Salmonella-Based Biorodenticides: Past Applications and Current Contradictions †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Dawn of Salmonella-Based Rodenticides
3. First Clouds in the Use of Salmonella as a Rodenticide
4. The Eve of Bacterial Rodenticides
5. New Horizons: Understanding of the Molecular Diversity of Salmonella
5.1. Direct Examination of Salmonella Specificity Factors
5.1.1. Adhesion to Host Cells
5.1.2. Propagation in Macrophages
5.1.3. Colonization of Mucosal Tissues
5.1.4. Later Stages of Infection
5.2. Indirect Identification of Salmonella Specificity Determinants
5.2.1. Comparative Genomics of Host-Restricted and Broad-Host-Range Serovars
5.2.2. Proteomic Studies of Salmonella Strains with Different Host Specificity
5.2.3. Revealing Alterations in Host Preferences
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stenseth, N.C.; Leirs, H.; Skonhoft, A.; Davis, S.A.; Pech, R.P.; Andreassen, H.P.; Singleton, G.R.; Lima, M.; Machang’u, R.S.; Makundi, R.H.; et al. Mice, Rats, and People: The Bio-Economics of Agricultural Rodent Pests. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel, L.H.; Swanepoel, C.M.; Brown, P.R.; Eiseb, S.J.; Goodman, S.M.; Keith, M.; Kirsten, F.; Leirs, H.; Mahlaba, T.A.M.; Makundi, R.H.; et al. A Systematic Review of Rodent Pest Research in Afro-Malagasy Small-Holder Farming Systems: Are We Asking the Right Questions? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, J.; Oyston, P.C.F.; Green, M.; Titball, R.W. Tularemia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, H.V.; Dang, D.T.; Tran Minh, N.N.; Nguyen, N.D.; Nguyen, T.V. Correlates of Environmental Factors and Human Plague: An Ecological Study in Vietnam. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabbir, M.; Aleem, M.; Javed, S.; Wagner, D.M.; Keim, P.S.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Bokhari, H. Spatial Analysis and Identification of High Risk Plague Regions in Pakistan Based on Associated Rodent Species Distribution. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erickson, W.; Urban, D. Potential Risk of Nine Rodenticides to Birds and Mammals: A Comparative Approach; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 192.
- Murphy, M.J. Rodenticides. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 32, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodzicki, K. Prospects for Biological Control of Rodent Populations. Bull. World Health Organ. 1973, 48, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singleton, G.R.; Petch, D.A. A Review of the Biology and Management of Rodent Pests in Southeast Asia. ACIAR Technical Reports No. 30; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research Canberra: Canberra, Australia, 1994; p. 65.
- Labuschagne, L.; Swanepoel, L.H.; Taylor, P.J.; Belmain, S.R.; Keith, M. Are Avian Predators Effective Biological Control Agents for Rodent Pest Management in Agricultural Systems? Biol. Control 2016, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M.S. Insect Pathogens as Biological Control Agents: Back to the Future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Skills to Succeed in the Host: Virulence and Regulation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 308–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loeffler, F. Über Epidemieen Unter Den Im Hygienischen Institute Zu Greifswald Gehaltenen Mäusen Und Über Die Bekämpfung Der Feldmausplage. Cent. Für Bakteriol. Und Parasitenkd. 1892, 11, 129–141. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, W.F. Epidemics among Mice. Nature 1898, 58, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, M. The Pest of Field-Mice in Thessaly and Loeffler’s Successful Method of Combating It. Science 1892, 20, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, M.; Köhler, W. Zentralblatt Für Bakteriologie--100 Years Ago: Bacteriological Warfare against Mice and Rats. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2005, 294, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danysz, J. Emploi Des Cultures Artificielles de Microbes Pathogènes à La Destruction Des Rongeurs (Campagnols et Mulots) En Grande Culture. Comptes Rendus Séances L’académie Sci. 1893, CXVII, 869–872. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Danysz, J. A Microbe Pathogenic to Rats (Mus Decumanus and Mus Ratus) and Its Use in the Destruction of These Animals. Br. Med. J. 1904, 1, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelmann, L. An Epidemic for Sale: Observation, Modification, and Commercial Circulation of the Danysz Virus, 1890–1910. Isis 2021, 112, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppelsa, P. Losing France’s Imperial War on Rats. J. West. Soc. Fr. Hist. 2021, 47, 67–87. [Google Scholar]
- Merezhkovsky, S.S. A Bacillus Isolated from Gophers and Suitable for the Extermination of Mice. Arkhiv Vet. Nauk 1895, 3, 1–17. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mereshkowsky, S.S. Feldversuche, Angestellt Zur Vertilgung Der Mäuse Mittelst Des Aus Zieselmäusen Ausgeschiedenen Bacillus. Cent. Für Bakteriol. Parasitenkd. Und Infekt. Erste Abtheilung 1896, 2/3, 85–94. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Merezhkovsky, S.S. About the Fate in Russia and Japan of the Bacillus for the Extermination of Mice. Arkhiv Vet. Nauk 1903, 8, 1–24. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Issatschenko, B. Zur Morphology Und Biolodie Des Ziesemaus Bacillus. Scr. Bot. Horti Univ. Imp. Petropolitanae 1897, XV, 1–12. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Issatschenko, B. Ueber Einen Neuen Für Ratten Pathogenen Bacillus. Cent. F. Bakteriol. Parasitenkd. U. Infektionskheiten. 1898, XXXIII, 873–874. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, R.O. Beitrag Zur Frage Der Pestähnlichen Rattenpathogenen Bakterien. Z. Für Hyg. Und Infect. 1903, 45, 450–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonovich, I.A.; Minina, G.N.; Bologova, E.V.; Ermolova, V.P.; Grishechkina, S.D.; Romanova, T.A. Salmonella Enteritidis Var. Issatchenko 32/3 Bacteria Strain as Means for Obtaining Biological Attractant against Mouse-like Rodents. 2014, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://i.moscow/patents/RU2520161C1_20140620 (accessed on 29 September 2022). (In Russian).
