Event-Triggered Security Consensus for Multi-Agent Systems with Markov Switching Topologies under DoS Attacks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Different from the topology switching process in reference [20], this paper uses the Markov process to establish the topological switching process. We study the consensus of the topology in the random switching process under the DoS attack. Compared with reference [20], this paper also needs to analyze the random process, so the theoretical analysis process is more complex.
- (2)
- In order to describe the issue of energy-limited DoS attack, the DoS attack suffered by the multi-agent systems is further analyzed and the upper limit of DoS attack intensity is given, which will be more in line with practical application scenarios.
- (3)
- Because of the influence of the DoS attacks, the channels between agents will be interrupted. After each attack, the controller of the system will be updated after the communication recovery. Therefore, with the premise of ensuring the secure consensus of the multi-agent systems, an event-triggered control is designed based on stochastic process analysis, a recursive method, and an inequality method to reduce the use of the controller.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Notations
2.2. Graph Theory
2.3. Markovian Switching Process
2.4. DoS Attack Model
3. Problem Formulation
- , ,
- , .
4. Results
4.1. Stability Analysis
4.2. Elimination of Zeno’s Behavior
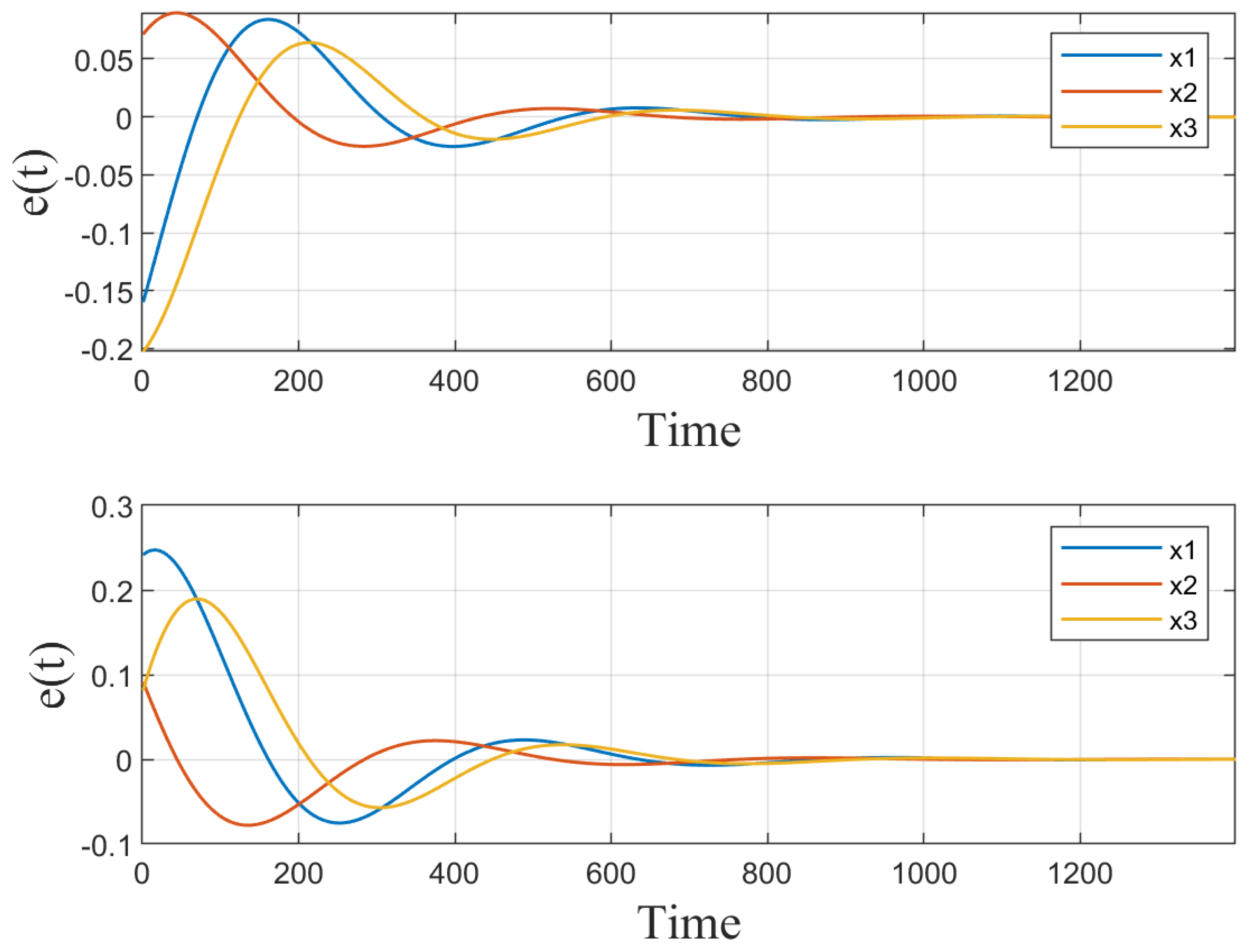
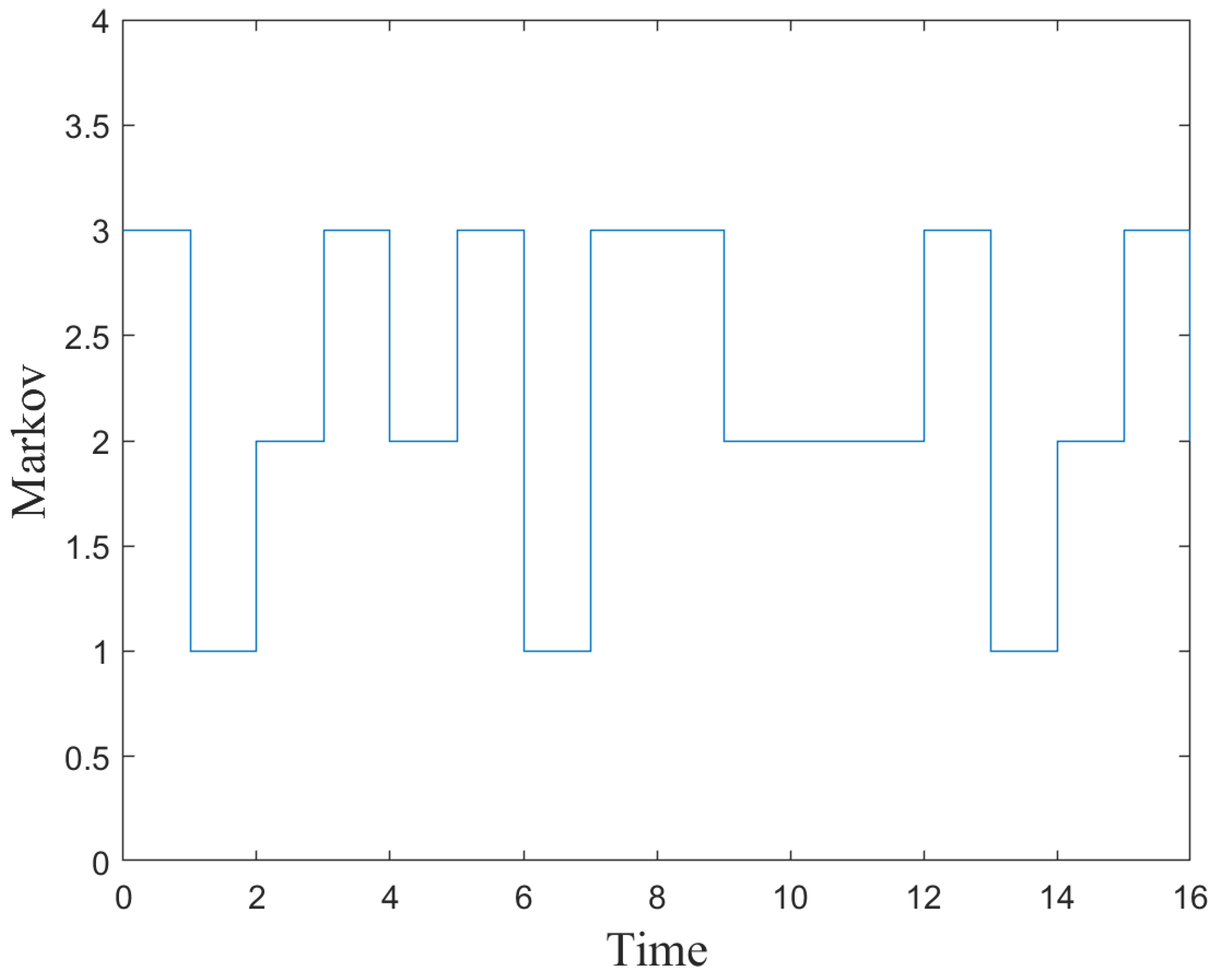
5. Numerical Simulations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, M. Distributed Formation Control for Multiple Quadrotor UAVs under Markovian Switching Topologies with Partially Unknown Transition Rates. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 5706–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yuan, C.; Stegagno, P.; Zeng, W.; Wang, C. Composite cooperative synchronization and decentralized learning of multi-robot manipulators with heterogeneous nonlinear uncertain dynamics. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 5049–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Xu, Q.; Wen, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, P. Distributed secondary control for power allocation and voltage restoration in islanded DC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Wang, R. Distributed impulsive control for heterogeneous multi-agent systems based on event-triggered scheme. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 9972–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, P.; Lim, C. Event-triggered sliding mode scaled consensus control for multi-agent systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2022, 359, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Cao, Q.; Xia, Y.; Gao, Y. Distributed MPC for formation of multi-agent systems with collision avoidance and obstacle avoidance. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 2068–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.; Yuling, L.; Liu, Y. Distributed Finite-Time Integral Sliding-Mode Control for Multi-Agent Systems with Multiple Disturbances Based on Nonlinear Disturbance Observers. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2021, 34, 995–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Bai, H.; George, J.; Chakrabortty, A. Model-Free Optimal Control of Linear Multi-Agent Systems via Decomposition and Hierarchical Approximation. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2021, 8, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D. Robust Stochastic Sampled-data-based Output Consensus of Heterogeneous Multi-agent Systems Subject to Random DoS Attack: A Markovian Jumping System Approach. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Yue, D.; Hu, S.; Ge, H.; Chen, L. Distributed event-triggered consensus of multi-agent systems under periodic DoS jamming attacks. Neurocomputing 2020, 400, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Mo, Z.; Han, Q.L.; Qian, F. Secure impulsive synchronization in Lipschitz-type multi-agent systems subject to deception attacks. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 5, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.; Tahoun, A. Cooperative control for cyber-physical multi-agent networked control systems with unknown false data-injection and replay cyber-attacks. ISA Trans. 2021, 110, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y. MPC-based defense strategy for distributed networked control systems under DoS attacks. Syst. Control Lett. 2019, 128, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amullen, E.M.; Shetty, S.; Keel, L.H. Secured Formation Control for Multi-agent Systems Under DoS Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), Waltham, MA, USA, 10–11 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.; Yang, G. Distributed Consensus Control for Multi-Agent Systems under Denial-of-Service. Inf. Sci. 2018, 439, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, J. Event-Triggered Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Pinning Control for Cluster Consensus of Heterogeneous Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems Under Aperiodic DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2, 1941–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Li, H.; Lu, R.; Shi, Y. Distributed Sliding-Mode Tracking Control of Second-Order Nonlinear Multiagent Systems: An Event-Triggered Approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 9, 3892–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Liu, J.; Cao, J. Resilient event-triggered consensus control for nonlinear muti-agent systems with DoS attacks. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 7071–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, G. Event-Triggered Distributed State Estimation for Multiagent Systems Under DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 99, 6901–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yue, D. Event-trigger-based consensus secure control of linear multi-agent systems under DoS attacks over multiple transmission channels. Inf. Sci. 2020, 5, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, M.; Shi, P.; Wu, Z.G. Event-Based Secure Consensus of Mutiagent Systems Against DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 8, 3468–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Feng, G. A New Switched System Approach to Leader-Follower Consensus of Heterogeneous Linear Multiagent Systems With DoS Attack. IEEE Trans. Syst. 2021, 2, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, C.Y.; He, D.F.; Wang, X. A Novel Intermediate Estimator Based Secure Consensus Control for Multi-agent Systems with Application to Networked Multi-axis Motion Synchronization. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2021, 4, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Guo, G. Exponential consensus of non-linear multi agent systems with semi-Markov switching topologies. IET Control Theory Appl. 2017, 18, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Guo, G. Event-based consensus for second-order multi-agent systems with actuator saturation under fixed and Markovian switching topologies. J. Frankl.-Inst.-Eng. Appl. Math. 2017, 14, 6098–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Mu, X. Stabilization for switched stochastic systems with semi-Markovian switching signals and actuator saturation. Inf. Sci. 2019, 483, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Mu, X. Event-triggered control for networked nonlinear semi-Markovian jump systems with randomly occurring uncertainties and transmission delay. Inf. Sci. 2019, 487, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhong, S. Improved results on consensus of nonlinear MASs with nonhomogeneous Markov switching topologies and DoS cyber attacks. J. Frankl.-Inst.-Eng. Appl. Math. 2021, 14, 7237–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Gong, Y. Leader-following secure consensus for second-order multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics and event-triggered control strategy under DoS attack. Neurocomputing 2019, 416, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, F.; Wen, G.H.; Hu, G.Q. Distributed secure coordinated control for multiagent systems under strategic attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Zhou, D. Event-based Distributed Filtering over Markovian Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2018, 64, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Liu, L. Cooperative output regulation of heterogeneous linear multi-agent systems by event-triggered control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, H.; Han, Q.; Wang, X. Event-Triggered Security Consensus for Multi-Agent Systems with Markov Switching Topologies under DoS Attacks. Energies 2022, 15, 5353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155353
Tian Y, Tian S, Li H, Han Q, Wang X. Event-Triggered Security Consensus for Multi-Agent Systems with Markov Switching Topologies under DoS Attacks. Energies. 2022; 15(15):5353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155353
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yuan, Sheng Tian, Huaqing Li, Qi Han, and Xiaonan Wang. 2022. "Event-Triggered Security Consensus for Multi-Agent Systems with Markov Switching Topologies under DoS Attacks" Energies 15, no. 15: 5353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155353
APA StyleTian, Y., Tian, S., Li, H., Han, Q., & Wang, X. (2022). Event-Triggered Security Consensus for Multi-Agent Systems with Markov Switching Topologies under DoS Attacks. Energies, 15(15), 5353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155353





