Effects of Water Absorption on the Insulating Properties of Polypropylene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Water Immersion Test
2.3. Water Absorption Rate Measurement
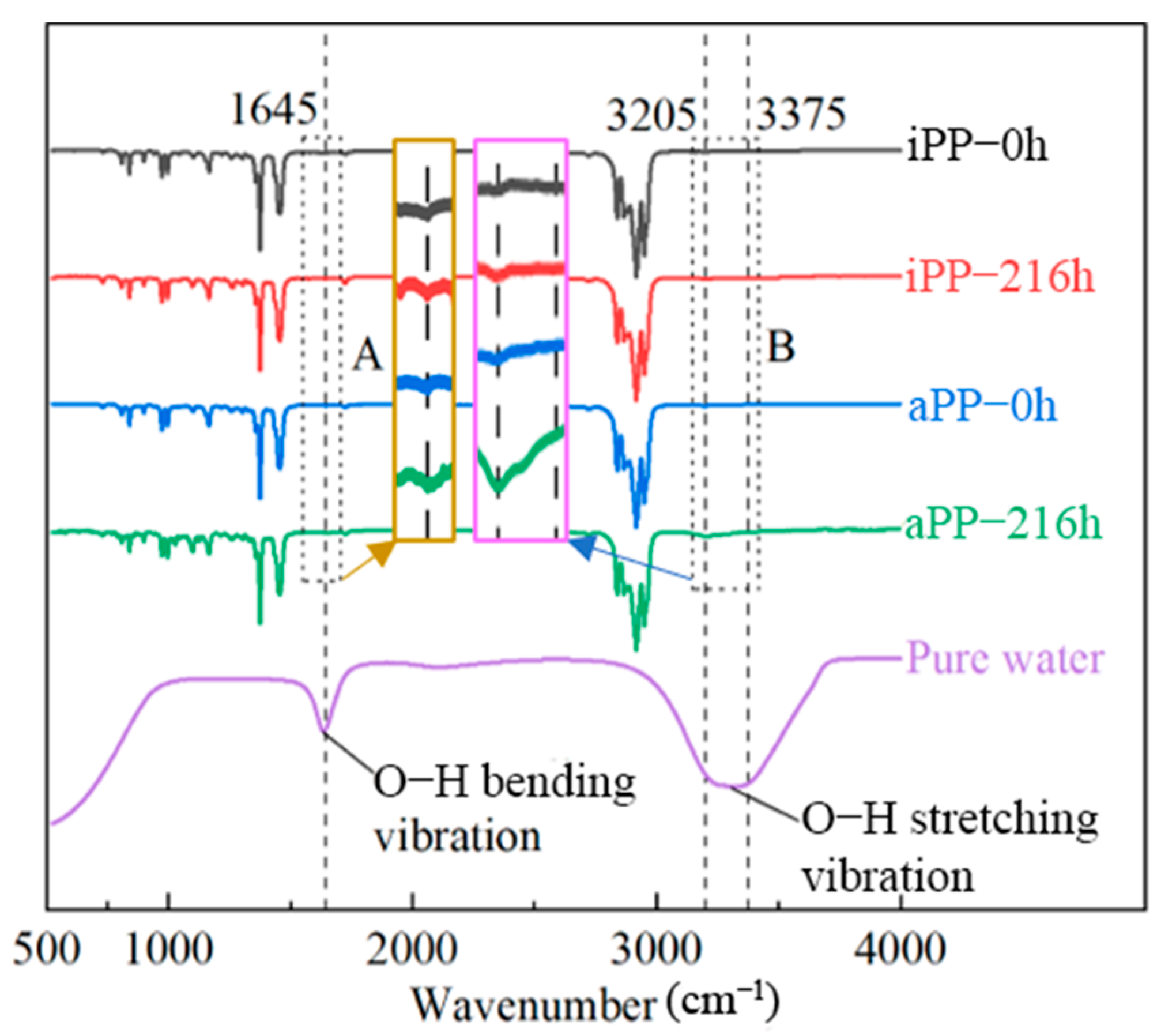
