The Black Box of Cellular and Molecular Events of Plasmodium vivax Merozoite Invasion into Reticulocytes
Abstract
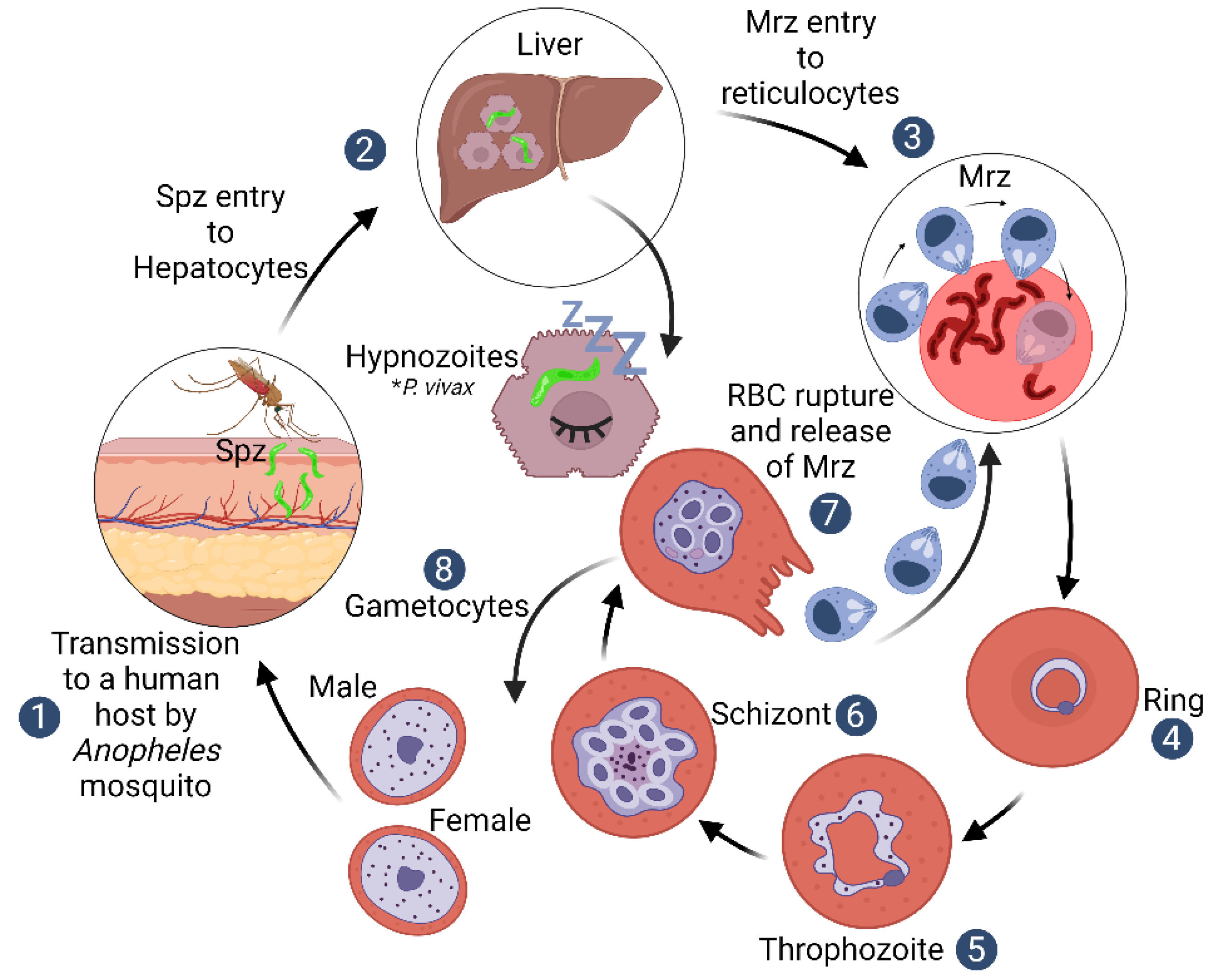
1. Introduction
2. Plasmodium vivax Biological Particularities
3. Plasmodium vivax Mrz Exclusive Invasion of Reticulocytes
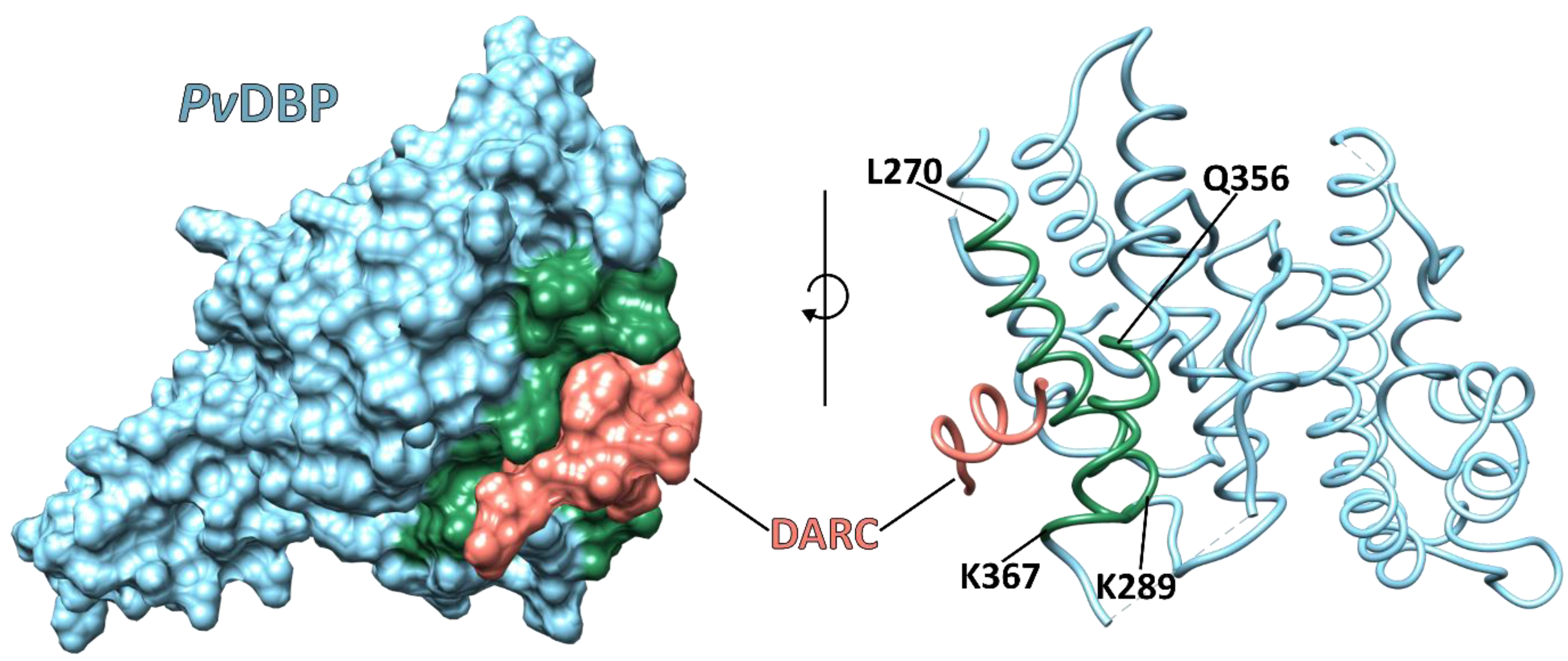
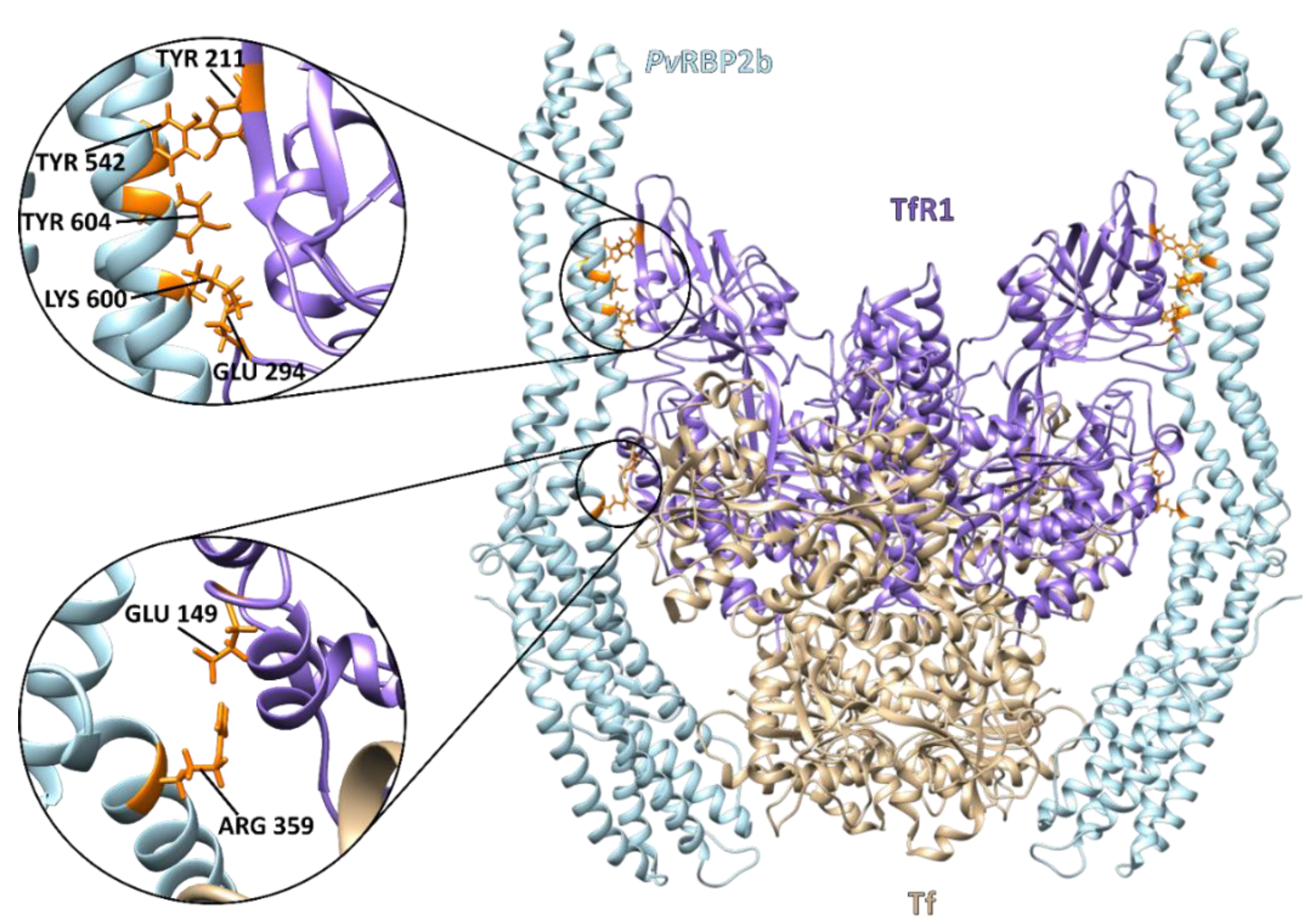
4. The Reticulocyte Gateway for Plasmodium vivax Mrz
5. Plasmodium vivax Infections in the DARC-Negative Population
| Population | Diagnostic Tools | Results | Year | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. vivax Infection | Duffy Genotyping | ||||
| 17,972 adults from the Democratic Republic of the Congo | PCR, nested-PCR | qPCR and sequencing | P. vivax was detected in 467 samples, 464 of which were Duffy-negative. | 2021 | [58] |
| 107 Duffy-negative and 305 Duffy-positive individuals in Ethiopia and Sudan | PCR | - | 412 P. vivax positive samples. 16/107 of these were Duffy-negative and 42/305 were Duffy-positive | 2021 | [59] |
| Febrile patients from Dshang (n:500), Santchou (n:400) and Kyé-ossi (n:100) in Cameroon | Nested PCR, sequencing | PCR-RFLP | P. vivax malaria was detected in 177 Duffy-negative population samples from Dshang, two from Santchou and two from Kyé-ossi. | 2021 | [60] |
| 1215 febrile patients from Botswana, Ethiopia and the Sudan | PCR | qPCR and sequencing | 21 patients in Botswana were positive for P. vivax; 18 of these were Duffy-negative. 210 patients in Ethiopia were P. vivax-positive, 24 of them being Duffy-negative. 101 patients in the Sudan were P. vivax-positive and seven Duffy-negative. | 2021 | [61] |
| 33 participants infected with Plasmodium spp. from Namibia | PCR and sequencing | PCR and sequencing | Three cases of P. vivax monoinfection were identified inDuffy-negative individuals from Namibia | 2021 | [62] |
| 242 individuals form Nigeria | Microscopy, RDT, PCR and sequencing | Sequencing | P. vivax infection was identified in four Nigerian isolates, either as single (three) or mixed (one) with P. falciparum. All P. vivax isolates were Duffy-negative. | 2020 | [63] |
| 42 P. vivax-infected blood samples collected from patients from different areas of Sudan | Rapid diagnostic kit (RDT), microscopy, nested PCR | Nested PCR, sequencing | 7 (16.7%) of the 42 Sudanese patients tested for P. vivax were Duffy-negative. | 2018 | [64] |
| 48 school children in the Kedougou region of south-eastern Senegal | Nested PCR | Sequencing | All Senegalese schoolchildren were classified as Duffy-negative. P. vivax infection was detected in 20.3% (15/74) of them. | 2018 | [65] |
| 292 samples from children in the Democratic Republic of the Congo | Nested PCR, species-specific PCR, sequencing | Nested PCR, sequencing | 14 P. vivax infections were identified in Congolese children; nine were coinfected with P. falciparum. All 14 individuals were confirmed as Duffy-negative. | 2018 | [66] |
| 436 febrile patients from Nigeria | Microscopy, RDT and PCR | Sequencing | Five P. vivax infections were identified (four mixed with another Plasmodium spp.) in Nigerian patients. All P. vivax isolates were Duffy-negative. | 2018 | [67] |
| 300 blood samples from 0- to 6-year-old children in Bandiagara, a Sahelian area of Mali, West Africa | Microscopy, qPCR, real-time PCR | PCR and sequencing | 25 cases of P. vivax malaria were identified in Malian patients. All P. vivax infections were found in Duffy-negative children. | 2017 | [68] |
| 992 microscope-positive malaria samples collected from central, northern and eastern parts of Sudan | Microscopy and nested PCR | PCR and sequencing | 186 P. vivax monoinfections and four mixed P. vivax and P. falciparum infections were identified in Sudan; 129 (67.9%) of them were Fy(a-b+), 14.2% Fy(a+b-) and 17.9% Fy(a-b-). | 2017 | [69] |
