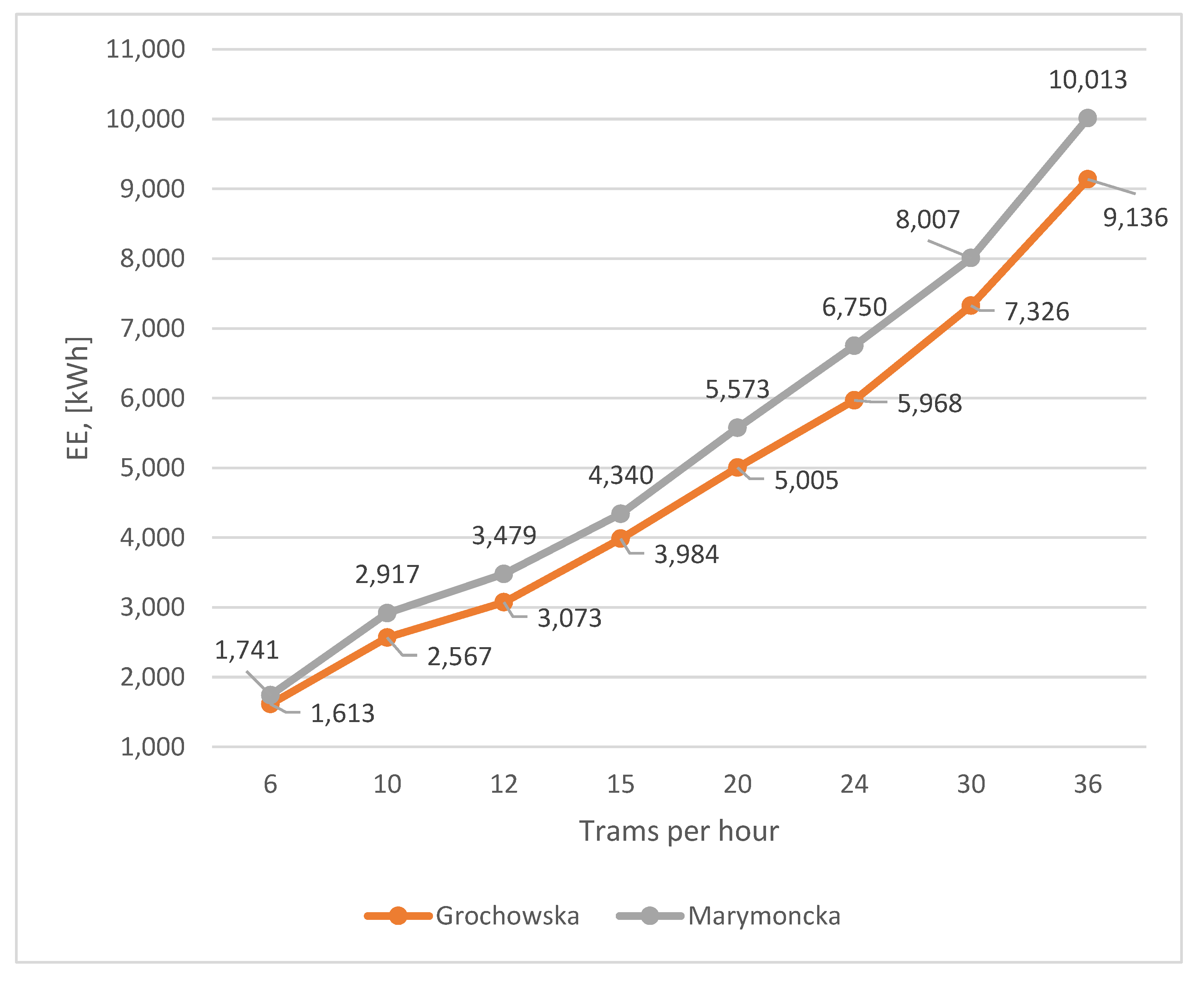Abstract
Traffic signal priority issues have been a research subject for several decades in Poland and worldwide. Traffic control algorithms have evolved considerably during this period and have become increasingly advanced. Most of them operate within coordinated street sequences, which adds to their complexity. Tramway priority affects traffic conditions for other road users, so many aspects must be taken into account when choosing a priority solution. Typically, one of the main criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of priority is reducing travel time for the priority vehicle while ensuring that the travel times of other traffic participants through the intersection are maintained or slightly deteriorated. However, the energy aspects are often overlooked. This publication aims to investigate how local priority for tramways in traffic signals of coordinated streets affects energy consumption for tramway traction needs. The study was conducted using a microscopic modeling method with PTV Vissim software (ver. 2021). The models were built for coordinated sequences with different levels of priority. Real traffic control algorithms with priority were implemented into the model on the sequence of Marymoncka Street and Grochowska Street in Warsaw. Then, by introducing changes to the parameters of the algorithms, their effect on traffic characteristics, including estimated power consumption, was studied. The results obtained from the computer simulation were statistically processed using R software (ver. 4.3.2). The analysis results prove the effectiveness of tramway priority operation, show its impact on electricity consumption, and allow us to determine the limits of its effective application. Thus, they complement the knowledge of the impact of tramway priority on traffic. The research results also have practical value, as they help us to make rational decisions in the process of designing traffic control algorithms at intersections with a multi-criteria approach.
1. Introduction
On each permanently inhabited continent, human activities have established road networks and traffic signaling systems [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Over time and with technological advancement, traffic regulations and control systems have become increasingly complex. Rail transportation has always served as the axis of urban development. Residents perceive tramways as a fast means of public transportation [7]. A tram network’s presence positively influences areas’ development and raises property values [8]. Introducing priority measures improves public transportation perception and makes trams more attractive to passengers [9]. Increasing travel speed is coupled with a reduced need for rolling stock, as shorter travel times enable the exact timetable to be maintained with fewer vehicles. This indirectly reduces energy consumption for traction by decreasing vehicle acceleration and deceleration cycles.
The issue of public transportation priority is an integral element of sustainable urban mobility strategies and is often included in a city’s transportation policy. One of the goals of this policy is to provide priority for selected categories of road users, primarily for public transportation, which can accommodate more passengers in less space.
A significant advantage of implementing priority measures is the reduction in electric energy consumption [10]. Priority in traffic signaling affects the energy loss level by minimizing the likelihood of a tram having to stop or reduce speed other than at designated stops or speed limits. Therefore, it follows that only tram approaches where stops have not been built have an impact on the energy balance. From an energy perspective, ensuring full priority in those cases is desirable. Furthermore, shortened travel times decrease energy expenditure for non-speed-dependent vehicle needs, such as air conditioning, ventilation, and passenger information displays.
Evaluating the impact of tram priority on traffic conditions is a complex issue. Constructing a universal model is challenging because intersections vary significantly in geometry, traffic volume, and control algorithms. The problem becomes more complicated when considering coordinated intersections. Thus, research findings in this area tend to be somewhat general or overly focused on specific, overly detailed, and rarely reproducible examples. Consequently, there is a need to develop a method that objectively assesses the impact of traffic control solutions on coordinated road traffic and electric energy demand.
This article proposes such a method and provides an example of its application to assess the impact of tram priority on traction energy consumption. Many publications focusing on priority only address technical aspects of vehicle detection [11,12] or rapid signal clearance for privileged vehicles [11,13,14,15,16]. Other aspects of the impact of priority on road traffic are often neglected. Another group in the literature focuses on benefits of prioritization as improving travel speed by 15% to 30% [17] or enhancing punctuality [18,19,20] due to reducing variability in travel time by minimizing random waiting times. Helsinki’s experience shows a 40% increase in punctuality [21].
Another benefit of tram priority is improving intersectional safety by eliminating the dilemma zone phenomenon. An example of this is when the length of the equivalent of a yellow signal for a tram is insufficient to guarantee a safe stopping of the tram and the extension of the signal is not allowed by the national regulations [22]. The dilemma zone phenomenon can be effectively eliminated through accommodative algorithms that prevent the signal’s deactivation for vehicles in the dilemma zone.
Prior research indicates that satisfying the needs of all road users during high traffic volume is challenging. Some studies argue that skillful prioritization does not adversely affect other road users [23,24]. In other works, it is suggested that deteriorating individual traffic conditions is a natural consequence of prioritization [20], or that it serves as the basis for lowering the level of priority [25]. These discrepancies in research results arise from the fact that most analyzed studies considered only simplified two-phase algorithms [26,27,28], or isolated intersections [29,30] or prioritization was controlled by a simplified algorithm that only extended the green light for the main direction [19], with no examination of the impact on other road users [31].
Many publications focus on optimizing control systems [32] and approaching traffic control using various models, including Petri nets [14], particle swarm optimization algorithms [33], fuzzy logic [5], and genetic algorithms [34], among others. However, these solutions relate to closed global systems. The authors of publications [23,28,35] view traffic signal control as a highly simplified phenomenon, making applying research results to solve the priority problem impractical. Few publications refer to more than two-phase solutions [13,30].
In the literature, there are also concepts of allocating priority only in the case of schedule delays [36], sufficient vehicle occupancy [37], the type of line (ordinary or express), or a sufficiently high stopping cost [3,38]. While current technology allows for the easy implementation of such proposals, they often lack substantive justification. The stability of the timetable is considered more important than accelerating a single crowded vehicle [39].
Publications describing practical priority implementations often include numerical indicators related to the actual effectiveness of these solutions [40]. For instance, it has been shown that implementation of partial traffic signal priority results in a 5% reduction in travel time, while significantly more effective solutions for traffic organization, such as dedicated tram lanes, lead to a 25% reduction in travel time. Experiences from Melbourne show a reduction in road incidents by over ten percent after implementing tram priority at 29 intersections [4].
Commonly used traffic coordination methods consider many important factors in tramway traffic [41]. Passive priority solutions [20] do not consider disruptions in tramway movement and are less effective than active priority solutions. The methods described in [42] consider public transport traffic but decrease the number of priority function calls, reducing the impact of public transport on overall traffic. The authors of the method described in [43,44] took a similar approach. In Poland, few studies have addressed integrated tram coordination, as seen in [45]. Currently, the automatization of processing in this area is unavailable. Results obtained by the authors of the publication [46], based on one of the proposed tram routes, were unsatisfactory.
In summary, tram priority is a current research problem in many countries. Different methods of preferring track vehicles have different impacts on traffic conditions. Commonly used control algorithms do not fully utilize the potential, especially on coordinated intersections. Clear guidance is lacking on how specific levels of priorities affect the electric energy demand for tram vehicles.
This study investigates how various variants of local priority algorithms in traffic signaling affect the electric energy consumption necessary for tram traction.
To this end, work has been conducted towards analyzing
- -
- The impact of the use of priority algorithms on the electricity consumption for tram traction needs;
- -
- The impact of parameterization of priority control algorithms on electricity consumption for tram traction needs;
- -
- The impact of tram traffic volume on electricity consumption on a route controlled by a priority algorithm.
To this end, computer simulation models were created, based on the characteristics of actual tram routes in Warsaw, data on tram traffic intensity, and other means of road transport. These models utilize real priority control algorithms modified for research purposes. Details of the model are presented in Section 2 of this article, while the results of modeling and their interpretation are provided in Section 3, Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
Warsaw’s tram network, in general, is characterized by separated tracks: more than 95% of tramway approaches of intersections with traffic lights are segregated from general traffic. Two coordinated routes in Marymoncka Street (Figure 1) and Grochowska Street (Figure 2) were selected for the study, where the tram track occurs beside the roadway and on the axis of the roadway. The geometrical solutions of the junctions in each route include both situations with and without dedicated lanes for turning onto the track. The routes also include pedestrian crossings with traffic lights outside the crossings.
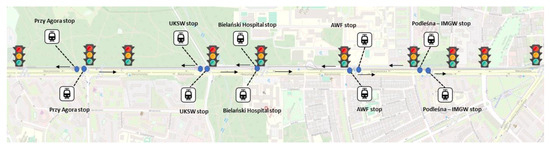
Figure 1.
Schematic of the Marymoncka Street route. Based on [47].
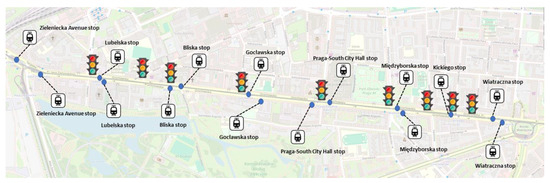
Figure 2.
Schematic of the Grochowska Street route. Based on [47].
Modeling tramway traffic is performed using a microscopic model, which allows analysis of the results, taking into account the analysis that considers individual interactions between individual vehicles. Therefore, the simulation was conducted using the PTV Vissim modeling environment [48], based on the Wiedemann car-following model developed in 1974 [49]. The software offers advanced capabilities for implementing complex traffic control algorithms, is highly efficient when working with large intersection networks [50,51] and features a rich user interface. All around the world, Vissim is widely used as a tool for testing theoretical solutions [41], comparing solution variants [1,52], optimizing simple traffic designs [53], and checking traffic control algorithms before their implementation.
