Abstract
Compared to the southern Tibetan Plateau, the northern part has been regarded as relatively lacking geothermal resources. However, there is no lack of natural hot springs exposed in beads along large-scale fracture systems, and research on them is currently limited to individual hot springs or geothermal systems. This paper focuses on the Wahongshan-Wenquan Fracture Zone (WWFZ), analyzes the formation of five hydrothermal activity zones along the fracture zone in terms of differences in hot water hydrochemical and isotopic composition, and then explores the hot springs’ hydrothermal control in the fracture zone. The results show that the main fractures of the WWFZ are the regional heat control structures, and its near-north–south- and near-east–west-oriented fractures form a fracture system that provides favorable channels for deep hydrothermal convection. Ice and snow meltwater from the Elashan Mountains, with an average elevation of more than 4,500 m above sea level, infiltrates along the fractures, and is heated by deep circulation to form deep geothermal reservoirs. There is no detectable mantle contribution source heat to the hot spring gases, and the heat source is mainly natural heat conduction warming, but the “low-velocity body (LVB)” in the middle and lower crust may be the primary heat source of the high geothermal background in the area. The hot springs’ hydrochemical components show a certain regularity, and the main ionic components, TDS, and water temperature tend to increase away from the main rupture, reflecting the WWFZ controlling effect on hydrothermal transport. In the future, the geothermal research in this area should focus on the hydrothermal control properties of different levels, the nature of fractures, and the thermal contribution of the LVB in the middle and lower crust.
1. Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau has the most vigorous geothermal activity in China, with the highest geothermal reserves and various surface geothermal manifestations throughout the region [1,2]. However, it is traditionally believed that the geothermal resources of the Tibetan Plateau are mainly concentrated in tectonically unstable areas such as southern Tibet, western Yunnan, and western Sichuan, while its northern and northeastern parts are in relatively stable blocks with average geothermal potential. Relevant studies have also focused on the north–south Himalayan rift zone [3,4,5], the Yunnan-Tibet geothermal zone [6,7], and several fault zones where hot springs in western Sichuan are relatively concentrated [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Only with the exploration of high-temperature hot dry rock resources in the Gonghe Basin on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau in recent years [15] has the region gained widespread attention, and a large number of studies have been carried out to address the mechanism of the heat source and the potential for development [16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
The Wahongshan-Wenquan Fracture Zone (WWFZ), located in the southwest of the Gonghe Basin, belongs to the southwest boundary fault of this basin, and is the separation zone between the southwest of Gonghe Basin and the northeast of the East Kunlun magmatic belt (Figure 1). Several hot springs were exposed in the northwest–southeast direction of the fault zone, indicating that the fault controlled the distribution of hot springs in this area to a certain extent. Therefore, research on the genesis of hot springs has significant implications for a deeper understanding of the heat control mechanism of the WWFZ, as well as on the deeper analysis of the Gonghe Basin’s high-temperature thermal background. The complexity of fracture systems in orogenic zones and the spatial heterogeneity of the permeability of their fracture–matrix systems are the difficulties in carrying out research on geothermal systems [23], while hydrogeochemical analysis can avoid direct analysis of the medium and channels of geothermal systems; thus, the hydraulic linkages and the evolution process of the chemical components can be analyzed by comparing the hydrochemical characteristics of the different geothermal systems [24], in order to provide a basis for research on the genesis mechanism of the geothermal systems in the fracture zones. Previous authors have conducted relevant hydrogeochemical analyses for some hot springs. Zhang et al. (2016) carried out principal component analysis of the chemical composition of some hot spring water in the area [25]. They proposed the geochemical genesis of the main components and the related hydrogeochemical processes. Ma et al. (2020) carried out a fluid geochemical and water–rock interaction study of the hot water in the southeastern section of the WWFZ [26]. They proposed that aluminosilicate minerals dissolution and recrystallization is the most crucial hydrogeochemical process controlling cations. In contrast, mineral dissolution and filtration during runoff are the main sources of anions. Wang et al. (2023a) conducted geochemical analysis and studied the hot springs genesis mechanism on the southwest side fracture [27]. They proposed that the hot springs belong to a deep-circulating convective geothermal system controlled by the fracture, with a geothermal reservoir temperature as high as 245–261 °C, and a deep circulation depth of 7700–8200 m. The previous studies focused on individual hot springs. They lacked comparative analyses on the elements of different geothermal systems and their genesis mechanisms.
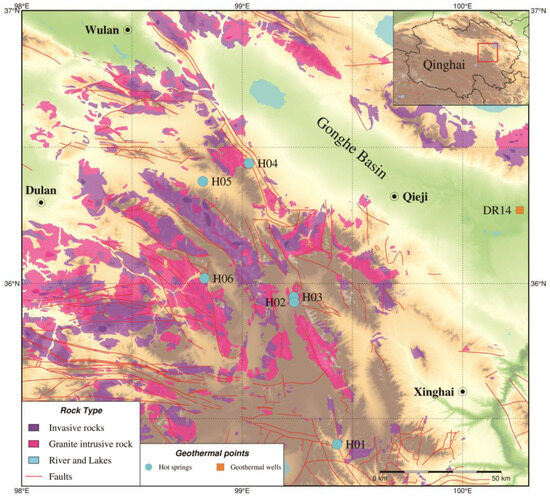
Figure 1.
Wahongshan-Wenquan Fractures Zone (WWFZ) geologic map and hot springs distribution.
The tectonic setting is the result of the long-term evolution of the Earth, which determines the temperature, fluid composition, reservoir characteristics, and mode of heat transfer (convection or conduction) in geothermal systems [28]. Geothermal fields around the world are invariably tectonically controlled [29,30]. Fractures are the most prevalent heat-controlling tectonics [31,32]. Under favorable geological and tectonic conditions, meteoric water seeps down along the fracture, and is warmed by deep circulation; then, it gathers and surges upward to be exposed on the surface along different high-angle fracture zones or steeply inclined permeable strata [33]. Thus, bead-like localized thermal anomaly zones can be formed near the fracture zones. In this paper, geothermal fluid and gas geochemical samples of different geothermal anomalies in the WWFZ were systematically collected, and the fluid geochemical characteristics and geothermal reservoir characteristics of the area were comparatively analyzed in combination with the regional geological and tectonic conditions. Research on the heat source mechanism of different geothermal systems was systematically carried out, and the controlling role of the WWFZ on the geothermal system was explored, which will provide a reference for further geothermal exploration in the area in the future.
