Comparison of Machine Learning Methods in Electrical Tomography for Detecting Moisture in Building Walls
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Methods for Identifying Moisture in Building Walls
1.2. EIT Algorithmic Methods
1.3. Objective of Research and Novelties
1.4. Structure of the Paper
2. Materials and Methods
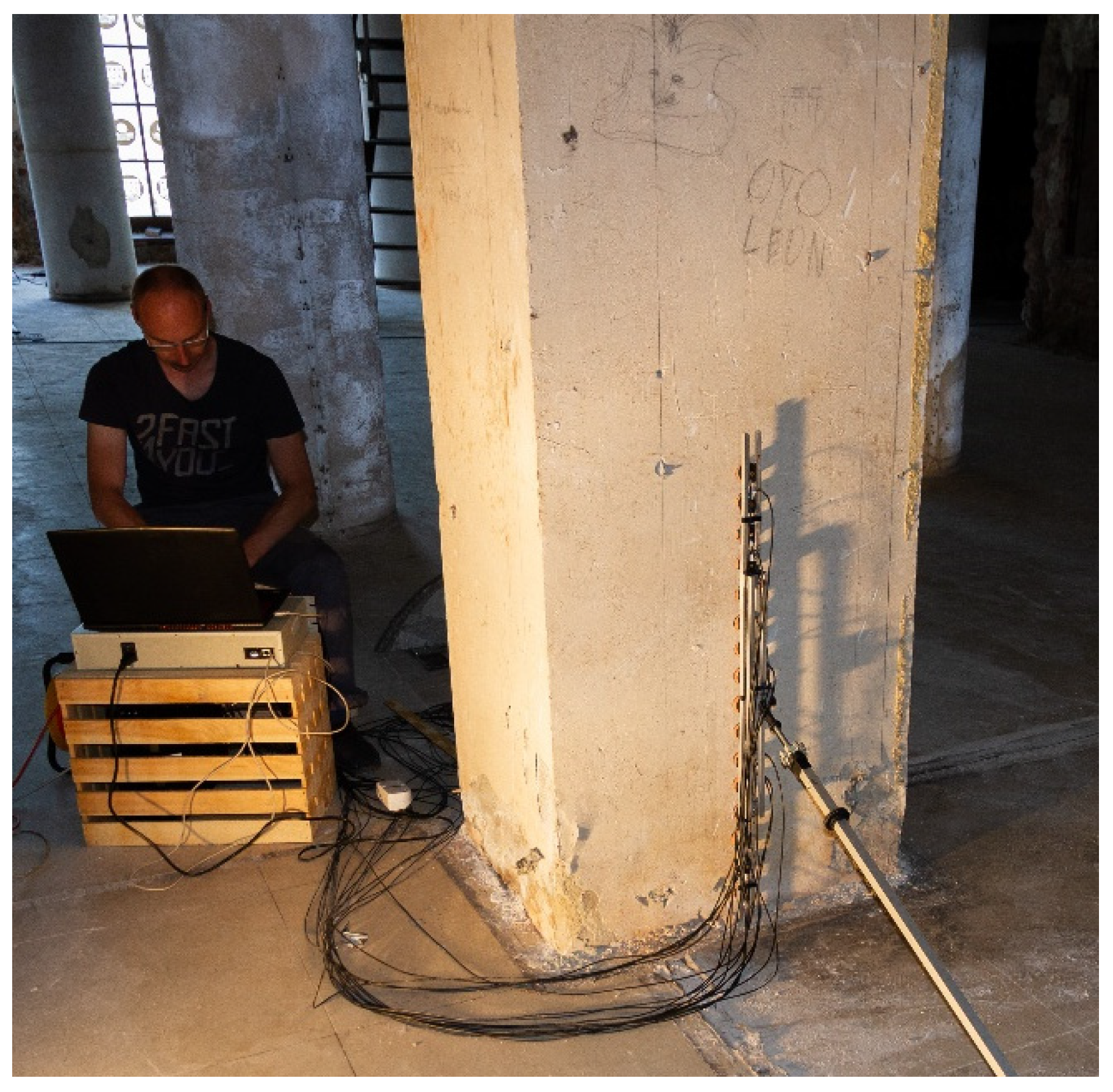
