Analysis of Natural Hydraulic Fracture Risk of Mudstone Cap Rocks in XD Block of Central Depression in Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
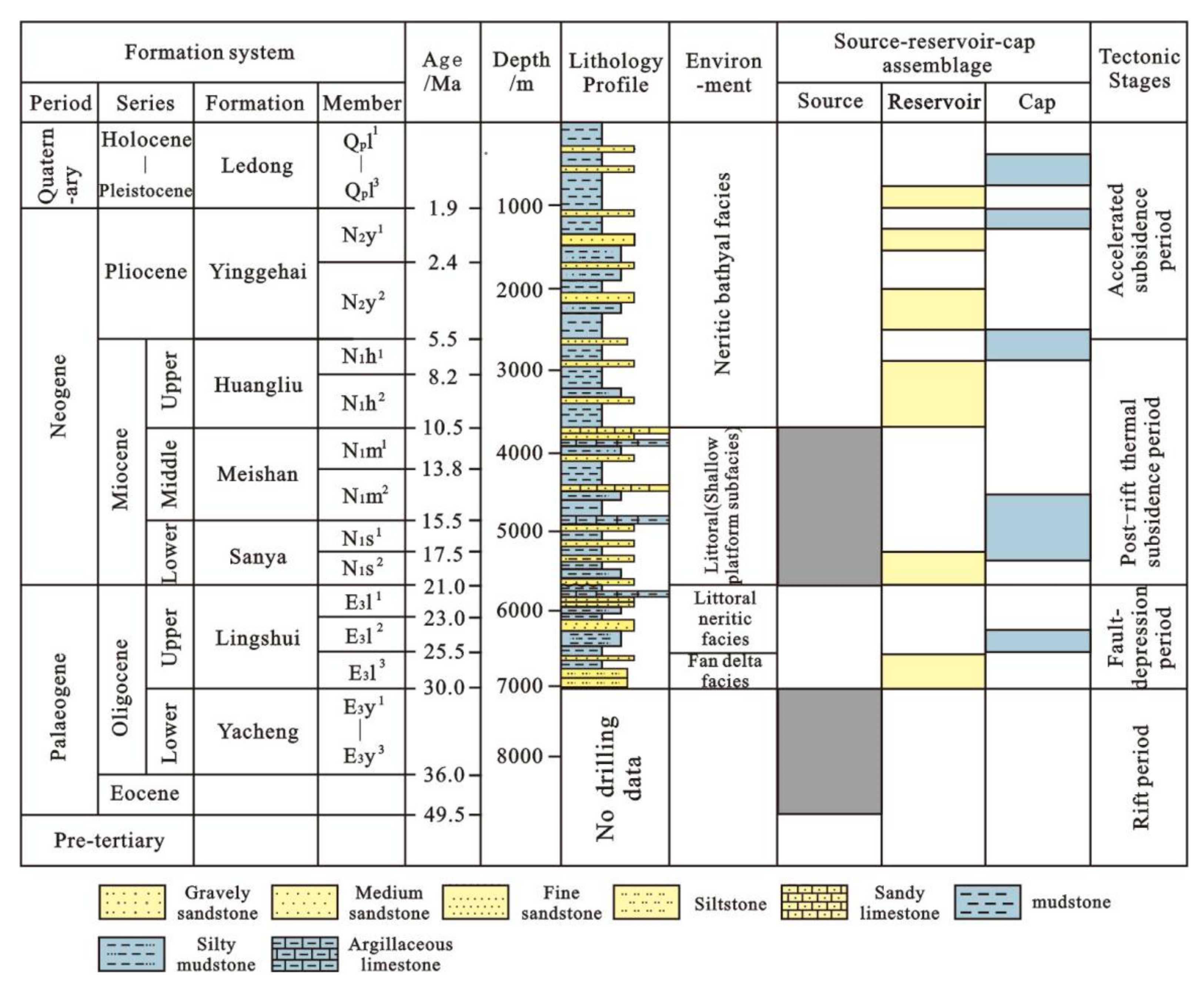
2. Geological Setting
3. Methods
3.1. Principle of Cap Rock Hydraulic Fracture Evaluation
3.2. Parameters of Cap Rock Hydraulic Fracture Evaluation
3.2.1. Vertical Principal Stress
3.2.2. Horizontal Principal Stress
3.2.3. Pore Fluid Pressure and Mechanical Parameters of Cap Rocks
4. Results
4.1. In-Situ Stress and Mechanical Properties of the Cap Rock
4.1.1. Pore Fluid Pressure
4.1.2. Vertical Principal Stress
4.1.3. Horizontal Principal Stress
Minimum Horizontal Principal Stress
Maximum Horizontal Principal Stress
4.1.4. Geomechanical Properties of the Cap Rock
4.2. Risk of Hydraulic Rupture of Mudstone Cap Rock
4.2.1. Risk of Hydraulic Fracture of Cap Rock in Present Conditions
4.2.2. The Evolution Process of Hydraulic Fracture in Cap Rock
5. Discussion
5.1. The Uncertainty of Calculation in Hydraulic Fracture Risk Factor
5.2. Control Effect of Hydraulic Fracturing on Gas Accumulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| FAST | Fault Analysis Seal Technology |
| XD-A, XD-B, XD-C, XD-D, XD-E | Typical block code in the study area |
| P | Fracture pressure, MPa |
| Pp | Pore pressure, MPa |
| PHF | Minimum hydraulic fracture pressure, MPa |
| S1 | Maximum principal stress, MPa |
| S3 | Maximum principal stress, MPa |
| S1 − S3 | Differential stress, MPa |
| Sn | Normal stress, MPa |
| Sv | Vertical stress, MPa |
| Shmin | Horizontal minimum principal stress, MPa |
| SHmax | Horizontal maximum principal stress, MPa |
| τ | Shear stress, MPa |
| T | Tensile strength of rock, MPa |
| C | Cohesion, MPa |
| μ | Coefficient of friction |
| ρw | Density of water, g/cm3 |
| Ρc | Density of overburden layers, g/cm3 |
| g | Gravitational acceleration constant, N/kg |
| hw | Water depth, m |
| h | Burial depth below sea level, m |
| FIT | Formation Integrity Tests |
| LOT | Leak-Off Test |
| XLOT | Extended Leak-Off Test |
| LOP | Leak-off Pressure, MPa |
| FBP | Formation Break-down Pressure, MPa |
| FPP | Fracture Propagation pressure, MPa |
| ISIP | Instantaneous Shut in Pressure, MPa |
| FCP | Fracture Closure Pressure, MPa |
| FRP | fracture reopening pressure, MPa |
| DST | Drill Stem Testing |
| MDT | Modular Formation Dynamics Test |
| CNOOC | China National Offshore Oil Corp. |
| GCTS | Geotechnical Consulting and Testing Systems |
| Ed | Dynamic modulus of elasticity, MPa |
| Vsh | Mudstone content, % |
| K | Correction coefficient, dimensionless |
| Rf | Hydraulic fracture risk factor of cap rock |
References
- Secor, D.T. Role of fluid pressure in jointing. Am. J. Sci. 1965, 263, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.J. Hydraulic fracturing and mineralization. J. Geol. Soc. 1972, 128, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaya, I. Analysis of natural hydraulic fracturing of mudstones during sedimentataion. SPE Prod. Eng. 1986, 1, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, N.L. Theoretical aspects of cap-rock and fault seals for single- and two-phase hydrocarbon columns. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1987, 4, 274–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.W. New insights on natural hydraulic fractures induced byabnormally high pore pressures. AAPG Bull. 1995, 79, 1005–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, S.J.; Nunn, J.A. Episodic fluid expulsion from geopressured sediments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1995, 12, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løseth, H.; Gading, M.; Wensaas, L. Hydrocarbon leakage interpreted on seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, R.H. Conditions for fault-valve behavior. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1990, 541, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, G.M.; Urai, J.L. Top-seal leakage through faults and fractures: The role of mudrock properties. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1999, 158, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildren, S.D.; Hillis, R.R.; Dewhurst, D.N.; Lyon, P.J.; Meyer, J.J.; Boult, P.J. FAST: A new approach to risking fault reactivation and related seal breach of fault seals. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 2005, 2, 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sibson, R.H. Fluid flow accompanying faulting: Field evidence and models. Earthq. Predict. 1981, 4, 593–603. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, J.; Huuse, M.; Aplin, A. Seal bypass systems. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 1141–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhlsdorff, L.; Spiess, S.V. Three-dimensional seismic characterization of a venting site reveals compelling indications of natural hydraulic fracturing. Geology 2004, 32, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, J.W. Hydraulic fracturing during the formation and deformation of a basin: A factor in the dewatering of low-permeability sediments. AAPG Bull. 2001, 85, 737–748. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Hooker, J.; Cartwright, J. Genesis of natural hydraulic fractures as an indicator of basin inversion. J. Struct. Geol. 2017, 102, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, E.S.; Evans, J.P.; Baure, S.J. Failure of cap-rock seals as determined from mechanical stratigraphy, stress history, and tensile-failure analysis of exhumed analogsStress History and Tensile Failure Analysis of Exhumed cap rock Seal Analogs. AAPG Bull. 2014, 98, 2365–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.A.O.; Jian-Zhang, L.I.U.; Hua-Yao, Z.O.U.; Peng-Peng, L.I. Mechanisms of natural gas accumulation and leakage in the overpressured sequences in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, offshore South China Sea. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ungerer, P.; Burrus, J.; Doligez, B.; Chenet, P.Y.; Bessis, F. Basin evaluation by integrated two-dimensional modeling of heat transfer, fluid flow, hydrocarbon generation, and migration. AAPG Bull. 1990, 74, 309–335. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xie, X. Hydrofracturing and episodic fluid flow in mudstone-rich basins-a numerical study. AAPG Bull. 1998, 82, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.N.; Li, S.T.; Wang, Q.Y. Hydraulic fracturing and episodic compaction of mudstones in sedimentary basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1997, 42, 2193–2195. [Google Scholar]
- Caillet, G. The cap rock of the Snorre Field, Norway: A possible leakage by hydraulic fracturing. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1993, 10, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Rouchet, J. Stress fields, a key to oil migration. AAPG Bull. 1981, 65, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.W.; Meng, L.D.; Feng, D.; Zhou, X.N.; Xia, N.; Wei, Z.P. Hydraulic fracturing mechanism and its application in stability evaluation of caprock and fault. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2015, 22, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gaarenstroom, L.; Tromp, R.; Brandenburg, A.M. Overpressures in the Central North Sea: Implications for trap integrity and drilling safety. In Proceedings of the Geological Society, London, Petroleum Geology Conference Series; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 1993; Volume 4, pp. 1305–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinovskaya, E.; Malo, M.; Castillo, D.A. Present-day stress analysis of the St. Lawrence Lowlands sedimentary basin (Canada) and implications for cap rock integrity during CO2 injection operations. Tectonophysics 2012, 518–521, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildren, S.D.; Hills, R.R.; Lyon, P.J.; Meyer, J.J.; Dewhurst, D.N.; Boult, P.J. FAST: A new technique for geomechanical assessment of the risk of reactivation-related breach of fault seals. AAPG Hedberg Ser. 2005, 2, 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.W. Hydraulic Fracturing Mechanism and Quantitative Evaluation Method of Cap Rock and Fault. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R. The Integrity of Cap Rocks and Gas Accumulation in Yingqiong Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.J.; Fan, C.W.; Fu, X.F.; Meng, L.; Liu, B.; Jia, R.; Cao, S.; Du, R.; Li, H.; Tan, J. Risk analysis of natural hydraulic fracturing in an overpressured basin with mud diapirs: A case study from the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; He, S.; Meng, L.D.; Fu, X.; Gong, L.; Wang, H. Sealing mechanisms in volcanic faulted reservoirs in Xujiaweizi extension, Northern Songliao Basin, Northeastern China. AAPG Bull. 2020. ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Junling, H.E.; Xiaofei, F.U.; Liang, Y.A.N.G.; Jilin, X.I.N.G.; Xiaoqing, Z.H.A.O. Reservoir space and enrichment model of shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Changling sag, southern Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Fu, X.; Liu, B.; Miao, F.; Zhou, X.; Meng, Q. Characterization, controlling factors and evolution of fracture effectiveness in shale oil reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.X.; Xia, B.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, B.M.; Sun, D.S. The regularity of oil and gas migration and accumulation and direction of exploration of northern south China sea continental shelf of the western. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 27, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.H. Sequence Stratigraphic Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation Models in Tectonically Active Basins: Case Study on the Yinggehai Basin; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, X.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Tong, C.X.; Zhong, Z.H.; Zhou, J.X.; He, S.L. Main controlling factors and formation models of natural gas reservoirs with high-temperature and overpressure in Yinggehai Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 601–609. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.F.; Chen, H.H.; Kong, L.T.; Wang, Q.R.; Liu, R. Vertical migration system and its control on natural gas accumulation in Yinggehai Basin. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2014, 39, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F.; Li, S.T.; Gong, Z.S.; Yang, J. Mechanism of diapirism and episodic fluid injections in the Yinggehai Basin. Sci. China Ser. D 2001, 31, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.W. The identification and characteristics of migration system induced by high pressure, and its hydrocarbon accumulation process in the Yingqiong Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2018, 39, 254–267. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.Y.; Lei, C. Tectonic stratigraphic framework of Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basins and its implication for tectonic province division in South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 3303–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Dong, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, W. Overpressuring mechanisms in the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. AAPG Bull. 2003, 87, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Ren, J.; Clift, P.D.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, C. The structure and formation of diapirs in the Yinggehai–Song Hong Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibsion, R.H. Structural permeability of fluid-driven fault-fracture meshes. J. Struct. Geol. 1996, 18, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibsion, R.H. Tensile overpressure compartments on low-angle thrust faults. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcgarr, A.; Gay, N.C. State of stress in the earth’s crust. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1978, 6, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwing, W.J.; Nafe, J.E.; Drake, C.L. Seismic refraction. In The Sea; Maxwell, A.E., Ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Volume 4, pp. 53–84. [Google Scholar]