| 484 individuals from Cameroon | PCR and sequencing | PCR-melting curve analysis | P. vivax infection was detected in 5.6% of Cameroon individuals (n = 27/484), all having the Duffy-negative genotype. | 2017 | [70] |
| 126 patients suspected of having malaria in the Wad Madani hospital in Gezira State, central Sudan | Microscopy, RDT and PCR | PCR-RFLP | 48 (38%) Sudanese patients were P. vivax-positive and four (8.3%) Duffy-negative. | 2016 | [71] |
| 1234 healthy blood donors in Benin | Microscopy, RDT and nested PCR | Sequencing | 84 samples from Benin were selected for nested PCR analysis, 13 being P. vivax-positive and all Duffy-negative. | 2016 | [72] |
| 60 malaria symptomatic patients from Cameroon | Nested PCR | Sequencing | 43/60 were found to be infected with malaria, 33 (76.7%) were due to P. falciparum and 10/60 (17%) were P. vivax monoinfections. All 10 were Duffy-negative. | 2016 | [73] |
| 485 malaria-symptomatic patients attending hospitals located in five areas of southern Cameroon | PCR | PCR and sequencing | Only 201 of the 485 samples from Cameroon were infected by malarial parasites. 93 (96%) were due to P. falciparum, six (3%) to P. vivax and two cases (1%) to mixed parasites. The eight native Cameroonians infected with P. vivax were Duffy-negative. | 2014 | [74] |
| 269 samples from Bolifamba (a rural, multi-ethnic environment, 530 m above sea level), located on the eastern slope of Mount Cameroon | Microscopy, nested PCR, rapid card assay and sequencing | PCR and sequencing | Overall parasite prevalence in the 269 Cameroonians was 32.3%. 14.9% (13/87) of the infections were caused exclusively or concomitantly by P. vivax. 50% of thosemonoinfected by P. vivax (6/12) were Duffy-negative. | 2014 | [75] |
| 160 P. vivax malaria patients and 160 control individuals from the south-east of Iran | Microscopy | PCR-RFLP, sequencing | 160 P. vivax-positive samples. 2/6 of these were Duffy-negative and 158/314 were Duffy-positive | 2014 | [76] |
| 1304 febrile patients from Harar (Jenela) health centre in eastern Ethiopia and 627 from Jimma health centre in southwestern Ethiopia | Microscopy and PCR | Sequencing | 74/98 (76%) P. vivax cases were identified in Harar, Ethiopia, and 70/107 (65%) P. falciparum cases in Jimma. 17/98 (17%) of these were reported as being Duffy-negative homozygous in Harar and 24/107 (22%) in Jimma. Three P. vivax-positive individuals from Harar were Duffy-negative. | 2013 | [77] |
| 738 patients from Anajás, Marajó Archipelago, State of Pará, Eastern Brazilian Amazon | Microscopy, real-time PCR, sequencing | PCR | Malaria was detected in 137 samples (20.2%) from the Eastern Brazilian Amazon. P. vivax prevalence was 13.9% (94/678), P. falciparum 5.8% (39/678) and P. vivax + P. falciparum 0.6% (4/678). 4.3% (29/678) were genotyped as Duffy-negative. 6.9% (2/29) Duffy-negative individuals were P. vivax-positive. | 2012 | [78] |
| 995 individuals from Angola (n = 898) and Equatorial Guinea (n = 97) | Nested PCR | PCR-RFLP, sequencing | P. vivax was detected in 15 individuals, from which five exhibited a single P. vixax infection. All 15 samples were genotyped as Duffy-negative. | 2011 | [79] |
| 11 participants from Kenya | Microscopy, PCR | Flow cytometry for Fy6 and Fy3 epitopes | P. vivax malaria was detected in 9 out of 11 Duffy-negative Kenyan individuals. | 2006 | [51] |
6. Plasmodium vivax and Proteomics