2. Study Area
The WWFZ starts from Agushar in the south, passes through the Harihad Mountains, and ends in Changshui in the south, with a length of about 275 km, and in the study area about 200 km. The main tectonic trace is NW–NNW oriented, which consists of several high-angle reverse faults trending in the north–northwestern direction, and it is an extrusive reverse strike-cum-rightward strike-slip fracture [34]. A few small-scale near-north–south- and near-east–west-oriented fractures cut the study area into diamond-shaped fracture blocks. Along the fracture zone, there are banded bedrock, intermittently distributed ultramafic rock, and localized moderately acidic intrusive rock [35]. The WWFZ has a considerable depth of influence and is a crustal fracture. It was formed at the end of the early Paleozoic Era, and its activity increased from the Hualixi period to the middle Indo-Chinese period. In the late Indo-Chinese-Himalayan period, the region entered the stage of intra-land orogeny, and the WWFZ and a series of basically synchronized fractures formed the north–northwestern Erasan slip tectonic zone with right-lateral slip, which controlled the intrusion of the middle-acidic magmatism in the Indo-Chinese period, and the distribution of the regional late Triassic volcano-sedimentary basins [36]. There is a cluster of distributed small earthquakes, which is an active structure [37].
Along the WWFZ, there are hot springs such as H01 (31–64 °C, Wenquan Township, Xinghai County), H02, H03 (65–78 °C, Sangchigou, Xinghai County), H04 (35–46 °C, Bayinggeli), H05 (67 °C, Angutan, Dulan County), and H06 (87 °C, Reshuigou, Dulan County). These hot springs are located at the intersection of different fractures (Figure 1). Most of these hot springs are in a primitive and undeveloped state, except for the H01 hot spring, which is currently under construction with related tourism and sanatorium facilities for tourists to bathe.
3. Materials and Methods
Sample Collection and Testing
The distribution of sampling sites is shown in Figure 1. The water chemistry and gas samples were collected from May to July 2022. A total of 6 sets of hot water samples and five gas samples were collected, and the testing items included complete analysis, trace elements, stable isotopes, conventional gas fractions, noble gas fractions, and isotopes. The water samples were first filtered through a 0.45 μm microporous filter membrane, then stored in polyethylene bottles, rinsed twice with deionized water, and dried. Hot water chemical composition and stable isotope analyses were carried out at the Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. Testing items included complete analysis and trace elements. The water samples were tested according to the National Standard of the People’s Republic of China, “Methods for examination of drinking natural mineral water” (GB/T8538-2008) [38]. A FP640 flame photometer and PHS-25 digital acidimeter were utilized for chemical composition testing, with a 3% anion/cation balance error. The isotope testing instrument was a Model L2130i Water Isotope Analyzer, and measurements were expressed as thousandths of a percent relative to the VSMOW standard. The drainage method was used to collect hot spring gas samples. They were analyzed and tested at the Oil and Gas Resources Research Center of the Northwest Institute of Ecology and Environmental Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NWIER, CAS). Concentrations and isotopes of He, Ne, and Ar gases were analyzed using the Noblesse rare gas isotope mass spectrometer. Helium isotopes were tested with an error of ±10% for R-values above 1 × 10−7 and ±15% for R-values between 1 × 10−8 and 1 × 10−7.
4. Results
4.1. Chemical Characterization of Hot Springs
The water chemistry of the different hot springs is shown in Table 1. Due to various geochemical processes occurring along the groundwater path circulation, in general, the chemical composition is relatively homogeneous. The cations are dominated by Na+, ranging between 150.0 and 861.0 mg/L. The Na+ near the primary fracture is around 300 mg/L, and the lowest value occurs at H04, where the spring water temperature is also the lowest (46 °C). Away from the primary fracture, the Na+ increased significantly, with the highest value (861 mg/L) occurring at H06 and with the highest spring temperature (87 °C). Cl− and SO42− dominate the anions, with ranges of 120.0–1461.0 and 36.3–329.0 mg/L, respectively. The trend of Cl− was the same as that of Na+, and away from the primary fracture, the content of Cl− was elevated, with the highest value (1461 mg/L) occurring at H06. There is no obvious pattern for SO42−, which should be related to the strata through which the hot water of different hot springs flowed on the way up.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions and stable isotopes of hot springs in WWFZ.
The hydrochemical types can roughly be categorized into the following two types: hot springs near the primary fracture are Cl−SO4-Na- or SO4-Cl−Na-type waters, including H01, H02, H03, and H04; those far away from the fracture show Cl−Na-type waters, including H05 and H06. The hydrochemical type of geothermal water is intricately associated with its circulation conditions; if the circulation is faster, then the degree of interaction between it and the surrounding environment is smaller, and the hydrochemical components are relatively low. If the circulation cycle is longer, the runoff pathway is farther, the interaction of the hot water with its surroundings is enhanced, and the hydrochemical components are relatively high. Geothermal reservoirs in the study area, which are located in the tectonic magma belt of the Elashan Mountain, are characterized by granitic rocks. Dissolution and recrystallization of primary aluminosilicate minerals in the geothermal system are the most important hydrogeochemical processes for the control of cations in the hot water, whereas under-seepage of recharge water coupled with dissolution and filtration from salt minerals during the hot-water runoff and upwelling processes is the main source of anions. The hot water in this study area contains high concentrations of Na+, SO42−, and Cl−, of which SO42− may originate from sulfate mineral dissolution, and may be affected by geochemical processes, for example, pyrite oxidation. In general, however, the water chemistry is mostly the same. All of the hot springs are clustered in the rightmost part of the diamond on the Piper diagram (Figure 2). However, the difference lies in the size of the TDS, which ranges from 552 to 2866 mg/L, with the smallest value being H04 near the main fracture zone; the most considerable value occurs at H06, which is far away from the primary fracture, reflecting the proximity of different circulating runoff paths.
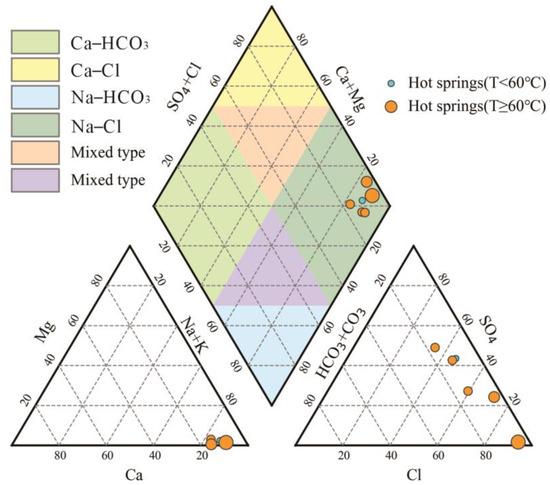
Figure 2.
