Fault-Tolerant Direct Torque Control of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Single Open-Phase Fault Based on Virtual Vectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Voltage Vectors Distribution of Five-Phase PMSM
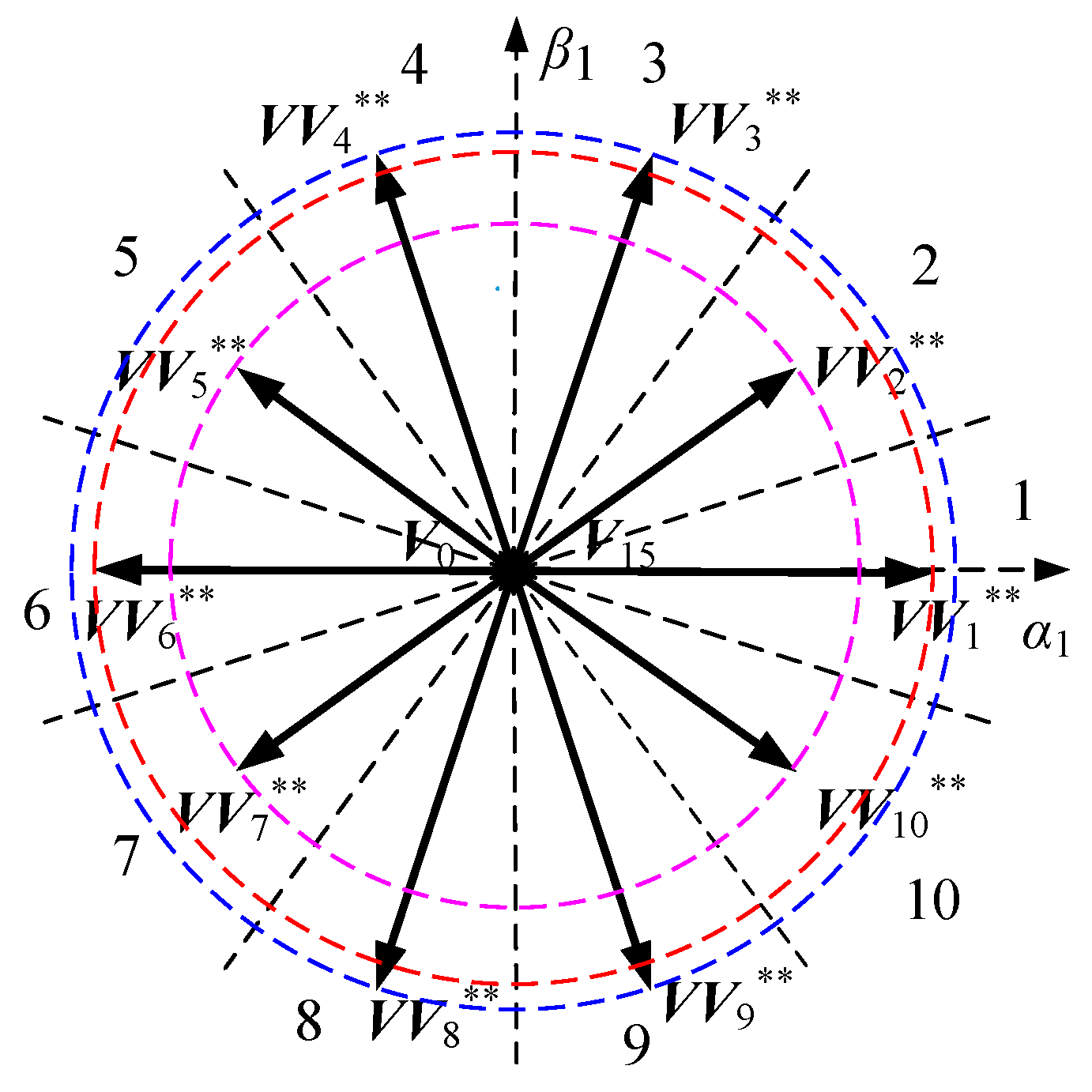
2.1. Voltage Vectors Distribution in the Healthy Operation
2.2. Voltage Vectors Distribution under the Single Open-Phase Fault
3. The DTC Strategy Based on Virtual Voltage Vectors in Healthy Operation
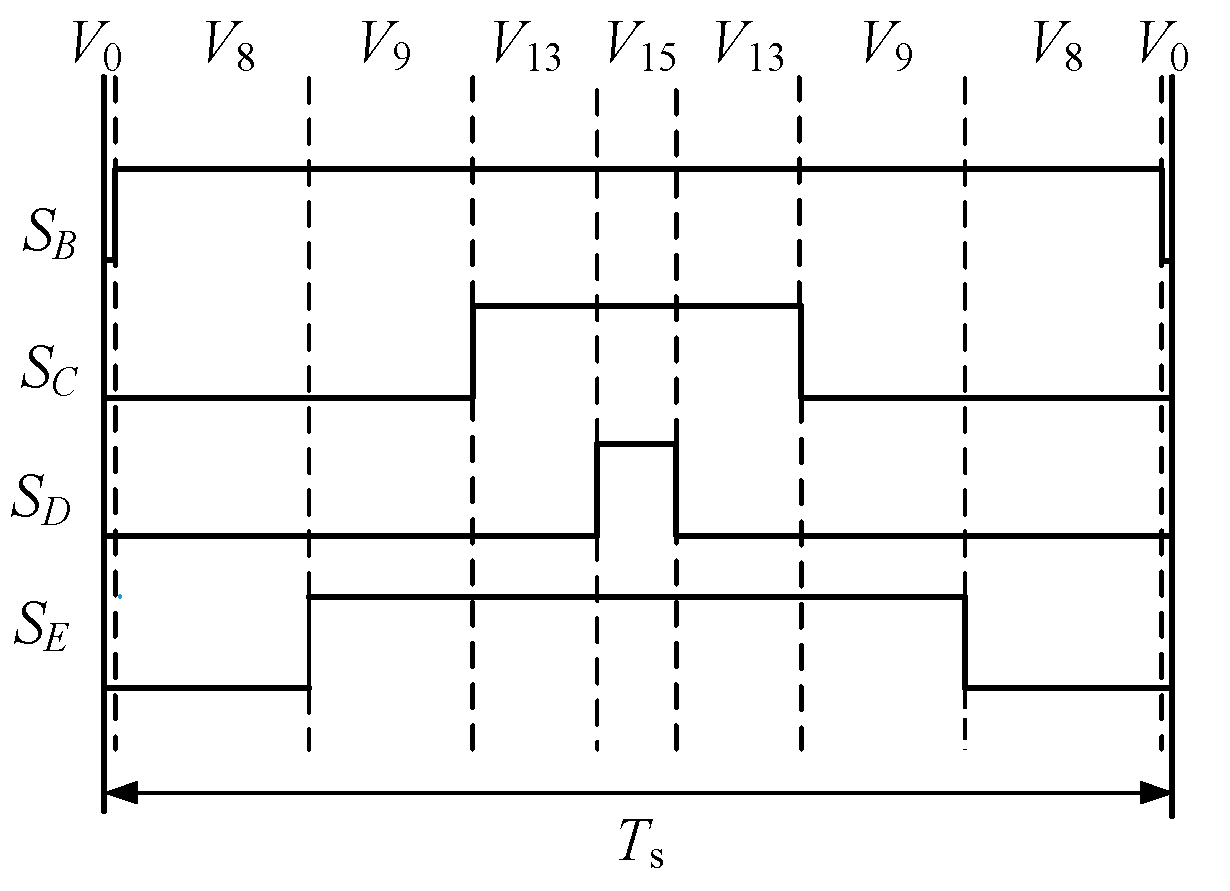
4. Indirect Correction Method of Virtual Vectors with Single Open-Phase Fault
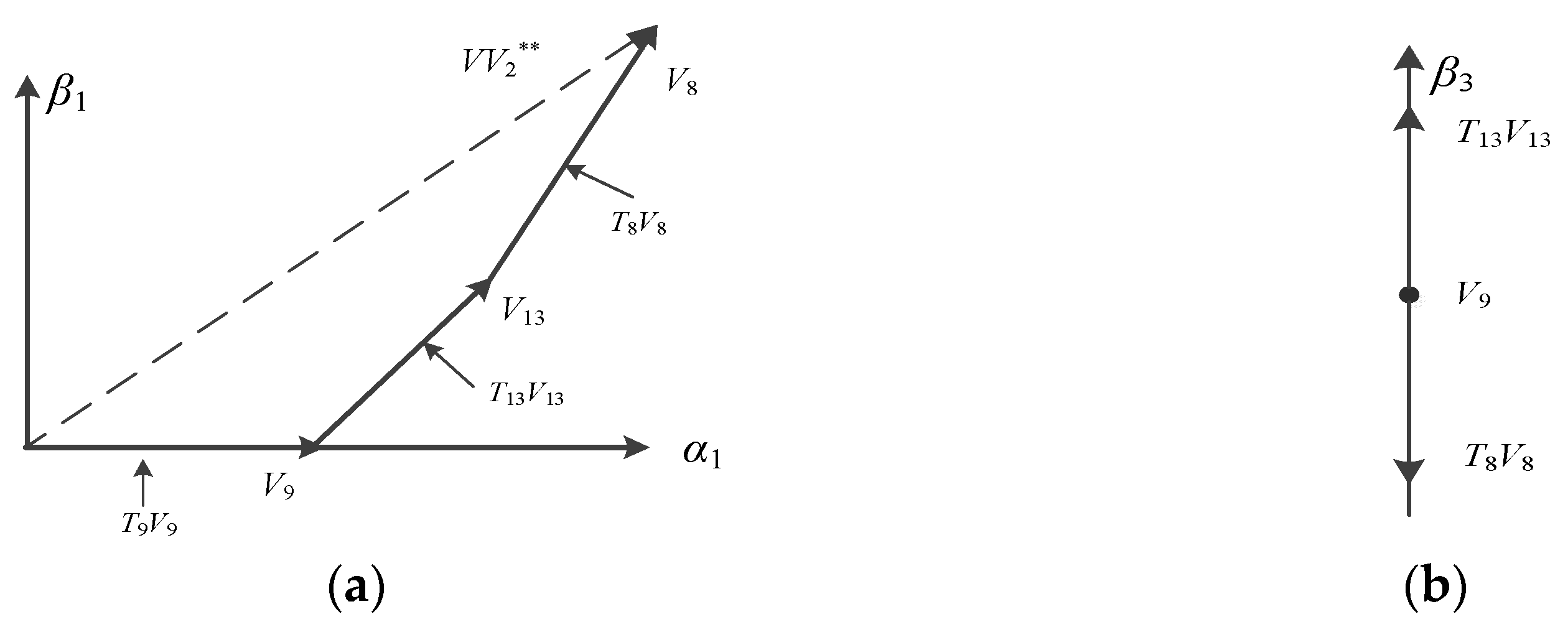
4.1. Equal-Amplitude Virtual Vectors
4.2. Maximum Amplitude Virtual Vectors
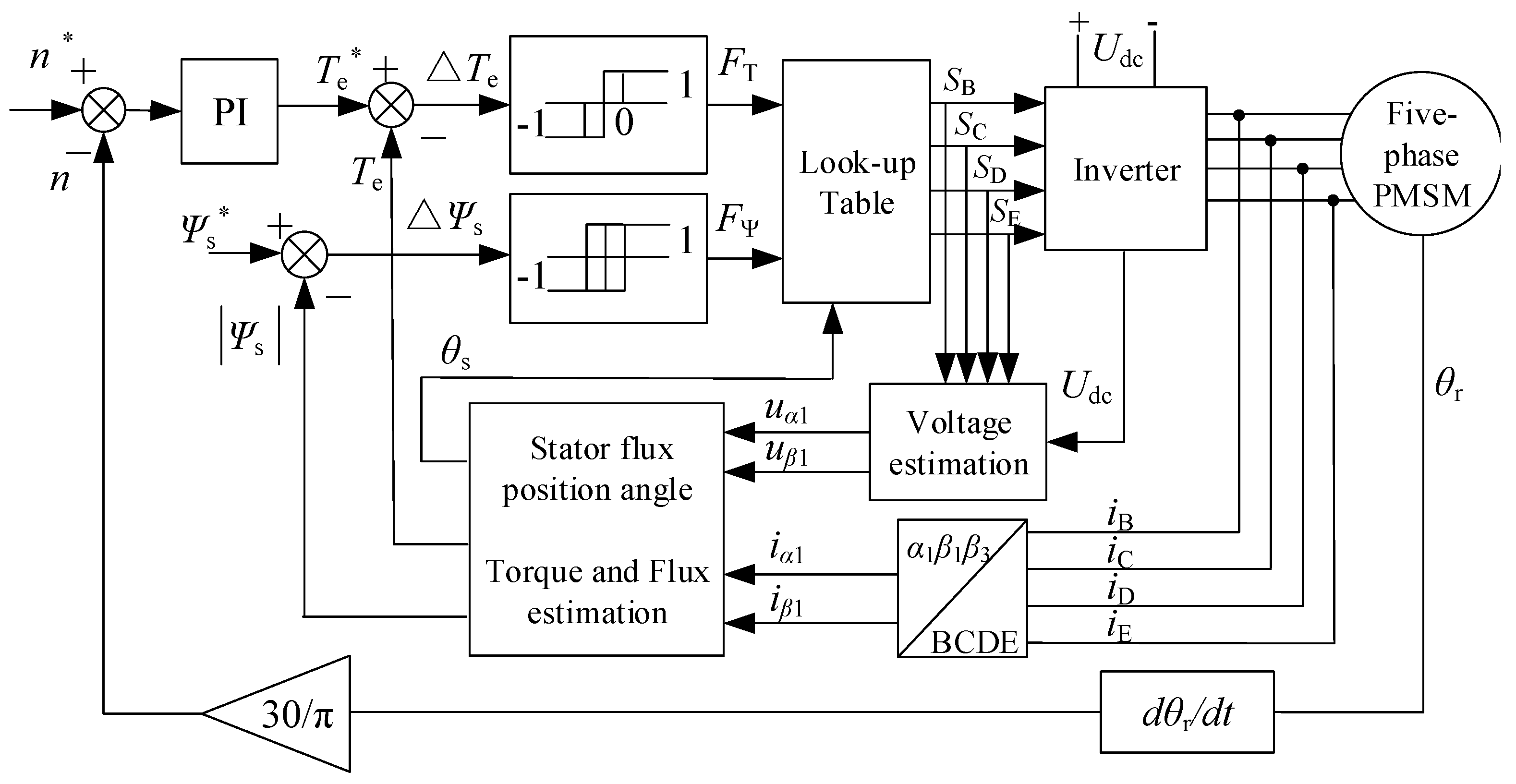
4.3. Implementation of the Proposed Fault-Tolerant Direct Torque Control Strategy
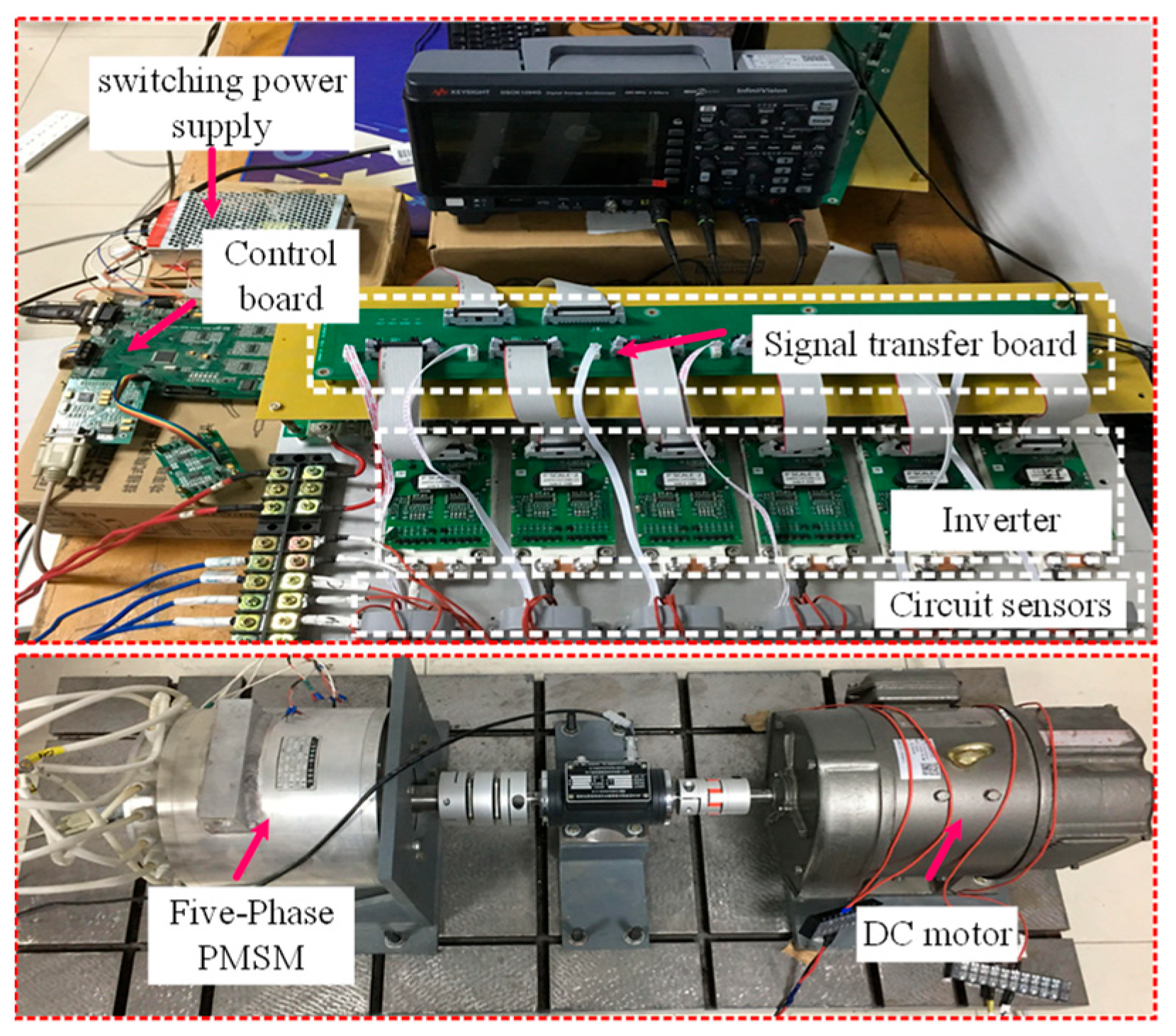
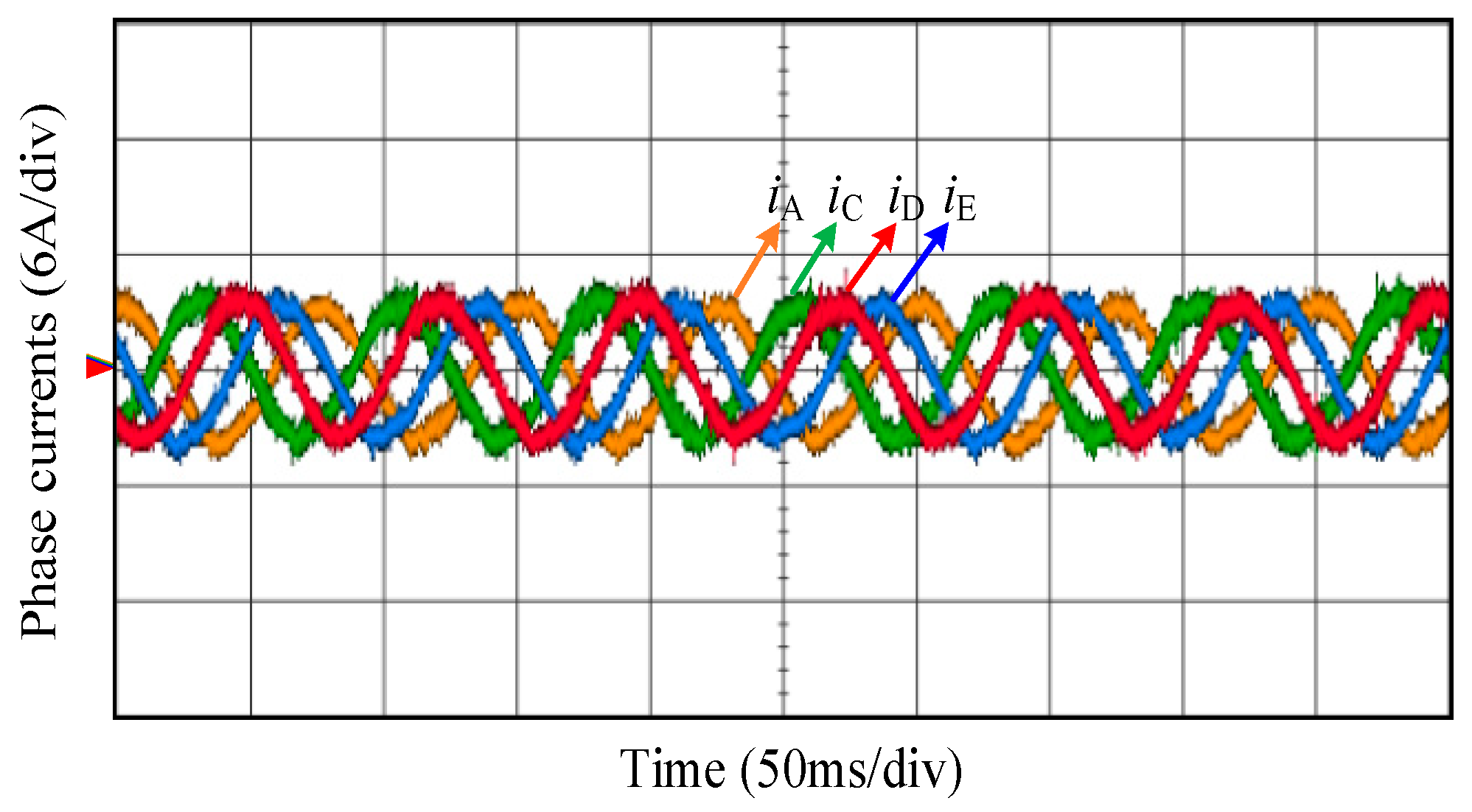
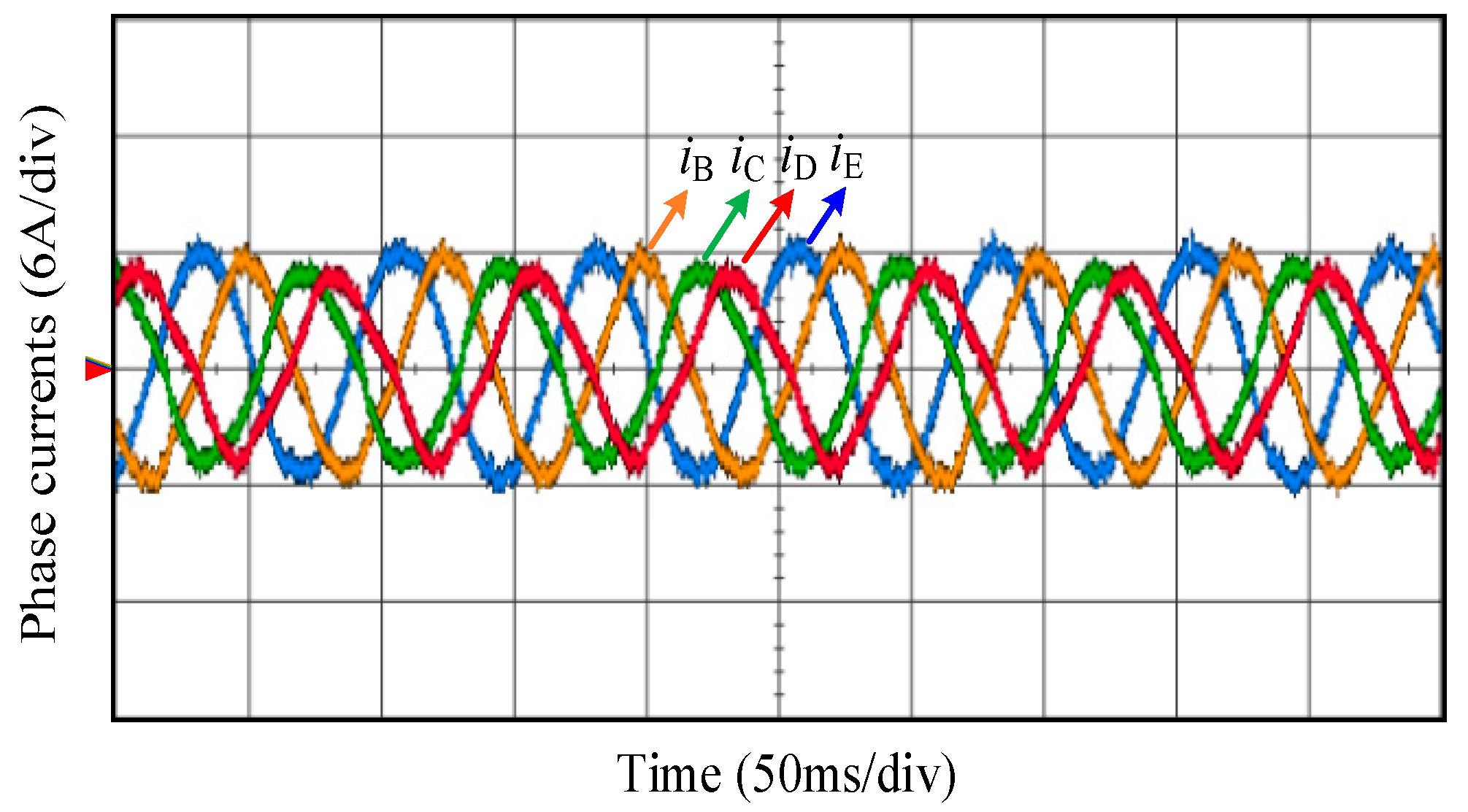
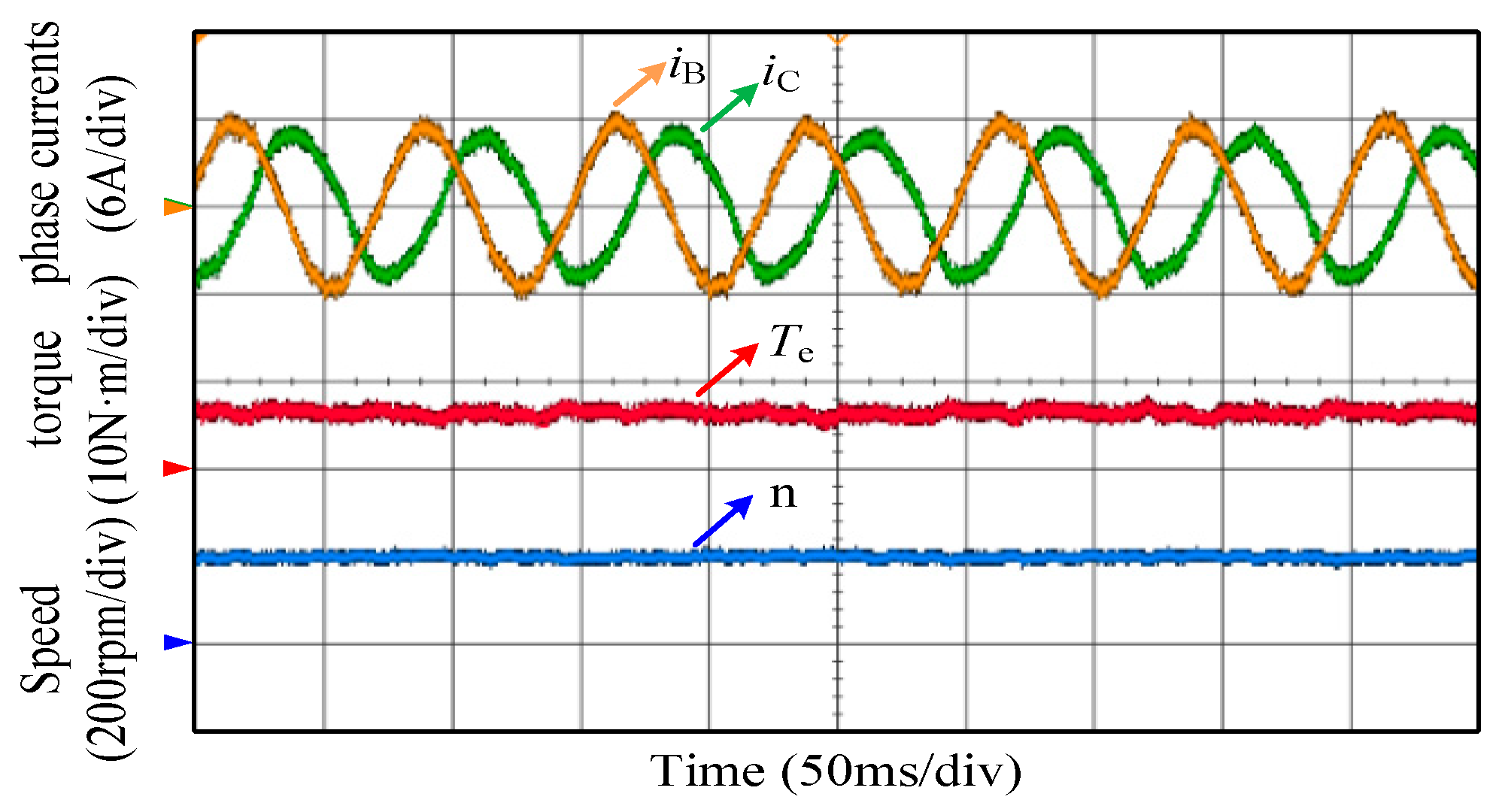
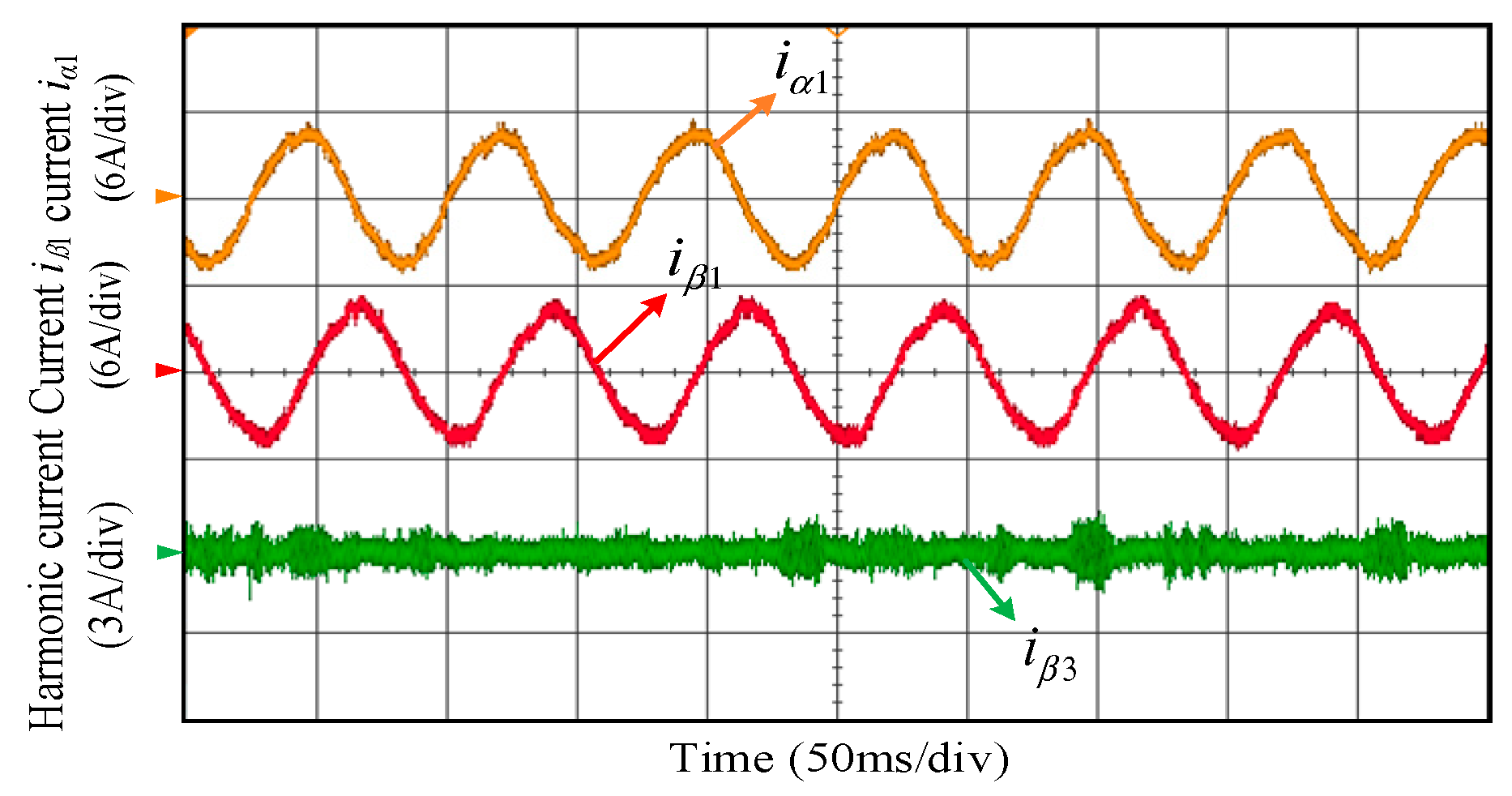
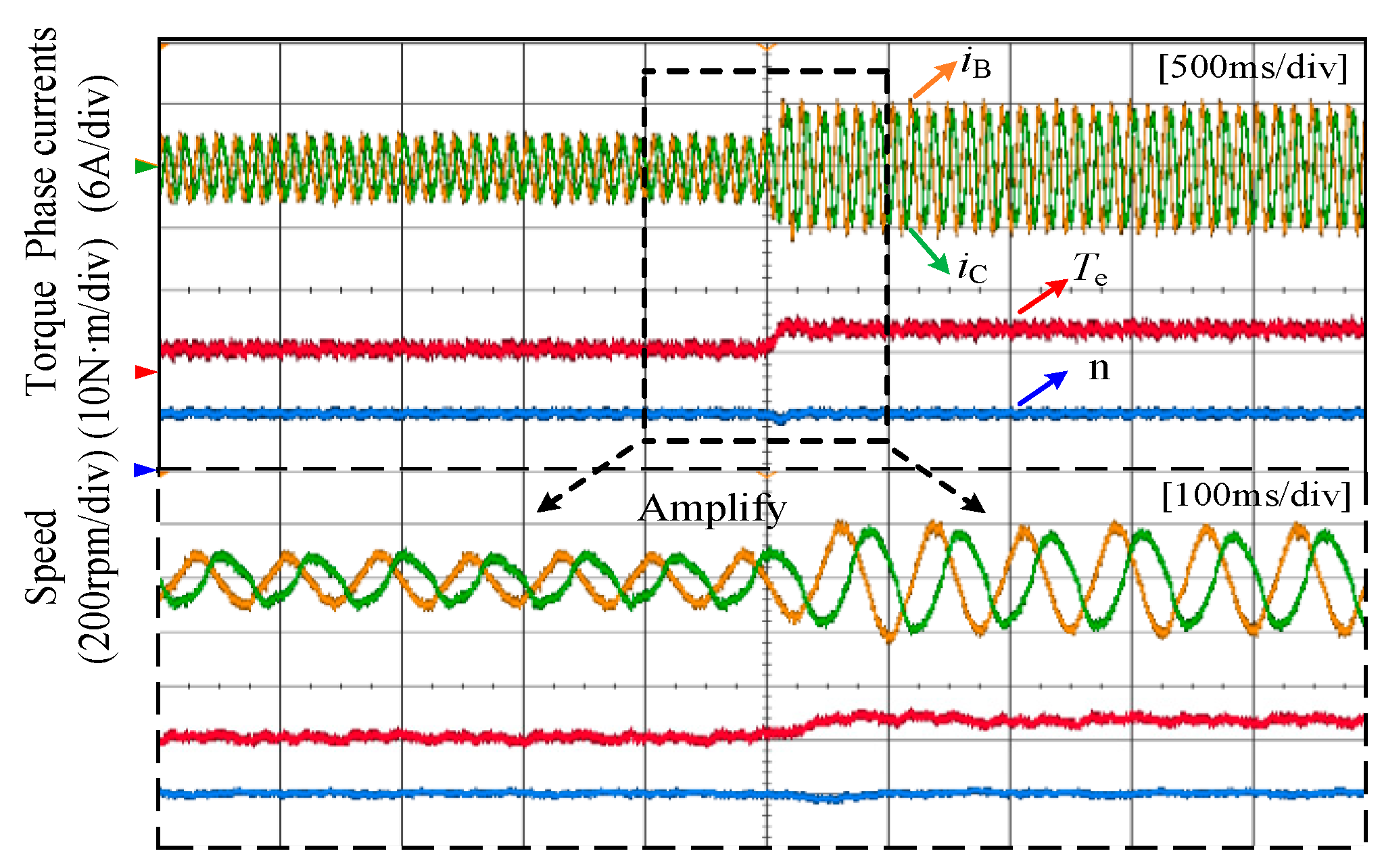
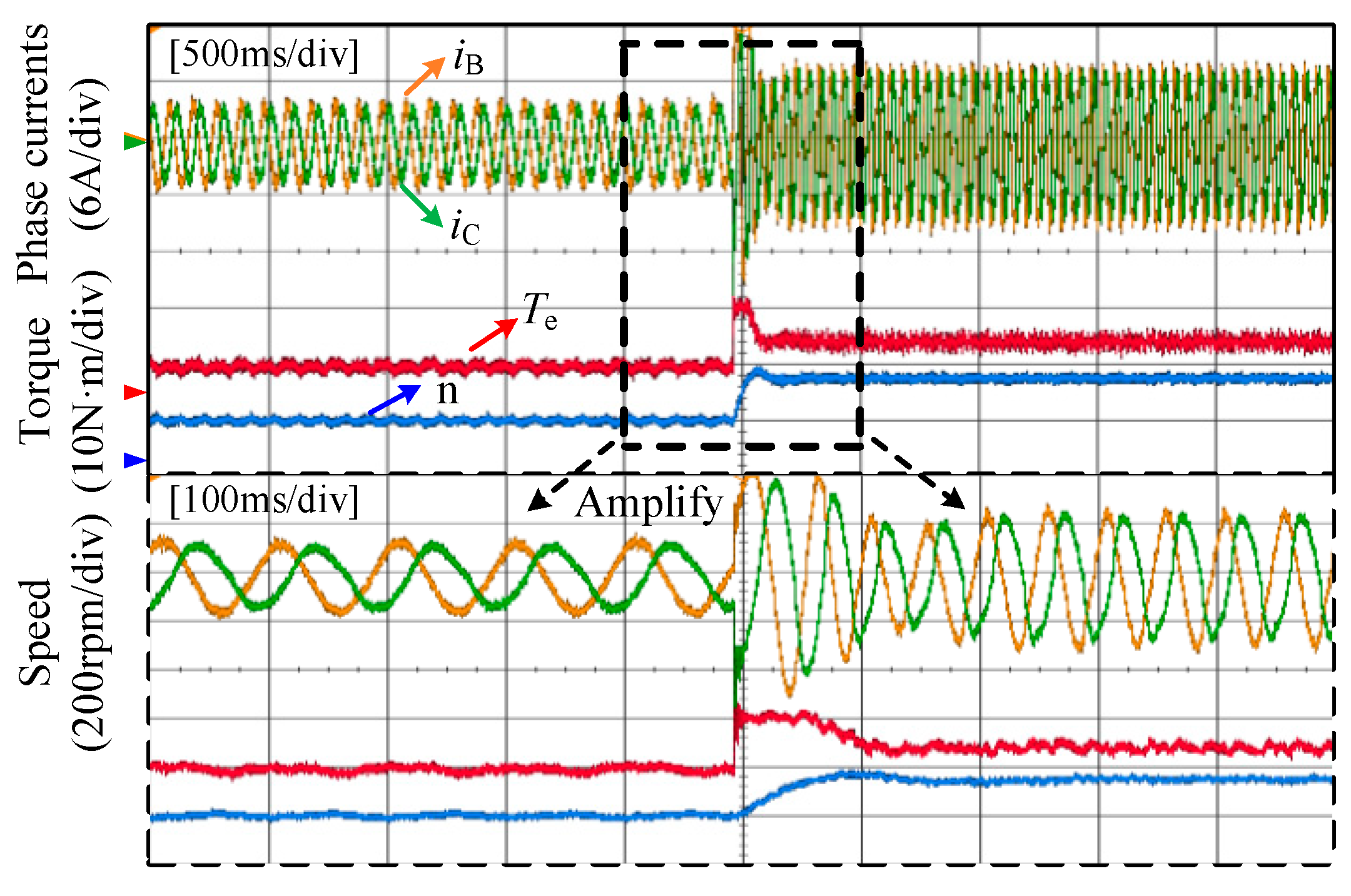
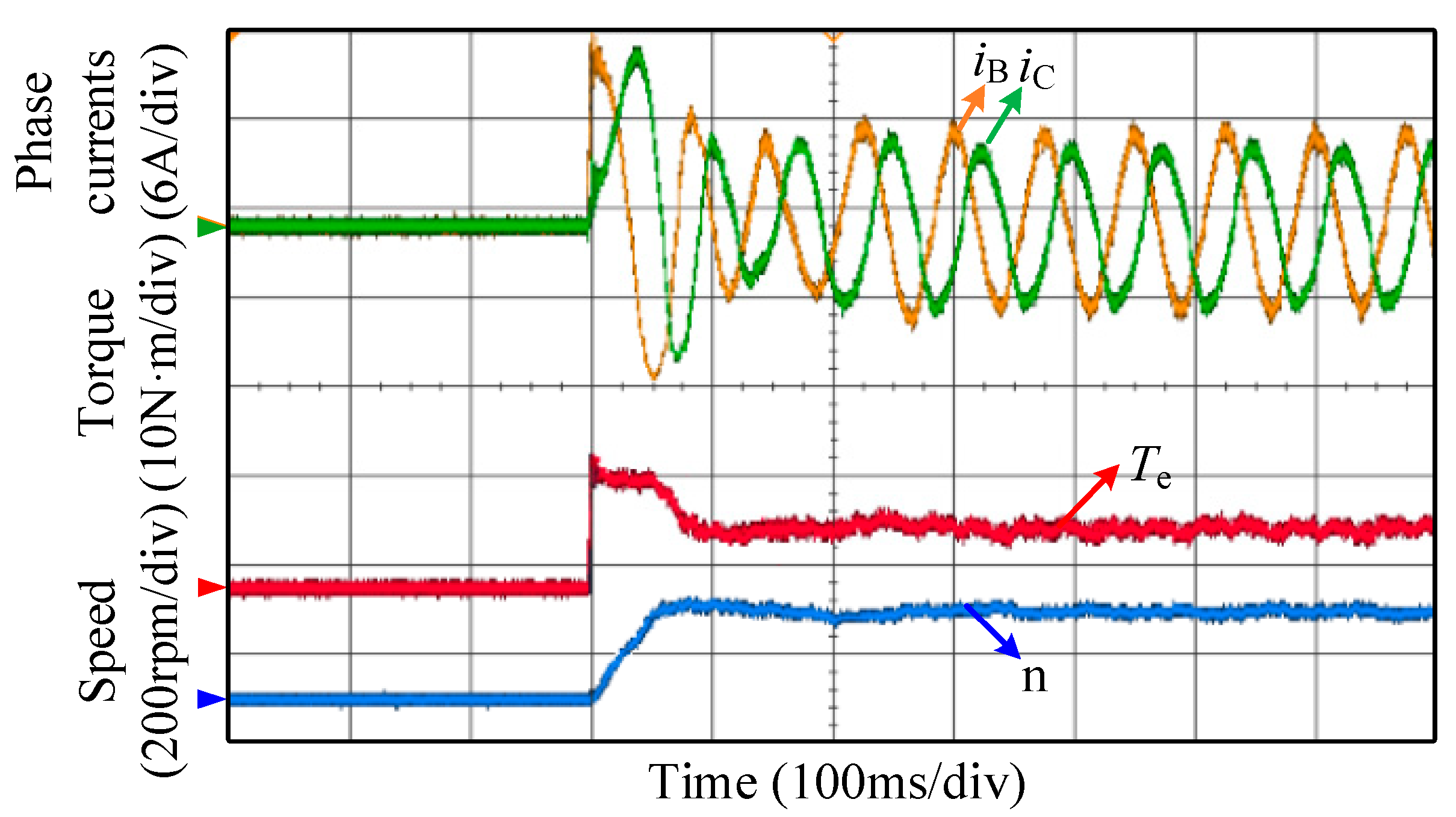
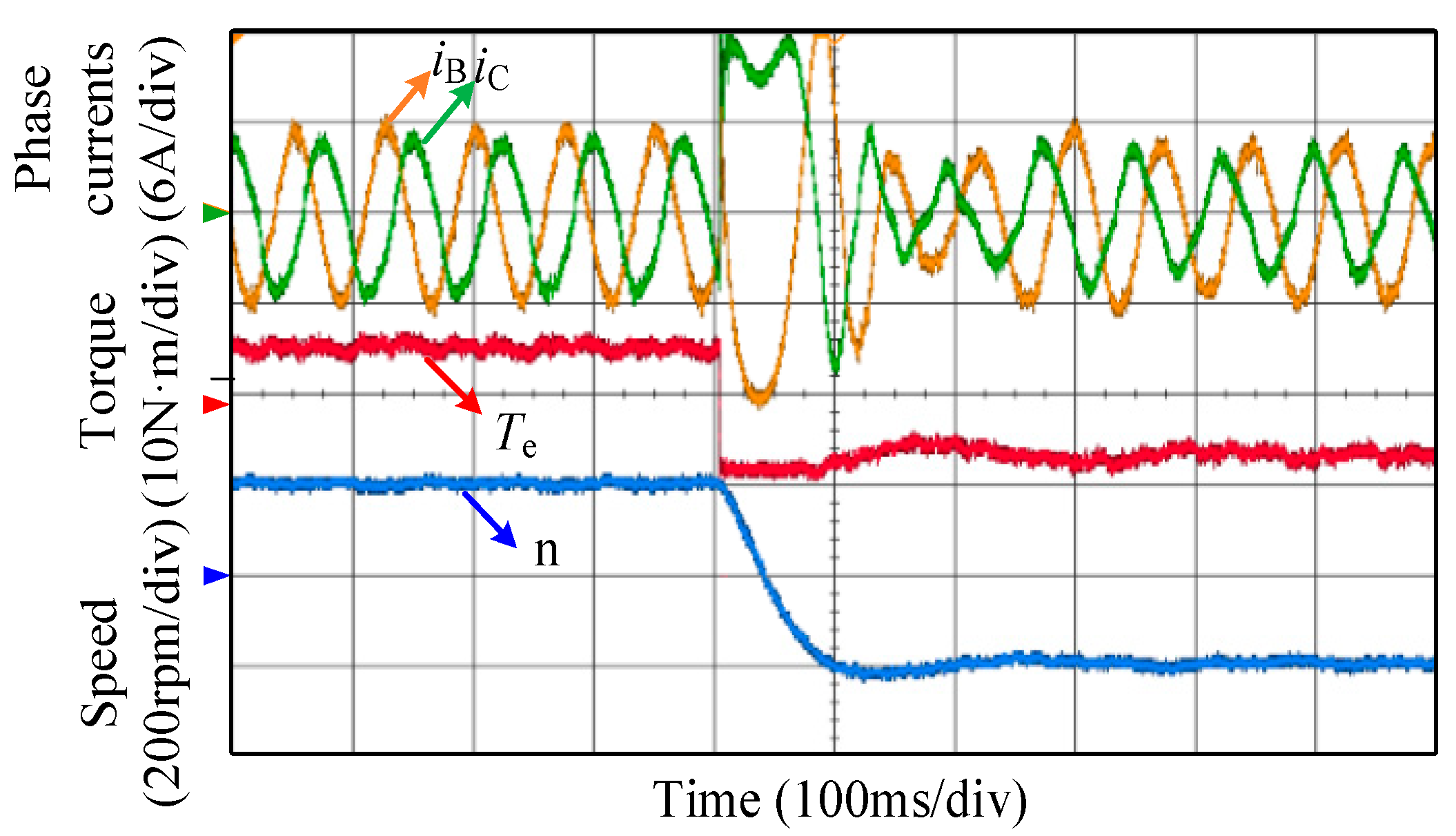
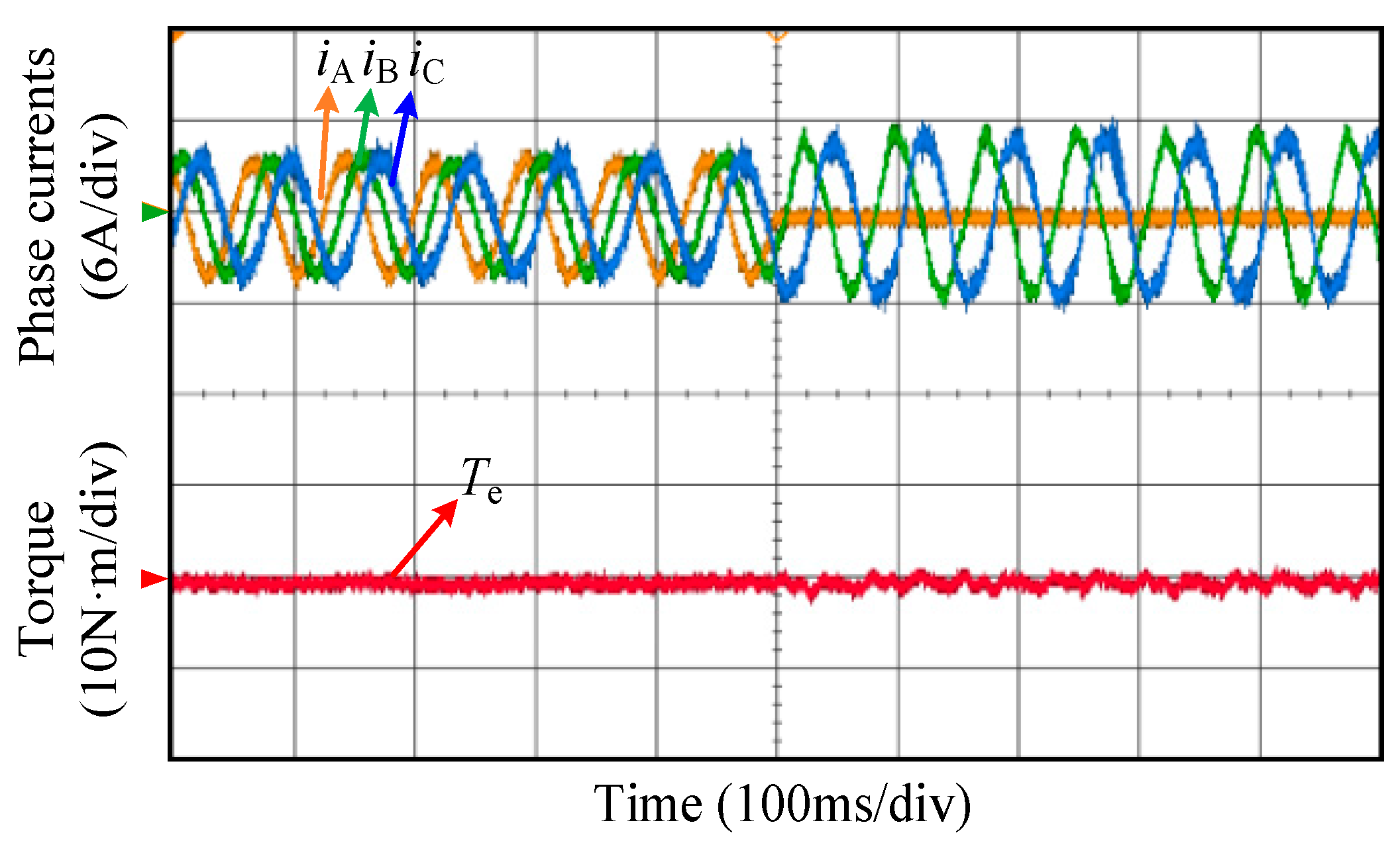
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levi, E. Advances in converter control and innovative exploitation of additional degrees of freedom for multiphase machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, F.; Duran, M.J. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines—Part 1. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.; Barrero, F. Recent advances in the design, modeling and control of multiphase machines—Part 2. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikha, M.A.; Croonen, J.; Deepak, K.; Benômar, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O. Multiphase Motors and Drive Systems for Electric Vehicle Powertrains: State of the Art Analysis and Future Trends. Energies 2023, 16, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalem, Y.; Abbassi, A.; Abbassi, R.; Jerbi, H.; Alturki, M.; Albaker, A.; Kouzou, A.; Abdelkrim, M. Speed tracking control design of a five-phase PMSM-based electric vehicle: A backstepping active fault-tolerant approach. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 2155–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehifar, M.; Arashloo, R.S.; Moreno-Eguilaz, J.M.; Sala, V.; Romeral, L. Observer-based open transistor fault diagnosis and fault tolerant control of five-phase permanent magnet motor drive for application in electric vehicles. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, M.; Nguyen, N.K.; Semail, E. Real-time switches fault diagnosis based on typical operating characteristics of five-phase permanent magnetic synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4683–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qu, L.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Q.; Xie, Y. Comparison of Two SVPWM Control Strategies of Five-Phase Fault-Tolerant Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6621–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Su, J. Unified Fault-tolerant Control Strategy with Torque Ripple Compensation for Five-phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Normal Decoupling. Energies 2019, 12, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.G.; Duran, M.J.; Garcia-Entrambasaguas, P.; Bermudez, M. Field-Oriented Control of Multiphase Drives with Passive Fault Tolerance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 7228–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Lu, R.; Hu, J. Single Line/Phase Open Fault-Tolerant Decoupling Control of a Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Different Stator Connections. Energies 2022, 15, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Song, C.; Chen, Q. FCS-MPC-Based Fault-Tolerant Control of Five-Phase IPMSM for MTPA Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 2882–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Prieto, I.; Duran, M.J.; Aciego, J.J.; Martin, C.; Barrero, F. Model predictive control of six-phase induction motor drives using virtual voltage vectors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Levi, E.; Jones, M.; Rahim, N.A.; Hew, W.P. FCS-MPC based current control of a five-phase induction motor and its comparison with PI-PWM control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, C. A simplified model predictive control for a dual three-phase PMSM with reduced harmonic currents. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9079–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, X.; Cheng, M. A fault-tolerant direct torque control for six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor with arbitrary two opened phases based on modified variables. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, J.K.; Aware, M.V.; Nemade, R.V.; Levi, E. Direct torque control scheme for a six-phase induction motor with reduced torque ripple. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 7118–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Fletcher, J.E.; Williams, B.W.; He, X. A novel direct torque control scheme for a sensorless five-phase induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Reduction of Both Harmonic Current and Torque Ripple for Dual Three-Phase Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Modified Switching-Table-Based Direct Torque Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6671–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.; Gonzalez-Prieto, I.; Barrero, F.; Guzman, H.; Duran, M.J.; Kestelyn, X. Open-phase fault-tolerant direct torque control technique for five-phase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Du, Q.; Zhang, M.; Song, C.; Zhang, M. A Fault Tolerant Control Strategy and Simulation Analysis of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Motors with Third-Harmonic Suppression. J. Xi’an Jiao Tong Univ. 2020, 54, 95–102+136. [Google Scholar]
- Payami, S.; Behera, R.K. An Improved DTC Technique for Low-Speed Operation of a Five-Phase Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.; Gonzalez-Prieto, I.; Barrero, F.; Guzman, H.; Kestelyn, X.; Duran, M.J. An Experimental Assessment of Open-Phase Fault-Tolerant Virtual-Vector-Based Direct Torque Control in Five-Phase Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikondra, B.; Muduli, U.R.; Behera, R.K. An Improved Open-Phase Fault-Tolerant DTC Technique for Five-Phase Induction Motor Drive Based on Virtual Vectors Assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 4598–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Qu, L.; Xu, G. Asymmetrical SVPWM Fault-Tolerant Control of Five-Phase PM Brushless Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Saeed, S.; Zhu, J. Enhanced Fault-Tolerant Model Predictive Current Control for a Five-Phase PM Motor with Continued Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 3236–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Xu, H.; Guan, T.; Zhou, P. A Constant Switching Frequency Multiple-Vector-Based Model Predictive Current Control of Five-Phase PMSM with Non-sinusoidal Back EMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
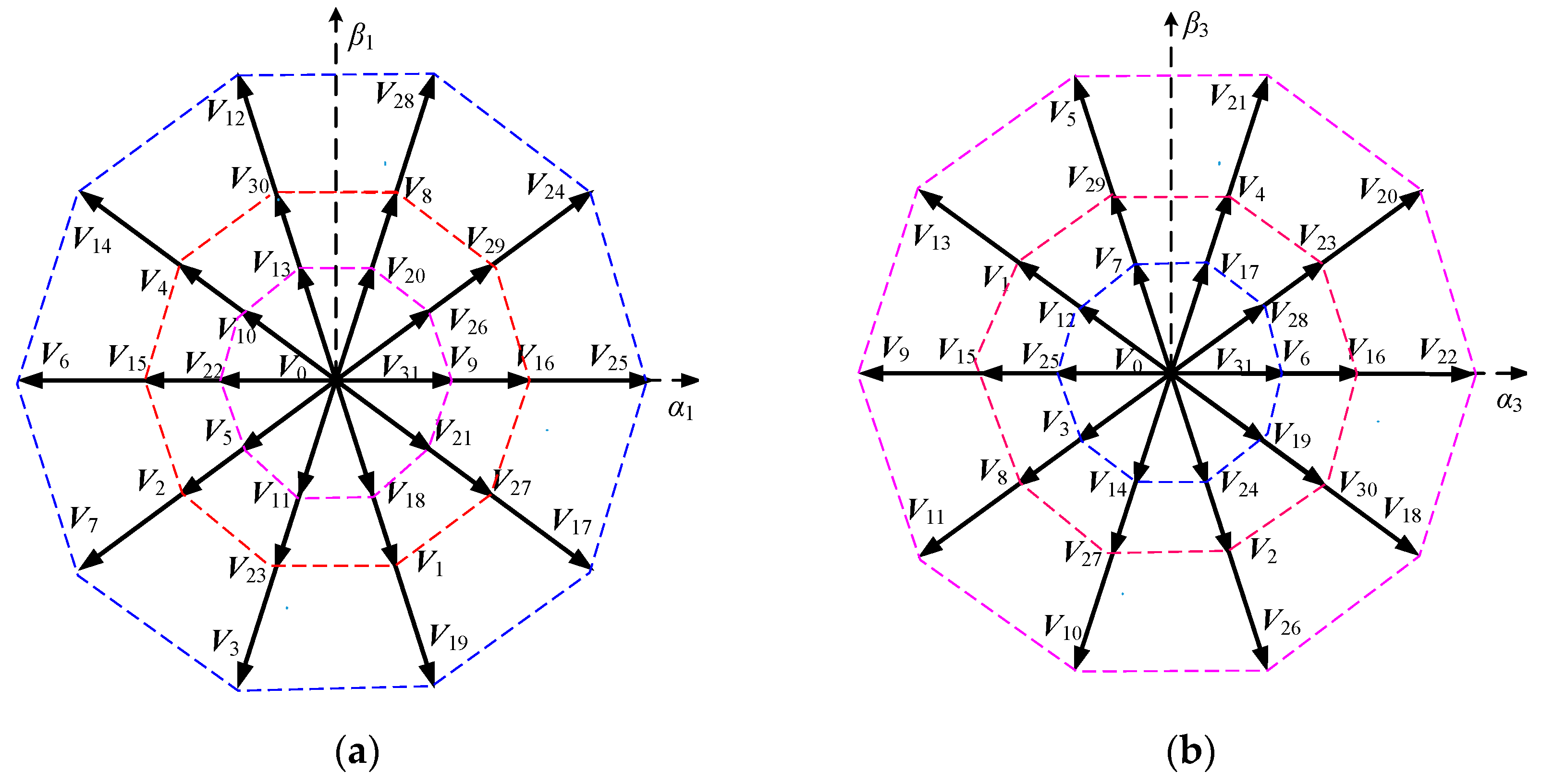
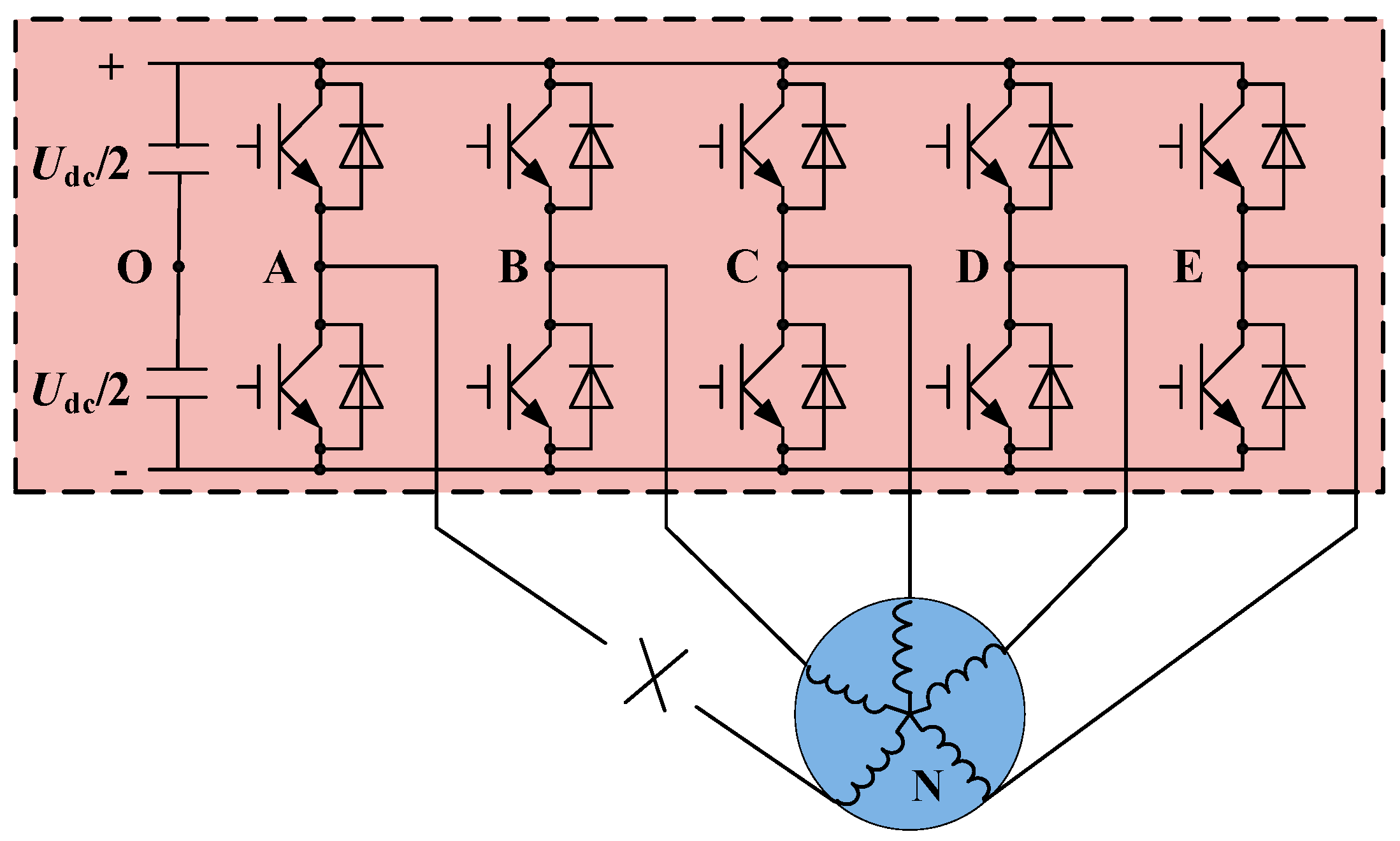

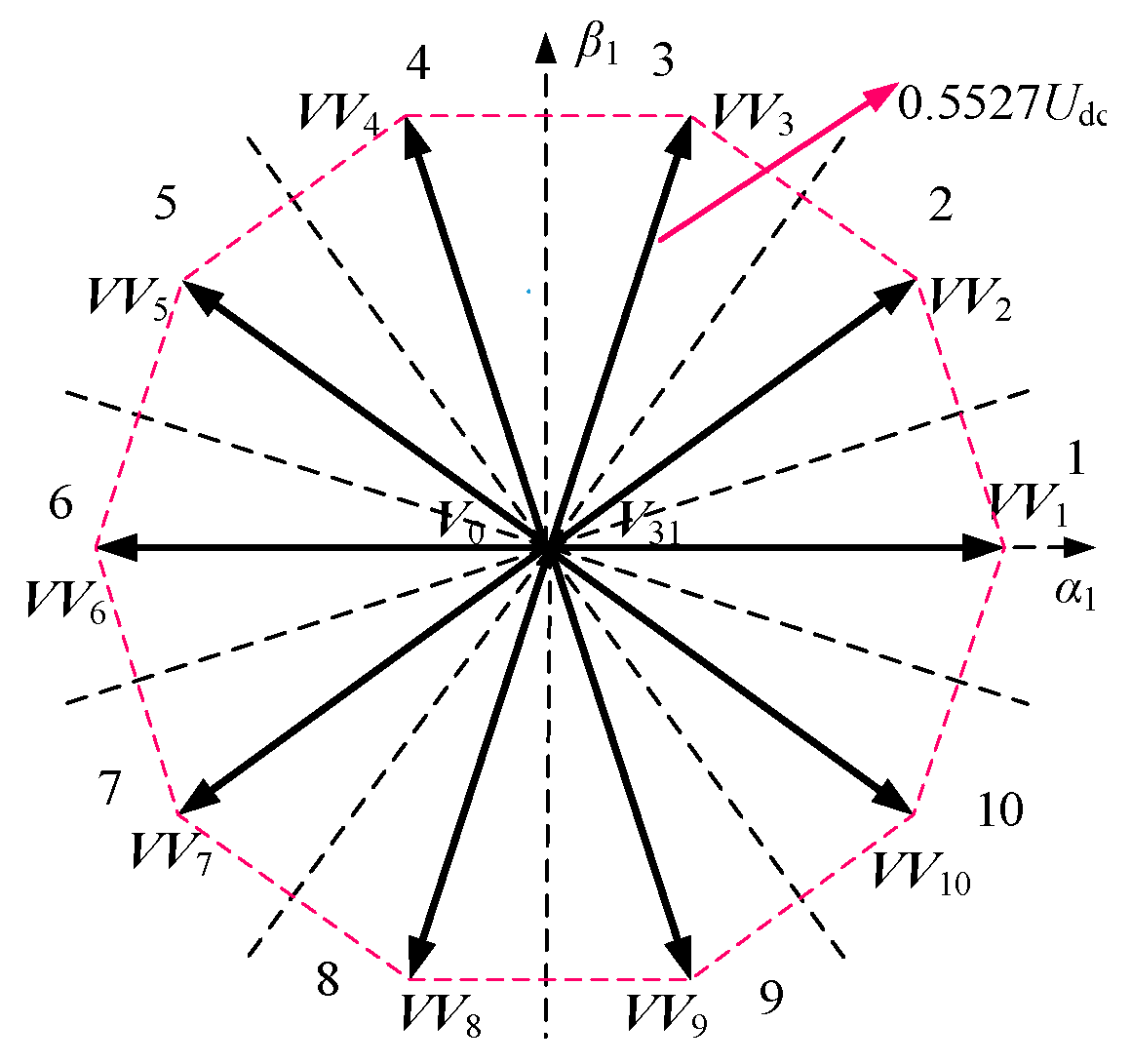
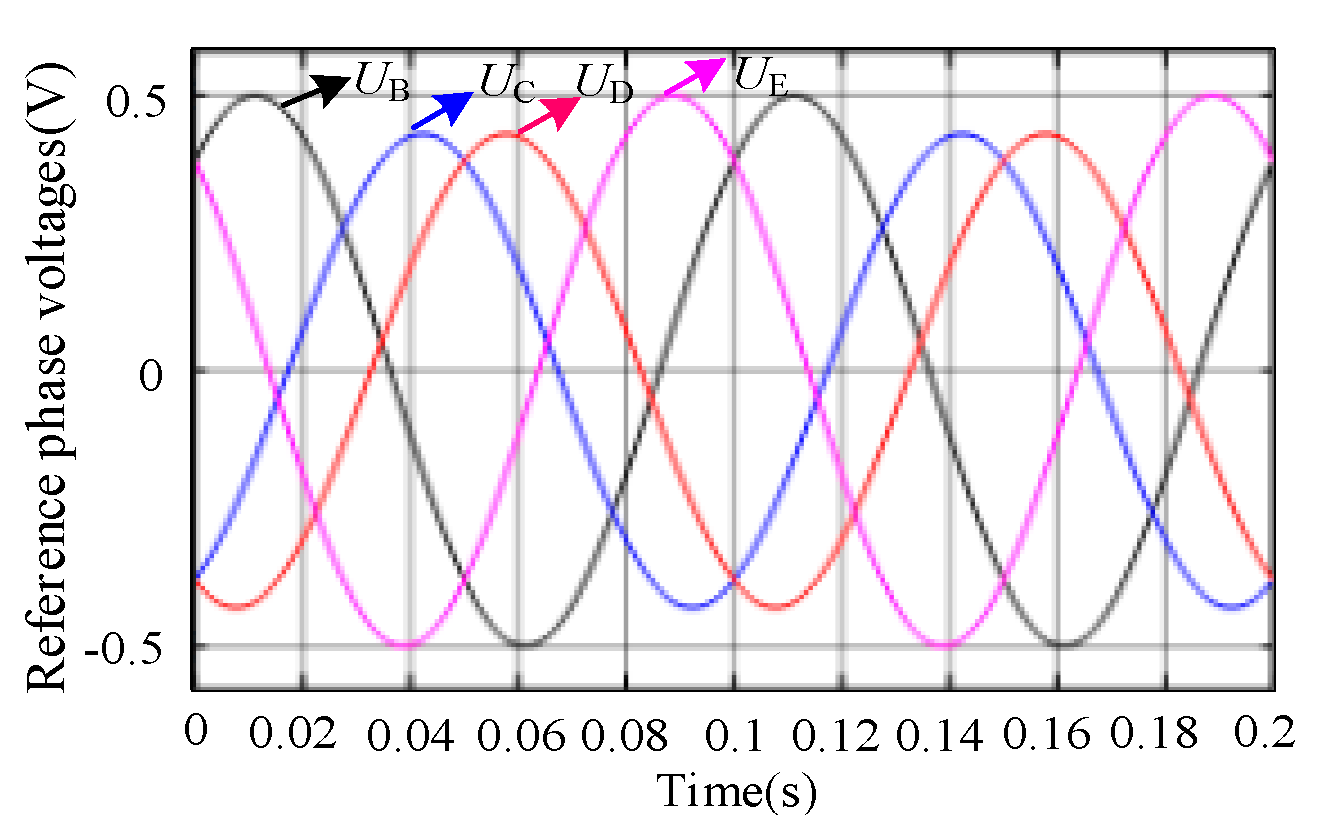

| Voltage Vectors | α1-β1 Subspace | β3 Pulse Subspace |
|---|---|---|
| V0 (0000) | 0∠0° | 0 |
