Reliability and Correlates of Intraindividual Variability in the Oculomotor System
Abstract
Introduction
Oculomotor functioning and variability
Oculomotor variability and ADHD symptomatology
Current research
Methods
Participants
Design
Materials
Procedure
Procedure
Results aim 1. Intra-individual reliability of oculomotor variability measures
Experiment 1. Reliability over time
Experiment 2. Reliability over time and days
Interim-discussion: How long should a resting state session be?
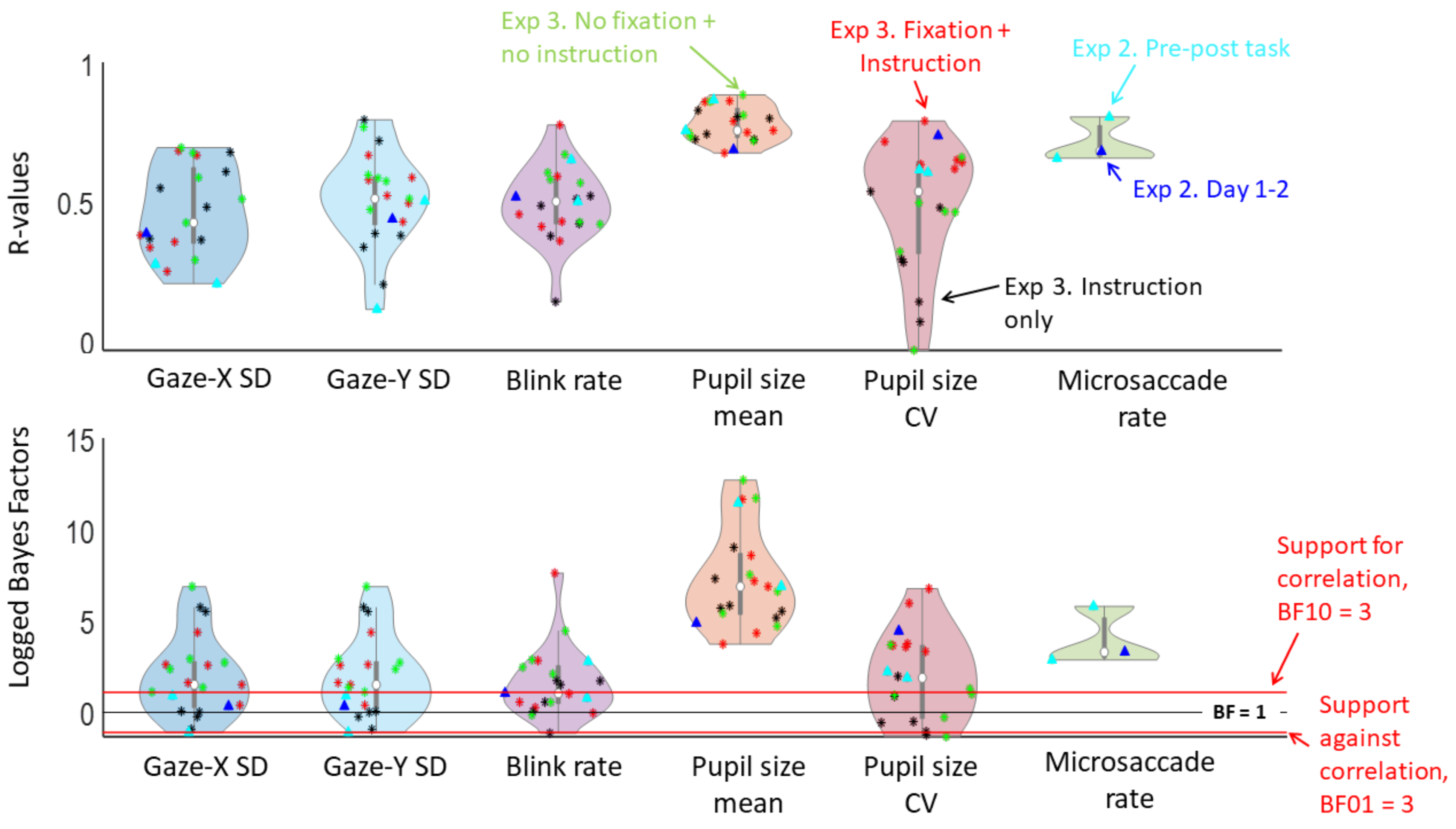
Experiment 3. Reliability over days and conditions
Results aim 2. Between-subject correlations between ADHD, mind wandering, and impulsivity
Results aim 3. No between-subject correlations between questionnaires and oculomotor behaviour
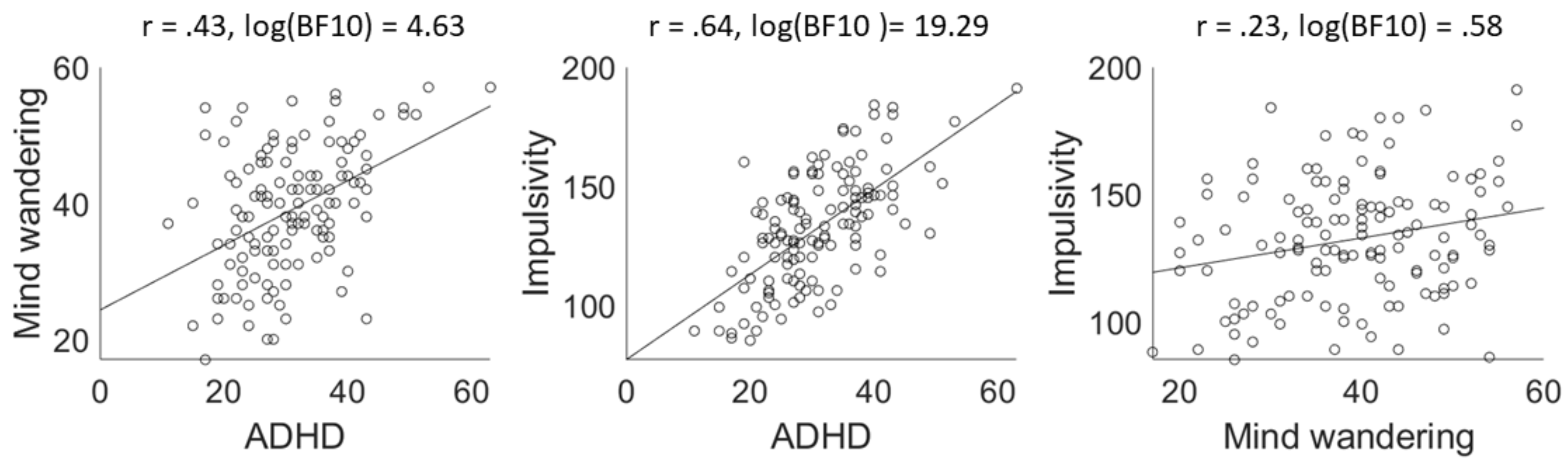

 |
Discussion
Reliability of oculomotor variability
Statistical power and sample size
Individual differences in oculomotor variability
Variability during rest: beneficial or detrimental?
Oculomotor measures: extraction and correlations
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, T. J., and D. M. Coppola. 1999. Idiosyncratic characteristics of saccadic eye movements when viewing different visual environments. Vision Research 39, 17: 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asendorpf, J. B., M. Conner, F. D. Fruyt, J. D. Houwer, J. J. A. Denissen, K. Fiedler, and J. M. Wicherts. 2013. Recommendations for increasing replicability in psychology. European Journal of Personality 27, 2: 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, R. A., G. T. Smith, J. Hopkins, J. Krietemeyer, and L. Toney. 2006. Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment 13, 1: 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A. T., R. A. Steer, and G.K. Brown. 1996. The Beck Depression Inventory-II. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A. T., and R. A. Steer. 1993. The Beck Anxiety Inventory. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J. M., R. D. Latzman, N. G. Bliwise, and S. O. Lilienfeld. 2015. Parsing the heterogeneity of impulsivity: A meta-analytic review of the behavioral implications of the UPPS for psychopathology. Psychological Assessment 27, 4: 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W. R., E. Becic, and A. F. Kramer. 2009. Stable individual differences in search strategy? The effect of task demands and motivational factors on scanning strategy in visual search. Journal of Vision 9, 3: 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainard, D. H. 1997. The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spatial Vision 10, 4: 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelhano, M. S., and J. M. Henderson. 2008. Stable individual differences across images in human saccadic eye movements. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology 62, 1: 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, K. J., and B. Tannen. 1995. Eye movement basics for the clinician. St. Louis: Mosby. [Google Scholar]
- Cronbach, L. J. 1951. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 16, 3: 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danker, Y., L. Shalev, M. Carrasco, and S. Yuval-Greenberg. 2017. Prestimulus inhibition of saccades in adults with and without Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder as an index of temporal expectations. Psychological Science 28, 7: 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R., and R. Kliegl. 2003. Microsaccades uncover the orientation of covert attention. Vision Research 43, 9: 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R., P. Sinn, K. Mergenthaler, and H. Trukenbrod. Microsaccade Toolbox. Available online: http://read.psych.unipotsdam.de/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=140:engbert-et-al-2015-microsaccade-toolbox-for-r&catid=26:publications&Itemid=34.
