Real-Time Control of a Battery Energy Storage System Using a Reconfigurable Synchrophasor-Based Control System †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Related Works
1.3. Contributions
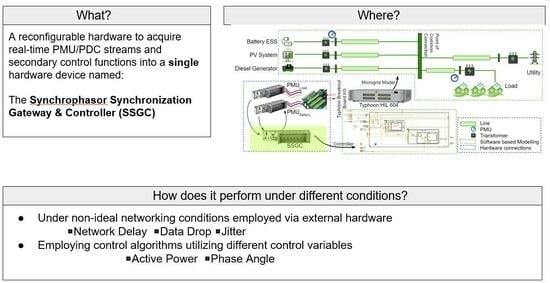
- The capabilities of the Khorjin library are extended to develop a Synchrophasor Synchronization Gateway and Control (SSGC) architecture, consisting of a synchronization layer and a control layer.
- A new PMU-based approach for control of the DERs is introduced and demonstrated by using real-time Controller Hardware-In-the-Loop (CHIL) including a microgrid model. This approach exploits the proposed SSGC architecture.
- The performance of the proposed SSGC architecture is analyzed under varying communication network conditions (including randomized configurations) with multiple PMU streams.
- The proposed control system is further enhanced by applying Low Pass Filters (LPFs) in the real-time controller’s control error signal to mitigate the overswitching of the primary controllers inside a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS).
- The real-time performance of the SSGC is demonstrated under the presence of faster transients in the system when the control signal is passed through the enhanced controller (with LPFs).
- The SSGC architecture was validated by deploying a second type of secondary controller. The controller utilizes the phase-angle difference between two PMU locations to control the active power output.
1.4. Paper Organization
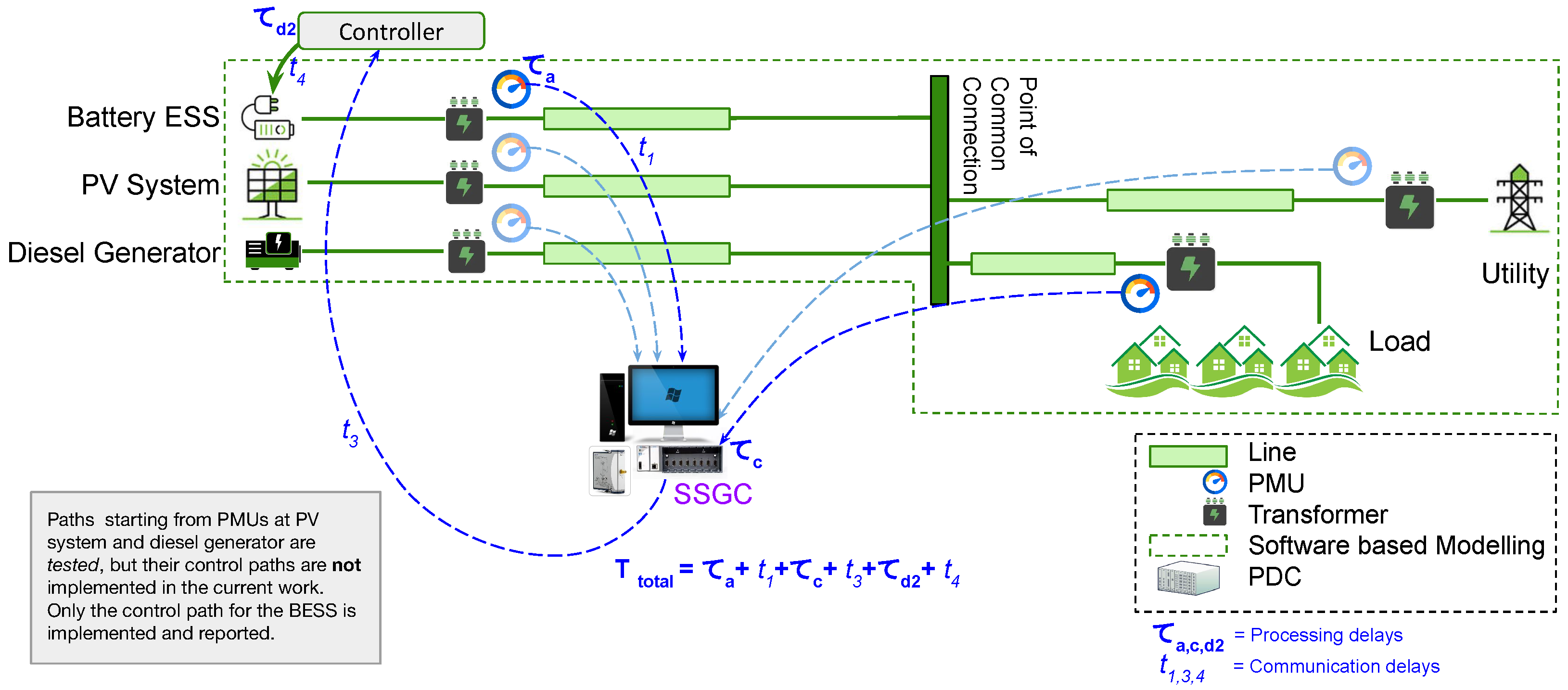
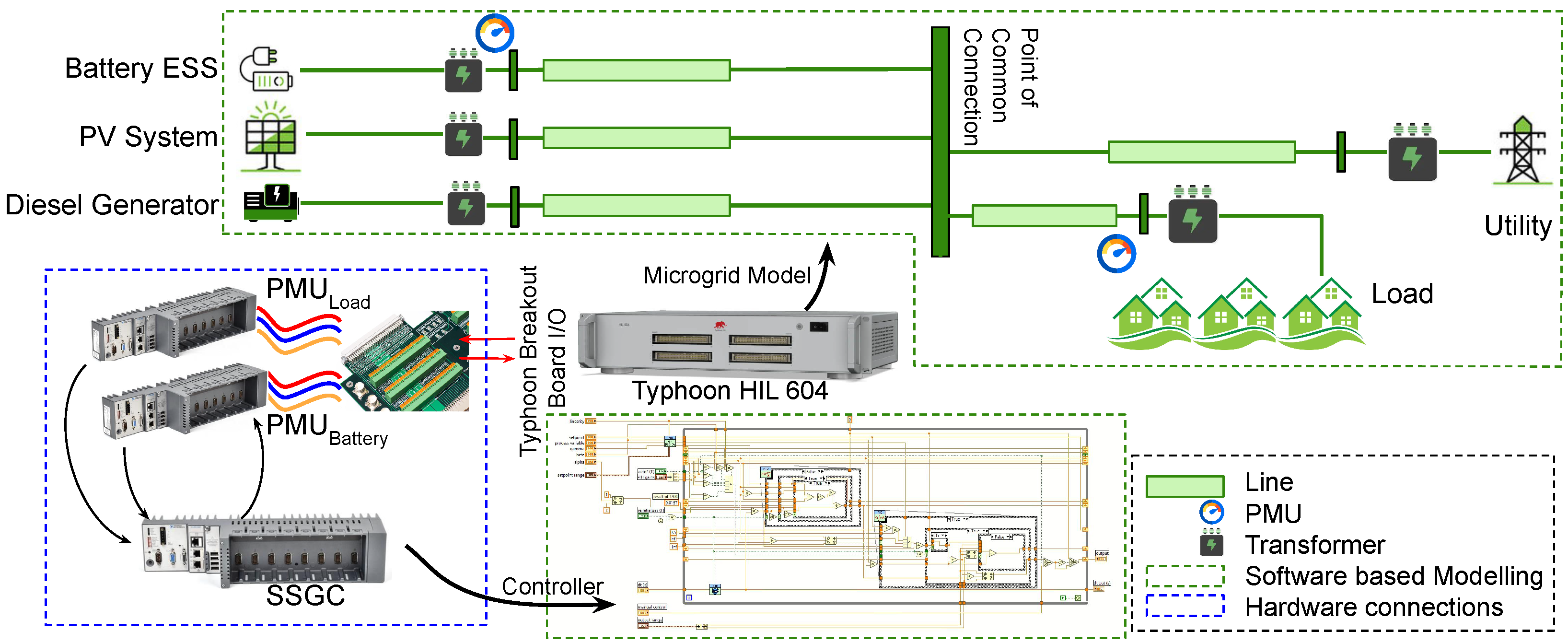
2. Architecture and Experimental Setup
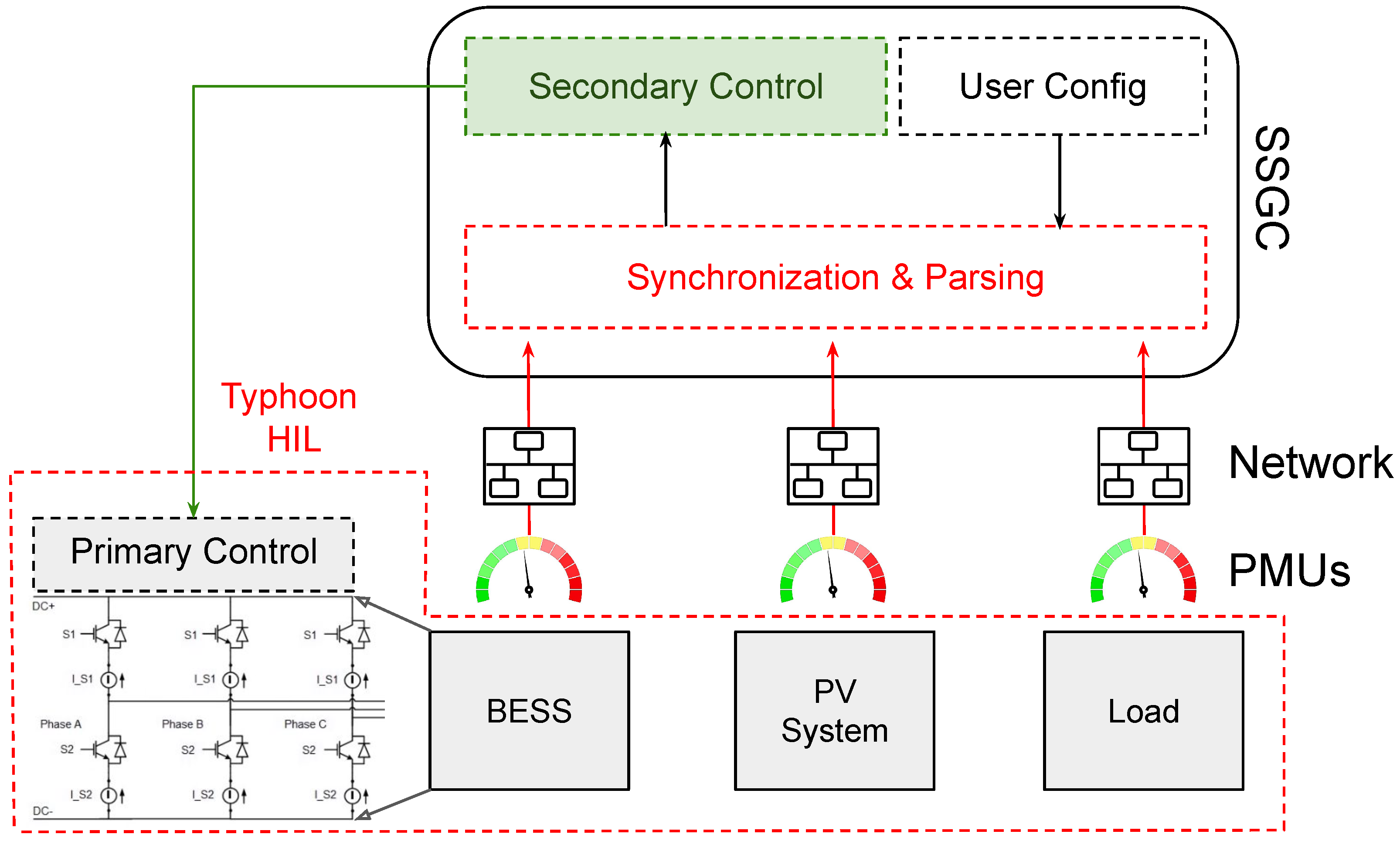
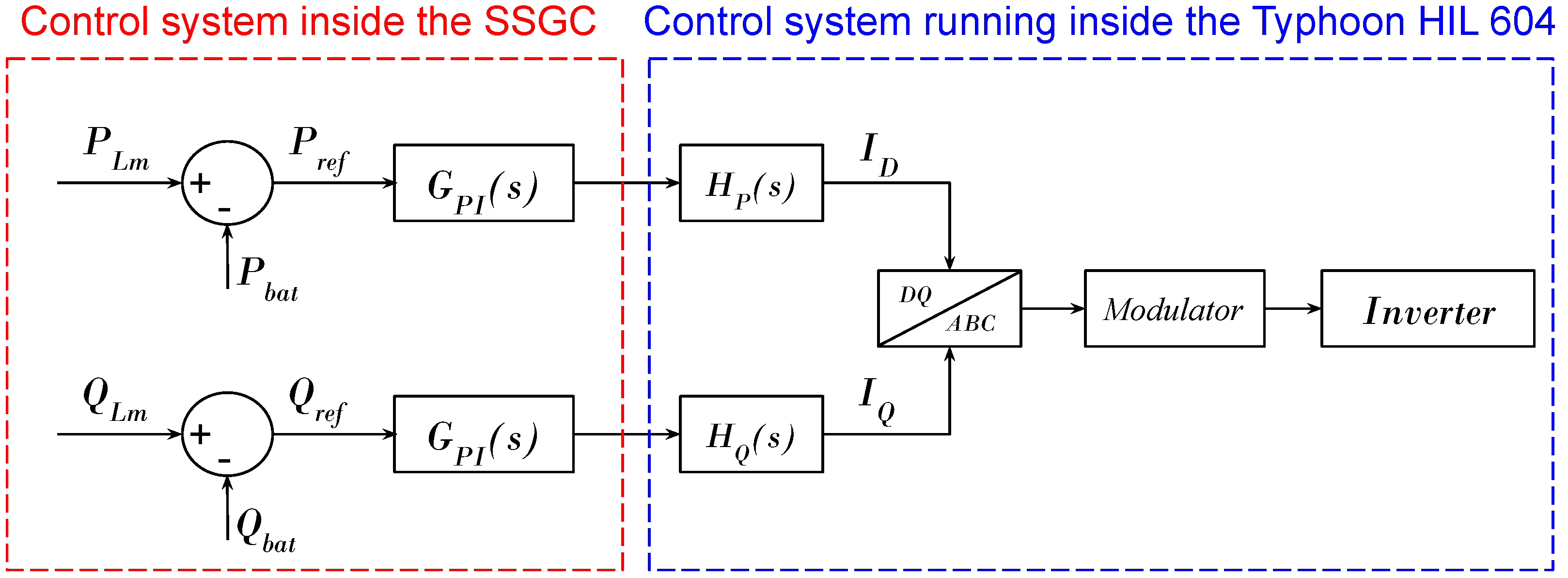
2.1. Controller Architecture
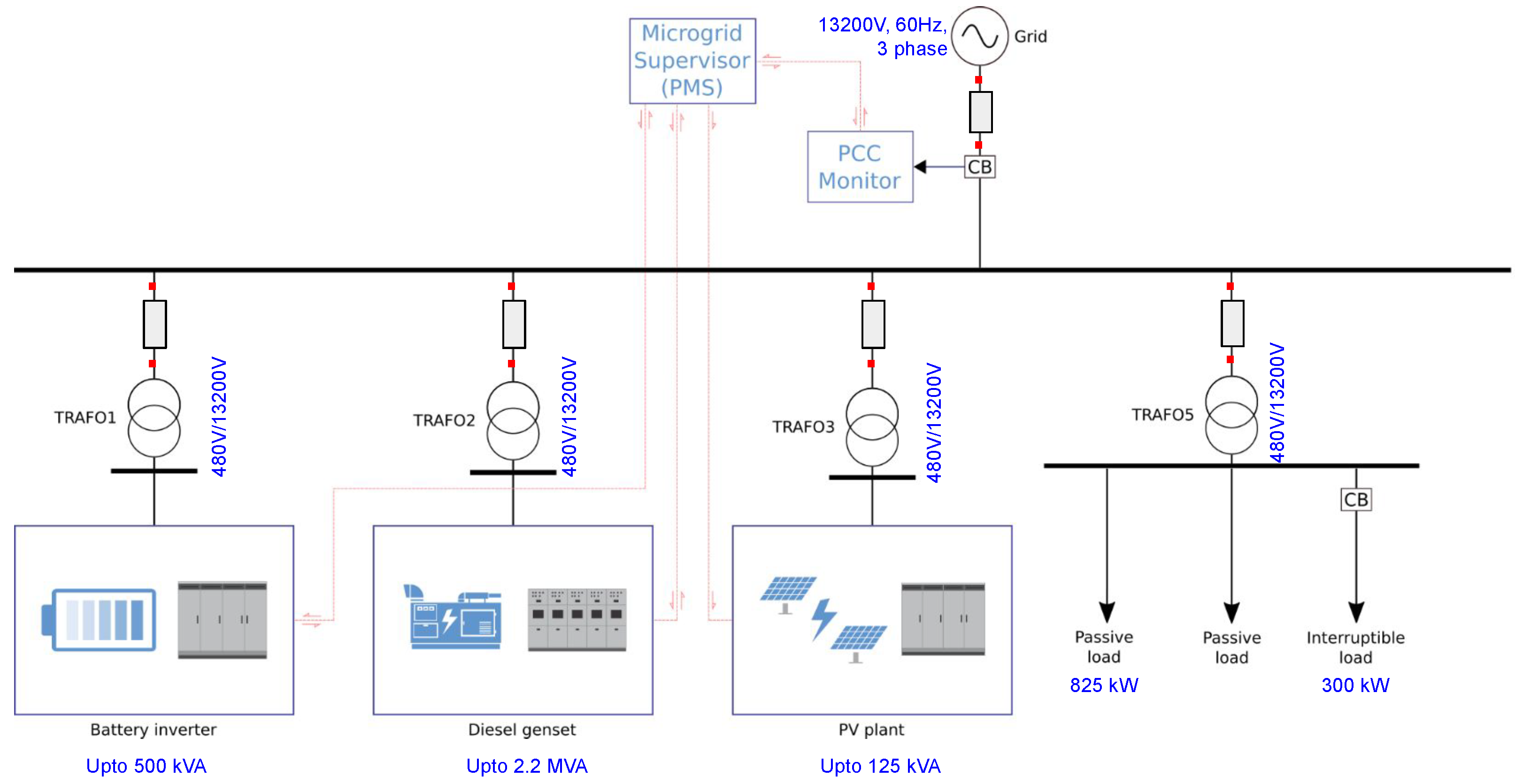
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.2.1. Scope of the Experiments Supported by the Experimental Setup
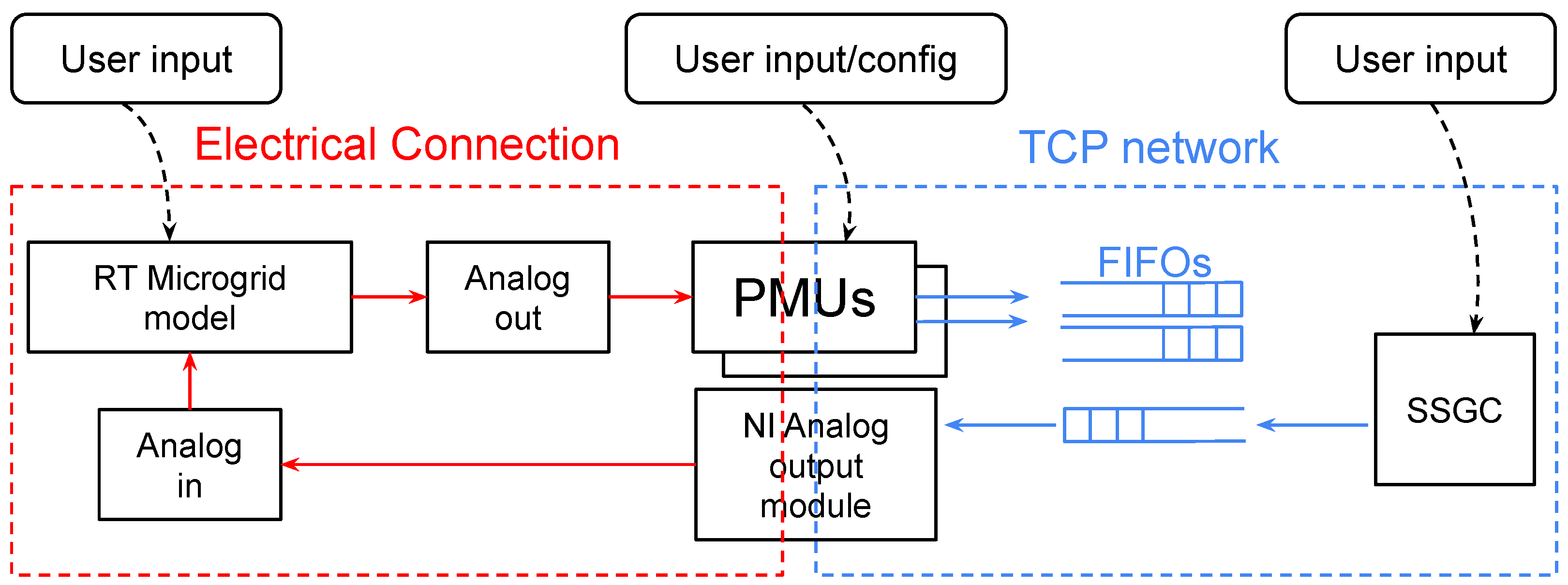
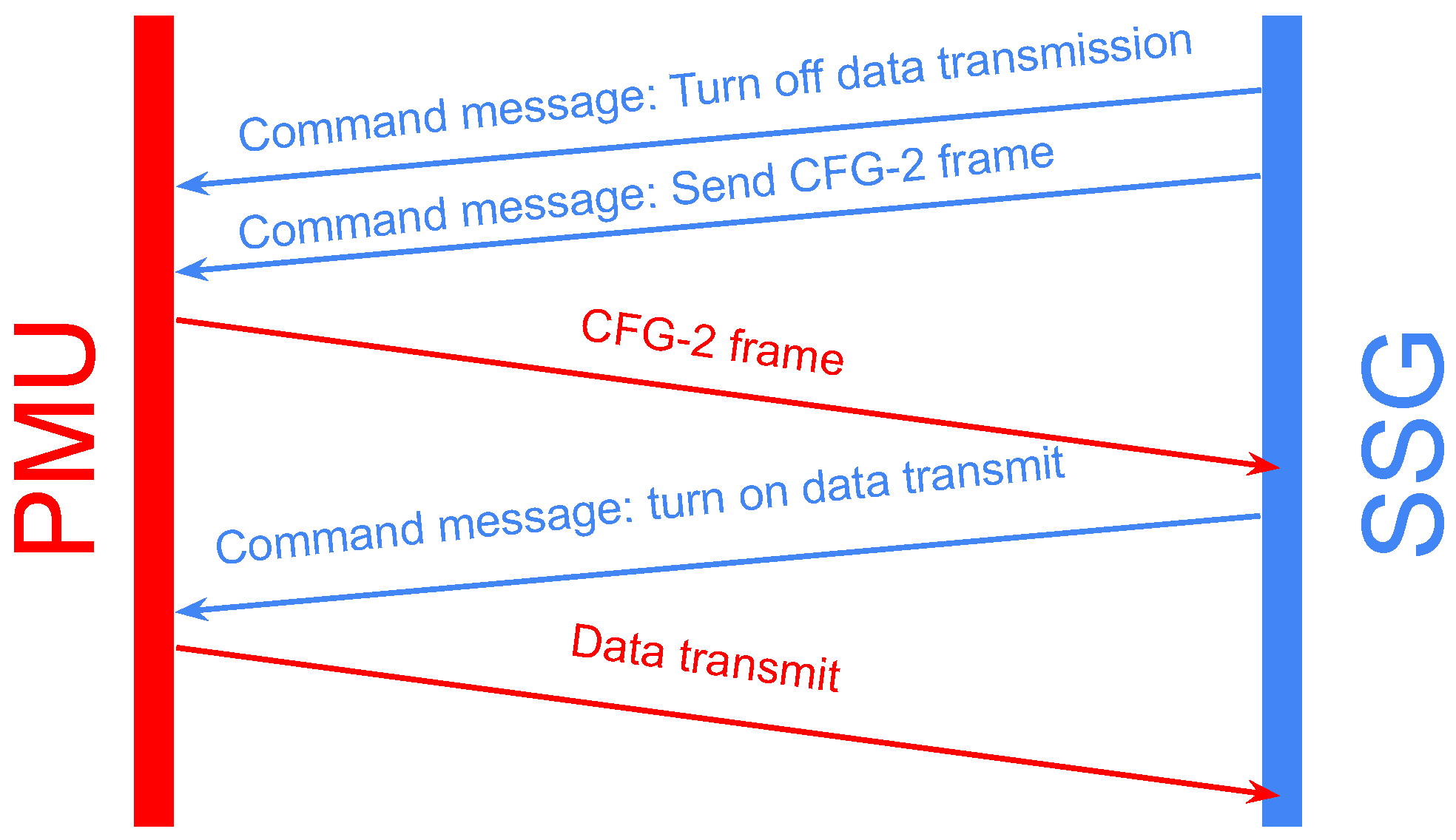
2.2.2. Real-Time Communications
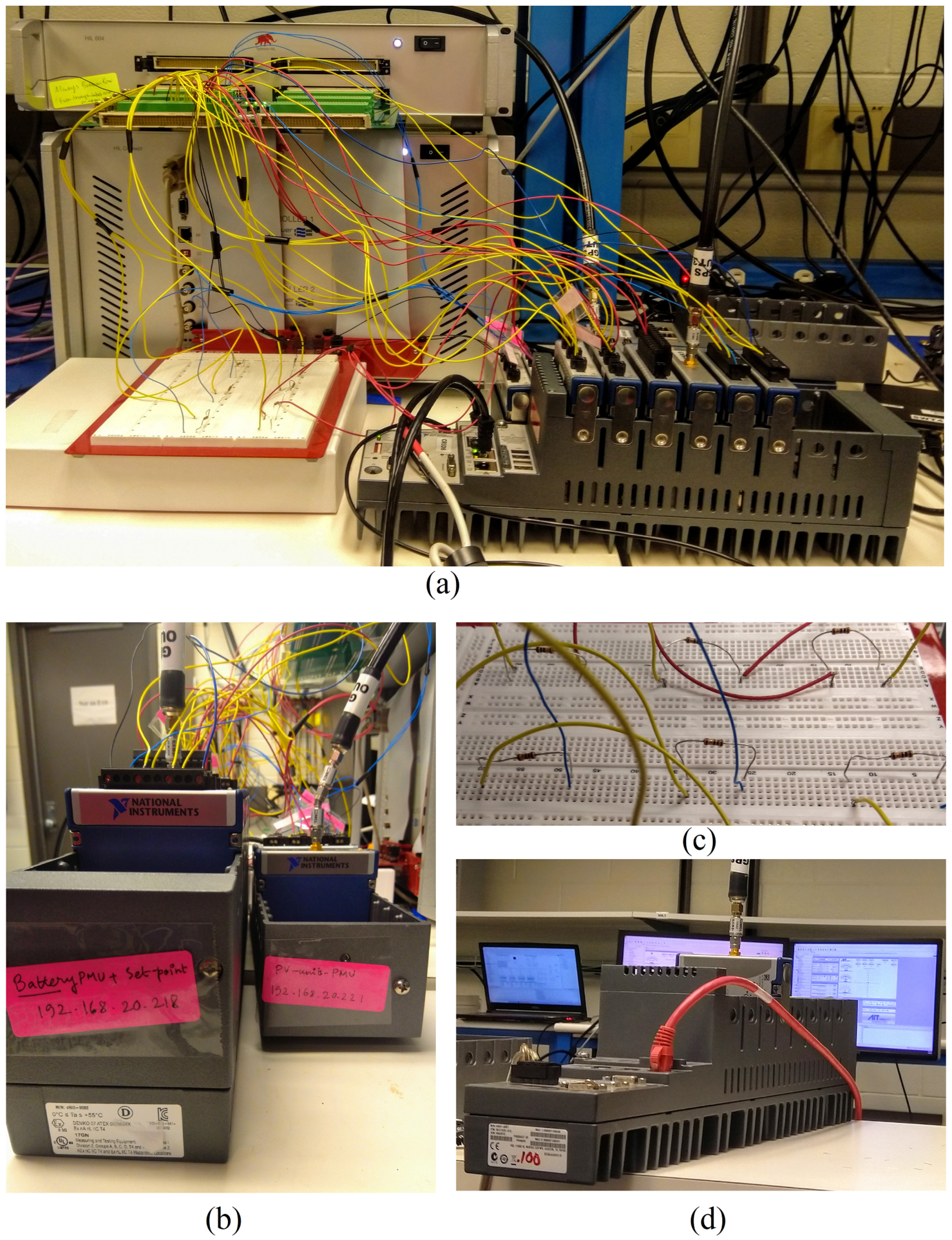
2.3. Hardware Integration
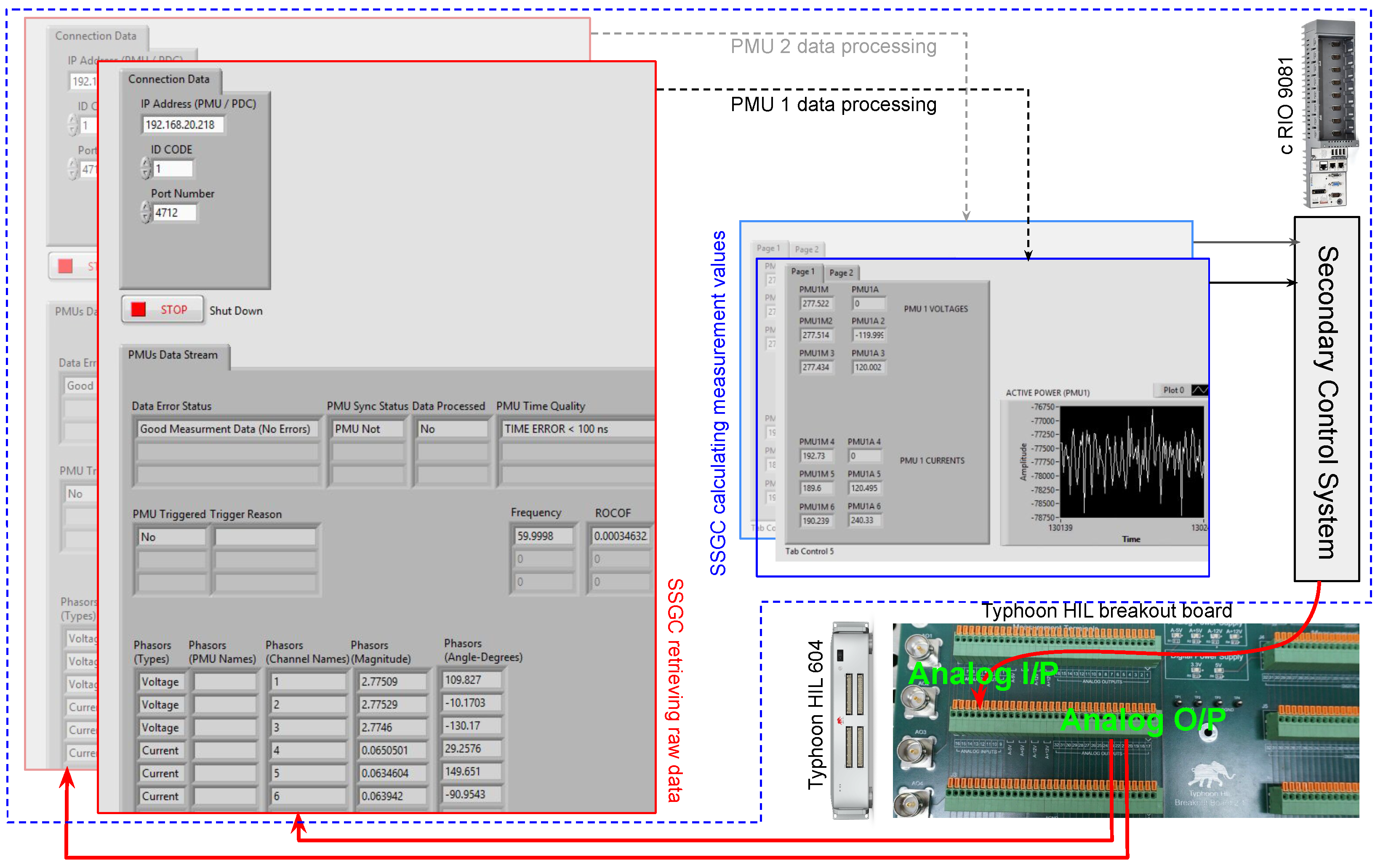
SSGC Configuration and Integration in the Experimental Setup
