Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Demographics
3.2. Metastases Characteristics and Outcomes
3.3. RANO-BM Response Criteria Verification
4. Discussion
4.1. RANO-BM Response Criteria and Potential Changes
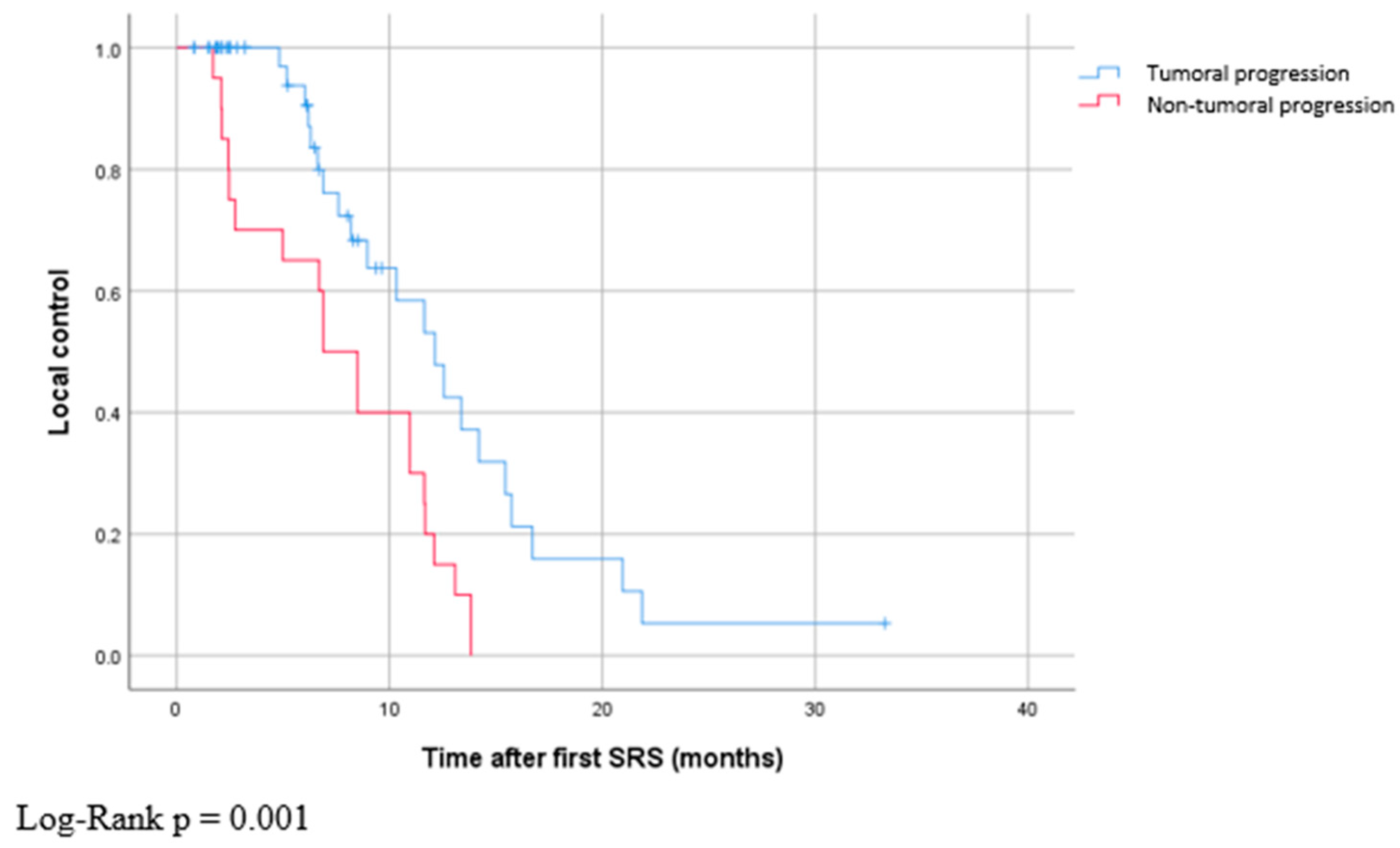
4.2. Non-Tumoral Progression vs. Tumoral Progression
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Impact of Our Study on the Current Clinical Management of Recurrent Brain Metastases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu-Emerson, C.; Eichler, A.F. Brain Metastases. Continuum 2012, 18, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achrol, A.S.; Rennert, R.C.; Anders, C.; Soffietti, R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Nayak, L.; Peters, S.; Arvold, N.D.; Harsh, G.R.; Steeg, P.S.; et al. Brain Metastases (Primer). Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.Y.; Loeffler, J.S. Management of Brain Metastases. Oncology 1999, 13, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Aoyama, H.; Barani, I.J.; Barboriak, D.P.; Baumert, B.G.; Bendszus, M.; Brown, P.D.; Camidge, D.R.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Response Assessment Criteria for Brain Metastases: Proposal from the RANO Group. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e270–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therasse, P.; Arbuck, S.G.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Wanders, J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Rubinstein, L.; Verweij, J.; Van Glabbeke, M.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Christian, M.C.; et al. New Guidelines to Evaluate the Response to Treatment in Solid Tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.B.; Hoogstraten, B.; Staquet, M.; Winkler, A. Reporting Results of Cancer Treatment. Cancer 1981, 47, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, D.R.; Cascino, T.L.; Schold, S.C.; Cairncross, J.G. Response Criteria for Phase II Studies of Supratentorial Malignant Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, H.; Kondziolka, D.; Lobato-Polo, J.; Zorro, O.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. T1/T2 Matching to Differentiate Tumor Growth from Radiation Effects after Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Linera, J. 3T MRI: Advances in Brain Imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 67, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, K.; Shi, F.; Rekik, I.; Gao, Y.; Shen, D. 7T-Guided Super-Resolution of 3T MRI. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, J.L.; Smith, M.; Chandra, S. Pseudoprogression of Melanoma Brain Metastases. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, S.B.; Meng, A.; Ebani, E.J.; Chiang, G.C. Imaging Glioblastoma Posttreatment: Progression, Pseudoprogression, Pseudoresponse, Radiation Necrosis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 57, 1199–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeie, B.S.; Enger, P.Ø.; Knisely, J.; Pedersen, P.-H.; Heggdal, J.I.; Eide, G.E.; Skeie, G.O. A Simple Score to Estimate the Likelihood of Pseudoprogression vs. Recurrence Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: The Bergen Criteria. Neurooncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio-Morin, C.; Mercure-Cyr, R.; Figueiredo, G.; Touchette, C.J.; Masson-Côté, L.; Mathieu, D. Repeat Stereotactic Radiosurgery for the Management of Locally Recurrent Brain Metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 145, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thust, S.C.; van den Bent, M.J.; Smits, M. Pseudoprogression of Brain Tumors. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| n (%) or Median (Range) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Median age at diagnosis of brain metastases | 53 (27–79) | |