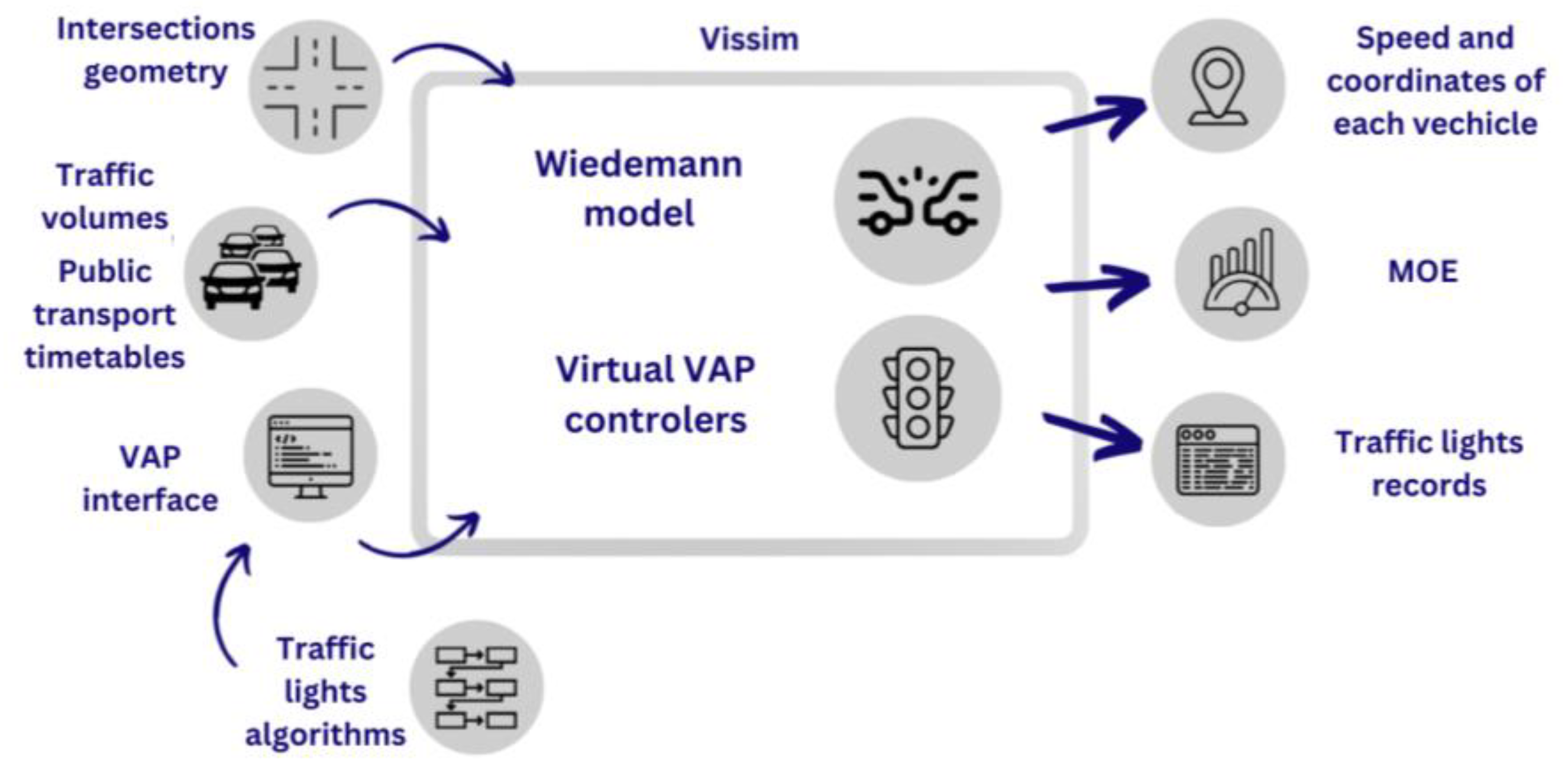
Input data for the traffic simulation model include geometric data describing the modeling area, traffic signal algorithms, and vehicle traffic volumes and directions, as well as public transportation parameters. The modeling results encompass vehicle speeds, spatial positions over time, derived measures of traffic conditions, auxiliary variables defined in the modeling algorithms and their values, and diagrams displaying signals (Figure 3).
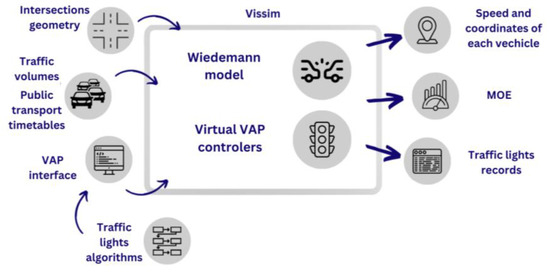
Figure 3.
Schematic of the simulation model. Developed using [54,55].
To represent the geometry of the modeling area, an orthophoto map provided by the capital city of Warsaw [56] was used. During the model construction, geometric data for intersections, lane counts, additional turning lanes, pedestrian crossings, curve geometries, detectors, and public transport stop locations, as well as speed limits, were incorporated.
The model in Vissim was prepared based on standard Wiedemann 74 parameters. The speed limit for trams and cars was set to 50 km/h, the desired speed on curves and minimum headway and gap time in collision fields were modified manually accordingly to the observations. The simulation length during the experiment was 11,800 s (3 h of observations + 1000 s for model filling). Traffic volumes and type and directional structure were adopted based on field measurements individually for each intersection approach.
Data describing vehicle traffic were acquired from traffic condition calculations included in traffic signal projects and tram schedules [57]. They encompass traffic volumes, directional traffic structures at various nodes of the model, vehicle types and desired speeds along the route, as well as public transportation schedules.
Real traffic control algorithms functioning at intersections and approved by the city traffic management authority were introduced into the model. These include both fixed-time base algorithms and complete adaptive traffic control algorithms with all logical and temporal conditions.
Unlike the articles presented in the other studies (where the algorithms are very simplified), our study was prepared on the basis of actual algorithms operating in Warsaw at 19 intersections gathered into two arterials. The volume of their documentation does not allow us to present them in full (171 A3 pages). It is worth mentioning here that the algorithms studied are algorithms without an objective function.
After developing road network models, the accuracy of lane alignments, distances between intersections, permissible relationships at individual intersections, and right-of-way rules at collision points were verified. The outcome of this verification is that the road network models for both examined routes adequately represent the geometry of the road network and the applied traffic organization for the research.
The results of computer simulation provide data describing the status of all traffic participants (trams, buses, cars, and pedestrians) moving within the network during the simulation. Files with a *.fzp extension are saved in CSV format with additional metadata in the header. Each row contains a record describing the status of a given vehicle during each simulation step. Another type of output file with a *.ldp extension contains data on the internal states of the traffic control algorithm for each intersection and controlled pedestrian crossings, recorded at 1-s intervals. The file includes values of variables, logical conditions of the algorithm, counters, and markers defined for the operation of tram priority, as needed for the work. Additional auxiliary files with a *.att extension are dictionaries of vehicle types, and data on traffic signal controllers, including the intersection name, cycle length, control type, and geometry of zones designated for analysis for individual intersections and entrances.
The overall research concept is presented in Figure 4.
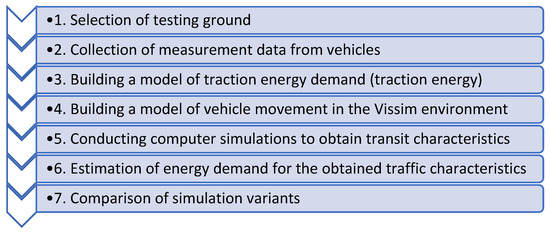
Figure 4.
Flow chart of the study.
The data obtained from computer simulations were subjected to analysis using mathematical methods from the field of statistics. The process begins with preprocessing, which involves loading records from files, correcting variable names (as the names generated in the Vissim software are not syntactic names in the R language), and merging data with the dictionary of vehicle types. Subsequently, the sets of output data are grouped by vehicle number and simulation number, and the average speed of each vehicle for a given simulation is calculated.
To analyze the impact of priority on the consumption of electric energy by the tramway traction system, a computer model described in [10] was used. The model was built based on actual measurements of energy consumption by PESA-type trams that operate on Warsaw’s routes. This resulted in a highly accurate model, with an error on test sets of <1%.
Measurement data were obtained during a single measurement day in November 2020 collected from all vehicles passing along the route with on-board recorders (modern low-floor trams of the Pesa Jazz model). The owner of the data is Warsaw Tramways Ltd., and they can be requested through public data access. The vehicles moved in real conditions, during a standard workday, according to the trams schedule in typical weather conditions. On-board recorders recorded electricity consumption for the vehicle’s traction needs, ignoring the vehicle’s own needs (other equipment on the vehicle), whose consumption does not depend on the driving mode.
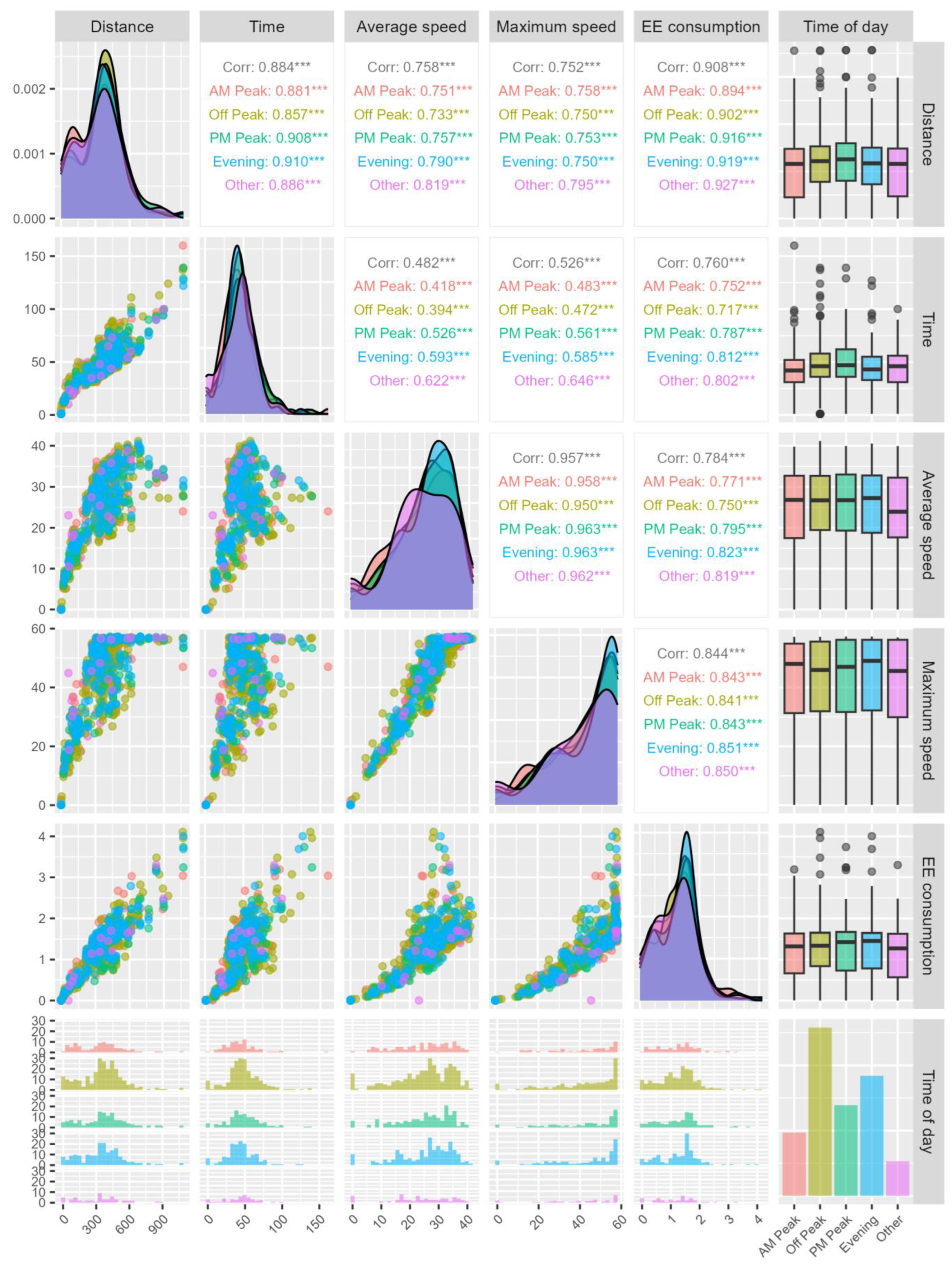
The authors of the article present the data in an aggregated manner for each time of day. They are shown in Figure 5, which include data on the length of stretches of uninterrupted driving, time, speed and power consumed for sections of the studied route.
