Design and Calculation of Multi-Physical Field of Ultra-High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor
Abstract
1. Introduction
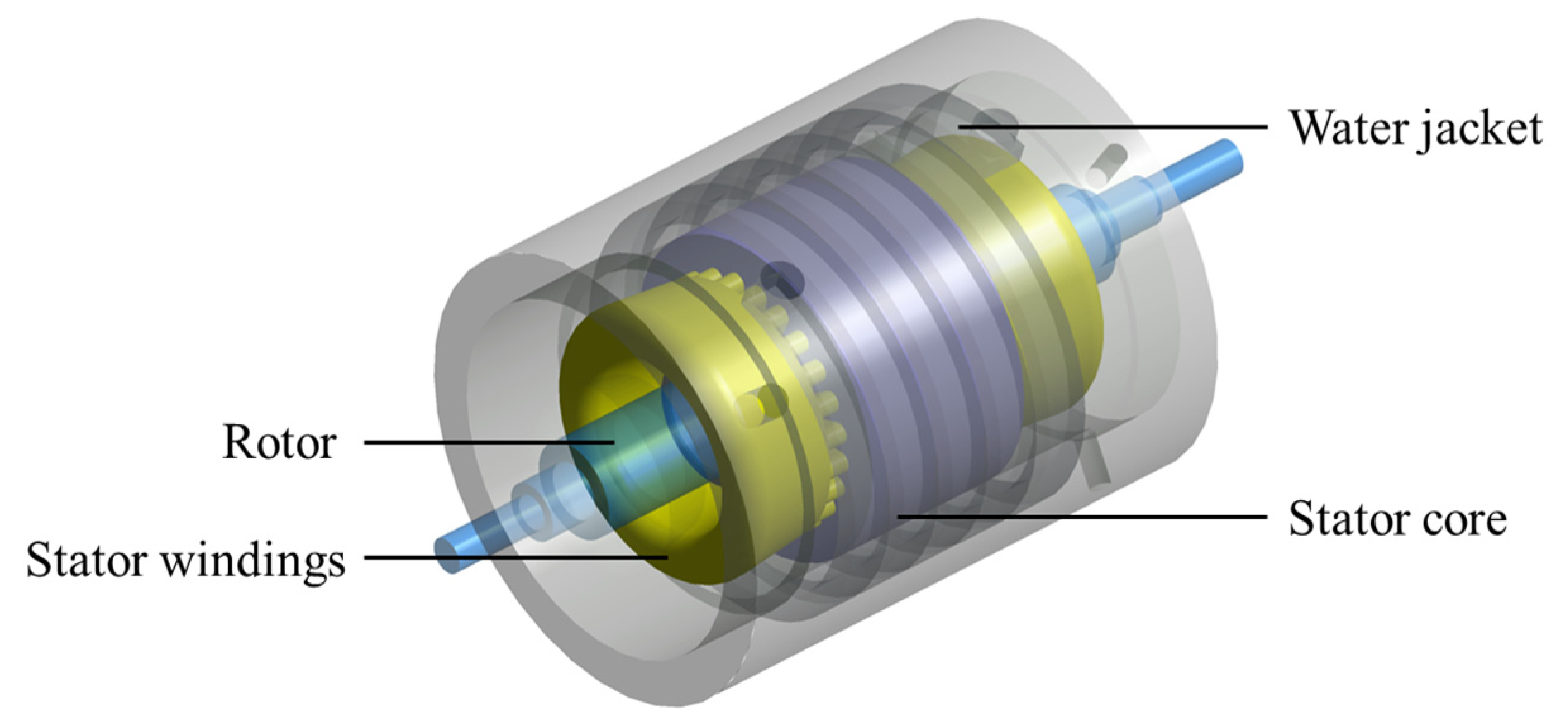
2. UHSPMM Design and Specifications
3. Power Loss Calculation and Thermal Distribution
3.1. Stator Iron Loss
3.2. Copper Loss
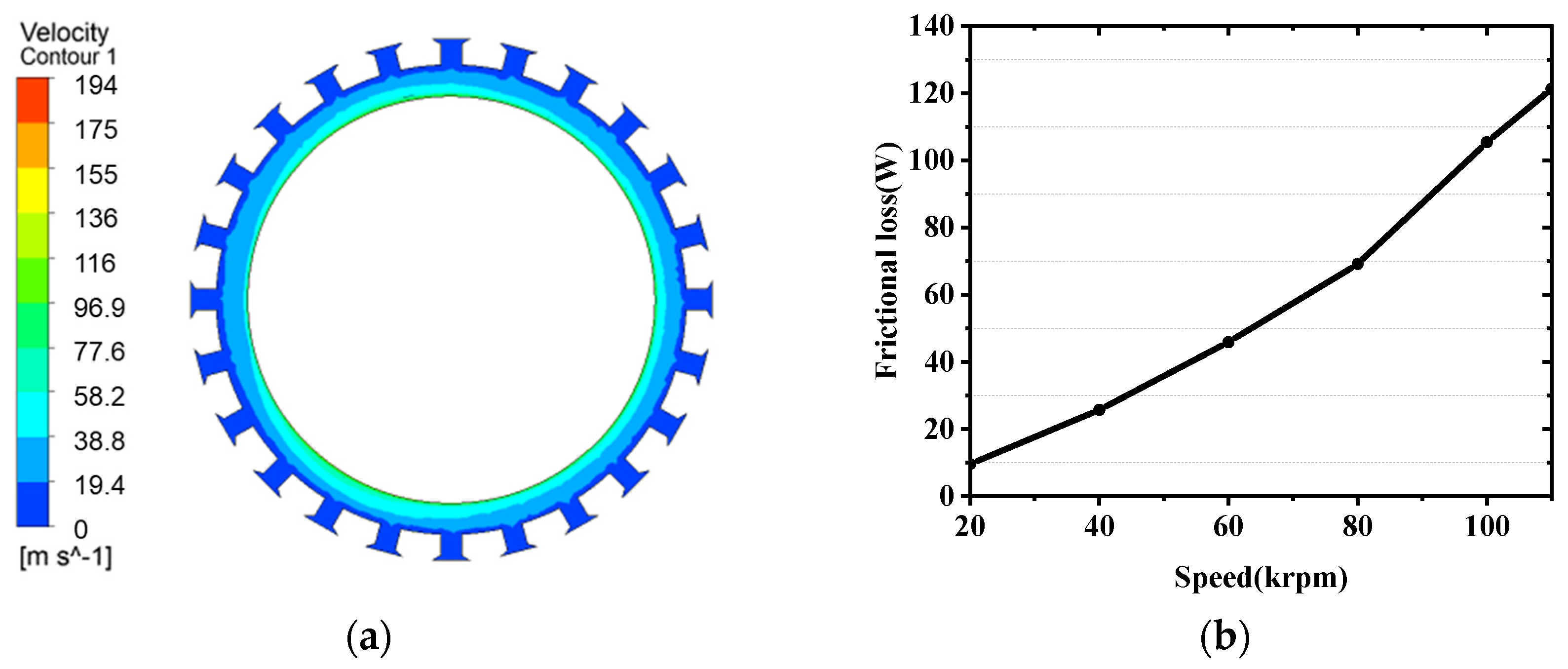
3.3. Frictional Loss
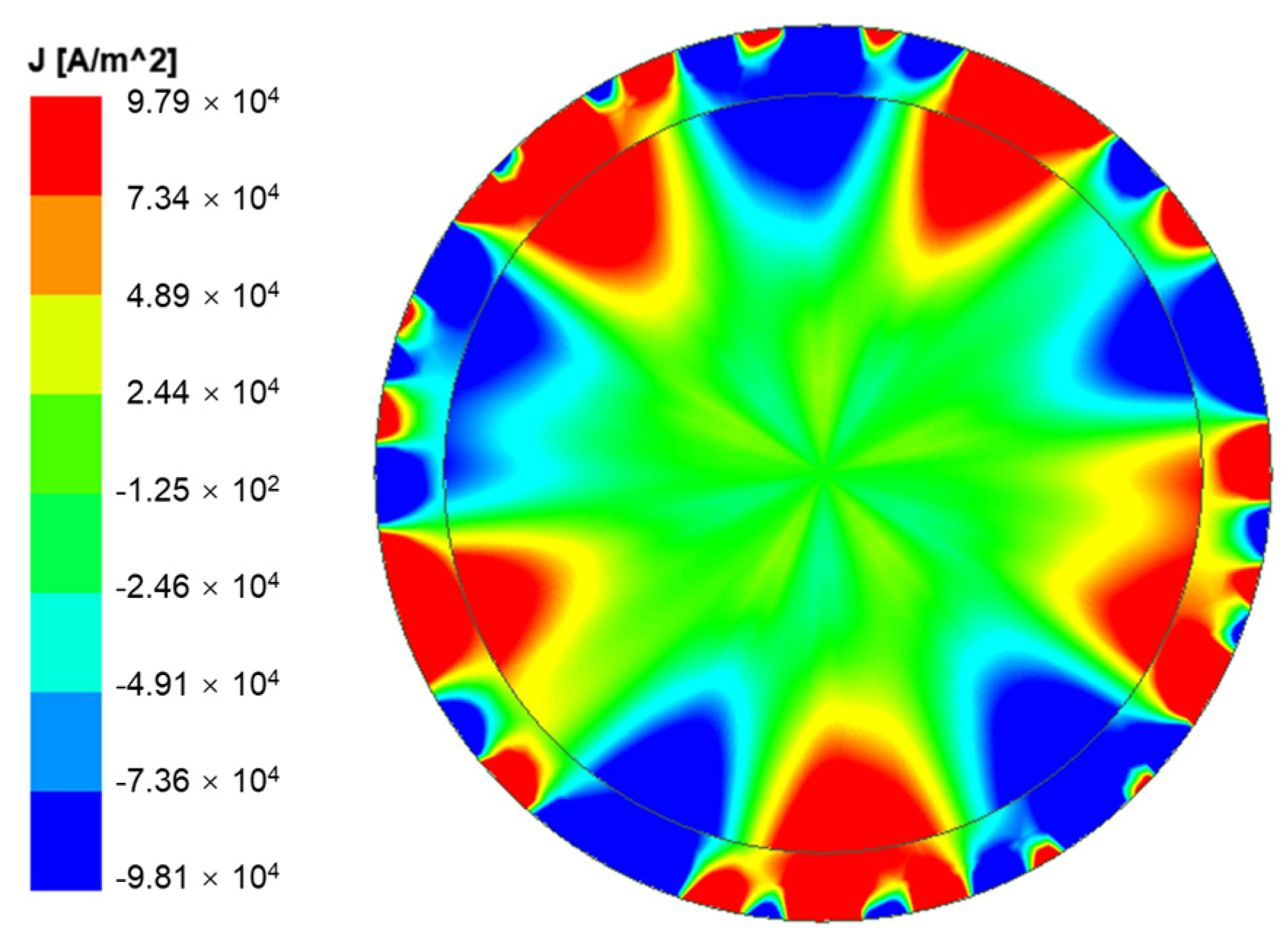
3.4. Rotor Eddy Current Loss
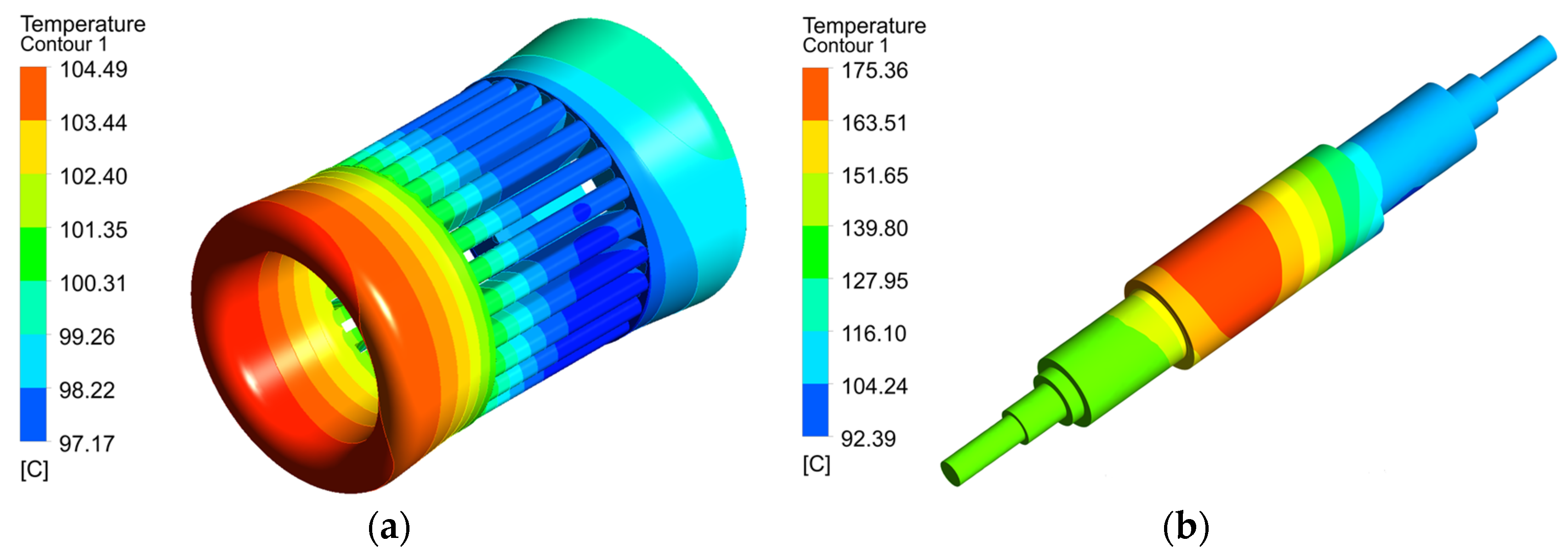
3.5. UHSPMM Temperature Calculation
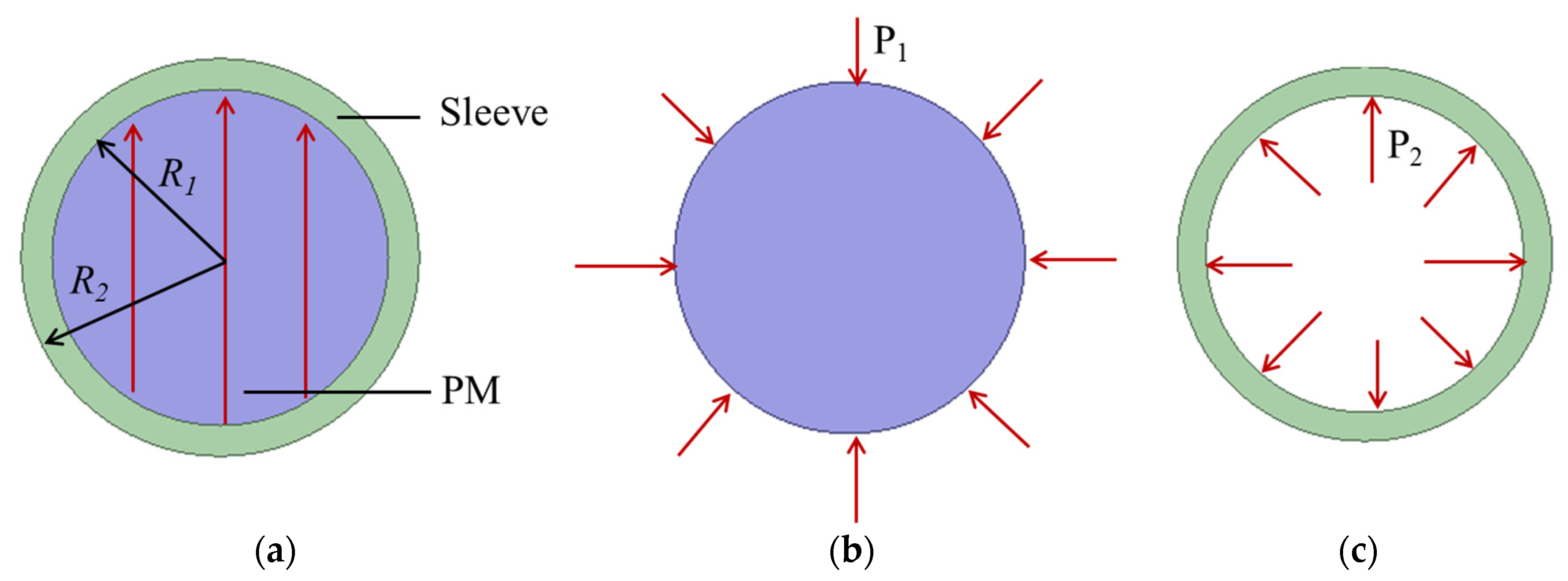
4. UHSPMM Rotor Strength Analysis
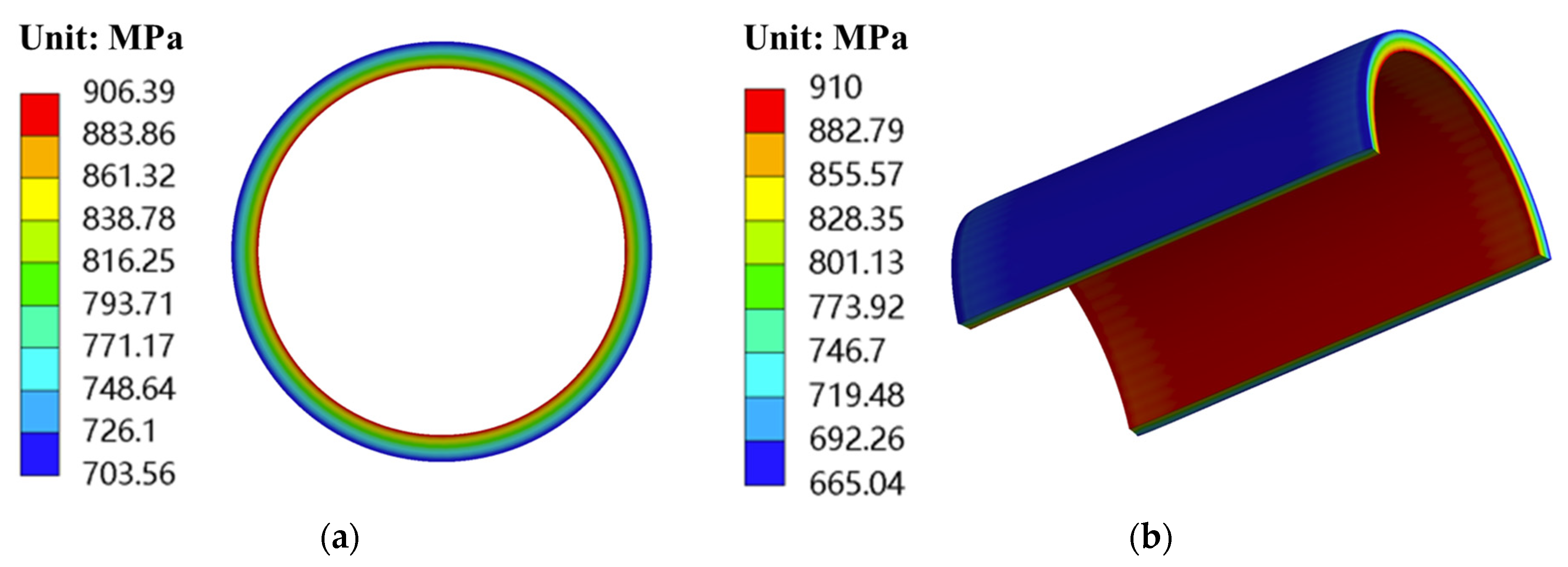
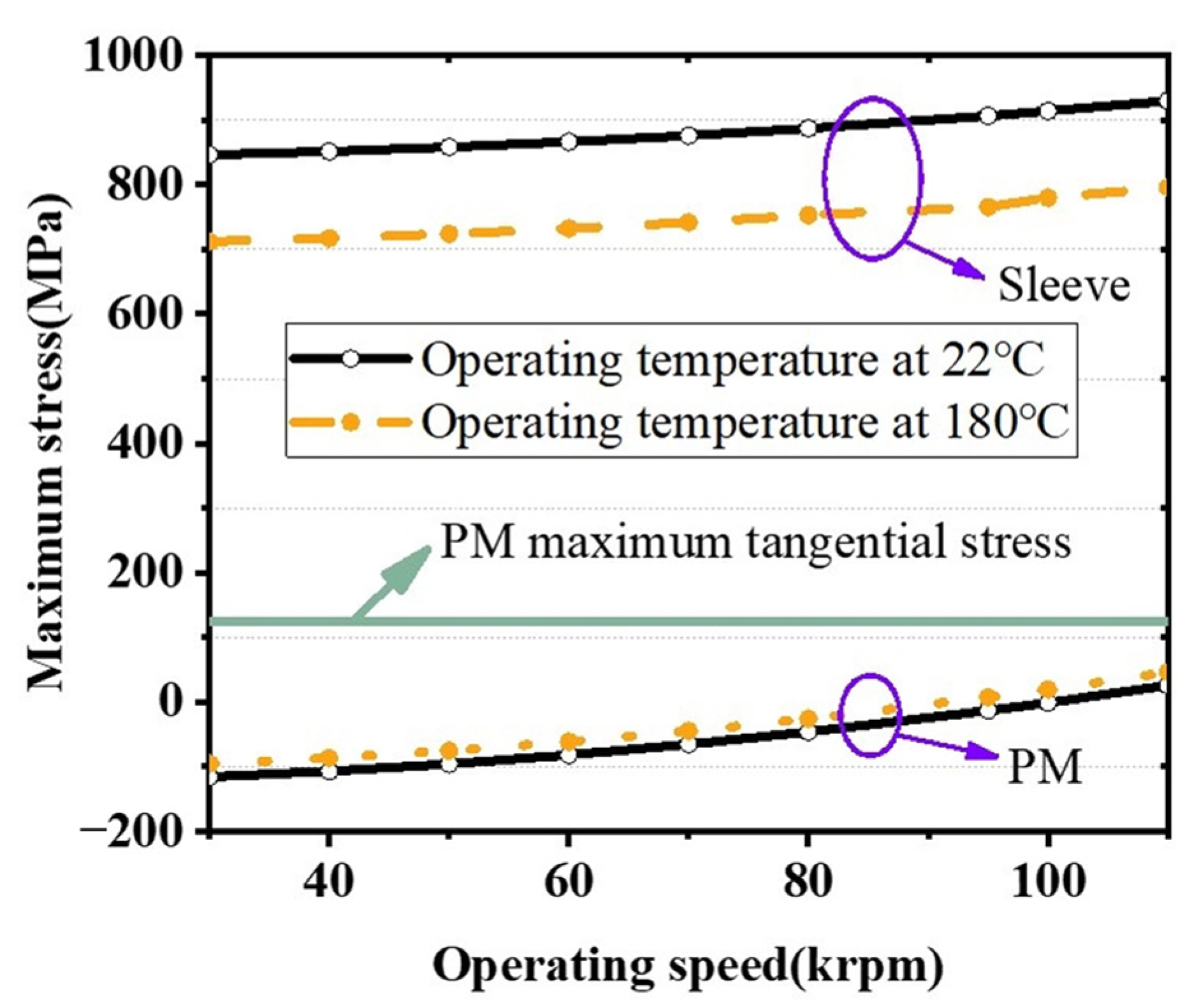
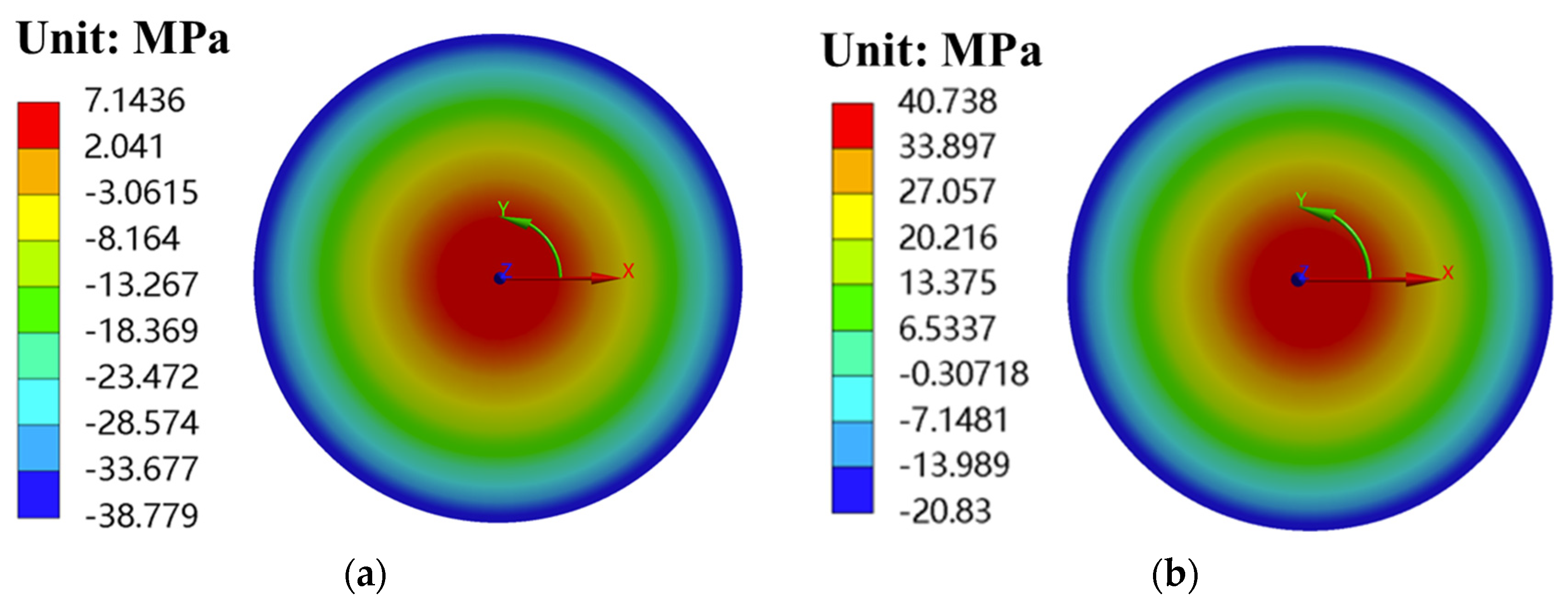
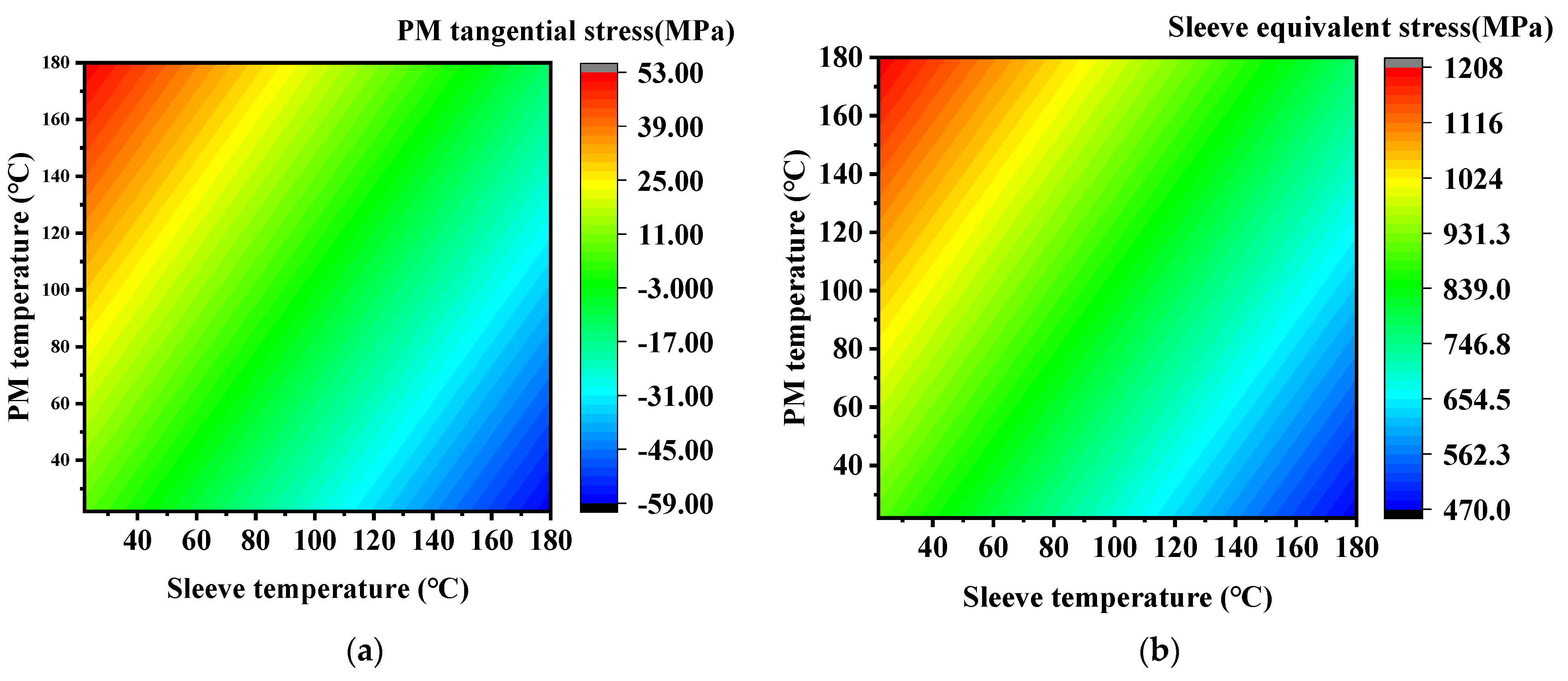
4.1. Rotor Stress with Extreme Speed and Extreme Temperature
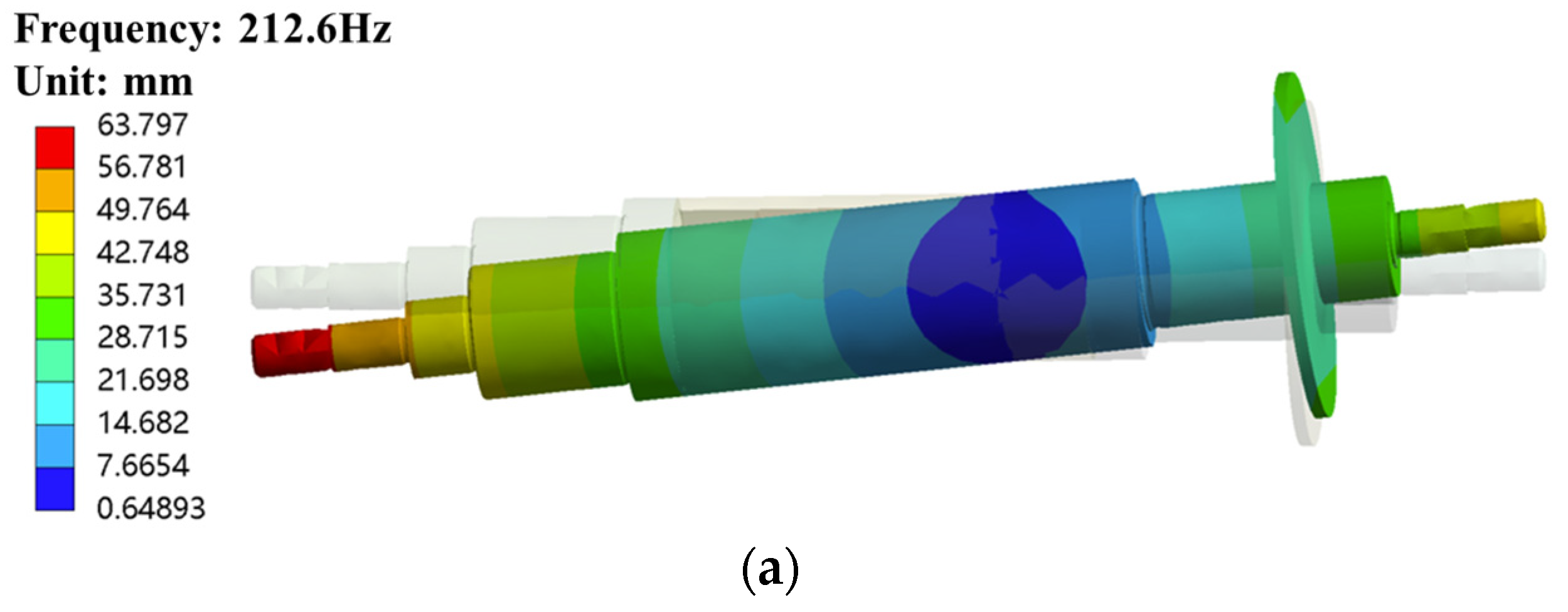
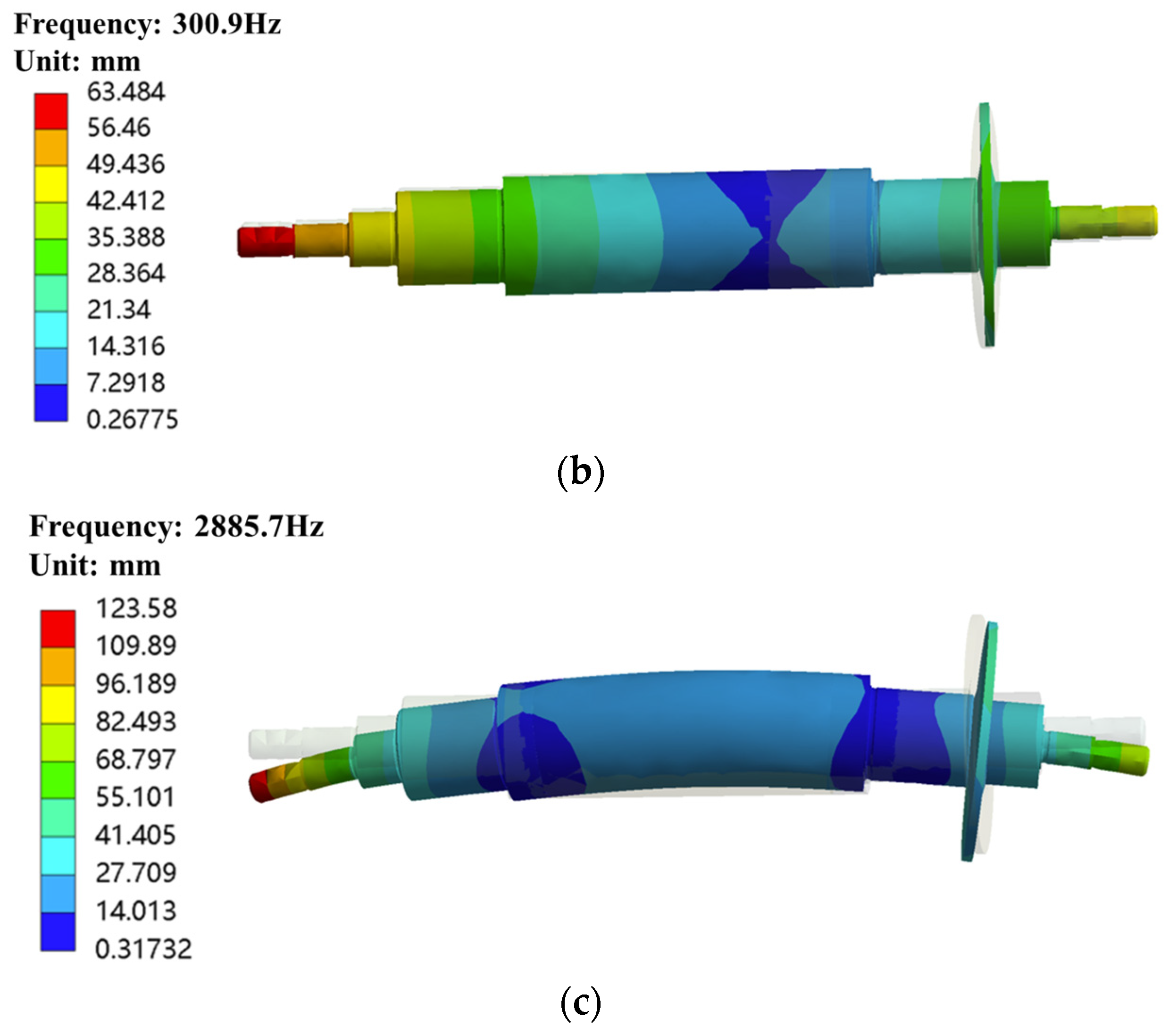
4.2. Rotor Dynamic Analysis with Extreme Temperature
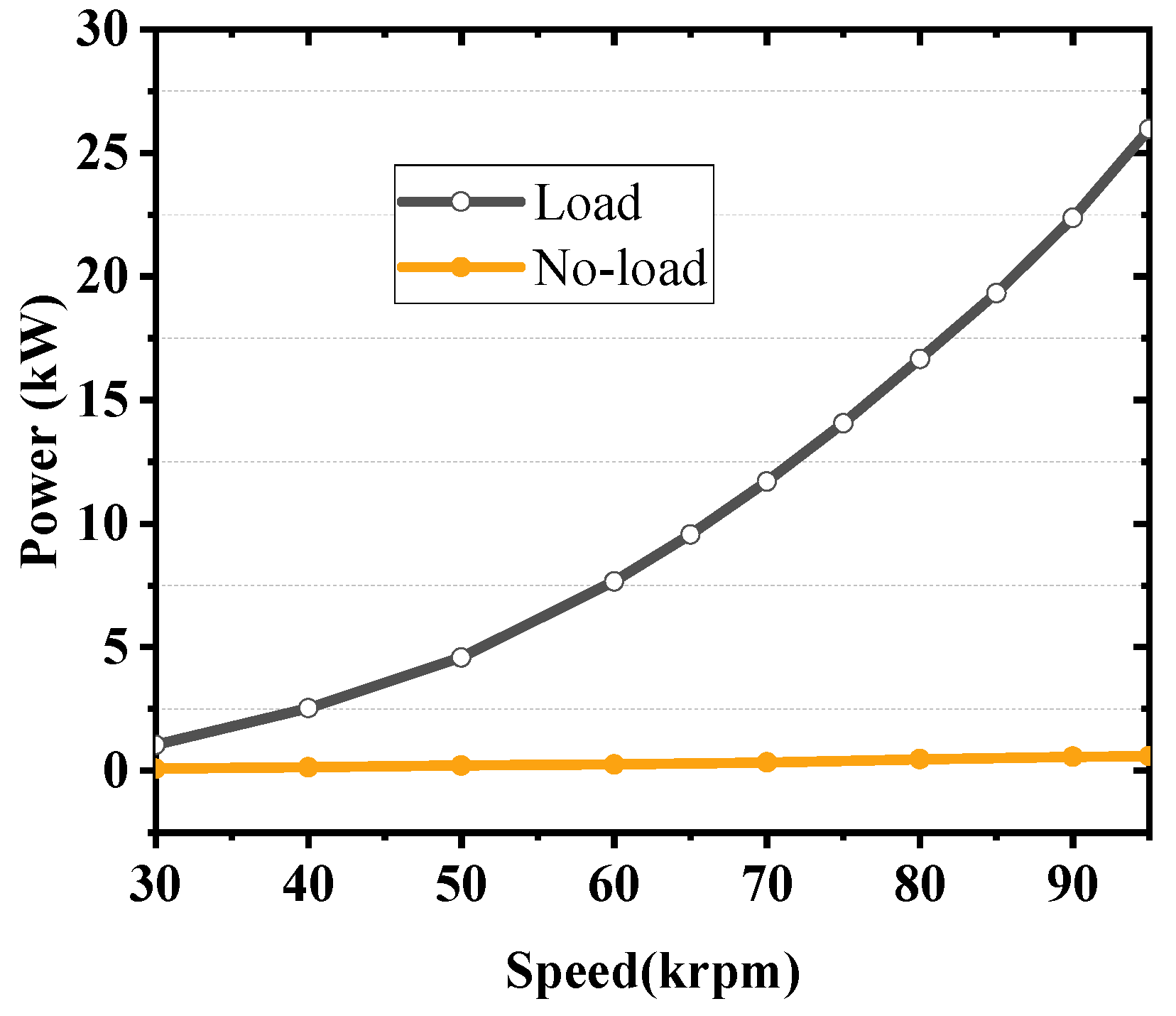
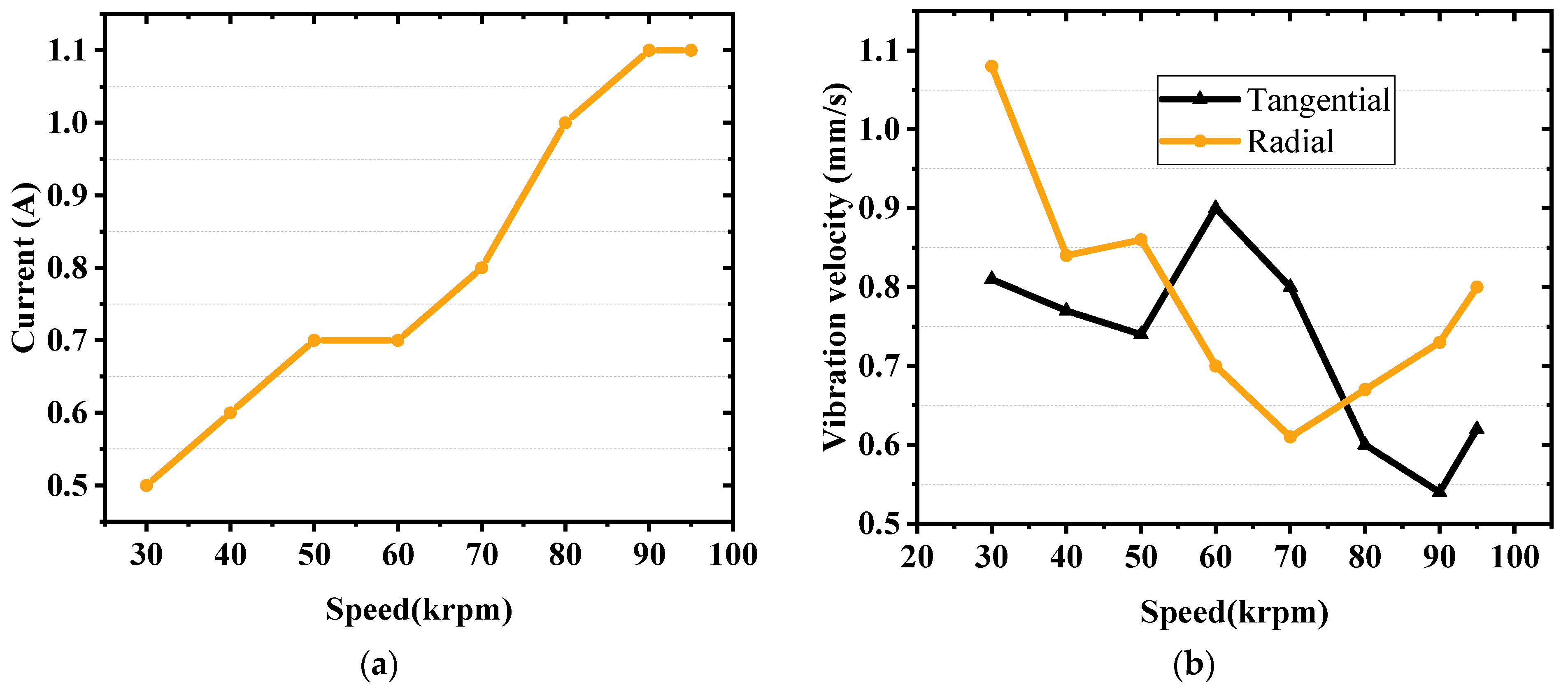
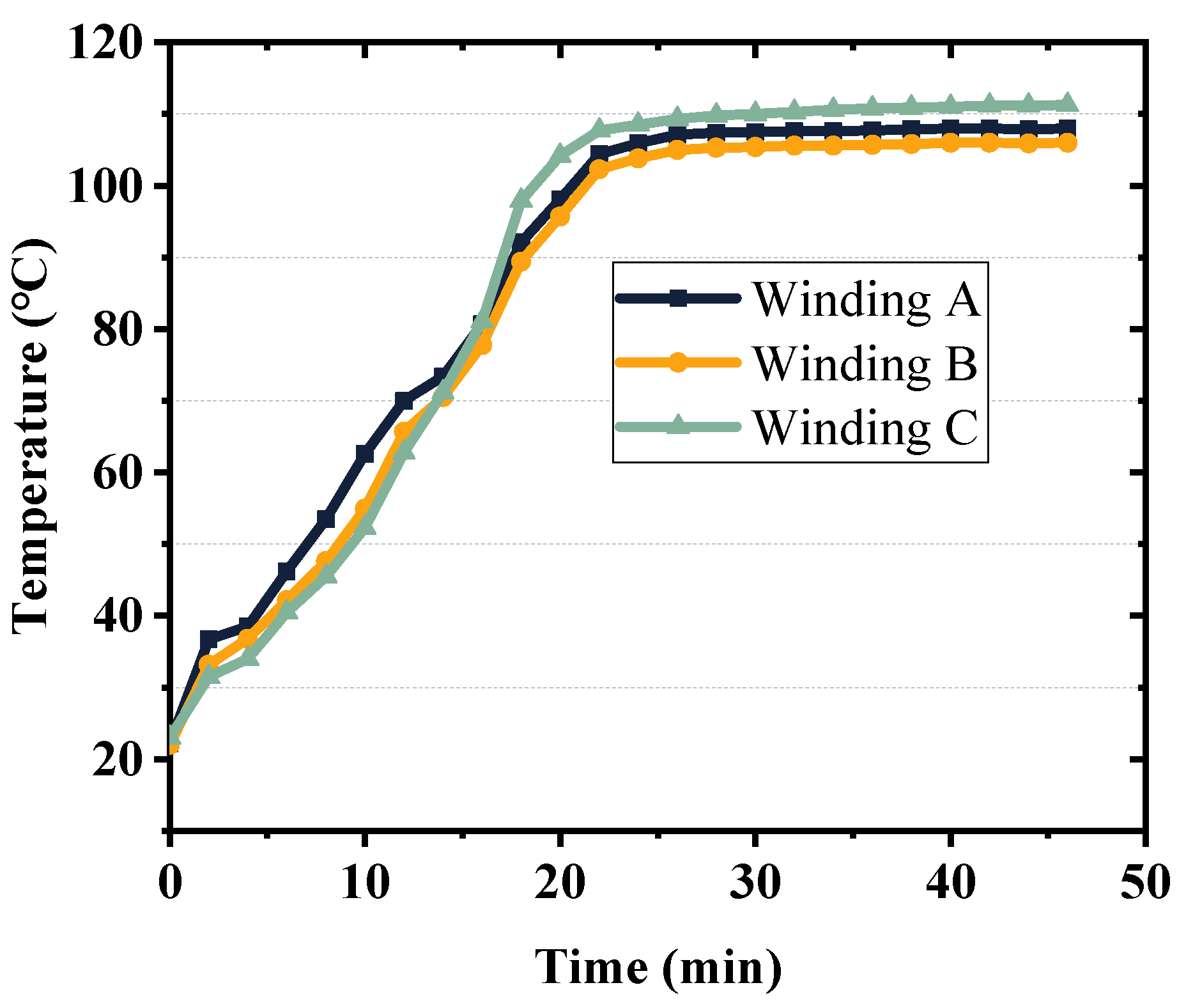
5. Prototype Design and Experimental Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-M.; Jung, Y.-H.; Lim, M.-S. Design of Ultra-High-Speed Motor for FCEV Air Compressor Considering Mechanical Properties of Rotor Materials. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yu, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, L. Design and Optimization of a High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Gas Compressors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Hua, W. Design and Key Technology of Oil-Free Centrifugal Air Compressor for Hydrogen Fuel Cell. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2022, 6, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-M.; Hwang, Y.-S.; Hong, J.-P. Design of an Ultra-High-Speed Permanent-Magnet Motor for an Electric Turbocharger Considering Speed Response Characteristics. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.-K.; Woo, B.-C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Koo, D.-H. Ultra High Speed Motor Supported by Air Foil Bearings for Air Blower Cooling Fuel Cells. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerada, D.; Mebarki, A.; Brown, N.L.; Gerada, C.; Cavagnino, A.; Boglietti, A. High-Speed Electrical Machines: Technologies, Trends, and Developments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2946–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenconi, A.; Vaschetto, S.; Vigliani, A. Electrical Machines for High-Speed Applications: Design Considerations and Tradeoffs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3022–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.-K.; Woo, B.-C.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Koo, D.-H.; Ahn, C.-W. Development of an ultra high speed permanent magnet synchronous motor. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y. High-speed permanent magnet electrical machines—Applications, key issues and challenges. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2018, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Choi, W.; Sarlioglu, B. High-Speed Electric Machines: Challenges and Design Considerations. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gerada, C. Rotor Eddy Current Loss and Multiphysics Fields Analysis for a High-Speed Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 5100–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Dong, J.; Peng, F.; Yao, Y. Rotor Eddy Current Loss Reduction with Permeable Retaining Sleeve for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolondzovski, Z.; Arkkio, A.; Larjola, J.; Sallinen, P. Power Limits of High-Speed Permanent-Magnet Electrical Machines for Compressor Applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2011, 26, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Huang, N.; He, H.; Lei, G.; Zhu, J. Parameter Design for a High-Speed Permanent Magnet Machine under Multiphysics Constraints. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, F.R.; Uzhegov, N.; Vavilov, V.E.; Bekuzin, V.I.; Ayguzina, V.V. Multidisciplinary Design of Ultra-High-Speed Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, Z.Q. Optimal split ratio in small high speed PM machines considering both stator and rotor loss limitations. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2019, 3, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, A.; Schneider, T.; Klohr, M. Fixation of buried and surface-mounted magnets in high-speed permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S.; Yi, R. Influence of Rotor-Sleeve Electromagnetic Characteristics on High-Speed Permanent-Magnet Generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3030–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Liao, X.; Wang, T.; He, X.; Zhang, J. Design and Analysis of the High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motors: A Review on the State of the Art. Machines 2022, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liang, D.; Liu, X. Optimal Design of the Rotor Structure of a HSPMSM Based on Analytic Calculation of Eddy Current Losses. Energies 2017, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.