2.4. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis
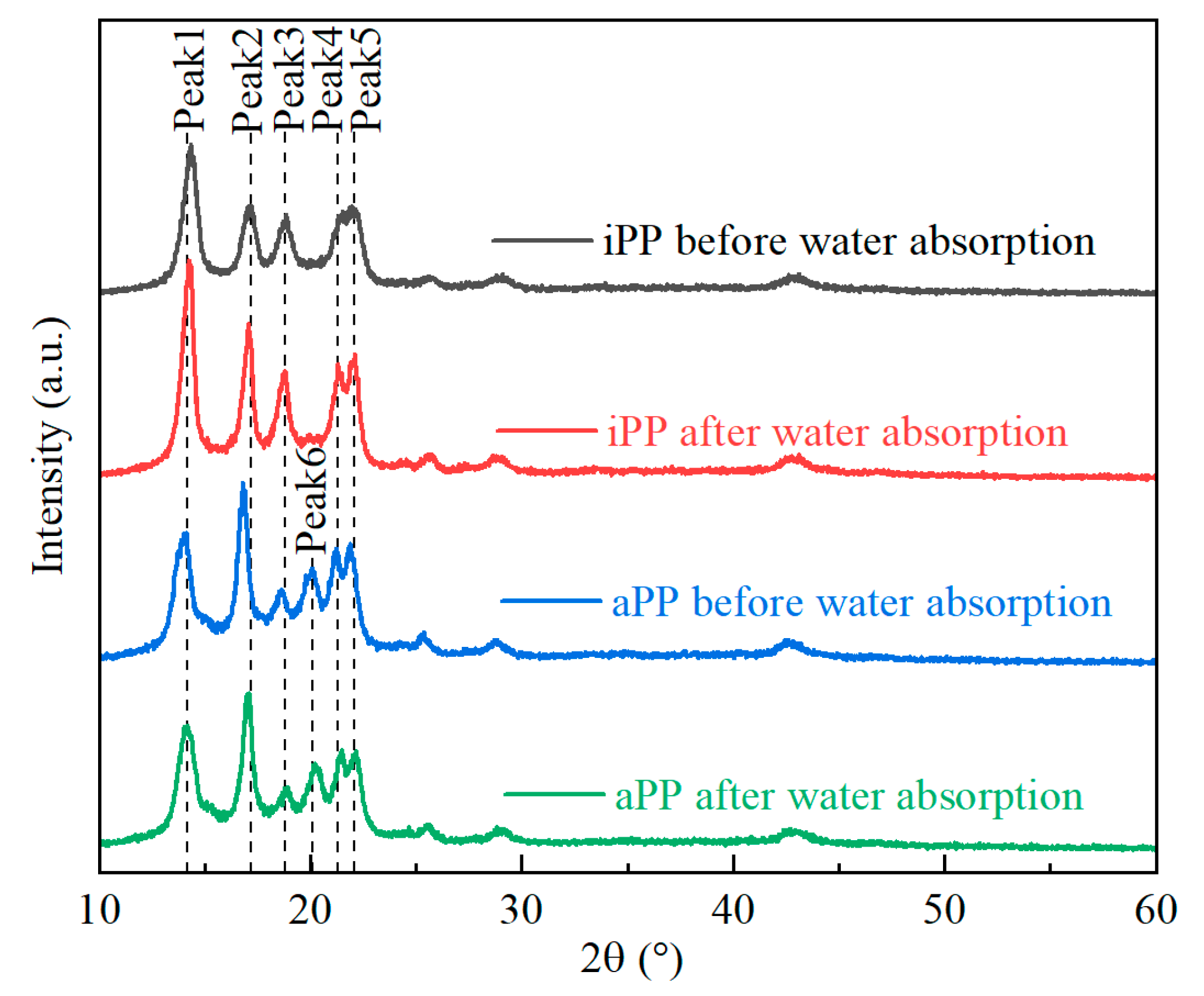
2.5. XRD Analysis
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimerty (DSC) Analysis
2.7. Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectrum (PALS) Analysis