- Prokhorov, M.I. Microbiological Method of Pest Control; Sel’khozizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1962; p. 133. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kandybin, N.V.; Dorodnykh, Y.L. Bactorodencid—A Worthy Alternative to Chemical Rodenticides. Zashchita I Karantin Rasteniy 2007, 4, 54–56. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V. Salmonella Serovars and Their Host Specificity. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2013, 1, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gal-Mor, O. Persistent Infection and Long-Term Carriage of Typhoidal and Nontyphoidal Salmonellae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00088-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenner, F.W.; Villar, R.G.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.; Swaminathan, B. Salmonella Nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2465–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worley, J.; Meng, J.; Allard, M.W.; Brown, E.W.; Timme, R.E. Salmonella enterica Phylogeny Based on Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Two New Clades and Novel Patterns of Horizontally Acquired Genetic Elements. mBio 2018, 9, e02303-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vo, A.T.T.; van Duijkeren, E.; Fluit, A.C.; Heck, M.E.O.C.; Verbruggen, A.; Maas, H.M.E.; Gaastra, W. Distribution of Salmonella enterica Serovars from humans, livestock and meat in Vietnam and the Dominance of Salmonella Typhimurium Phage Type 90. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 113, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajere, S.M. A Review of Salmonella enterica with Particular Focus on the Pathogenicity and Virulence Factors, Host Specificity and Antimicrobial Resistance Including Multidrug Resistance. Vet. World 2019, 12, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Genus Salmonella Lignières, 1900: Issued by the Salmonella Subcommittee of the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society for Microbiology. J. Hyg. 1934, 34, 333–350. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popoff, M.Y. Antigenic Formulas of the Salmonella Serovars, 8th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, C.; Johnson, R.P.; Forsberg, C.M.; Irwin, R.J. Salmonella Enteritidis and Other Salmonella in Laying Hens and Eggs from Flocks with Salmonella in Their Environment. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 56, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rumeu, M.T.; Suárez, M.A.; Morales, S.; Rotger, R. Enterotoxin and Cytotoxin Production by Salmonella Enteritidis Strains Isolated from Gastroenteritis Outbreaks. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 82, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezal, E.H.; Sabol, A.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, N.; Stefanova, R.; Khan, A.A. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis from Poultry House and Clinical Samples during 2010. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabees, R.; Elsayed, M.S.A.; Shawish, R.; Basiouni, S.; Shehata, A.A. Isolation and Characterization of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium from Chicken Meat in Egypt. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäumler, A.; Fang, F.C. Host Specificity of Bacterial Pathogens. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a010041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evangelopoulou, G.; Kritas, S.; Govaris, A.; Burriel, A.R. Animal Salmonelloses: A Brief Review of “Host Adaptation and Host Specificity” of Salmonella spp. Vet. World 2013, 6, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakov, A.V.; Mastriani, E.; Liu, S.-L.; Schifferli, D.M. Association of Salmonella Virulence Factor Alleles with Intestinal and Invasive Serovars. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, N.A.; Yakovlev, A.A. Genetic Diversity of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Enteritidis in the Siberia and Far East of Russia Based on Plasmid Profiles. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Hung, M.-C.; Hung, S.-C.; Wang, H.-P.; Cho, H.-L.; Lai, M.-C.; Wang, J.-T. Salmonella enterica Subspecies Arizonae Infection of Adult Patients in Southern Taiwan: A Case Series in a Non-Endemic Area and Literature Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krath, M.L.; Little, S.V.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Lawhon, S.D. Salmonella enterica Subsp. Arizonae Isolated from a Canine Clinical Case of Prostatitis. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00118-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giner-Lamia, J.; Vinuesa, P.; Betancor, L.; Silva, C.; Bisio, J.; Soleto, L.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Puente, J.L.; Salmonella CYTED Network; García-Del Portillo, F. Genome Analysis of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Diarizonae Isolates from Invasive Human Infections Reveals Enrichment of Virulence-Related Functions in Lineage ST1256. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castañeda-Ruelas, G.M.; Burgeño-Román, A.; Jiménez-Edeza, M. Genetics and Physiology of Salmonella Houtenae Isolated from a River in Mexico Provides Insight into the Aquatic Habitat Influence on Its Adaptation and Pathogenesis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 83, 104326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, J.-H.; Bao, H.-X.; Liu, H.; Ding, T.-M.; Liu, G.-R.; Li, Y.-G.; Johnston, R.N.; Cao, F.-L.; et al. Genetic Boundaries Delineate the Potential Human Pathogen Salmonella Bongori into Discrete Lineages: Divergence and Speciation. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Li, F.; Dong, N.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Xie, J.; et al. Investigation of a Salmonellosis Outbreak Caused by Multidrug Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium in China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoleoni, M.; Villa, L.; Barco, L.; Busani, L.; Cibin, V.; Lucarelli, C.; Tiengo, A.; Dionisi, A.M.; Conti, F.; da Silva Nunes, F.R.; et al. A Strong Evidence Outbreak of Salmonella Enteritidis in Central Italy Linked to the Consumption of Contaminated Raw Sheep Milk Cheese. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Sayed, F.; Sapriel, G.; Fawal, N.; Gruber, A.; Bauer, T.; Heym, B.; Dupont, C.; Garchon, H.-J.; Gaillard, J.-L.; Rottman, M.; et al. In-Host Adaptation of Salmonella enterica Serotype Dublin during Prosthetic Hip Joint Infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2360–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinello, P.; Granata, G.; Galati, V.; Taglietti, F.; Topino, S.; Caraffa, E.; Venditti, C.; Bevilacqua, N.; Sbardella, L.; Bilei, S.; et al. Salmonella Hessarek Gastroenteritis with Bacteremia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabsch, W.; Andrews, H.L.; Kingsley, R.A.; Prager, R.; Tschäpe, H.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium and Its Host-Adapted Variants. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.R.; Kingsley, R.A. Evolution of Salmonella within Hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porwollik, S.; Santiviago, C.A.; Cheng, P.; Florea, L.; Jackson, S.; McClelland, M. Differences in Gene Content between Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Isolates and Comparison to Closely Related Serovars Gallinarum and Dublin. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6545–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.; Feng, Y.; Chien, A.-C.; Hu, S.; Chu, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-H. Evolution of Genes on the Salmonella Virulence Plasmid Phylogeny Revealed from Sequencing of the Virulence Plasmids of S. Enterica Serotype Dublin and Comparative Analysis. Genomics 2008, 92, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, M.-D.; Kidgell, C.; Nair, S.; Holt, K.E.; Turner, A.K.; Hinds, J.; Butcher, P.; Cooke, F.J.; Thomson, N.R.; Titball, R.; et al. Variation in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi IncHI1 Plasmids during the Global Spread of Resistant Typhoid Fever. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivaprasad, H.L. Fowl Typhoid and Pullorum Disease. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2000, 19, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langridge, G.C.; Fookes, M.; Connor, T.R.; Feltwell, T.; Feasey, N.; Parsons, B.N.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Barquist, L.; Stedman, A.; Humphrey, T.; et al. Patterns of Genome Evolution That Have Accompanied Host Adaptation in Salmonella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, S.; Octavia, S.; Feng, L.; Liu, B.; Reeves, P.R.; Lan, R.; Wang, L. Genomic Diversity and Adaptation of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium from Analysis of Six Genomes of Different Phage Types. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felten, A.; Vila Nova, M.; Durimel, K.; Guillier, L.; Mistou, M.-Y.; Radomski, N. First Gene-Ontology Enrichment Analysis Based on Bacterial Coregenome Variants: Insights into Adaptations of Salmonella Serovars to Mammalian- and Avian-Hosts. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilyas, B.; Tsai, C.N.; Coombes, B.K. Evolution of Salmonella-Host Cell Interactions through a Dynamic Bacterial Genome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelludat, C.; Mirold, S.; Hardt, W.-D. The SopEPhi Phage Integrates into the SsrA Gene of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium A36 and Is Closely Related to the Fels-2 Prophage. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5182–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; McCormick, B.A. Mucosal Inflammatory Response to Salmonella Typhimurium Infection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondel, C.J.; Jiménez, J.C.; Contreras, I.; Santiviago, C.A. Comparative Genomic Analysis Uncovers 3 Novel Loci Encoding Type Six Secretion Systems Differentially Distributed in Salmonella Serotypes. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sana, T.G.; Flaugnatti, N.; Lugo, K.A.; Lam, L.H.; Jacobson, A.; Baylot, V.; Durand, E.; Journet, L.; Cascales, E.; Monack, D.M. Salmonella Typhimurium Utilizes a T6SS-Mediated Antibacterial Weapon to Establish in the Host Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5044-51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sana, T.G.; Lugo, K.A.; Monack, D.M. T6SS: The Bacterial “Fight Club” in the Host Gut. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, S.E.; Thiennimitr, P.; Winter, M.G.; Butler, B.P.; Huseby, D.L.; Crawford, R.W.; Russell, J.M.; Bevins, C.L.; Adams, L.G.; Tsolis, R.M.; et al. Gut Inflammation Provides a Respiratory Electron Acceptor for Salmonella. Nature 2010, 467, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzman, N.H.; Chou, M.M.; de Jong, H.; Liu, L.; Porter, E.M.; Paterson, Y. Enteric Salmonella Infection Inhibits Paneth Cell Antimicrobial Peptide Expression. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunn, J.S.; Miller, S.I. PhoP-PhoQ Activates Transcription of PmrAB, Encoding a Two-Component Regulatory System Involved in Salmonella Typhimurium Antimicrobial Peptide Resistance. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6857–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vimal, D.B.; Khullar, M.; Gupta, S.; Ganguly, N.K. Intestinal Mucins: The Binding Sites for Salmonella Typhimurium. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2000, 204, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Zhang, P.; Piao, R.; Wang, Y. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI-1) and Its Complex Regulatory Network. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dorsey, C.W.; Laarakker, M.C.; Humphries, A.D.; Weening, E.H.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium MisL Is an Intestinal Colonization Factor That Binds Fibronectin. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, R.G.; Jäckel, D.; Geymeier, N.; Hensel, M. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 4-Mediated Adhesion Is Coregulated with Invasion Genes in Salmonella enterica. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4697–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galyov, E.E.; Wood, M.W.; Rosqvist, R.; Mullan, P.B.; Watson, P.R.; Hedges, S.; Wallis, T.S. A Secreted Effector Protein of Salmonella Dublin Is Translocated into Eukaryotic Cells and Mediates Inflammation and Fluid Secretion in Infected Ileal Mucosa. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 25, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Tejero, M.; Galán, J.E. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Pathogenicity Island 1-Encoded Type III Secretion System Translocases Mediate Intimate Attachment to Nonphagocytic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubori, T.; Matsushima, Y.; Nakamura, D.; Uralil, J.; Lara-Tejero, M.; Sukhan, A.; Galán, J.E.; Aizawa, S.I. Supramolecular Structure of the Salmonella Typhimurium Type III Protein Secretion System. Science 1998, 280, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubori, T.; Sukhan, A.; Aizawa, S.I.; Galán, J.E. Molecular Characterization and Assembly of the Needle Complex of the Salmonella Typhimurium Type III Protein Secretion System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10225–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGhie, E.J.; Brawn, L.C.; Hume, P.J.; Humphreys, D.; Koronakis, V. Salmonella Takes Control: Effector-Driven Manipulation of the Host. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tafazoli, F.; Magnusson, K.-E.; Zheng, L. Disruption of Epithelial Barrier Integrity by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Requires Geranylgeranylated Proteins. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphreys, D.; Hume, P.J.; Koronakis, V. The Salmonella Effector SptP Dephosphorylates Host AAA+ ATPase VCP to Promote Development of Its Intracellular Replicative Niche. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haraga, A.; Ohlson, M.B.; Miller, S.I. Salmonellae Interplay with Host Cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knodler, L.A.; Celli, J.; Hardt, W.-D.; Vallance, B.A.; Yip, C.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella Effectors within a Single Pathogenicity Island Are Differentially Expressed and Translocated by Separate Type III Secretion Systems. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.I.; Kukral, A.M.; Mekalanos, J.J. A Two-Component Regulatory System (PhoP PhoQ) Controls Salmonella Typhimurium Virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5054–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slauch, J.M.; Lee, A.A.; Mahan, M.J.; Mekalanos, J.J. Molecular Characterization of the OafA Locus Responsible for Acetylation of Salmonella Typhimurium O-Antigen: OafA Is a Member of a Family of Integral Membrane Trans-Acylases. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5904–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen-Wester, I.; Hensel, M. Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands Encoding Type III Secretion Systems. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Bossi, N.; Bossi, L. Inducible Prophages Contribute to Salmonella Virulence in Mice. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, B.K.; Wickham, M.E.; Brown, N.F.; Lemire, S.; Bossi, L.; Hsiao, W.W.L.; Brinkman, F.S.L.; Finlay, B.B. Genetic and Molecular Analysis of GogB, a Phage-Encoded Type III-Secreted Substrate in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium with Autonomous Expression from Its Associated Phage. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.G.; Holden, D.W. Dynamics of Growth and Dissemination of Salmonella in Vivo. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Adkins, J.N.; Coleman, J.R.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Dohnkova, A.; Mottaz, H.M.; Norbeck, A.D.; Purvine, S.O.; Manes, N.P.; Smallwood, H.S.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Isolated from RAW 264.7 Macrophages: Identification of a Novel Protein That Contributes to the Replication of Serovar Typhimurium inside Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29131–29140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haneda, T.; Ishii, Y.; Danbara, H.; Okada, N. Genome-Wide Identification of Novel Genomic Islands That Contribute to Salmonella Virulence in Mouse Systemic Infection. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 297, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogomolnaya, L.M.; Santiviago, C.A.; Yang, H.-J.; Baumler, A.J.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.L. “Form Variation” of the O12 Antigen Is Critical for Persistence of Salmonella Typhimurium in the Murine Intestine. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, P.H. The Bacteriological Classification of the Principal Cultures Used in Rat and Mouse Control in Great Britain. J. Hyg. 1942, 42, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, M.W. Calf Paratyphoid I. In A General Discussion of the Disease in Relation to Animals and Man; The Government Printer: Pretoria, South Africa, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Kokko, U.P. A gastroenteritis epidemic caused by S. enteritidis var. danysz (Rating). Nord. Med. 1947, 36, 2325. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedman, C.R.; Malcolm, G.; Rigau-Pérez, J.G.; Arámbulo, P.; Tauxe, R. v Public Health Risk from Salmonella-Based Rodenticides. Lancet 1996, 347, 1705–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, J.A.; Mølbak, K.; Sonne-Hansen, J.; Barrett, T.; Wells, J.G.; Tauxe, R. v Salmonella-Based Rodenticides and Public Health. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlfall, E.J.; Ridley, A.M.; Ward, L.R.; Rowe, B. Assessment of Health Risk from Salmonella-Based Rodenticides. Lancet 1996, 348, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenda, R.; Ugorski, M.; Grzymajlo, K. Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Salmonella Type 1 Fimbriae, but Were Afraid to Ask. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Han, X.; de Masi, L.; Zhu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Schmieder, R.; Kaushik, R.S.; Fraser, G.P.; et al. Allelic Variation Contributes to Bacterial Host Specificity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzymajlo, K.; Ugorski, M.; Suchanski, J.; Kedzierska, A.E.; Kolenda, R.; Jarzab, A.; Biernatowska, A.; Schierack, P. The Novel Type 1 Fimbriae FimH Receptor Calreticulin Plays a Role in Salmonella Host Specificity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolenda, R.; Burdukiewicz, M.; Schiebel, J.; Rödiger, S.; Sauer, L.; Szabo, I.; Orłowska, A.; Weinreich, J.; Nitschke, J.; Böhm, A.; et al. Adhesion of Salmonella to Pancreatic Secretory Granule Membrane Major Glycoprotein GP2 of Human and Porcine Origin Depends on FimH Sequence Variation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, J.S.; Wang, L.; Rabino, A.F.; Everitt, J.; Alvarez, M.I.; Awadia, S.; Wittchen, E.S.; Garcia-Mata, R.; Ko, D.C. ARHGEF26 Enhances Salmonella Invasion and Inflammation in Cells and Mice. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keestra, A.M.; de Zoete, M.R.; van Aubel, R.A.M.H.; van Putten, J.P.M. Functional Characterization of Chicken TLR5 Reveals Species-Specific Recognition of Flagellin. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Dehinwal, R.; Rakov, A.V.; Grams, N.; Clemens, E.C.; Hofmann, J.; Okeke, I.N.; Schifferli, D.M. The Not so Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Differential Bacterial Adhesion and Invasion Mediated by Salmonella PagN Allelic Variants. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallis, T.S.; Galyov, E.E. Molecular Basis of Salmonella-Induced Enteritis. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velge, P.; Wiedemann, A.; Rosselin, M.; Abed, N.; Boumart, Z.; Chaussé, A.M.; Grépinet, O.; Namdari, F.; Roche, S.M.; Rossignol, A.; et al. Multiplicity of Salmonella Entry Mechanisms, a New Paradigm for Salmonella Pathogenesis. Microbiologyopen 2012, 1, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosselin, M.; Virlogeux-Payant, I.; Roy, C.; Bottreau, E.; Sizaret, P.-Y.; Mijouin, L.; Germon, P.; Caron, E.; Velge, P.; Wiedemann, A. Rck of Salmonella enterica, Subspecies Enterica Serovar Enteritidis, Mediates Zipper-like Internalization. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, M.A.; Smith, S.G.J. The PagN Protein of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Is an Adhesin and Invasin. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosselin, M.; Abed, N.; Virlogeux-Payant, I.; Bottreau, E.; Sizaret, P.