Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.-J.S.; Methodology, W.-J.S.; Software, W.-J.S.; Validation, W.-J.S.; Formal analysis, W.-J.S. and B.K.L.; Investigation, W.-J.S.; Resources, B.K.L.; Data curation, W.-J.S.; Writing—original draft, W.-J.S.; Writing—review & editing, B.K.L.; Visualization, W.-J.S.; Supervision, B.K.L.; Project administration, B.K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
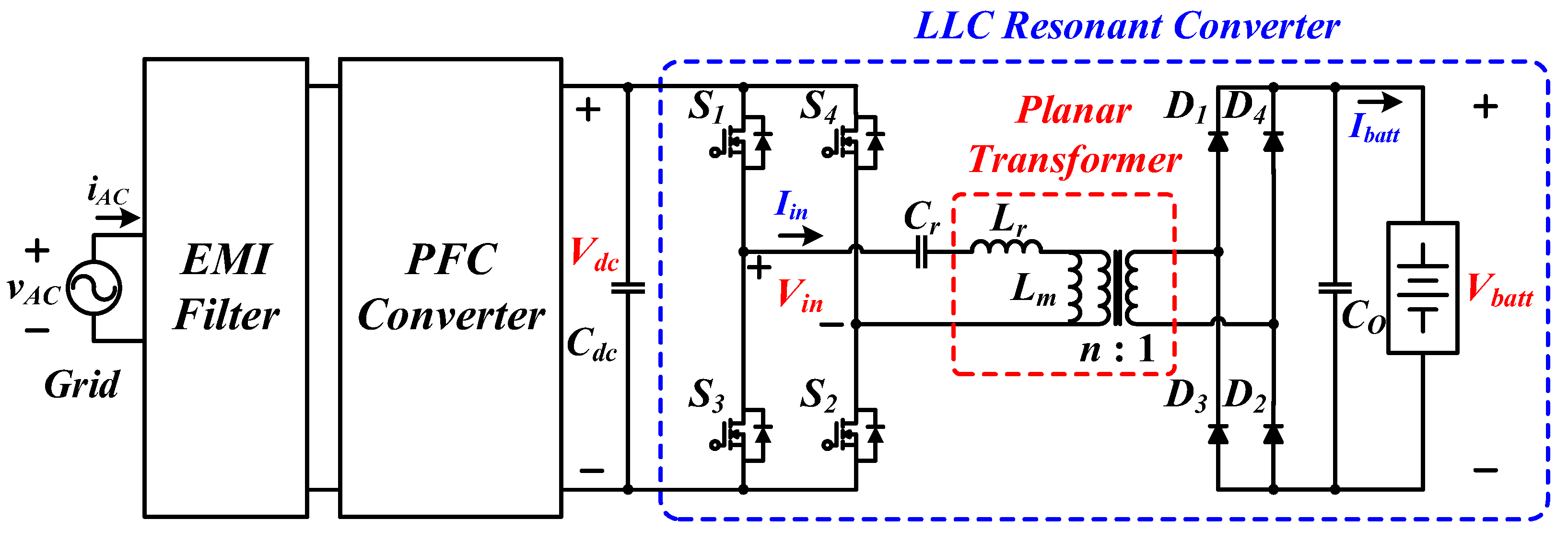
Figure 1.
Single-phase OBC system with planar transformer.
Figure 1.
Single-phase OBC system with planar transformer.
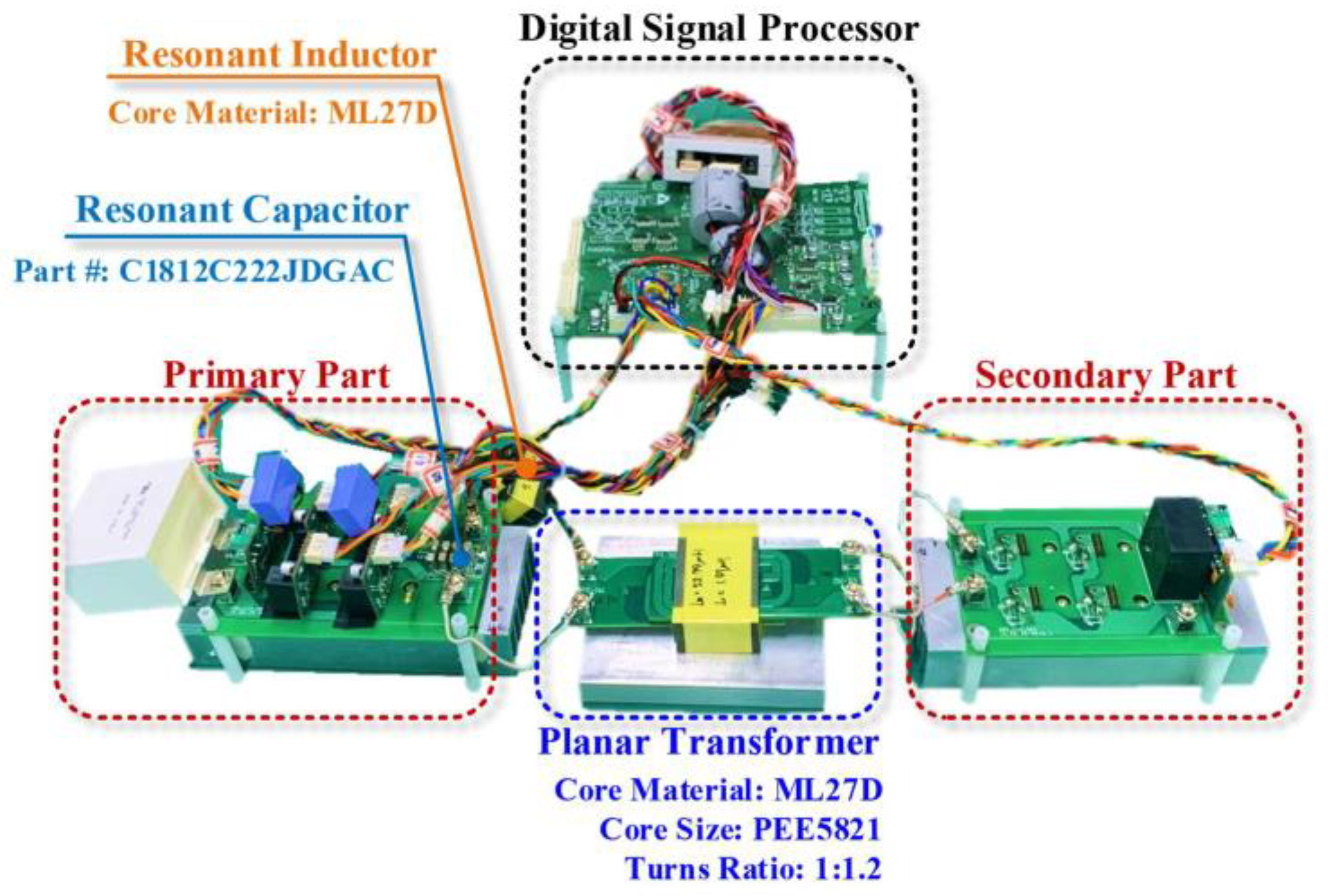
Figure 2.
Initial designed planar transformer.
Figure 2.
Initial designed planar transformer.