Piper diagram [39] of hot springs in WWFZ.
The ratio between some ions in groundwater can help to analyze the various states and groundwater geological effects, which can be used to analyze the hot water transport and hosting environment [40]. Different ionic characterization coefficients were calculated from the hot water chemistry data, as shown in Table 2. γNa+/γCl− characterizes the groundwater metamorphism coefficients, which can respond to the strata confinement, the degree of metamorphism of the groundwater, and its activity. The smaller the γNa+/γCl−, the higher the metamorphism and the better environmental closure of the groundwater; the larger the γNa+/γCl−, the more the groundwater is affected by infiltrating water. It can be seen that far away from the main fracture of the WWFZ, its γNa+/γCl− gradually becomes smaller, reflecting that the environment tends to be closed, and the influence of surface and shallow groundwater recharge is gradually reduced. γCl−/γCa2+ characterizes the hydrodynamic characteristics of groundwater; the larger γCl−/γCa2+ is, the condition of groundwater flow is poorer, and the groundwater flow is slower. As can be seen in Table 2, except for H02 and H03, in general, the flow conditions gradually become worse from the primary fracture to the two sides, and H02 and H03 are exposed in the open valley between the mountains. The flow conditions may have received the influence of the thicker quaternary cover on the surface. The salinization coefficient γCl−/(γHCO3−) mainly reflects the concentration degree of stratum water, and the big value reflects the longer groundwater flow path and the slower water circulation. The Cl−/(γHCO3−) values near the main fracture of the WWFZ are less than 7. In contrast, H05 and H06 are greater than 18, which reflects that the groundwater cycle is faster in the vicinity of the primary fracture, and gradually slows down far away from the primary fracture.

Table 2.
Ionic characterization coefficients of hot water in WWFZ.
4.2. Hydrogen–Oxygen Stable Isotope Characterization of Hot Water
Hot springs are generally derived from meteoric water, and there is a depth effect in the infiltration process of meteoric water in the fracture zone, i.e., the δ2H and δ18O contents in hot water decrease with increasing depth. In the deep high-temperature environment, the hot water interacts with the surrounding rocks, resulting in “oxygen drift”, which increases the δ18O content. Therefore, according to the hot springs’ isotopic composition, we can analyze underground hot water’s circulation process, recharge rate, and geological events (water–rock interactions) encountered in the fracture zones, as well as support the analysis of the fracture zones’ controlling role on the geothermal system. The stable isotope δ2H -δ18O relationships for geothermal wells, cold springs, salt lakes, rainwater, and snow water in the Gonghe Basin neighboring the WWFZ were analyzed for comparison (Figure 3). All of the collected water samples showed hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes falling around GMWL and LMWL [41], suggesting that the recharge source is meteoric water. The δ2H and δ18O values of the hot springs in the WWFZ are significantly smaller than those of other water bodies within the Gonghe Basin, suggesting that the hot water in the study area is derived from meteoric water at higher elevations, or from meteoritic water in colder climates. The WWFZ is located in the Elashan Mountains with an average elevation 4500 m, in combination with the topography. The δ2H and δ18O values gradually decrease with rising elevation, making the δ2H and δ18O values significantly smaller than those of other water bodies neighboring the Gonghe Basin. A map of the possible extent of magma water genesis (Figure 3), based on stable isotope intervals between ice-melt water and magma water in the area, reveals that there is no magma-influenced hot water in the area. The weak oxygen drifts in H01 and H02 suggest that water–rock interactions occur at hot water depths, which is in accordance with the Gibbs diagram results.
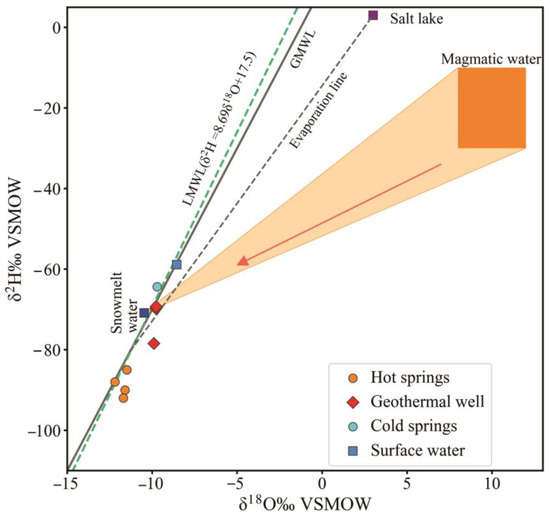
Figure 3.
Stable isotope compositions of different hot springs in WWFZ.
Hot springs’ recharge elevations can be determined based on meteoric water isotope elevation effects, calculated as follows [42]:
where H is the altitude of groundwater recharge; δs is the isotope value of hot springs at the sampling point; δp is the isotope value of meteoric water; k is the value of the isotope height gradient; and h is the altitude of the sampling point. The average value of the oxygen isotope of local rainwater was taken to be −7.97‰, and the value of the isotope height gradient was 3‰; Table 1 shows the results of the calculations. The altitude of the hot spring recharge area is between 5155 and 5525 m, indicating that the recharge areas of the hot springs are all located in the central main ridge of the Ngola Shan Mountains where they are located.
4.3. Chemical Characterization of Hot Spring Gases
4.3.1. Hot Spring Gas Composition
The gases in hydrothermal areas (Table 3) can be broadly categorized into two types in the Tibetan Plateau according to their composition and genesis: CO2-type gases, which have both magmatic hot water and deep circulation genesis, and N2-type gases, which have only deep circulation genesis [43]. The gas concentration data (Figure 4) show that the major composition of all hot water is N2. The mean N2 concentration value is >80%, belonging to the N2 type of gas, indicating that the genesis type of hydrothermal activity in the WWFZ belongs to the deep circulation category. In the samples, H2, H2S, and SO2 were undetectable due to their low concentrations. Higher levels of O2 were found in hot spring water samples at higher temperatures, likely because atmospheric oxygen dissolves in the hot water as it rises. However, the contamination of the samples due to unregulated operation during sampling cannot be excluded. Atmospheric composition was not adjusted in this study to accurately characterize the area of hydrothermal activity. Most of the samples had relatively low CO2 concentrations, averaging only 0.7%, except for sample H06, which had a relatively high CO2 concentration of 7.83%.

Table 3.
Gas compositions and isotopes of hot springs in WWFZ.
