Spatiotemporal Evolution and Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions Using Nighttime Light Data: A Quantitative Case Study at the City Scale in Northeast China
Abstract
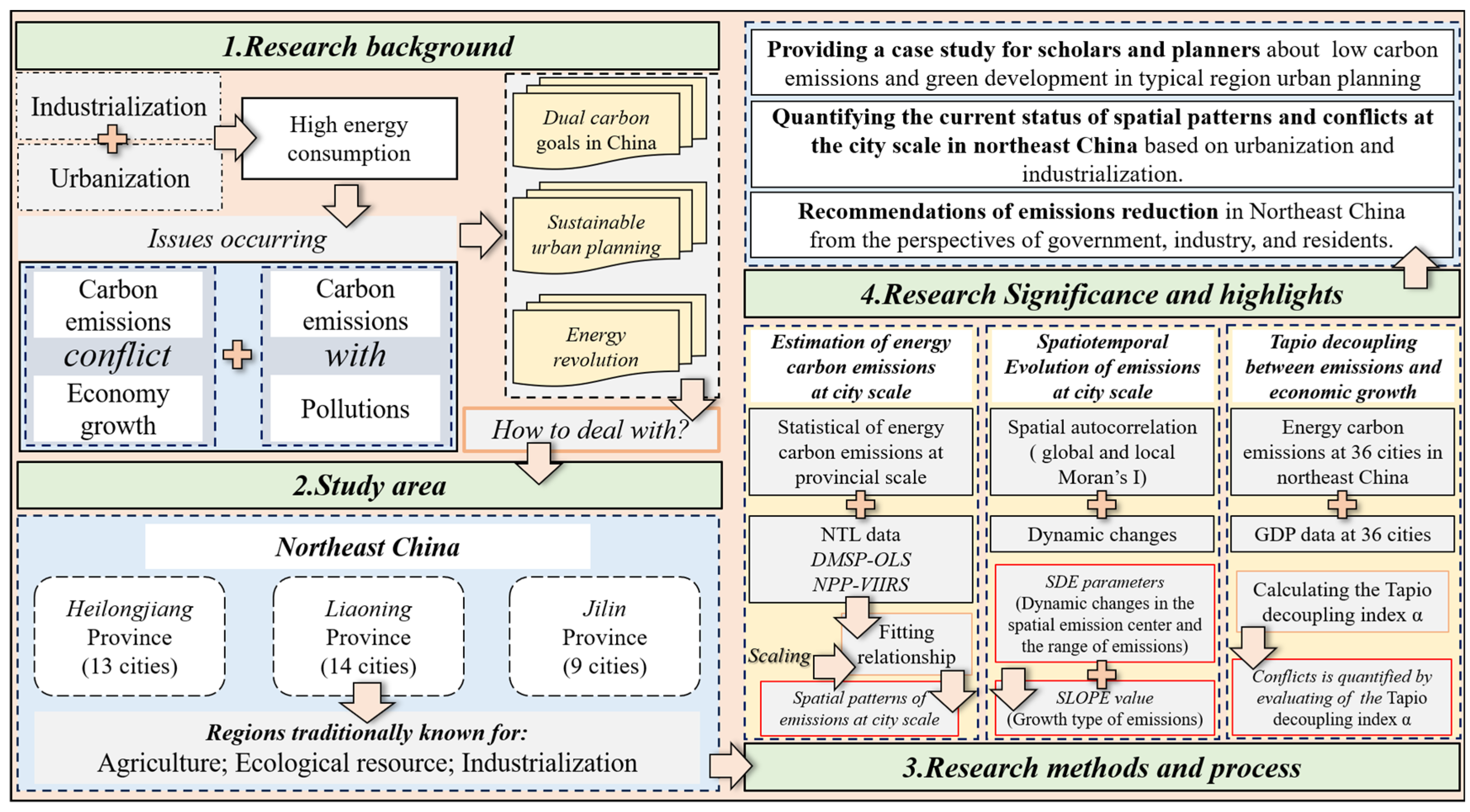
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
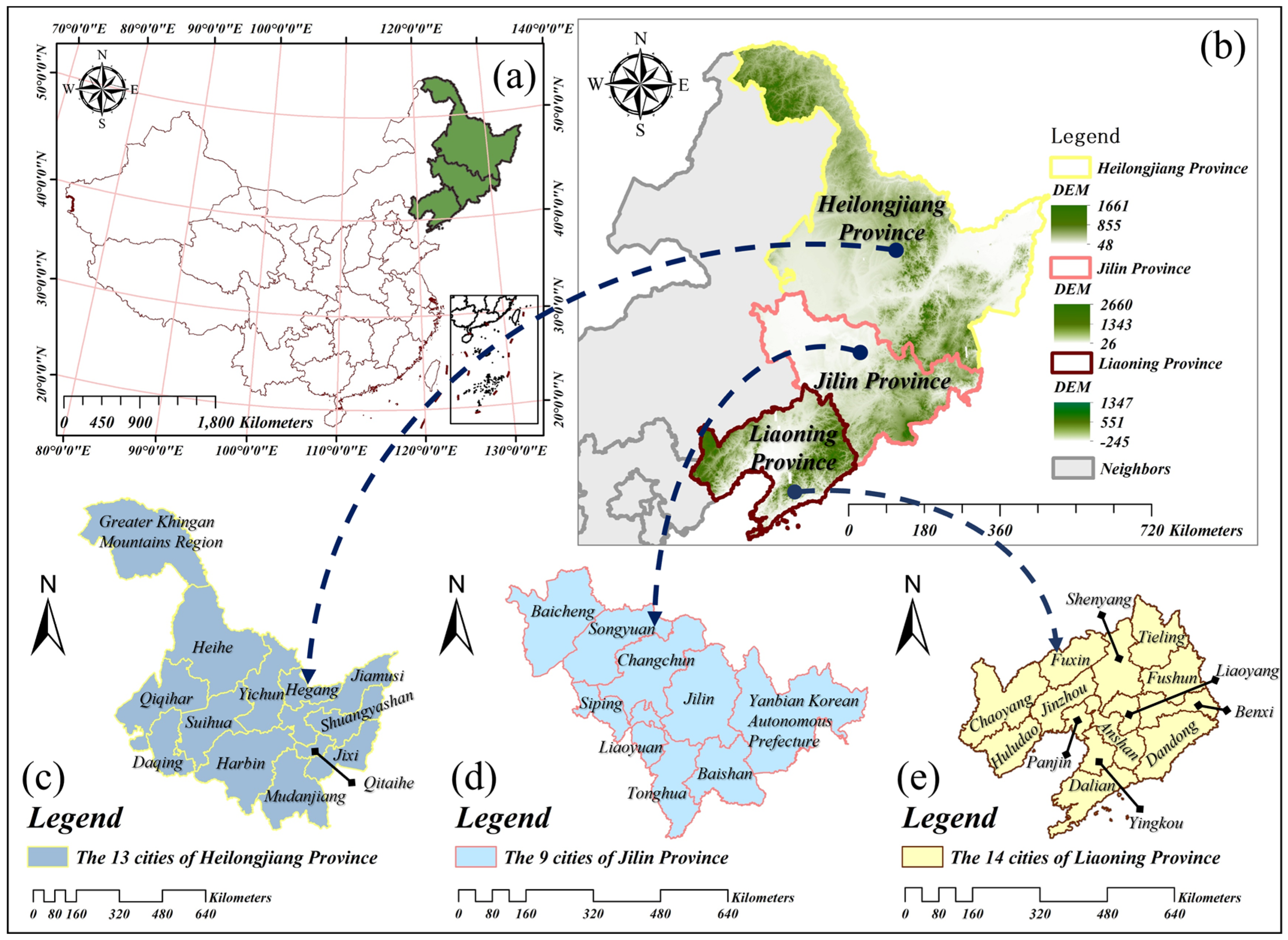
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Data
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Statistical Data