2.1. Historical Building as a Research Object
2.2. Validation Measurements
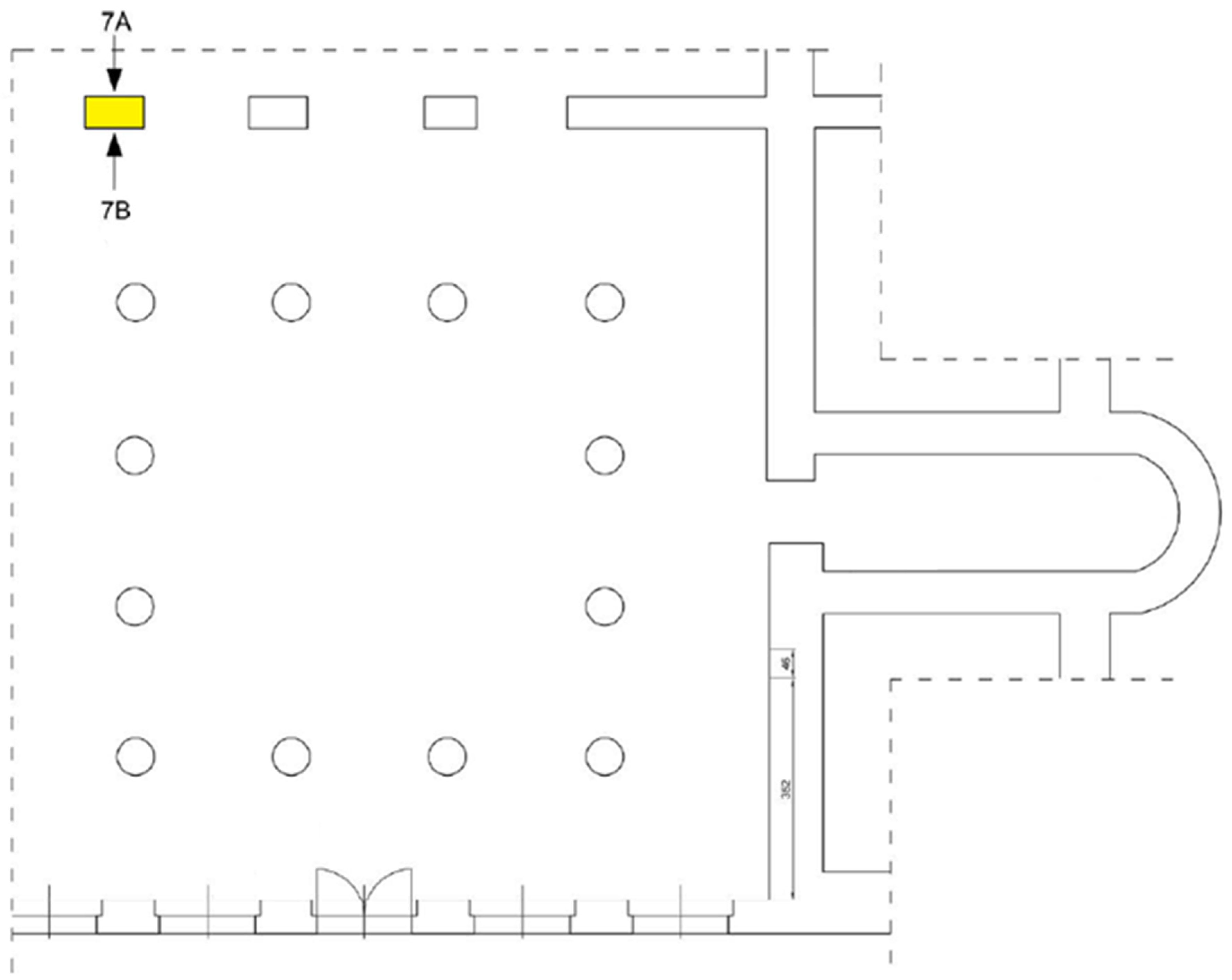
 ”. The sites for sampling the wall for invasive measurements using the gravimetric method are marked with the symbol “
”. The sites for sampling the wall for invasive measurements using the gravimetric method are marked with the symbol “ ”. All distances are in millimeters.