-H.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Jang, I.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.-J. Design method of an ultra-high speed PM Motor/Generator for Electric-Turbo Compounding System. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 5202804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y. Influence of sleeve thickness and various structures on eddy current losses of rotor parts and temperature field in surface mounted permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Hong, D.-K. Rotor Design, Analysis and Experimental Validation of a High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Turbocharger. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 21955–21969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrans, S.; Mallin, L. Mechanical Design of Rotors with Surface Mounted Permanent Magnets. In Electric Machines for Smart Grids Applications—Design, Simulation and Control; El-Shahat, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, A.; Schneider, T. High-speed inverter-fed AC drives. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics, Bodrum, Turkey, 10–12 September 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.; Han, C.; Kim, C.; Choi, J. Rotor Design of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Rotor Magnet and Sleeve Materials. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 5201504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionel, D.M.; Popescu, M.; McGilp, M.I.; Miller, T.J.E.; Dellinger, S.J.; Heideman, R.J. Computation of Core Losses in Electrical Machines Using Improved Models for Laminated Steel. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-Q.; Xue, S.; Chu, W.; Feng, J.; Guo, S.; Chen, Z.; Peng, J. Evaluation of Iron Loss Models in Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Deodhar, R.P.; Liu, Y.; Pride, A.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Bremner, J.J. Influence of PWM on the Proximity Loss in Permanent-Magnet Brushless AC Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelac, J.-P.; Ziogas, P.D. A novel approach for minimizing high-frequency transformer copper losses. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1988, 3, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowski, J.W. Turbulent Flow Between Coaxial Cylinders with the Inner Cylinder Rotating. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1984, 106, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.N.; Martin, W.J. Windage loss reduction study for TFTR pulse generator. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE/NPSS Symposium Fusion Engineering (Cat. No.97CH36131), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–9 October 1997; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1125–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgen, E.; Boulos, R. Functional Dependence of Torque Coefficient of Coaxial Cylinders on Gap Width and Reynolds Numbers. J. Fluids Eng. 1973, 95, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Sun, Q.; Peng, C.; Gu, Y.; Pang, G. Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of Rotor Harmonic Eddy-Current Loss in High-Speed Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 8100811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.F.; Koenig, A.C.; Vanek, L.D. Calculation of eddy current losses in conductive sleeves of synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2008 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Wang, K.; Han, B.; Zheng, S. Thermal Analysis and Experimental Validation of a 30 kW 60,000 r/min High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor with Magnetic Bearings. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 92184–92192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, J. Thermal analysis of high speed induction machines. In Acta polytechnica Scandinavica El; Electrical Engineering Series; Finnish Acad. of Technology: Espoo, Finland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Huang, Y.; Jin, L.; Guo, B.; Zhou, T.; Lin, H.; Dong, J. Development of an air-cooled 150 kW high speed permanent magnet motor with Gramme ring windings for turbo blowers. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3534–3538. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.-K.; Woo, B.-C.; Koo, D.-H. Rotordynamics of 120,000 r/min 15 kW Ultra High Speed Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2831–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.-K.; Woo, B.-C.; Ahn, C.-W.; Koo, D.-H. Unbalance Analysis of 15 KW, 120 krpm, Ultra High Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the 2012 Sixth International Conference on Electromagnetic Field Problems and Applications, Dalian, China, 19–21 June 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.; Gu, J.; Xia, S.; Wang, Z. Advanced