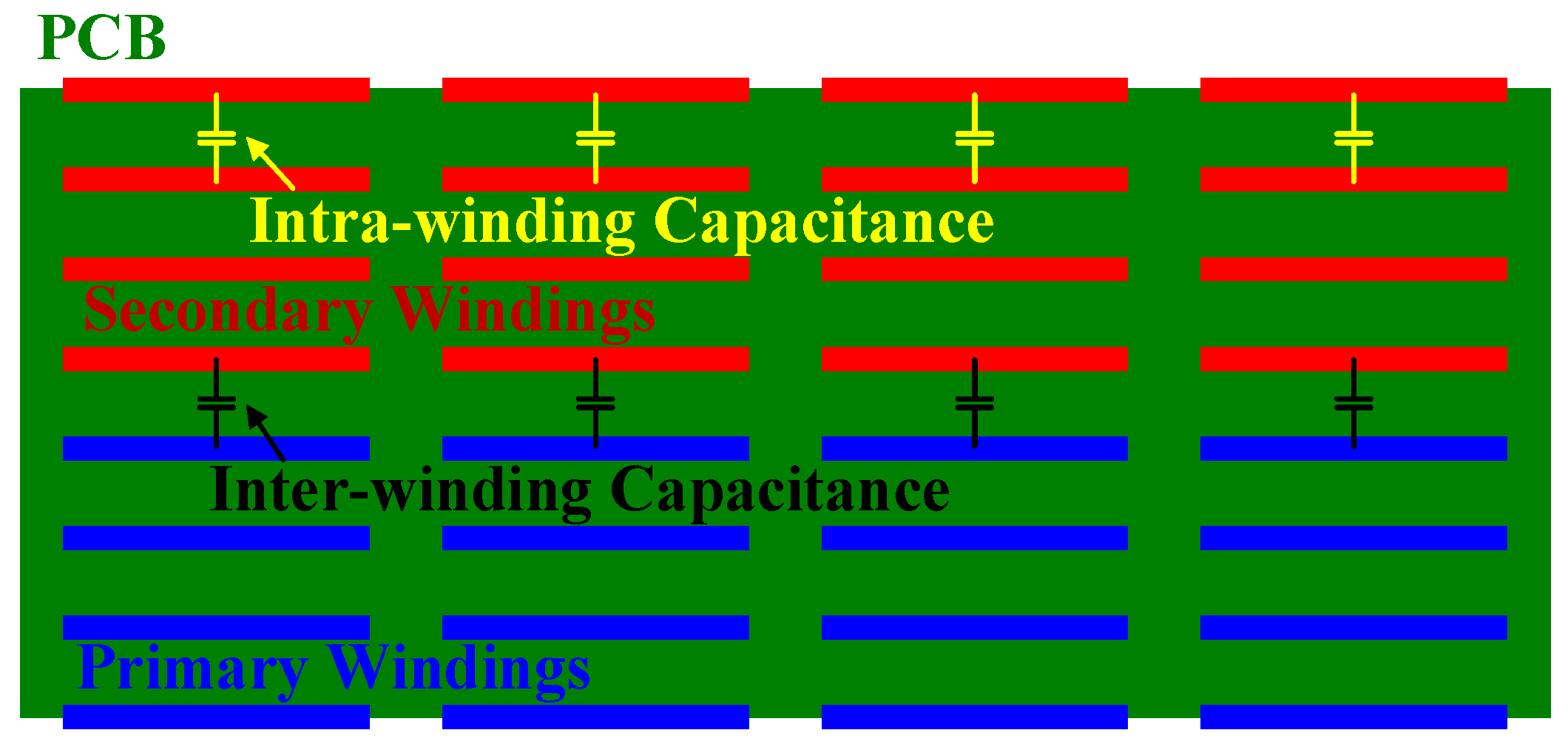
Figure 3.
Conceptual diagram of parasitic capacitance inside the PCB pattern.
Figure 3.
Conceptual diagram of parasitic capacitance inside the PCB pattern.
Figure 4.
LLC resonant converter circuit considering equivalent parasitic capacitance.
Figure 4.
LLC resonant converter circuit considering equivalent parasitic capacitance.
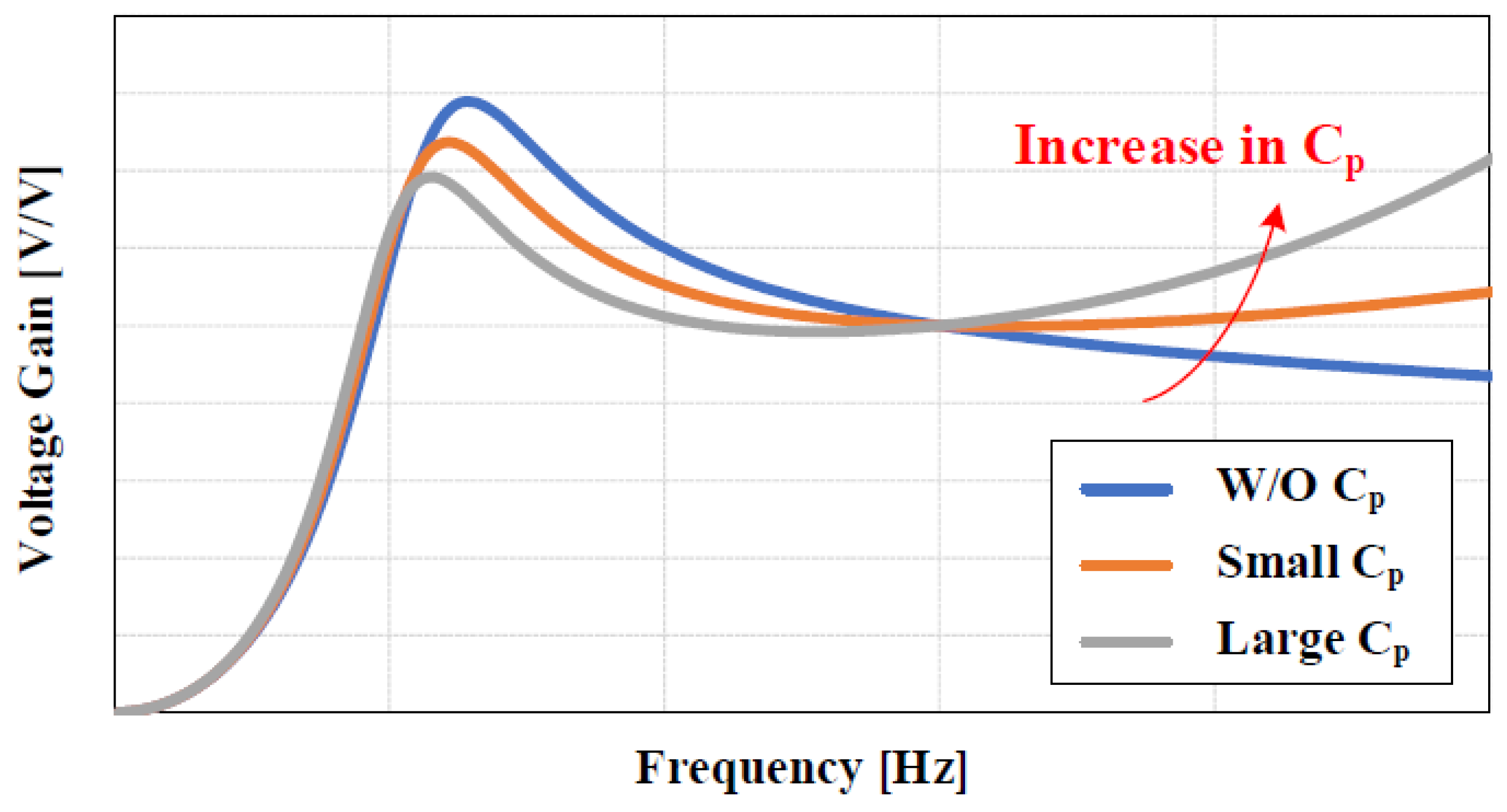
Figure 5.
LLC resonant converter voltage gain curve change with parasitic capacitance size.
Figure 5.
LLC resonant converter voltage gain curve change with parasitic capacitance size.