| V1 (0001) | 0.4412Udc∠−59.55° | 0.2351Udc |
| V2 (0010) | 0.3245Udc∠−133.56° | −0.3804Udc |
| V3 (0011) | 0.6155Udc∠−90° | −0.1453Udc |
| V4 (0100) | 0.3245Udc∠133.56° | 0.3804Udc |
| V5 (0101) | 0.1453Udc∠−90° | 0.6155Udc |
| V6 (0110) | 0.4472Udc∠180° | 0 |
| V7 (0111) | 0.4412Udc∠120.45° | 0.2351Udc |
| V8 (1000) | 0.4412Udc∠59.55° | −0.2351Udc |
| V9 (1001) | 0.4472Udc∠0° | 0 |
| V10 (1010) | 0.1453Udc∠90° | −0.6155Udc |
| V11 (1011) | 0.3245Udc∠−46.44° | −0.3804Udc |
| V12 (1100) | 0.6155Udc∠90° | 0.1453Udc |
| V13 (1101) | 0.3245Udc∠46.44° | 0.3804Udc |
| V14 (1110) | 0.4412Udc∠120.45° | −0.2351Udc |
| V15 (1111) | 0∠0° | 0 |
| Fψ | FT | Sectors | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| 1 | 1 | VV3 | VV4 | VV5 | VV6 | VV7 | VV8 | VV9 | VV10 | VV1 | VV2 |
| −1 | VV9 | VV10 | VV1 | VV2 | VV3 | VV4 | VV5 | VV6 | VV7 | VV8 | |
| 0 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | |
| −1 | 1 | VV4 | VV5 | VV6 | VV7 | VV8 | VV9 | VV10 | VV1 | VV2 | VV3 |
| −1 | VV8 | VV9 | VV10 | VV1 | VV2 | VV3 | VV4 | VV5 | VV6 | VV7 | |
| 0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | V31 | V0 | |
| Virtual Vector | Voltage Vector and Its Proportion | Amplitude of the Virtual Vector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V0, V15 | V9 | 0.3406Udc | |||
| 0.2384 | 0.7616 | ||||
| V0, V15 | V8 | V9 | V13 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.0758 | 0.3808 | 0.3081 | 0.2353 | ||
| V0, V15 | V8 | V12 | V13 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.2662 | 0.3530 | 0.2631 | 0.1177 | ||