- Engelder, T. Stress Regimes in the Lithosphere; Princeton University Press: Kandy, Sri Lanka, 1993; Volume 102, p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.J.; Traugott, M.O.; Swarbrick, R.E. The use of leak-off tests as means of predicting minimum in-situ stress. Pet. Geosci. 2002, 8, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudy, M.; Zoback, M.D. Drilling-induced tensile wall-fractures: Implications for determination of in-situ stress orientation and magnitude. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1999, 36, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoback, M.D.; Barton, C.A.; Brudy, M.; Castillo, D.A.; Finkbeiner, T.; Grollimund, B.R.; Moos, D.B.; Peska, P.; Ward, C.D.; Wiprut, D.J. Determination of stress orientation and magnitude in deep wells. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2003, 40, 1049–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, M.K.; Aime, M.; Willis, D.G.; Aime, J.M. Mechanics of hydraulic fracturing. Pet. Trans. AIME 1957, 210, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, R. Pore pressure/stress coupling and its implications for seismicity. Explor. Geophys. 2000, 31, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingay, M.R.P.; Hills, R.R.; Morley, C.K.; Swarbrick, R.E.; Okpere, E.C. Pore pressure/stress coupling in Brunei Darussalam—implications for mudstone injection. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 216, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Hao, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. In Situ stress analysis in the Yinggehai Basin, northwestern South China Sea: Implication for the pore pressure-stress coupling process. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, K.P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. Determination of rock fracture toughness K IIC and its relationship with tensile strength. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2011, 44, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.P.; Ferrill, D.A.; Mcginnis, R.N. Using fault displacement and slip tendency to estimate stress states. J. Struct. Geol. 2016, 83, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidbach, O.; Reinecker, J.; Tingay, M.; Müller, B.; Sperner, B.; Fuchs, K.; Wenzel, F. Plate boundary forces are not enough: Second-and third-order stress patterns highlighted in the World Stress Map database. Tectonics 2007, 26, TC6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.S.; Li, S.T. Continental Margin Basin Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Northern South China Sea; China Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]










| Fracture Mode | Fracture Criterion | Differential Stress Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Extensional fracture | P = S3 + T | S1 − S3 < 4T |
| Extensional shear fracture | P = Sn + (4T2 − τ2)/4T | 4T < S1 − S3 < 6T |
| Shear fracture | P = Sn + (C − τ)/μ | S1 − S3 > 6T |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, R.; Fan, C.; Liu, B.; Fu, X.; Jin, Y. Analysis of Natural Hydraulic Fracture Risk of Mudstone Cap Rocks in XD Block of Central Depression in Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Energies 2021, 14, 4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144085
Jia R, Fan C, Liu B, Fu X, Jin Y. Analysis of Natural Hydraulic Fracture Risk of Mudstone Cap Rocks in XD Block of Central Depression in Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Energies. 2021; 14(14):4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144085
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Ru, Caiwei Fan, Bo Liu, Xiaofei Fu, and Yejun Jin. 2021. "Analysis of Natural Hydraulic Fracture Risk of Mudstone Cap Rocks in XD Block of Central Depression in Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea" Energies 14, no. 14: 4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144085
APA StyleJia, R., Fan, C., Liu, B., Fu, X., & Jin, Y. (2021). Analysis of Natural Hydraulic Fracture Risk of Mudstone Cap Rocks in XD Block of Central Depression in Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Energies, 14(14), 4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144085