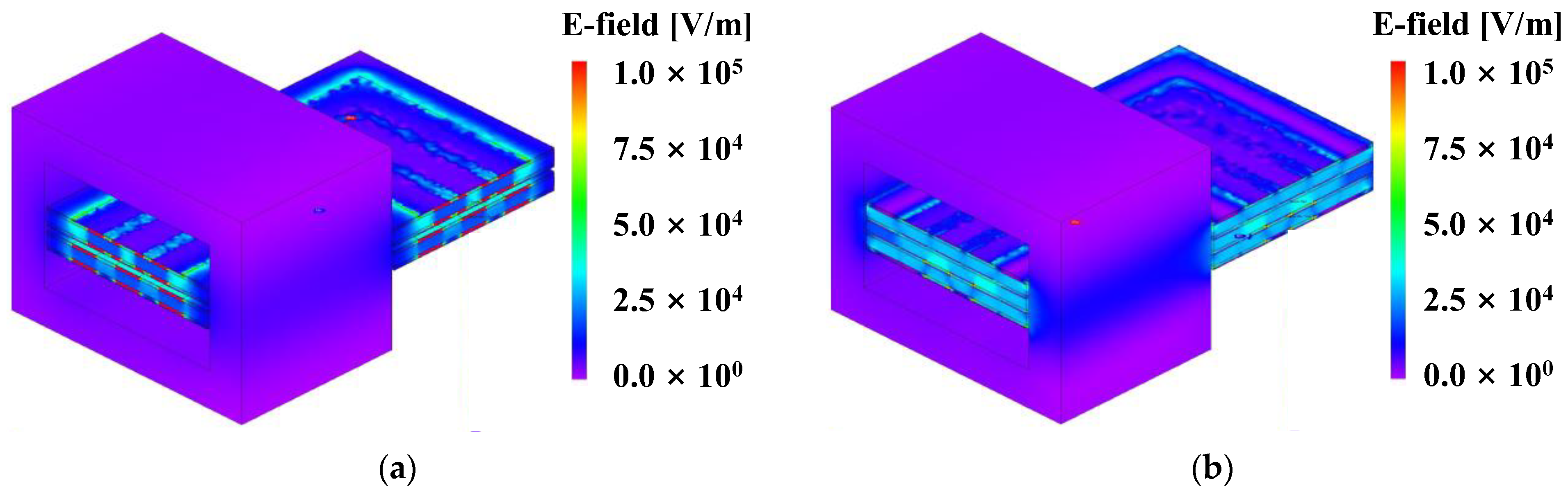
Figure 6.
JMAG simulation pattern layout for parasitic capacitance measurement. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap.
Figure 6.
JMAG simulation pattern layout for parasitic capacitance measurement. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap.
Figure 7.
JMAG simulation parasitic measurement results according to PCB pattern arrangement. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap.
Figure 7.
JMAG simulation parasitic measurement results according to PCB pattern arrangement. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap.
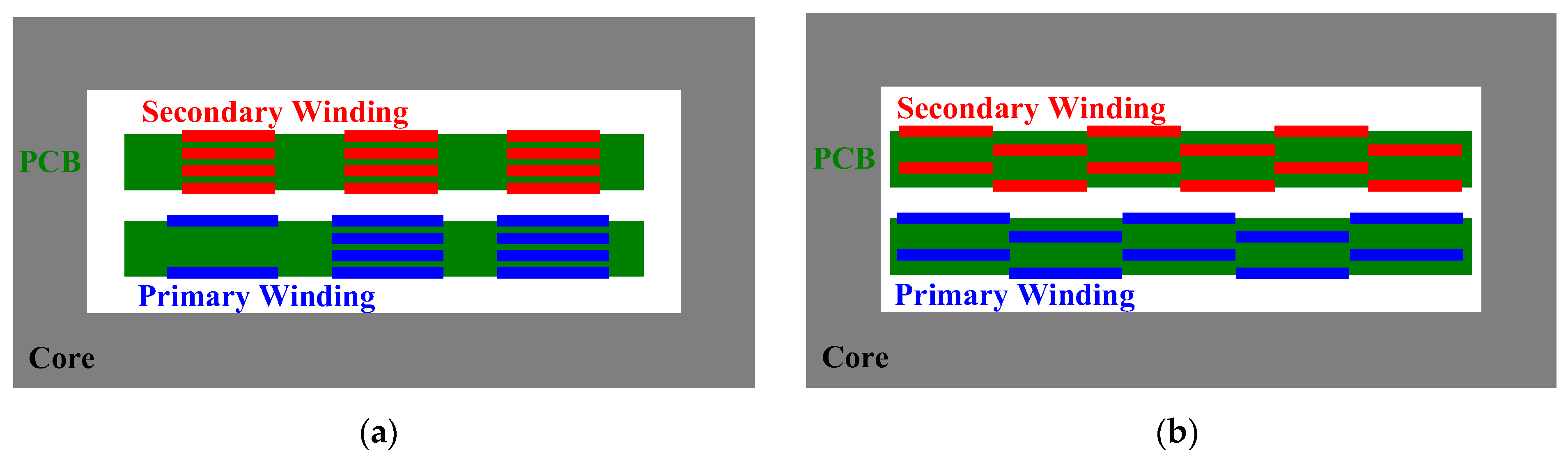
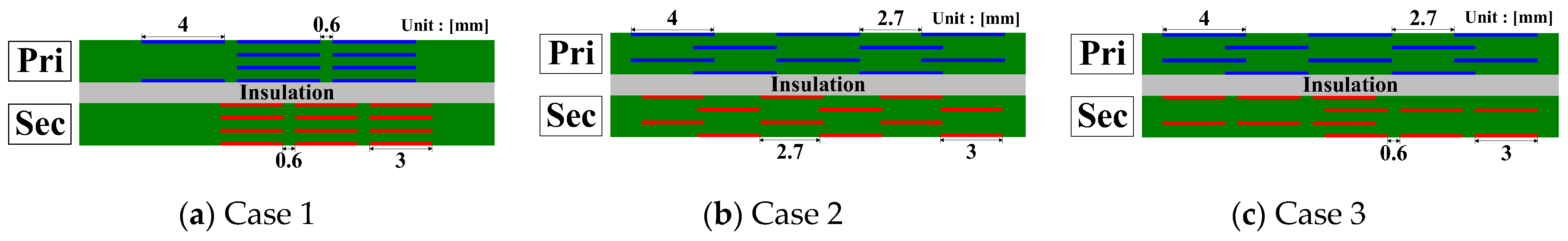
Figure 8.
PCB internal pattern layout under various conditions. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap. (c) Intermediate pattern overlap.
Figure 8.
PCB internal pattern layout under various conditions. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap. (c) Intermediate pattern overlap.
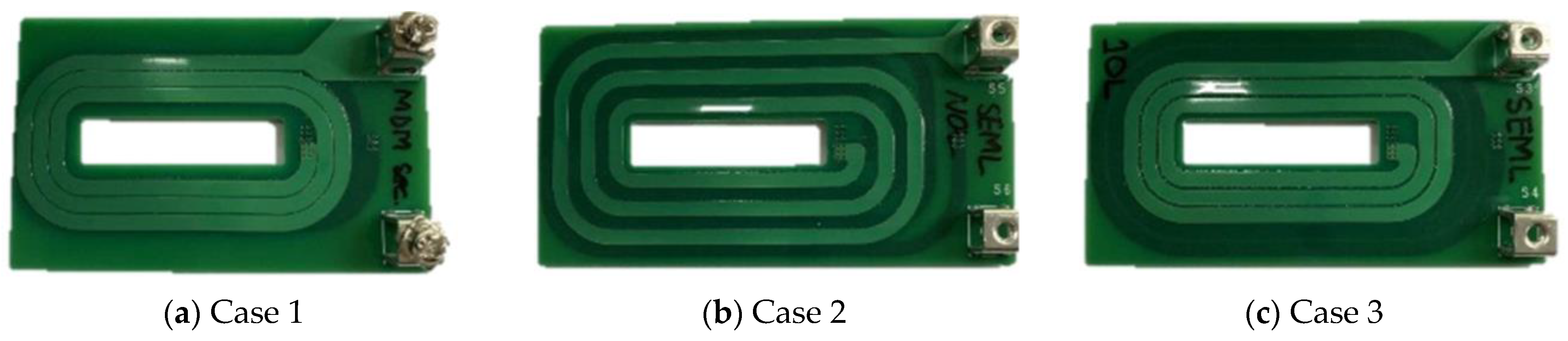
Figure 9.