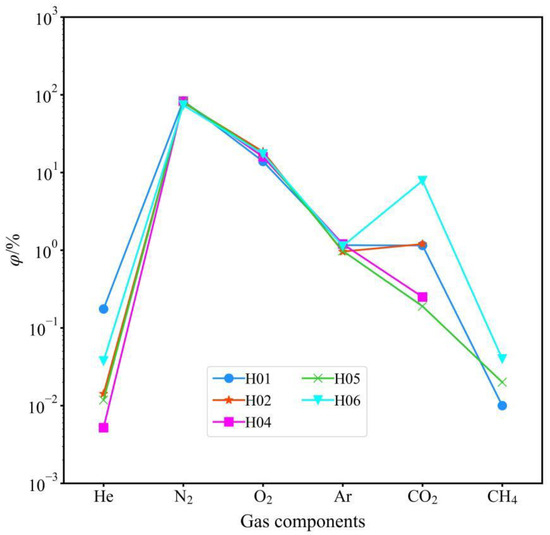
Figure 4.
Chemical compositions of hot spring gases in WWFZ.
Nitrogen (N2) consistently appears as a major component in low- to medium-temperature geothermal systems. Nitrogen exhibits limited geochemical activity and possesses chemical stability akin to noble gases. Prior to the replenishment of geothermal water by meteoric water, N2 in geothermal gases, along with Ar, is thought to originate from dissolved air. Following prolonged runoff in a reducing environment, the depletion of oxidizing gas components, such as oxygen, leads to the accumulation of rare gas components like nitrogen and argon, which become the dominant constituents [44]. Giggenbach and Glover He–Ar–N2 diagrams show (Figure 5) that the N2/Ar values of all samples fall within the interval between the meteoric water value (38) and the atmospheric value (84) and are closer to the atmospheric value (84), indicating that the N2 component in the hot springs is dominated by atmospheric genesis [45]. The presence of helium (He) primarily stems from the radioactive decay of uranium and thorium within the Earth’s crust [46]. However, it cannot be ruled out that certain samples (such as H01) are in proximity to the helium end, typically associated with mantle origins, hinting at the potential presence of a minor mantle component in these samples. Seismic profiles along the Gonghe Basin–Yushu highway indicate vertical stacking of high- and low-velocity crustal bodies in Wenquan Township, with the Chabcha area and the LVB buried at depths of 15–43 km and with S-wave velocities below 3.4 km/s [47]. Recently, scholars studying the seismicity of the Gonghe Basin in light of deep hot dry rock exploration generally attribute the phenomenon to a young (Quaternary) intrusion of mantle-derived melt into the crust [48,49,50,51]. Therefore, the release of gases from the melt offers the potential for the occurrence of mantle-derived helium in surface hot springs.
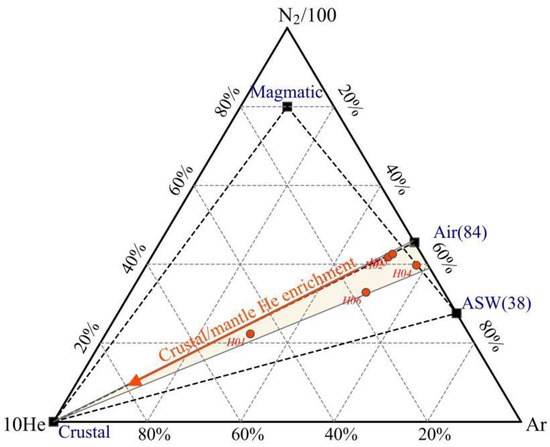
Figure 5.
Relative He, Ar and N2 contents of hot spring gases samples in WWFZ.
4.3.2. Isotopic Characterization of Hot Spring Gases
Helium (He) exists in two natural isotopes, 3He and 4He, with the predominant release during mantle degassing being geogenic 3He. This process also involves the transfer of mantle heat to shallow fluids as they ascend along tectonic channels. Conversely, the main origin of helium within the crust stems from the α-decay production of 4He through the natural radioactive decay of 238U, 235U, and 232Th [46]. Variations in helium isotope ratios among different source gases prompt the use of atmospheric helium (Ra = 1.43 × 10−6) as a reference; mid-oceanic ridge basalt (MORB) usually exhibits ratios around (8 ± 1) Ra, representing the upper mantle, while crustal helium ratios range from 0.005 to 0.02 Ra [52]. Consequently, examining the helium isotope ratios in hot spring gases offers valuable insights into the regional geothermal context, fracture propagation patterns, activity, and fluid circulation dynamics.
As atmospheric components may inadvertently mix into samples during gas collection procedures, Duchkov (2010) suggested adjusting the R-value of geothermal gas samples using the 4He/20Ne ratio to mitigate the impact of atmospheric contamination during sampling [53]. The atmospheric ratio of 4He/20Ne is approximately 0.318. Therefore, when the 4He/20Ne ratio of a sample closely approaches 0.318, it indicates that the helium in the sample is predominantly of atmospheric origin. The correction equation is as follows:
In the equation, the subscripts c, m, and a correspond to the calibration value, test value, and characteristic value of the atmospheric source, respectively. Sano (1982) suggested the presence of three helium sources in natural gases: atmospheric, mantle, and crustal [54]. They devised a formula to determine the mixing ratio of different helium sources in gas samples using the ratios of 3He/4He and 4He/20Ne, along with a graphical representation of the relationship between 3He/4He and 4He/20Ne. This method streamlines the process and enhances the clarity of helium source identification. The formulas for helium source determination are as follows:
The subscripts A, M, and C represent atmospheric, mantle, and crustal sources, respectively, and fA, fM, and fC represent the proportions of the three sources in the gas samples, of which (3He/4He)A = 1.4 × 10−6, (3He/4He)M = 1.1 × 10−5, (3He/4He)C = 1.5 × 10−8, (4He/20Ne)A = 0.318, (4He/20Ne)M = 1000, and ( 4He/20Ne)C = 0.1000. The results are shown in Table 2. The helium content in samples H01 and H05 primarily originates from the α-decay of 238U, 235U, and 232Th in the crust’s natural radioactive systems, accounting for over 97% on average. A plot of the 3He/4He-4He/20Ne relationship of the geothermal gases in the study area is shown in Figure 6, and the He isotope R/Ra values (ratio relative to the atmosphere) of the hot-water gases in these two locations belong to the crustal helium domain (<0.05), indicating that they are predominantly crustal in origin.
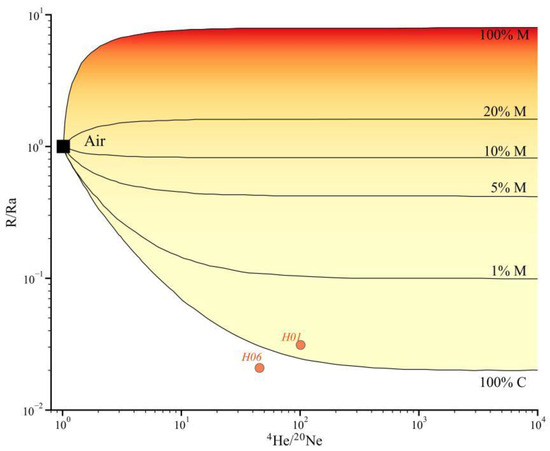
Figure 6.