2.8. Volume Resistivity Measurement
2.9. Relative Permittivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Structure Differences between iPP and aPP
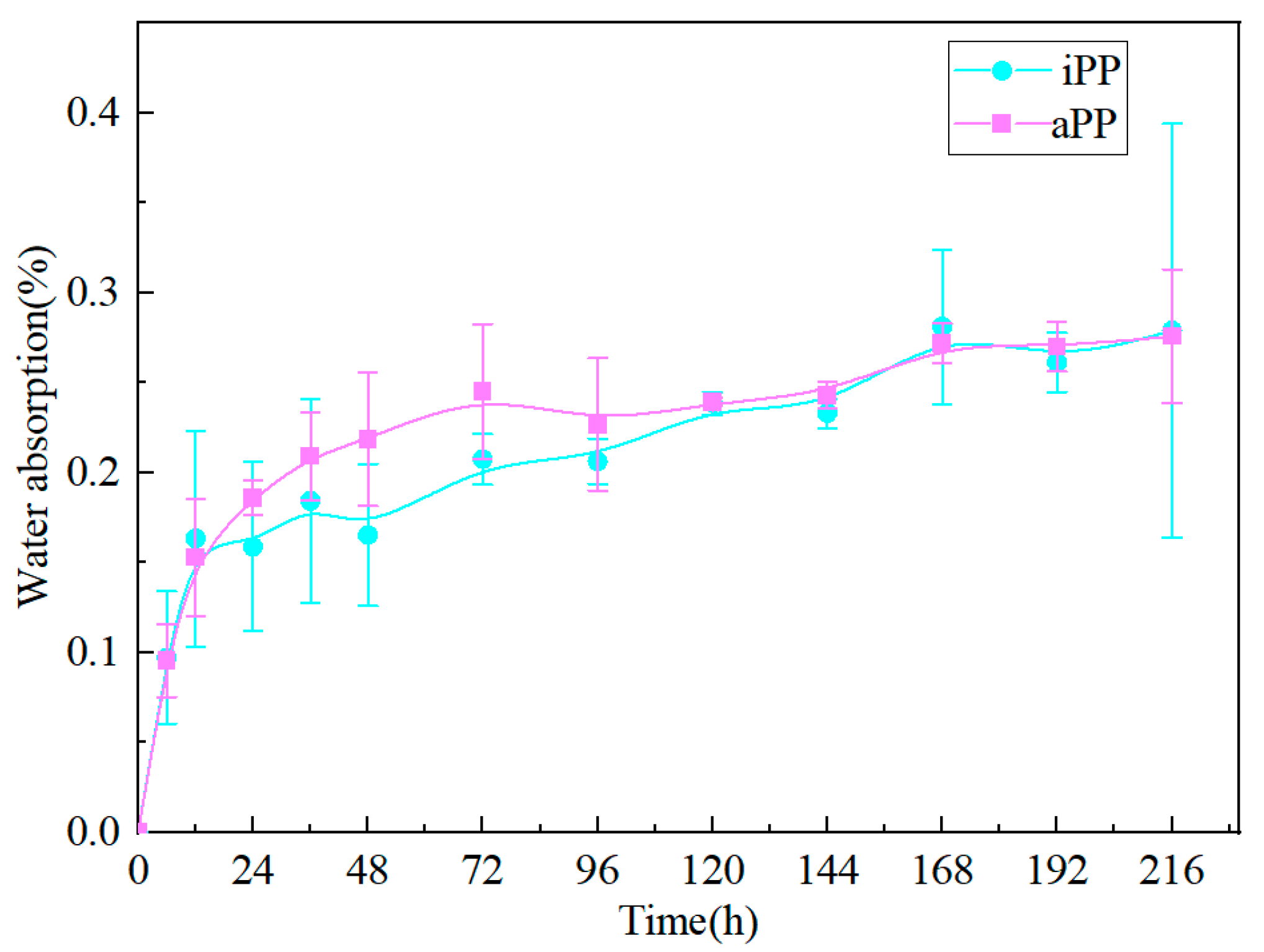
