Abstract
Purpose: Measuring near point of convergence (NPC) has recently emerged as a concussion assessment tool. Differences in administration of the test can be seen within the literature, which may affect results and normative values. There has been little investigation examining if clinically accessible target types affects NPC and no examination of NPC in a healthy, active young adult population. Methods: NPC was measured in 39 subjects using 5 different targets two times each with an accommodative ruler. Results: NPC ranged from 1.5-10cm in this population with an overall mean of 5.9±1.6 cm. There were significant differences between the middle sized font and the line (p = .024) and pen (p = .047), and also between the largest sized font and the line (p = .026). Conclusion: For physically active young adults, the measurement of NPC is affected by target type.
Introduction
The near point of convergence (NPC) is commonly assessed in vision exams as it measures the closest point in space where a patient can see one target with binocular vision. Typically an abnormal NPC is used to help diagnose individuals with convergence insufficiency, which is a vision disorder characterized by symptoms such as double vision, eyestrain, headaches, blurred vision, or trouble reading (Lavrich 2010). This particular symptom can be missed during a routine eye examine because patients with otherwise normal vision can exhibit an abnormal NPC. Several structures within the brain such as the frontal eye fields (Gamlin & Yoon 2000), supraoculomotor area, edinger-westphal nucleus, and cerebellum all help influence vergence movements (Haines 2006). These structures could potentially become compromised during a brain injury such as concussion.
A concussion is an injury that can negatively affect multiple brain functions including eye movements. Visual tracking has been studied as a promising clinical tool for assessing concussion (Galetta et al., 2011; Maruta et al., 2010; Pearson et. al., 2007) and post concussion syndrome (Heitger et al. 2000). Likewise, examining a person’s NPC has also been shown as a valuable tool in assessing traumatic brain injury (Ciuffreda et al. 2007). More recently, a receded NPC has been identified in individuals suffering with a mild traumatic brain injury (Mucha et al., 2014; Szymanowicz et al., 2012). With further standardization of this simple test, it could potentially be incorporated into a concussion assessment.
The NPC can be easily and quickly measured; however, there have been conflicting findings for normative values of this measurement ranging from 5 to 15 cm’s (Capobianco et al., 1952; Cohen et al., 1983; Davies 1946; Helveston et al., 1985; Hayes et al., 1998; Hoffman et al., 1980; Mohindra et al., 1980; Mucha et al., 2014; Pickwell et al, 1981; Scheiman et al., 2003). These variations may be due to the difference in administration techniques (Scheiman et al., 2003). Authors have either not disclosed the targets used in their study (Davies et al., 1946; Pickwell et al., 1981), or have used different target types including a penlight (Adler et al., 2007; Capobianco et al., 1952; Scheiman et al., 2003), a black line on a white card (Adler et al., 2007; Pickwell et al, 1981; Siderov et al., 2001), pen or pencil tip (Adler et al., 2007; Siderov et al., 2001), fingertip (Adler et al., 2007; Siderov et al., 2001) and/or letters (Hayes et al., 1998; Scheiman et al., 2003). The lack of test procedure standardization in the literature limits clinical usefulness of measuring NPC.
The variability in normative values for this measurement may also be due to differences in ages examined. Recently, an investigation (Mucha et al., 2014) in youth athletes demonstrated the clinical usefulness in using NPC to diagnose a concussion and suggested a cut point of ≥5cm. This cut point may not be generalizable to other at risk populations. Considering those without brain injury may also experience convergence insufficiency, it may be most appropriate to use the test in conjunction with baseline measurements. There has been no investigation of NPC in a young adult aged, healthy, physically active population. The effect of clinically accessible target types on NPC has also not been evaluated in this population. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine if target type (font sizes, pen tip, or black line on a card) influences NPC in a healthy, physically active, young adult aged population in order to further standardize this assessment tool.