3He/4He-4He/20Ne relations of hot spring gases in WWFZ.
4.4. Geothermal Reservoir Temperatures and Circulation Depths
4.4.1. Water–Rock Equilibrium Analysis
The Na–K–Mg triangulation diagram, proposed by Giggenbach in 1988, categorizes water samples into fully equilibrated, partially equilibrated, and immature water regions, serving as a common tool to evaluate water–rock equilibrium and differentiate between different types of water samples [55]. The Na, K, and Mg concentrations of various hot springs in the study area were plotted on the Na–K–Mg equilibrium triangulation diagram (Figure 7). Four hot springs were identified in the immature water region at the apex of the lower-right corner, suggesting they are in the initial stage of water–rock interaction. Two hot springs, H03 and H05, were observed in the partially equilibrated or mixed water region, signifying ongoing adjustments in the ionic equilibrium between water and rock. Dissolution continues to occur, or the hot water may have undergone mixing with shallow cold water during its ascent. Moreover, examination of the Na–K–Mg equilibrium triangulation diagram indicates that the geothermal reservoir temperatures of all hot spring sites fall within the range of 120 °C to 270 °C. Notably, H06 exhibits the highest potential geothermal reservoir temperature, aligning with the highest temperature recorded in its spring water.
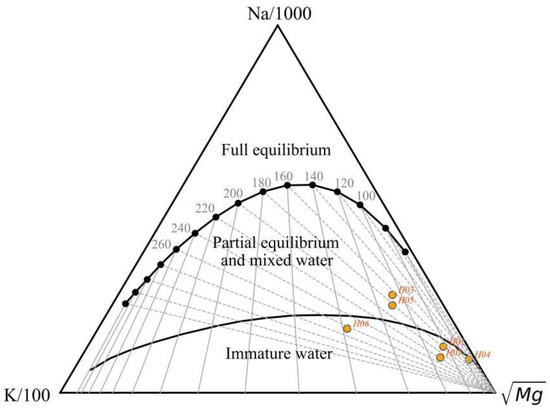
Figure 7.
Na–K–Mg diagrams for various hot springs in WWFZ.
4.4.2. Geothermal Reservoir Temperatures by Multi-Mineral Saturation Indices
Reed and Spycher (1983) proposed a multi-mineral equilibrium mapping method for assessing the whole chemical equilibrium between fluids and minerals in geothermal systems [56]. The underlying principle is that the solubility of numerous minerals in water is temperature dependent. If a set of minerals at a specific temperature is nearly in equilibrium simultaneously, it suggests that the hot water and the mineral group have attained equilibrium, with the equilibrium temperature representing the temperature of the deep geothermal reservoir.
Aluminum-bearing silicate minerals could not be produced because the aluminum concentration in the hot water in the study area was not detected below the detection limit. In many geothermal systems, one or two aluminum-containing silicate minerals have typically achieved equilibrium. Consequently, Pang and Reed (1998) suggested employing aluminum fixation to restore equilibrium to aluminum-containing silicate minerals in geothermal systems [57]. Under multi-component, non-homogeneous chemical equilibrium conditions in geothermal systems, the balance of alumino-silicate minerals is interdependent because each of these minerals has a specific chemical composition. When the concentration of aluminum is unknown, it can be estimated at various temperatures by assuming that the activity of aluminum is fixed by an aluminum-bearing mineral such as microplagioclase feldspar. A value for the aluminum concentration is obtained, and then used to calculate saturation indices for other aluminosilicate minerals. This method of estimating aluminum concentration values applies to specific geothermal waters because most geothermal waters require at least two aluminosilicate minerals to be in equilibrium.
Based on the hydrochemical data, we calculated each mineral’s saturation index at different temperatures. We plotted the log(Q/K)–T curve (Figure 8) using the temperature and log(Q/K) values as horizontal and vertical coordinates, respectively. Based on the data from the petromineralogical investigations in the study area, we made a choice of 11 common minerals: quartz (Quartz), chalcedony (Chalcedony), potassium feldspar (K-feldspar), calcite (Calcite), fluorite (Fluorite), aragonite (Aragonnite), gypsum (Gypsum), and magnesite (Magnesite), and plotted their log(Q/K)–T curves (H02 and H03 are located in the same geothermal field, and only the higher-temperature H02 hot spring was calculated). Among them, the curves of H01, H02, H05, and H06 converged a certain temperature, and their geothermal reservoir temperatures were 135 °C, 139 °C, 152 °C, and 159 °C, respectively. The curve of H04 is more dispersed, and its geothermal reservoir temperature was about 80 °C. H06 has the highest geothermal reservoir temperature among all of the hot springs, which is consistent with the highest temperature of its spring water.
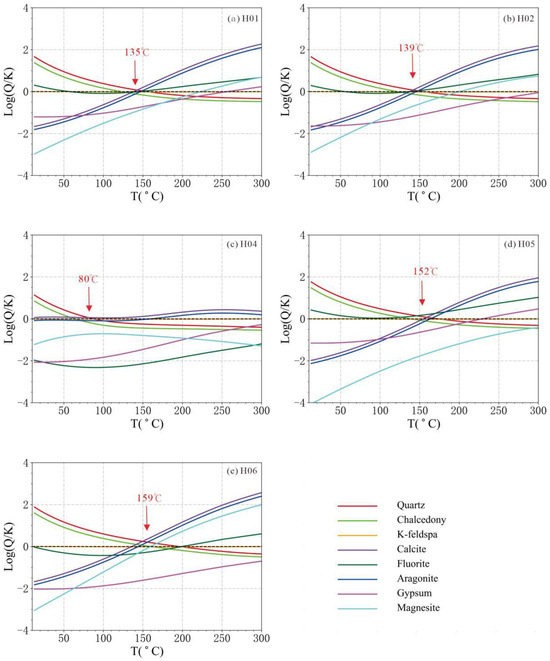
Figure 8.
Mineral saturation diagrams for a typical hot spring in WWFZ.