3.2. Variation of Water Absorpiton with Time for PPs
3.3. Structure Changes before and after Water Absorption of PPs
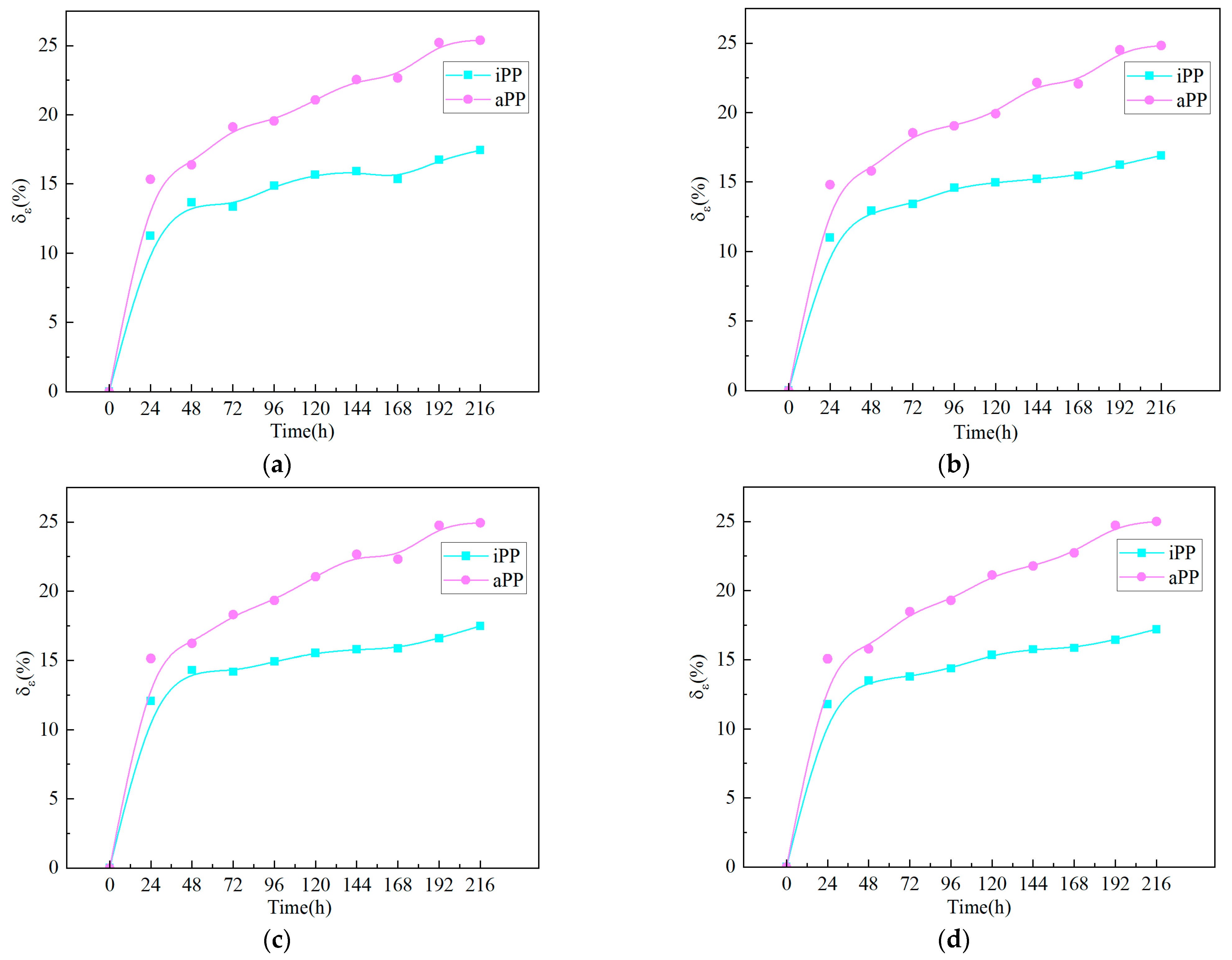
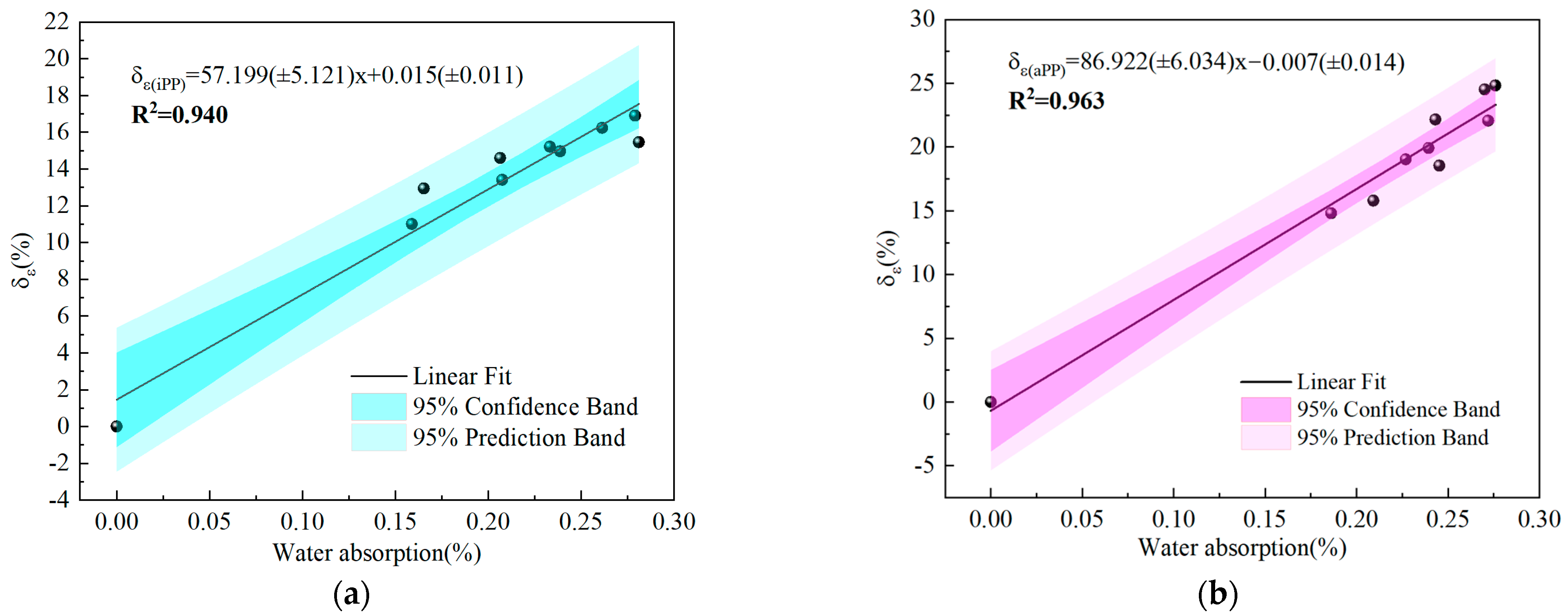
3.4. Variation of Electrical Properties with Water Immersion Time for PPs
