A Probabilistic Approach for Eye-Tracking Based Process Tracing in Catalog Browsing
Abstract
:Introduction
Consumer Decision Processes
Catalog Browsing States
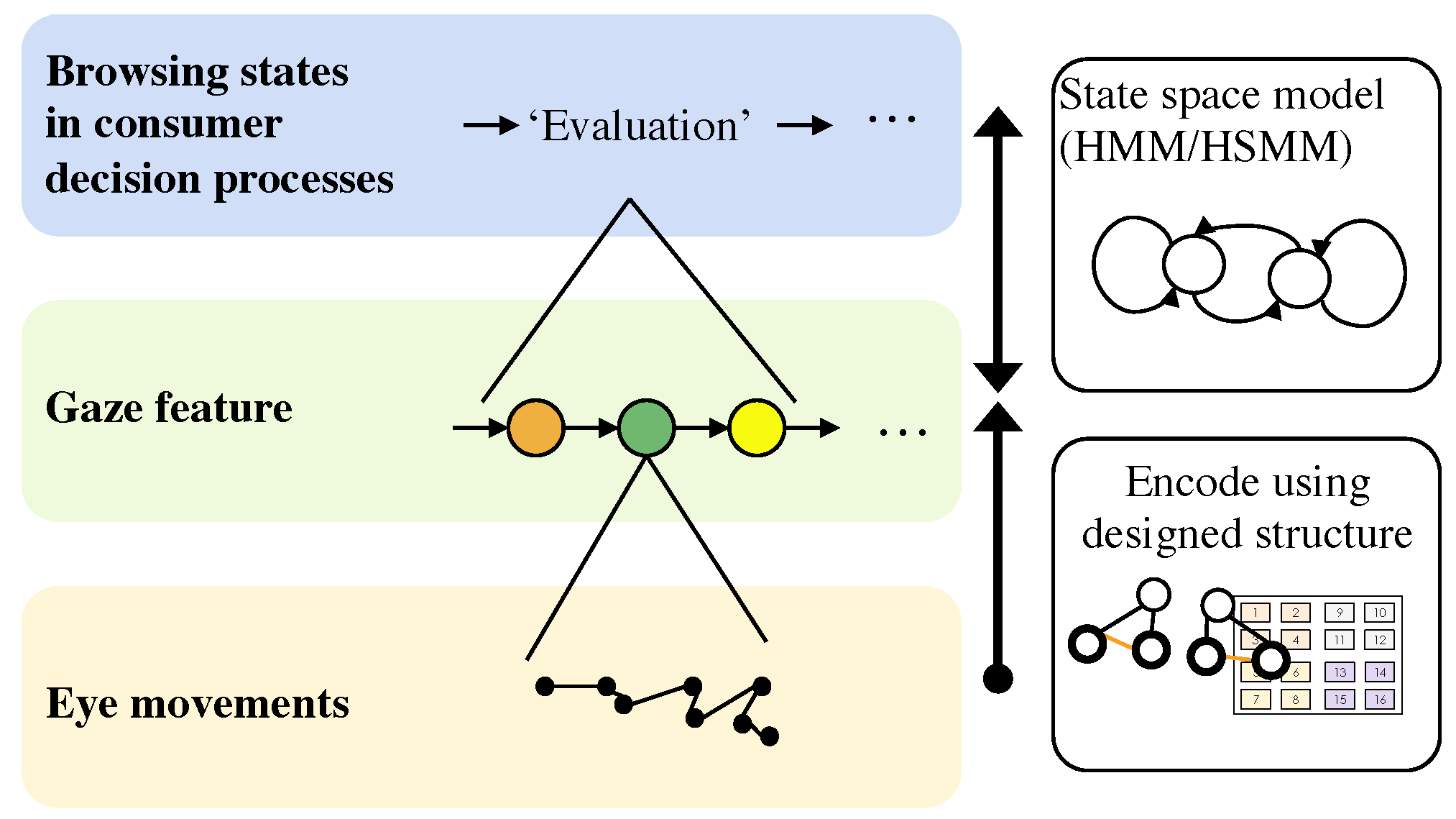
Probabilistic approach in modeling information processing states
Browsing states and task complexities
Approach of this study
Data Collection
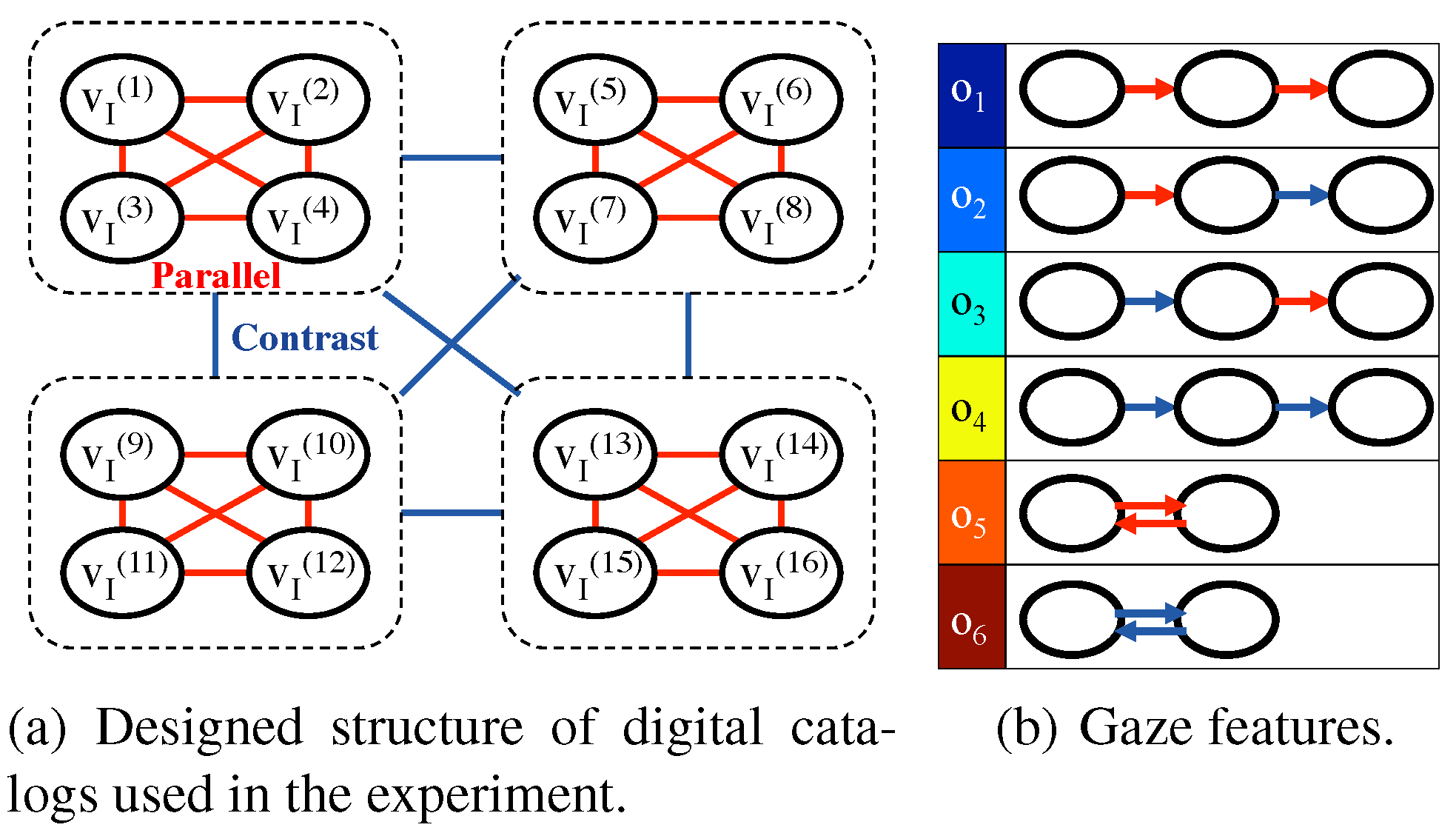
Digital catalogs
Task complexity
Procedure
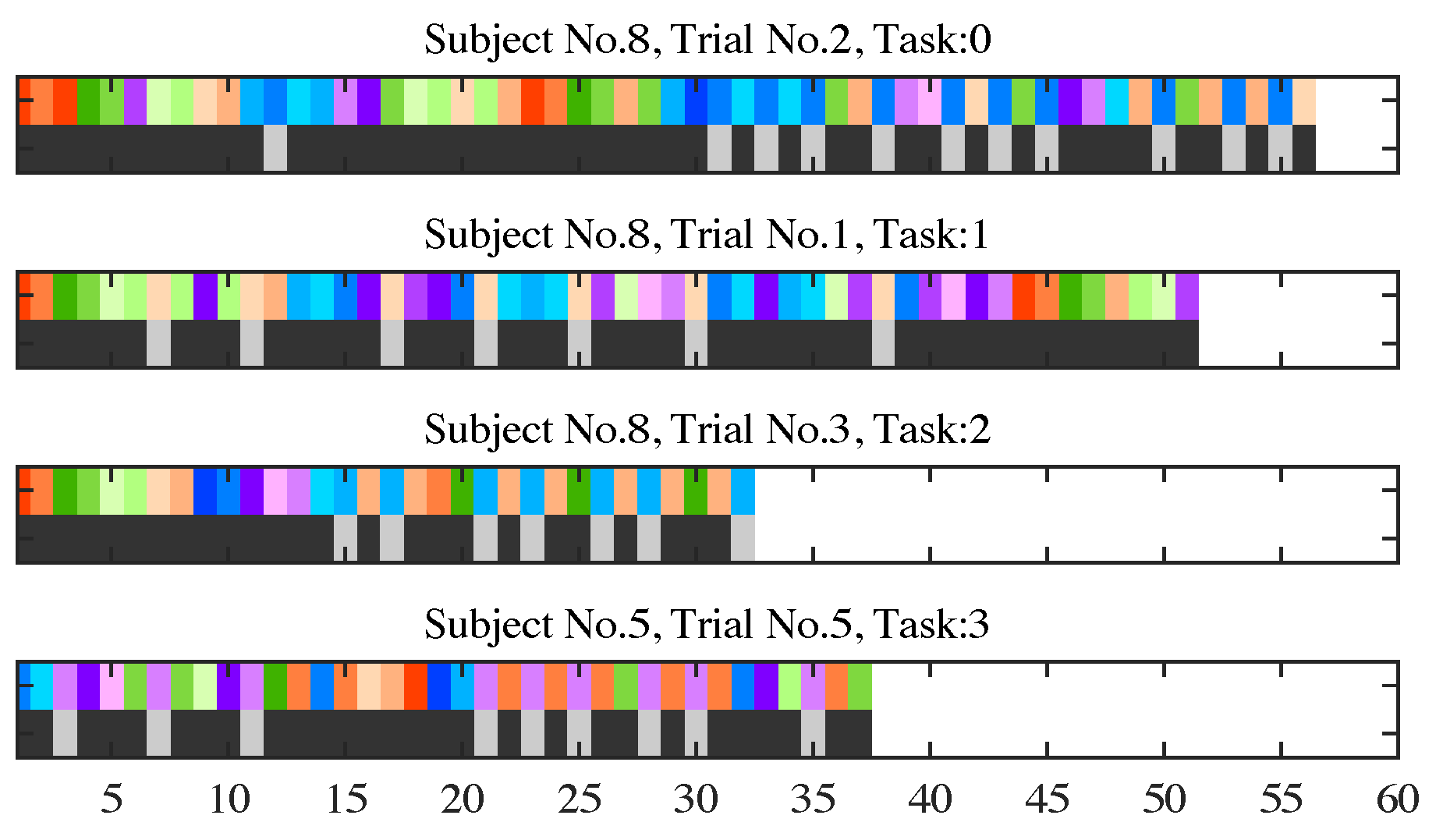
Examples of collected gaze data
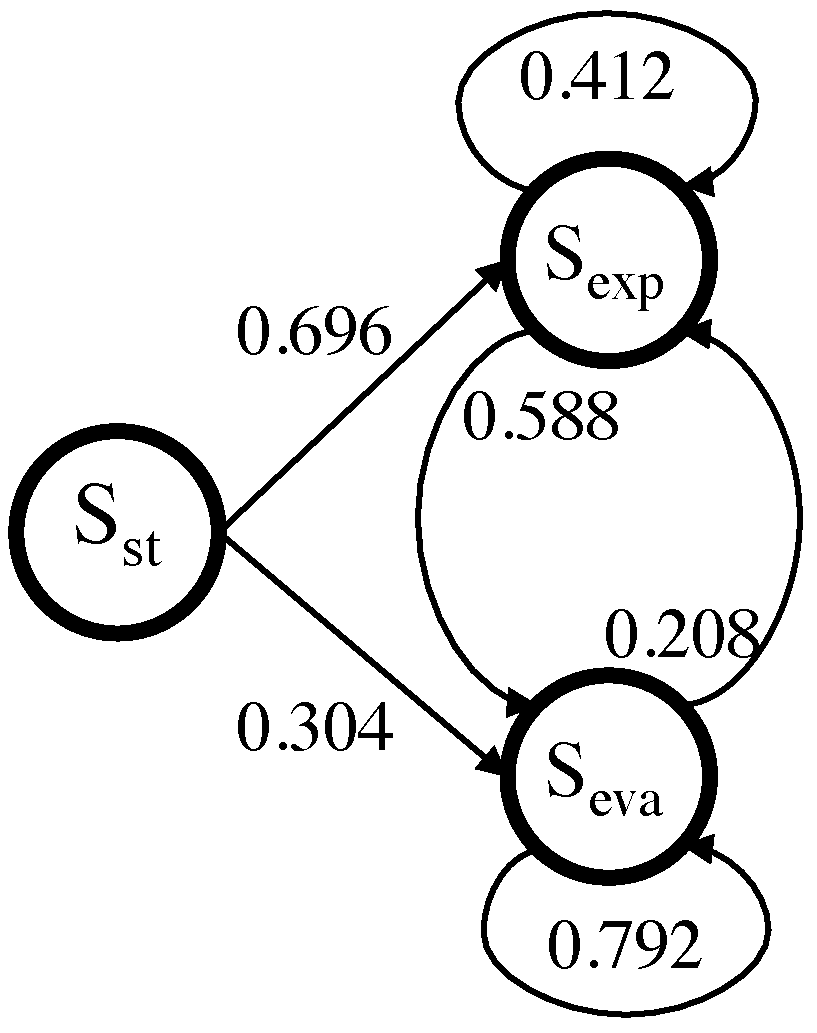
Proposed Model
The basic assumption of browsing states
The proposed choice behavior model
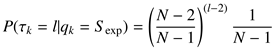
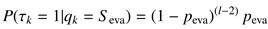
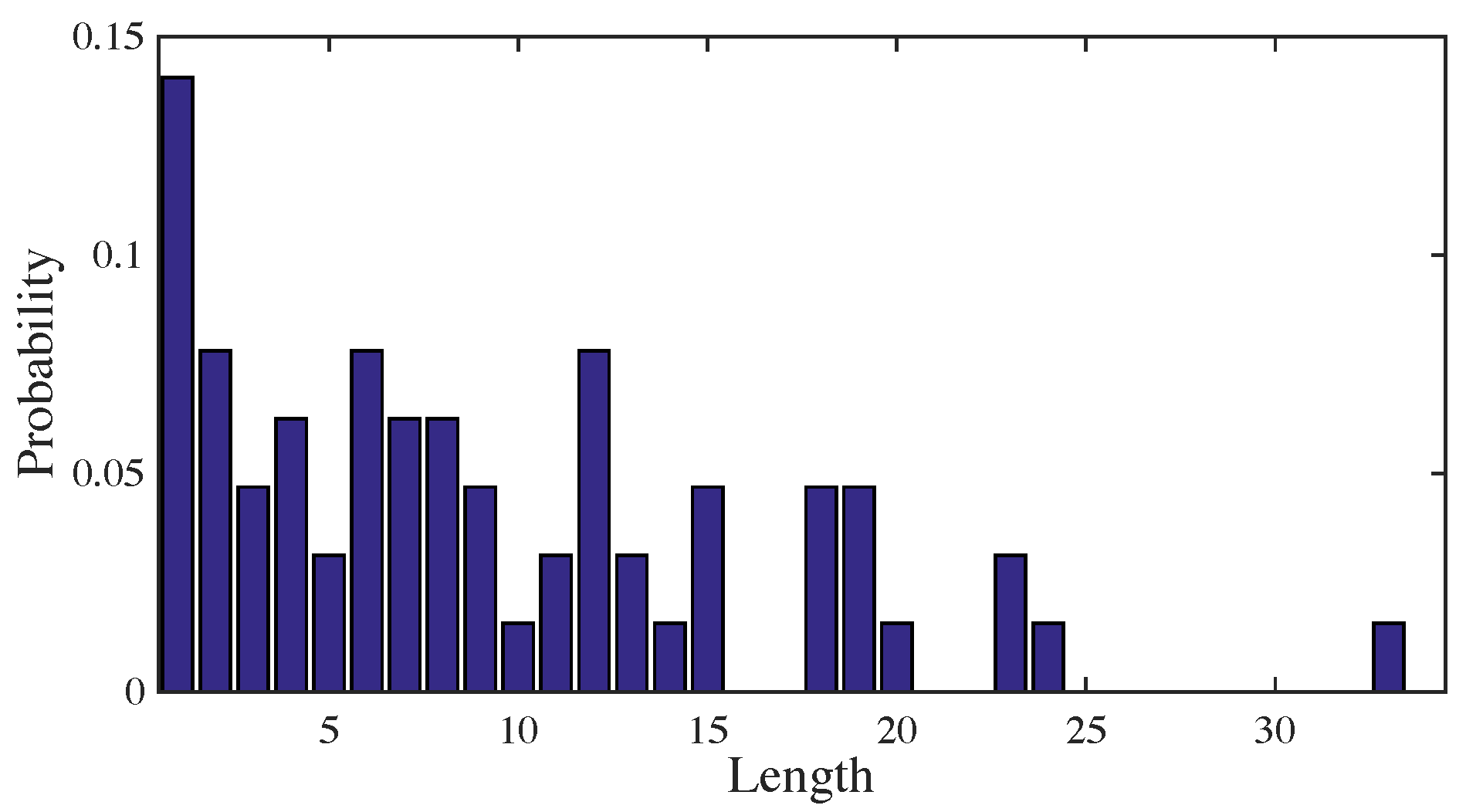
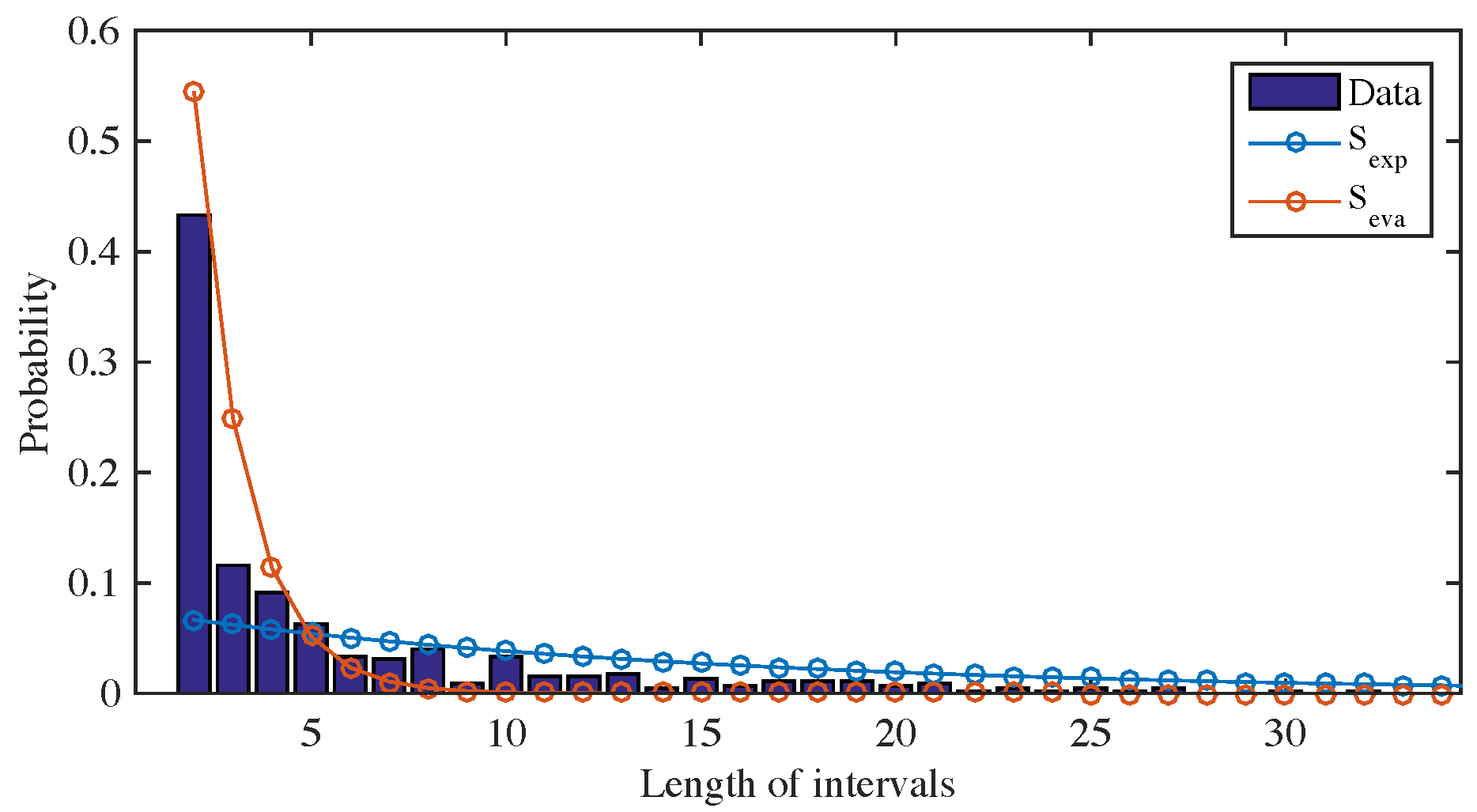
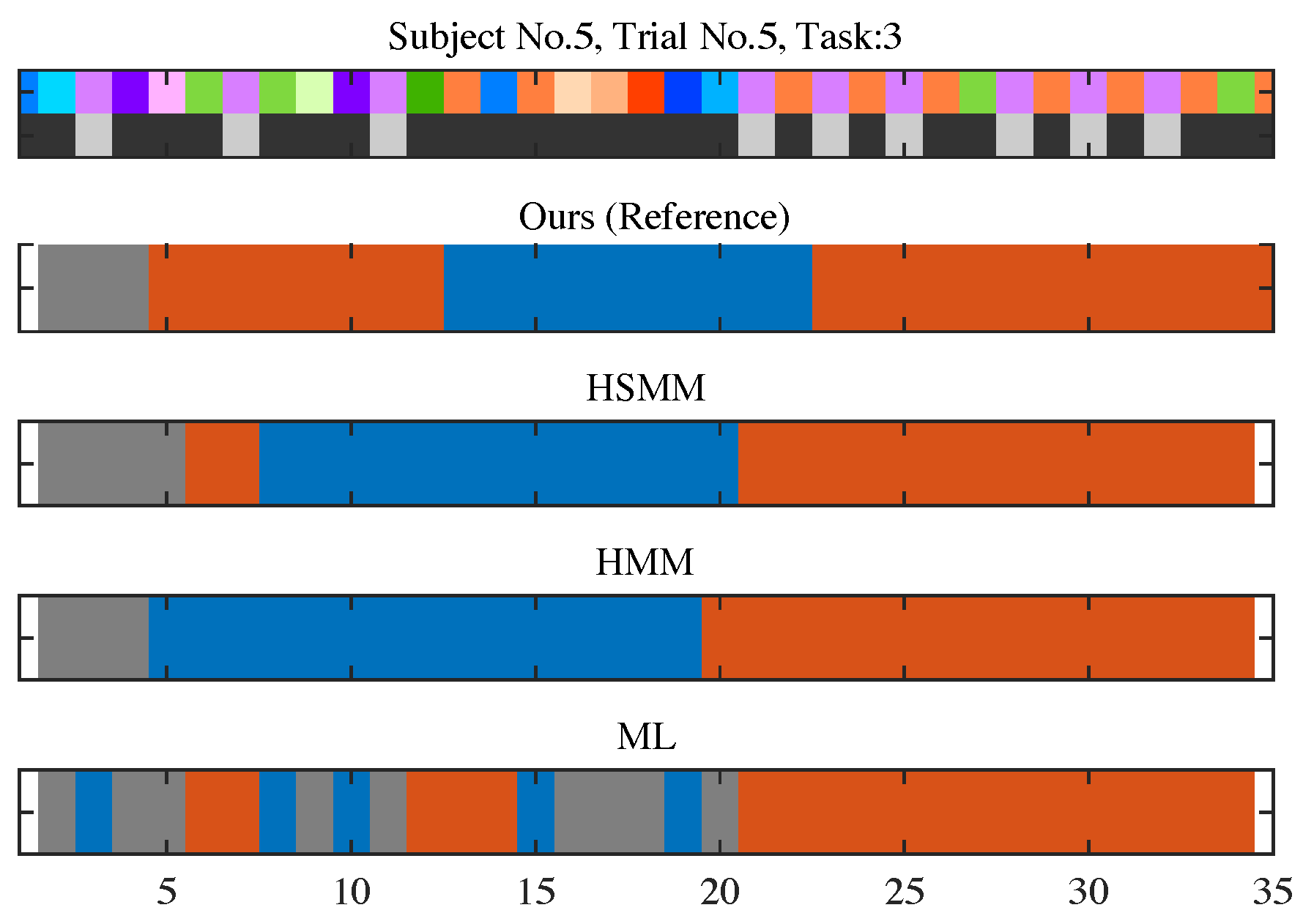
Evaluation
Application: Estimation of Browsing States