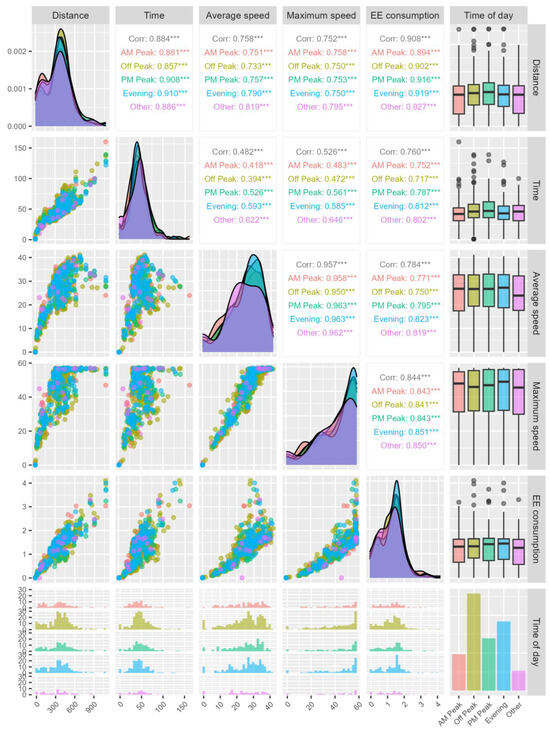
Figure 5.
Aggregated data obtained during the measurement, (*** correlation is statistically significant, with a p-value of less than 0.001).
The model for emissions calculations was fed with data (positions, speeds, and accelerations) generated from the Vissim model based on vehicle movement diagrams. The differences between the variants were due to the different movement characteristics of the trams in each variant. Energy consumption was calculated according to the basic principles of physics outlined below.
For discrete calculations, we used the formula:
where
is electrical energy in Joules (J);
is the Power in the i-th time interval, expressed in Watts (W);
is the length of the i-th time interval, expressed in seconds (s);
is the number of time intervals.
Power was calculated by knowing instantaneous values of voltage and current in the time interval, which makes Energy formula look like
The comparative analysis included the computer simulation scenarios presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Description of computer simulation variants.
The fixed-time programs (A) and original accommodation programs (C) are faithfully replicated traffic signal design projects for individual intersections that have been introduced into the model in accordance with the approval of the Traffic Management Bureau, the traffic management authority in the city. The research used traffic volumes and signal programs reflecting the morning peak on Grochowska Street and the afternoon peak on Marymoncka Street. All subsequent simulation scenarios were based on the original accommodation projects (C).
Accommodation programs without priority (B) are algorithms in which the priority modules are disabled. They operate with full accommodation, treating trams like other road users.
Scenario (D) implements a simulation variant in which full accommodation algorithms are active, but trams have been removed from the model. This variant allows for determination of traffic performance indicators that are derived only from the movement of other road users and are independent of tram traffic.
Accommodation projects with reduced detection (E) implement a simulation variant in which full-priority module functionality is maintained, but tram detection is limited to a detector placed before the stop line. Such a solution is often used in practice to reduce construction costs by eliminating distant detectors. It may result in detection deficits, causing trams to be detected too late or imprecisely, making it impossible to guarantee tram passage without stopping.
Subsequent simulation scenarios were developed to study the impact of signal priority on other vehicles on the corridor by determining the extent to which algorithms disrupt the basic operation of traffic signals. This disruption is referred to as the “aggressiveness” of priority. To investigate this issue, two basic parameters were modified: the intersection cycle coordination return speed and the potential for priority phase extensions.
The first parameter affecting the aggressiveness of priority is the flexibility of offset synchronization. When granting priority to trams, it is possible to extend the cycle duration beyond the variant adopted in the base traffic signal program. After such an extension, it is necessary to synchronize the offsets between subsequent signals. The accommodation variant with limited cycle regeneration capabilities (F) assumes a 50% reduction in the time parameters of the algorithm compared to the base variant (C), while the accommodation with extensive cycle regeneration capabilities (G) assumes a 150% increase in the time parameters compared to the original variant (150%).
The second parameter affecting the aggressiveness of priority is the maxPT parameter, determining the maximum duration of the tram phase when granting priority. In the slightly aggressive accommodation variant (H), allowable tram phase extensions and reductions were reduced by 50% compared to the original variant (C). The strongly aggressive accommodation variant (I) combines the last two extensions, allowing maximum phase extension or reduction times to be increased to 150% while also increasing the ability to synchronize offsets, as in variant F.
The R language was chosen as the statistical analysis tool, using the RStudio graphical interface (version 2023.12.0).
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Run and Model Verification
The simulation parameters included simulation speed and duration, the number of simulation steps per second (recalculation frequency), and the random number generator seed, which forms the basis for generating parameters for individual road traffic participants. For the experiment, the simulation duration was set to 11,800 s (3 h of observation + 1000 s to fill the model).
As a result of the simulation, 170 files containing vehicle data and algorithm parameters were obtained for Marymoncka Street, and 153 for Grochowska Street, in total 12.84 GB of data.
The correctness of tram traffic was verified by generating vehicles at specified time intervals and observing their movement. Automatic verification was performed for tram stops, subsequent traffic lights, and the time spent at stops. An example of the registration process is shown in Figure 6.
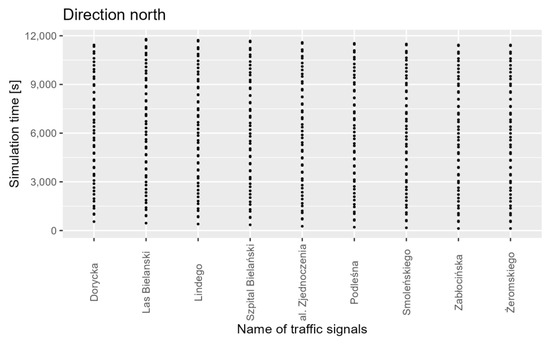
Figure 6.
Tram notification moments at each traffic light.
Next, travel times between stops were calculated and compared to the carrier’s schedule data [57]. The compatibility of model travel times with the timetables is an indicator of the correct operation of the models because the punctuality of Tramwaje Warszawskie (Warsaw Tramways) is 98% [58]. The comparison is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of modelled and scheduled [57] tram travel times.
A parameter describing the movement of passenger cars in the model is the desired speed and traffic intensities. Traffic intensities in the model are consistent with measurements made along the route for the purpose of designing traffic lights. The correctness of the vehicle generator configurations and the generation of vehicles on free-flow sections were verified. Situations in which vehicles were unable to enter the network were eliminated from the models. Running the simulation showed that the model with default settings (following leader driving parameters) adequately replicates reality.
3.2. Impact of the Use of Prioritized Algorithms on Electricity Consumption for Tram Traction Needs
The text mentions Table 3, which presents the results of the estimation of the total electric energy consumption (EE) for tram traction, considering the basic traffic control algorithms on the route, both with and without priority. The tram traffic intensity was set to match real-life conditions and was 16 trams per hour on Marymoncka Street and 17 trams per hour on Grochowska Street.

Table 3.
Aggregate EE consumption for baseline variants to simulation.
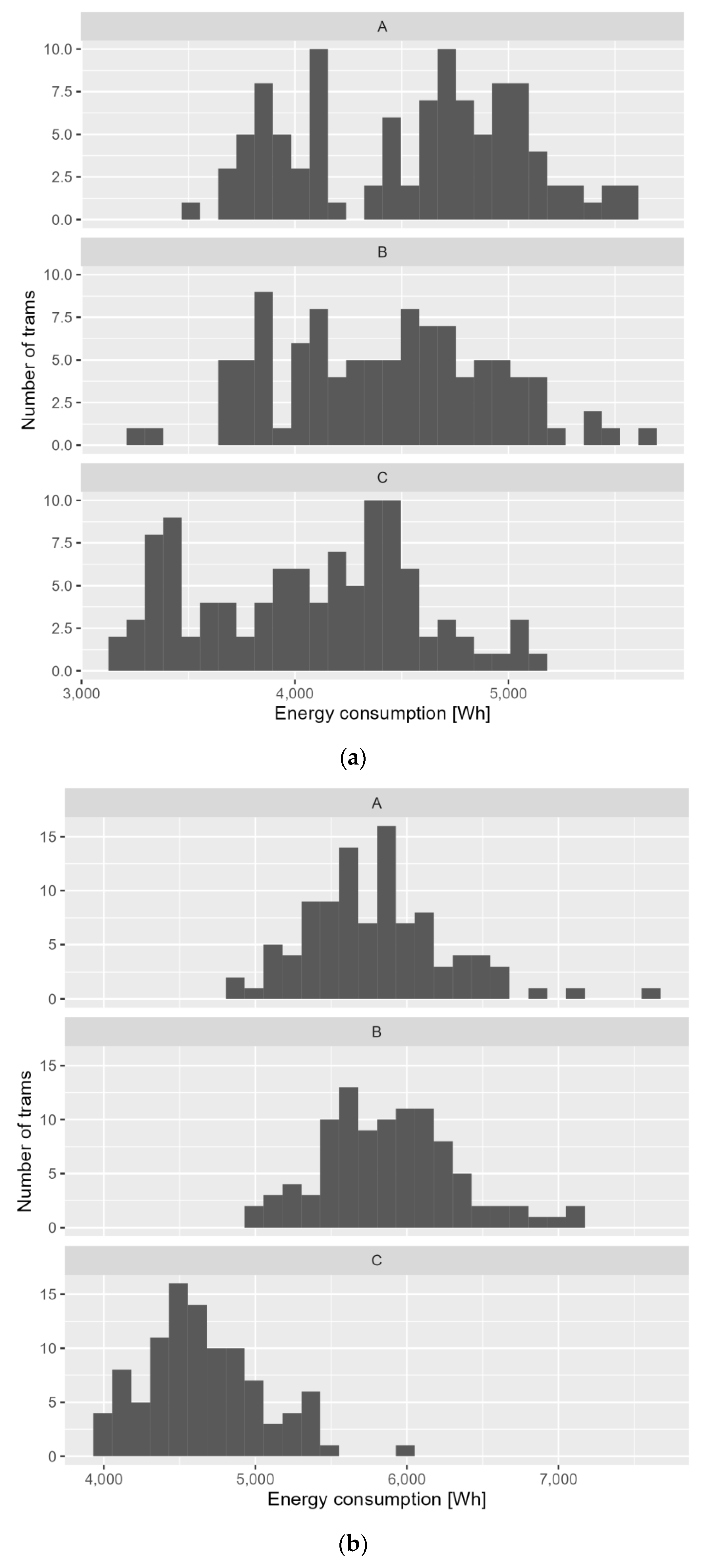
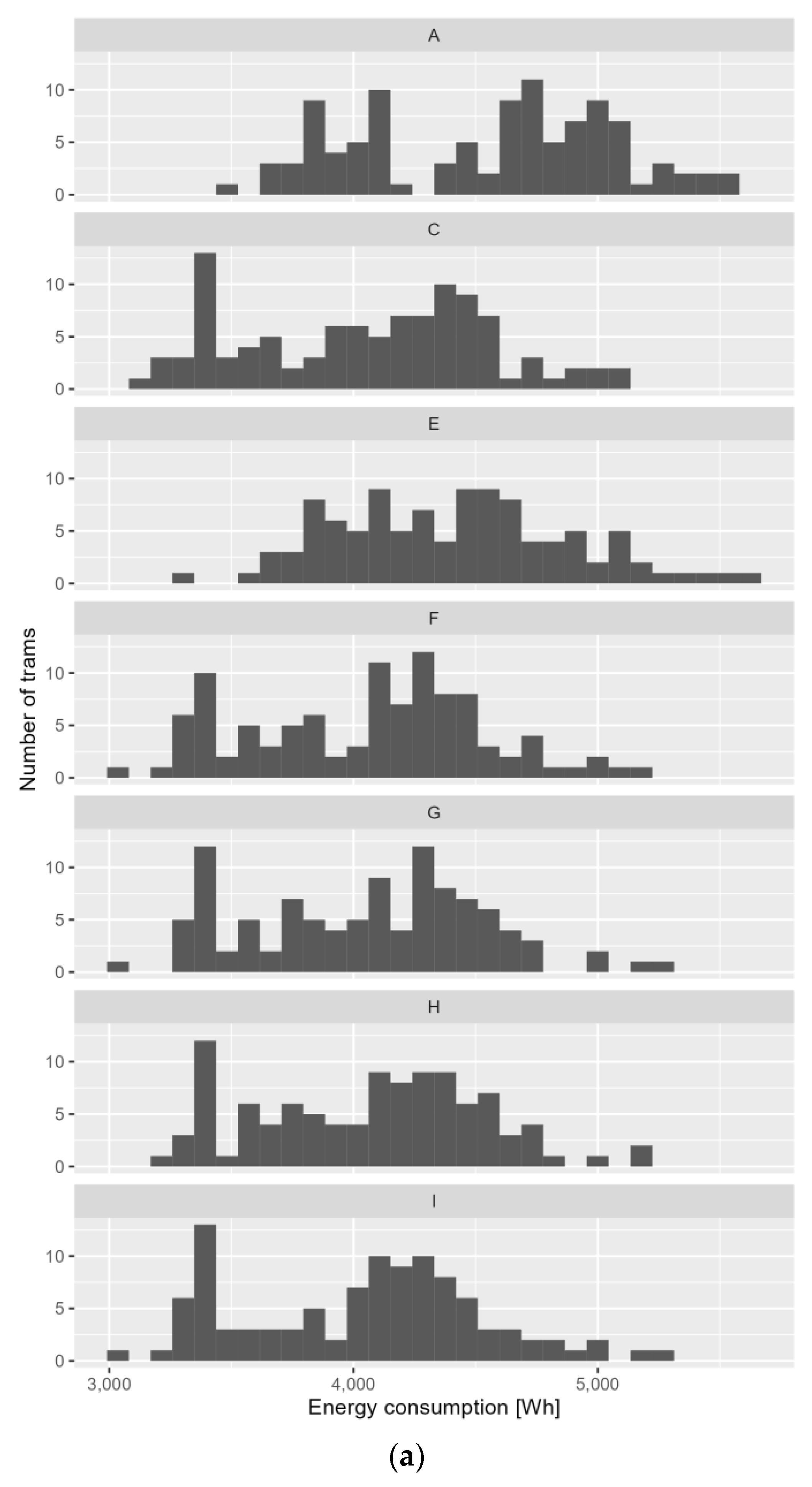
Figure 7 illustrates a histogram of electric energy consumption for tram traction, categorized by the number of trams participating in the simulation for both examined routes. The histogram shows how energy consumption varies based on the number of trams involved in the simulation.