- Fried, M., E. Tsitsiashvili, Y. S. Bonneh, A. Sterkin, T. Wygnanski-Jaffe, T. Epstein, and U. Polat. 2014. ADHD subjects fail to suppress eye blinks and microsaccades while anticipating visual stimuli but recover with medication. Vision Research 101: 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambra, L. M. 1980. Sex Differences in Daydreaming and Related Mental Activity from the Late Teens to the Early Nineties. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development 10, 1: 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultsch, D. F., S. W. S. MacDonald, and R. A. Dixon. 2002. Variability in reaction time performance of younger and older adults. The Journals of Gerontology: Series B 57, 2: P101–P115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JASP Team. 2017. JASP (Version 0.8.5).
- Kessler, R. C., Adler, L., Ames, M., Demler, O., Faraone, S., Hiripi, E., … Walters, E. E. 2005. The World Health Organization adult ADHD self-report scale (ASRS): a short screening scale for use in the general population. Psychological Medicine 35, 2: 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, M., D. H. Brainard, and D. Pelli. 2007. What’s new in Psychtoolbox-3? Perception 36, 14: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T. K., and M. Y. Li. 2016. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine 15, 2: 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M. A., S. R. Bishop, Z. V. Segal, T. Buis, N. D. Anderson, L. Carlson, and G. Devins. 2006. The Toronto Mindfulness Scale: development and validation. Journal of Clinical Psychology 62, 12: 1445–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M. D., and E. J. Wagenmakers. 2013. Bayesian data analysis for cognitive science: A practical course.
- Lynam, D. R., G. T. Smith, S. P. Whiteside, and M. A Cyders. 2006. The UPPS-P: Assessing five personality pathways to impulsive behavior (Technical Report). West Lafayette: Purdue University. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Conde, S., J. Otero-Millan, and S. L. Macknik. 2013. The impact of microsaccades on vision: towards a unified theory of saccadic function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 14, 2: 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, R. 2004. Biomarkers: potential uses and limitations. NeuroRx: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics 1, 2: 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, G. H. 2000. Increasing statistical power without increasing sample size. American Psychologist 55, 8: 963–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihali, A., A. G. Young, L. A. Adler, M. Halassa, and W. J. T. Ma. 2018. Perceptual and executive behavioral deficits in ADHD and their differential correlation with microsaccade rate. Biological Psychiatry 83: S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D. J., K. J. Derefinko, D. R. Lynam, R. Milich, and M. T. Fillmore. 2010. Impulsivity and Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder: subtype classification using the UPPS Impulsive Behavior Scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment 32, 3: 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, M., R. Andersson, D. C. Niehorster, and I. Hooge. 2017. Searching for monocular microsaccades–A red Hering of modern eye trackers? Vision Research 140: 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Millan, J., S. L. Macknik, R. E. Langston, and S. Martinez-Conde. 