The overview of our estimation method
Gaze features
Modeling probabilistic relations of gaze features and browsing states

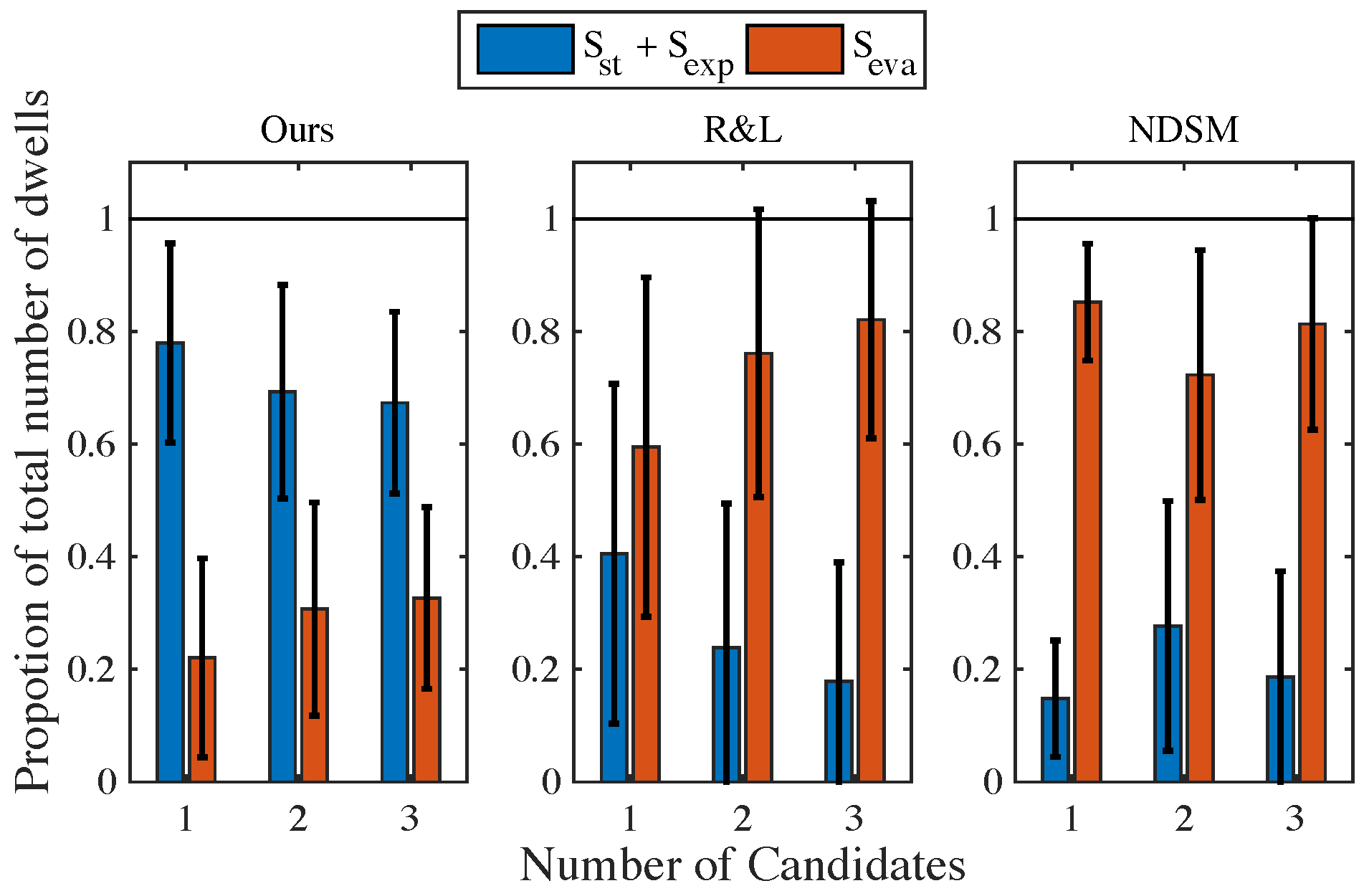
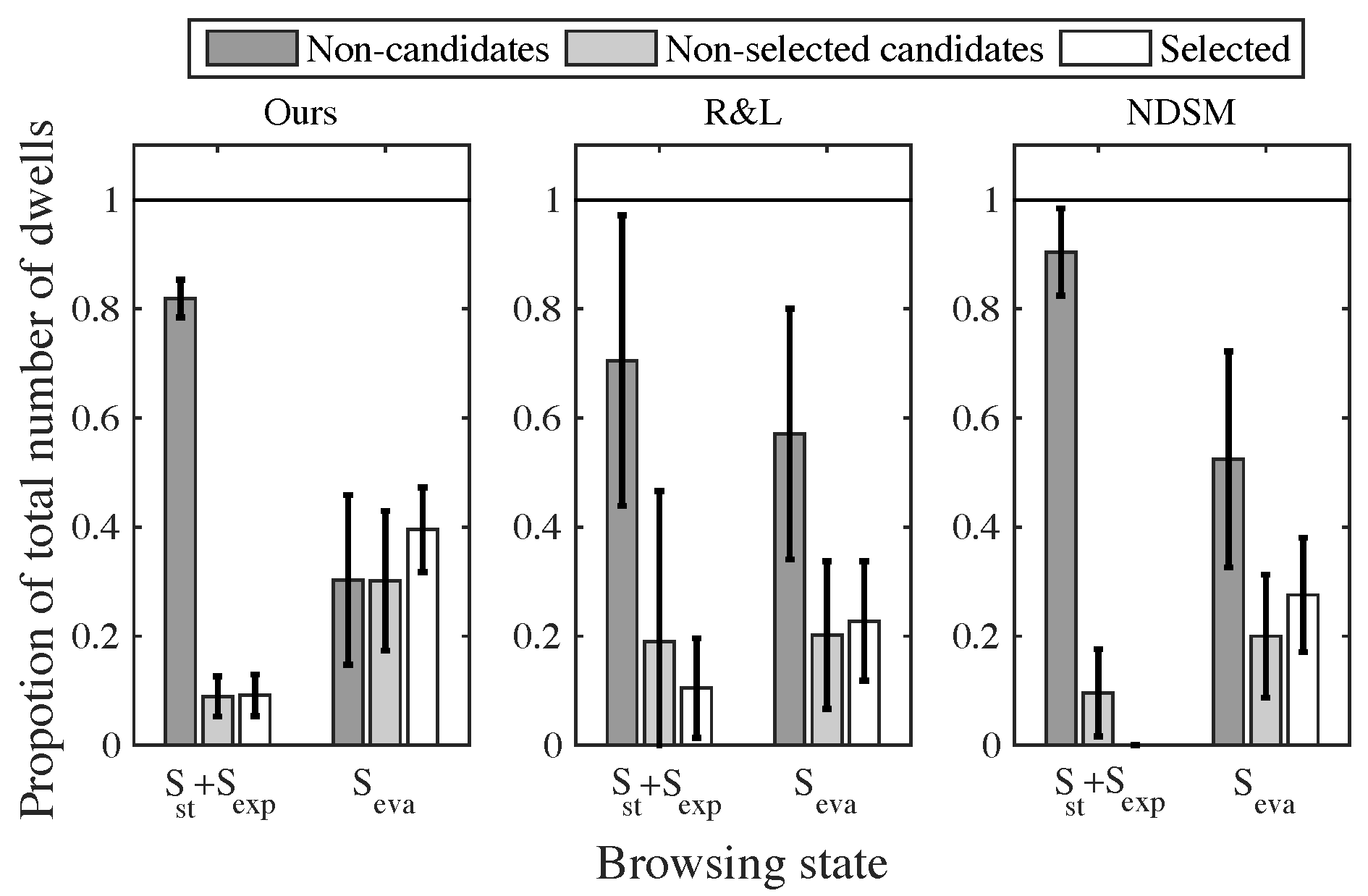
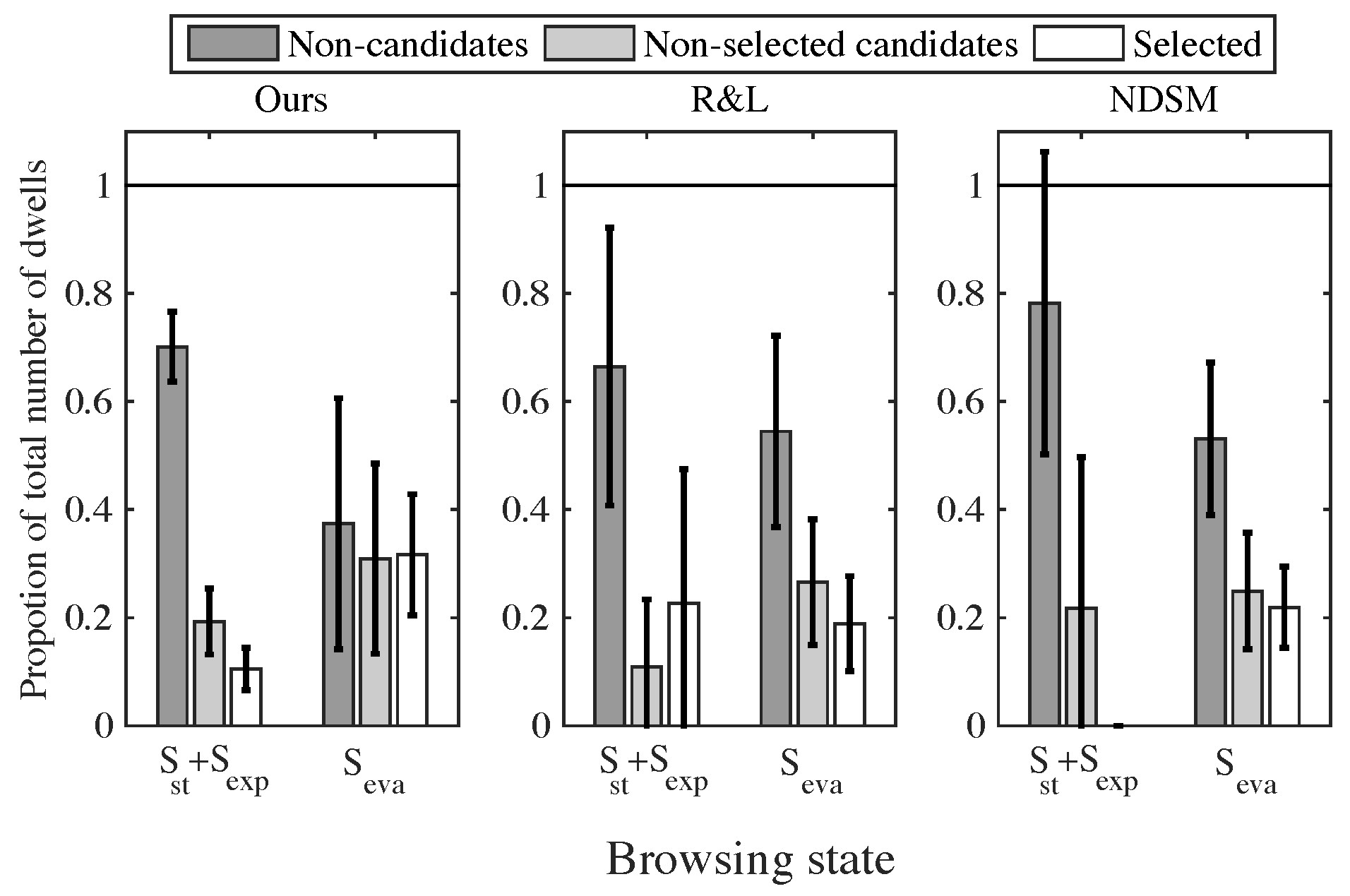
Evaluation
Discussion
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Baum, L. E.; Petrie, T.; Soules, G.; Weiss, N. A maximization technique occurring in the statistical analysis of probabilistic functions of markov chains. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 1970, 41(1), 164–171. Available online: http://projecteuclid.org/euclid.aoms/1177697196. [CrossRef]
- Bulling, A.; Ward, J. A.; Gellersen, H.; Troster, G. Eye movement analysis for activity recognition using electrooculography. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2011, 33(4), 741–753. Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5444879/. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J. Visual influence on in-store buying decisions: An eye-track experiment on the visual influence of packaging design. Journal of Marketing Management 2007, 23(9-10), 917–928. Available online: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1362/026725707X250395. [CrossRef]
- Gidlöf, K.; Wallin, A.; Dewhurst, R.; Holmqvist, K. Using eye tracking to trace a cognitive process: Gaze behaviour during decision making in a natural environment. Eye Movement Research 2013, 6(1), 1–14. Available online: http://www.jemr.org/online/6/1/3. [CrossRef]
- Glaholt, M. G.; Reingold, E. M. Eye movement monitoring as a process tracing methodology in decision making research. Journal of Neuroscience, Psychology, and Economics 2011, 4(2), 125–146. Available online: http://psycnet.apa.org/journals/npe/4/2/125/. [CrossRef]
- Glöckner, A.; Herbold, A.-K. An eyetracking strudy on information processing in risky decisions: Evidence for compensatory strategies based on automatic processes. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 2011, 24(1), 71–98. Available online: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bdm.684/abstract. [CrossRef]
- Groner, R.; Groner, M. Groner, R., Fraisse, P., Eds.; Towards a hypothetico-deductive theory of cognitive activity. In Cognition and eye movements; North Holland; Amsterdam, 1982; pp. 100–121. [Google Scholar]
- Groner, R.; Groner, M. Groner, R., Menz, C., Fisher, D., Monty, R., Eds.; A stochastic hypothesis testing model for multi-term series problems, based on eye fixations. In Eye movements and psychological functions: International views; Lawrence Erlbaum, 1983; pp. 257–274. [Google Scholar]
