Abstract
This study aims to evaluate the clinical outcome of stereotactic radiosurgery as the sole treatment for brain metastases and to assess prognostic factors influencing survival. A total of 108 consecutive patients with 213 metastases were retrospectively analyzed. Treatment was determined with close-meshed MRI follow-up. Various prognostic factors were assessed, and several prognostic indices were compared regarding their reliability to estimate overall survival. Median overall survival was 15 months; one-year overall survival was 50.5%. Both one- and two-year local controls were 90.9%. The rate of new metastases after SRS was 49.1%. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors revealed that the presence of extracranial metastases, male sex, lower KPI, and progressive extracranial disease were significant risk factors for decreased survival. Of all evaluated prognostic indices, the Basic Score for Brain Metastases (BSBMs) showed the best correlation with overall survival. A substantial survival advantage was found for female patients after SRS when compared to male patients (18 versus 9 months, p = 0.003). SRS of brain metastasis is a safe and effective treatment option when frequent monitoring for new metastases with MRI is performed. Common prognostic scores lack reliable estimation of survival times. Female sex should be considered as an additional independent positive prognostic factor influencing survival.
1. Introduction
Brain metastases (BMs) are the most frequent malignant intracranial lesions in adults, accounting for up to 40% of all intracranial tumors. Improvements in cancer therapy increasingly prolong patient survival and lead to an increased rate of BM [1,2]. While newer targeted therapies have become a viable treatment option for selected patients in recent years, surgical resection and radiotherapy represent the cornerstones of modern treatment [3]. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) can provide high local control (LC) rates by delivering a large and highly conformal single radiation dose while sparing surrounding brain tissue. SRS has a favorable impact on neurocognition and quality of life in comparison to whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT). Therefore, SRS is the standard therapy option for single or limited-in-number, non-resectable BM [4]. Recent data increasingly show that survival after SRS as an initial treatment for up to 10 brain metastases is non-inferior compared to 2–4 BMs [5,6,7]. However, SRS also entails a significant risk of radiation necrosis (RN), previously reported to occur in 8–24% of treated metastases [8,9], which can be lowered by technical advances [10]. The diagnosis of RN, and especially the distinction from real tumor progression, is challenging but critical to evaluate therapy options [11,12]. While SRS alone delivers impressive LC rates, intracranial control and the time to appearance of new metastases are significantly reduced when compared to WBRT. Frequent monitoring for new BM is therefore imperative, in addition to conducting more studies, for the determination of dose tolerance parameters across a broad spectrum of patients.
In the present study, we report our experience with LINAC-based SRS in routinely treating BM, thereby dedicating special attention to the validation of relevant prognostic indices and independent factors.
2. Materials and Methods
Between August 2003 and March 2018, 108 consecutive patients underwent single fraction linear accelerator-based SRS without adjuvant WBRT as initial therapy for intracranial metastases. Patients were chosen for SRS treatment in case of synchronous or metachronous, singular or multiple brain metastases (up to 5 lesions), with a KPI of at least 6. Patients with large or symptomatic metastases were assigned to surgical resection unless unsuitable for surgery.
All retrospectively analyzed patients received conformal SRS applying five to seven non-coplanar arcs with cone collimators. Head immobilization was performed either by using rigid stereotactic fixation, or non-invasively by multi-layered thermoplastic masks. Target volumes were determined by using planning CT scans together with fused contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scans. GTV was expanded by a margin of 1 mm for frameless SRS, and no expansion was used for frame-based SRS. The median prescribed dose to the 80% isodose was 20 Gy and ranged from 15 to 22 Gy, depending on metastasis volume, location, proximity to vital structures, history of WBRT or previous SRS, and tumor histology. Patient position was corrected and verified by means of cone-beam CT verification prior to treatment. Position accuracy was corrected to <1 mm xyz translation and <1° rotation.
Follow-up by contrast-enhanced MRI scans and clinical examination was performed every 3 months until death, or at any time if clinically indicated. Two neuroradiologists independently diagnosed local recurrence, pseudo-progression, and RN. Local progression was defined as increased radiologic volume not explainable by RN or pseudo-progression. In the case of indicated surgical resection, histologic analysis was used to distinguish local recurrence from RN. PTV size as a risk factor for local recurrence was evaluated. Toxicity was assessed according to the RTOG common toxicity criteria.