4.4.3. Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Estimation by Geothermometers
According to the previous analysis, the hot spring waters are all immature or partially equilibrated (mixed); this did not meet the conditions for cationic geothermometers, so we adopted the silica geothermometer to estimate geothermal reservoir temperatures. The total concentration of silicon is a function of temperature. When there is no vapor loss from hot water during its ascent to the surface or when only conduction cooling is present, the quartz silica geothermometer uses the no vapor loss expression. When hot water has a maximum steam loss at a given temperature during ascent to the surface or when adiabatic cooling is predominant, the maximum steam loss geothermometer expression is used. Calculations are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Geothermal reservoir temperatures estimated by different methods and circulation depths of hot springs.
4.4.4. Silicon-Enthalpy Mixing Model for Estimating Cold Water Mixing Ratio
The silicon-enthalpy mixing model (SEMM) estimates the mixing proportion of shallow cold water during hot spring ascent. This method obtains the mixing proportion of cold water and estimates the hot spring’s geothermal reservoir temperature. However, according to Dong (2000), the result of the SEMM is too high, which may be due to the loss of steam from the expansion of the underground hot water before mixing with the cold water; thus, the measured SiO2 content of the spring water is too high [58]. The overall geothermal reservoir temperatures calculated using the SEMM are relatively high (Table 4) and are for reference only. The results show a significant amount of cold water mixing in the springs throughout the study area, with the percentage of cold water mixing ranging from 56.9 to 79.0%.
4.4.5. Hot Water Circulation Depth Estimates
Combining the equilibrium states of each hot spring’s water, the multi-mineral equilibrium analysis, and the results of different geothermometers (Table 4), the quartz no vapor loss geothermometer is closest to the multi-mineral equilibrium analysis results, so we chose the interval of the results of two methods as the interval of the possible geothermal reservoir temperatures (Figure 9).
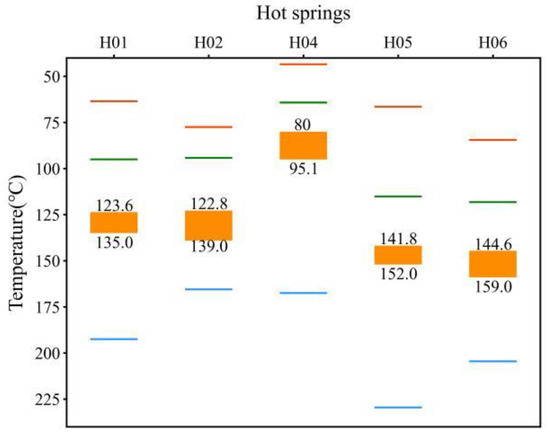
Figure 9.
Geothermal reservoir temperatures of different hot springs obtained by different methods. Orange bars show geothermal reservoir temperature ranges as determined by quartz geothermometers (no vapor loss) and the multi-mineral saturation index method; blue lies illustrate geothermal reservoir temperatures derived from mixed silicon enthalpy models; the green lines indicate the geothermal reservoir temperature obtained from the chalcedony geothermometer; and the red line shows the temperature of the hot springs at the surface.
According to the monitoring data, the average annual temperature of the Xinghai, Wulan, and Dulan areas is 2.7 °C, and the depth of the normal temperature zone is about 45 m. The geothermal temperature gradient is about 4.5 °C/100 m, and the ranges of circulating depths of different hot water springs obtained from the calculations are shown in Table 4. Among them, the circulating depth of H06 is the deepest, about 3198–3518 m, and the hot water circulating in H04 is the shallowest, which is only about 1763–2098 m.
Ma et al. (2020) used quartz geothermal geothermometers and calculated the six springs with thermal storage temperatures of 109.3–137.0 °C in the H01 hot spring group [26], which are basically consistent with the results of 123.6–135.0 °C estimated in this paper. Wang et al. (2023a) used quartz geothermometers, the silica enthalpy model, and the Na-Li cation geothermometer to calculate the thermal storage temperatures of the H06 hot spring [27]. The results were as high as 245–261 °C, much higher than the results of 144.6–159 °C in this study. Based on the preceding analysis, it is evident that H06 falls into the category of immature water, rendering the cationic geothermometer inapplicable. Additionally, while the Na-Li geothermometer is suitable for carbonate rocks, its accuracy diminishes for other lithologies. The silicon-enthalpy mixing model assumes that the dissolved SiO2 in the deep hot water is saturated and subject to the secondary equilibrium of the water–rock reaction that does not occur after mixing with cold water, while the actual situation is often far from the ideal model. Therefore, the authors consider the results to be questionable.
5. Discussion
Fractures are often favorable channels for water (hot or cold), which may affect the geothermal conditions in a particular range to a certain extent, thus forming geothermal anomaly zones. The WWFZ is a crustal fracture that cuts through the entire crust and contacts the upper mantle, which is favorable for mantle heat flow to be transported upward along the fracture, forming a regional heat-controlling fracture. At the same time, the fracture is cut by some near-north–south and near-east–west secondary fractures, and these fracture systems with different depths and crisscrosses provide favorable channels for deep hot water convection circulation in the region. By comparing and analyzing the fluid geochemical characteristics, geothermal reservoir depths, recharge heights, and heat source mechanisms of different hot springs within the WWFZ, a model of the water–heat cycle has been established (Figure 10).
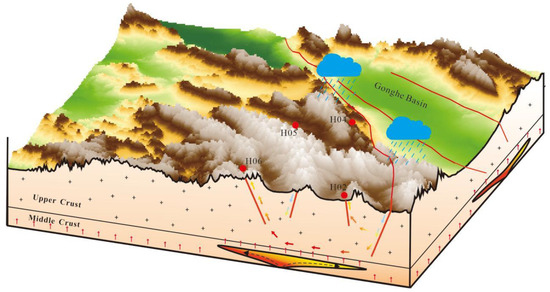
Figure 10.
Hot spring formation pattern in the WWFZ.
5.1. Water and Heat Sources
The δ2H and δ18O values of all hot springs in the WWFZ are significantly lower than those of other water bodies in the Gonghe Basin, suggesting that hot springs in the study area are recharged from meteoric water at higher elevations or from meteoric water in colder climates. According to the hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of the hot spring water, it is estimated that the recharge altitude is between 5155 and 5525 m, which means that all the hot spring water is derived from the snow and ice-melt water of the Ngola Shan Mountains, which is 5100 m above sea level. The gas test results show that all of the hot springs in the area are N2-type gases, i.e., the hot water is caused by deep-cycle heating. The He isotopes of the gases fall into the helium domain of the crust, i.e., the gases are mainly generated by α-decay of the natural radioactive systems of 238U, 235U, and 232Th in the crust, with no additional heat contribution from the mantle source. Low-velocity bodies of unknown nature in the lower and middle crust of the region may have provided an additional source of heat to the high-temperature thermal background of the study area [16,19,47,48,49,50,51], where hot springs were formed by deep circulation heating of snow and ice meltwater.