- Groner, R.; Spada, H. Spada, H., Kempf, W., Eds.; Some markovian models for structural learning. In Structural models of thinking and learning; Huber, 1977; pp. 131–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, E.; Kawashima, H.; Matsuyama, T. Using designed structure of visual content to understand content-browsing behavior. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems 2015, 98(8). Available online: http://repository.kulib.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/2433/202911/1/transinf.2014EDP7422.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Kübler, T. C.; Kasneci, E.; Rosenstiel, W. Subsmatch: Scanpath similarity in dynamic scenes based on subsequence frequencies. Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications 2014, 14, 1–5. Available online: http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2578206&dl=ACM&coll=DL&CFID=691207058&CFTOKEN=21972424. [CrossRef]
- Liechty, J.; Pieters, R.; Wedel, M. Global and local covert visual attention: Evidence from a bayesian hidden markov model. Psychometrika 2003, 68(4), 519–541. Available online: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2FBF02295608. [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Ishii, R. Estimating user’s engagement from eye-gaze behaviors in human-agent conversations. In The 15th international conference on intelligent user interfaces; 2010; pp. 139–148. Available online: http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1719990. [CrossRef]
- Orquin, J. L.; Loose, S. M. Attention and choice: A review on eye movements in decision making. Acta psychologica 2013, 144(1), 190–206. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0001691813001364. [CrossRef]
- Payne, J. W. Task complexity and contingent processing in decision making: An information search and protocol analysis. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance 1976, 16(2), 366–387. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0030507376900222. [CrossRef]
- Payne, J. W.; Bettman, J. R.; Johnson, E. J. The adaptive decision maker; Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993; Available online: http://www.cambridge.org/us/academic/subjects/psychology/cognition/adaptive-decision-maker?format=PB&isbn=9780521425261.
- Pfeiffer, J.; Meißner, M.; Prosiegel, J.; Pfeiffer, T. Classification of goal-directed search and exploratory search using mobile eye-tracking. In The 5th international conference on information systems; 2014; pp. 1–14. Available online: http://aisel.aisnet.org/icis2014/proceedings/GeneralIS/21/.