Evaluation of 4 of the 108 consecutively SRS-treated BM patients was incomplete because of unavailable imaging within the 6 months before death.
Overall survival (OS) was defined as the elapsed time from the first SRS treatment until death. All patients alive at the end of the study (N = 24, 22.6%) were censored on the day of the last follow-up. Distant intracranial control was defined as the elapsed time until the appearance of new intracranial metastases.
Several known prognostic factors for survival, including KPS, age, status of systemic disease, primary tumor control, presence of extracranial metastases, number of intracranial metastases, volume of the treated metastases, and time from primary tumor diagnosis to CNS treatment, were assessed according to RPA [13], GPA [14], SIR [15], BSBM [16], and Rades et al [17]. All listed PIs were calculated and ranked regarding their prognostic reliability in our patient cohort. In addition, sex, prescribed dose, histology of primary tumors as well as diagnosis-specific molecular parameters and mutations (lung: EGFR, ALK; melanoma: BRAF; breast: ER/PR receptor status, HER2) were investigated regarding their potential as independent prognostic factors.
IBM SPSS Statistics 24 (IBM Cooperation, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analysis. OS, intracranial control, and local control were determined by Kaplan–Meier analysis; log-rank test was used to evaluate prognostic factors. The Cox proportional hazard model was applied for uni- and multivariate analyses of prognostic factors. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROCs) were used to compare the reliability of PIs. A binominal logistic regression model (with ascertained linearity of continuous variables by the Box–Tidwell procedure) was used to assess whether prognostic factors might differ between sexes. This model was chosen to ensure that an unequal distribution of prognostic factor values between sex groups did not bias our analysis.
3. Results
A total of 108 patients (213 metastases) were analyzed. The patient characteristics are presented in Table 1. The median follow-up was 11 months (range: 0–99 months). The median tumor volume was 0.53 ccm and ranged from 0.04 to 13.29 ccm.

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
3.1. Outcomes
The outcome data are shown in Figure 1. The median OS after SRS was 15 months. The overall rate of patients surviving 1 and 2 years was 50.5% and 32.5%, respectively. A total of 8.1% of the investigated patients survived more than 5 years after SRS. A substantial difference in OS was observed depending on the type of primary tumor, which was statistically significant (p < 0.001). Of all BM histologies, breast cancer (N = 11) had the best prognosis, with a median OS of 24 months. The median OS was 17 months for NSCLC adenocarcinoma (N = 40), 6 months for NSCLC squamous cell carcinoma (N = 9), 11 months for RCC (N = 9), and 9 months for melanoma (N = 20).
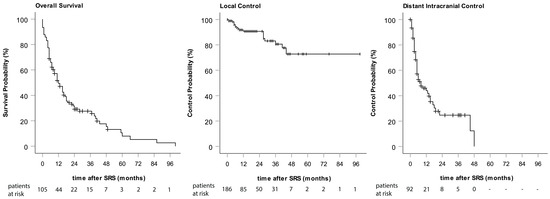
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival, local control, and distant intracranial control.
An overall LC of 89.8% was achieved by SRS of BMs. In total, only 19 metastases recurred locally. One- and two-year LC rates were 90.7% (Figure 1). A PTV size of larger than 1 ccm correlated with a higher risk for local recurrence (Pearson Chi-Square X2(1) = 6.565 p = 0.01). However, PTV size had no influence on OS. Metastases were surgically removed after SRS in the cases of six suspected local recurrences: two of these turned out to represent RN, whereas four were confirmed to be local recurrences.
A total of 49.1% of our patients developed new BMs after SRS. Of these, 39.6% received WBRT (21.5% of the total). The median time from the first SRS to the appearance of new metastases was 9 months. The one- and two-year distant intracranial control rates were 47.4% and 28.3%, respectively (Figure 1).
Of all treated metastases, 37 (19.4%) showed evidence of either RN or pseudo-progression. Medium time to RN was 7 months, and the latest onset of RN was 41 months after SRS. Diagnosis of RN had no significant impact on OS. A PTV of >1 ccm was significantly correlated with the occurrence of RN (p = 0.021).