Materials and Methods
A cross-sectional repeated measures design was used in this investigation with near point of convergence being the dependent variable and target type being the independent variable. Thirty nine subjects, who signed Institutional Review Board approved consent forms, participated in the study (males =13; females =26). All participants were between 18 and 30 years of age (23.6 ± 3.1yrs) and exercised at least three times a week for 30 minutes or more. Exclusionary criteria included not using corrective eyewear (e.g. contact lenses, glasses, etc.); any disease, disability, or other issue that affects the ocular system; recent (within 6 months), unresolved, or chronic brain injury. A health history questionnaire was used to determine participant testing eligibility. Participants answered a battery of questions regarding age, gender, weekly activity level, history of concussions, and ocular health. If the participants answered yes, they were asked to provide additional information (e.g. how many concussions and when, balance issues,) to determine if these issues would be considered exclusionary criteria.
Using a near point rule (Figure 1), the NPC was measured for all subjects using three different sized letters (8, 11, and 14 pt font) in reduced Snellen chart format, a pen tip, and a black line. The target was moved towards the subjects nose at a slow pace of about 1-2 cm/s. The break point, or point at which diplopia was experienced or ocular alignment was lost, was recorded. All subjects were simply instructed to alert to examiner as to when the target became not just blurry, but double in appearance. Each target was tested twice and all trials were randomized. Statistical analysis was performed using a repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA), which was followed up using paired samples t-tests.
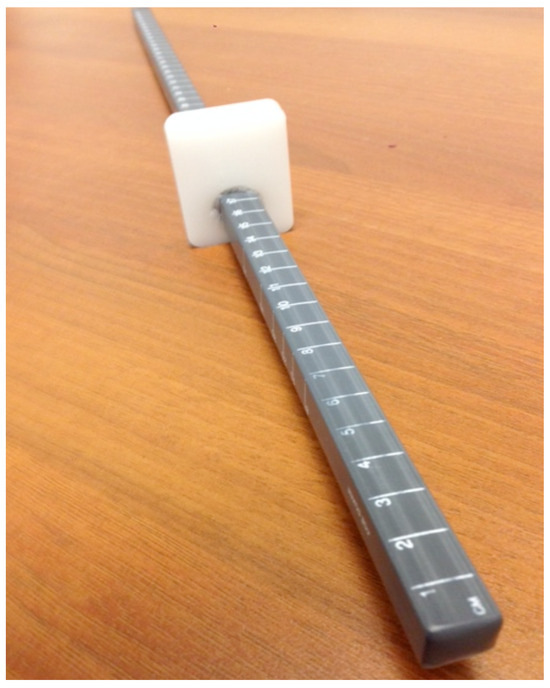

Figure 1.
Accommodative Ruler
Results
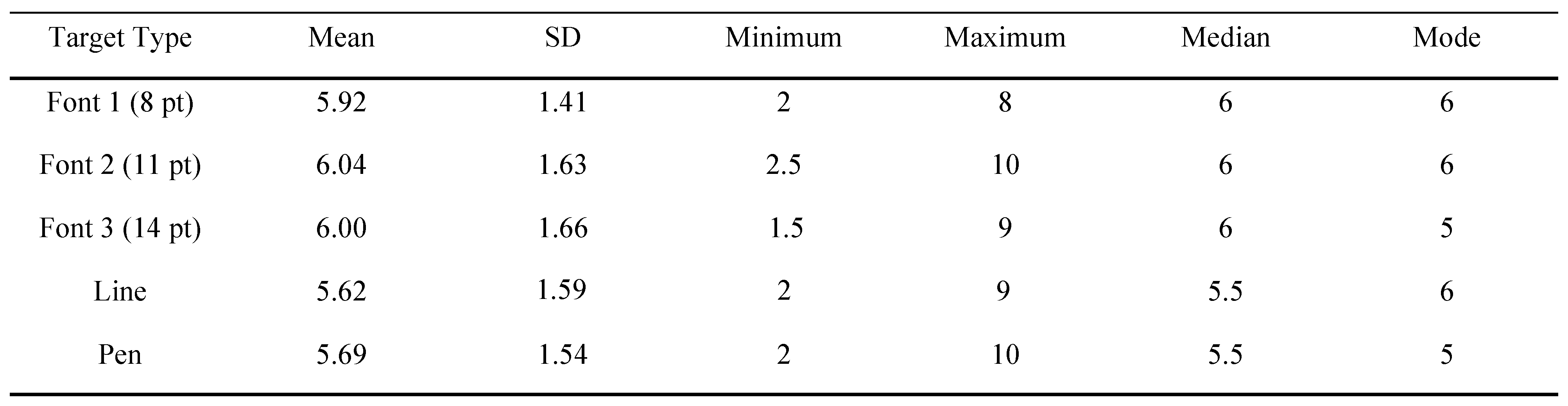
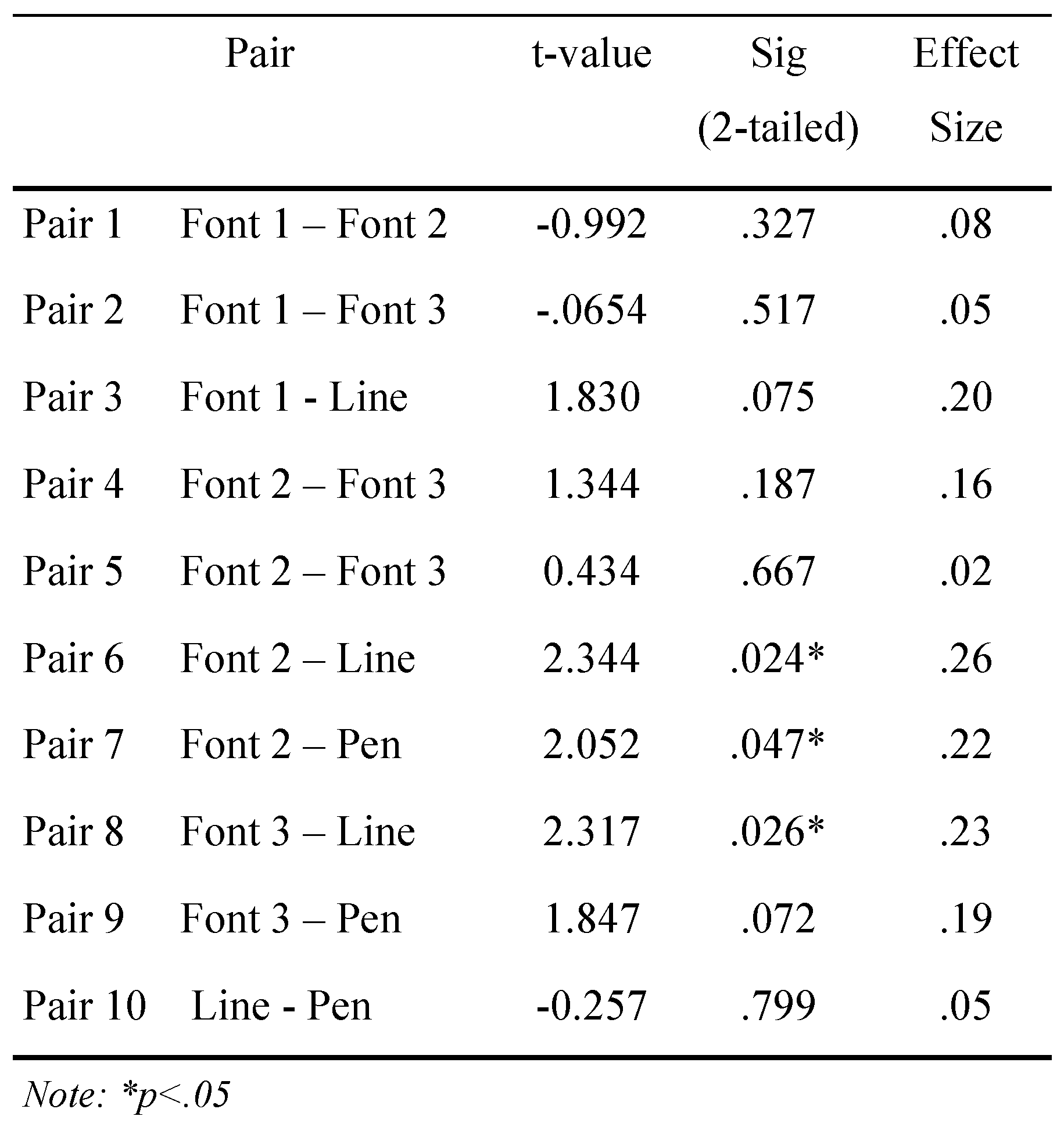
Descriptive statistics for NPC values by target type are summarized in Table 1. Measurements for the NPC ranged from 1.5 to 10cm. The repeated measures ANOVA showed a significant main effect for target type (Table 1). Subsequently, post hoc paired samples t-tests (Table 2) revealed significant differences between the mid size font and both the drawn line and pen tip, and the largest font and the drawn line. Specifically, NPC for the mid sized font was 7% and 6% greater than the draw line pen tip, respectively. Also, NPC for the largest font was 6% greater than the drawn line. Effect sizes for the significant findings ranged from .22 to .26. No other statistically significant results were obtained. Intra-rater reliability was found to be .75.