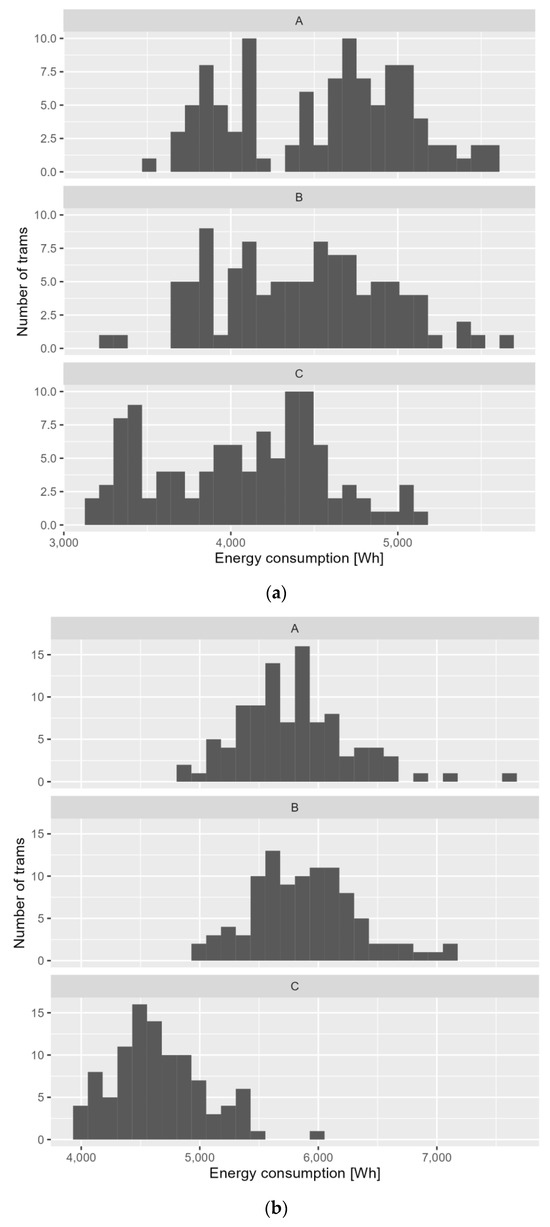
Figure 7.
Histogram of electricity consumption for traction under different control variants: (a) Grochowska Street; (b) Marymoncka Street.
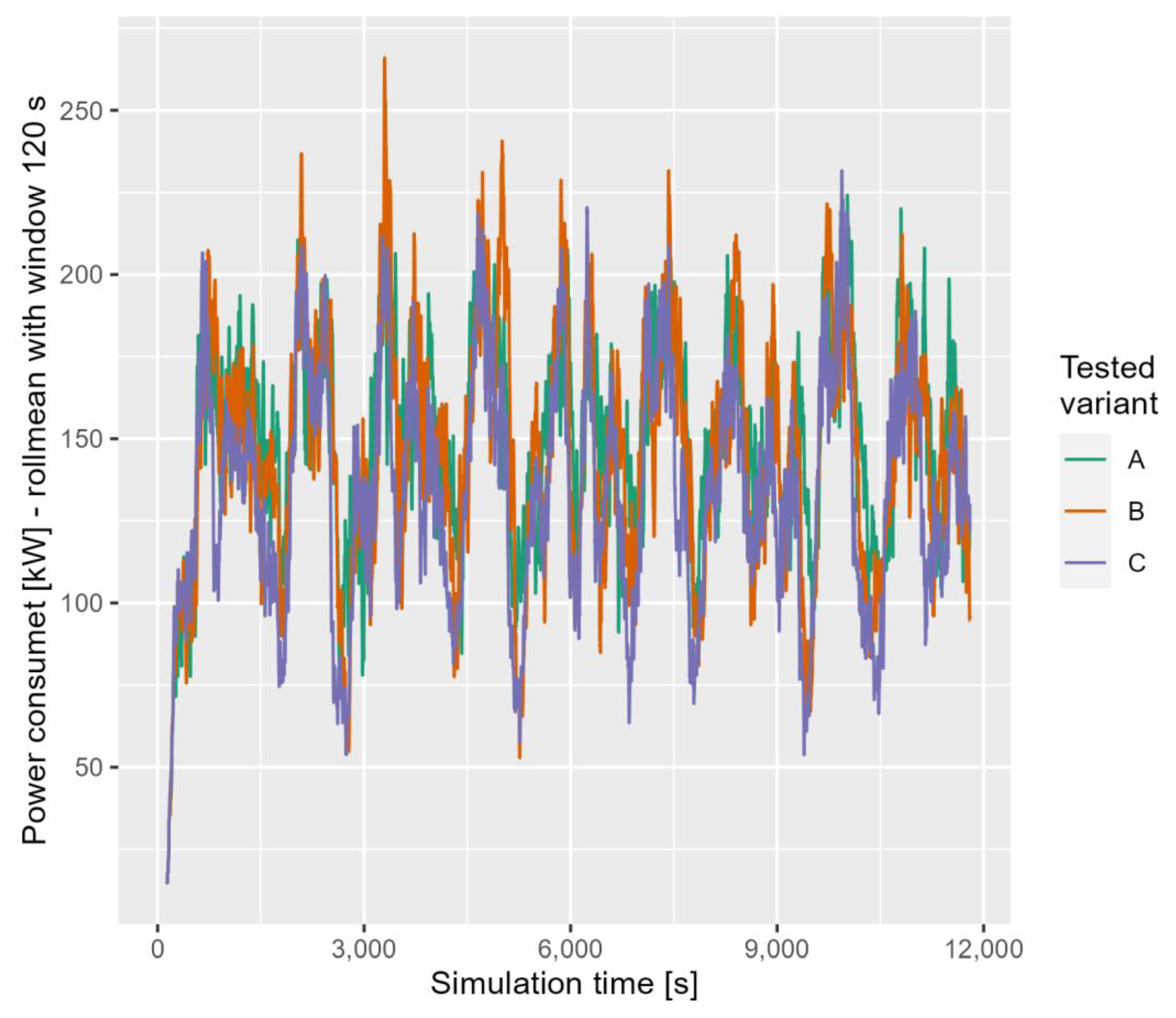
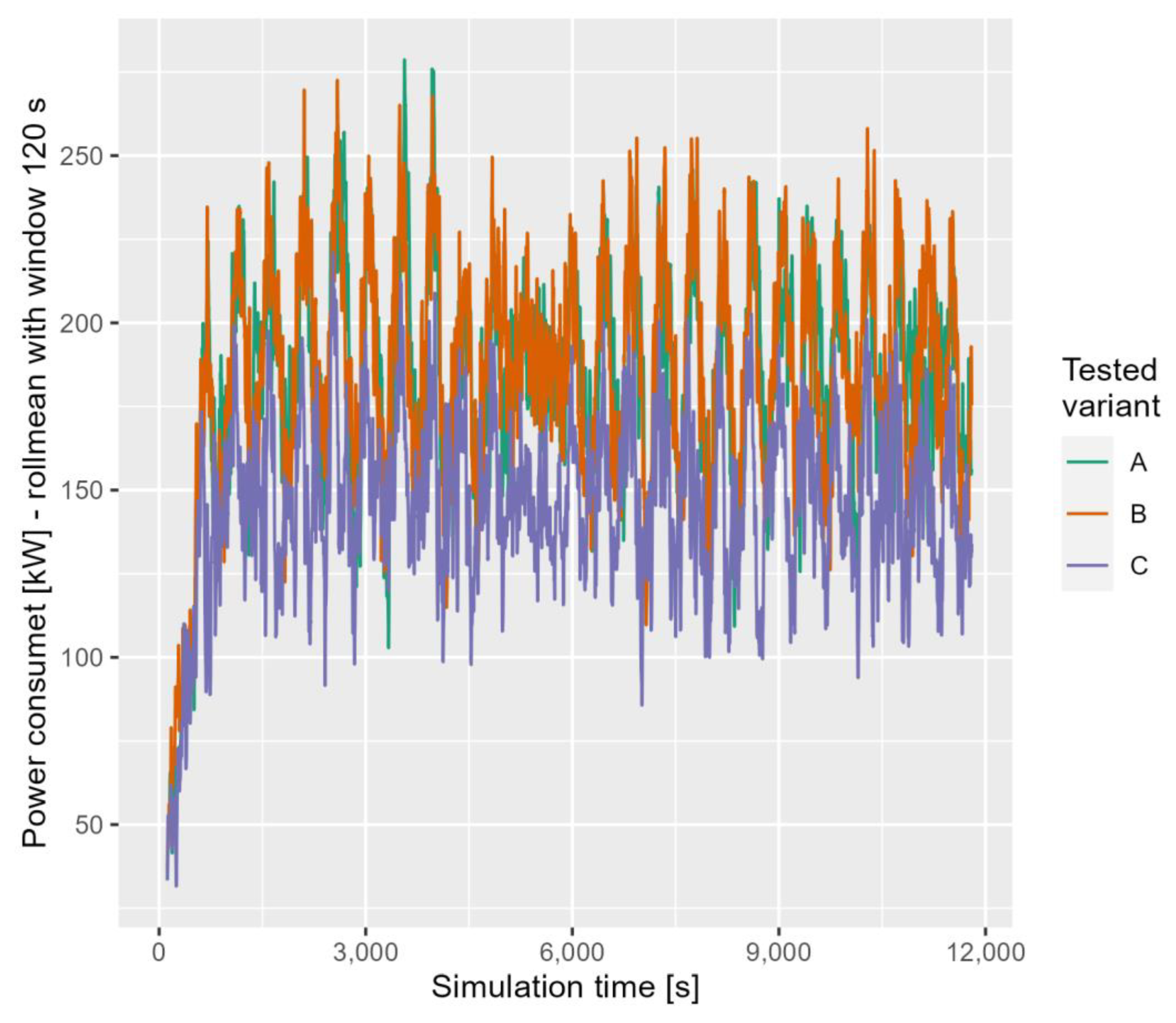
The course of the power taken from the overhead contact line for Grochowska Street and Marymoncka Street is shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, respectively. The value shown in the diagrams is a weighted average over a period of 120 s.