| Median number of brain metastases per patient | 4 (1–22) | |
| Sex | Female | 44 (66%) |
| Male | 23 (34%) | |
| Primary cancer histology | NSCLC | 38 (57%) |
| Breast | 13 (19%) | |
| Melanoma | 6 (9%) | |
| Colorectal | 5 (7%) | |
| SCLC | 2 (3%) | |
| Thyroid | 1 (2%) | |
| Renal | 1 (2%) | |
| Unknown | 1 (2%) | |
| Primary cancer surgery before SRS | No | 29 (44%) |
| Partial resection | 8 (12%) | |
| Complete resection | 29 (44%) | |
| Primary cancer radiation before SRS | No | 41 (61%) |
| Fractionated radiotherapy | 25 (37%) | |
| SRS | 1 (2%) | |
| Primary cancer systemic treatment before SRS | No | 13 (19%) |
| Chemotherapy | 48 (72%) | |
| Targeted therapy | 6 (9%) | |
| n (%) or Median (Range) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Metastasis initial maximal diameter (mm) | 5.8 (1.4–27.3) | |
| Metastasis location | Cerebrum | 207 (83%) |
| Cerebellum | 41 (16%) | |
| Brainstem | 3 (1%) | |
| Time between first SRS and second SRS (months) | 13.5 (2.8–47) | |
| Metastasis tumor progression | 58 (23%) | |
| Metastasis non-tumoral progression | 20 (8%) | |
| Median time to non-tumoral progression | 6.9 (1.7–13.8) | |
| Median time to tumor progression | 12.1 (0.8–33.3) | |
| Median-diameter increase in non-tumoral progression | 11.5 (5.8–25.9) | |
| Median-diameter increase in tumoral progression | 5.7 (1.6–26.2) | |
| WBRT after first SRS for tumor progression | 13 (5%) | |
| Threshold Values | 20% | 0.7 mm | 2.5 mm | 3.3 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| True positives | 22 | 54 | 48 | 45 |
| False negatives | 36 | 4 | 10 | 13 |
| True negatives | 182 | 155 | 167 | 176 |
| False positives | 9 | 36 | 24 | 15 |
| Sensitivity | 38% | 93% | 83% | 77% |
| Specificity | 95% | 81% | 87% | 92% |
| Positive predictive value | 71% | 60% | 67% | 75% |
| Negative predictive value | 84% | 98% | 94% | 93% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Douri, K.; Iorio-Morin, C.; Mercure-Cyr, R.; Figueiredo, G.; Touchette, C.J.; Masson-Côté, L.; Mathieu, D. Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9382-9391. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110679
Douri K, Iorio-Morin C, Mercure-Cyr R, Figueiredo G, Touchette CJ, Masson-Côté L, Mathieu D. Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(11):9382-9391. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110679
Chicago/Turabian StyleDouri, Keiss, Christian Iorio-Morin, Rosalie Mercure-Cyr, Gabrielle Figueiredo, Charles Jean Touchette, Laurence Masson-Côté, and David Mathieu. 2023. "Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria" Current Oncology 30, no. 11: 9382-9391. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110679
APA StyleDouri, K., Iorio-Morin, C., Mercure-Cyr, R., Figueiredo, G., Touchette, C. J., Masson-Côté, L., & Mathieu, D. (2023). Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria. Current Oncology, 30(11), 9382-9391. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110679