Table 1.
Descriptive Statistics for NPC by Target Type

Table 2.
Paired Samples t test
Discussion
This study investigated whether target type makes a difference in the assessment of NPC, and if clinically accessible tools, like a pen, would yield similar results to more traditional evaluation tools. The fonts yielded more remote measurements upon comparison to the line and pen tip. The effect size for these measurements was greater than .2 indicating there is a small yet clinically meaningful difference between these targets.
To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine the measurement of NPC in a young adult aged, healthy, active population. Our results were similar to Siderov et al. and Adler et al. findings and their averages for NPC. Contrarily, Scheiman et al. (2003) results yielded less remote measurements for NPC (Table 1). Ultimately, because of their findings, Scheiman et al. recommended a clinical cut off point of 5cm for NPC measurement indicating dysfunction. Scheiman et al. investigated the most appropriate target to be used for NPC assessment using 175 optometry students ranging in age from 22 to 37 years old. The targets investigated were a penlight with red and green glasses, and an accommodative target with a single 20/30 letter. Like our study, statistically significant differences between target types were found.
Adler et al. (2007) used a pencil, fingertip, penlight, letter, and a line on a card to examine NPC within different age groups ranging from 6 to 30 years. The penlight was found to produce significantly more remote NPC measurements. Additionally, they reported that when using a Royal Air Force (RAF) rule, similar to the accommodative ruler used in our study, more remote measurements were produced. The value of convenience in using such an instrument was noted and ultimately the studied concluded that different targets do not affect NPC. Similarly, Siderov et al. (2001) examined NPC using the RAF rule, pencil tip, and fingertip. This investigator used a small sample of 14 optometry students with a mean age of 25 years and also concluded that target type does not affect NPC assessment.
Previous studies (Adler et al., 2007; Scheiman et al., 2003; Siderov et al., 2001) agreed that targets with high accommodative demand evoke more accurate measurement of NPC. These targets cause the eyes to elicit an accommodative response, which is closely related to the process of convergence because it helps the eye focus on objects at different distances. Because such a target utilizes all aspects of convergence including fusional, proximal, and accommodative convergence, they produce the best results. Accommodative targets have also been recommended, over pen light targets, for less variability has been found in measurements found with an accommodative target (Ciuffreda 1974). Beyond this discrepancy, target type does not seem to affect NPC within normal, healthy individuals
The populations examined in three of these recent investigations (Adler et al., 2007; Scheiman et al., 2003; Siderov et al., 2001) consisted of optometry students. Assessing individuals whom are familiar with the aims of this visual measurement can be problematic for they anticipate the appropriate response and may be able to influence these movements. Differences between those knowledgeable of the test, and those naïve to its purpose have been identified in measuring vergence (Hoffman & Riddell 2010). This could account for a variance in NPC measurements between these studies.
Recently, there was an investigation (Mucha et al., 2014) to see if a battery of tests, including NPC, could help identify young athletes with a concussion. Sixty-four patients were examined with this tool after having suffered a concussion and compared to 78 controls. The control group averaged significantly better (1.9 ± 3.2cm) than the concussed group (5.9 ± 7.7cm). Based on their findings, the investigators recommended a cutoff of ≥5cm when identifying patients with a concussion. With this cutoff, many of our healthy participants fell above this cutoff as our overall average for NPC was 5.85cm with a range of 1.5-10cm. The NPC assessment was administered in the same way as our study, using a 14 point size font as a target. One difference between the studies was the age group being assessed. Mucha et al. examined subjects aged 13.9 ± 2.5 years, while we examined subjects 23.6 ± 3.1 years of age. Beginning around the age of 5 years, accommodation, a closely related visual mechanism to convergence, begins to decrease throughout ones life (Earnes et al., 1961; World et al., 1967). Some evidence (Bruce et al., 1994) has also indicated that the accommodation convergence interactions decrease from 20 to 40 years of age. In the absence of a baseline, these age differences should be accounted for when assessing a person’s NPC as it may change a possible concussion cutoff score.