2.2.3. Emission Conversion Factors Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Energy Carbon Emissions at the Provincial Scale
2.3.2. Estimation of Energy Carbon Emissions at the City Scale: Scaling and NTL Data
- (1)
- Conversion and organization of two types of NTL data
- (2)
- Establishing the fitting relationship between provincial-scale emissions and NTL data
- (3)
- Estimating energy carbon emissions at the city-scale based on scaling
2.3.3. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Energy Carbon Emissions
- (1)
- From the perspective of spatial autocorrelation: Moran’s I and Local Moran’s I
- (2)
- From the perspective of spatial dynamic changes
2.3.4. Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy Carbon Emissions
3. Results
3.1. Results of Energy Carbon Emissions at the City Scale in Northeast China
3.1.1. Statistical Results of Energy Carbon Emissions in Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning Provinces
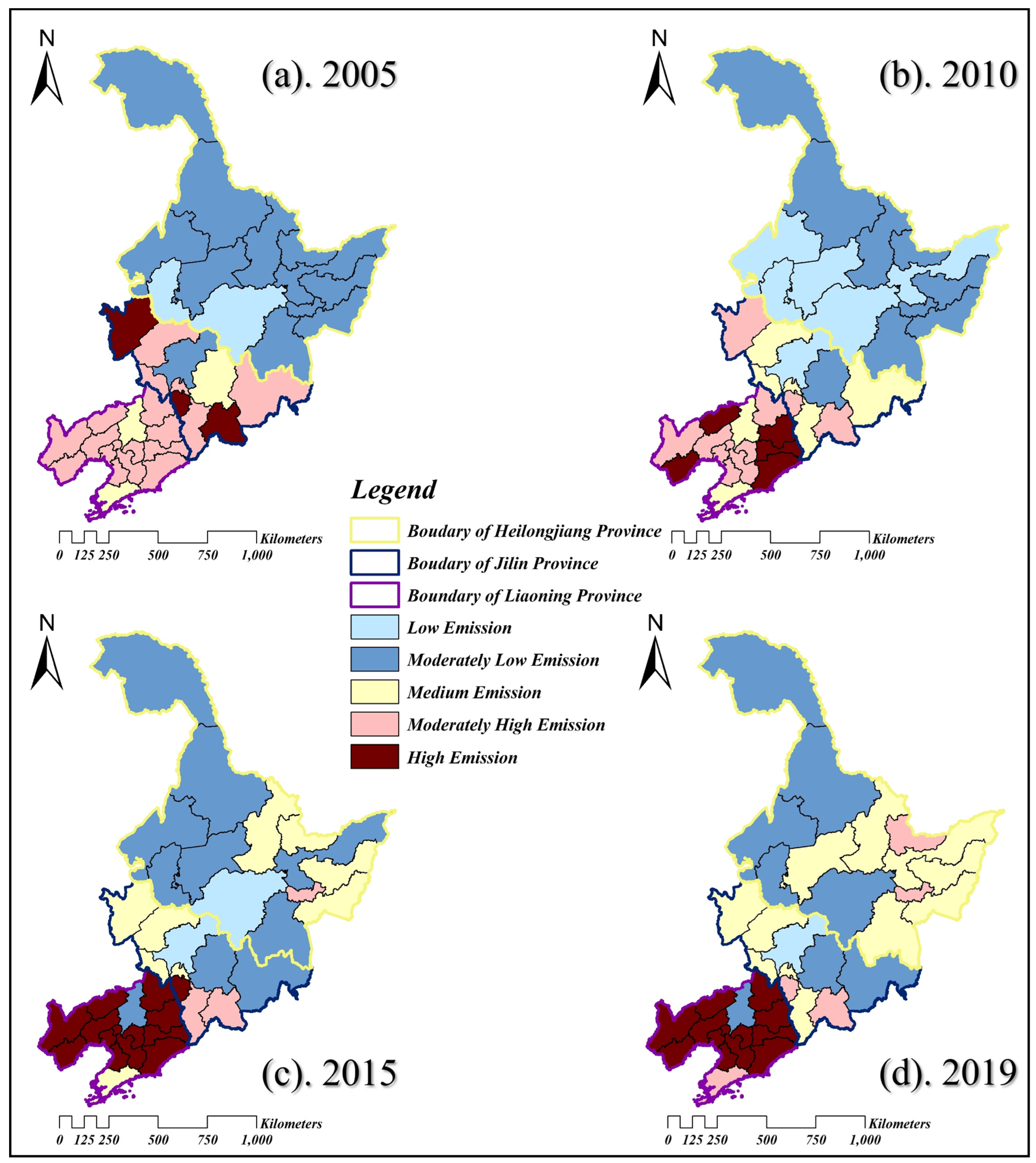
3.1.2. Spatial Patterns of Energy Carbon Emissions in 36 Cities in Northeast China
3.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Energy Carbon Emissions at the City Scale in Northeast China
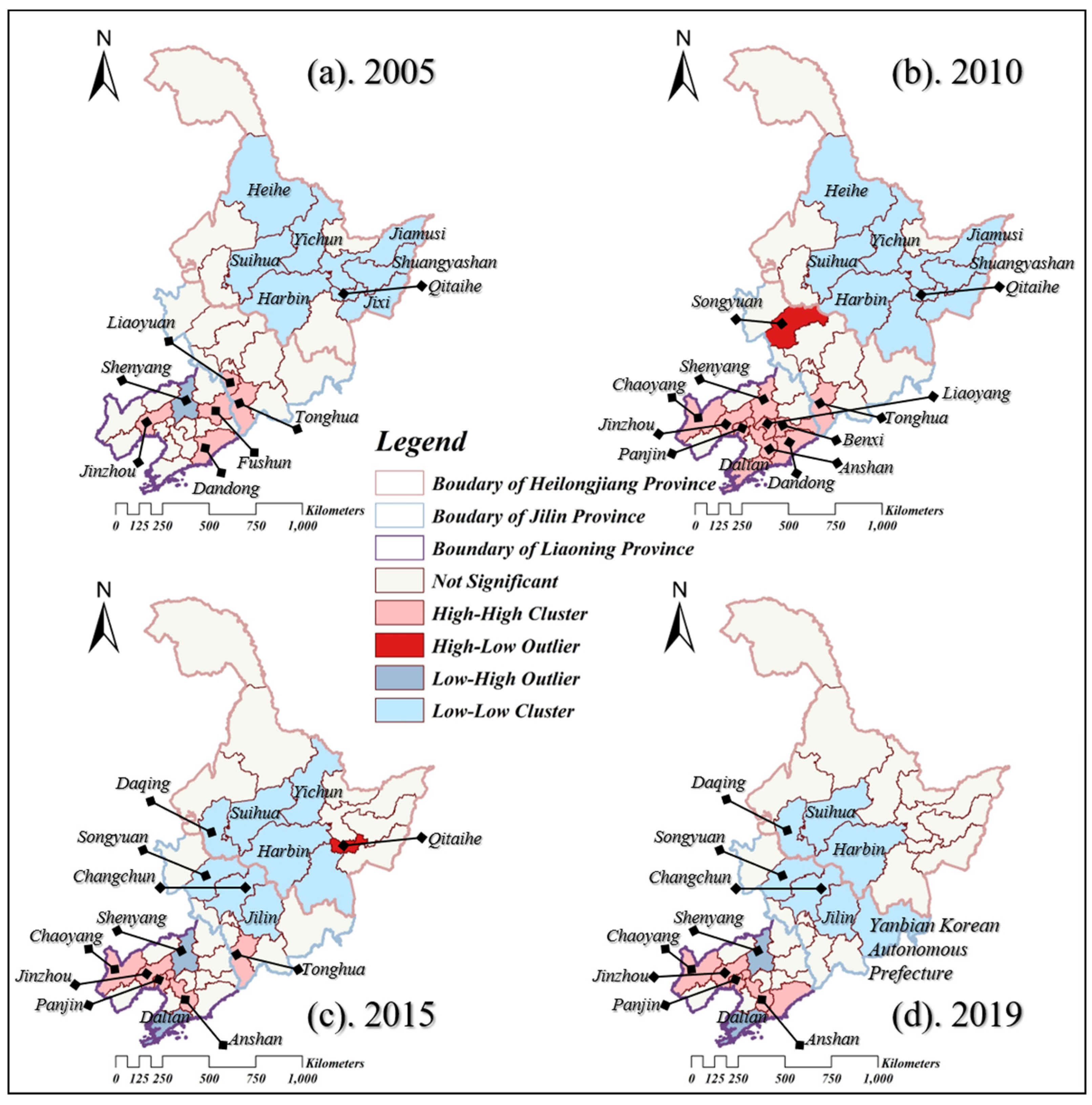
3.2.1. Spatial Autocorrelation of Energy Carbon Emissions at the City Scale