Manufactured PCBs under various conditions. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap. (c) Intermediate pattern overlap.
Figure 9.
Manufactured PCBs under various conditions. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap. (c) Intermediate pattern overlap.
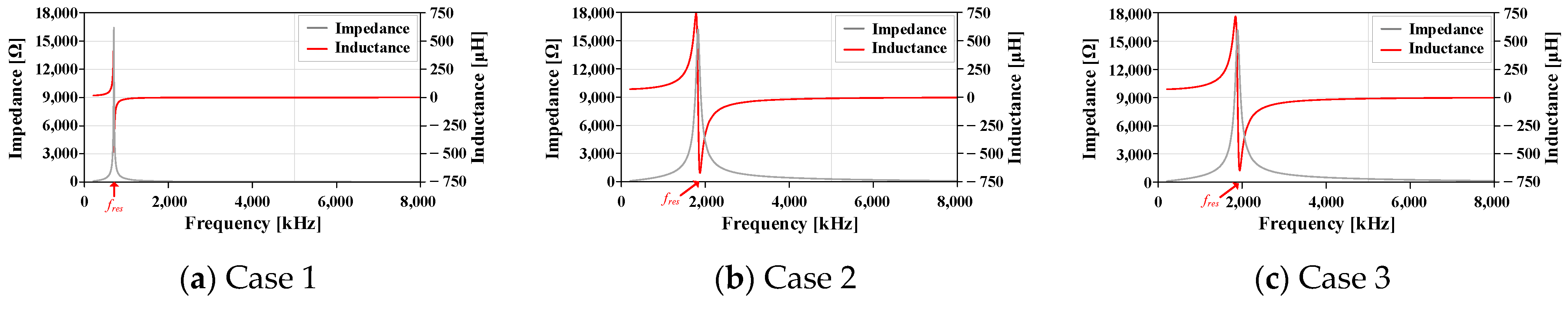
Figure 10.
Impedance characteristic curve according to frequency of various PCBs. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap. (c) Intermediate pattern overlap.
Figure 10.
Impedance characteristic curve according to frequency of various PCBs. (a) Maximum pattern overlap. (b) Minimum pattern overlap. (c) Intermediate pattern overlap.
Figure 11.
Voltage gain curve of actual LLC resonant converter with each parasitic capacitance.
Figure 11.
Voltage gain curve of actual LLC resonant converter with each parasitic capacitance.
Figure 12.
Experimental setup of the LLC resonant converter with planar transformer.
Figure 12.
Experimental setup of the LLC resonant converter with planar transformer.
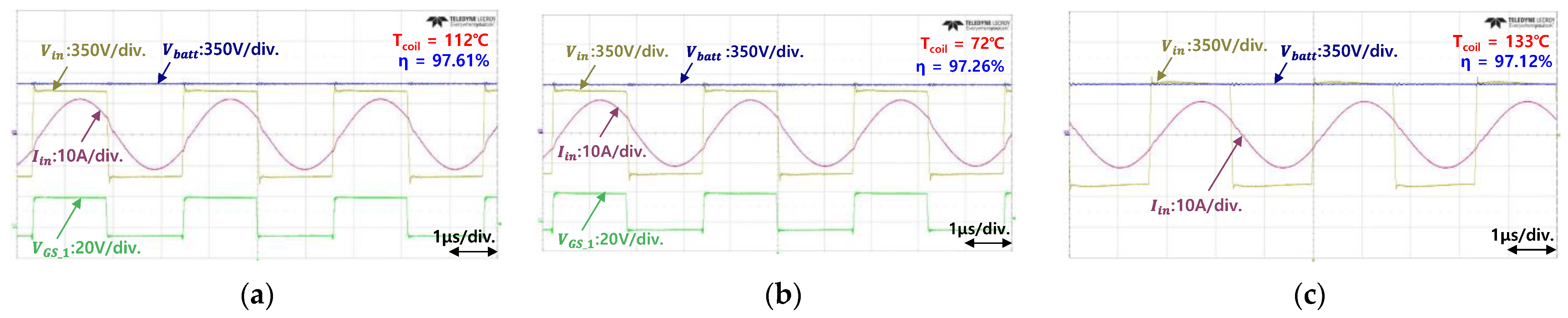
Figure 13.
Experimental waveforms and efficiency of the LLC converter with different transformer types. (a) Conventional Litz wire. (b) Case 1 planar transformer. (c) Case 2 planar transformer. (d) Case 3 planar transformer.
Figure 13.
Experimental waveforms and efficiency of the LLC converter with different transformer types. (a) Conventional Litz wire. (b) Case 1 planar transformer. (c) Case 2 planar transformer. (d) Case 3 planar transformer.
Figure 14.
Various cores for the planar transformer. (a) PEE core. (b) UI core. (c) H core.
Figure 14.
Various cores for the planar transformer. (a) PEE core. (b) UI core. (c) H core.
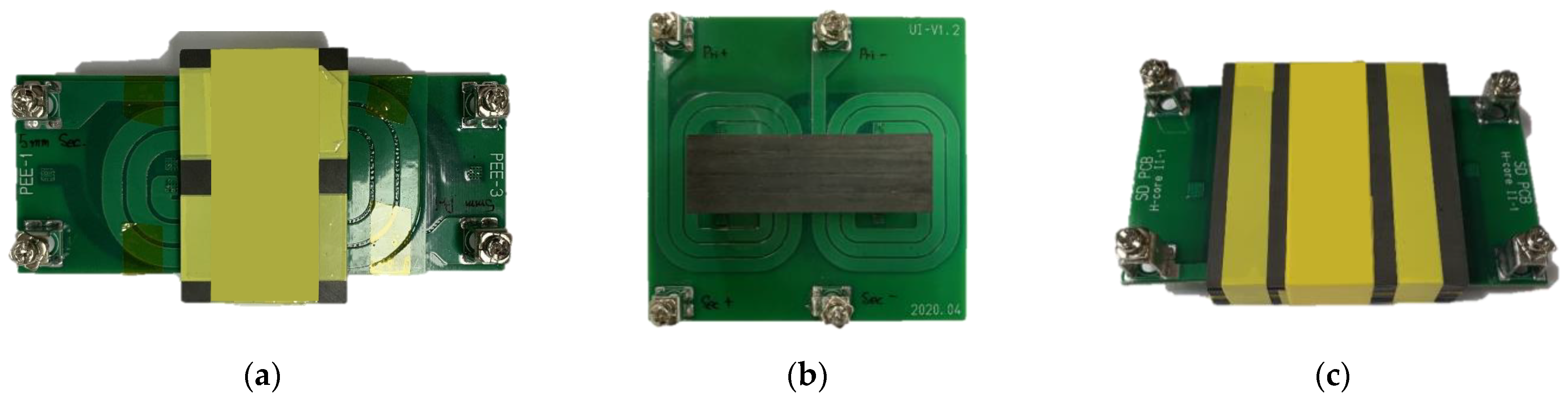
Figure 15.