Rotor Dynamic—Theory, Technology and Application; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- American Petroleum Institute. Tutorial on the Api Standard Paragraphs Covering Rotor Dynamics and Balancing: An Introduction to Lateral Critical and Train Torsional Analysis and Rotor Balancing; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Fang, J.; Liu, X.; Han, B. Loss Calculation and Thermal Analysis of Rotors supported by Active Magnetic Bearings for High-speed Permanent Magnet Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 63, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power | 25 kW | Rated speed | 95,000 rpm |
| Stator outer diameter | 100 mm | Extreme speed | 110,000 rpm |
| Stator slot number | 24 | Rotor outer diameter | 39 mm |
| Stator inner diameter | 45 mm | Pole pair number | 2 |
| Slot opening width | 2 mm | Pole arc pole pitch | 1 |
| Winding Connection | Y | PM material | Sm2Co17 |
| Winding layer number | 2 | PM thickness | 16.5 mm |
| Iron core length | 56 mm | Sleeve thickness | 3 mm |
| Conductors per slot | 12 | PM conductivity | 110,000 S/m |
| Phase number | 3 | Sleeve conductivity | 610,000 S/m |
| No Load | Rated Load | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | 3D | 2D | 3D | |
| Sleeve (W) | 32.86 | 31.23 | 154.19 | 147.69 |
| PM (W) | 0.51 | 0.49 | 23.8 | 22.67 |
| Total (W) | 33.37 | 31.72 | 177.99 | 170.36 |
| Stator Iron Loss | Copper Loss | Wind Frictional Loss | PM Eddy Current Loss | Sleeve Eddy Current Loss | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss (W) | 371.42 | 240.3 | 95.3 | 23.8 | 154.8 |
| Inconel 718 | Sm2Co17 | |