”. All distances are in millimeters.2.3. Methods of Creating a Tomographic Image
2.3.1. Gauss–Newton (GN)
2.3.2. Linear Regression with SVM Learner (LR-SVM)
2.3.3. Linear Regression with Least Squares Learner (LR-LS)
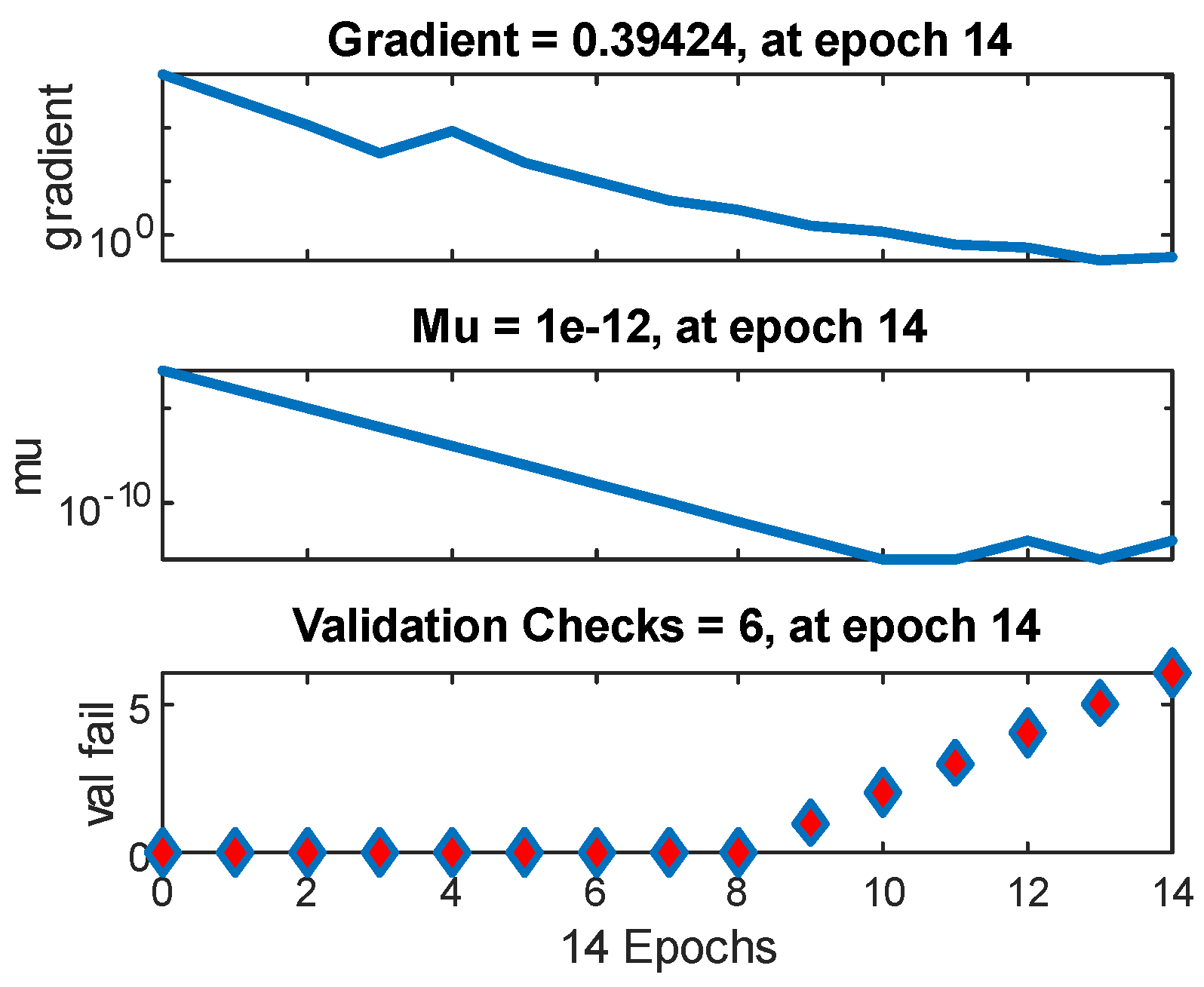
2.3.4. Artificial Neural Network
3. Results
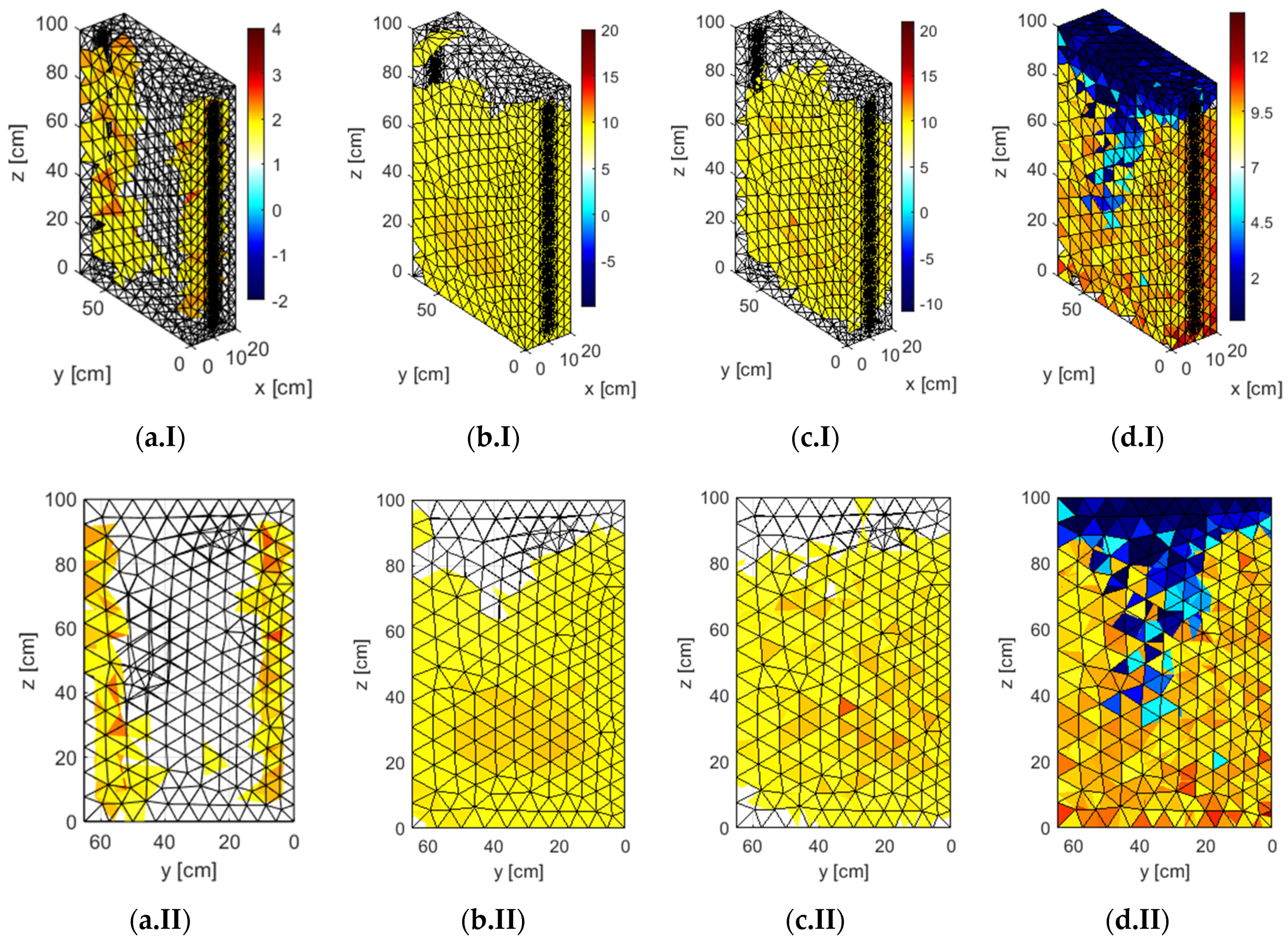
3.1. Visualizations of Real Measurements
3.2. Comparison of Methods Based on Simulation Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rymarczyk, T.; Kłosowski, G.; Kozłowski, E. A Non-Destructive System Based on Electrical Tomography and Machine Learning to Analyze the Moisture of Buildings. Sensors 2018, 18, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, A. Measuring of the moisture content in brick walls of historical buildings-the overview of methods. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 251. [Google Scholar]
- Rymarczyk, T.; Kłosowski, G.; Hoła, A.; Hoła, J.; Sikora, J.; Tchórzewski, P.; Skowron, Ł. Historical Buildings Dampness Analysis Using Electrical Tomography and Machine Learning Algorithms. Energies 2021, 14, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiak, R.; Wajman, R.; Jaworski, T.; Fiderek, P.; Fidos, H.; Nowakowski, J.; Sankowski, D. Study on two-phase flow regime visualization and identification using 3D electrical capacitance tomography and fuzzy-logic classification. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2014, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbaa, H.; Jackowska-Strumiłło, L.; Grudzień, K.; Romanowski, A. Application of electrical capacitance tomography and artificial neural networks to rapid estimation of cylindrical shape parameters of industrial flow structure. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2016, 65, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryszyn, J.; Smolik, W. Toolbox for 3D modelling and image reconstruction in electrical capacitance tomography. Inform. Control Meas. Econ. Environ. Prot. 2017, 7, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryszyn, J.; Wanta, D.M.; Smolik, W.T. Gain Adjustment for Signal-to-Noise Ratio Improvement in Electrical Capacitance Tomography System EVT4. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 8107–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrowicz, M.; Kapusta, P.; Jackowska-Strumiłło, L.; Sankowski, D. Acceleration of image reconstruction process in the electrical capacitance tomography 3D in heterogeneous, multi-GPU system. Inform. Control Meas. Econ. Environ. Prot. 2017, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajman, R.; Fiderek, P.; Fidos, H.; Jaworski, T.; Nowakowski, J.; Sankowski, D.; Banasiak, R. Metrological evaluation of a 3D electrical capacitance tomography measurement system for two-phase flow fraction determination. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 065302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraj, A.; Korzeniewska, E.; Krawczyk, A. Classification algorithms to identify changes in resistance. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2015, 1, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesny, A.; Korzeniewska, E. Selection of the method for the earthing resistance measurement. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2018, 94, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kłosowski, G.; Rymarczyk, T.; Gola, A. Increasing the reliability of flood embankments with neural imaging method. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, F.R.M.; Azida, N.A.N.; Nor Ayob, N.M.; Pusppanathan, J.; Jumaah, M.F.; Goh, C.L.; Rahim, R.A.; Ahmad, A.; Md Yunus, Y.; Rahim, H.A. Simulation Study of Bubble Detection Using Dual-Mode Electrical Resistance and Ultrasonic Transmission Tomography for Two-Phase Liquid and Gas. Sens. Transducers J. 2013, 150, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Romanowski, A. Contextual Processing of Electrical Capacitance Tomography Measurement Data for Temporal Modeling of Pneumatic Conveying Process. In Proceedings of the 2018 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS), Poznan, Poland, 9–12 September 2018; pp. 