5.2. Hydrothermal Transport Channel
The northwesterly Wahongshan-Wenquan fracture and the transverse near-north–south or near-east–west fracture form a fracture system that provides a favorable channel for deep hot water convection circulation in the study area. According to the fluid geochemical characteristics of different hot springs in the area, the hot springs can be categorized into two runoff channels: long and short. Hot springs near the primary fracture of the WWFZ have relatively short runoff pathways, better deep hydrodynamic conditions, relatively open underground environments, and lower TDS of hot water. Away from the primary fracture, the content of Na+ and Cl− ions in the hot springs increased significantly, and the groundwater circulation rate slowed down, showing the characteristics of deep circulation and long runoff type.
5.3. Geothermal Reservoir
The study area is a convective geothermal reservoir system, and the fracture system formed by the north–west-trending WWFZ and a small number of fractures that transect the near-north–south or near-east–west direction constitute the primary geothermal reservoir system. Except for H04, which has a low geothermal reservoir temperature (about 80–95.1 °C) due to its shallow hot-water runoff depth of about 1763–2098 m, the rest of the hot springs have a geothermal reservoir temperature higher than 120 degrees; the highest one is located in H06, with a high geothermal reservoir temperature of 144.9–159.0 °C, and accordingly, its hot-water runoff is also the deepest (3198–3518 m).
5.4. Insulation Cover
For convective geothermal systems, the role of the cover is generally not noticeable. The poor hydrodynamic conditions (large γCl−/γCa2+ values) of the H02 and H03 hot springs near the primary fracture may be related to the thicker quaternary cover of the intermountain valley in which they are located.
To summarize, under normal or high regional thermal background, Elashan Mountain ice-melt water or meteoric water seeps down through the fracture network or fracture zone of the main fracture of the WWFZ, and runs off to the depths driven by the difference in the hydraulic head, with a gradual increase in temperature at depth; the groundwater continuously draws heat from the surrounding rocks to form geothermal water, and then rises up to the surface due to the difference in density, and is exposed in the appropriate tectonic part (generally at the intersection of two sets of fractures) to form hot springs. Some of the hot springs have a shallow circulation depth and short runoff path, and are exposed in the secondary fractures near the main fracture of the WWFZ, with a lower temperature (H04); meanwhile, the hot springs farther away from the main fracture (H06) have the highest spring water temperature and geothermal reservoir temperature, and their hydrochemistry type is Cl−Na, and the TDS is nearly twice as high as that of the hot springs near the main fracture zone, reflecting their longer runoff path, deeper circulation depth, and the controlling effect of the main fracture and its secondary fractures of the WWFZ on the geothermal system in the area.
6. Conclusions
The Wahongshan-Wenquan Fracture Zone is located in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, and several hot springs are exposed in the zone. In contrast to previous studies focusing on individual hot springs, this paper examined the hydrothermal control of the area’s hot springs collectively, beginning with variations in hydrochemistry and isotopic composition across all hot springs. The results show that the ice and snow meltwater from the Elashan Mountains is the water source for all the hot springs in the area, and its heat source is dominated by the normal heating of the crust, and no contribution of mantle-source heat is detected. Ice and snow meltwater infiltrated along the fractures and formed a deep geothermal reservoir by deep circulation heating. The chemical components of the hot springs’ water display a certain regularity in the plane, and away from the main fault, their main ionic components, TDS, water temperature, etc. have a tendency to increase by degrees, reflecting the controlling effect of the Wahongshan-Wenquan Fracture on the hydrothermal conditions in the area. However, most of the hot springs are located in areas that are rarely visited by people, and it is difficult to develop and utilize them. Based on the understanding of this research, it is important to systematically carry out the distribution and characterization of different levels of fractures in the region, as well as determine the target area of geothermal development potential in the concentrated population zones, which is the focus and difficulty of future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and T.L.; methodology, W.L.; software, T.L.; validation, R.L., W.X. and W.L.; formal analysis, T.L.; investigation, L.L.; resources, J.Z.; data curation, T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.; writing—review and editing, W.L.; visualization, L.L.; supervision, J.Z.; project administration, R.L.; funding acquisition, W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (grant no. 2021YFB1507401), the Clean Energy Minerals Special Project of Qinghai Provincial Department of Natural Resources (no. 2022013004qj004), and the Geological Survey Project of China Geological Survey (no. DD20221676, no. DD20230019).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liao, Z. Thermal Springs and Geothermal Energy in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and the Surroundings; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lin, W. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wen, H.; Hao, Y. Geochemical evidence for the nonexistence of supercritical geothermal fluids at the Yangbajing geothermal field, southern Tibet. J. Hydrol. 2021, 604, 127243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X. Hot spring gas geochemical characteristics and geological implications of the northern Yadong-Gulu Rift in the Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 863559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Tian, J.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Qiu, G.; Du, F.; Zhang, X.; et al. Hydrogeochemical Study of Hot Springs along the Tingri—Nyima Rift: Relationship between Fluids and Earthquakes. Water 2023, 15, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y. Magma chamber and crustal channel flow structures in the Tengchong volcano area from 3-D MT inversion at the intracontinental block boundary southeast of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 11112–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Guan, L.; Takahata, N.; Sano, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. First estimates of hydrothermal helium fluxes in continental collision settings: Insights from the Southeast Tibetan Plateau margin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Cui, Y.; Du, J. Gas geochemistry of the hot spring in the Litang fault zone, Southeast Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 79, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C.; Xing, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, W. Genesis of geothermal fluid in typical geothermal fields in western Sichuan, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Pang, Z.; Liao, D.; Zhou, X. Fluid geochemistry and its implications on the role of deep faults in the genesis of high temperature systems in the eastern edge of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 131, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Geothermal Springs in the Aba Area, Western Sichuan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Chen, S. Geothermal-type lithium resources in southern Xizang, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Li, J.; Dong, J.; Tian, J.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, F. Relationship between hydrogeochemical characteristics of hot springs and seismic activity in the Jinshajiang fault zone, Southeast Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1015134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Wei, S.; Yue, C.; Jiang, G.; Liao, Y. Geothermal anomalies in the Xianshuihe area: Implications for tunnel construction along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway, China. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, G.; Shao, J.; Gan, H.; Tan, X. Distribution and exploration of hot dry rock resources in China: Progress and inspiration. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, G.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Hu, S. Terrestrial heat flow and crustal thermal structure of the Gonghe-Guide area, northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Geothermics 2018, 72, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tian, C.; Cai, J.; Tang, B. Occurrence geological characteristitics and development potential of hot dry rocks in Qinghai Gonghe basin. J. Geomech. 2019, 25, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Gu, P.