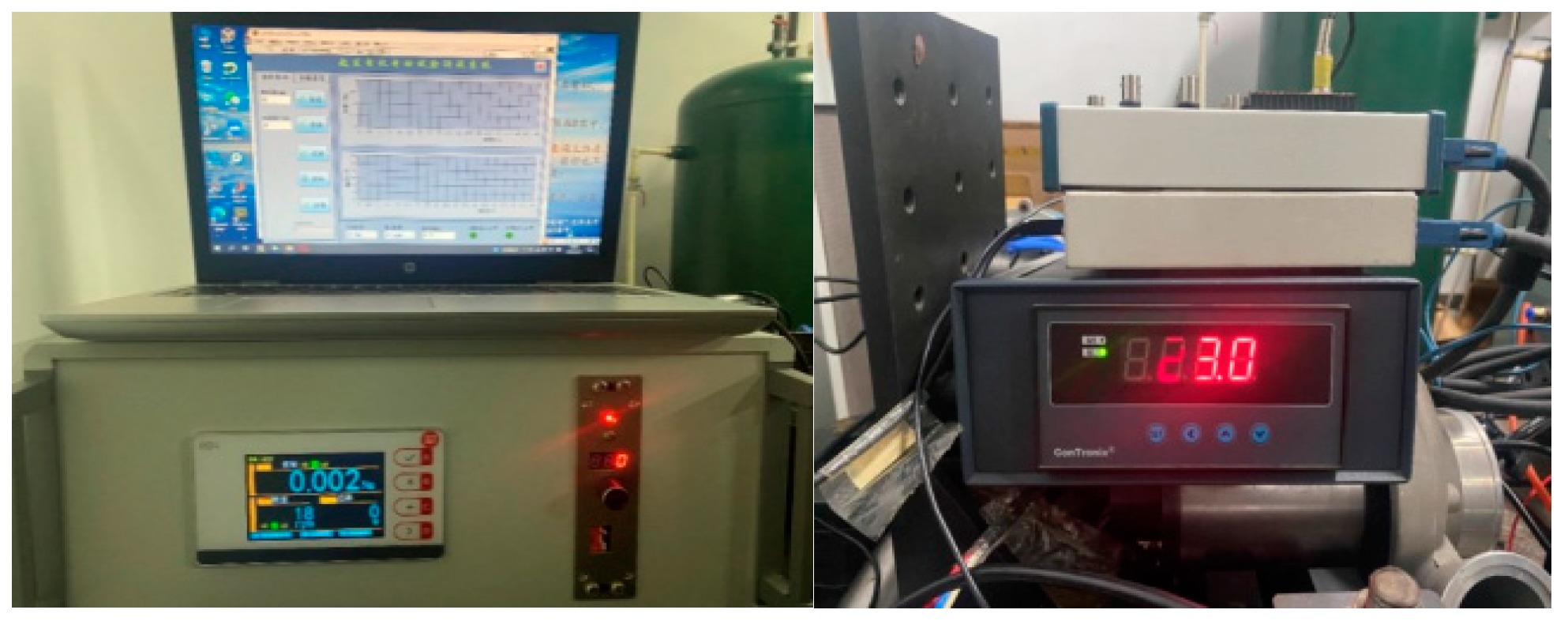
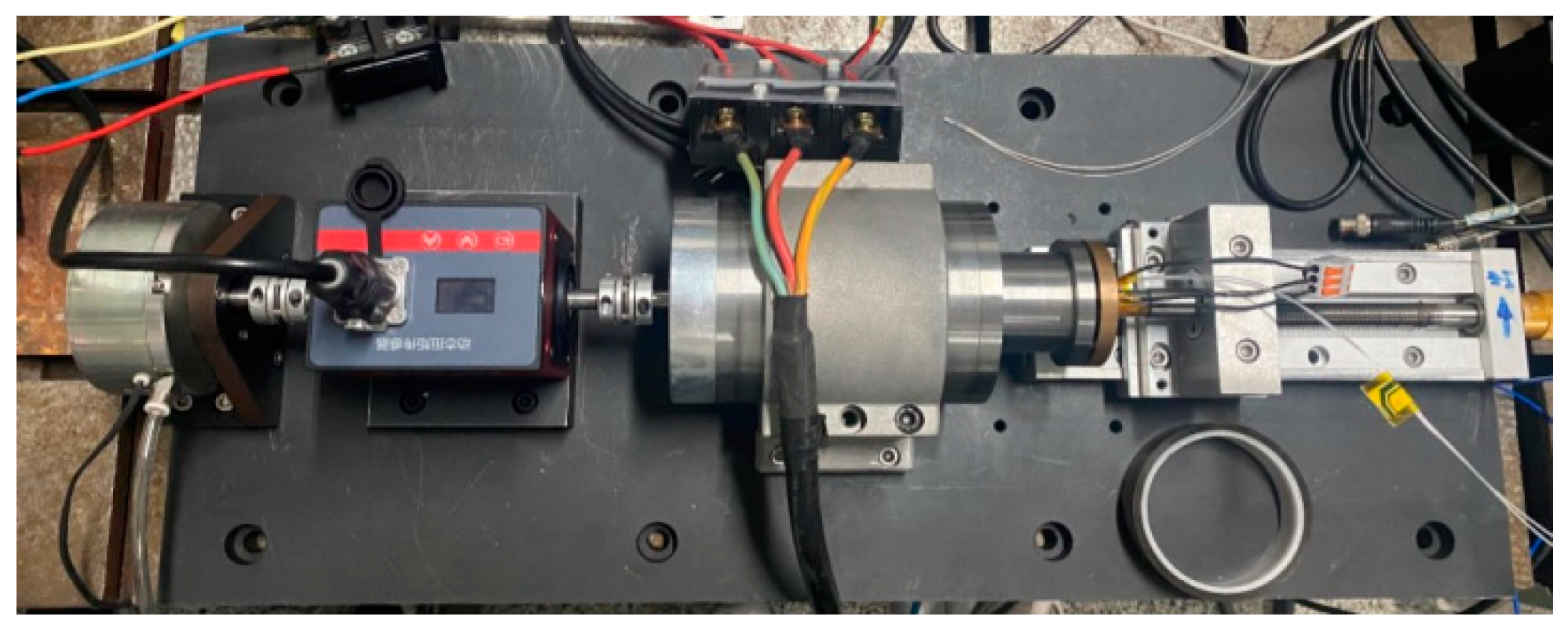
6. Experiments
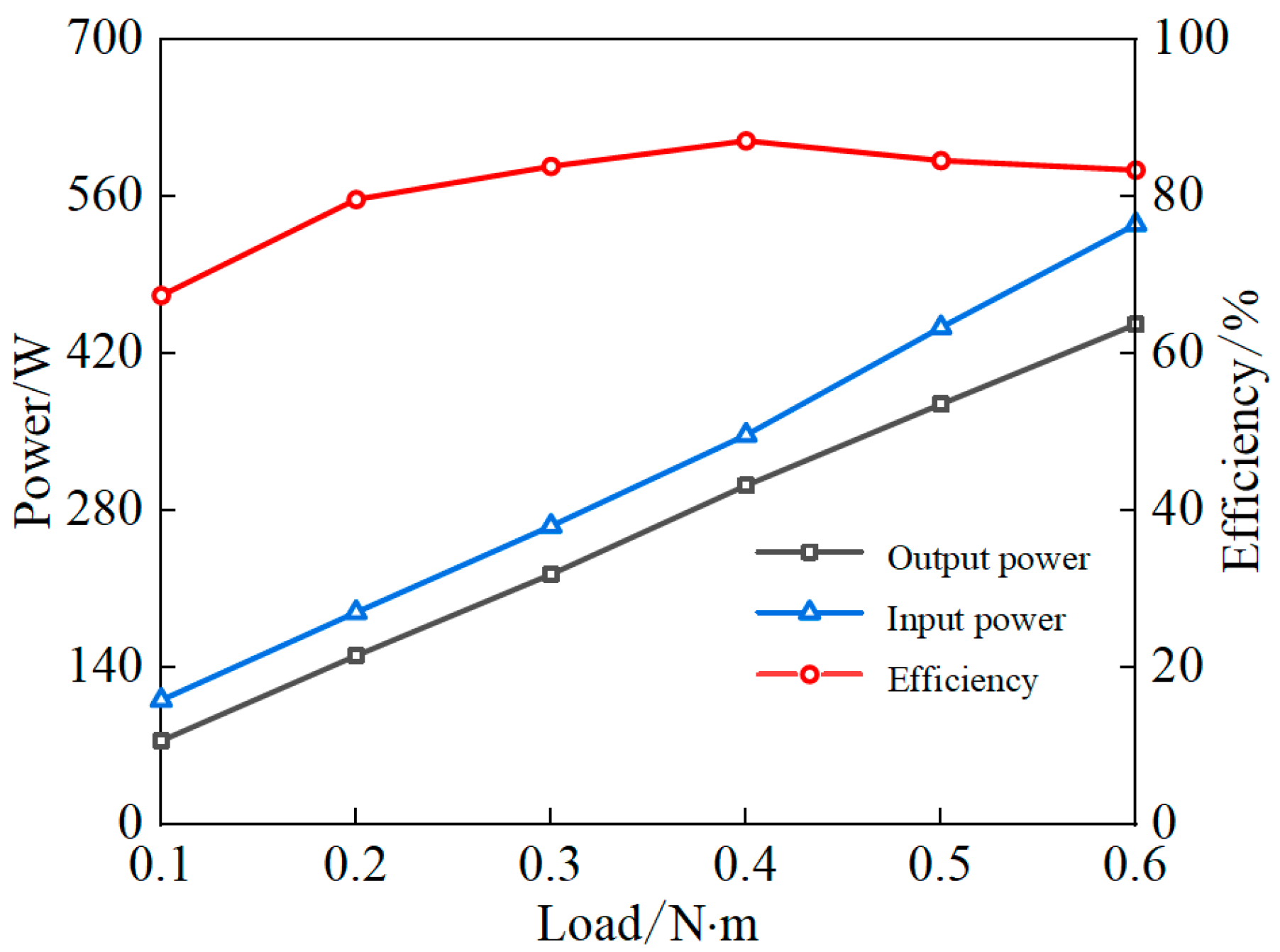
6.1. Load Test
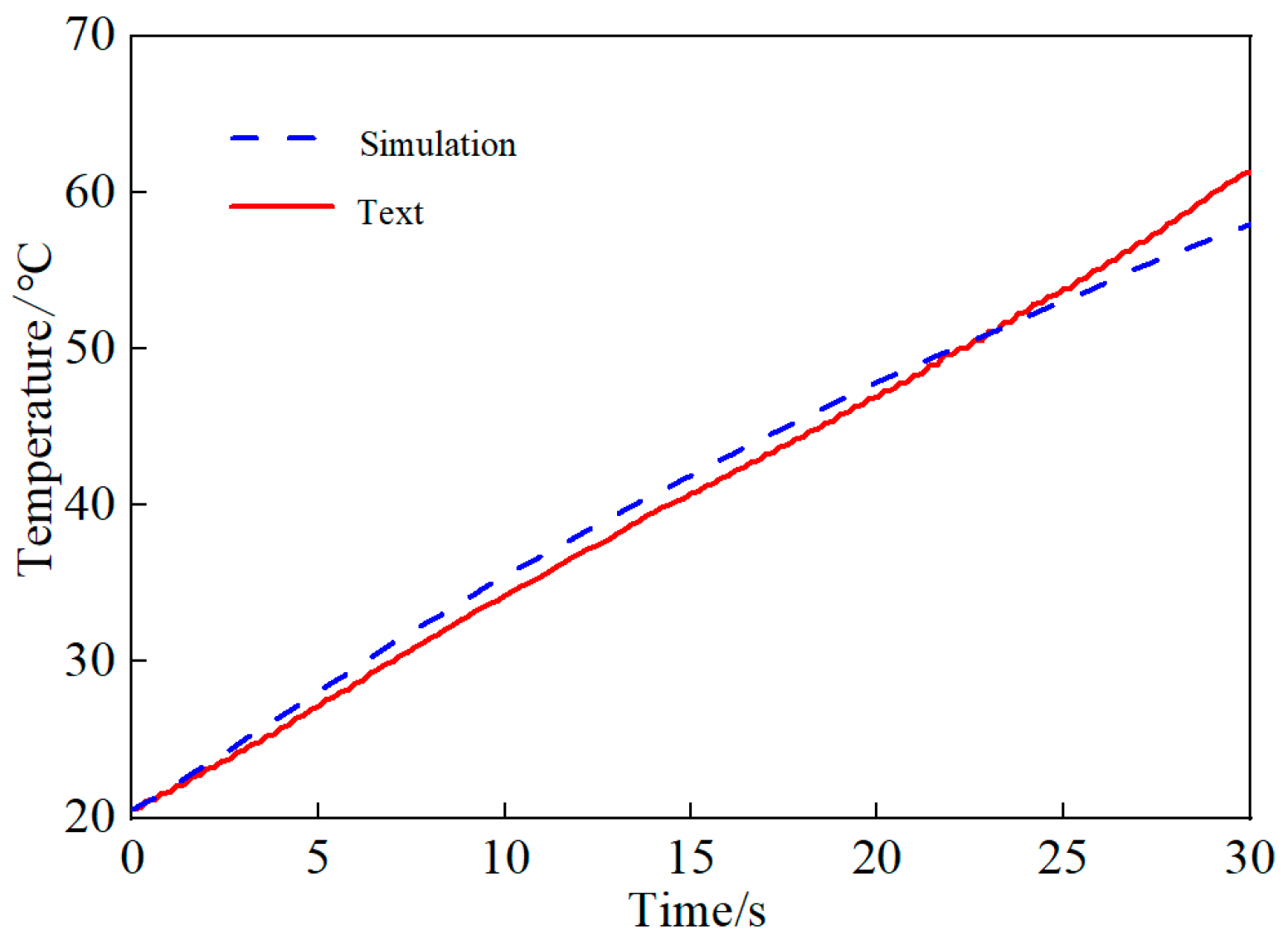
6.2. Temperature Rise Experiment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noland, J.K.; Leandro, M.; Suul, J.A.; Molinas, M. High-Power Machines and Starter-Generator Topologies for More Electric Aircraft: A Technology Outlook. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130104–130123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Shi, L.; Guo, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhou, X. Investigation of the working mechanism and characteristics of dual-mode doubly salient starter generator with variable winding. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C.H.T. Design and Analysis of a Doubly Salient Wound Field Starter Generator for Cost-Effective Automobile Application. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 6900–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavilov, V.Y.; Argakov, A.S.; Garipov, I.R. Integrated Starter-Generator for a More Electric Engine: A Brief Overview. In Proceedings of the 2023 Russian Workshop on Power Engineering and Automation of Metallurgy Industry: Research & Practice (PEAMI), Magnitogorsk, Russia, 29 September–1 October 2023; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, J.-I.; Kawamura, K.; Koshikizawa, H.; Abe, K. Control Strategy for Starter Generator in UAV with Micro Jet Engine. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018-ECCE Asia), Niigata, Japan, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingzhi, G.; Liwei, S.; Wenchao, Z.; Wenping, C.; Byung-Il, K. Research on 3/6-phase Winding Switching Integrated Starter Generator for Range Extender Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2019—ECCE Asia), Busan, Republic of Korea, 27–30 May 2019; pp. 2492–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Miyama, Y.; Kitao, J.; Takahashi, T.; Kumagai, K.; Ohashi, N.; Ota, N.; Totsuka, F. Low-Noise and High-Power Spoke-Type Magnet-Assisted Flat-Plate IPMSM for Integrated Starter Generator Motor. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Nashville, TN, USA, 29 October–2 November 2023; pp. 3924–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Kitao, J.; Miyama, Y.; Hazeyama, M.; Isoda, H.; Arita, H.; Nishizawa, K.; Nishimura, T.; Nakano, M. Development of a 48V Integrated Starter Generator for Mild Hybrid Vehicles. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2022, 11, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kou, B.; Zhang, L. Design and Analysis of a Stator Field Control Permanent Magnet Synchronous Starter–Generator System. Energies 2023, 16, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, R.; Yao, W.; Gao, Y.; Sun, G.; Liu, J.; Peretti, L.; Wu, L. Observer-Based Prescribed Performance Speed Control for PMSMs: A Data-Driven RBF Neural Network Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 7502–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, C.; Yao, W.; Liu, Z.; Shen, X.; Xu, R.; Sun, G.; Liu, J. Observer-Based Fixed-Time Control for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors with Parameter Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4335–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnikov, A.N. Modeling of integrated starter-generator. In Proceedings of the 2015 16th International Conference of Young Specialists on Micro/Nano technologies and Electron Devices (EDM), Erlagol, Russia, 29 June–3 July 2015; pp. 470–471. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, D.; Liu, Z.; Tian, L. Emulation of Integrated Starter/Generator Using Power Electronic Devices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 6556–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Vakil, G.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Gerada, C. Optimization and Analysis of a High Power Density and Fault Tolerant Starter–Generator for Aircraft Application. Energies 2021, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnikov, A.N.; Khlebnikov, A.S. Modeling of integrated starter-generator in generator mode. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference of Young Specialists on Micro/Nanotechnologies and Electron Devices (EDM), Novosibirsk, Russia, 30 June–4 July 2014; pp. 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J. Multiobjective Optimization of High Power Density Outer Rotor PM Starter Generator Considering Electromagnetic and Temperature Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 8339–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rocca, A.; Xu, Z.; Arumugam, P.; Pickering, S.J.; Eastwick, C.N.; Gerada, C. Thermal management of a high speed permanent magnet machine for an aeroengine. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 2732–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, D. Thermal analysis of the permanent magnet synchronous generator with the use of Ansys Fluent. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Electrodynamic and Mechatronic Systems (SELM), Opole-Zawiercie, Poland, 15–18 May 2013; pp. 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Improved thermal model of forced air-cooled motors considering heat transfer in wire-wound winding and end region. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Jin, M.-J.; Shen, J.-X.; Yuan, C. A Permanent Magnet Integrated Starter Generator for Electric Vehicle Onboard Range Extender Application. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarthik, R.S.; Amitkumar, K.S.; Pillay, P. Emulation of a Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator in Real-Time Using Power Hardware-in-the-Loop. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gerada, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tighe, C.; Zhang, H.; Gerada, C. Back-iron extension thermal benefits for electrical machines with concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Zhu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z. Windings indirect liquid cooling method for a compact outer-rotor pm starter/generator with concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3282–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gerada, D.; Xu, Z.; Tighe, C.; Zhang, H.; Yan, L.; Gerada, C. Electrical machine slot thermal condition effects on back-iron extension thermal benefits. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Name | Value | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poles and slots | 8P9S | Pitch | 1 |
| Outer diameter of stator (mm) | 30.7 | Conductors per slot | 10 |
| Inner diameter of stator (mm) | 13.8 | Polar arc coefficient | 0.72 |