3.2. Prognostic Factor Evaluation
Univariate analysis of prognostic factors showed that the presence of extracranial metastases, male sex, a lower KPI, and progressive systemic disease status were significant risk factors for impaired survival. Of these factors, only male sex, lower KPI, and progressive systemic disease were also significant in poor OS prognosis when analyzed by multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression (Table 2). Diagnosis-specific molecular markers (EGFR, ALK, BRAF, HER2, and ER/PR) showed no significant impact on the outcome of SRS.

Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate analyses of prognostic factors influencing survival after SRS.
3.3. Evaluation of Prognostic Indices
OS data related to BSBM, GPA, RPA, SIR, and the scoring of Rades et al. are shown in Table 3 and Figure 2. With the exception of SIR, all prognostic indices were significantly associated with survival when applied to our cohort of patients.

Table 3.
Kaplan–Meier analysis of overall survival for different prognostic indices.
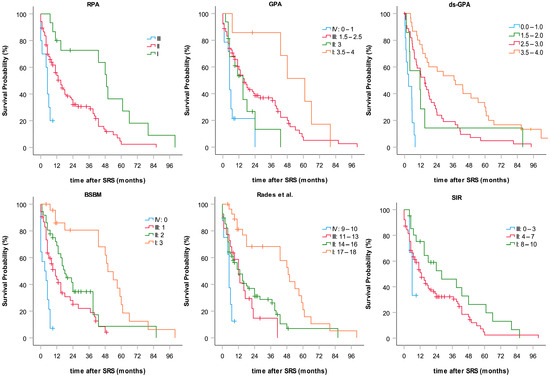
Figure 2.
Subgroup-categorized Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival calculated for six common prognostic indices.
Using Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis to evaluate the accuracy of one-year OS prediction, the best reliability was found for BSBM (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.75, p < 0.001), followed by the diagnosis-specific GPA (AUC = 0.71, p = 0.001), the original GPA (AUC = 0.64, p = 0.022), the score of Rades et al. (AUC = 0.62, p = 0.037), and RPA (AUC = 0.56, p = 0.28). SIR was determined as the least discriminative (AUC = 0.55, p = 0.40) (Figure 3).
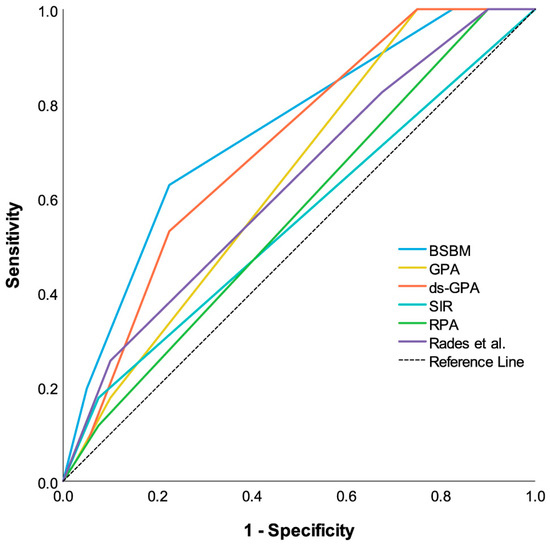
Figure 3.
Comparative receiver operating characteristic curves (ROCCs) for each prognostic index estimating one-year survival probability after SRS. Predictive power of each PI is indicated by area under the curve of ROCC. Larger area under the curve indicates greater prognostic potential.
3.4. Sex and OS
Regarding their OS, female patients exhibited a markedly increased survival compared to males (median OS: 18 versus 9 months). The sex-related difference in OS was significant (log-rank X2(1) = 7.878, p = 0.005). This finding is still valid after the exclusion of patients affected by mainly sex-specific breast-cancer-derived BMs from comparative statistical analysis (log-rank X2(1) = 5.728, p = 0.017). To ascertain sex as an independent prognostic factor, a binomial logistic regression model was used to analyze and rule out all other investigated prognostic factors, which might potentially differ between male and female patients. None of the investigated prognostic factors differed significantly between men and women, except for the number of BMs, i.e. female patients were affected by even more metastases than male patients (mean male = 1.4; mean female = 1.8; p = 0.01).