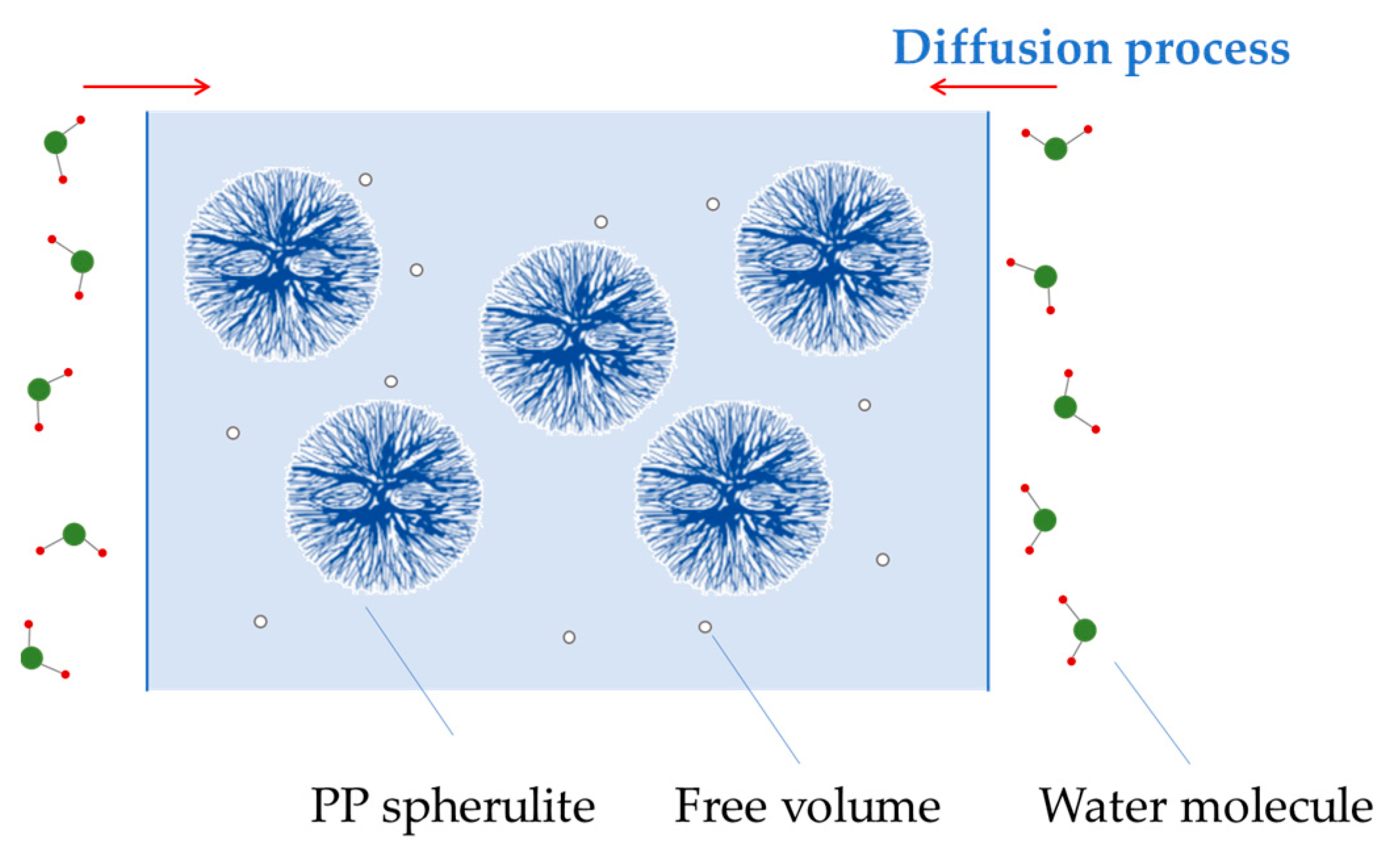
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The water absorption rates of both iPP and aPP increase with extended water immersion, eventually reaching a saturation level of approximately 0.28% after around 216 h. Although the crystal form of PPs remains unchanged in a water environment, water intrusion causes the interplanar spacing of iPP to increase, while the interplanar spacing of aPP decreases slightly.