3. Results
3.1. SSGC Performance under Ideal Network Conditions
3.2. SSGC Performance under Nonideal Communication Network Conditions
3.2.1. Network Tampering by Introducing Fixed Delay
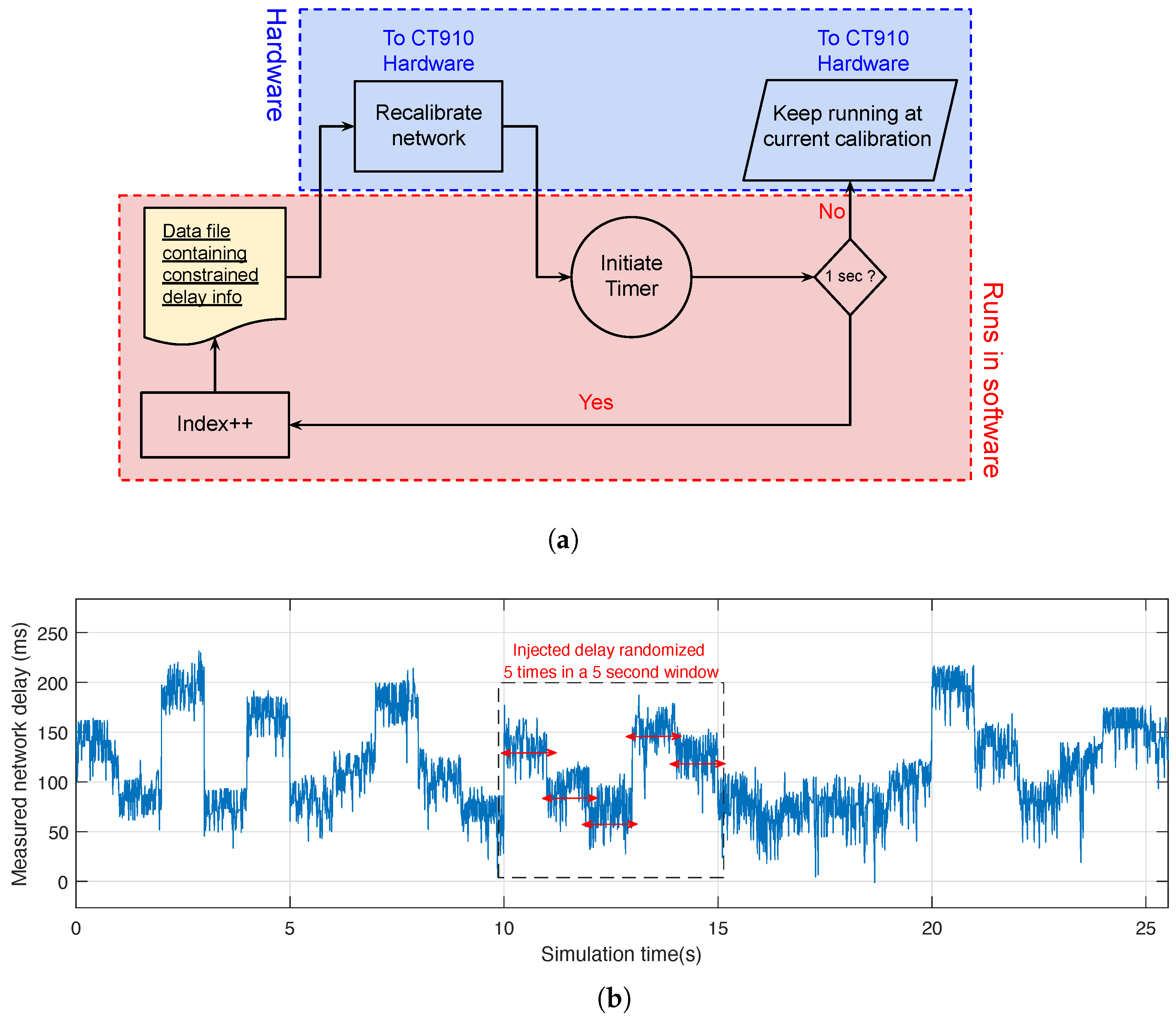
3.2.2. Network Tampering by Introducing Varying Delay
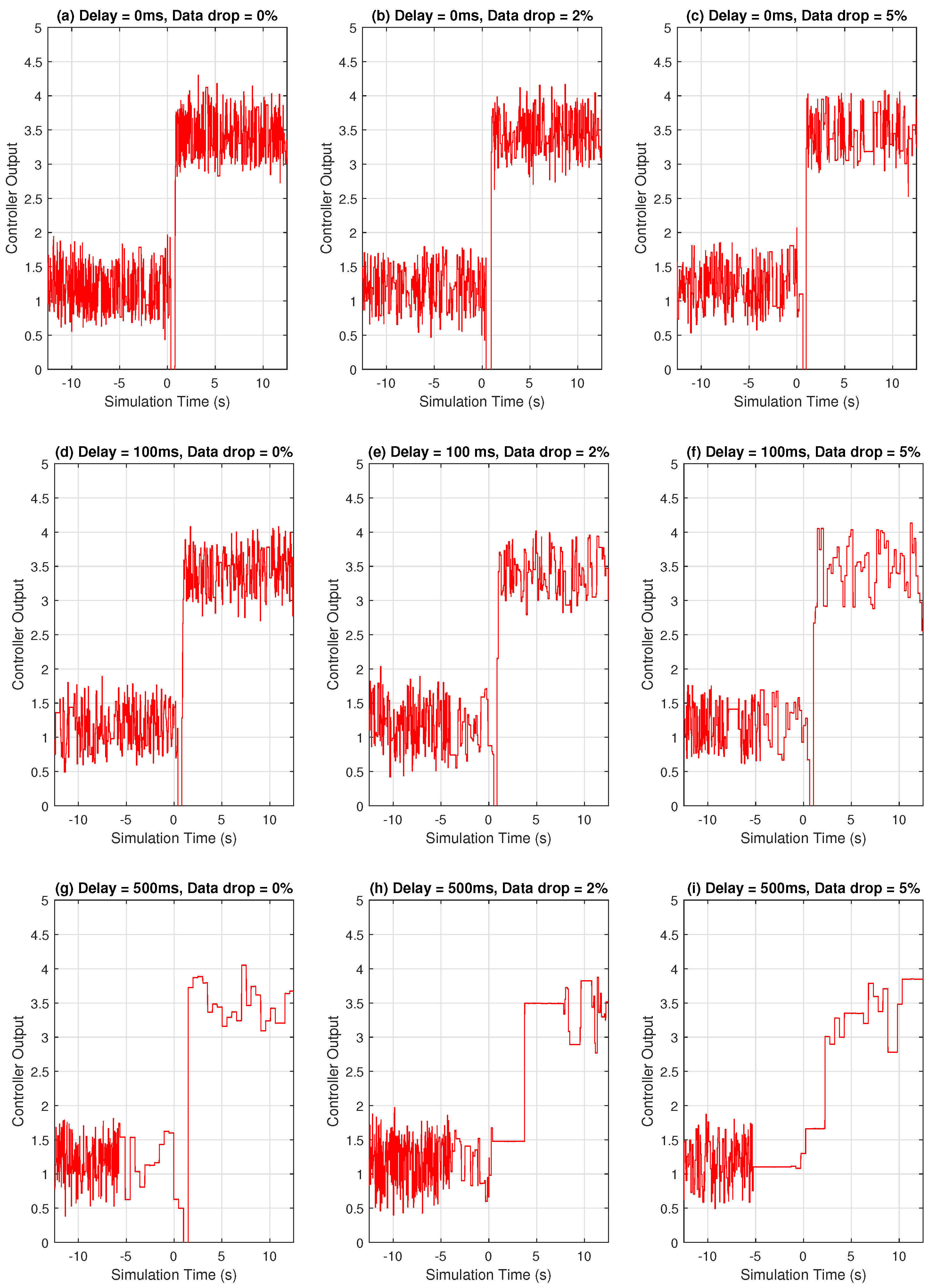
3.2.3. Effect of Data Drop in the Communication Network
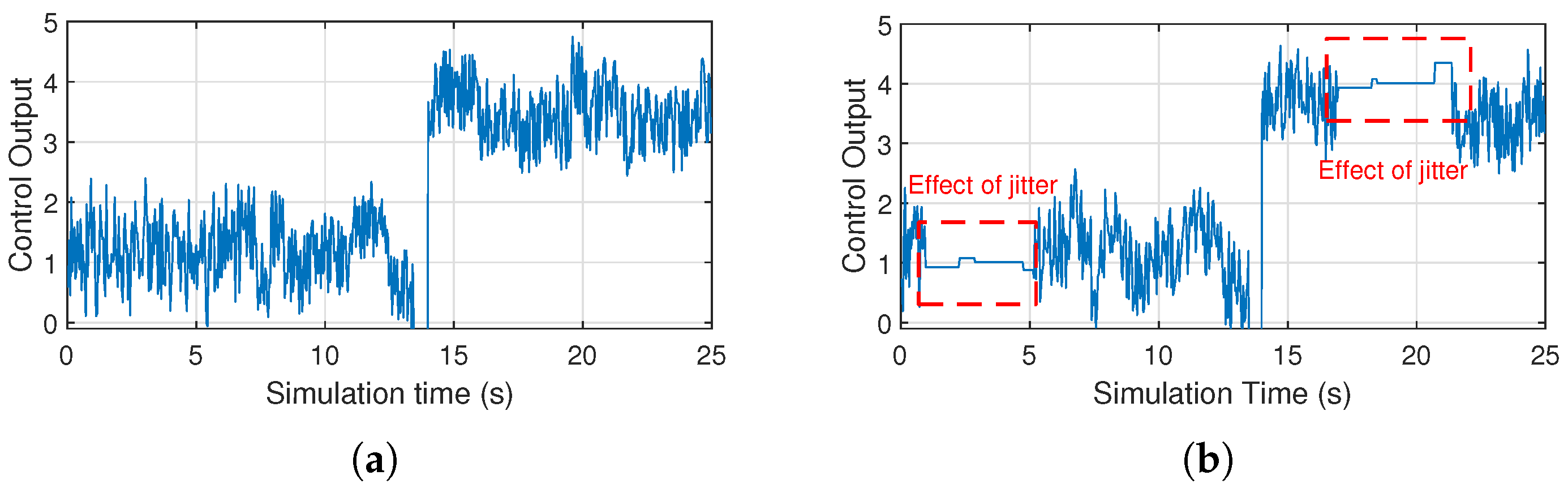
3.2.4. Effect of Jitter on the Communication Network
3.3. Control Performance Enhancement through LPF Functions
3.4. Control System Redesign to Utilize Phase-Angle Measurements
4. Future Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BESS | Battery Energy Storage System |
| DER | Distributed Energy Resources |
| HIL | Hardware-In-the-Loop |
| CHIL | Controller Hardware-In-the-Loop |
| LPF | Low Pass Filter |
| PCC | Point of common coupling |
| PMU | Phasor Measurement Unit |
| PDC | Phasor Data Concentrator |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| SSG | Synchrophasor Synchronization Gateway |
| SSGC | Synchrophasor Synchronization Gateway and Controller |
| WACS | Wide-area control system |
| WAMPAC | Wide-Area Monitoring Protection and Control System |
References
- IEEE Std C37.118.2-2011; IEEE Standard for Synchrophasor Data Transfer for Power Systems. Revision of IEEE Std C37.118-2005. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–53. [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.gegridsolutions.com/multilin/catalog/p30.htm (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Available online: https://selinc.com/products/3573/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Available online: https://nrec.com/en/index.php/product/productInfo/571.html (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Castello, P.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Sulis, S. Low-cost implementation of an active phasor data concentrator for smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2018 Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT, Brescia, Italy, 16–18 April 2018; pp. 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, M.G.; Kanabar, M.; Rodriquez, J.; Zadeh, M.D. Design and implementation of a synchrophasor data concentrator. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE PES Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Middle East, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 17–20 December 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retty, H.; Delport, J.; Centeno, V. Development of tests and procedures for evaluating phasor data concentrators. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Grenoble Conference, Grenoble, France, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanfretti, L.; Jónsdóttir, G.M.; Almas, M.S.; Rebello, E.; Firouzi, S.R.; Baudette, M. Audur—A platform for synchrophasor-based power system wide-area control system implementation. SoftwareX 2018, 7, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, C.F.M.; Vanfretti, L.; Almas, M.S.; Choompoobutrgool, Y.; Gjerde, J.O. Analysis of communication network challenges for synchrophasor-based wide-area applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IREP Symposium Bulk Power System Dynamics and Control—IX Optimization, Security and Control of the Emerging Power Grid, Rethymno, Greece, 25–30 August 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; You, S.; Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhan, L.; Liu, Y. A Fast Load Control System Based on Mobile Distribution-Level Phasor Measurement Unit. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; You, S.; Yao, W.; Cui, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. A Distribution Level Wide Area Monitoring System for the Electric Power Grid–FNET/GridEye. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Zhao, J.; Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y. FNET/GridEye for Future High Renewable Power Grids—Applications Overview. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PES Transmission & Distribution Conference and Exhibition—Latin America (T & D-LA), Lima, Peru, 18–21 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhou, D.; Wu, L.; You, S.; Liu, H.; Zhan, L.; Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Gao, W.; et al. Recent developments of FNET/GridEye—A situational awareness tool for smart grid. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 2, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, E.O.; Whitehead, D.; Zweigle, G.; Ravikumar, K.G. Synchrophasor-based power system protection and control applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 63rd Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers, College Station, TX, USA, 29 March–1 April 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, Y.R.; Abdelaziz, M.; Wang, L. D-PMU Based Secondary Frequency Control for Islanded Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenelis, I.; Wang, X.; Kamwa, I. Online PMU-Based Wide-Area Damping Control for Multiple Inter-Area Modes. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 5451–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenine, M.; Nordström, L. Investigation of communication delays and data incompleteness in multi-PMU Wide Area Monitoring and Control Systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electric Power and Energy Conversion Systems, (EPECS), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 10–12 November 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Microgrid Knowledge. Available online: https://microgridknowledge.com/microgrids-navigant/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Lasseter, R.H. MicroGrids. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting, Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.01CH37194), Columbus, OH, USA, 28 January–1 February 2001; Volume 1, pp. 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziargyriou, N.; Asano, H.; Iravani, R.; Marnay, C. Microgrids. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2007, 5, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidram, A.; Davoudi, A. Hierarchical Structure of Microgrids Control System. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canciello, G.; Cavallo, A.; Guida, B. Control of Energy Storage Systems for Aeronautic Applications. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 2458590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.; Canciello, G.; Guida, B. Energy Storage System Control for Energy Management in Advanced Aeronautic Applications. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 4083132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.M.; Vanfretti, L. Delay Analysis of a Real-Time Hard Reconfigurable Synchrophasor Synchronization Gateway. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control and Optimization of Renewable Energy Systems (CORES), Anaheim, CA, USA, 6–7 December 2019; Available online: https://www.actapress.com/PaperInfo.aspx?paperId=456528 (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Firouzi, S.R.; Vanfretti, L.; Ruiz-Alvarez, A.; Hooshyar, H.; Mahmood, F. Interpreting and implementing IEC 61850-90-5 Routed-Sampled Value and Routed-GOOSE protocols for IEEE C37.118.2 compliant wide-area synchrophasor data transfer. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 144, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttayak, S.; Wornpuen, A.; Promparn, N.; Charbkaew, N.; Bunyagul, T. Design of Phasor Data Concentrator for phasor monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Sustainable Utilization and Development in Engineering and Technology (STUDENT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 6–9 October 2012; pp. 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, S.P.; Sadhu, P.K.; Sarita, K.; Khan, B.; Arya, L.D.; Saket, R.K.; Kothari, D.P. A Comprehensive Review of Microgrid Control Mechanism and Impact Assessment for Hybrid Renewable Energy Integration. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 88942–88958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Matas, J.; de Vicuna, L.G.; Castilla, M. Hierarchical Control of Droop-Controlled AC and DC Microgrids—A General Approach Toward Standardization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourramezan, R.; Seyedi, Y.; Karimi, H.; Zhu, G.; Mont-Briant, M. Design of an advanced phasor data concentrator for monitoring of distributed energy resources in smart microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaud, X.; Faruque, M.O.; Teninge, A.; Hariri, A.H.; Vanfretti, L.; Paolone, M.; Dinavahi, V.; Mitra, P.; Lauss, G.; Dufour, C.; et al. Applications of Real-Time Simulation Technologies in Power and Energy Systems. IEEE Power Energy Technol. Syst. J. 2015, 2, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konakalla, S.A.R.; Valibeygi, A.; de Callafon, R.A. Microgrid dynamic modeling and islanding control with synchrophasor data. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, P.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Sulis, S. Active phasor data concentrator performing adaptive management of latency. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2018, 16, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.M.; Vanfretti, L.; Mishra, C.; Jones, K.D. A Reconfigurable Synchrophasor Synchronization Gateway & Controller Architecture for DERs. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Smart Grid Synchronized Measurements and Analytics (SGSMA), Split, Croatia, 24–26 May 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microgrids. Available online: https://bit.ly/TyphoonHILMG (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Almas, M.S.; Baudette, M.; Vanfretti, L. Utilizing synchrophasor-based supplementary damping control signals in conventional generator excitation systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 157, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Maroto, L.; Vanfretti, L.; Almas, M.S.; Jónsdóttir, G.M.; Rouco, L. A WACS exploiting generator Excitation Boosters for power system transient stability enhancement. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 148, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, E.; Vanfretti, L.; Almas, M.S. Experimental Testing of a Real-Time Implementation of a PMU-Based Wide-Area Damping Control System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 25800–25810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompoobutrgool, Y.; Vanfretti, L. Using PMU signals from dominant paths in power system wide-area damping control. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2015, 4, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plug-and-Play Microgrid Library and Testing of Microgrid Controller. Available online: https://bit.ly/TyphoonControl (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- NI Expertise: Power Quality Analysis. Available online: https://bit.ly/NIPQAnalysis (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Derviškadić, A.; Romano, P.; Pignati, M.; Paolone, M. Architecture and experimental validation of a low-latency phasor data concentrator. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LabVIEW Electrical Power Toolkit API Reference. Available online: https://bit.ly/NIPMUvis (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Adhikari, P.M.; Hooshyar, H.; Vanfretti, L. Experimental Quantification of Hardware Requirements for FPGA-Based Reconfigurable PMUs. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57527–57538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.typhoon-hil.com/products/hil-connect/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- CT 910. Available online: https://www.candelatech.com/ct910_product.php (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Song, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, W. Analysis on the Response Time of the Battery Energy Storage System. Mater. Sci. Energy Eng. (CMSEE 2014) 2015, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, A.; Mehraban, A.S.; Rahman, M.; Gyugyi, L.; Arabi, S.; Reitman, T. Controlling the flow of real and reactive power. IEEE Comput. Appl. Power 1998, 11, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.E.; Hamilton, B.W. Phase-angle control of system interconnections. Electr. Eng. 1939, 58, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolissaint, C.H.; Arvanitidis, N.V.; Luenberger, D.G. Decomposition of Real and Reactive Power Flows: A Method Suited for On-Line Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1972, PAS-91, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| References | Hardware/ Software | RT Compliant | Suitable for Control | Available at Production Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | Hardware | Yes | Yes | No | Cannot utilize existing PMUs in the network |
| [11,12,13] | Both | Yes | No | Yes | Control applications not tested |
| [14] | Hardware | Yes | No | Yes | Tested only for local control |
| [15,16] | Software | No | Yes | No | No major hardware development |