4. Discussion
Our reported OS data (median OS = 15 months; 1-year OS rate = 50.5%) are comparable to other studies investigating SRS as the sole treatment for BMs, which show a median OS of 8-15 months [8,18,19,20,21,22,23]. In our single-center study with 108 patients treated for 1–5 BMs, the overall LC was 89.7%, with both a 1- and 2-year LC rate of 90.9%. Lutterbach et al. [24] reported a 1-year LC of 91% after SRS alone in a cohort of 101 patients, who suffered from 1–3 BMs. Minniti et al. [9] demonstrated similar results in 1-year and 2-year LC rates (92% and 84%, with 206 patients). Applying SRS alone in 153 patients, Pirzkall et al. [25] found an LC rate of 89% and 72% after one and two years of follow-up, respectively. LC after two years in the SRS-only arm of the EORTC 22952-26001 study [8] was 69%. In an analogous work, Brown et al. [23] reported a 1-year LC of 72.8% for 111 patients. Concerning former reports, our OS and LC data are highly comparable to studies with the lowest local recurrence and longest OS rates.
While LC correlates with appropriate dose delivery [26], the risk of RN rises with elevated prescribed doses and greater target volumes [27,28,29]. Wiggenraad et al. [30] systematically reviewed that a dose delivery of less than 20 Gy severely impairs LC. Bohoudi et al. [28] proposed a method for isotoxic SRS planning based on V12Gy, a known predictor for RN. In the present study, a dose of 20 Gy to the tumor outline was pursued if permitted by size and location. As a result, an acceptable 19.4% of all treated metastases developed radiographic evidence for RN (grades 1–3). Our finding is congruent with comparable studies reporting on RN rates (grades 1–3), ranging from 12.1% up to 24% when applying similar dose concepts [9,10].
The debate is ongoing on whether it is advantageous to combine WBRT and SRS. Studies have shown that adding WBRT can improve local and distant intracranial control and delay the appearance of new metastases [31]. Aoyama et al. [21] found that 1-year freedom from new BMs improved from 41.5% to 63.7% by adding WBRT to SRS treatment.
However, this measure is accompanied by worse neurocognitive outcomes and diminished quality of life. Chang et al. [22] evaluated neurocognitive function using the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised (HVLT-R) in a group of 58 patients randomized to SRS or SRS+WBRT. SRS alone was found to provide a substantial neurocognitive benefit. Kocher et al. [8] reported that WBRT added to SRS has a detrimental effect on quality of life and does not improve the median duration of functional independence despite improving local and intracranial control. Brown et al. [23] reported a significant deterioration in immediate recall, delayed recall, and verbal fluency in a large randomized cohort of 213 patients with 1–3 BMs treated with WBRT. All these reports provide evidence that in patients with a limited number of metastases, the risks of adding WBRT to SRS outweigh the benefits. Adjuvant WBRT adds approximately 2 weeks of treatment time, offsetting one of the benefits of SRS in a palliative indication. In addition, WBRT might increase the risk of RN. Despite an increased intracranial control, randomized controlled trials did not show a survival benefit by combining SRS and WBRT [8,21].
Of all patients in our study treated with SRS alone, 39.6% later received WBRT for multiple new metastases. The high brain recurrence rate of 52.6% within 1 year demonstrates that while omitting or postponing WBRT has a favorable impact on cognition and quality of life, frequent monitoring for new metastases with MRI is crucial and, therefore, routinely performed at our clinics.
Our study further confirms that SRS as the single modality to treat solitary or multiple brain lesions is suitable and effective, delivering high local control rates, postponing neurotoxic WBRT, and avoiding invasive surgical intervention. However, in contemporary personalized treatment approaches, the value of histologic and molecular assessment becomes more and more relevant in multidisciplinary decision making. Tumor-specific markers, such as EGFR, BRAF, and HER2, enable targeted treatment options. Surgical resection should be considered alone or in combination with SRS, especially in symptomatic cases or in the case of larger lesions that have a high risk of radiation necrosis after SRS. In addition to achieving rapid symptom relief, in these circumstances, surgical resection also provides tissue for pathological diagnosis and individualized treatment choices. For instance, patients with EGFR mutations have been demonstrated to exhibit better prognoses with brain metastases. This finding has been considered in the updated diagnosis-specific Lung-molGPA score [32]. In our smaller cohort of mixed metastatic histologies specifically treated with SRS, EGFR status did not reveal a significant correlation with survival. However, reports from larger prospective studies have discussed the importance of integrating molecular markers in the prognosis assessment, which can also be presumed relevant in the case of SRS treatment planning [33,34].