Planar transformers manufactured in various core shape. (a) PEE core. (b) UI core. (c) H core.
Figure 15.
Planar transformers manufactured in various core shape. (a) PEE core. (b) UI core. (c) H core.
Figure 16.
Experimental waveforms and efficiency of the LLC converter with different transformer core types. (a) PEE core. (b) UI core. (c) H core.
Figure 16.
Experimental waveforms and efficiency of the LLC converter with different transformer core types. (a) PEE core. (b) UI core. (c) H core.
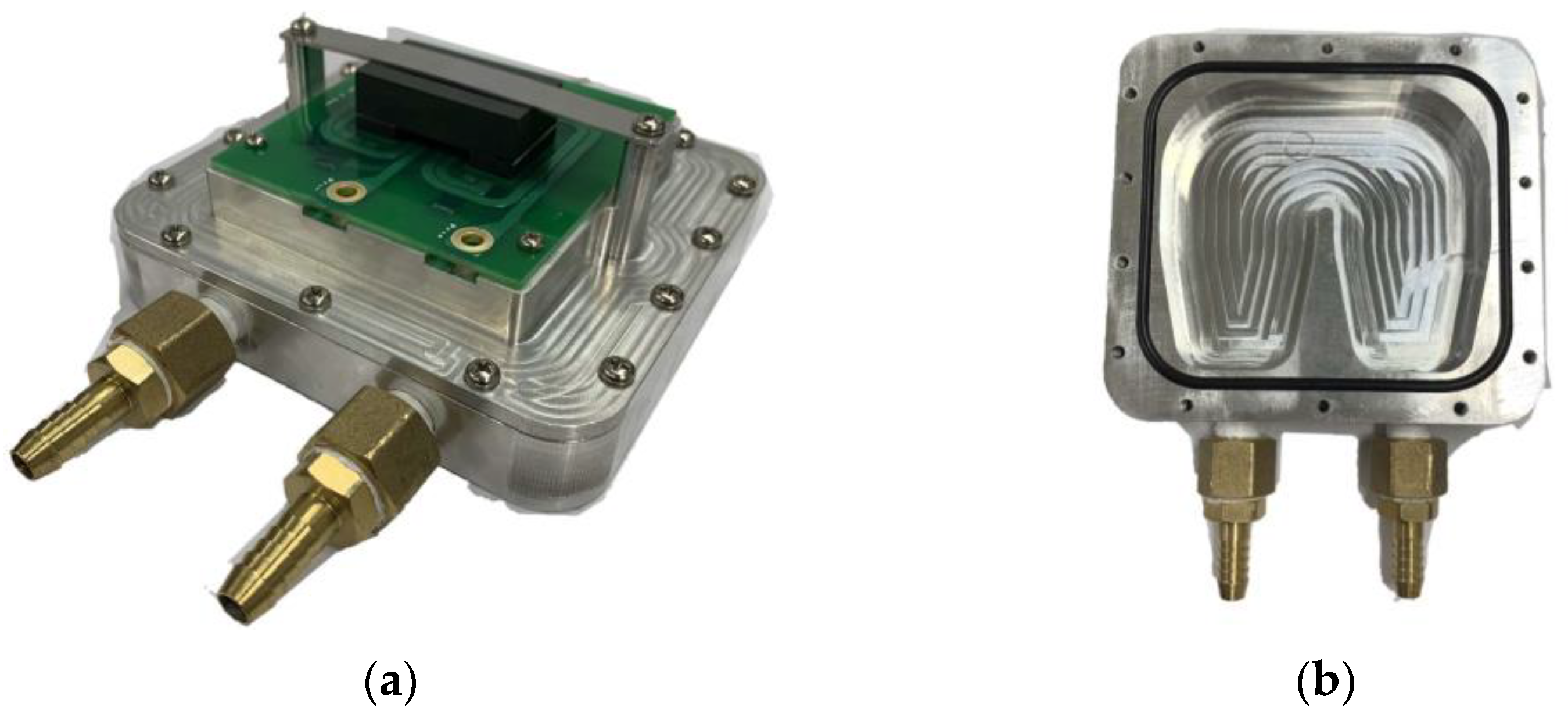
Figure 17.
Planar transformer system with water cooling. (a) Planar transformer. (b) Bottom cooling water passage.
Figure 17.
Planar transformer system with water cooling. (a) Planar transformer. (b) Bottom cooling water passage.
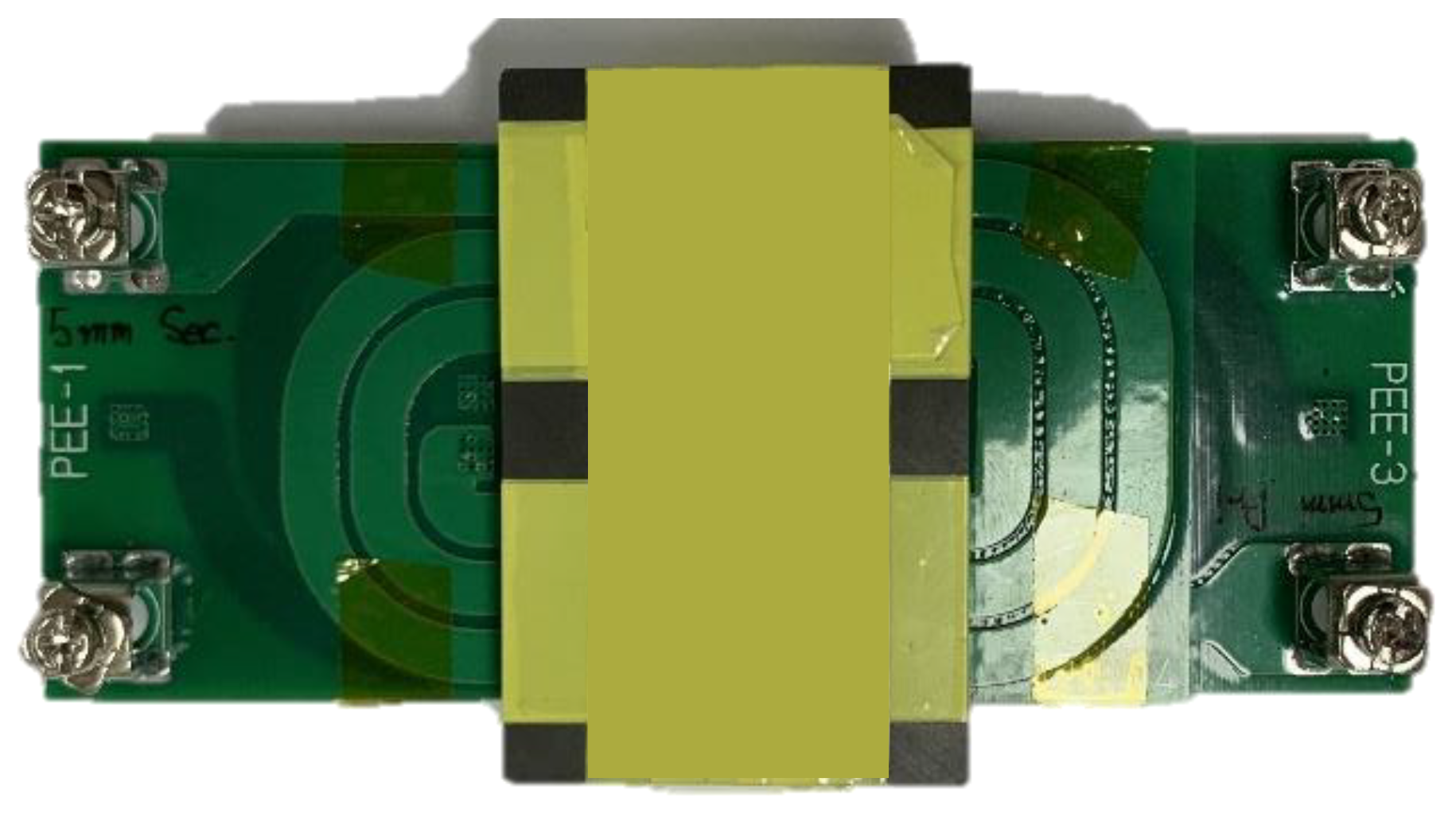
Figure 18.