| V0, V15 | V4 | V12 | V14 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.2662 | 0.1177 | 0.2631 | 0.3530 | ||
| V0, V15 | V4 | V6 | V14 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.0758 | 0.2353 | 0.3081 | 0.3808 | ||
| V0, V15 | V6 | 0.3406Udc | |||
| 0.2384 | 0.7616 | ||||
| V0, V15 | V2 | V6 | V7 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.0758 | 0.2353 | 0.3081 | 0.3808 | ||
| V0, V15 | V2 | V3 | V7 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.2662 | 0.1177 | 0.2631 | 0.3530 | ||
| V0, V15 | V1 | V3 | V11 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.2662 | 0.3530 | 0.2631 | 0.1177 | ||
| V0, V15 | V1 | V9 | V11 | 0.3406Udc | |
| 0.0758 | 0.3808 | 0.3081 | 0.2353 | ||
| Virtual Vector | Voltage Vector and Its Proportion | The Maximum Amplitude of the Virtual Vector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V0, V15 | V9 | 0.4472Udc | |||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| V0, V15 | V8 | V9 | V13 | 0.3685Udc | |
| 0 | 0.4120 | 0.3334 | 0.2546 | ||
| V0, V15 | V8 | V12 | V13 | 0.4642Udc | |
| 0 | 0.4811 | 0.3585 | 0.1604 | ||
| V0, V15 | V4 | V12 | V14 | 0.4642Udc | |
| 0 | 0.1604 | 0.3585 | 0.4811 | ||
| V0, V15 | V4 | V6 | V14 | 0.3685Udc | |
| 0 | 0.2546 | 0.3334 | 0.4120 | ||
| V0, V15 | V6 | 0.4472Udc | |||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| V0, V15 | V2 | V6 | V7 | 0.3685Udc | |
| 0 | 0.2546 | 0.3334 | 0.4120 | ||
| V0, V15 | V2 | V3 | V7 | 0.4642Udc | |
