Silent Versus Reading Out Loud modes: An Eye-Tracking Study
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
Participants
Stimuli
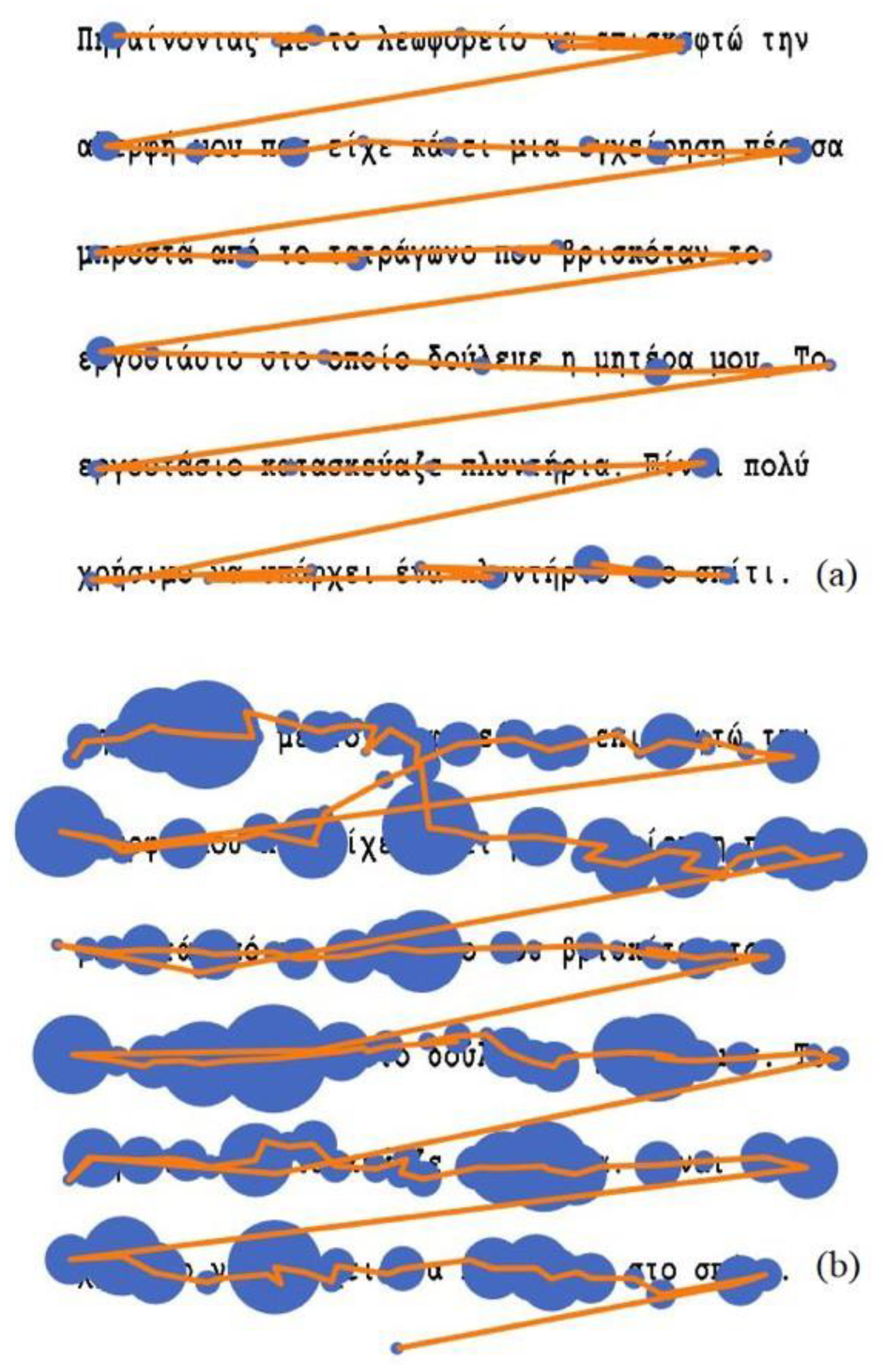
Text stimuli
Apparatus
Procedure
Calibration and validation stimuli
Silent reading and reading aloud
Results
- Part 1: Reading speed in relation to age
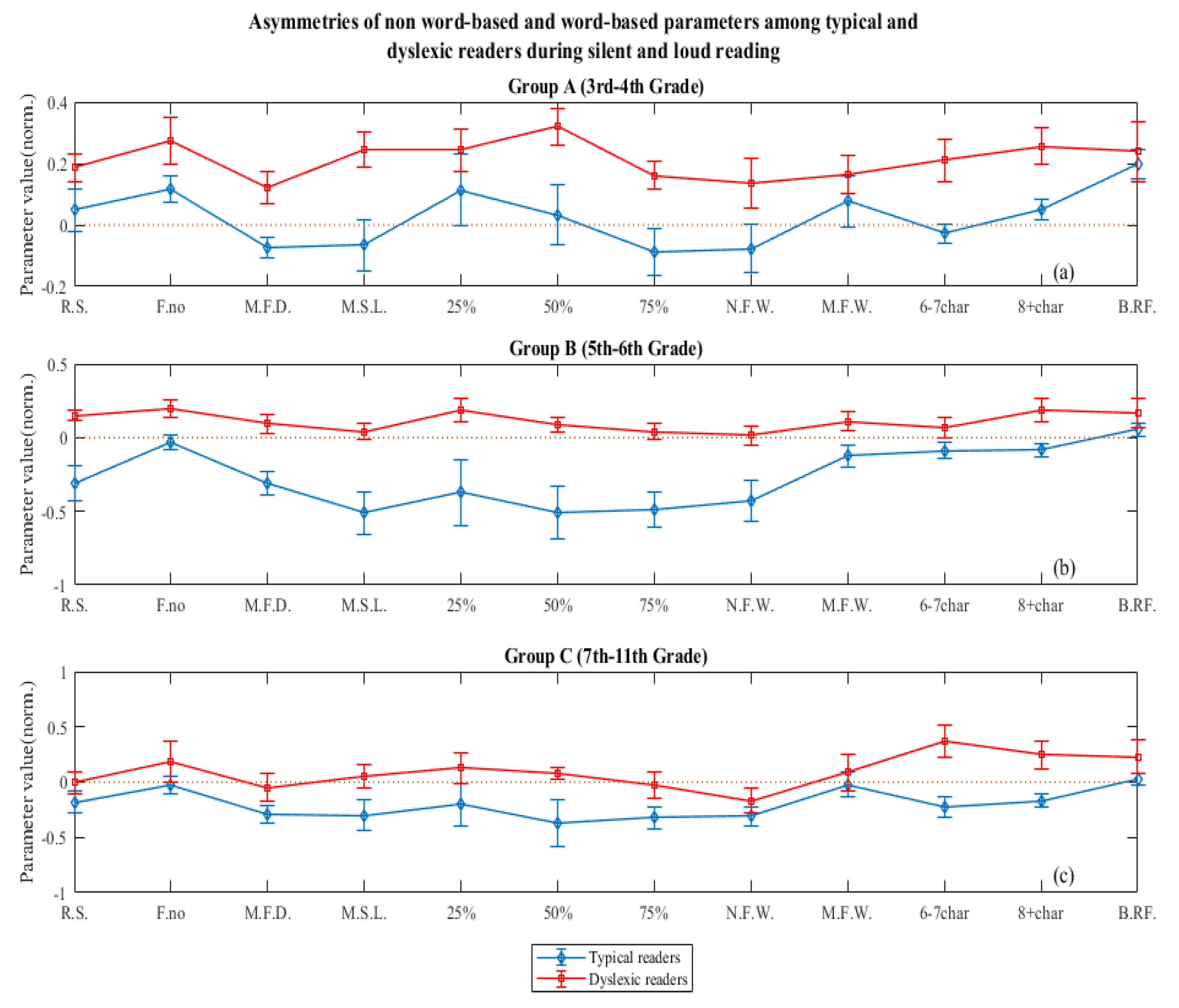
- Part 2: Asymmetries of the parameters
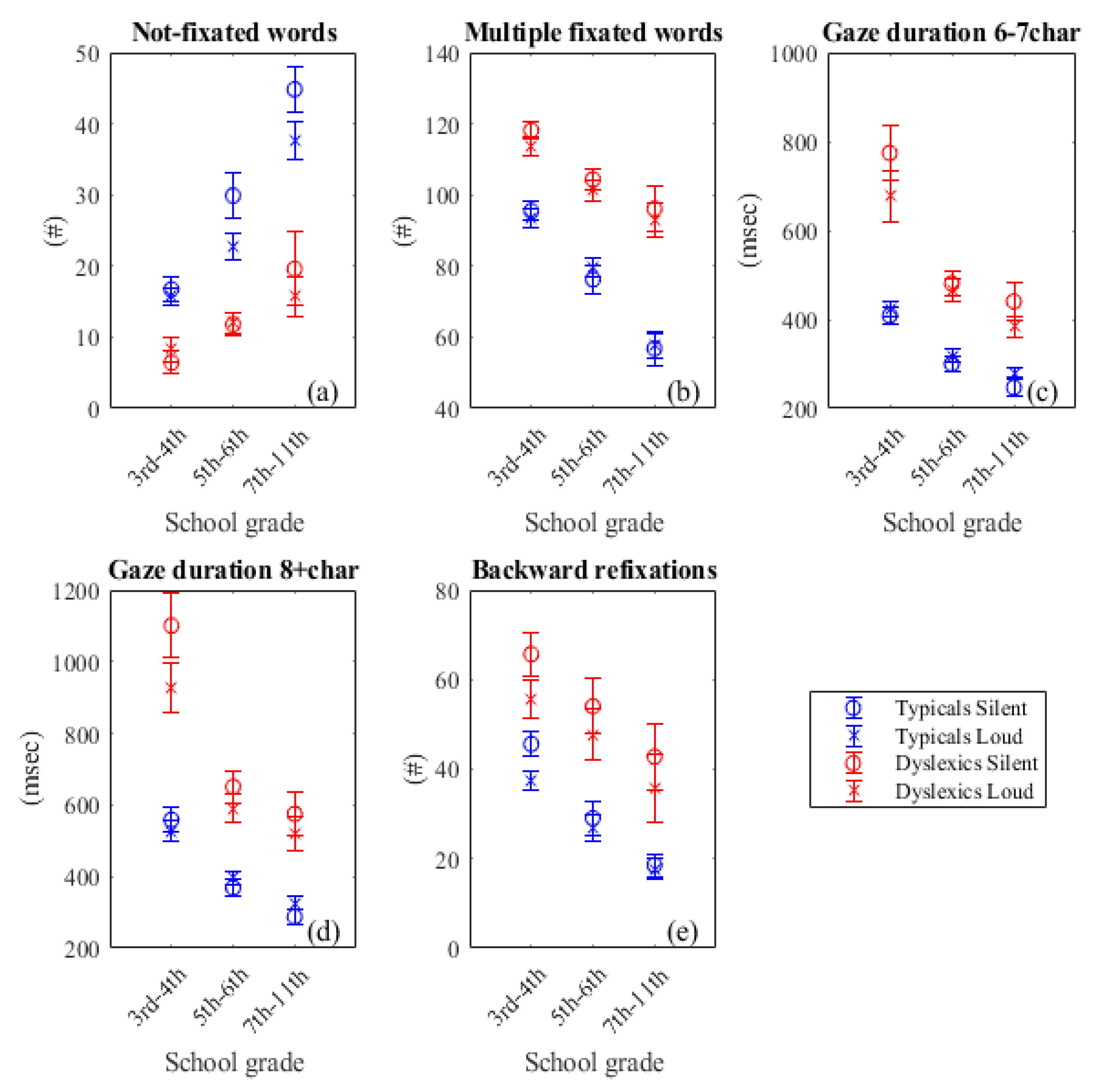
- Eye-tracking parameters examined
Asymmetry directionality
- Part 3: Analysis on parameters’ values
Discussion
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Aaron, P., C. F. Baxter, and J. Lucenti. 1980. Developmental dyslexia and acquired alexia: Two sides of the same coin? Brain and Language 11, 1: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, L. M., C. Reis, and Â. Pinheiro. 2015. Prosody and reading in dyslexic children. Dyslexia 21, 1: 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA, A. P. A. 2013. DSM-V Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. In American Psychiatric Association. Arlington, VA. [Google Scholar]
- Bilbao, C., and D. P. Piñero. 2020. Diagnosis of oculomotor anomalies in children with learning disorders. Clinical and Experimental Optometry 103, 5: 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, H., and H. Joseph. 2011. Edited by L. S., G. I. I. and E. S. Children’s eye movements during reading. Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Borleffs, E., B. A. Maassen, H. Lyytinen, and F. Zwarts. 2019. Cracking the code: The impact of orthographic transparency and morphological-syllabic complexity on reading and developmental dyslexia. Frontiers in Psychology 9, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, M. P., M. Vernet, C.-L. Gerard, and Z. Kapoula. 2009. Normal speed and accuracy of saccade and vergence eye movements in dyslexic reader children. Journal of ophthalmology 2009.