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani, M.; Mitchell, C.N.; Banasiak, R.; Wajman, R.; Adler, A. Four-dimensional electrical capacitance tomography imaging using experimental data. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2009, 90, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, S. Computationally efficient image reconstruction algorithm for electrical capacitance tomography. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2019, 41, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babout, L.; Grudzień, K.; Wiącek, J.; Niedostatkiewicz, M.; Karpiński, B.; Szkodo, M. Selection of material for X-ray tomography analysis and DEM simulations: Comparison between granular materials of biological and non-biological origins. Granul. Matter 2018, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulka, J. GPU-Accelerated Reconstruction of T2 Maps in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2015, 15, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.; Korzeniewska, E. Magnetophosphenes–history and contemporary implications. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2018, 1, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Adler, A.; Dai, T.; Peyton, A.J. Application of a single step temporal imaging of magnetic induction tomography for metal flow visualisation. Insight Non Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2008, 50, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, E.; Rymarczyk, T.; Klosowski, G. Logistic regression application to image reconstruction in UST. In Proceedings of the 2019 Applications of Electromagnetics in Modern Engineering and Medicine, PTZE, Janow Podlaski, Poland, 9–12 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rymarczyk, T.; Kozłowski, E.; Kłosowski, G.; Niderla, K. Logistic Regression for Machine Learning in Process Tomography. Sensors 2019, 19, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabanikhin, S.I. Definitions and examples of inverse and ill-posed problems. J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl. 2008, 16, 