- (2)
- The volume resistivity of both PPs decreases as the water absorption rate increases, with iPP showing greater sensitivity to water intrusion. The increase in the water absorption rate leads to an increase in the relative permittivity of PP materials. In response to the saturated water absorption, the relative permittivity of iPP increased by approximately 17%, whereas that of aPP rose by about 25%, indicating that the relative permittivity of aPP is more affected by water.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Khalidi, H.; Kalam, A. The impact of underground cables on power transmission and distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Power and Energy Conference, Putra Jaya, Malaysia, 28–29 November 2006; pp. 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.M.; Babu, T.S.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Kasinathan, P.; Solanki, S.G.; Raveendran, S.K. Empowering smart grid: A comprehensive review of energy storage technology and application with renewable energy integration. J. Energy Storage 2004, 39, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi-Fayegh, S.; Rosen, M.A. A review of energy storage types, applications and recent developments. J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Chen, P.X.; Li, H.; Li, J.Y.; Chen, Z.Z. Improved DC performance of crosslinked polyethylene insulation depending on a higher purity. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, M. Influence of insulating material properties on partial discharges at DC voltage. Energies 2020, 13, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.D.; Vaughan, A.S.; Stevens, G.C.; Pye, A.; Sutton, S.J.; Geussens, T.; Fairhurst, M.J. Thermoplastic cable insulation comprising a blend of isotactic polypropylene and a propylene-ethylene copolymer. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.W.; Du, B.X.; Li, Z.L.; Su, J.G.; Jiang, J.P.; Kong, X.X. Electrical tree characteristics in polypropylene under impulse superimposed DC voltage in LN2. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 7701403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.W.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, S.J.; Wu, D.H.; Yan, H.D.; Dang, Z.M. Improvement of space charge suppression of polypropylene for potential application in HVDC cables. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Fan, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.K. Polypropylene based thermoplastic polymers for potential recyclable HVDC cable insulation applications. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Nam, C.; Chung, T.C.M.; Petersson, L.; Hillborg, H. Polypropylene copolymer containing cross-linkable antioxidant moieties with long-term stability under elevated temperature conditions. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7041–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Miyashita, Y.; Demura, T.; Ueda, A.; Yoshino, K. The application of novel polypropylene to the insulation of electric power cable. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2006, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.K.; Tanaka, T. Material progress toward recyclable insulation of power cables. Part 1: Polyethylene based thermoplastic materials: Dedicated to the 80th birthday of professor Toshikatsu Tanaka. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2019, 35, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chi, X.H.; Yan, C.Y.; Xie, D.R.; Liu, X.W.; Wen, Y.N.; Liu, W.F.; Li, S.T. Polypropylene nanocomposite for power equipment: A review. IET Nanodielectrics 2018, 1, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Du, B. Polymeric insulation for high-voltage DC extruded cables: Challenges and development directions. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2018, 34, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Z.; Du, F.; Bi, J.G.; Yuan, S.; Yang, Y. Assessment of creeping discharge initiated by metal particles on the silicone rubber/XLPE interface in cable joints. J. Electr. Eng. 2019, 70, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Song, S.; Yue, Z.; Wei, H.; Ming, H. Study on the electric-field characteristics of water tree region on the dry or wet condition in XLPE cables. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Chengdu, China, 19–22 September 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.F.; Pu, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, B.H.; Zhao, A.X.; Deng, J.B.; Zhang, G.J.; Hui, N.; Fan, M.H. Research on the defect development of cable accessories under AC voltage. In Proceedings of the 2017 1st International Conference on Electrical Materials and Power Equipment (ICEMPE), Xi’an, China, 14–17 May 2017; pp. 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Liang, X.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, X.J.; Wei, Y.H.; Hao, C.C.; Lei, Q.Q.; Li, S.T. Insulation properties and interface defect simulation of distribution network cable accessories under moisture condition. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2022, 29, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Yin, G.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Ouyang, B. The effect of accelerated water tree ageing on the properties of XLPE cable insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Calcara, L.; D’Orazio, L.; Ricci, D.; Derviškadić, A.; He, H. Joints defectiveness of MV underground cable and the effects on the distribution system. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 192, 107004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.K.; Li, Z.; Sheng, G.H.; Jiang, X. Insulating property of polypropylene nanocomposites filled with nano-MgO of different concentration. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.X.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.; He, J. Surface-modification effect of MgO nanoparticles on the electrical properties of polypropylene nanocomposite. High Volt. 2020, 5, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.R.; Min, D.M.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.T.; Nazir, M.T.; Phung, B.T. Classified effects of nanofillers on DC breakdown and partial discharge resistance of polypropylene/alumina nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2019, 26, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60212-2014; Standard Conditions for Use Prior to and During the Testing of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): London, UK, 2014.