-Y.; Velge, P.; Wiedemann, A. Heterogeneity of Type III Secretion System (T3SS)-1-Independent Entry Mechanisms Used by Salmonella Enteritidis to Invade Different Cell Types. Microbiology 2011, 157, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleh, S.; van Puyvelde, S.; Staes, A.; Timmerman, E.; Barbé, B.; Jacobs, J.; Gevaert, K.; Deborggraeve, S. Salmonella Typhi, Paratyphi A, Enteritidis and Typhimurium Core Proteomes Reveal Differentially Expressed Proteins Linked to the Cell Surface and Pathogenicity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, S.M.; González, P.A.; Carreño, L.J.; Tobar, J.A.; Mora, G.C.; Pereda, C.J.; Salazar-Onfray, F.; Kalergis, A.M. The Capacity of Salmonella to Survive inside Dendritic Cells and Prevent Antigen Presentation to T Cells Is Host Specific. Immunology 2008, 124, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Maloy, S.; McGuire, K.L. Macrophages Influence Salmonella Host-Specificity in Vivo. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 47, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Fresno, A.H.; Skov, S.; Olsen, J.E. Dynamics and Outcome of Macrophage Interaction Between Salmonella Gallinarum, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Salmonella Dublin and Macrophages From Chicken and Cattle. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Ni, J.; Guo, J.; Yao, Y.-F.; Wu, W. Whole-Genome Comparative and Pathogenicity Analysis of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Rissen. G3 2020, 10, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasmans, F.; van Immerseel, F.; Heyndrickx, M.; Martel, A.; Godard, C.; Wildemauwe, C.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F. Host Adaptation of Pigeon Isolates of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Variant Copenhagen Phage Type 99 Is Associated with Enhanced Macrophage Cytotoxicity. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6068–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, E.; Azriel, S.; Auster, O.; Gal, A.; Zitronblat, C.; Mikhlin, S.; Scharte, F.; Hensel, M.; Rahav, G.; Gal-Mor, O. Pathoadaptation of the Passerine-Associated Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Lineage to the Avian Host. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Askar, B.; Hulme, S.; Neilson, P.; Barrow, P.; Foster, N. Differential Immune Phenotypes in Human Monocytes Induced by Non-Host-Adapted Salmonella enterica Serovar Choleraesuis and Host-Adapted S. Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00509-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Retamal, P.; Castillo-Ruiz, M.; Villagra, N.A.; Morgado, J.; Mora, G.C. Modified Intracellular-Associated Phenotypes in a Recombinant Salmonella Typhi Expressing S. Typhimurium SPI-3 Sequences. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, J.R.; Chiok, K.L.; Paul, N.C.; Haldorson, G.; Guard, J.; Shah, D.H. The Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 13 Contributes to Pathogenesis in Streptomycin Pre-Treated Mice but Not in Day-Old Chickens. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, D.H.; Lee, M.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Eo, S.-K.; Kwon, J.-T.; Chae, J.-S. Identification of Salmonella Gallinarum Virulence Genes in a Chicken Infection Model Using PCR-Based Signature-Tagged Mutagenesis. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3957–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinoza, R.A.; Silva-Valenzuela, C.A.; Amaya, F.A.; Urrutia, Í.M.; Contreras, I.; Santiviago, C.A. Differential Roles for Pathogenicity Islands SPI-13 and SPI-8 in the Interaction of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhi with Murine and Human Macrophages. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzzau, S.; Leori, G.S.; Petruzzi, V.; Watson, P.R.; Schianchi, G.; Bacciu, D.; Mazzarello, V.; Wallis, T.S.; Rubino, S. Salmonella enterica Serovar-Host Specificity Does Not Correlate with the Magnitude of Intestinal Invasion in Sheep. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3092–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.A.; Wigley, P.; Page, K.L.; Hulme, S.D.; Barrow, P.A. Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Requires the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 2 Type III Secretion System but Not the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System for Virulence in Chickens. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5471–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieye, Y.; Ameiss, K.; Mellata, M.; Curtiss, R. The Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI) 1 Contributes More than SPI2 to the Colonization of the Chicken by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Yang, Y.-A.; Milano, S.K.; Nguyen, T.; Ahn, C.; Sim, J.H.; Thompson, A.J.; Hillpot, E.C.; Yoo, G.; Paulson, J.C.; et al. Salmonella Typhoid Toxin PltB Subunit and Its Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Ortholog Confer Differential Host Adaptation and Virulence. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 937–949.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, K.M.; Ali, M.M.; Radwan, M.I.; Kim, H.K.; Han, J. Comparative Proteomic Analysis on Salmonella Gallinarum and Salmonella Enteritidis Exploring Proteins That May Incorporate Host Adaptation in Poultry. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, S.; Galán, J.E. A Rab32-Dependent Pathway Contributes to Salmonella Typhi Host Restriction. Science 2012, 338, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohler, A.C.; Spanò, S.; Galán, J.E.; Stebbins, C.E. Structural and Enzymatic Characterization of a Host-Specificity Determinant from Salmonella. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2014, 70, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urrutia, I.M.; Fuentes, J.A.; Valenzuela, L.M.; Ortega, A.P.; Hidalgo, A.A.; Mora, G.C. Salmonella Typhi ShdA: Pseudogene or Allelic Variant? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 26, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chien, K.-Y.; Chen, H.-L.; Chiu, C.-H. Pseudogene Recoding Revealed from Proteomic Analysis of Salmonella Serovars. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Rankin, S.C.; Blanchet, R.T.; Nulton, J.D.; Edwards, R.A.; Schifferli, D.M. Diversification of the Salmonella Fimbriae: A Model of Macro- and Microevolution. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswarappa, S.M.; Janice, J.; Balasundaram, S.V.; Dixit, N.M.; Chakravortty, D. Host-Specificity of Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum: Insights from Comparative Genomics. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswarappa, S.M.; Janice, J.; Nagarajan, A.G.; Balasundaram, S.V.; Karnam, G.; Dixit, N.M.; Chakravortty, D. Differentially Evolved Genes of Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands: Insights into the Mechanism of Host Specificity in Salmonella. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, S.D.; Shashidhar, R.; Karani, M.; Bandekar, J.R. Distribution of Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI)-8 and SPI-10 among Different Serotypes of Salmonella. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, M.R.; Jansen, V.A.A.; Woodward, M.J. Comparative Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovars Derby and Mbandaka, Two Prevalent Serovars Associated with Different Livestock Species in the UK. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Lundstrøm, I.; Tran-Dien, A.; Duchêne, S.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Langridge, G.; Fotakis, A.K.; Nair, S.; Stenøien, H.K.; et al. Pan-Genome Analysis of Ancient and Modern Salmonella Enterica Demonstrates Genomic Stability of the Invasive Para C Lineage for Millennia. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2420–2428.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charles, R.C.; Harris, J.B.; Chase, M.R.; Lebrun, L.M.; Sheikh, A.; LaRocque, R.C.; Logvinenko, T.; Rollins, S.M.; Tarique, A.; Hohmann, E.L.; et al. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the PhoP Regulon in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi versus Typhimurium. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Li, Q.; Olsen, J.E.; Jiao, X. A Bioinformatic Approach to Identify Core Genome Difference between Salmonella Pullorum and Salmonella Enteritidis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiang, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Jiao, X. Loss and Gain in the Evolution of the Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Biovar Pullorum Genome. mSphere 2019, 4, e00627-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Sanguiné, A.Y.; D’Alessandro, B.; Langleib, M.; Traglia, G.M.; Mónaco, A.; Durán, R.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Betancor, L.; Yim, L. Salmonella enterica Serovars Dublin and Enteritidis Comparative Proteomics Reveals Differential Expression of Proteins Involved in Stress Resistance, Virulence, and Anaerobic Metabolism. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00606-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encheva, V.; Wait, R.; Begum, S.; Gharbia, S.E.; Shah, H.N. Protein Expression Diversity amongst Serovars of Salmonella enterica. Microbiology 2007, 153, 4183–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kingsley, R.A.; Kay, S.; Connor, T.; Barquist, L.; Sait, L.; Holt, K.E.; Sivaraman, K.; Wileman, T.; Goulding, D.; Clare, S.; et al. Genome and Transcriptome Adaptation Accompanying Emergence of the Definitive Type 2 Host-Restricted Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Pathovar. mBio 2013, 4, e00565-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, A.P.; Gibson, D.L.; Kim, W.; Kay, W.W.; Surette, M.G. Thin Aggregative Fimbriae and Cellulose Enhance Long-Term Survival and Persistence of Salmonella. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Römling, U.; Sierralta, W.D.; Eriksson, K.; Normark, S. Multicellular and Aggregative Behaviour of Salmonella Typhimurium Strains Is Controlled by Mutations in the AgfD Promoter. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, K.D.; Wang, Y.; Musicha, P.; Hansen, E.G.; Palmer, M.B.; Herman, D.J.; Feasey, N.A.; White, A.P. Parallel Evolution Leading to Impaired Biofilm Formation in Invasive Salmonella Strains. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Affected Hosts | Non-Susceptible Rodents |
|---|---|