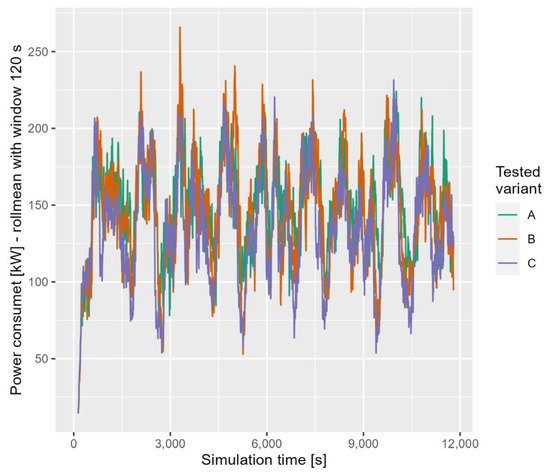
Figure 8.
The course of the power taken from the overhead line for Grochowska Street.
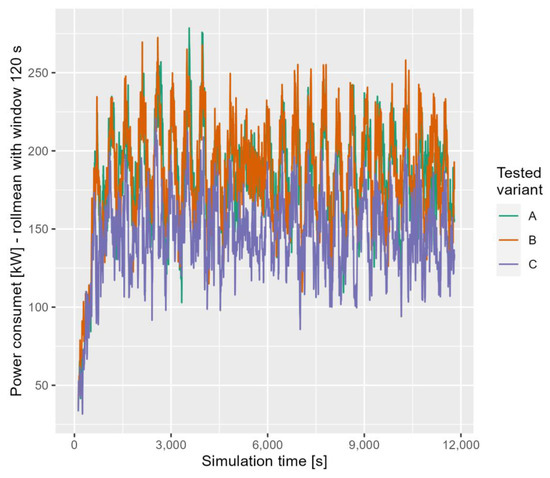
Figure 9.
The course of the power taken from the overhead line for Marymoncka Street.
Assessing the normality of the EE consumption distributions using Pearson’s χ2 method showed that the distributions for variants A and C for Grochowska Street were not normal. Therefore, further analyses of these variants were conducted using the Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn tests.
3.3. Influence of Parameterization of Control Algorithms with Priority on Electricity Consumption for Tram Traction Needs
Traffic control algorithms that take tram priority into account can be tuned to individual traction characteristics by means of parameters. A study of the impact of the parameterization of priority control algorithms on traction energy consumption was conducted on both trains using the scenarios described in Table 1. The results of the simulations are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summarized electricity consumption for traction for priority control algorithms with different parameters.
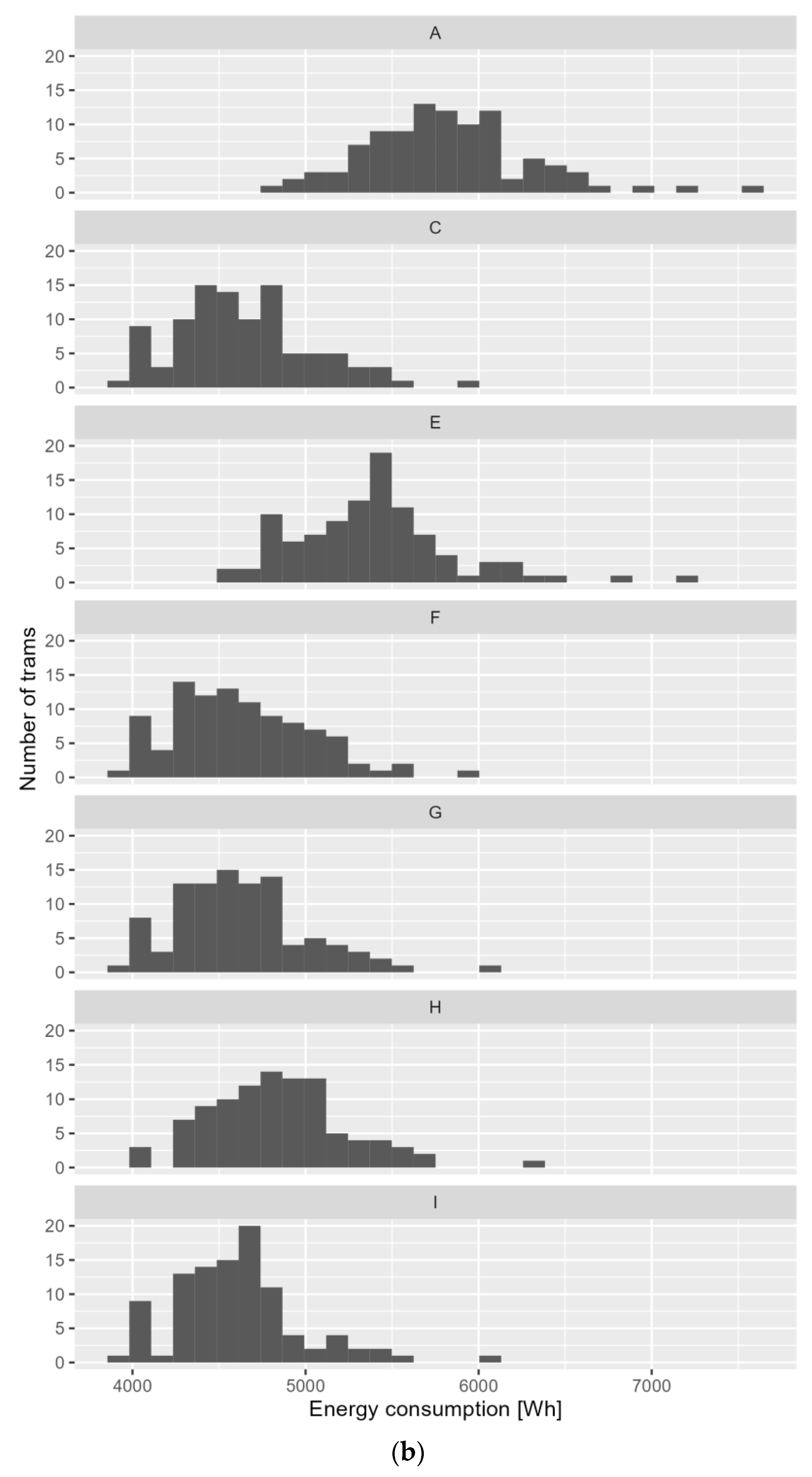
Figure 10 presents the histograms of the EE consumption of the different parameters of control algorithms with priority.
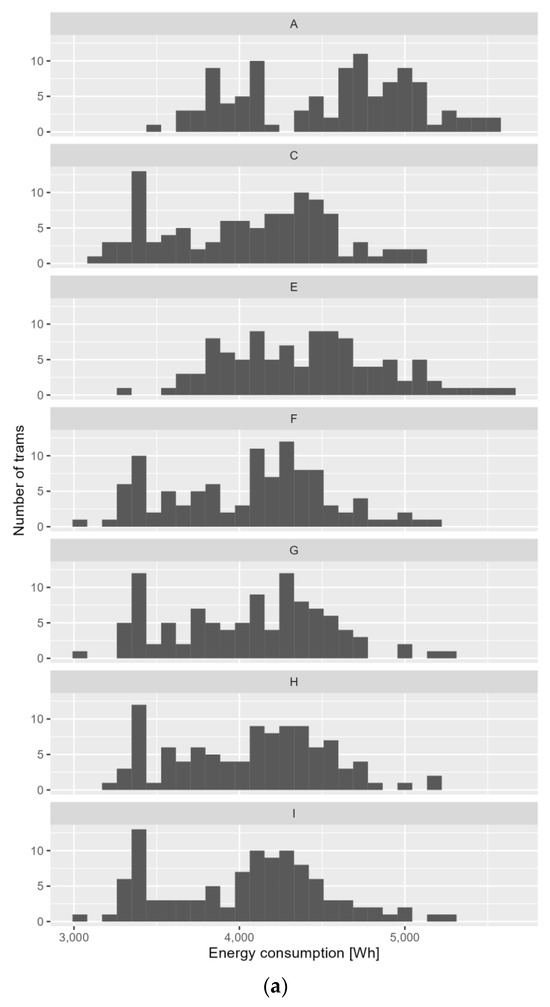
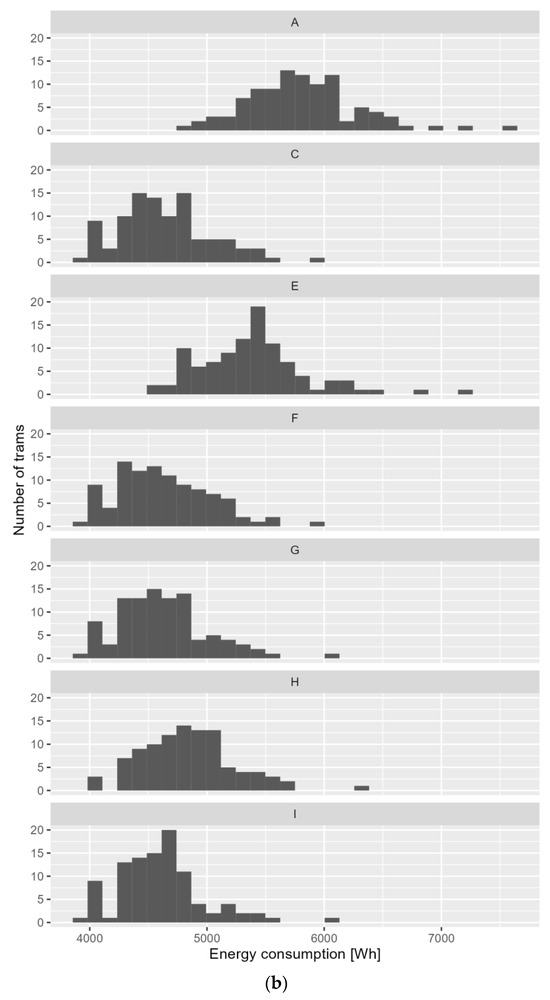
Figure 10.
Histogram of electricity consumption for different parameters of control algorithms with priority: (a) Grochowska Street; (b) Marymoncka Street.
3.4. Influence of Tram Traffic Volume on Electricity Consumption on a Route Controlled by a Priority Algorithm
As the base scenario for further analysis, scenario (C) was selected, which involves real traffic control algorithms with tram priority. The variable parameter in each independently run simulation was the tram traffic intensity, expressed as the number of trams per hour (1/h). The range of frequencies used in this study corresponded to the frequencies observed in the Warsaw tram network, ranging from sporadically operating trams (every 10 min) to the network’s capacity limit (36 vehicles per direction during peak hours).
The results of the computer simulations conducted to analyze the impact of tram traffic intensity on electric energy consumption (EE) are presented in Table 5. Modeling was conducted for the algorithms used in scenario C, which includes adaptive traffic signal control with full or high priority for trams.

Table 5.
Summary EE consumption for control algorithms with different parameters.
The total electric energy consumption for tram traction in accordance with the simulation scenarios presented in Table 5 is depicted in Figure 11.
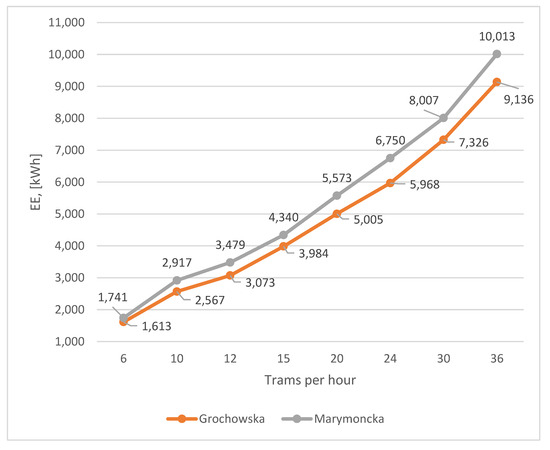
Figure 11.
Dependence of EE consumption on tram traffic volume.
4. Discussion
The first stage of the study, the results of which are presented in Section 3.2, aimed to determine whether the use of priority-based algorithms would result in a noticeable effect in terms of reducing the total electric energy consumption for tram traction compared to classical traffic control algorithms without tram priority.
The analysis of statistically significant differences between scenarios with priority (C) and scenarios without priority (A and B) revealed that the application of adaptive control algorithms without priority (B) did not significantly affect the electric energy consumption of trams compared to the baseline scenario (A). The analysis of travel times for these two cases also did not show a statistically significant reduction in travel time.