317–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiulewicz-Kaczmarek, M.; Antosz, K.; Wyczółkowski, R.; Mazurkiewicz, D.; Sun, B.; Qian, C.; Ren, Y. Application of MICMAC, Fuzzy AHP, and Fuzzy TOPSIS for Evaluation of the Maintenance Factors Affecting Sustainable Manufacturing. Energies 2021, 14, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, E.; Mazurkiewicz, D.; Żabiński, T.; Prucnal, S.; Sęp, J. Assessment model of cutting tool condition for real-time supervision system. Eksploat. I Niezawodn. Reliab. 2019, 21, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yang, Y. Image Reconstruction in Electrical Impedance Tomography Based on Structure-Aware Sparse Bayesian Learning. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 37, 2090–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Khambampati, A.K.; Seppänen, A.; Du, J. A Parametric Level set Method for Imaging Multiphase Conductivity Using Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging Comput. Imaging 2018, 4, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jia, J. Accelerated Structure-Aware Sparse Bayesian Learning for Three-Dimensional Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5033–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Tan, C.; Jia, J. Efficient Multitask Structure-Aware Sparse Bayesian Learning for Frequency-Difference Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymarczyk, T.; Kozłowski, E.; Tchórzewski, P.; Kłosowski, G.; Adamkiewicz, P. Applying the logistic regression in electrical impedance tomography to analyze conductivity of the examined objects. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2020, 64, S235–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymarczyk, T.; Oleszek, M.; Szumowski, J.; Tchorzewski, P.; Adamkiewicz, P.; Sikora, J. A hybrid tomography system for the analysis of wall dampness. In Proceedings of the 2018 Applications of Electromagnetics in Modern Techniques and Medicine, PTZE, Racławice, Poland, 9–12 September 2018; pp. 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Jauhiainen, J.; Kuusela, P.; Seppanen, A.; Valkonen, T. Relaxed gauss-newton methods with applications to electrical impedance tomography. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2020, 13, 1415–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Maass, P. An analysis of electrical impedance tomography with applications to Tikhonov regularization. ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var. 2012, 18, 1027–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Lin, C.J. Large-scale linear support vector regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 3323–3348. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, C.J.; Keerthi, S.S.; Sundararajan, S. A dual coordinate descent method for large-scale linear SVM. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 408–415. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L. Dual averaging methods for regularized stochastic learning and online optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 2543–2596. [Google Scholar]









| Methods of Testing the Moisture Content in Masonry Walls | ||
|---|---|---|
| Destructive (Invasive) Methods | Non-Destructive (Non-Invasive) Indirect Methods | |
| Direct Methods | Indirect Methods | |
|
|
|
| # of Spot | Side of the Wall | Distance of the Measuring Point to the Floor Level | Dielectric Meter Indication | Microwave Meter Indication | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
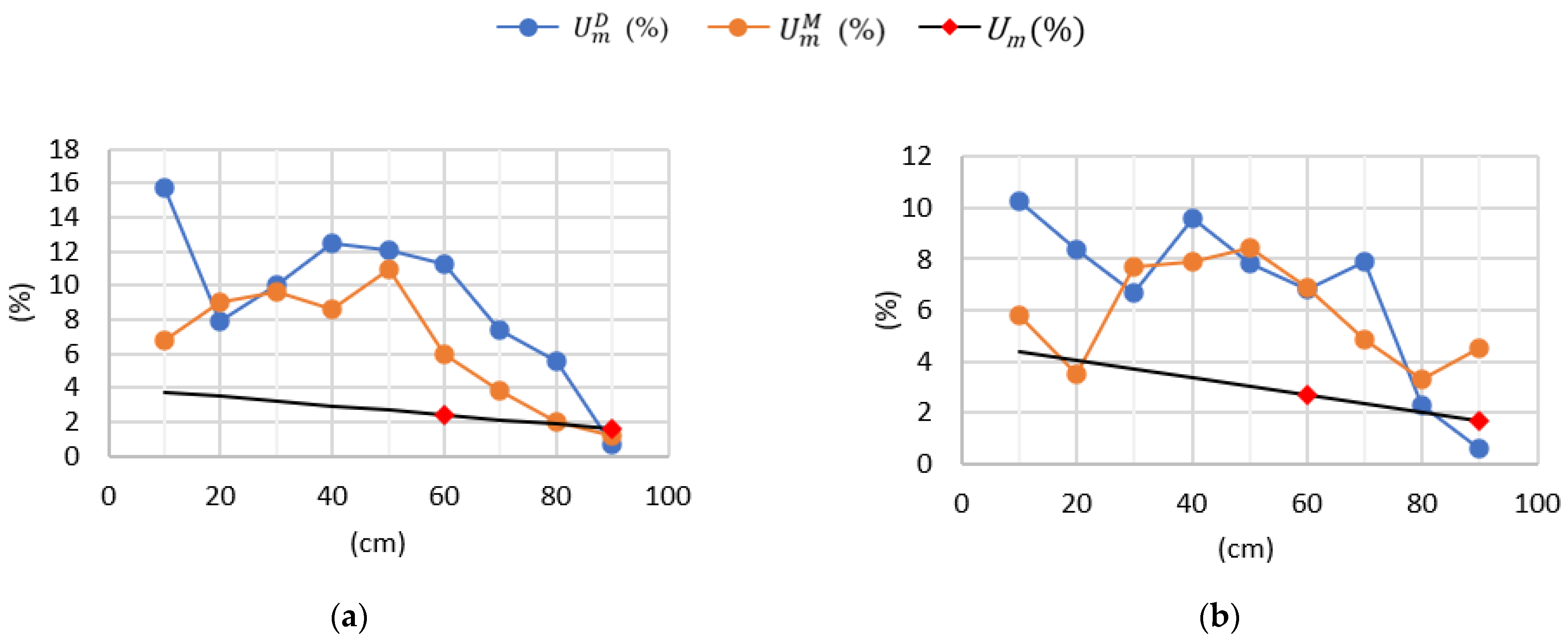
| 109 | 7B | 10 cm | 98.5 | 10.25 | 36.8 | 5.8 | - |
| 110 | 20 cm | 87.3 | 8.3 | 30.1 | 3.5 | - | |
| 111 | 30 cm | 77.6 | 6.7 | 42.5 | 7.7 | - | |
| 112 | 40 cm | 94.8 | 9.6 | 43.0 | 7.9 | - | |
| 113 | 50 cm | 84.2 | 7.8 | 44.6 | 8.4 | - | |
| 114 | 60 cm | 78.1 | 6.8 | 40.0 | 6.9 | 2.70% | |
| 115 | 70 cm | 84.6 | 7.9 | 34.1 | 4.8 | - | |
| 116 | 80 cm | 51.6 | 2.3 | 29.5 | 3.3 | - | |
| 117 | 90 cm | 41.2 | 0.6 | 33.2 | 4.5 | 1.70% | |
| 118 | 7A | 10 cm | 131.2 | 15. 8 | 39.9 | 6.8 | - |
| 119 | 20 cm | 84.8 | 7.9 | 46.3 | 9.0 | - | |
| 120 | 30 cm | 97.5 | 10.1 | 48.1 | 9.6 | - | |
| 121 | 40 cm | 111.9 | 12.5 | 45.2 | 8.6 | - | |
| 122 | 50 cm | 109.6 | 12.1 | 52.0 | 11.0 | - | |