| House mouse (Mus musculus), mound-building mouse (Mus spicilegus); harvest mouse (Micromys minutus), common vole (Microtus arvalis), Brandt’s vole (Microtus brandti), Major’s pine vole (Microtus majori), field vole (Microtus agrestis), narrow-headed vole (Microtus gregalis), steppe lemming (Lagurus lagurus), bank vole (Myodes glareolus), European water vole (Arvicola terrestris), gray hamster (Cricetutus migratorius), mole vole (Ellobius talpinus), social vole (Microtus socialis) | Field mouse (Apodemus agrarius); wood mouse (Apodemus silvaticus), yellow-necked mouse (Apodemus flavicollis), hamsters (Cricetus raddei and C. auratus), forest dormouse (Dryomys nitedula) |
| Salmonella enterica Serovars | Affected Group of Animals | Comments | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Choleraesuis | pigs | host-adapted, asymptomatically exist in other animals | [56] |
| Dublin | cattle | host-adapted, asymptomatically exist in other animals | [57,58] |
| Typhi | humans and higher primates | host-restricted | [59] |
| Gallinarum | poultry | host-restricted | [60,61] |
| Abortusovis | ovine | host-restricted | [42] |
| Typhisuis | pigs | host-restricted | [43] |
| Abortusequi | equine | host-restricted | [43] |
| Typhimurium | humans, poultry, cattle, pigs, mice | non-host-adapted | [55,62] |
| S. Typhimurium phage type DT2 | pigeons | host-restricted | [55] |
| Enteritidis | humans, poultry, cattle, pigs, mice | non-host-adapted | [42] |
| Pullorum | avian | host-restricted | [63] |
| Hessarek | avian | host-restricted | [54] |
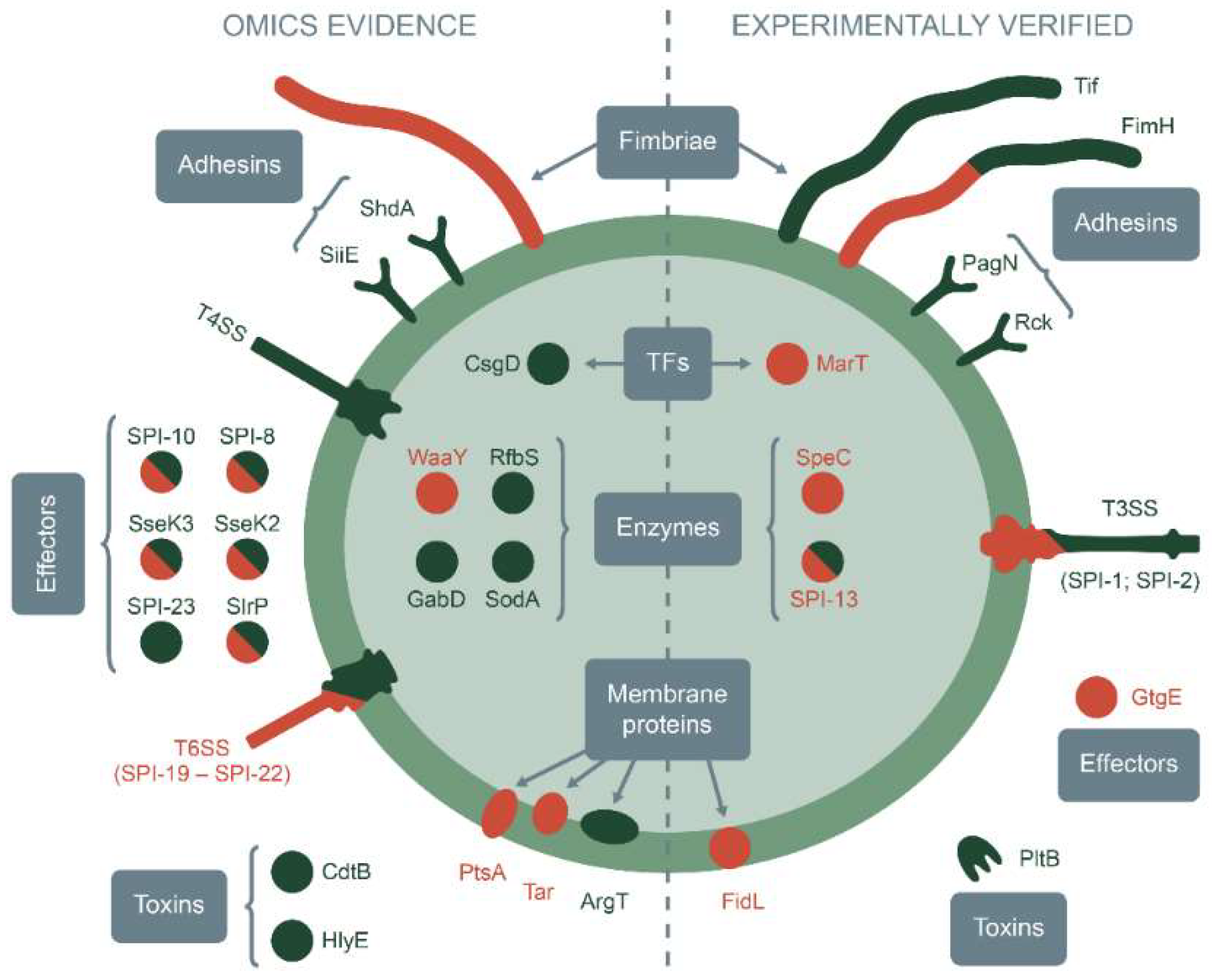
| Gene/Locus | Product | Type | Impact * | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimentally-validated specificity factors | ||||
| fimH | FimH adhesin forming type 1 fimbriae | Fimbral proteins | +/− | [101,102,103] |
| tcf operon | S. Typhi colonization factor | Fimbral proteins | + | [117] |
| pagN | PagN invasin | Adhesins | + | [107] |
| rck | Rck invasin | Adhesins | + | [109,112] |
| SPI-1; SPI-2 | Type III protein secretion system | Secretion systems | +/− | [108,109,110,111,125,126,127] |
| marT | Putative transcriptional regulator MarT | Transcription factors | − | [121] |
| fidL | Predicted inner membrane protein FidL | Membrane proteins | − | [121] |
| SPI-13 | Putative aromatic monoamines-catabolism enzumes | Enzymes | +/− | [121,122,123,124] |
| speC | Ornithine decarboxylase | Enzymes | − | [129] |
| pltB | Typhoid toxin binding subunit PltB | Toxins | + | [128] |
| gtgE | Secreted cysteine protease GtgE | Effectors | − | [130,131] |
| Predicted by omics studies specificity determinants | ||||
| Gene clusters of fimbrial components (sba, sbb, sbc, sdc, sdd, sde, sdf, sdg, sdh, sdi, sdj, sdk, sdl, peh) | Fimbriae | Fimbral proteins | − | [134] |
| siiE | Non-fimbrial giant adhesin SiiE | Adhesins | + | [44] |
| shdA | Fibronectin-binding adhesin shdA | Adhesins | + | [44,138] |
| T4SS-encoding loci | Type IV secretion system | Secretion systems | + | [141] |
| SPI19–SPI-22 | Type VI secretion system | Secretion systems | +/− | [50,67,141] |
| csgD | Major biofilm transcriptional regulator CsgD | Transcription factors | + | [138,147] |
| argT | Lysine arginine ornithine (LAO)-binding amino acid transporter ArgT | Membrane proteins | + | [144] |
| tar | Aspartate receptor for chemotaxis Tar | Membrane proteins | − | [145] |
| ptsA | Carbohydrate phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent transporter | Membrane proteins | − | [53] |
| waaY | LPS-inner core-forming HepII-kinase | Enzymes | − | [53] |
| rfbS | Paratose synthase RfbS | Enzymes | + | [129] |
| sodA | Superoxide dismutase SodA | Enzymes | + | [144] |
| gabD | Succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase GabD | Enzymes | + | [144] |
| cdtB | Cytolethal distending toxin subunit B | Toxins | + | [140] |
| hlyE | Pore-forming toxin hemolysin E | Toxins | + | [140] |
| SPI-8 | Putative secreted effector | Effectors | +/− | [137] |
| SPI-10 | Putative secreted effector | Effectors | +/− | [137] |
| SPI-23 | Putative secreted effector | Effectors | + | [138] |
| sseK2 | Translocated effector protein K2 | Effectors | +/− | [48] |
| sseK3 | Translocated effector protein K3 | Effectors | +/− | [48] |
| slrP | Secreted E3 ubiquitin ligase SlrP | Effectors | +/− | [48] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shikov, A.E.; Belousova, M.E.; Belousov, M.V.; Nizhnikov, A.A.; Antonets, K.S. Salmonella-Based Biorodenticides: Past Applications and Current Contradictions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314595
Shikov AE, Belousova ME, Belousov MV, Nizhnikov AA, Antonets KS. Salmonella-Based Biorodenticides: Past Applications and Current Contradictions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314595
Chicago/Turabian StyleShikov, Anton E., Maria E. Belousova, Mikhail V. Belousov, Anton A. Nizhnikov, and Kirill S. Antonets. 2022. "Salmonella-Based Biorodenticides: Past Applications and Current Contradictions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314595
APA StyleShikov, A. E., Belousova, M. E., Belousov, M. V., Nizhnikov, A. A., & Antonets, K. S. (2022). Salmonella-Based Biorodenticides: Past Applications and Current Contradictions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314595