Ocular-motor function has been studied as a possible assessment tool for concussion (Galetta et al., 2011; Maruta et al., 2010; Pearson et. al., 2007) and post concussion syndrome (Heitger et al. 2000). Due to the potential poor outcomes associated with history of concussion in some athletes, it is important for sports medicine personnel to identify any occurrence and ensure proper rehabilitation and recovery from this injury. Dysfunction of the vergence system could lead to a slowed rehabilitative progress after concussion, but with early ocular-motor intervention there is the possibility of resolving other symptoms that were secondary to an abnormal NPC.
Investigating the effects of different targets on the measurement of NPC is especially useful when performing this examination outside of a Optometry office. Within nontraditional settings, such as an athletic sideline, traditional targets or tools may not be accessible to practitioners, leading them to use instruments such as a pen tip. Understanding the effect of these targets on NPC will help to guide practitioners in their assessment of a possible injury such as a concussion.
Conclusion
For healthy young adult subjects whom are physically active, the measurement of NPC is affected by target type. Statistically different results were found between the middle sized font and the line and pen, and also between the largest sized font examined and the line. These differences suggest there is a small yet clinically meaningful difference when examining a healthy population with different targets. Furthermore, NPC measurements may range from 1.5 to 10cm indicating a cutoff point of > 5cm may not be appropriate to diagnose dysfunction for this age group. Consistency in administration of this test is imperative to produce meaningful results, especially when comparing baseline to post-injury scores.
References
- Adler, P. M., M. Cregg, A. J. Viollier, and J. Margaret Woodhouse. 2007. Influence of target type and RAF rule on the measurement of near point of convergence. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 27, 1: 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, S. P., J. T. Eckner, H. L. Paulson, and J. S. Kutcher. 2012. Cognitive decline and aging: The role of concussive and subconcussive impacts. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews 40, 3: 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, A. S., D. A. Atchison, and H. Bhoola. 1995. Accommodation-convergence relationships and age. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 36, 2: 406–413. [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco, N. M. 1952. The subjective measurement of the near point of convergence and its significance in the diagnosis of convergence insufficiency. The American Orthoptic Journal 2: 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, K. J. 1974. Near point of convergence as a function of target accommodative demand. Opt J Rev Optom. 111: 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ciuffreda, K.J., N. Kapoor, D. Rutner, I.B. Suchoff, M.E. Han, and S. Craig. 2007. Occurrence of oculomotor dysfunctions in acquired brain injury: a retrospective analysis. Optometry 78, 4: 155–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A. H., S. Lieberman, M. Stolzberg, and J. M. Ritty. 1983. The NYSOA vision screening battery--a total approach. Journal of the American Optometric Association 54, 11: 979. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, C. E. 1946. Orthoptic treatment in convergence insufficiency. Canadian Medical Association Journal 55, 1: 47. [Google Scholar]
- De Beaumont, L., H. Theoret, D. Mongeon, J. Messier, S. Leclerc, S. Tremblay, and M. Lassonde. 2009. Brain function decline in healthy retired athletes who sustained their last sports concussion in early adulthood. Brain 132, 3: 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eames, T. H. 1961. Accommodation in school children, aged five, six, seven, and eight years. American Journal of Ophthalmology 51: 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galetta, K.M., L.E. Brandes, K. Maki, M.S. Dziemianowicz, E. Laudano, M. Allen, K. Lawler, B. Sennett, D. Wiebe, S. Devick, L.V. Messner, S.L. Galetta, and L.J. Balcer. 2011. The King-Devick test and sports-related concussion: study of a rapid visual screening tool in a collegiate cohort. Journal of Neurological Sciences 309, 1-2: 34–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamlin, P. D., and Y. Kyunghee. 2000. An area for vergence eye movement in primate frontal cortex. Nature 407.6807, 2000: 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guskiewicz, K. M., M. McCrea, S. W. Marshall, R. C. Cantu, C. Randolph, W. Barr, J. A. Onate, and J. P. Kelly. 