- Pieters, R.; Warlop, L. Visual attention during brand choice: The impact of time pressure and task motivation. Research in Marketing 1999, 16(1), 1–16. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167811698000226. [CrossRef]
- Reutskaja, E.; Nagel, R.; Camerer, C. F.; Rangel, A. Search dynamics in consumer choice under time pressure: An eye-tracking study. The American Economic Review 2011, 101(2), 900–926. Available online: https://www.aeaweb.org/articles?id=10.1257/aer.101.2.900. [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.; Leclerc, F. An eye-fixation analysis of choice processes for consumer nondurables. Consumer Research 1994, 21(2), 274–290. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2489820. [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.; Rosen, L. An eye fixation analysis of multialternative choice. Memomry & Cognition 1975, 3(3), 267–276. Available online: http://link.springer.com/article/10.3758/BF03212910. [CrossRef]
- Shi, S. W.; Wedel, M.; Pieters, F. R. Information acquisition during online decision making: A model-based exploration using eye-tracking data. Management Science 2013, 59(5), 1009–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojo, S.; Simion, C.; Shimojo, E.; Scheier, C. Gaze bias both reflects and influences preference. Nature Neuroscience 2003, 6(12), 1317–1322. Available online: http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v6/n12/full/nn1150.html. [CrossRef]
- Simola, J.; Salojärvi, J.; Kojo, I. Using hidden markov model to uncover processing states from eye movements in information search tasks. Cognitive Systems Research 2008, 9(4), 237–251. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1389041708000132. [CrossRef]
- Stüttgen, P.; Boatwright, P.; Monroe, R. T. A satisficing choice model. Marketing Schience 2012, 31(6), 878–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Kasai, H.; Ogaki, K. Image preference estimation with a data-driven approach: A comparative study between gaze and image features. Eye Movement Research 2014, 7(3), 1–9. Available online: http://www.jemr.org/online/7/3/5. [CrossRef]
- Wedell, D. H.; Senter, S. M. Looking and weighting in judgment and choice. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 1997, 70(1), 41–64. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749597897926923. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-Z. Hidden semi-markov models. Artificial Intelligence 2010, 174(2), 215–243. Available online: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0004370209001416. [CrossRef]

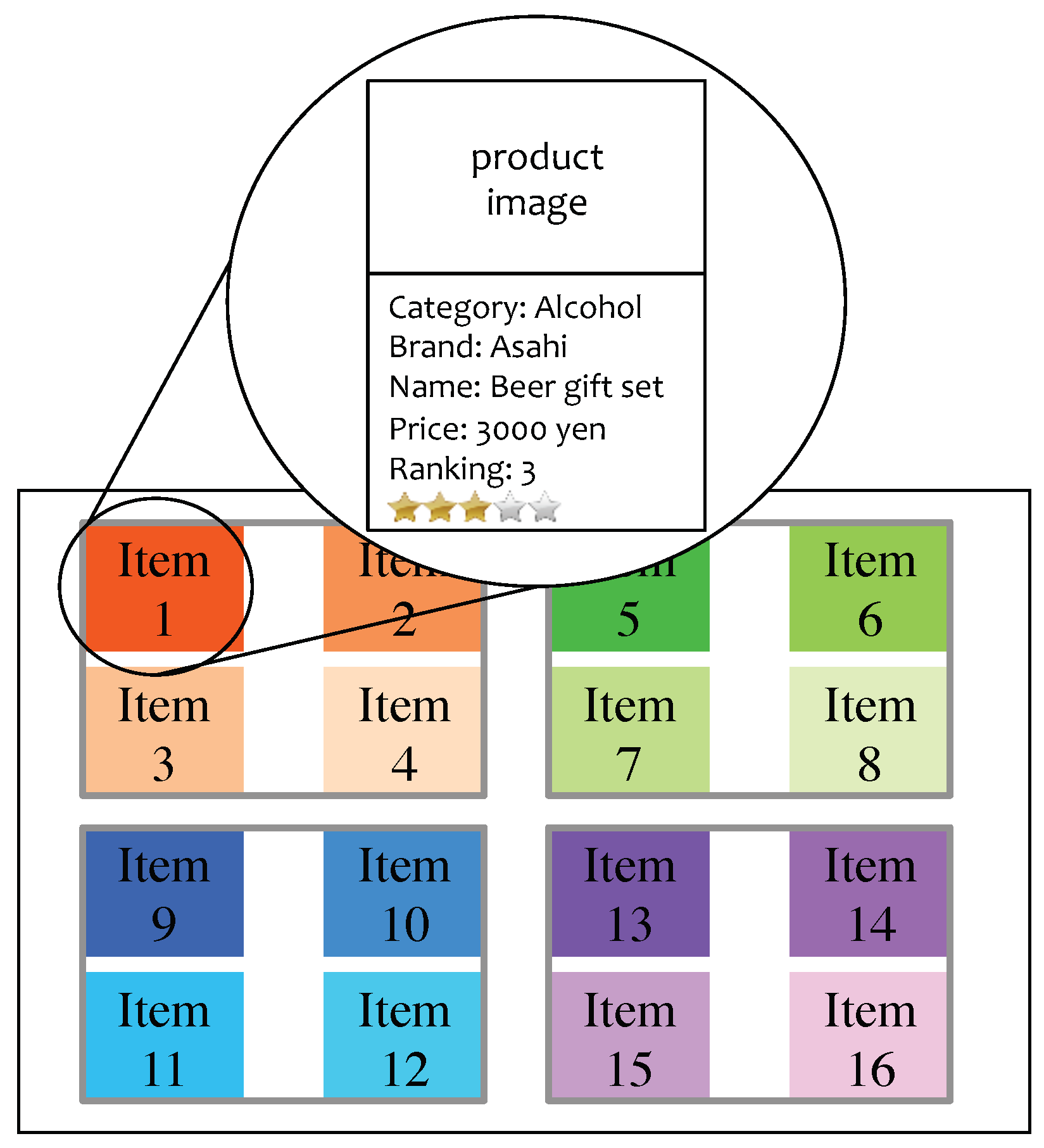



| Category | Price (yen) | Ranking | Review |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delicatessen | 1001-3000 | 1-4th | 1-star |
| Sweets | 3001-5000 | 11-14th | 2-star |
| Alcohol | 5001-7000 | 21-24th | 3-star |
| Household goods | 7001- | 31-34th | 4-star |
| 5-star |
| Number of candidates | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Total |
| Number of sequences | 16 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 62 |
| HSMM | HMM | ML | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Seva, others) | 0.811 | 0.807 | 0.734 |
| (Sst , Sexp, Seva) | 0.639 | 0.621 | 0.437 |
Copyright © 2024. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Schaffer, E.I.; Kawashima, H.; Matsuyama, T. A Probabilistic Approach for Eye-Tracking Based Process Tracing in Catalog Browsing. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2016, 9, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.7.4
Schaffer EI, Kawashima H, Matsuyama T. A Probabilistic Approach for Eye-Tracking Based Process Tracing in Catalog Browsing. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2016; 9(7):1-14. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.7.4
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchaffer, Erina Ishikawa, Hiroaki Kawashima, and Takashi Matsuyama. 2016. "A Probabilistic Approach for Eye-Tracking Based Process Tracing in Catalog Browsing" Journal of Eye Movement Research 9, no. 7: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.7.4
APA StyleSchaffer, E. I., Kawashima, H., & Matsuyama, T. (2016). A Probabilistic Approach for Eye-Tracking Based Process Tracing in Catalog Browsing. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 9(7), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.7.4