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Horuk, R.; Chitnis, C.E.; Darbonne, W.C.; Colby, T.J.; Rybicki, A.; Hadley, T.J.; Miller, L.H. A Receptor for the Malarial Parasite Plasmodium vivax: The Erythrocyte Chemokine Receptor. Science 1993, 261, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human Malaria Parasites in Continuous Culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjee, U.; Rangel, G.W.; Clark, M.A.; Duraisingh, M.T. Molecular and Cellular Interactions Defining the Tropism of Plasmodium vivax for Reticulocytes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 46, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, R.W.; Sharaf, H.; Hastings, C.H.; Ho, Y.S.; Nair, M.B.; Rchiad, Z.; Knuepfer, E.; Ramaprasad, A.; Mohring, F.; Amir, A.; et al. Normocyte-Binding Protein Required for Human Erythrocyte Invasion by the Zoonotic Malaria Parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7231–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, R.; Chu, T.T.; Tripathi, J.; Hu, Y.; Subramanian, G.; Tong, J.X.; Tripathi, P.; Fang, K.; Tan, K.S.; Lim, C.T.; et al. Reticulocyte Infection Leads to Altered Behaviour, Drug Sensitivity and Host Cell Remodelling by Plasmodium falciparum. bioRxiv 2019, bioRxiv:862169. [Google Scholar]
- Malleret, B.; Li, A.; Zhang, R.; Tan, K.S.W.; Suwanarusk, R.; Claser, C.; Cho, J.S.; Koh, E.G.L.; Chu, C.S.; Pukrittayakamee, S.; et al. Plasmodium vivax: Restricted Tropism and Rapid Remodeling of CD71-Positive Reticulocytes. Blood 2015, 125, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, W.E.; Jeffery, G.M. Plasmodium ovale: Parasite and Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.; Moreno-Pérez, D.A.; Arévalo-Pinzón, G.; Curtidor, H.; Patarroyo, M.A. Plasmodium vivax in Vitro Continuous Culture: The Spoke in the Wheel. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotoski, W.A. Discovery of the Hypnozoite and a New Theory of Malarial Relapse. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 79, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, I.; Galinski, M.R.; Baird, J.K.; Carlton, J.M.; Kochar, D.K.; Alonso, P.L.; del Portillo, H.A. Key Gaps in the Knowledge of Plasmodium vivax, a Neglected Human Malaria Parasite. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgard, C.; Albrecht, L.; Kayano, A.C.A.V.; Sunnerhagen, P.; Costa, F.T.M. Plasmodium vivax Biology: Insights Provided by Genomics, Transcriptomics and Proteomics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, P.L.; Luo, Z.; Divis, P.C.S.; Friedrich, V.K.; Conway, D.J.; Singh, B.; Barnwell, J.W.; Carlton, J.M.; Sullivan, S.A. Characterizing the Genetic Diversity of the Monkey Malaria Parasite Plasmodium Cynomolgi. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 40, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adapa, S.R.; Taylor, R.A.; Wang, C.; Thomson-Luque, R.; Johnson, L.R.; Jiang, R.H.Y. Plasmodium vivax Readiness to Transmit: Implication for Malaria Eradication. BMC Syst. Biol. 2019, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moras, M.; Lefevre, S.D.; Ostuni, M.A. From Erythroblasts to Mature Red Blood Cells: Organelle Clearance in Mammals. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palis, J. Primitive and Definitive Erythropoiesis in Mammals. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmeyer, L.; Westha üser, R. Reifungsstadien an Ub Erlebenden Reticu-Lozyten In Vitro Und Ihre Bedeutung FR die Schaetzung der Täglichen Haemoglobin-Produktion In Vivo. Z. Für Klin. Med. 1932, 121, 361–379. [Google Scholar]