- Kouini, B. Water absorption and hygrothermal aging behaviors of polyamide66/maleated polypropylene/nanoclay nanocomposites. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A-Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 57, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Yu, J.; Guo, S.Y. Structure and properties of polypropylene composites filled with magnesium hydroxide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 4943–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, M.; Hu, S.C.; Zhang, Z.B. Mechanical properties and crystallization behavior of polycarbonate/polypropylene blends. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B-Phys. 2012, 52, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Pujari, P.K. Role of free volume characteristics of polymer matrix in bulk physical properties of polymer nanocomposites: A review of positron annihilation lifetime studies. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 75, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kobayashi, S.; AbdurRahim, M.A.; Zhang, M.J.; Khusainova, A.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Abdala, A.A.; Macosko, C.W. Graphene/polyethylene nanocomposites: Effect of polyethylene functionalization and blending methods. Polymer 2011, 52, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Peng, Z.; Gong, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, P.; Kong, L. Mechanism of a green graphene oxide reduction with reusable potassium carbonate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11966–11972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Li, J.X.; Shen, L.G.; Lin, H.J.; Shan, Y.D. The observation of PP/EVA blends in which isotactic PP was preradiated with different radiation absorbed doses. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, P.Y. Two-Dimensional ATR−FTIR spectroscopic investigation on water diffusion in polypropylene film: Water bending vibration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 18, 4424–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluri, S.; Sowinski, P.; Svyntkivska, M.; Bartczak, Z.; Makowski, T.; Piorkowska, E. Structure and mechanical properties of iPP-based nanocomposites crystallized under high pressure. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.; Peng, J.; Sheng, J.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, E.; Jiang, Y. Real-space imaging of interfacial water with submolecular resolution. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Isotacticity/% | Melt Index/(g/10 min) (230 °C/2.16 kg) | Density/(g/cm3) (23 °C) | Tensile Strength /MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iPP | 98% | 3.0 | ~0.91 | 32.8 |
| aPP | \ | 2.5 | ~0.90 | 28.0 |
| Peaks | iPP | aPP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Water Absorption | After Water Absorption | Before Water Absorption | After Water Absorption | |||||
| 2θ/° | d/Å | 2θ/° | d/Å | 2θ/° | d/Å | 2θ/° | d/Å | |
| Peak 1 | 14.3 | 6.20 | 14.2 | 6.25 | 14.0 | 6.34 | 14.2 | 6.25 |
| Peak 2 | 17.2 | 5.16 | 17.1 | 5.19 | 16.8 | 5.29 | 17.1 | 5.19 |
| Peak 3 | 18.9 | 4.70 | 18.8 | 4.73 | 18.6 | 4.78 | 18.9 | 4.70 |
| Peak 4 | 21.4 | 4.16 | 21.3 | 4.18 | 21.2 | 4.20 | 21.5 | 4.14 |
| Peak 5 | 22.1 | 4.03 | 22.1 | 4.03 | 21.9 | 4.07 | 22.2 | 4.01 |
| Peak 6 | / | / | / | / | 20.1 | 4.42 | 20.2 | 4.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, R.; Jiang, Q.; Cao, L.; Li, C.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.; Gui, Y.; Tang, C. Effects of Water Absorption on the Insulating Properties of Polypropylene. Energies 2024, 17, 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184576
Xi R, Jiang Q, Cao L, Li C, He J, Zhang Y, He G, Gui Y, Tang C. Effects of Water Absorption on the Insulating Properties of Polypropylene. Energies. 2024; 17(18):4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184576
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Rui, Qiyang Jiang, Liang Cao, Chuping Li, Jiaxun He, Ya Zhang, Gaohui He, Yingang Gui, and Chao Tang. 2024. "Effects of Water Absorption on the Insulating Properties of Polypropylene" Energies 17, no. 18: 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184576
APA StyleXi, R., Jiang, Q., Cao, L., Li, C., He, J., Zhang, Y., He, G., Gui, Y., & Tang, C. (2024). Effects of Water Absorption on the Insulating Properties of Polypropylene. Energies, 17(18), 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184576