| 0 | 0.1604 | 0.3585 | 0.4811 | ||
| V0, V15 | V1 | V3 | V11 | 0.4642Udc | |
| 0 | 0.4811 | 0.3585 | 0.1604 | ||
| V0, V15 | V1 | V3 | V11 | 0.3685Udc | |
| 0 | 0.4120 | 0.3334 | 0.2546 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Zhong, R.; Sun, G.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, X.; Jing, G. Fault-Tolerant Direct Torque Control of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Single Open-Phase Fault Based on Virtual Vectors. Energies 2024, 17, 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112660
Zhou C, Zhong R, Sun G, Zhao D, Zhao X, Jing G. Fault-Tolerant Direct Torque Control of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Single Open-Phase Fault Based on Virtual Vectors. Energies. 2024; 17(11):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112660
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Changpan, Rundong Zhong, Guodong Sun, Dongdong Zhao, Xiaopeng Zhao, and Guoxiu Jing. 2024. "Fault-Tolerant Direct Torque Control of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Single Open-Phase Fault Based on Virtual Vectors" Energies 17, no. 11: 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112660
APA StyleZhou, C., Zhong, R., Sun, G., Zhao, D., Zhao, X., & Jing, G. (2024). Fault-Tolerant Direct Torque Control of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Single Open-Phase Fault Based on Virtual Vectors. Energies, 17(11), 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112660