2013. An oculomotor continuum from exploration to fixation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110, 15: 6175–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Millan, J., X. G. Troncoso, S. L. Macknik, I. Serrano-Pedraza, and S. Martinez-Conde. 2008. Saccades and microsaccades during visual fixation, exploration, and search: Foundations for a common saccadic generator. Journal of Vision 8, 14: 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidi, M., P. Overton, and T. Stafford. 2017. Increased microsaccade rate in individuals with ADHD traits. Journal of Eye Movement Research 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelli, D. G. 1997. The VideoToolbox software for visual psychophysics: Transforming numbers into movies. Spatial Vision 10, 4: 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perquin, M. N., J. Yang, C. Teufel, P. Sumner, C. Hedge, and A. Bompas. 2019. Inability to improve performance with control shows limited access to inner states. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynter, W., M. Barber, J. Inman, and C. Wiggins. 2013. Individuals exhibit idiosyncratic eye-movement behavior profiles across tasks. Vision Research 89: 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K., X. Li, C. C. Williams, K. R. Cave, and A. D. Well. 2007. Eye movements during information processing tasks: Individual differences and cultural effects. Vision Research 47, 21: 2714–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M., P. Kirsch, and J. Hennig. 2006. Inferring candidate genes for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) assessed by the World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS). Journal of Neural Transmission 113, 7: 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M., B. K. Ashinoff, F. X. Castellanos, and M. Carrasco. 2018. When attention is intact in adults with ADHD. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 25, 4: 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfs, M. 2009. Microsaccades: Small steps on a long way. Vision Research 49, 20: 2415–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salthouse, T. A. 2012. Psychometric properties of with-in-person across-session variability in accuracy of cognitive performance. Assessment 19, 4: 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, C. W. N., R. Pawling, M. Trullinger, D. Daley, J. Intriligator, and C. Klein. 2011. On the stability of instability: Optimising the reliability of intra-subject variability of reaction times. Personality and Individual Differences 51, 2: 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, C. W. N., Shikhare, S., Iyengar, S., Daley, D., Intriligator, J., Boehm, S. G., …, Klein, C. 2012. Is reaction time variability consistent across sensory modalities? Insights from latent variable analysis of single-trial P3b latencies. Biological Psychology 91, 2: 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbrodt, F. D., and M. Perugini. 2013. At what sample size do correlations stabilize? Journal of Research in Personality 47, 5: 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seli, P., J. Smallwood, J. A. Cheyne, and D. Smilek. 2015. On the relation of mind wandering and ADHD symptomatology. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 22, 3: 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G. A., and L. Giambra. 1993. Task-unrelated thoughts of college students diagnosed as hyperactive in childhood. Developmental Neuropsychology 9, 1: 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, J. L., and J. S. Antrobus. 1963. A Factor-Analytic Study of Daydreaming and Conceptually-Related Cognitive and Personality Variables. Perceptual and Motor Skills 17, 1: 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R. M. 1965. Effect of target size, luminance, and color on monocular fixation. JOSA 55, 9: 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks, Inc. 2016. MATLAB 9. Natick, Massachusetts, United States. [Google Scholar]