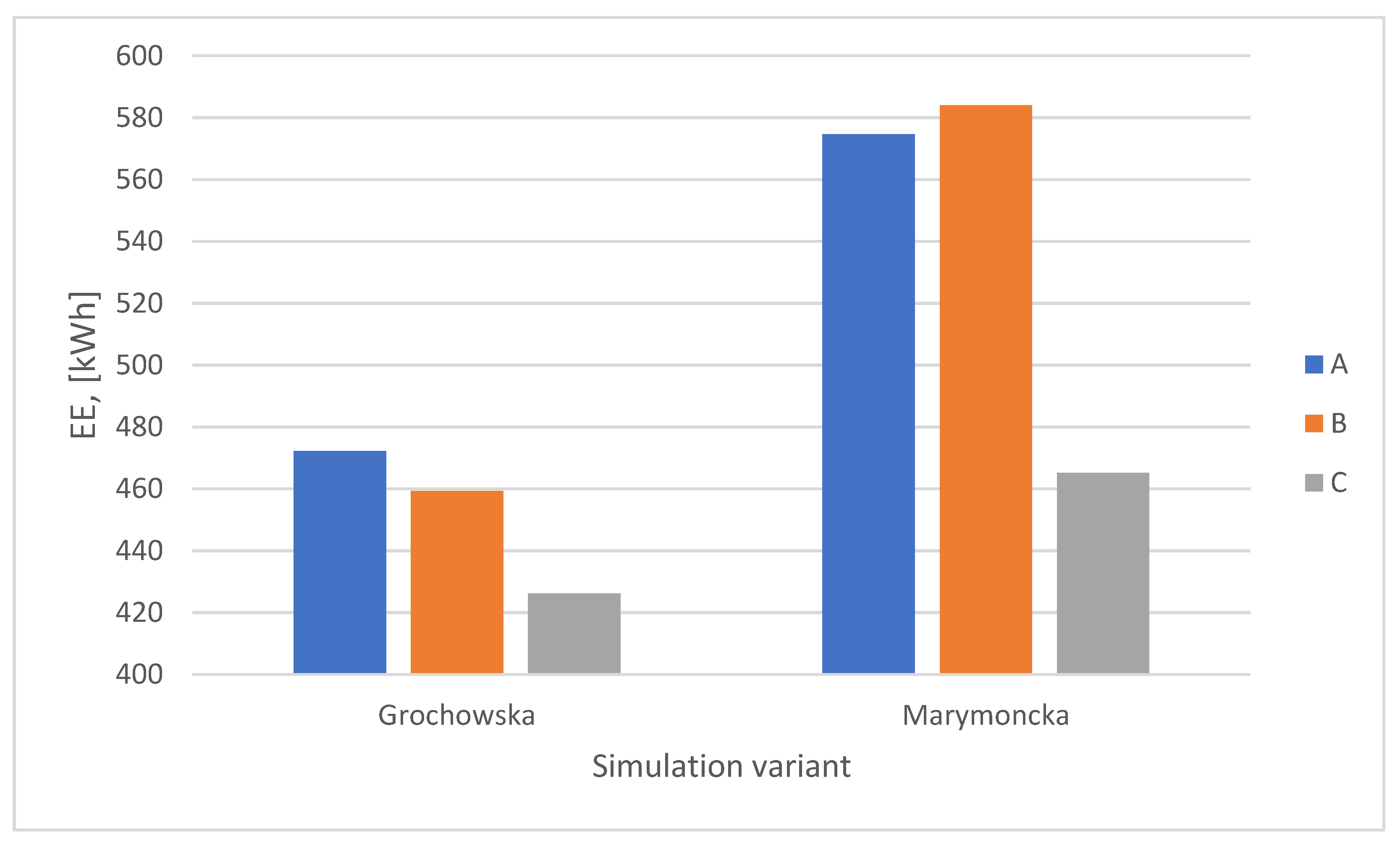
On the other hand, the use of tram priority-based traffic control algorithms (C) led to an approximate 10% reduction in energy consumption on Grochowska Street and about a 19% reduction on Marymoncka Street compared to fixed-time algorithms (Figure 12). It should be noted that for the Marymoncka Street route, the use of accommodation algorithms resulted in an increase in energy consumption compared to the baseline algorithm.
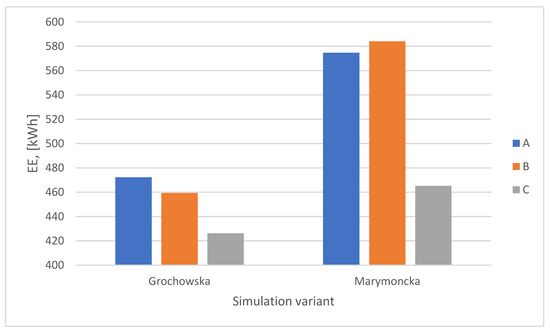
Figure 12.
Summary of total traction power consumption for traffic control algorithms with and without priority.
The conclusion from the first stage of the study: the introduction of tram priority on the route contributes to a reduction in the demand for electric energy for tram traction. The subsequent stages of the study aimed to determine the extent of this change and its dependence on the parameterization of traffic control algorithms with priority, as well as the traffic intensity on the routes.
The aim of the second stage of the study, the results of which are presented in Section 3.3, was to answer the following question: how does changing the parameter values of the priority algorithms (the so-called “aggressiveness” of the priority) affect the electricity consumption of the traction? The modifications of the parameters of the priority control algorithms listed in Table 1 were used for the study. A visualization of the simulation results for the different variants is shown in Figure 13.
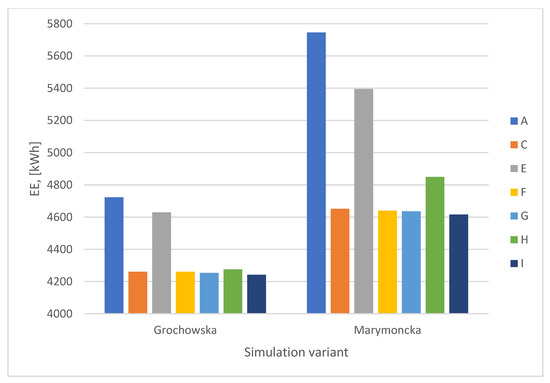
Figure 13.
EE consumption for the different parameterization variants of the priority control algorithms.
Based on the analysis of the simulation results, it can be concluded that changing the parameters of traffic control algorithms with tram priority does not significantly impact energy consumption for tram traction. Both fixed-time priority-based algorithms and those with limited detection priority result in higher electric energy consumption (up to ~9% for Grochowska Street and up to ~20% for Marymoncka Street) compared to the scenario with minimal EE consumption (Scenario I—increased maximum times). Therefore, it can be stated that the selection of parameter values for priority-based traffic control algorithms can be made without considering the criterion of energy consumption minimization.
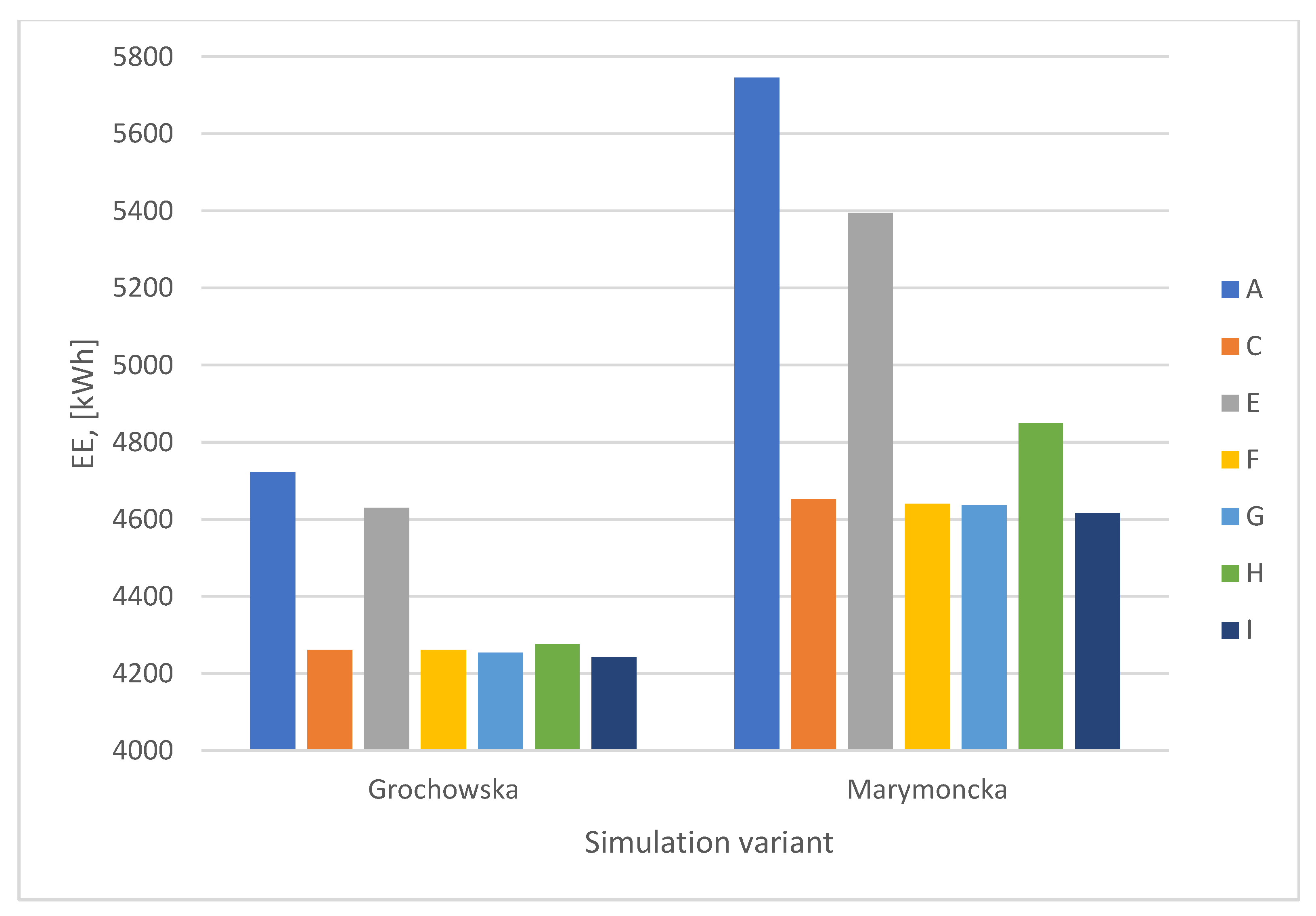
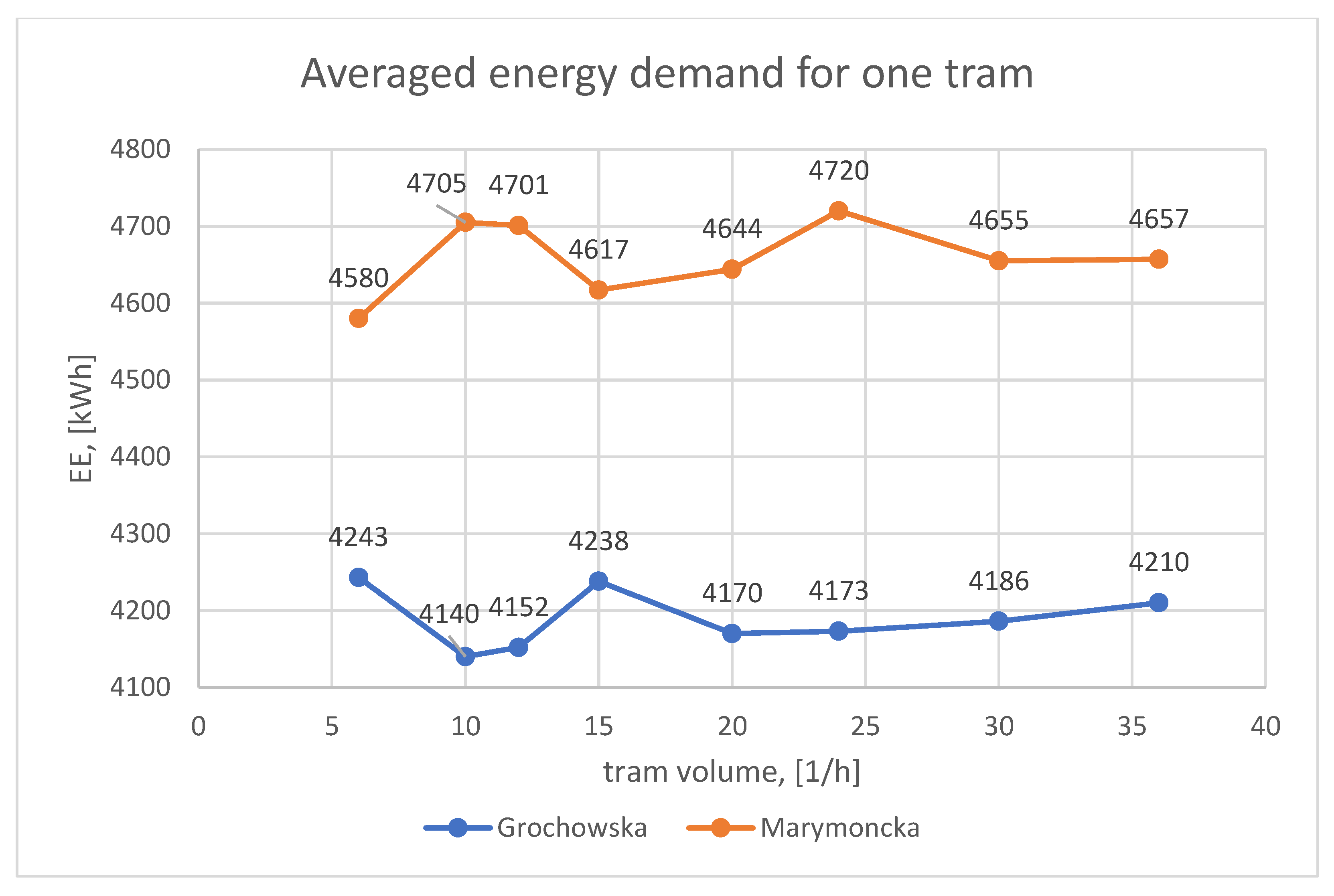
The aim in the next stage of the study, the results of which are presented in Section 3.4, was to analyze the impact of tram traffic intensity on routes controlled by priority-based algorithms on energy consumption for trams. Based on the results presented in Table 5, the average electric energy consumption per tram participating in the simulation was calculated. Figure 14 shows a bar chart illustrating the average energy demand for one tram, depending on the traffic intensity on the route.