Planar transformer PCB manufactured in various pattern widths.
Figure 18.
Planar transformer PCB manufactured in various pattern widths.
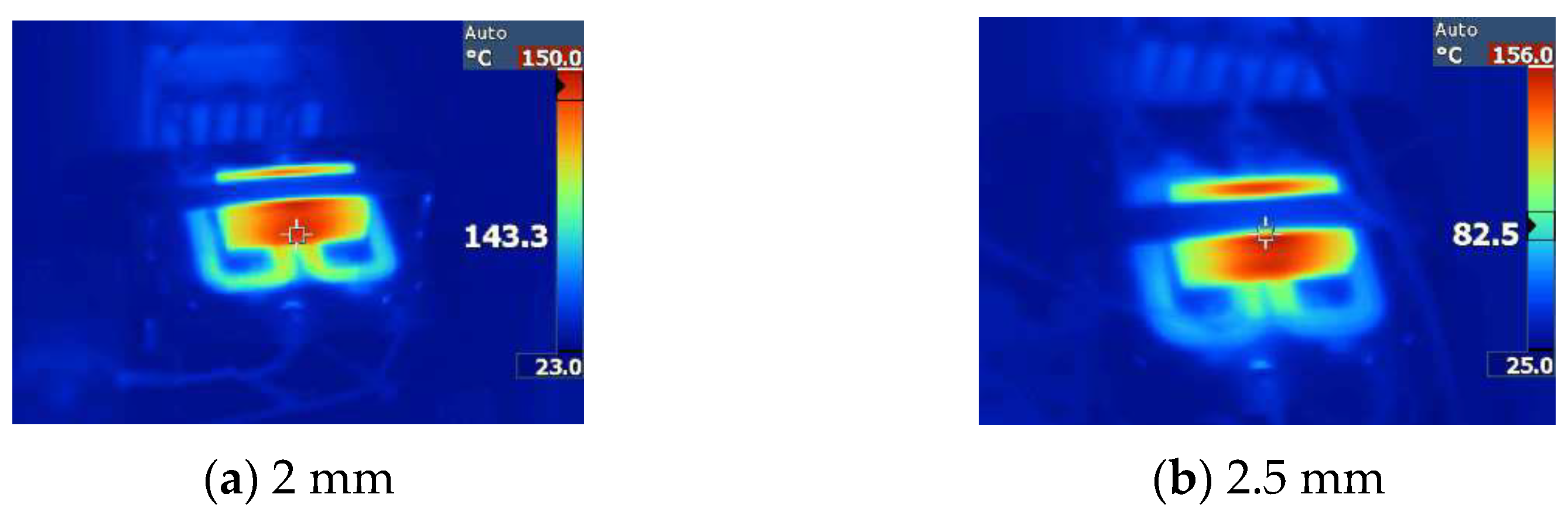
Figure 19.
Thermal image of the planar transformer. (a) 3 oz/2 mm. (b) 3 oz/2.5 mm. (c) 3 oz/3 mm. (d) 3 oz/4 mm.
Figure 19.
Thermal image of the planar transformer. (a) 3 oz/2 mm. (b) 3 oz/2.5 mm. (c) 3 oz/3 mm. (d) 3 oz/4 mm.
Figure 20.
Transformer pattern temperature measurement results over time. (a) 3 oz/2 mm. (b) 3 oz/2.5 mm. (c) 3 oz/3 mm. (d) 3 oz/4 mm.
Figure 20.
Transformer pattern temperature measurement results over time. (a) 3 oz/2 mm. (b) 3 oz/2.5 mm. (c) 3 oz/3 mm. (d) 3 oz/4 mm.
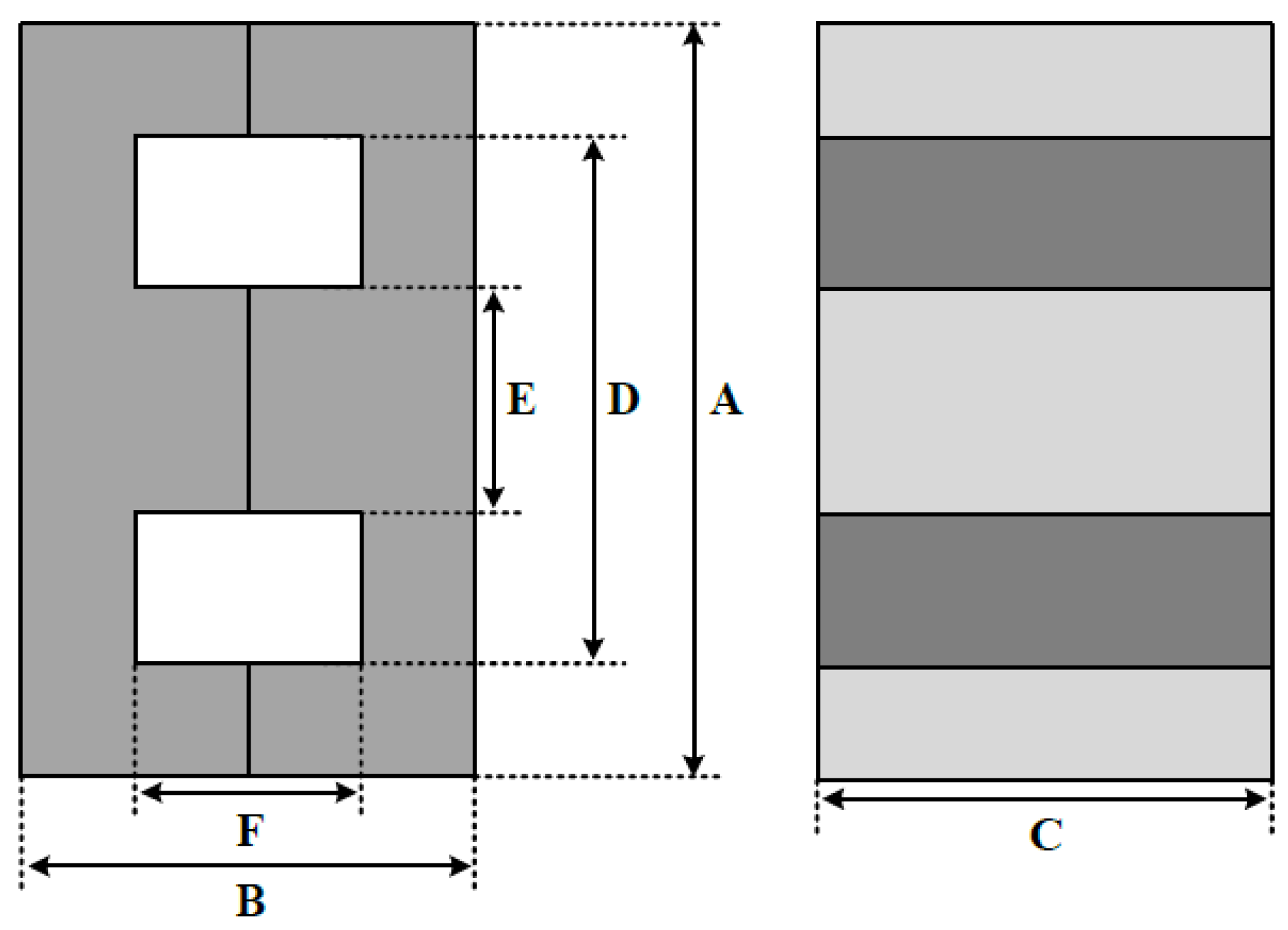
Figure 21.