Numerous prognostic factors have been proposed in order to improve the estimation of survival, including age, KPS, histology, the number and volume of lesions, the time to appearance of BMs, the status of systemic disease, and the presence of neurologic symptoms and extracranial metastases, as well as response to steroids. According to Kondziolka et al. [35], the prediction of OS in BM patients needs to be improved by considering these prognostic factors. In this study, a survey among physicians was conducted, asking them to estimate individual patient’s survival before SRS treatment based on these parameters. Thus, Kondziolka et al. [35] demonstrated that 49% of physician’s predictions deviated more than 6 months from actual survival, and 18% were off by more than 12 months. This result clearly indicates a continued strong need for more objectifiable assessment criteria to enable treating radiotherapists to communicate more reliable prognoses to their BM patients.
Our study revealed that the presence of extra-cerebral metastases, unfavorable histology, lower KPI, progressive systemic disease, and male sex were significantly associated with shorter survival upon univariate analysis. By multivariate analysis, only lower KPI, progressive systemic disease, and, again, male sex turned out to be significant factors impairing life expectance. No correlation between age and survival could be found, indicating that SRS is a safe and effective treatment option also for elderly patients. This is congruent with the results of Rades et al., who investigated treatment approaches for BMs in elderly patients and confirmed SRS to be a viable option for non-resectable BMs [36].
Two negative effects derive from erroneous prognosis assessment. Overestimating survival may lead to overtreatment by subjecting patients with actually poor prognosis to invasive, complicated, and cost-intensive measures. On the other hand, underestimating survival prognosis may lead to inadequate therapy in terms of best supportive care or WBRT only, thereby putting the patient at risk of premature death and long-term cognitive side effects, as well as limiting options for later salvage therapies. Thus, a variety of PIs have been developed in order to better estimate patient survival and to guide physicians in selecting the most suitable therapy for the individual patient.
Of all the compared indices in our study, the SIR score is the most complex PI considering the largest amount of prognostic factors, and as the only PI, it requires the additional assessment of the volume of the largest metastasis before treatment planning. In our study, however, SIR also turned out to be the only PI not significantly associated with survival. The score tends to unevenly distribute patients between prognostic subgroups, which has already been noticed in previous reports [14]. When applying the SIR score in our cohort, only three patients were attributed to the poor prognosis subgroup, whereas 102 were classified intermediately and 21 as having a good prognosis. In particular, the SIR cut-offs for the largest lesion size (I: 0–5 ccm, II: 5–13 ccm, and III: >13 ccm) may not be suitable to adequately sub-categorize average patients, which might potentially profit from SRS treatment. As evidence, only 1 of our patients exhibited the largest metastasis volume of more than 13 ccm, 16 patients of 5–13 ccm, and 90 of less than 5 ccm. This inherent weakness of the SIR score is likely to be the main cause for the missing correlation with OS evidenced in our study.
The comparatively simple BSBM score showed the strongest correlation with survival and the clearest distinction between prognostic groups. The score was created and validated on patients treated with SRS only. It requires just three parameters (KPS, control of primary tumor, and extracranial metastases) divided into two categories each, all of which can easily be assessed before treatment.
However, OS prediction based on any applied prognostic scoring did not deliver acceptable consistency with the OS monitored in our patient cohort. Even according to the most reliable BSBM score, originally published OS prediction for the classified patient sub-groups differs substantially from our data set. Lorenzoni et al. [16] reported median OS in the four prognostic groups of 1.9, 3.3, 13.1, and >32 months. The actual median OS observed in our study was 3, 10, 18, and 50 months for the corresponding groups. Superior survival might be explained by continuously improved cancer treatment regimens during the last decade. In addition, several indices (RPA, GPA, and that of Rades et al.) were validated for patients primarily treated with WBRT, thereby lacking representation of SRS patients only. In conclusion, more recent median survival data often substantially differ from the original PI studies. This finding indicates that improved OS data of state-of-the-art cancer treatment regimens should finally be considered when presenting OS estimations still performed based on PIs that have been partially established for decades.