- Thome, J., Ehlis, A.-C., Fallgatter, A. J., Krauel, K., Lange, K. W., Riederer, P., …, Gerlach, M. 2012. Biomarkers for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). A consensus report of the WFSBP task force on biological markers and the World Federation of ADHD. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry: The Official Journal of the World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry 13, 5: 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, M., E. Betta, and M. Turatto. 2007. Visual oddballs induce prolonged microsaccadic inhibition. Experimental Brain Research 177, 2: 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, N., M. K. Robison, and A. L. Miller. 2019. Individual differences in baseline oculometrics: Examining variation in baseline pupil diameter, spontaneous eye blink rate, and fixation stability. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D., L. A. Clark, and A. Tellegen. 1988. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 54, 6: 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzels, R., and E.-J. Wagenmakers. 2012. A default Bayesian hypothesis test for correlations and partial correlations. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 19, 6: 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, S. P., and D. R. Lynam. 2001. The Five Factor Model and impulsivity: using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Personality and Individual Differences 30, 4: 669–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcutt, E. G., A. E. Doyle, J. T. Nigg, S. V. Faraone, and B. F. Pennington. 2005. Validity of the Executive Function Theory of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: a meta-analytic review. Biological Psychiatry 57, 11: 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterstein, B. P., P. J. Silvia, T. R. Kwapil, J. C. Kaufman, R. Reiter-Palmon, and B. Wigert. 2011. Brief assessment of schizotypy: Developing short forms of the Wisconsin Schizotypy Scales. Personality and Individual Differences 51, 8: 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




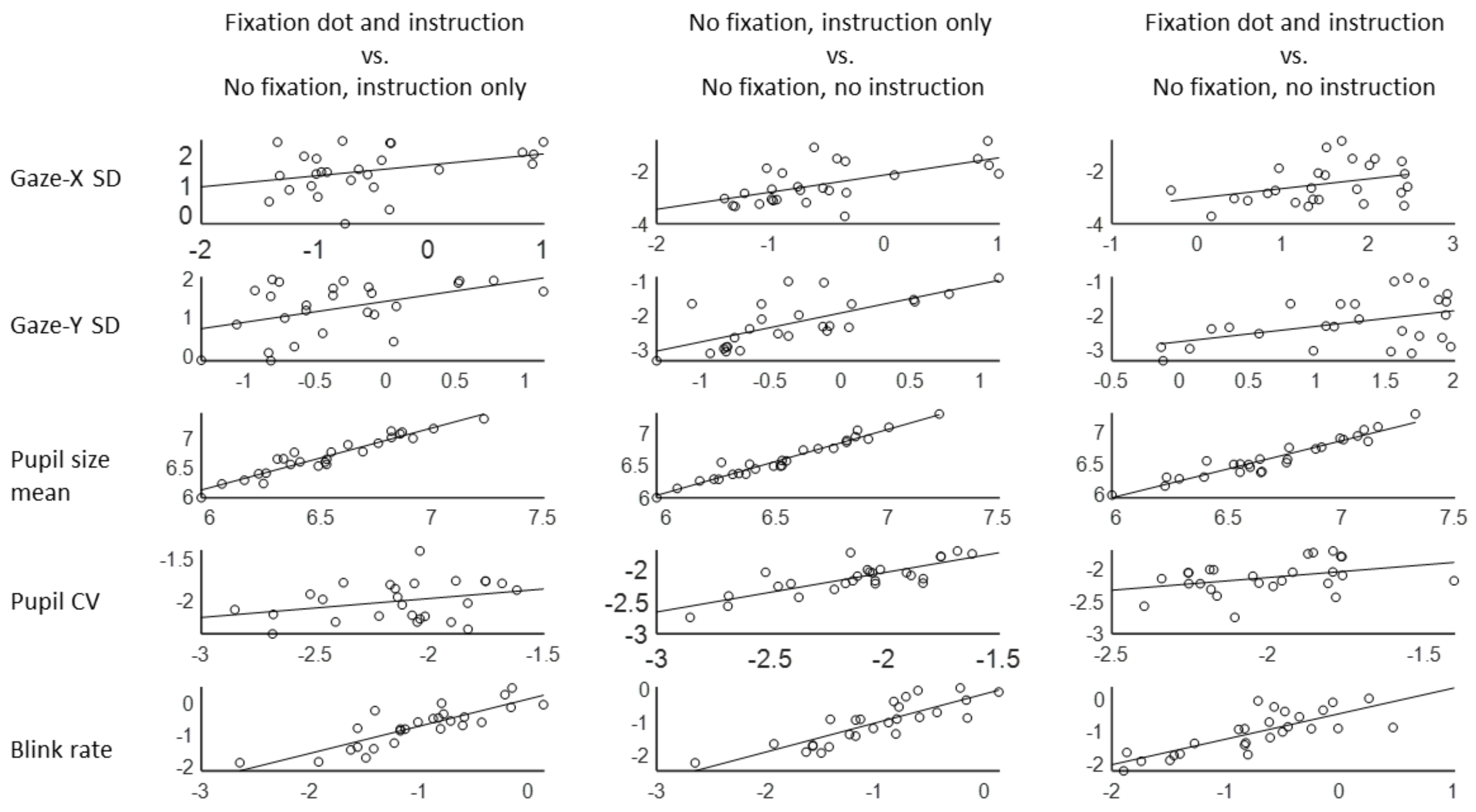
 |
 |
 |
Copyright © 2019. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Perquin, M.N.; Bompas, A. Reliability and Correlates of Intraindividual Variability in the Oculomotor System. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2019, 12, 1-22. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.6.11
Perquin MN, Bompas A. Reliability and Correlates of Intraindividual Variability in the Oculomotor System. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2019; 12(6):1-22. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.6.11
Chicago/Turabian StylePerquin, Marlou Nadine, and Aline Bompas. 2019. "Reliability and Correlates of Intraindividual Variability in the Oculomotor System" Journal of Eye Movement Research 12, no. 6: 1-22. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.6.11
APA StylePerquin, M. N., & Bompas, A. (2019). Reliability and Correlates of Intraindividual Variability in the Oculomotor System. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 12(6), 1-22. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.6.11