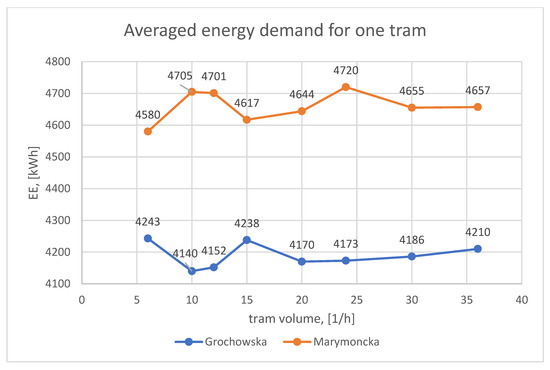
Figure 14.
Averaged energy demand for one tram, depending on the volume of traffic on the route.
The average energy consumption for one tram was 4189 kWh for Grochowska Street and 4659 kWh for Marymoncka Street, respectively. The standard deviation as a percentage of the mean in both cases did not exceed 3%. Based on this, it can be concluded that increasing the traffic intensity on the route does not significantly affect electric energy consumption per unit. A slight downward trend in energy consumption with an increase in the number of trams on the route resulted from the prioritization of larger groups of trams by traffic control algorithms, which allowed for a slight reduction in the number of stops. At the same time, an increase in energy demand was observed as traffic intensity approached the upper limit defined by the route’s capacity.
In summary, in this chapter, the computer modeling process and subsequent statistical analysis provided answers to the research questions posed. These answers, in a synthesized form, will be presented in the Conclusions section. It should be emphasized that the article did not delve deeply into other aspects of tram priority and its impact on other road users. Due to the breadth of the topic, this would require a separate article. Nonetheless, some interesting, yet not obvious, conclusions can already be presented.
Firstly, the introduction of priority had a significantly positive impact on tram traffic. Average tram speeds in the studied scenarios increased by approximately 19% and 14%. At the same time, for other vehicles, there was a decrease of just under 3% for Marymoncka Street and an increase of 9% for Grochowska Street. These differences result from the nature of traffic on these routes. Marymoncka Street has lower traffic volume, so the introduction of local priority caused the temporary disruption of coordination for cars, resulting in more stops and a decrease in their average speed. In the case of Grochowska Street, a highly congested route, introducing priority improved the main traffic flow, also for other vehicles, which is related to the appropriate distribution of public transport stops and adjustments to pedestrian phase opening times.
Secondly, during the study of the impact of tram traffic intensity on priority operation, a difference in average speeds of passenger cars was observed. With the introduction of high priority, the speed decreased slightly from 32.57 km/h to 31.57 km/h, while for full priority, a decrease was observed from 30.91 km/h to 28.02 km/h. Therefore, it is not recommended to use full priority on routes with very high tram traffic. This relationship is also confirmed by the time losses, where the standard deviation starts to increase sharply when the tram intensity reaches 20 trams per hour in one direction.
Thirdly, the results of the time loss analysis show that changes in individual priority parameters (unit cycle regeneration range for scenarios F and G and maximum tram phase extension in scenarios H and I) did not significantly affect the previously achieved results. Additional testing of priority operation in cases with detection deficits resulted in a slight decrease in tram speeds, along with a significant increase in time losses. The only statistically significant changes were observed for the implementation of the lack of a detection variant, proving that proper placement of detection devices is a key aspect of implementing traffic signal priority.
5. Comparative Analysis
The energy consumption studies were conducted for railways [59,60,61] and metro [62,63,64]. Due to the nature of the movement of these vehicles, the analysis focused on the movement of a single vehicle within the network segment. However, the tram network significantly differs from railway and metro systems. Trams are not separated from other traffic participants. In this case, interactions with other vehicles and pedestrians occur. Even greater interactions occur in the case of trolleybuses, whose movement resembles that of buses, with only the power source being analogous to trams [65].
Energy consumption studies for trams focus on the driving style of a driver [66] and the creation of schedules [67], resulting in energy savings ranging from several to over a dozen percent. These studies assume no influence on infrastructure-related factors. In other works, authors developed energy-optimal driving methods considering only the influence of traffic signals [68], yielding model efficiencies of over 23% energy savings [69]. However, this study presented an analysis for a single intersection, and the traffic control method is not detailed.
The approach proposed in this article is innovative as it involves matching the traffic lights to the way the vehicle is driven, resulting in a reduction in the number of stops. The obtained results align with the outcomes of an experiment conducted by temporarily disabling the traffic signal priority on Marymoncka Street. A recent field study [10] showed a 13% energy increase due to the priority system’s deactivation, similar to the 10% and 19% energy reduction obtained in this article depending on the analyzed stretch. The difference in research outcomes may stem from the fact that the applied model does not account for energy recuperation, an assumption often made in energy consumption studies, e.g., in [68].
Other studies focus on energy storage in the vehicle and the optimization of tram movement [70,71,72,73]; those topics are not covered in this article. The study [74] indicates 2.5% energy savings, while study [75] shows a 5% reduction, both inferior to the solution proposed in this work, emphasizing the significance of designing traffic signals to reduce energy consumption, potentially yielding greater savings. The prediction error for regression models in energy consumption was approximately 2% [76], comparable to the effects of some studies. Comparative analysis indicates that incorporating tram movement into traffic signals yields excellent results; however, combining such a solution with other energy-saving methods should provide synergistic effects, enabling energy cost reduction and, in the case of trams with energy storage, reducing the required supercapacitor or battery capacity.
The resulting method also has some limitations. The method does not take into account the recuperation of electrical energy. In the case of tramways, the energy extracted during the braking of the vehicle is given back to the power grid, if the grid has the capacity to receive it. So it does not directly affect the distribution of EE to traction. Since the calculation model was built on data that do not take into account recuperation, a comparison of different simulation variants is possible (when calculating differences in EE consumption, recuperation is not taken into account).
The method does not take into account the possibility of the line being served by different types of trams. The introduction of a new type of tram into service will require the construction of its model in the simulation program; among other things, measurement data for this model will be needed.
Undoubtedly, a characteristic feature of the method is that it is based on real data, with which it is necessary to feed the model, which can be considered both a disadvantage (the need for measurements) and an advantage (high accuracy) of the model.
Our research method can be used for any control method that can be connected to Vissim. The program has the ability to be used to control vehicle traffic in a traffic signal controller emulator model. It is also possible to control using an external traffic control model described in Python, so it would be possible to use reinforcement learning control too. With the method we developed, it would be possible to compare the results of the control algorithm used in the study and the control using RL. This is an interesting direction for further research. Recently, there have been many studies published related to traffic signal control using RL, such as [34,77,78]. Most of them are implemented based on SUMO software (version 1.18.0) [79]. SUMO software is less sophisticated when it comes to tools for analyzing traffic data and exporting them. However, it is possible to include in the Python script used for traffic control (e.g., using RL) data acquisition analogous to that obtained by the authors from Vissim software in .fzp and .ldp files. Then, in the case of the study [34,77,78], after adjusting the data to the same structure, the comparison methods developed by the authors can be used.
The genesis of the method stemmed from the requirements of Polish regulations, which mandate an explicit description of the operation of the control algorithm [80]. A neural network or any other machine learning algorithm does not meet this requirement. The methods used may be used in other countries that have such requirements in regulations or guidelines.
6. Conclusions
The use of traffic control algorithms with tram priority on road networks not only shortens travel times and reduces the number of stops but also lowers the demand for electrical energy. Depending on the type of priority applied, the reduction in energy consumption for the selected analyzed road sections reached a maximum of 10% and 19%. It is worth emphasizing that while the study focused on two typical road sections, in practice, the achieved effect will always depend on the specific configuration of these sections. This is why it is crucial to model traffic during the design of new road solutions or when planning the modernization of existing ones. An interesting finding from the study is the low dependence of energy consumption on the parameters of priority control algorithms. In practice, this can be used to fine-tune a selected priority control algorithm more precisely to improve traffic indicators for other participants. Another conclusion from the research that supports the use of priority control algorithms is the low dependence of average energy consumption on the number of trams on the section, at least until approaching the section’s capacity limits.
It is important to emphasize that mathematical models commonly used to describe priority-controlled traffic at individual intersections become highly complex in the case of a network of intersections. Hence, the research used a computer model built using Vissim software. This model exhibits a high degree of fidelity to real-world conditions, as confirmed by the validation results using real-world data.
The innovative aspect of the study presented in this article primarily stems from the fact that it addresses not just one intersection (as shown in the literature review in the introduction) but a network of interconnected intersections. It uses algorithms that are genuinely used in the field and parameterizes them appropriately for computer simulation.