|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 8190 | 8400 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (1/K) | 13 10−6 | 9 10−6 |
| Young’s Modulus (GPa) | 211 | 151 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 1036 | 42 (tensile) 900 (compressive) |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.27 | 0.294 |
| Sleeve | PM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | Radial (MPa) | Tangential (MPa) | |
| A | 906.39 | −95.01 | −13.17 |
| B | 772.44 | −74.67 | 7.14 |
| C | 830.24 | −56.77 | 40.74 |
| CFD | Measurement | |
|---|---|---|
| Winding (°C) | 104.5 | 108.3 |
| Rotor surface (°C) | 175.4 | 169.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Pei, R. Design and Calculation of Multi-Physical Field of Ultra-High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor. Energies 2024, 17, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133072
Cheng M, Li Z, Xu S, Pei R. Design and Calculation of Multi-Physical Field of Ultra-High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor. Energies. 2024; 17(13):3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133072
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Ming, Zhiye Li, Shibo Xu, and Ruilin Pei. 2024. "Design and Calculation of Multi-Physical Field of Ultra-High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor" Energies 17, no. 13: 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133072
APA StyleCheng, M., Li, Z., Xu, S., & Pei, R. (2024). Design and Calculation of Multi-Physical Field of Ultra-High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor. Energies, 17(13), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133072