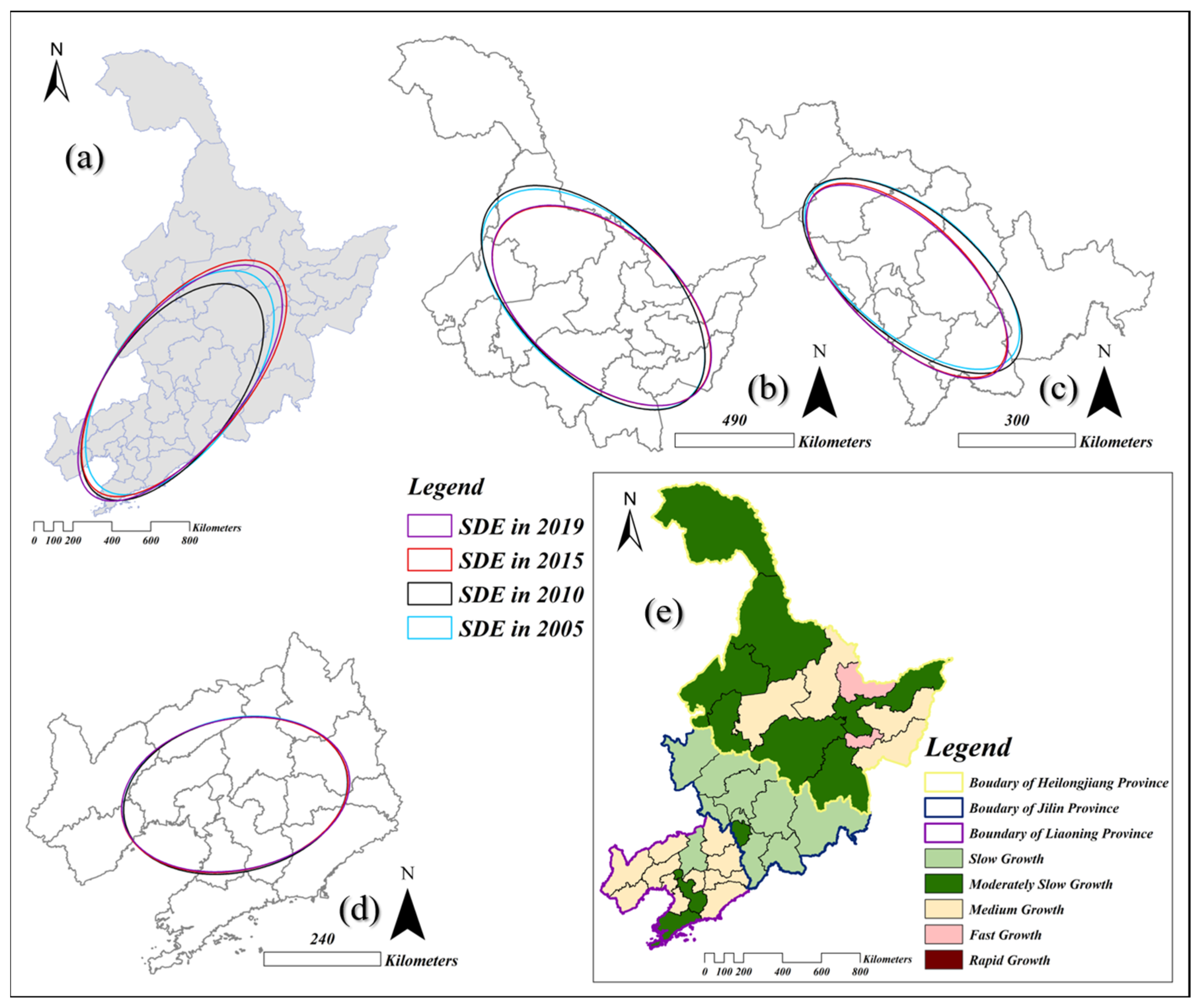
3.2.2. Spatial Dynamic Changes of Energy Carbon Emissions
3.3. Economic Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy Carbon Emissions at the City Scale in Northeast China
3.3.1. Data Preprocessing of GDP
3.3.2. Results of Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy Carbon Emissions
- (1)
- Tapio Decoupling Analysis of 36 Cities in Northeast China, grouped by years from 2005 to 2007.