PEE core design dimensions.
Figure 21.
PEE core design dimensions.
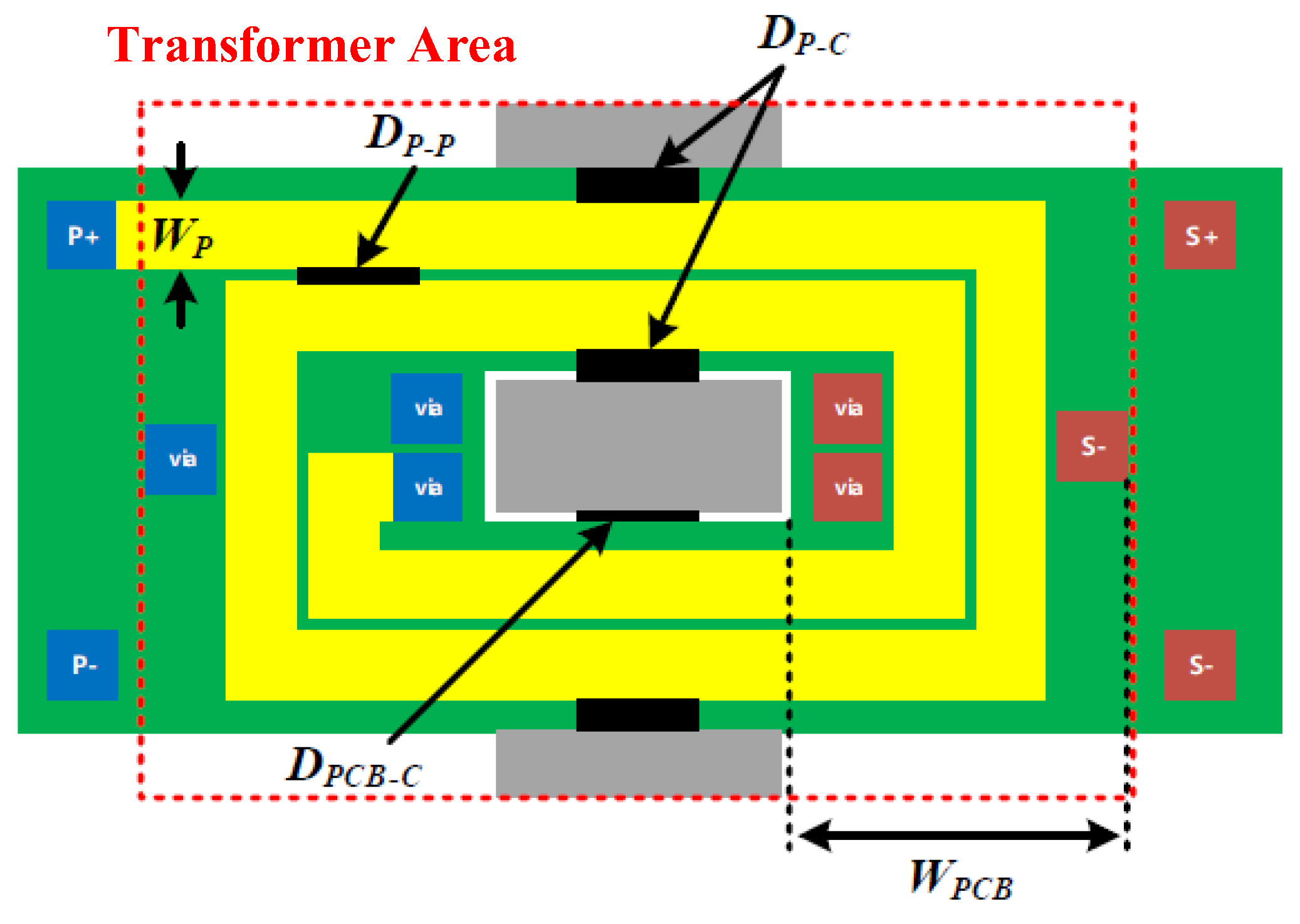
Figure 22.
Parameters for planar transformer design.
Figure 22.
Parameters for planar transformer design.
Figure 23.
Transformer area and volume according to the number of turns.
Figure 23.
Transformer area and volume according to the number of turns.
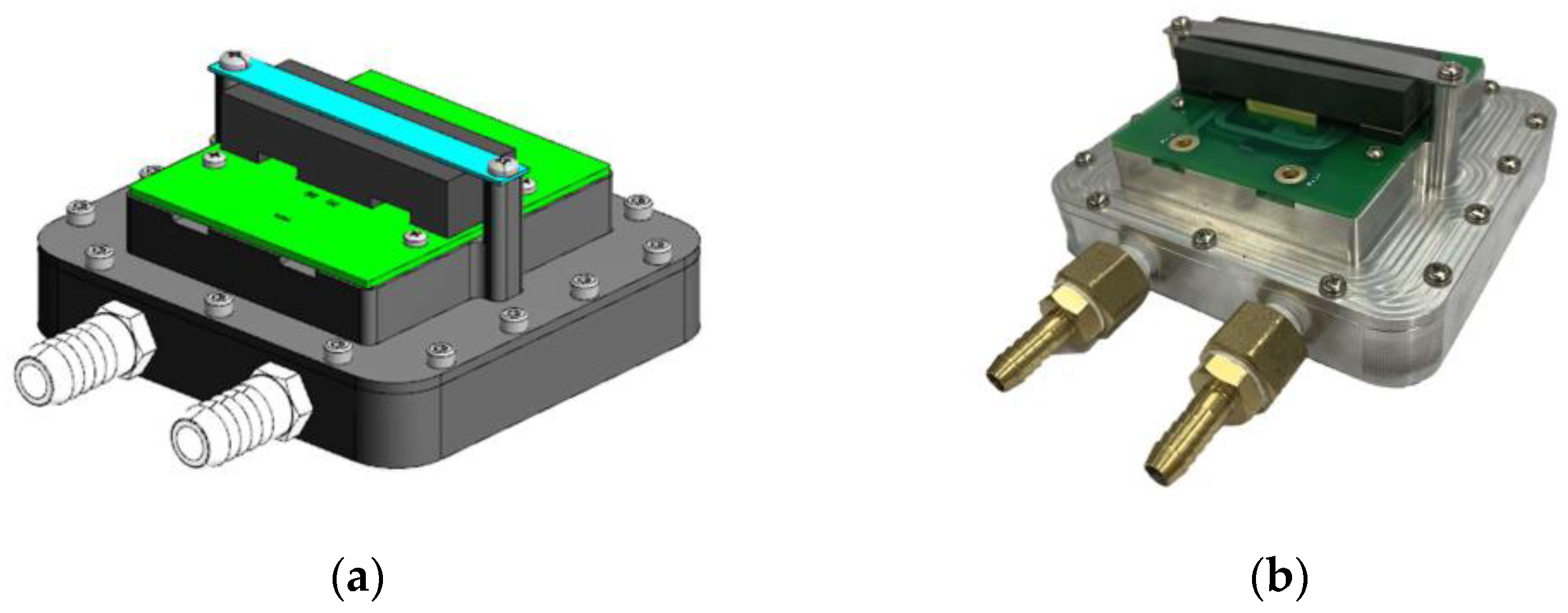
Figure 24.
Optimally designed planar transformer. (a) 3D model. (b) Manufactured transformer.
Figure 24.
Optimally designed planar transformer. (a) 3D model. (b) Manufactured transformer.
Figure 25.
Transformer pattern temperature measurement results over time.
Figure 25.
Transformer pattern temperature measurement results over time.