| Inner diameter of PM (mm) | 32.5 | Core length (mm) | 57 |
| Outer diameter of PM (mm) | 35.5 | Sleeve material | 4Cr13 |
| Number of parallel branches | 1 | PM material | N35UH |
| Outer diameter of protective sleeve (mm) | 38 | Silicon steel sheet | 10JNEX900 |
| Heat Source | Loss (W) | Volume (mm3) | Heat Generation Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windings | 14.7 | ||
| Stator iron | 43.8 | ||
| PM and sleeve | 16.4 |
| Load Torque (N·m) | Simulation Value (°C) | Experimental Value (°C) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 22.3 | ||
| 0.2 | 26.5 | ||
| 0.3 | 31.8 | 33.5 | 5.35 |
| 0.4 | 43.1 | 45.5 | 5.57 |
| 0.5 | 51.3 | 54.7 | 6.63 |
| 0.6 | 57.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Chen, Z.; Du, R.; Feng, M. Loss and Thermal Analysis of a High-Power-Density Permanent Magnet Starter/Generator. Energies 2024, 17, 5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205049
Ren X, Chen Z, Du R, Feng M. Loss and Thermal Analysis of a High-Power-Density Permanent Magnet Starter/Generator. Energies. 2024; 17(20):5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205049
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xiaojun, Zhikai Chen, Rui Du, and Ming Feng. 2024. "Loss and Thermal Analysis of a High-Power-Density Permanent Magnet Starter/Generator" Energies 17, no. 20: 5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205049
APA StyleRen, X., Chen, Z., Du, R., & Feng, M. (2024). Loss and Thermal Analysis of a High-Power-Density Permanent Magnet Starter/Generator. Energies, 17(20), 5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205049