- (2)
- Tapio Decoupling Analysis of 36 Cities in Northeast China, grouped by years from 2008 to 2010.
- (3)
- Tapio Decoupling Analysis of 36 Cities in Northeast China, grouped by years from 2011 to 2013
- (4)
- Tapio Decoupling Analysis of 36 Cities in Northeast China, grouped by years from 2014 to 2016
- (5)
- Tapio Decoupling Analysis of 36 Cities in Northeast China, grouped by years from 2017 to 2019
4. Discussion
4.1. Result Analysis and Interpretation
4.1.1. Spatial Patterns of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions
4.1.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions: Spatial Autocorrelation of Emissions and Shifts in Emission Centers
4.1.3. Tapio Decoupling of Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions
4.2. Policy Recommendations
4.2.1. Recommendations from the Perspective of Government
4.2.2. Recommendations from the Perspective of Industry
4.2.3. Recommendations from the Perspective of Residents
5. Conclusions
5.1. Conclusion of Spatial Patterns of Energy Carbon Emissions
5.2. Conclusion of Spatiotemporal Evolution of Energy Carbon Emissions
5.3. Conclusion of the Tapio Decoupling Relationship
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, X.; Wei, H.; Lu, S.; Dai, Q.; Su, H. Assessment on the urbanization strategy in China: Achievements, challenges and reflections. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yan, F. Revealing Characteristics of the Spatial Structure of Megacities at Multiple Scales with Jobs-Housing Big Data: A Case Study of Tianjin, China. Land 2021, 10, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Tao, S.; Chen, Y.; Ciais, P.; Güneralp, B.; Ru, M.; Zhong, Q.; Yun, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, T.; et al. Urbanization-induced population migration has reduced ambient PM2.5 concentrations in China. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.T.J.; Munshi-South, J. Evolution of life in urban environments. Science 2017, 358, eaam8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, Q. Decomposition analysis of PM2.5 emissions based on LMDI and Tapio decoupling model: Study of Hunan and Guangdong. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43443–43458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Nie, R. The environmental Kuznets curve for PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China: A spatial panel data approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, Y.; Wang, R. Editorial: Special Issue on Geographical Analysis and Modeling of Urban Heat Island Formation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Frame, D.J.; Huntingford, C.; Jones, C.D.; Lowe, J.A.; Meinshausen, M.; Meinshausen, N. Warming caused by cumulative carbon emissions towards the trillionth tonne. Nature 2009, 458, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F. Carbon emission accounting and spatial distribution of industrial entities in Beijing—Combining nighttime light data and urban functional areas. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and energy consumption in China using ARDL (autoregressive distributed lag) and FDM (factor decomposition model). Energy 2009, 34, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gui, S.; Zhang, W. Decoupling Analysis of China’s Product Sector Output and Its Embodied Carbon Emissions—An Empirical Study Based on Non-Competitive I-O and Tapio Decoupling Model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, N.; Chen, Y. Decoupling Analysis of Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions from the Perspective of City Scale. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 295, 052010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, W. Decoupling between Economic Development and Carbon Emissions and Its Driving Factors: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, K.; Liu, J. Decoupling relationship between carbon emissions and economic development and prediction of carbon emissions in Henan Province: Based on Tapio method and STIRPAT model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52679–52691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F. Coupling coordination development of energy-economy-carbon emissions in China under the background of ‘double carbon’. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. The Impact of the Digital Economy on Regional Carbon Emissions: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Sun, J.; Yao, M. Carbon Emission Inversion Model from Provincial to Municipal Scale Based on Nighttime Light Remote Sensing and Improved STIRPAT. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Sun, W. Analysis of the Decoupling Relationship between China’s Economy and the Indicators of the Power Industry from National and Provincial Aspects. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 4183–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Fujita, T.; Chiu, A.; Dai, H.; Hao, H. Responding to the Paris Climate Agreement: Global climate change mitigation efforts. Front. Energy 2018, 12, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleussner, C.-F.; Ganti, G.; Rogelj, J.; Gidden, M.J. An emission pathway classification reflecting the Paris Agreement climate objectives. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyper, J.; Schroeder, H.; Linnér, B.-O. The Evolution of the UNFCCC. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2018, 43, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Allan, A.; Cui, J. The impact of polycentric urban development on commuting behaviour in urban China: Evidence from four sub-centres of Beijing. Habitat Int. 2015, 50, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing urban forms and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Guan, X.; Pang, B.; Urbanisation, H.M. Energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A panel data analysis of China’s provinces. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, W.; He, C.; Yu, B.; Li, X.; Elvidge, C.D.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C. Applications of Satellite Remote Sensing of Nighttime Light Observations: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, L. Estimating spatiotemporal dynamics of county-level fossil fuel consumption based on integrated nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, C. Spatiotemporal variations of urban CO2 emissions in China—A multiscale perspective. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X. China’s city-level energy-related CO2 emissions: Spatiotemporal patterns and driving forces. Appl. Energy 2017, 200, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China׳s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ziskin, D.; Tuttle, B.T. Creating a Global Grid of Distributed Fossil Fuel CO2 Emissions from Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Energies 2010, 3, 1895–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Ji, G.; Wang, Z. Residential carbon dioxide emissions at the urban scale for county-level cities in China: A comparative study of nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Shen, L.; Zhong, S. Spatio-temporal pattern of carbon emissions based on nightlight data of Shanxi-Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia region of China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunyan, L.; Qing, S.; Jian, D. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Derived from Integrated DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 447–454. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ma, Z.; Mi, Z.; Kelsey, J.; Zheng, J.; Yin, W.; Yan, M. Spatio-temporal simulation of energy consumption in China’s provinces based on satellite night-time light data. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, S.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. Carbon Emission Intensity Characteristics and Spatial Spillover Effects in Counties in Northeast China: Based on a Spatial Econometric Model. Land 2022, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Revitalizing old industrial base of Northeast China: Process, policy and challenge. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Shumei, L.; Shuting, X. Multiscale Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emissions in Northeast China Based on DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiangli, W.; Yuanhe, C.; Jia, Z.; Dasha, F.; Chang, Z. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of carbon emissions from energy consumption and its driving mechanism in Northeast China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 4554–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Duan, Z.; Shan, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.; Song, J.; Wang, X. Low-carbon developments in Northeast China: Evidence from cities. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Duan, Z.; Shan, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.; Song, J.; Wang, X. Multiscale Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emission of Energy Consumption in Yellow River Basin Based on the Nighttime Light Datasets. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, P.; Huang, W. Research on Spatial and Temporal Pattern Evolution and Driving Factors of County Carbon Emissions in Underdeveloped Regions: Gansu Province of Western China as an Example. Sustainability 2022, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, Q. The Uncertainty of Nighttime Light Data in Estimating Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China: A Comparison between DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wu, Y.; Schlink, U.; Singh, R.P. Spatiotemporal Variations of City-Level Carbon Emissions in China during 2000–2017 Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Ali, S.H.; Ma, R.; Cheng, J. Can Nighttime Light Data Be Used to Estimate Electric Power Consumption? New Evidence from Causal-Effect Inference. Energies 2019, 12, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, R. The Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Regional Development in Shandong Province of China from 2012 to 2021 Based on Nighttime Light Remote Sensing. Sensors 2023, 23, 8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Mao, X.; Feng, L.; Zhang, M.; Gui, X.; Wu, X. Investigating the Direct and Spillover Effects of Urbanization on Energy-Related Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Xia, X. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Spatial Heterogeneity of Influencing Factors of SO2 Emissions in Chinese Cities: Fresh Evidence from MGWR. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, H.; Yuan, W.; Xia, X. The Spatial Pattern of the Prefecture-Level Carbon Emissions and Its Spatial Mismatch in China with the Level of Economic Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Decoupling economic development from municipal solid waste generation in China’s cities: Assessment and prediction based on Tapio method and EKC models. Waste Manag. 2021, 133, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Su, B.; Yang, X. Using a new two-dimensional decoupling model to evaluate the decoupling state of global energy footprint. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Energy Type | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row Coal | Coke | Crude Oil | Gasoline | Kerosene | Diesel | Fuel Oil | Natural Gas | |
| Standard Coal Conversion Factor | 0.7143 | 0.9714 | 1.4286 | 1.4714 | 1.4714 | 1.4571 | 1.4286 | 1.1~1.33 |
| Carbon Emission Factor | 0.7559 | 0.855 | 0.5857 | 0.5538 | 0.5714 | 0.5912 | 0.6185 | 0.4483 |
| Year | Fitting Function | Provincial Scale | City Scale | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 1.027993 * | 0.9998 | 1.032559 * | 0.9937 | |
| 2014 | 0.774832 * | 0.9989 | 0.802069 * | 0.9823 | |
| 2015 | 0.759962 * | 0.9996 | 0.784954 * | 0.9721 | |
| 2016 | 0.768292 * | 0.9994 | 0.791088 * | 0.9670 | |
| 2017 | 0.675622 * | 0.9914 | 0.698667 * | 0.9588 | |
| 2018 | 0.664843 * | 0.9974 | 0.672048 * | 0.9634 | |
| 2019 | 0.614259 * | 0.9890 | 0.631141 * | 0.9670 | |
| Province | Results of Relationship |
|---|---|
| Heilongjiang Province | |
| Jilin Province | |
| Liaoning Province |
| Province | Student’s t-Statistic | p-Value (t-Statistic) | Fisher’s-Statistic | p-Value (F-Statistic) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heilongjiang Province | −1.9608 (a) 1.9658 (b) −1.9022 (c) 1.9078 (d) | 0.0757 (a) * 0.0751 (b) * 0.0836 (c) * 0.0829 (d) * | 15.9967 | 0.000252 ** |
| Jilin Province | 2.0341 (a) −2.3306 (b) 2.5757 (c) −2.2053 (d) | 0.0668 (a) * 0.0398 (b) ** 0.0258 (c) ** 0.0496 (d) ** | 8.83572 | 0.002874 ** |
| Liaoning Province | 2.4333 (a) −2.7063 (b) 3.0193 (c) −3.0469 (d) | 0.0332 (a) ** 0.0204 (b) ** 0.0117 (c) ** 0.0111 (d) ** | 11.9560 | 0.000871 ** |
| Growth Type | Slow Growth | Moderately Slow Growth | Medium Growth | Fast Growth | Rapid Growth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLOPE |
| State | Tapio | Decoupling Index | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decoupling | Strong Decoupling | Economic growth with a decrease in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: −, GDP growth rate: +) | |
| Weak Decoupling | Economic growth with a slower increase in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: +, GDP growth rate: +) | ||
| Recessive Decoupling | Economic decline with a significant decrease in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: −, GDP growth rate: −) | ||
| Negative Decoupling | Strong Negative Decoupling | Economic growth with a decrease in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: +, GDP growth rate: −) | |
| Weak Negative Decoupling | Economic decline with a slower decrease in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: −, GDP growth rate: −) | ||
| Expansive Negative Decoupling | Economic growth with a significant increase in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: +, GDP growth rate: +) | ||
| Coupling | Expansive Coupling | Economic growth with an equivalent increase in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: +, GDP growth rate: +) | |
| Recessive Coupling | Economic decline with an equivalent decrease in carbon emissions (carbon emissions growth rate: −, GDP growth rate: −) |
| Variable | Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2019 | |
| Global Moran’s I | 0.62838 | 0.72879 | 0.48901 | 0.54525 |
| Z-scores | 5.8093 | 6.6866 | 4.6581 | 5.1620 |
| p-values | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Lv, J. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions Using Nighttime Light Data: A Quantitative Case Study at the City Scale in Northeast China. Energies 2024, 17, 4795. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194795
Liu B, Lv J. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions Using Nighttime Light Data: A Quantitative Case Study at the City Scale in Northeast China. Energies. 2024; 17(19):4795. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194795
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bin, and Jiehua Lv. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions Using Nighttime Light Data: A Quantitative Case Study at the City Scale in Northeast China" Energies 17, no. 19: 4795. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194795
APA StyleLiu, B., & Lv, J. (2024). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Tapio Decoupling Analysis of Energy-Related Carbon Emissions Using Nighttime Light Data: A Quantitative Case Study at the City Scale in Northeast China. Energies, 17(19), 4795. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194795