As mentioned in the introduction, this article provided a detailed analysis of just one of the consequences of implementing complex priority control algorithms on coordinated road sections: electrical energy consumption for traction. The direction of further research is to compare the obtained results with changes in the situation for other road users, primarily cars (waiting time at intersections, the number of vehicles in the queue, etc.), and the associated effects, such as emissions of pollutants and delays. Conducting such studies will help to specify guidelines for selecting control algorithms considering a wider range of criteria.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C., A.G. and T.K.; methodology, A.C. and T.K.; software, A.C., T.K. and A.G.; validation, A.G. and T.K.; formal analysis, A.C.; investigation, T.K. and A.C.; resources, A.G.; data curation, T.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G. and A.C.; writing—review and editing, A.G. and T.K.; visualization, A.G., A.C. and T.K.; supervision, A.C.; project administration, A.G.; funding acquisition, A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Warsaw University of Technology founds, Grant RND ILGiT 2023.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy policy of cooperating companies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Desta, R.; Tesfaye, D.; Tóth, J. Microscopic Traffic Characterization of Light Rail Transit Systems at Level Crossings. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, D.; Meleby, P.; Miao, L. Recent Advances in Traffic Signal Performance Evaluation. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. Engl. Ed. 2022, 9, 507–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, B. Bus Priority Signal Control Considering Delays of Passengers and Pedestrians of Adjacent Intersections. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naznin, F.; Currie, G.; Sarvi, M.; Logan, D. An Empirical Bayes Safety Evaluation of Tram/Streetcar Signal and Lane Priority Measures in Melbourne. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, G.G.; Iano, Y.; Vaz, G.C.; Negrete, P.D.M.; Negrete, J.C.M.; Chuma, E.L. Intelligent Mobility: A Proposal for Modeling Traffic Lights Using Fuzzy Logic and IoT for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the Soft Computing and its Engineering Applications; Patel, K.K., Doctor, G., Patel, A., Lingras, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1572, pp. 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Blokpoel, R.; Lu, M. Adaptive Green Wave with Speed Advice for Automated Vehicles. In Proceedings of the ITS Europe congress, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 3–6 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, H.; Kawazoe, N. Promoting Urban Light Rail Transit in a Compact City Context: The Case of Toyama City, Japan. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2022, 9, 776–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadziński, J.; Radzimski, A. The First Rapid Tram Line in Poland: How Has It Affected Travel Behaviours, Housing Choices and Satisfaction, and Apartment Prices? J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 54, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabay, L.; Meira, L.H.; de Andrade, M.O.; de Oliveira, L.K. A Portrait of the Crisis in the Brazilian Urban Bus System: An Analysis of Factors Influencing the Reduction in Usage. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2021, 9, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerepicki, A.; Górka, A.; Szustek, J. Analysis of Trams’ Consumption Depending on the Type of Traffic Light Used. Nauka Teh. 2019, 18, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellore, K.; Hancke, G.P. Traffic Management for Emergency Vehicle Priority Based on Visual Sensing. Sensors 2016, 16, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, R.; Hebbar, S.; Golla, V. Implementing Intelligent Traffic Control System for Congestion Control, Ambulance Clearance, and Stolen Vehicle Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.S.; Tiwari, A.; Sinha, P.R. Adaptive and Optimised Emergency Vehicle Dispatching Algorithm for Intelligent Traffic Management System. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 57, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Shiue, J.-Y.; Luo, J. A Traffic Signal Control Policy for Emergency Vehicles Preemption Using Timed Petri Nets. IFAC Pap. 2015, 48, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, A.; Elkosantini, S.; Darmoul, S.; Louati, H. Multi-Agent Preemptive Longest Queue First System to Manage the Crossing of Emergency Vehicles at Interrupted Intersections. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathi, V.; Surya, M.; Akshay, B.; Murali Siva, K.; Vasudevan, S.K. Smart Control of Traffic Signal System Using Image Processing. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrjas, G.; Szustek, J.; Górka, A.; Guralski, B.; Stasiak, M. Dziesięć lat wdrażania priorytetu tramwajowego w Warszawie.(eng. Ten years of implementing tramway priority in Warsaw). In Proceedings of the Krakowskie Dni Bezpieczeństwa w Miastach, Kraków, Poland, 12–14 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dera, P. Stosowanie priorytetów dla pojazdów transportu zbiorowego w szczególności w zakresie wspólnych pasów autobusowo-tramwajowych w Krakowie. (The use of priority for public transport vehicles, especially in terms of shared tram-bus lanes in Kraków). Transp. Miej. I Reg. 2013, 6, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, M.; Mension, J.; Salicrú, M. Operation of Transit Corridors Served by Two Routes: Physical Design, Synchronisation, and Control Strategies. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 130, 103283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, T. Integrated Optimization of Tram Schedule and Signal Priority at Intersections to Minimise Person Delay. J. Adv. Transp. 2019, 2019, 4802967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, M.; Kulmala, R. Benefits of Pilot Implementation of Public Transport Signal Priorities and Real-Time Passenger Information. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1799, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgüngör, A.P.; Mercan, E.Z. An Analysis of Type I Dilemma Zone at Signalised Intersections. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2021, 112, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Barbosa, R.; Shoaib Ayub, M.; Lopes Rosa, R.; Zegarra Rodríguez, D.; Wuttisittikulkij, L. Lightweight PVIDNet: A Priority Vehicles Detection Network Model Based on Deep Learning for Intelligent Traffic Lights. Sensors 2020, 20, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górka, A.; Szustek, J. Wdrożenie priorytetu dla tramwajów na rondzie Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” w Warszawie metodą dekompozycji na podskrzyżowania częściowe. (Implementation of the priority for trams on the “Zgrupowanie AK Radosław” roundabout in Warsaw using the partial intersections division method). Transp. Miej. I Reg. 2018, 12, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Molecki, A. Dostosowywanie układu drogowego w kontekście funkcjonalności sieci tramwajowe. (Adaptation of the road system in the context of the tram network functionality). TTS Tech. Transp. Szyn. 2020, 5–6, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chentoufi, M.A.; Ellaia, R. A Novel Metaheuristic for Adaptive Signal Timing Optimization Considering Emergency Vehicle Preemption and Tram Priority. SAE Int. J. Transp. Saf. 2019, 7, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounsell, N.B.; McLeod, F.N.; Shrestha, B.P. Bus Priority at Traffic Signals: Investigating the Options. In Proceedings of the 12th IEE International Conference on Road Transport Information and Control 2004 (RTIC 2004), London, UK, 20–22 April 2004; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Du, Y.; Jiang, S. Performance Evaluation of Transit Signal Priorities on Bus Transit Corridor Based on Data Envelopment Analysis. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, Q.; Xu, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, Y. Design of Real-Time Actuated Control System for Modern Tram at Arterial Intersections Based on Logic Rules. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 168781401881542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ou, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y. Research on Tram Detector Location Based on Vehicle–Infrastructure Communication. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies for Rail Transportation (EITRT) 2017; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 915–925. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, L.A.; Seman, L.O.; Kraus, W.; Camponogara, E. Real-Time Integrated Holding and Priority Control Strategy for Transit Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2019, 20, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchandani, P.; Head, L. A Real-Time Traffic Signal Control System: Architecture, Algorithms, and Analysis. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2001, 9, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celtek, S.A.; Durdu, A.; Ali, M.E.M. Real-Time Traffic Signal Control with Swarm Optimization Methods. Measurement 2020, 166, 108206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Ito, M.; Shiratori, N. Adaptive Traffic Signal Control: Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithm with Experience Replay and Target Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthaputchakun, C.; Sun, Z. A Novel Traffic Light Scheduling Based on TLVC and Vehicles’ Priority for Reducing Fuel Consumption and CO2 Emission. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Bu, F.; Zhang, W. Active Signal Priority for Light Rail Transit at Grade Crossings. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 2035, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrowicz, J.; Stróżek, A. Priorytet dla pojazdów transportu zbiorowego w programie sygnalizacji świetlnej na podstawie liczby pasażerów. (Priority for public transport vehicles in a traffic light control plan based on number of passengers). Transp. Miej. I Reg. 2021, 3, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, A.H.F.; Sha, R.; Li, S. Centralised and Decentralised Signal Timing Optimisation Approaches for Network Traffic Control. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 113, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecki, A. Kształtowanie priorytetu tramwajowego w procesie wdrażania ITS we Wrocławiu. (Shaping tram priority in the process of ITS implementation in Wroclaw). Przegląd Komun. 2015, 22, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Vujičić, M.; Prester, J. Assessing Service Quality of Public Tram Transport in Zagreb City Using P-Transqual Model. Zb. Ekon. Fak. U Zagreb 2019, 17, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lv, S.; Li, D.; Quan, M. Coordinated Control Method for Trams on Urban Arterial. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 587, 012092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, X.; Zou, N. Passive Transit Signal Priority for High Transit Demand: Model Formulation and Strategy Selection. Transp. Lett. 2019, 11, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, Y. Tram Passive Signal Priority Strategy Based on the MAXBAND Model. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; Lyu, C. Traffic Signal Coordination for Tramlines with Passive Priority Strategy. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, M. Zintegrowana Koordynacja Tramwajów i Pojazdów Indywidualnych w Korytarzach Transportowych (Integrated Coordination of Trams and Individual Vehicles in Transportation Corridors). In Proceedings of the VIII Konferencja Naukowo, Techniczna, Rosnówko, 15–17 June 2011; SITK: Poznań, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Górka, A.; Szustek, J. Związek Priorytetu Dla Tramwajów w Sygnalizacji Świetlnej z Zużyciem Energii Elektrycznej (Relation of Priority for Trams in Traffic Signals to Electricity Consumption). Plan. Ruchu A Wyzwania Glob. Annały Inżynierii Ruchu I Badań Transp. 2019, 3, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- OpenStreetMap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Vissim 21 User Manual; PTV Planung Transport Verkehr AG: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2021.
- Wiedemann, R. Simulation Des Straßenverkehrsflusses (Traffic Flow Simulations); Publication series of the Institute for Traffic, University of Karlsruhe; Institute for Traffic, University of Karlsruhe: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, G.; Ioannou, P.; Pitsillides, A.; Aphamis, T.; Maimaris, A. Development and Evaluation of Bus Priority Scenarios via Microscopic Simulation Models. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2009, 42, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejercito, P.M.; Nebrija, K.G.E.; Feria, R.P.; Lara-Figueroa, L.L. Traffic Simulation Software Review. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), Larnaca, Cyprus, 27–30 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bandi, M.M.; George, V. Microsimulation Modelling in VISSIM on Short-Term and Long-Term Improvements for Mangalore City Road Network. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 48, 2725–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, S.; van Vuren, T.; MacDonald, M.; Priest, N. Public Transport Priority Schemes–Comparing Microsimulation with Traditional TRANSYT and LINSIG Models. In Proceedings of the European Transport Conference (Etc) 2003, Strasbourg, France, 8–10 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shastry, K. Code Icon–Free PNG & SVG 2187377–Noun Project. Available online: https://thenounproject.com/icon/code-2187377/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- SAM Designs. Performance Icon–Free PNG & SVG 5329663–Noun Project. Available online: https://thenounproject.com/icon/performance-5329663/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Map of Warsaw. Available online: https://mapa.um.warszawa.pl/mapaApp1/mapa?service=mapa&L=pl (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Timetables–Warsaw Public Transport. Available online: https://www.wtp.waw.pl/rozklady-jazdy/ (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- Zarząd Transportu Miejskiego. Raport Roczny 2022; Annual Report; Public Transport Authority: Warszawa, Poland, 2022.
- Miyatake, M.; Ko, H. Optimization of Train Speed Profile for Minimum Energy Consumption. IEEJ Trans. Elec Engng. 2010, 5, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicre, C.; Cucala, P.; Fernández, A.; Jiménez, J.A.; Ribera, I.; Serrano, A. A Method to Optimise Train Energy Consumption Combining Manual Energy Efficient Driving and Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer System Design and Operation in Railways and Other Transit Systems, Beijing, China, 4 August 2010; pp. 549–560. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Yu, Y. Research on the Cooperative Train Control Strategy to Reduce Energy Consumption. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2017, 18, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.; Fernández, A.; Cucala, A.P.; Lukaszewicz, P. Optimal Design of Metro Automatic Train Operation Speed Profiles for Reducing Energy Consumption. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2011, 225, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Shan, S.; Liu, J.; Li, X. An Integrated Optimization Model of Metro Energy Consumption Based on Regenerative Energy and Passenger Transfer. Appl. Energy 2020, 264, 114770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Skibniewski, M.J. Long-Term Equilibrium Relationship Analysis and Energy-Saving Measures of Metro Energy Consumption and Its Influencing Factors Based on Cointegration Theory and an ARDL Model. Energy 2023, 263, 125965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwambeleko, J.J.; Kulworawanichpong, T.; Greyson, K.A. Tram and Trolleybus Net Traction Energy Consumption Comparison. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 2164–2169. [Google Scholar]
- Kubin, J.; Ferkova, Z. Influnce of Driving Style of a Tram Driver on the Tram’s Energy Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Drives and Power Electronics (EDPE), Tatranska Lomnica, Slovakia, 21–23 September 2015; pp. 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Mao, B.; Xu, Q.; Feng, J. Timetable Optimization for a Two-Way Tram Line with an Active Signal Priority Strategy. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 176896–176911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, Y.; Long, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J. Energy-Efficient Tram Speed Trajectory Optimization Considering the Influence of the Traffic Light. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 963275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Jia, L. Energy Consumption Optimization of Tramway Operation Based on Improved PSO Algorithm. Energy 2022, 258, 124848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, W.; Chen, W. Operation Optimization and Control Method Based on Optimal Energy and Hydrogen Consumption for the Fuel Cell/Supercapacitor Hybrid Tram. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, D. Energy Consumption Modeling and Energy Saving Analysis of Supercapacitor Tramcar. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference of Intelligent Robotic and Control Engineering (IRCE), Lanzhou, China, 24–27 August 2018; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Liu, J. Hierarchical Management Control Based on Equivalent Fitting Circle and Equivalent Energy Consumption Method for Multiple Fuel Cells Hybrid Power System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, J.-P.; Cohuau, J.-L. STEEM: ALSTOM and RATP Experience of Supercapacitors in Tramway Operation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Su, B.; Liu, J.; Ma, L. Optimal Energy Management and Control in Multimode Equivalent Energy Consumption of Fuel Cell/Supercapacitor of Hybrid Electric Tram. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6065–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Qi, L. An Optimal Method of the Energy Consumption for Fuel Cell Hybrid Tram. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 20304–20311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaolu, S.; Liwei, D. Prediction of Tram Energy Consumption Based on Modified Regression Model. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Safety Produce Informatization (IICSPI), Chongqing, China, 28–30 November 2019; pp. 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kolat, M.; Kővári, B.; Bécsi, T.; Aradi, S. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Traffic Signal Control: A Cooperative Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinaly, Z.; Sojoodi, M.; Bolouki, S. A Resilient Intelligent Traffic Signal Control Scheme for Accident Scenario at Intersections via Deep Reinforcement Learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUMO User Documentation. Available online: https://eclipse.dev/sumo/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Infrastruktury z Dnia 3 Lipca 2003 r. w Sprawie Szczegółowych Warunków Technicznych Dla Znaków i Sygnałów Drogowych Oraz Urządzeń Bezpieczeństwa Ruchu Drogowego i Warunków ich Umieszczania na Drogach (t.j. Dz. U. z 2019 r. poz. 2311 z późn. zm.). poz. 2311 z późn. zm.). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20190002311 (accessed on 7 January 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).