| [17] | Software | Yes | No | No | Proposed a PDC placement scheme for control |
| (ms) | 5 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 200 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ms) | |||||||
| 50 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | |
| 100 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | |
| 200 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 9/10 | |
| 500 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 5/10 | 5/10 | 4/10 | 3/10 | |
| 750 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 | |
| Delay | 0% | 0.5% | 1% | 2% | 5% | 10% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drop Rate (%) | |||||||
| 0 ms | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 3/10 | |
| 50 ms | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 9/10 | 0/10 | |
| 100 ms | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 9/10 | 7/10 | 0/10 | |
| 200 ms | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 6/10 | 2/10 | 0/10 | |
| 500 ms | 10/10 | 10/10 | 5/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | |
| 750 ms | 1/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adhikari, P.M.; Vanfretti, L.; Chang, H.; Kar, K. Real-Time Control of a Battery Energy Storage System Using a Reconfigurable Synchrophasor-Based Control System. Energies 2023, 16, 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196909
Adhikari PM, Vanfretti L, Chang H, Kar K. Real-Time Control of a Battery Energy Storage System Using a Reconfigurable Synchrophasor-Based Control System. Energies. 2023; 16(19):6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196909
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdhikari, Prottay M., Luigi Vanfretti, Hao Chang, and Koushik Kar. 2023. "Real-Time Control of a Battery Energy Storage System Using a Reconfigurable Synchrophasor-Based Control System" Energies 16, no. 19: 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196909
APA StyleAdhikari, P. M., Vanfretti, L., Chang, H., & Kar, K. (2023). Real-Time Control of a Battery Energy Storage System Using a Reconfigurable Synchrophasor-Based Control System. Energies, 16(19), 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196909