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, G. Research on relationship between the deep structure and geothermal resource distribution in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Geol. China 2021, 48, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, L.; Gan, H.; Tan, X. Heat aggregation mechanisms of Hot Dry Rocks resources in the Gonghe Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Song, X.; Li, G.; Xu, R.; Cao, W.; Zhao, C. Multi-objective optimization of geothermal extraction from the Enhanced Geothermal System in Qiabuqia geothermal field, Gonghe Basin. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 1844–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wen, D.; Wang, G.; Yan, W.; Wang, W.; Ye, C.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Tan, X.; Weng, W.; et al. The first power generation test of hot dry rock resources exploration and production demonstration project in the Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province, China. China Geol. 2022, 5, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, G.; Gan, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yue, G.; Long, X. Heat source model for Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) under different geological conditions in China. Gondwana Res. 2023, 122, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Xian, C. Permeability measurement of the fracture-matrix system with 3D embedded discrete fracture model. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Xian, C.; Tsau, J.; Zuo, X.; Jia, W. Status and outlook of oil field chemistry-assisted analysis during the energy transition period. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 12917–12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Liu, M.; Luo, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; Guo, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, C. Hydrogeochemical processes occurring in the hydrothermal systems of the Gonghe–Guide basin, northwestern China: Critical insights from a principal components analysis (PCA). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, B.; Su, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Geochemical characteristics of geothermal fluids and water-rock interaction in geothermal reservoirs in and around the Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 27, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qin, X.; Ren, E.; Feng, N.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Li, G.; Jiang, Z. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the geothermal waters from the Reshui area, Dulan of Qinghai, China. Water 2023, 15, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lin, W.; Liu, F.; Gan, H.; Wang, S.; Yue, G.; Long, X.; Liu, Y. Theory and survey practice of deep heat accumulation in geothermal system and exploration practice. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A. Tectonic and Structural Controls on Geothermal Systems. In Geological and Geo-Environmental Processes on Earth; Shandilya, A.K., Singh, V.K., Bhatt, S.C., Dubey, C.S., Eds.; Springer Natural Hazards; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, I.C.; Rowland, J.V.; Dempsey, D. The relationship between geothermal fluid flow and geologic context: A global review. Geotherm. Resour. Counc. Trans. 2018, 42, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixner, J.; Schill, E.; Grimmer, J.C.; Gaucher, E.; Kohl, T.; Klingler, P. Structural control of geothermal reservoirs in extensional tectonic settings: An example from the Upper Rhine Graben. J. Struct. Geol. 2016, 82, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwiquet, H.; Guillou-Frottier, L.; Arbaret, L.; Magri, F.; Guillon, T.; Bellanger, M.; Lopez, S.; Penhoët, E.; Heap, M.J. Crustal Fault Zones as underexploited geothermal resources: Contribution of numerical modelling and comparison with natural systems. In Proceedings of the 47th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford, CA, USA, 7–9 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.E.; Muffler, L.J.P.; Truesdell, A.H. Vapor-dominated hydrothermal systems compared with hot-water systems. Econ. Geol. 1971, 66, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, P.; Liu, B.; Gan, W.; Mao, F.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Guo, H. Geometrical imagery and tectonic transformation of Late Quaternary active tectonics in northeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin. 2004, 78, 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, D.; Hao, L.; Kong, Z. The geothermal formation mechanism in the Gonghe Basin: Discussion and analysis from the geological background. China Geol. 2018, 1, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X. The relationship between the copper polymetallic mineral sources and Indosinian igneous rocks in Elashan area, Qinghai Province. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2014, 88, 952–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Y. Source parameters of the Gonghe, Qinghai Province, China, earthquake from inversion of digital broadband waveform data. Acta Seimol. Sin. 1997, 10, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 8538-2008; Methods for Examination of Drinking Natural Mineral Water. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.C.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, V.S.; Saxena, V.K. Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Li, L. The variation characteristics of δ18O and δD in precipitation and river water, Qinghai Lake Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 1552–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Isotope Hydrology—Learning, Teaching and Applying Isotope Techniques in Hydrology; Non-Serial Publications; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Xie, E.; Dor, J.; Jin, J.; Hu, X.; Du, S.; Yao, Z. Geochemical charact eristics of geothermal gases and their geological implications in Tibet. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2002, 18, 539–550. [Google Scholar]
- Giggenbach, W.F. The composition of gases in geothermal and volcanic systems as a function of tectonic setting. Proc.—Int. Symp. Water-Rock Interact. 1992, 7, 873–878. Available online: https://eurekamag.com/research/020/306/020306849.php (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Giggenbach, W.F.; Glover, R.B. Tectonic regime and major processes governing the chemistry of water and gas discharges from the rotorua geothermal field, New Zealand. Geothermics 1992, 21, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Isotopic and Chemical Techniques in Geothermal Exploration, Development and Use: Sampling Methods, Data Handling, Interpretation—Edited by Stefán Arnórsson; Non-Serial Publications; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Qian, H. The Broadband Seismicexploration as Well as the Crust upper Mantle Structure in the Orogenic Plateau, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Itsadjacent Area; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jia, X.; Li, S.; Fu, L.; Gao, L.; Xin, H. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric imaging of the geothermal system beneath the Gonghe Basin, Northeast Tibetan Plateau. Geothermics 2018, 76, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric imaging of the SE Gonghe Basin: Implication for the orogenic uplift in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau. Tectonophysics 2020, 789, 228525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, S.; Song, R.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, G.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z. Genesis of the hot dry rock gethermal resoureces in the Gonghe basin: Constraints from the radiogenic heat production rate of rocks. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Tang, H. Crustal structure and geothermal mechanism of the Gonghe-Guide Basin based on EIGEN-6C4 satellite gravity and aeromagnetic data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 2735–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Wakita, H. Geographical distribution of 3He/4He ratios in Japan: Implications for arc tectonics and incipient magmatism. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 8729–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchkov, A.D.; Rychkova, K.M.; Lebedev, V.I.; Kamenskii, I.L.; Sokolova, L.S. Estimation of heat flow in Tuva from data on helium isotopes in thermal mineral springs. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2010, 51, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Tominaga, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Wakita, H. 3He/4He ratios of methane-rich natural gases in Japan. Geochem. J. 1982, 16, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.; Spycher, N. Calculation of pH and mineral equilibria in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 48, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Reed, M. Theoretical chemical thermometry on geothermal waters: Problems and methods. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liao, Z.; Liu, S. Geothermal in Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 1–300. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).