- Burge, P. D. 1983. Comprehension and rate: Oral vs. silent reading for low achievers. Reading Horizons: A Journal of Literacy and Language Arts 23, 3: 11. [Google Scholar]
- Buswell, G. T. 1921. The relationship between eye-perception and voice-response in reading. Journal of Educational Psychology 12, 4: 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldani, S., C.-L. Gerard, H. Peyre, and M. P. Bucci. 2020a. Pursuit eye movements in dyslexic children: evidence for an immaturity of brain oculomotor structures? Journal of Eye Movement Research 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldani, S., C.-L. Gerard, H. Peyre, and M. P. Bucci. 2020b. Visual attentional training improves reading capabilities in children with dyslexia: An eye tracker study during a reading task. Brain sciences 10, 8: 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J. F., and C. A. Stone. 2005. Exploring the role of morphemes in word reading. Reading research quarterly 40, 4: 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M., M. Borrelli, A. Judica, D. Spinelli, and P. Zoccolotti. 2002. Reading words and pseudowords: an eye movement study of developmental dyslexia. Brain and Language 80, 3: 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M., M. Pontillo, S. Primativo, D. Spinelli, and P. Zoccolotti. 2013. The eye-voice lead during oral reading in developmental dyslexia. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 7, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Noto, P., S. Uta, and J. F. DeSouza. 2013. Eye exercises enhance accuracy and letter recognition, but not reaction time, in a modified rapid serial visual presentation task. PLoS One 8, 3: e59244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, G. 1937. The relation between eye-movements and voice in the oral reading of good and poor silent readers. Psychological Monographs 48, 3: 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga González, G., I. I. Karipidis, and J. Tijms. 2018. Dyslexia as a neurodevelopmental disorder and what makes it different from a chess disorder. Brain sciences 8, 10: 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, A., M. Ciuffo, M. Ingrassia, E. Ghidoni, D. Angelini, L. Benedetto, ..., and G. Stella. 2015. Silent reading fluency: Implications for the assessment of adults with developmental dyslexia. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 37, 9: 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, A. D., C. H. Skinner, J. Williams, R. Hawkins, C. E. Neddenriep, and J. Dizer. 2007. Comparing comprehension following silent and aloud reading across elementary and secondary students: Implication for curriculum-based measurement. The Behavior Analyst Today 8, 1: 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, M., F. Tokoglu, Z. Sun, R. J. Schafer, P. Skudlarski, J. C. Gore, and R. T. Constable. 2006. Connectivity–behavior analysis reveals that functional connectivity between left BA39 and Broca's area varies with reading ability. Neuroimage 31, 2: 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutzler, F., and H. Wimmer. 2004. Eye movements of dyslexic children when reading in a regular orthography. Brain and Language 89, 1: 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarlou, F., F. Jarollahi, M. Ahadi, and V. Sadeghi-Firoozabadi. 2020. Effects of oculomotor rehabilitation on the cognitive performance of dyslexic children with concurrent eye movement abnormalities. Early Child Development and Care, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvilehto, T., V.-M. Nurkkala, and K. Koskela. 2009. The role of anticipation in reading. Pragmatics & Cognition 17, 3: 509–526. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, J., D. Galin, G. Fein, C. Yingling, J. Herron, and M. Marcus. 1984. Regional brain activity in dyslexic and control children during reading tasks: visual probe event-related potentials. Brain and Language 21, 2: 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juel, C., and B. Holmes. 1981. Oral and silent reading of sentences. Reading research quarterly, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, P. 2020. Dyslexia debated, then and now: A historical perspective on the dyslexia debate. Oxford Review of Education 46, 4: 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkby, J. A., L. A. Webster, H. I. Blythe, and S. P. Liversedge. 2008. Binocular coordination during reading and non-reading tasks. Psychol Bull 134, 5: 742–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneev, A., E. Y. Matveeva, and T. Akhutina. 2017. Silent reading in Russian primary schoolchildren: an eye tracking study. Psikhologiya 14, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Krieber, M., K. D. Bartl-Pokorny, F. B. Pokorny, D. Zhang, K. Landerl, C. Körner, ..., and P. B. Marschik. 2017. Eye movements during silent and oral reading in a regular orthography: Basic characteristics and correlations with childhood cognitive abilities and adolescent reading skills. PLoS One 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, G. R., S. Shaywitz, and B. Shaywitz. 2003. A definition of dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia 53, 1: 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, N., and F. Huettig. 2014. Word reading skill predicts anticipation of upcoming spoken language input: A study of children developing proficiency in reading. J Exp Child Psychol 126, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, F., and J. Vila. 1990. Differences in eye movements control among dyslexic, retarded and normal readers in the Spanish population. Reading and Writing 2, 2: 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, K. 2019. Children’s reading difficulties, language, and reflections on the simple view of reading. Australian Journal of Learning Difficulties 24, 1: 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychroni, F. 2001. Specific Learning Difficulties. Athens: Pedio. [Google Scholar]
- Protopapas, A., and E. L. Vlahou. 2009. A comparative quantitative analysis of Greek orthographic transparency. Behav Res Methods 41, 4: 991–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radach, R., and A. Kennedy. 2013. Eye movements in reading: Some theoretical context. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 66, 3: 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, K. 1998. Eye movements in reading and information processing: 20 years of research. Psychological Bulletin 124, 3: 372–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K., K. H. Chace, T. Slattery, and J. Ashby. 2009. Eye movements as reflections of comprehension processes in reading. Scientific Studies of Reading 10, 3: 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siok, W. T., J. A. Spinks, Z. Jin, and L. H. Tan. 2009. Developmental dyslexia is characterized by the co-existence of visuospatial and phonological disorders in Chinese children. Current biology 19, 19: R890–R892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowling, M. J. 1983. The comparison of acquired and developmental disorders of reading: A discussion.