Consistently, in our present study, even the most reliable score classification (BSBM) did not deliver superior OS predictions when compared to physicians just estimating their patient’s survival on the basis of their clinical experience, as reported by Kondziolka et al. [35]. Of the 2700 OS predictions, physicians were able to correctly estimate survival in 51% of cases within ± 6 months. As an analogy, when applying the best predicting BSBM score to our patient cohort, only 46% of OS predictions deviated less than 6 months from the median observed OS in each corresponding prognostic subgroup. Using the same score, a prognostic deviation of more than 12 months was found in 28% of our patients, as compared to the reported 18% physician’s predictive inaccuracy by Kondziolka et al.
However, score reliability might be enhanced by including more recently discovered independent prognostic factors, such as initial brain metastasis velocity (iBMV) [37], also defined by others as distant metastasis velocity (DMV) [38]. Furthermore, the inclusion of histology-specific biomarkers is reported to improve survival estimation. The diagnosis-specific GPA score adds EGFR, BRAF, hemoglobin, HER2, and breast cancer subtype as factors that enhance the scoring accuracy for the respective tumors. Indeed, in our analysis, the updated ds-GPA score markedly improved the correlation with survival in comparison with the original GPA. However, even at the cost of added complexity, it did not outperform the much simpler BSBM score. In addition, female sex has also been shown to be an advantageous prognostic factor in several tumor entities [39,40,41,42]. However, none of the common PIs includes sex as a prognostic factor, although correlations between OS and sex in SRS treatment of BMs have occasionally been reported in the literature [9]. While most scoring systems have been developed to estimate survival rates across all patients with BMs regardless of the treatment method, our study focuses specifically on patients who received SRS alone. Similarly, other research examining comparable patient groups has identified significant survival differences based on sex [5,9,43]. To assess whether sex acts as an independent factor in survival outcomes, we conducted a multivariate analysis that included various primary tumor types. This analysis confirmed that the survival benefit associated with the female sex exists independently of the primary tumor origin. This finding underscores the importance of considering sex in the context of treatment decisions, even as the pharmacogenetic and molecular mechanisms underlying the survival advantages observed in females continue to be explored. These observed differences are nevertheless crucial for clinicians making treatment decisions.
Our results significantly affirm a substantially prolonged OS of female patients versus male patients with a doubled median survival time, as recently reported [44]. This difference might be explained, only partially, by the fact that breast cancer predominantly occurs in women and exhibits a better prognosis when compared to other histologies. However, even when breast cancer patients are excluded from the analysis, females still exhibit a significant survival advantage (15 months versus 9 months in males) after SRS of BMs. In fact, by excluding sex-specific tumor histologies from the analysis, no significant inhomogeneity of known outcome-influencing parameters could be detected, which could explain the female survival advantage over male patients, except for the number of brain metastases. Unexpectedly, however, female patients in our cohort presented an even higher average number of BMs, which is actually considered, by itself, a negative predictor of survival. This finding clearly indicates a yet unknown mechanism directly related to the female sex, which effectively enhances OS after SRS of brain metastasis.
After further validating and confirming our results in larger studies, sex, and eventually other independent parameters, should finally be included in revised prognostic indices for the treatment of BMs with SRS to enhance the reliability of prognostic scoring.