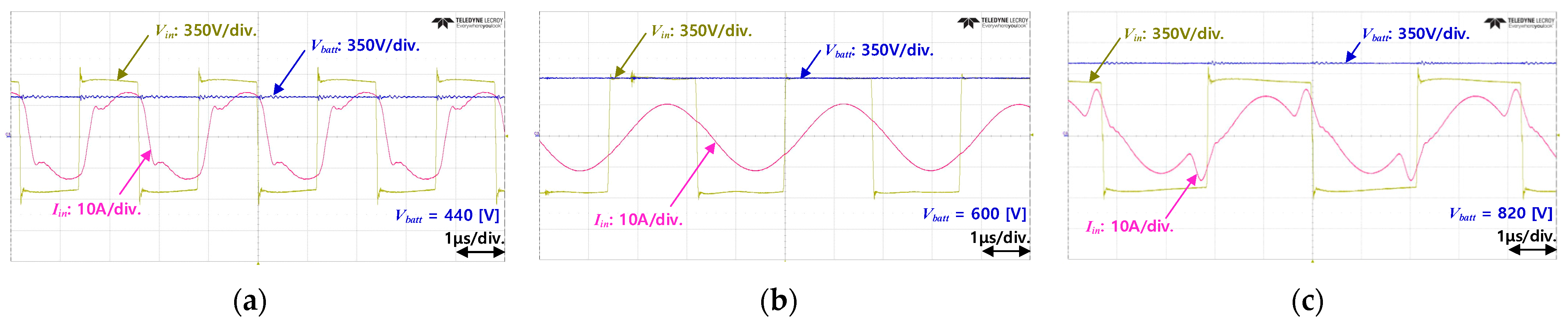
Figure 26.
Experimental waveforms and efficiency of the LLC converter according to the battery voltage. (a) Vbatt = 440 V. (b) Vbatt = 600 V. (c) Vbatt = 820 V.
Figure 26.
Experimental waveforms and efficiency of the LLC converter according to the battery voltage. (a) Vbatt = 440 V. (b) Vbatt = 600 V. (c) Vbatt = 820 V.
Table 1.
Specification of the LLC resonant converter.
Table 1.
Specification of the LLC resonant converter.
| Parameters | Value |
|---|
| DC link voltage, Vdc | 500 V |
| Battery voltage, Vbatt | 440–820 V |
| Rated output power, Po | 3.3 kW |
| Switching frequency, fsw | 200–450 kHz |
| Resonant frequency, fres | 300 kHz |
Table 2.
Parameters of the LLC resonant converter.
Table 2.
Parameters of the LLC resonant converter.
| Parameters | Value |
|---|
| Magnetizing inductance, Lm | 79.3 μH |
| Leakage inductance, Lr | 25.8 μH |
| Resonant capacitor, Cr | 10.91 nF |
| Turns ratio, n | 10:12 |
Table 3.
Parasitic capacitance simulation results according to PCB pattern arrangement.
Table 3.
Parasitic capacitance simulation results according to PCB pattern arrangement.
| Pattern Arrangement | Maximum Capacitance | Minimum Capacitance |
|---|
| Maximize overlap | 8.14 pF | 0.77 pF |
| Minimize overlap | 2.70 pF | 0.68 pF |
Table 4.
Parasitic capacitance measurement results according to PCB pattern arrangement.
Table 4.
Parasitic capacitance measurement results according to PCB pattern arrangement.
| Case | Lm | fres | Ceq |
|---|
| Case 1 | 78.3 μH | 0.7 MHz | 676 pF |
| Case 2 | 74.2 μH | 1.82 MHz | 103 pF |
| Case 3 | 74.0 μH | 1.88 MHz | 96.7 pF |
Table 5.
Operation verification experimental condition.
Table 5.
Operation verification experimental condition.
| Parameters | Value |
|---|
| DC link voltage, Vdc | 500 V |
| Battery voltage, Vbatt | 600 V |
| Rated output power, Po | 3.3 kW |
| Resonant frequency, fres | 300 kHz |
Table 6.
Characteristics of planar transformer core shape.
Table 6.
Characteristics of planar transformer core shape.
| Planar Transformer | PEE Core | UI Core | H Core |
|---|
| Advantage | Low height | Wide pattern heat dissipation area | Low height |
| Narrow area required | Implementing a large number of turns | Minimum volume |
| Disadvantage | Narrow pattern heat dissipation area | Wide area required | Difficult pattern heat dissipation |
| Implementing a large number of turns | High height | Implementing a large number of turns |
Table 7.
Specifications for each planar transformer core shape.
Table 7.
Specifications for each planar transformer core shape.
| Planar Transformer | PEE Core | UI Core | H Core |
|---|
| Size [W × D × H] [mm] | 60 × 100 × 22 | 96 × 55 × 41 | 64 × 74 × 14 |
| Area | 6000 mm2 | 5280 mm2 | 4992 mm2 |
| Volume | 132,000 mm3 | 216,480 mm3 | 69,888 mm3 |
| Magnetizing inductance | 78.32 μH | 78.90 μH | 77.56 μH |
| Leakage inductance | 3.98 μH | 0.73 μH | 4.67 μH |
Table 8.
Current density according to pattern width.
Table 8.
Current density according to pattern width.
| Parameters | Value |
|---|
| Current | 9.8 Arms |
| Thickness | 3 oz |
| Width | 2 mm | 2.5 mm | 3 mm | 4 mm |
| Current density | 46.3 A/mm2 | 37 A/mm2 | 30.9 A/mm2 | 23.1 A/mm2 |
Table 9.
Effective area according to the number of turns.
Table 9.
Effective area according to the number of turns.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Np | 4 turns | 5 turns | 6 turns | 7 turns | 8 turns | 9 turns | 10 turns |
| Ac | 1250.0 mm2 | 1000.0 mm2 | 833.3 mm2 | 714.3 mm2 | 625.0 mm2 | 555.6 mm2 | 500.0 mm2 |
Table 10.
Spacing distance conditions for planar transformer.
Table 10.
Spacing distance conditions for planar transformer.
| Parameters | Value |
|---|
| Spacing distance between patterns, DP-P | 0.6 mm |
| Spacing distance between pattern and core, DP-C | 3 mm |
| Spacing distance between PCB and core, DPCB-C | 1 mm |
Table 11.
Design results of PEE core parameters according to the number of turns.
Table 11.
Design results of PEE core parameters according to the number of turns.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Np | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Ac | 1250.0 mm2 | 1000.0 mm2 | 833.3 mm2 | 714.3 mm2 | 625.0 mm2 | 555.6 mm2 | 500.0 mm2 |
| A | 96.6 mm | 92.4 mm | 85.8 mm | 80.6 mm | 76.4 mm | 77.6 mm | 74.8 mm |
| B | 46.6 mm | 40.6 mm | 37.3 mm | 34.7 mm | 32.6 mm | 29.6 mm | 28.2 mm |
| C | 32.4 mm | 30.8 mm | 28.6 mm | 26.9 mm | 25.5 mm | 25.9 mm | 25.0 mm |
| D | 58.6 mm | 59.9 mm | 56.5 mm | 53.9 mm | 51.8 mm | 56.0 mm | 54.6 mm |
| E | 38.6 mm | 32.6 mm | 29.3 mm | 26.7 mm | 24.6 mm | 21.6 mm | 20.2 mm |
| F | 8 mm | 8 mm | 8 mm | 8 mm | 8 mm | 8 mm | 8 mm |
| Area | 63 cm2 | 65 cm2 | 59 cm2 | 54 cm2 | 50 cm2 | 56 cm2 | 54 cm2 |
| Volume | 294 cm3 | 264 cm3 | 218 cm3 | 186 cm3 | 162 cm3 | 167 cm3 | 151 cm3 |