- Snowling, M. J., C. Hulme, and K. Nation. 2020. Defining and understanding dyslexia: past, present and future. Oxford Review of Education 46, 4: 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger-Charolles, L., L. Siegel, J. Jimenez, and J. Ziegler. 2011. Prevalence and reliability of phonological, surface, and mixed profiles in dyslexia: A review of studies conducted in languages varying in orthographic depth. Scientific Studies of Reading 15, 6: 498–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J. 2018. What is developmental dyslexia? Brain sciences 8, 2: 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talli, I., L. Sprenger-Charolles, and S. Stavrakaki. 2016. Specific language impairment and developmental dyslexia: What are the boundaries? Data from Greek children. Research in Developmental Disabilities 49, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S. E. 2006. Fluency in silent reading. Retrieved January 15: 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thiagarajan, P., K. J. Ciuffreda, J. E. Capo-Aponte, D. P. Ludlam, and N. Kapoor. 2014. Oculomotor neurorehabilitation for reading in mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI): an integrative approach. NeuroRehabilitation 34, 1: 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobii. 2016. Tobii 4c Eye Tracker. Retrieved from: https://help.tobii.com/hc/en-us/articles/213414285-Specifications-for-the-Tobii-Eye-Tracker-4C.
- Vorstius, C., R. Radach, and J. C. Loniganb. 2014. Eye movements in developing readers: A comparison of silent and oral sentence reading. Visual Cognition 22, 3-4: 458–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| School Grades | Typical readers | Dyslexic readers |
| Grade 3 | 20 | 10 |
| Grade 4 | 16 | 15 |
| Grade 5 | 12 | 11 |
| Grade 6 | 9 | 15 |
| Grade 7 | 2 | 7 |
| Grade 8 | 5 | 2 |
| Grade 9 | 0 | 1 |
| Grade 10 | 4 | 0 |
| Grade 11 | 1 | 0 |
| Groups created for analysis | ||
| Group A (3rd & 4th grade) | 36 | 25 |
| Group B (5th & 6th grade) | 21 | 26 |
| Group C (7th - 11th grade) | 12 | 10 |
| Total word count: | 181 |
| Unique words: | 114 |
| Total number of characters: | 1168 |
| Number of characters without spaces: | 986 |
| Average characters per word: | 5.44 |
| Average syllables per word: | 2.37 |
| Sentence count: | 13 |
| Max sentence length (words): | 8 |
| Min sentence length (words): | 2 |
Copyright © 2021. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Smyrnakis, I.; Andreadakis, V.; Rina, A.; Bοufachrentin, N.; Aslanides, I.M. Silent Versus Reading Out Loud modes: An Eye-Tracking Study. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2021, 14, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.14.2.1
Smyrnakis I, Andreadakis V, Rina A, Bοufachrentin N, Aslanides IM. Silent Versus Reading Out Loud modes: An Eye-Tracking Study. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2021; 14(2):1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.14.2.1
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmyrnakis, Ioannis, Vassilios Andreadakis, Andriani Rina, Nadia Bοufachrentin, and Ioannis M. Aslanides. 2021. "Silent Versus Reading Out Loud modes: An Eye-Tracking Study" Journal of Eye Movement Research 14, no. 2: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.14.2.1
APA StyleSmyrnakis, I., Andreadakis, V., Rina, A., Bοufachrentin, N., & Aslanides, I. M. (2021). Silent Versus Reading Out Loud modes: An Eye-Tracking Study. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 14(2), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.14.2.1