5. Conclusions
SRS of brain metastases of different histological origins is confirmed to represent a safe and effective treatment option, with advantages regarding quality of life and local control, when frequent monitoring of new metastases with MRI is performed. At best, prognostic indices in use are helpful tools to roughly estimate survival. Finally, our findings strongly indicate that sex represents a novel independent prognostic factor for survival after radiosurgery of brain metastases. Consequently, sex should be considered a reliable candidate to be incorporated into revised prognostic indices for cranial SRS treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M., C.R.A. and M.N.-S.; methodology, J.M., C.R.A. and S.M.; formal analysis, J.M. and C.R.A.; investigation, J.M., D.M., C.R.A., S.M., S.M.V., M.S., M.N.-S., J.K. and M.D.; resources, P.L. and U.G.; data curation, J.M., C.R.A., M.N.-S. and D.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M. and T.S.; writing—review and editing, J.M., T.S., S.M., S.M.V., M.S., M.N.-S., J.K. and D.M.; visualization, J.M.; supervision, P.L. and U.G.; project administration, J.M. and C.R.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the research ethics committee of the Medical University of Innsbruck (reference number: EK 1160/2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective study design.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Linskey, M.E.; Andrews, D.W.; Asher, A.L.; Burri, S.H.; Kondziolka, D.; Robinson, P.D.; Ammirati, M.; Cobbs, C.S.; Gaspar, L.E.; Loeffler, J.S.; et al. The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: A systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 96, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilovic, I.T.; Posner, J.B. Brain metastases: Epidemiology and pathophysiology. J. Neurooncol. 2005, 75, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Brown, P.D.; Burri, S.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gondi, V.; Jordan, J.T.; Maues, J.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: ASCO Guideline Endorsement of ASTRO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, JCO2200333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soffietti, R.; Kocher, M.; Abacioglu, U.M.; Villa, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. A European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: Quality-of-life results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.J.; Lomax, N.; Alonso, S.; Lazeroms, T.; Riesterer, O. Radiosurgery for Five to Fifteen Brain Metastases: A Single Centre Experience and a Review of the Literature. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 866542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giantini-Larsen, A.M.; Juthani, R.G.; Pannullo, S.C.; Knisely, J.P.S. Novel approaches to the management of patients with 5-15 brain metastases: A narrative review. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villa, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Grimm, J.; Gui, C.; Shen, C.J.; Redmond, K.J.; Sloan, L.; Hazell, S.; Moore, J.; Huang, E.; Spoleti, N.; et al. Updated risk models demonstrate low risk of symptomatic radionecrosis following stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellayappan, B.; Tan, C.L.; Yong, C.; Khor, L.K.; Koh, W.Y.; Yeo, T.T.; Detsky, J.; Lo, S.; Sahgal, A. Diagnosis and Management of Radiation Necrosis in Patients With Brain Metastases. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggenraad, R.; Verbeek-de Kanter, A.; Mast, M.; Molenaar, R.; Kal, H.B.; Lycklama à Nijeholt, G.; Vecht, C.; Struikmans, H. Local progression and pseudo progression after single fraction or fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for large brain metastases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2012, 188, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.G.; Byhardt, R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Berkey, B.; Gaspar, L.E.; Mehta, M.; Curran, W. A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: An analysis of 1,960 patients in the RTOG database. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltman, E.; Salvajoli, J.V.; Brandt, R.A.; de Morais Hanriot, R.; Prisco, F.E.; Cruz, J.C.; de Oliveira Borges, S.R.; Wajsbrot, D.B. Radiosurgery for brain metastases: A score index for predicting prognosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 46, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzoni, J.; Devriendt, D.; Massager, N.; David, P.; Ruiz, S.; Vanderlinden, B.; Van Houtte, P.; Brotchi, J.; Levivier, M. Radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases: Estimation of patient eligibility using three stratification systems. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Dunst, J.; Schild, S.E. A new scoring system to predicting the survival of patients treated with whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2008, 184, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Pluemer, A.; Veninga, T.; Hanssens, P.; Dunst, J.; Schild, S.E. Whole-brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery for patients in recursive partitioning analysis classes 1 and 2 with 1 to 3 brain metastases. Cancer 2007, 110, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, S.J.; Xia, J.L.; Fan, F.Y.; Shi, M.; Wei, L.C. Brain metastasis: Experience of the Xi-Jing hospital. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2002, 78, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, J.; Suntharalingam, M.; Kennedy, A.S.; Amin, P.P.; Chen, Z.; Yin, R.; Guo, S.; Han, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Comparison of three treatment options for single brain metastasis from lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 90, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs Radiosurgery With Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients With 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterbach, J.; Cyron, D.; Henne, K.; Ostertag, C.B. Radiosurgery followed by planned observation in patients with one to three brain metastases. Neurosurgery 2008, 62 (Suppl. S2), 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzkall, A.; Debus, J.; Lohr, F.; Fuss, M.; Rhein, B.