2003. Cumulative effects associated with recurrent concussion in collegiate football players: The NCAA concussion study. Journal of the American Medical Association 290, 19: 2549–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guskiewicz, K.M., S.L. Bruce, R.C. Cantu, and et al. 2004. National Athletic Trainers’ Association position statement: Management of sport-related concussion. Journal of Athletic Training 39: 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guskiewicz, K. M. 2005. Association between recurrent concussion and late-life cognitive impairment in retired professional football players. Neurosurgery 57, 4: 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guskiewicz, K. M. 2007. Recurrent concussion and risk of depression in retired professional football players. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 39, 6: 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, D. E. 2006. Fundamental neuroscience for basic and clinical applications. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, G.J., B.E. Cohen, M.W. Rouse, and P.N. De Land. 1998. Normative values for the nearpoint of convergence of elementary schoolchildren. Optometry & Vision Science 75, 7: 506–512. [Google Scholar]
- Heitger, M.H., R.D. Jones, A.D. Macleod, D.L. Snell, C.M. Frampton, and T.J. Anderson. 2009. Impaired eye movements in post-concussion syndrome indicate suboptimal brain function beyond the influence of depression, malingering or intellectual ability. Brain 132, 10: 2850–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helveston, E.M., J.C. Wever, K. Miler, K. Robertson, G. Hohberger, and R. Estes. 1985. Visual function and academic performance. American Journal of Ophthalmology 99: 346–355. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, L. G., and M. Rouse. 1980. Referral recommendations for binocular function and/or developmental perceptual deficiencies. Journal of the American Optometric Association 51, 2: 119. [Google Scholar]
- Horwood, A. M., and P. M. Riddell. 2010. Differences between naïve and expert observers’ vergence and accommodative responses to a range of targets. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 30, 2: 152–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavrich, J. B. 2010. Convergence insufficiency and its current treatment. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology 21, 5: 356–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makdissi, M., D. Darby, P. Maruff, A. Ugoni, P. Bronker, and P. McCrory. 2010. Natural history of concussion in sport: markers of severity and implications for management. American Journal Sports Medicine 38: 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Maruta, J., M. Suh, S.N. Niogi, P. Mukherjee, and J. Ghajar. 2010. Visual tracking synchronization as a metric for concussion screening. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation 25, 4: 293–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCrea, M., K. M. Guskiewicz, S. W. Marshall, W. Barr, C. Randolph, and R. C. Cantu. 2003. Acute effects and recovery time following concussion in collegiate football players. JAMA 290, 19: 2556–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohindra, I., and J. Molinari. 1980. Convergence insufficiency: its diagnosis and management - part 1. Optometry Monthly 71: 155–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mucha, A., M. W. Collins, R. J. Elbin, J. M. Furman, C. Troutman-Enseki, R. M. DeWolf, and A. P. Kontos. 2014. A Brief Vestibular/Ocular Motor Screening (VOMS) Assessment to Evaluate Concussions Preliminary Findings. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 0363546514543775. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, B.C., K.R. Armitage, C.W. Horner, and R.H. Carpenter. 2007. Saccadometry: the possible application of latency distribution measurement for monitoring concussion. British Journal of Sports Medicine 41, 9: 610–2. [Google Scholar]
- Pickwell, L. D., and R. Hampshire. 1981. The significance of inadequate convergence. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 1, 1: 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiman, M., M. Gallaway, K. A. Frantz, R. J. Peters, S. Hatch, M. Cuff, and G. L. Mitchell. 2003. Near-point of convergence: test procedure, target selection, and normative data. Optometry & Vision Science 80, 3: 214–225. [Google Scholar]
- Siderov, J., S. C. Chiu, and S. J. Waugh. 2001. Differences in the nearpoint of convergence with target type. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 21, 5: 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderploeg, R. D., G. Curtiss, C. A. Luis, and A. M. Salazar. 2007. Long-term morbidities following self-reported mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 29, 6: 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, R. M. 1967. The spectacle amplitude of accommodation of children aged six to ten. American Journal of Optometry and Archives of American Academy of Optometry 44, 10: 642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Copyright © 2015. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.