| 123 | 60 cm | 104.4 | 11.2 | 37.5 | 6.0 | 2.41% | |
| 124 | 70 cm | 81.8 | 7.4 | 31.1 | 3.8 | - | |
| 125 | 80 cm | 70.6 | 5.5 | 25.7 | 2.0 | - | |
| 126 | 90 cm | 41.8 | 0.7 | 23.5 | 1.2 | 1.59% | |
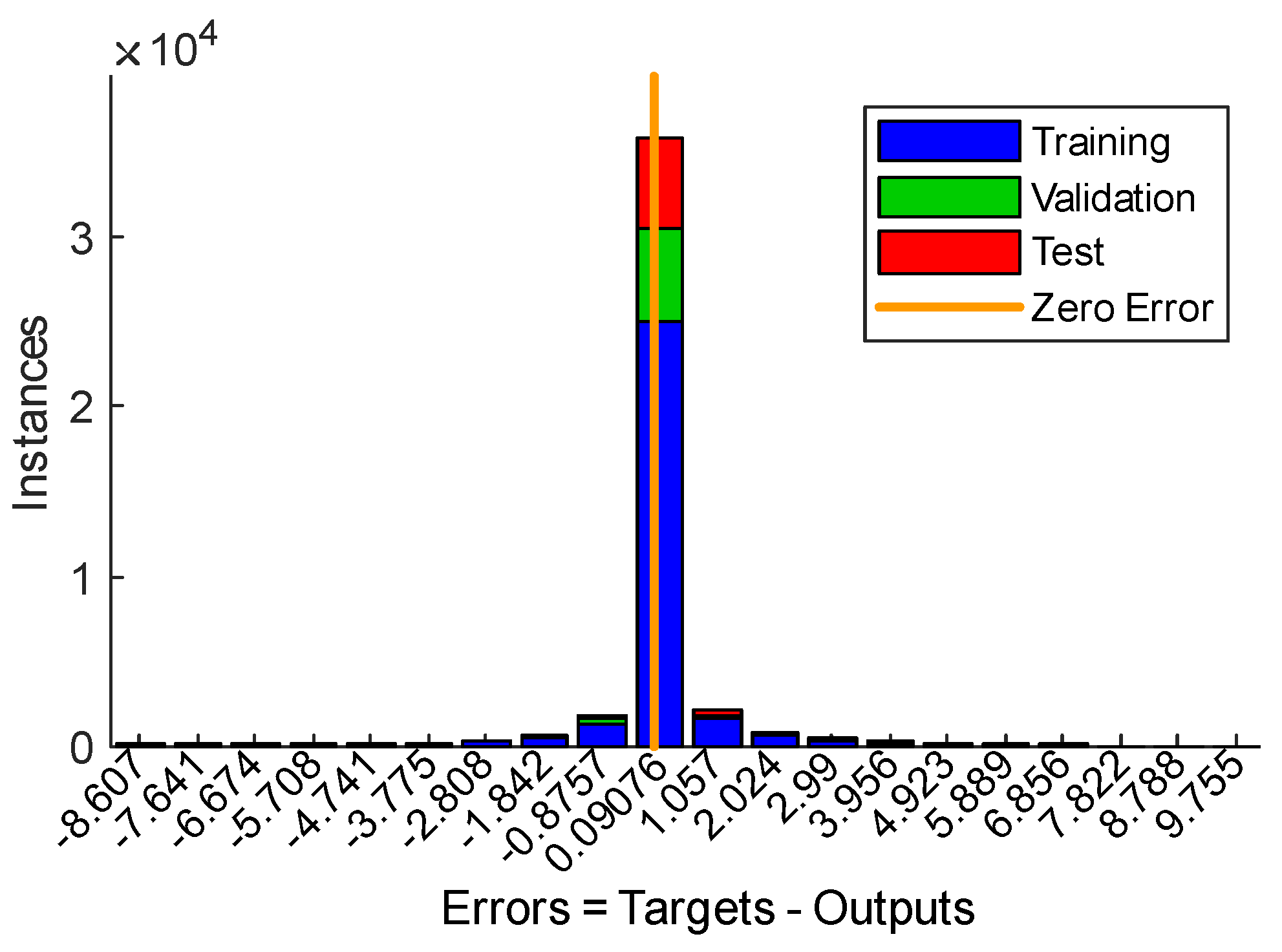
| Division of Data into Sets | Number of Cases in a Given Set | Mean Square Error (MSE) | Regression (R) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set (70%) | 30,800 | 1.80529 | 0.953182 |
| Validation set (15%) | 6600 | 2.20707 | 0.942070 |
| Testing set (15%) | 6600 | 2.26530 | 0.940561 |
| Indicator | Methods of Reconstruction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN | LR-SVM | LR-LS | ANN | |
| RMSE | 4.3799 | 1.7329 | 1.8647 | 0.7428 |
| RIE | 0.7944 | 0.3143 | 0.3382 | 0.1347 |
| PE | 79% | 31% | 34% | 14% |
| ICC | 0.5542 | 0.9077 | 0.8915 | 0.9836 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rymarczyk, T.; Kłosowski, G.; Hoła, A.; Sikora, J.; Wołowiec, T.; Tchórzewski, P.; Skowron, S. Comparison of Machine Learning Methods in Electrical Tomography for Detecting Moisture in Building Walls. Energies 2021, 14, 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14102777
Rymarczyk T, Kłosowski G, Hoła A, Sikora J, Wołowiec T, Tchórzewski P, Skowron S. Comparison of Machine Learning Methods in Electrical Tomography for Detecting Moisture in Building Walls. Energies. 2021; 14(10):2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14102777
Chicago/Turabian StyleRymarczyk, Tomasz, Grzegorz Kłosowski, Anna Hoła, Jan Sikora, Tomasz Wołowiec, Paweł Tchórzewski, and Stanisław Skowron. 2021. "Comparison of Machine Learning Methods in Electrical Tomography for Detecting Moisture in Building Walls" Energies 14, no. 10: 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14102777
APA StyleRymarczyk, T., Kłosowski, G., Hoła, A., Sikora, J., Wołowiec, T., Tchórzewski, P., & Skowron, S. (2021). Comparison of Machine Learning Methods in Electrical Tomography for Detecting Moisture in Building Walls. Energies, 14(10), 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14102777