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R.; Wannenmacher, M. Radiosurgery alone or in combination with whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 3563–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rades, D.; Hornung, D.; Blanck, O.; Martens, K.; Khoa, M.T.; Trang, N.T.; Hüppe, M.; Terheyden, P.; Gliemroth, J.; Schild, S.E. Stereotactic radiosurgery for newly diagnosed brain metastases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, Y.R.; Li, X.A.; el Naqa, I.; Hahn, C.A.; Marks, L.B.; Merchant, T.E.; Dicker, A.P. Radiation dose-volume effects in the brain. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohoudi, O.; Bruynzeel, A.M.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Cuijpers, J.P.; Slotman, B.J.; Palacios, M.A. Isotoxic radiosurgery planning for brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 120, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.; Scott, C.; Souhami, L.; Dinapoli, R.; Bahary, J.P.; Kline, R.; Wharam, M.; Schultz, C.; Davey, P.; Loeffler, J.; et al. Radiosurgery for the treatment of previously irradiated recurrent primary brain tumors and brain metastases: Initial report of radiation therapy oncology group protocol (90-05). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1996, 34, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggenraad, R.; Verbeek-de Kanter, A.; Kal, H.B.; Taphoorn, M.; Vissers, T.; Struikmans, H. Dose-effect relation in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. A systematic review. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 98, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Kueter, J.-D.; Hornung, D.; Veninga, T.; Hanssens, P.; Schild, S.E.; Dunst, J. Comparison of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) alone and whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) plus a stereotactic boost (WBRT + SRS) for one to three brain metastases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2008, 184, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J.; Beal, K.; Pan, H.; Brown, P.D.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Yeh, N.; Gaspar, L.E.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Estimating Survival in Patients With Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases: An Update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Lung Cancer Using Molecular Markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Mesko, S.; Li, J.; Cagney, D.; Aizer, A.; Lin, N.U.; Nesbit, E.; Kruser, T.J.; Chan, J.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Survival in Patients With Brain Metastases: Summary Report on the Updated Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment and Definition of the Eligibility Quotient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasini, P.; Serdjebi, C.; Khobta, N.; Metellus, P.; Ouafik, L.H.; Nanni, I.; Greillier, L.; Loundou, A.; Fina, F.; Mascaux, C.; et al. EGFR and KRAS Mutations Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondziolka, D.; Parry, P.V.; Lunsford, L.D.; Kano, H.; Flickinger, J.C.; Rakfal, S.; Arai, Y.; Loeffler, J.S.; Rush, S.; Knisely, J.P.; et al. The accuracy of predicting survival in individual patients with cancer. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Pluemer, A.; Veninga, T.; Schild, S.E. Comparison of different treatment approaches for one to two brain metastases in elderly patients. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2008, 184, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M. Prognostic and Predictive Markers of Limited (1-4) Brain Metastases in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma After Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Retrospective Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 164, e671–e680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, J.; Badra, E.V.; Adilovic, S.; Christ, S.M.; Ahmadsei, M.; Mayinger, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N. Distant metastasis velocity as a novel prognostic score for overall survival after disease progression following stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic disease. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roengvoraphoj, O.; Eze, C.; Niyazi, M.; Li, M.; Hildebrandt, G.; Fietkau, R.; Belka, C.; Manapov, F. Prognostic role of patient gender in limited-disease small-cell lung cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2017, 193, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.C.; Gani, C.; Rehm, H.M.E.; Eckert, F.; Bamberg, M.; Hehr, T.; Weinmann, M. Are there biologic differences between male and female breast cancer explaining inferior outcome of men despite equal stage and treatment?! Strahlenther. Onkol. 2012, 188, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-W.; Park, S.; Shin, A.; Oh, C.-M.; Kong, H.-J.; Jun, J.K.; Won, Y.-J. Do Female Cancer Patients Display Better Survival Rates Compared with Males? Analysis of the Korean National Registry Data, 2005–2009. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.B.; McGlynn, K.A.; Devesa, S.S.; Freedman, N.D.; Anderson, W.F. Sex disparities in cancer mortality and survival. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zindler, J.D.; Jochems, A.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Beumer, R.; Troost, E.G.C.; Eekers, D.B.P.; Compter, I.; van der Toorn, P.P.; Essers, M.; Oei, B.; et al. Individualized early death and long-term survival prediction after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases of non-small cell lung cancer: Two externally validated nomograms. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangesius, J.; Seppi, T.; Bates, K.; Arnold, C.R.; Minasch, D.; Mangesius, S.; Kerschbaumer, J.; Lukas, P.; Ganswindt, U.; Nevinny-Stickel, M. Hypofractionated and single-fraction radiosurgery for brain metastases with sex as a key predictor of overall survival. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).