- Mel, H.; Prenant, M.; Mohandas, N. Reticulocyte Motility and Form: Studies on Maturation and Classification. Blood 1977, 49, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Gaudernack, G.; Sandberg, S. A New Method for Isolation of Reticulocytes: Positive Selection of Human Reticulocytes by Immunomagnetic Separation. Blood 1990, 76, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakarnsanga, K.; Griffiths, R.E.; Wilson, M.C.; Blair, A.; Satchwell, T.J.; Meinders, M.; Cogan, N.; Kupzig, S.; Kurita, R.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. An Immortalized Adult Human Erythroid Line Facilitates Sustainable and Scalable Generation of Functional Red Cells. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 14750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Ichiba, S.; Takahashi, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hitomi, K.; Sasaki, R.; Tada, K.; Imura, H. Establishment of an Erythroid Cell Line (JK-1) That Spontaneously Differentiates to Red Cells. Cancer 1990, 66, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsangpetch, R.; Somsri, S.; Panichakul, T.; Chotivanich, K.; Sirichaisinthop, J.; Yang, Z.; Cui, L.; Sattabongkot, J. Short-Term in Vitro Culture of Field Isolates of Plasmodium vivax Using Umbilical Cord Blood. Parasitol. Int. 2007, 56, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasini, E.M.; Kocken, C.H.M. Parasite-Host Interaction and Pathophysiology Studies of the Human Relapsing Malarias Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale Infections in Non-Human Primates. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 614122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, C.; Roobsoong, W.; Kangwanrangsan, N.; Bardelli, M.; Rawlinson, T.A.; Dambrauskas, N.; Trakhimets, O.; Parthiban, C.; Goswami, D.; Reynolds, L.M.; et al. A Humanized Mouse Model for Plasmodium vivax to Test Interventions That Block Liver Stage to Blood Stage Transition and Blood Stage Infection. iScience 2020, 23, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golenda, C.F.; Li, J.; Rosenberg, R. Continuous in Vitro propagation of the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium vivax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6786–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitnis, C.E.; Miller, L.H. Identification of the Erythrocyte Binding Domains of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi Proteins Involved in Erythrocyte Invasion. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyk, J.; Kanjee, U.; Chan, L.-J.; Menant, S.; Malleret, B.; Lim, N.T.Y.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Mok, Y.-F.; Lin, K.-M.; Pearson, R.D.; et al. Transferrin Receptor 1 Is a Reticulocyte-Specific Receptor for Plasmodium vivax. Science 2018, 359, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, J.D.; Malpede, B.M.; Omattage, N.S.; DeKoster, G.T.; Henzler-Wildman, K.A.; Tolia, N.H. Red Blood Cell Invasion by Plasmodium vivax: Structural Basis for DBP Engagement of DARC. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBuskirk, K.M.; Sevova, E.; Adams, J.H. Conserved Residues in the Plasmodium vivax Duffy-Binding Protein Ligand Domain Are Critical for Erythrocyte Receptor Recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15754–15759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Tobian, J.; King, C.L. Diversity and Natural Selection in Plasmodium vivax Duffy Binding Protein Gene. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 127, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchynnikova, E.; Aglialoro, F.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; Vidarsson, G.; Salinas, N.D.; von Lindern, M.; Tolia, N.H.; van den Akker, E. DARC Extracellular Domain Remodeling in Maturating Reticulocytes Explains Plasmodium vivax Tropism. Blood 2017, 130, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Mukherjee, P.; Shakri, A.R.; Singh, A.; Pandey, G.; Bakshi, M.; Uppal, G.; Jena, R.; Rawat, A.; Kumar, P.; et al. Malaria Vaccine Candidate Based on Duffy-Binding Protein Elicits Strain Transcending Functional Antibodies in a Phase I Trial. npj Vaccines 2018, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimberg, B.T.; Udomsangpetch, R.; Xainli, J.; McHenry, A.; Panichakul, T.; Sattabongkot, J.; Cui, L.; Bockarie, M.; Chitnis, C.; Adams, J.; et al. Plasmodium vivax Invasion of Human Erythrocytes Inhibited by Antibodies Directed against the Duffy Binding Protein. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Tobian, J.L.; Michon, P.; Biasor, M.; Richards, J.S.; Beeson, J.G.; Mueller, I.; King, C.L. Strain-Specific Duffy Binding Protein Antibodies Correlate with Protection against Infection with Homologous Compared to Heterologous Plasmodium vivax Strains in Papua New Guinean Children. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4009–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xainli, J.; Cole-Tobian, J.L.; Baisor, M.; Kastens, W.; Bockarie, M.; Yazdani, S.S.; Chitnis, C.E.; Adams, J.H.; King, C.L. Epitope-Specific Humoral Immunity to Plasmodium vivax Duffy Binding Protein. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Urusova, D.; Carias, L.; Huang, Y.; Nicolete, V.C.; Popovici, J.; Roesch, C.; Salinas, N.D.; Dechavanne, S.; Witkowski, B.; Ferreira, M.U.; et al. Structural Basis for Neutralization of Plasmodium vivax by Naturally Acquired Human Antibodies That Target DBP. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntumngia, F.B.; Schloegel, J.; Barnes, S.J.; McHenry, A.M.; Singh, S.; King, C.L.; Adams, J.H. Conserved and Variant Epitopes of Plasmodium vivax Duffy Binding Protein as Targets of Inhibitory Monoclonal Antibodies. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.T.; Teng, K.; Wu, C.; Adam, M.; Johnstone, R.M. Electron Microscopic Evidence for Externalization of the Transferrin Receptor in Vesicular Form in Sheep Reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, J.; Roesch, C.; Rougeron, V. The Enigmatic Mechanisms by Which Plasmodium vivax Infects Duffy-Negative Individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyk, J.; Huang, R.K.; Chan, L.-J.; Menant, S.; Hong, C.; Murphy, J.M.; Mok, Y.-F.; Griffin, M.D.W.; Pearson, R.D.; Wong, W.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of an Essential Plasmodium vivax Invasion Complex. Nature 2018, 559, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.-J.; Gandhirajan, A.; Carias, L.L.; Dietrich, M.H.; Vadas, O.; Visentin, R.; França, C.T.; Menant, S.; Soldati-Favre, D.; Mueller, I.; et al. Naturally Acquired Blocking Human Monoclonal Antibodies to Plasmodium vivax Reticulocyte Binding Protein 2b. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleret, B.; El Sahili, A.; Tay, M.Z.; Carissimo, G.; Ong, A.S.M.; Novera, W.; Lin, J.; Suwanarusk, R.; Kosaisavee, V.; Chu, T.T.T.; et al. Plasmodium vivax Binds Host CD98hc (SLC3A2) to Enter Immature Red Blood Cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brevern, A.G.; Wong, H.; Tournamille, C.; Colin, Y.; Le Van Kim, C.; Etchebest, C. A Structural Model of a Seven-Transmembrane Helix Receptor: The Duffy Antigen/Receptor for Chemokine (DARC). Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2005, 1724, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seixas, S.; Ferrand, N.; Rocha, J. Microsatellite Variation and Evolution of the Human Duffy Blood Group Polymorphism. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sanger, R.; Race, R.R.; Jack, J. The Duffy Blood Groups of New York Negroes: The Phenotype Fy (a-b-). Br. J. Haematol. 1955, 1, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höher, G.; Fiegenbaum, M.; Almeida, S. Molecular Basis of the Duffy Blood Group System. Blood Transfus. 2018, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michon, P.; Woolley, I.; Wood, E.M.; Kastens, W.; Zimmerman, P.A.; Adams, J.H. Duffy-Null Promoter Heterozygosity Reduces DARC Expression and Abrogates Adhesion of the P. vivax Ligand Required for Blood-Stage Infection. FEBS Lett. 2001, 495, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, E.; Hostetler, J.B.; Yewhalaw, D.; Pearson, R.D.; Hamid, M.M.A.; Gunalan, K.; Kepple, D.; Ford, A.; Janies, D.A.; Rayner, J.C.; et al. Frequent Expansion of Plasmodium vivax Duffy Binding Protein in Ethiopia and Its Epidemiological Significance. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, R.E.; Patil, A.P.; Piel, F.B.; Nyangiri, O.A.; Kabaria, C.W.; Gething, P.W.; Zimmerman, P.A.; Barnadas, C.; Beall, C.M.; Gebremedhin, A.; et al. The Global Distribution of the Duffy Blood Group. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.H.; Mason, S.J.; Clyde, D.F.; McGinniss, M.H. The Resistance Factor to Plasmodium vivax in Blacks: The Duffy-Blood-Group Genotype, FyFy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 295, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.R.; Stoute, J.A.; Amon, J.; Dunton, R.F.; Mtalib, R.; Koros, J.; Owour, B.; Luckhart, S.; Wirtz, R.A.; Barnwell, J.W.; et al. Evidence for Transmission of Plasmodium vivax among a Duffy Antigen Negative Population in Western Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, D.; Chan, E.R.; Benedet, C.; Ratsimbasoa, A.; Kim, S.; Chim, P.; Do, C.; Witkowski, B.; Durand, R.; Thellier, M.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing of Field Isolates Reveals a Common Duplication of the Duffy Binding Protein Gene in Malagasy Plasmodium vivax Strains. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, C.; Popovici, J.; Bin, S.; Run, V.; Kim, S.; Ramboarina, S.; Rakotomalala, E.; Rakotoarison, R.L.; Rasoloharimanana, T.; Andriamanantena, Z.; et al. Genetic Diversity in Two Plasmodium vivax Protein Ligands for Reticulocyte Invasion. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanjee, U.; Grüring, C.; Babar, P.; Meyers, A.; Dash, R.; Pereira, L.; Mascarenhas, A.; Chaand, M.; Rangel, G.W.; Clark, M.A.; et al. Plasmodium vivax Strains Use Alternative Pathways for Invasion. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunalan, K.; Lo, E.; Hostetler, J.B.; Yewhalaw, D.; Mu, J.; Neafsey, D.E.; Yan, G.; Miller, L.H. Role of Plasmodium vivax Duffy-Binding Protein 1 in Invasion of Duffy-Null Africans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6271–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechavanne, C.; Dechavanne, S.; Metral, S.; Roeper, B.; Krishnan, S.; Fong, R.; Bennett, S.; Carias, L.; Chen, E.; Salinas, N.D.; et al. Duffy Antigen Expression in Erythroid Bone Marrow Precursor Cells of Genotypically Duffy Negative Individuals. bioRxiv 2018, bioRxiv:508481. [Google Scholar]
- Gunalan, K.; Niangaly, A.; Thera, M.A.; Doumbo, O.K.; Miller, L.H. Plasmodium vivax Infections of Duffy-Negative Erythrocytes: Historically Undetected or a Recent Adaptation? Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazeau, N.F.; Mitchell, C.L.; Morgan, A.P.; Deutsch-Feldman, M.; Watson, O.J.; Thwai, K.L.; Gelabert, P.; van Dorp, L.; Keeler, C.Y.; Waltmann, A.; et al. The Epidemiology of Plasmodium vivax among Adults in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepple, D.; Hubbard, A.; Ali, M.M.; Abargero, B.R.; Lopez, K.; Pestana, K.; Janies, D.A.; Yan, G.; Hamid, M.M.; Yewhalaw, D.; et al. Plasmodium vivax From Duffy-Negative and Duffy-Positive Individuals Share Similar Gene Pools in East Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeunang Dongho, G.B.; Gunalan, K.; L’Episcopia, M.; Paganotti, G.M.; Menegon, M.; Sangong, R.E.; Georges, B.M.; Fondop, J.; Severini, C.; Sobze, M.S.; et al. Plasmodium vivax Infections Detected in a Large Number of Febrile Duffy-Negative Africans in Dschang, Cameroon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, E.; Russo, G.; Pestana, K.; Kepple, D.; Abagero, B.R.; Dongho, G.B.D.; Gunalan, K.; Miller, L.H.; Hamid, M.M.A.; Yewhalaw, D.; et al. Contrasting Epidemiology and Genetic Variation of Plasmodium vivax Infecting Duffy-Negative Individuals across Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyambo, D.H.; Aleksenko, L.; Mumbengegwi, D.; Bock, R.; Uusiku, P.; Malleret, B.; Rénia, L.; Quaye, I.K. Children with Plasmodium vivax Infection Previously Observed in Namibia, Were Duffy Negative and Carried a c.136G > A Mutation. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oboh, M.A.; Singh, U.S.; Ndiaye, D.; Badiane, A.S.; Ali, N.A.; Bharti, P.K.; Das, A. Presence of Additional Plasmodium vivax Malaria in Duffy Negative Individuals from Southwestern Nigeria. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, M.R.; Elfaki, M.M.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Lee, S.-K.; Muh, F.; Ali Albsheer, M.M.; Hamid, M.M.A.; Han, E.-T. Diversity Pattern of Duffy Binding Protein Sequence among Duffy-Negatives and Duffy-Positives in Sudan. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, M.; Sane, R.; Sow, A.; Sadio, B.D.; Chy, S.; Legrand, E.; Faye, O.; Diallo, M.; Sall, A.A.; Menard, D.; et al. Asymptomatic Plasmodium vivax Infections among Duffy-Negative Population in Kedougou, Senegal. Trop. Med. Health 2018, 46, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likwela, J.L.; Tshefu, A.K.; Doctor, S.M.; Meshnick, S.R.; Whitesell, A.N.; Juliano, J.J.; Mwandagalirwa, M.K.; Keeler, C.; Brazeau, N.F. Plasmodium vivax Infections in Duffy-Negative Individuals in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Oboh, M.A.; Badiane, A.S.; Ntadom, G.; Ndiaye, Y.D.; Diongue, K.; Diallo, M.A.; Ndiaye, D. Molecular Identification of Plasmodium Species Responsible for Malaria Reveals Plasmodium vivax Isolates in Duffy Negative Individuals from Southwestern Nigeria. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niangaly, A.; Gunalan, K.; Ouattara, A.; Coulibaly, D.; Sá, J.M.; Adams, M.; Travassos, M.A.; Ferrero, J.; Laurens, M.B.; Kone, A.K.; et al. Plasmodium vivax Infections over 3 Years in Duffy Blood Group Negative Malians in Bandiagara, Mali. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albsheer, M.M.A.; Pestana, K.; Ahmed, S.; Elfaki, M.; Gamil, E.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Musa, A.M.; Lo, E.; Hamid, M.M.A. Distribution of Duffy Phenotypes among Plasmodium vivax Infections in Sudan. Genes 2019, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Faggioni, G.; Paganotti, G.M.; Djeunang Dongho, G.B.; Pomponi, A.; De Santis, R.; Tebano, G.; Mbida, M.; Sanou Sobze, M.; Vullo, V.; et al. Molecular Evidence of Plasmodium vivax Infection in Duffy Negative Symptomatic Individuals from Dschang, West Cameroon. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, M.H.; Albsheer, M.M.A.; Mohamed, H.S.; Amin, M.; Abdel Hamid, M.M. Transmission of Plasmodium vivax in Duffy-Negative Individuals in Central Sudan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, P.; Doderer-Lang, C.; Atchade, P.S.; Lemoine, J.-P.; de l’Isle, M.-L.C.; Abou-bacar, A.; Pfaff, A.W.; Brunet, J.; Arnoux, L.; Haar, E.; et al. The Hide and Seek of Plasmodium vivax in West Africa: Report from a Large-Scale Study in Beninese Asymptomatic Subjects. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngassa Mbenda, H.G.; Gouado, I.; Das, A. An Additional Observation of Plasmodium vivax Malaria Infection in Duffy-Negative Individuals from Cameroon. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ngassa Mbenda, H.G.; Das, A. Molecular Evidence of Plasmodium vivax Mono and Mixed Malaria Parasite Infections in Duffy-Negative Native Cameroonians. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fru-Cho, J.; Bumah, V.V.; Safeukui, I.; Nkuo-Akenji, T.; Titanji, V.P.; Haldar, K. Molecular Typing Reveals Substantial Plasmodium vivax Infection in Asymptomatic Adults in a Rural Area of Cameroon. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri-Moghaddam, E.; Bameri, Z.; Mohamadi, M. Duffy Blood Group Genotypes among Malaria Plasmodium vivax Patients of Baoulch Population in Southeastern Iran. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldearegai, T.G.; Kremsner, P.G.; Kun, J.F.J.; Mordmüller, B. Plasmodium vivax Malaria in Duffy-Negative Individuals from Ethiopia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.A.; Queiroz, M.G.; Cardoso, G.L.; Diniz, I.G.; Silva, A.N.; Pinto, A.Y.; Guerreiro, J.F. Plasmodium vivax Infection in Anajás, State of Pará: No Differential Resistance Profile among Duffy-Negative and Duffy-Positive Individuals. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, C.; Dias, F.; Figueiredo, J.; Mora, V.G.; Cano, J.; de Sousa, B.; do Rosário, V.E.; Benito, A.; Berzosa, P.; Arez, A.P. Duffy Negative Antigen Is No Longer a Barrier to Plasmodium vivax—Molecular Evidences from the African West Coast (Angola and Equatorial Guinea). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.; Pallavi, R.; Chandran, S.; Chakravarti, H.; Middha, S.; Acharya, J.; Kochar, S.; Kochar, D.; Subudhi, A.; Boopathi, A.P.; et al. A Glimpse into the Clinical Proteome of Human Malaria Parasites Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Prot. Clin. Appl. 2009, 3, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.; Pallavi, R.; Chandran, S.; Dandavate, V.; Sayeed, S.K.; Rochani, A.; Acharya, J.; Middha, S.; Kochar, S.; Kochar, D.; et al. Clinical Proteomics of the Neglected Human Malarial Parasite Plasmodium vivax. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roobsoong, W.; Roytrakul, S.; Sattabongkot, J.; Li, J.; Udomsangpetch, R.; Cui, L. Determination of the Plasmodium vivax Schizont Stage Proteome. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Pérez, D.A.; Dégano, R.; Ibarrola, N.; Muro, A.; Patarroyo, M.A. Determining the Plasmodium vivax VCG-1 Strain Blood Stage Proteome. J. Proteom. 2015, 113, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.C.; Lapp, S.A.; Barnwell, J.W.; Galinski, M.R. A Large Scale Plasmodium vivax- Saimiri Boliviensis Trophozoite-Schizont Transition Proteome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkel, J.M. Single-Cell Proteomics Takes Centre Stage. Nature 2021, 597, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Pérez, D.A.; Baquero, L.A.; Chitiva-Ardila, D.M.; Patarroyo, M.A. Characterising PvRBSA: An Exclusive Protein from Plasmodium Species Infecting Reticulocytes. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molina-Franky, J.; Reyes, C.; Picón Jaimes, Y.A.; Kalkum, M.; Patarroyo, M.A. The Black Box of Cellular and Molecular Events of Plasmodium vivax Merozoite Invasion into Reticulocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314528
Molina-Franky J, Reyes C, Picón Jaimes YA, Kalkum M, Patarroyo MA. The Black Box of Cellular and Molecular Events of Plasmodium vivax Merozoite Invasion into Reticulocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314528
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolina-Franky, Jessica, César Reyes, Yelson Alejandro Picón Jaimes, Markus Kalkum, and Manuel Alfonso Patarroyo. 2022. "The Black Box of Cellular and Molecular Events of Plasmodium vivax Merozoite Invasion into Reticulocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314528
APA StyleMolina-Franky, J., Reyes, C., Picón Jaimes, Y. A., Kalkum, M., & Patarroyo, M. A. (2022). The Black Box of Cellular and Molecular Events of Plasmodium vivax Merozoite Invasion into Reticulocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314528







