[18F]FDG PET/CT and PET/MR in Patients with Adrenal Lymphoma: A Systematic Review of Literature and a Collection of Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FDG PET Acquisition and Interpretation
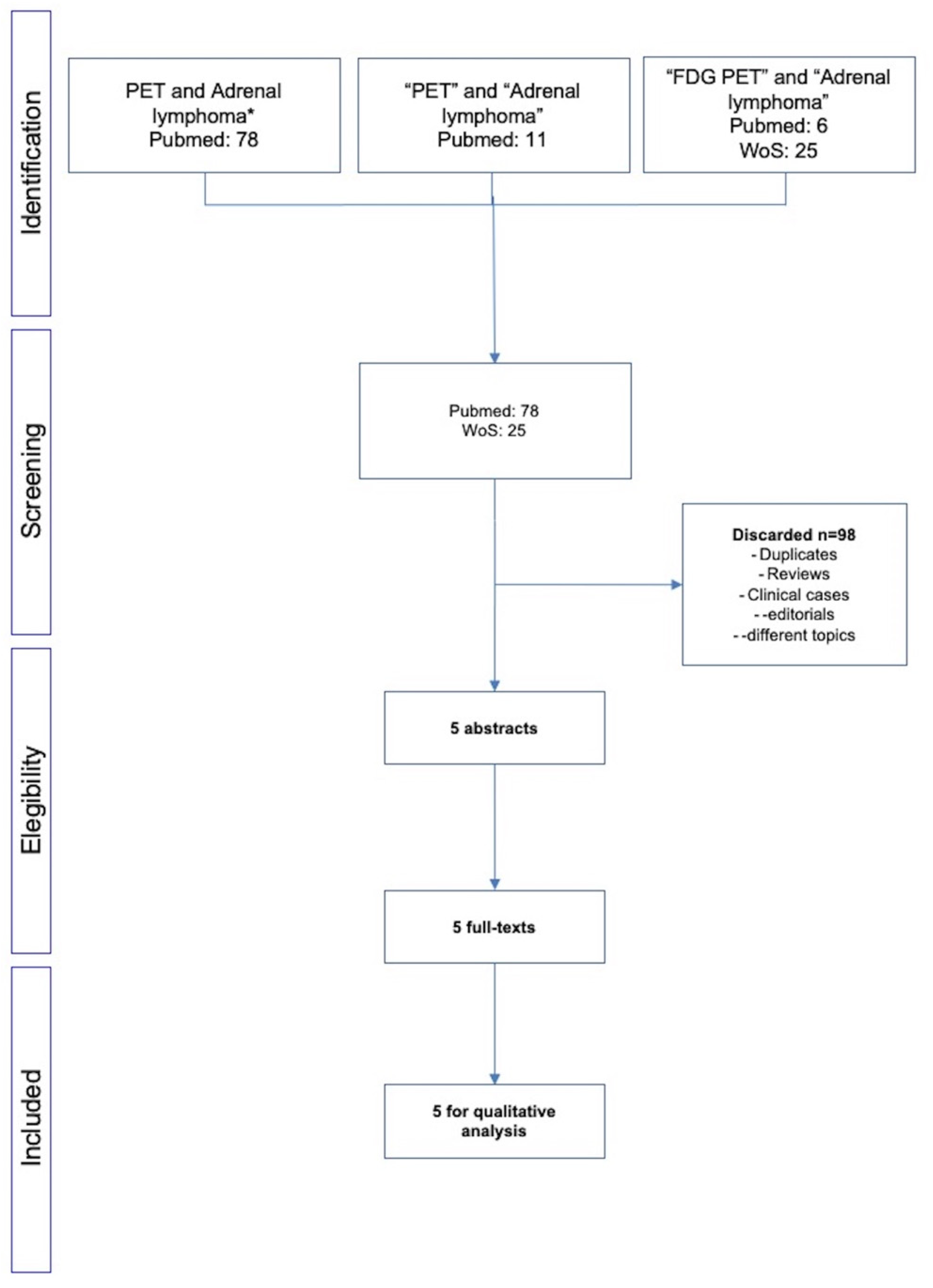
2.2. Literature Search
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Available Papers
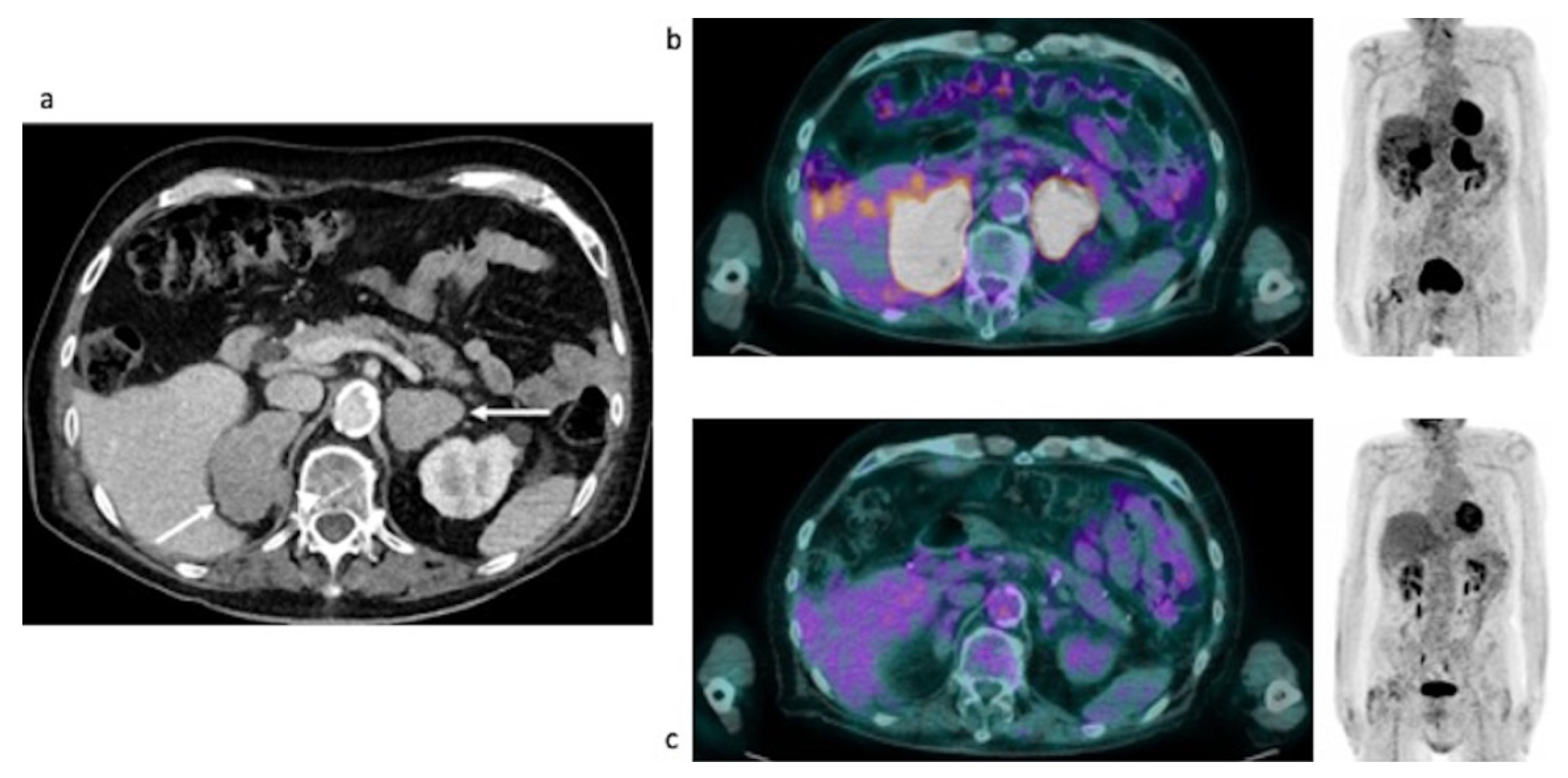
3.2. Clinical Cases
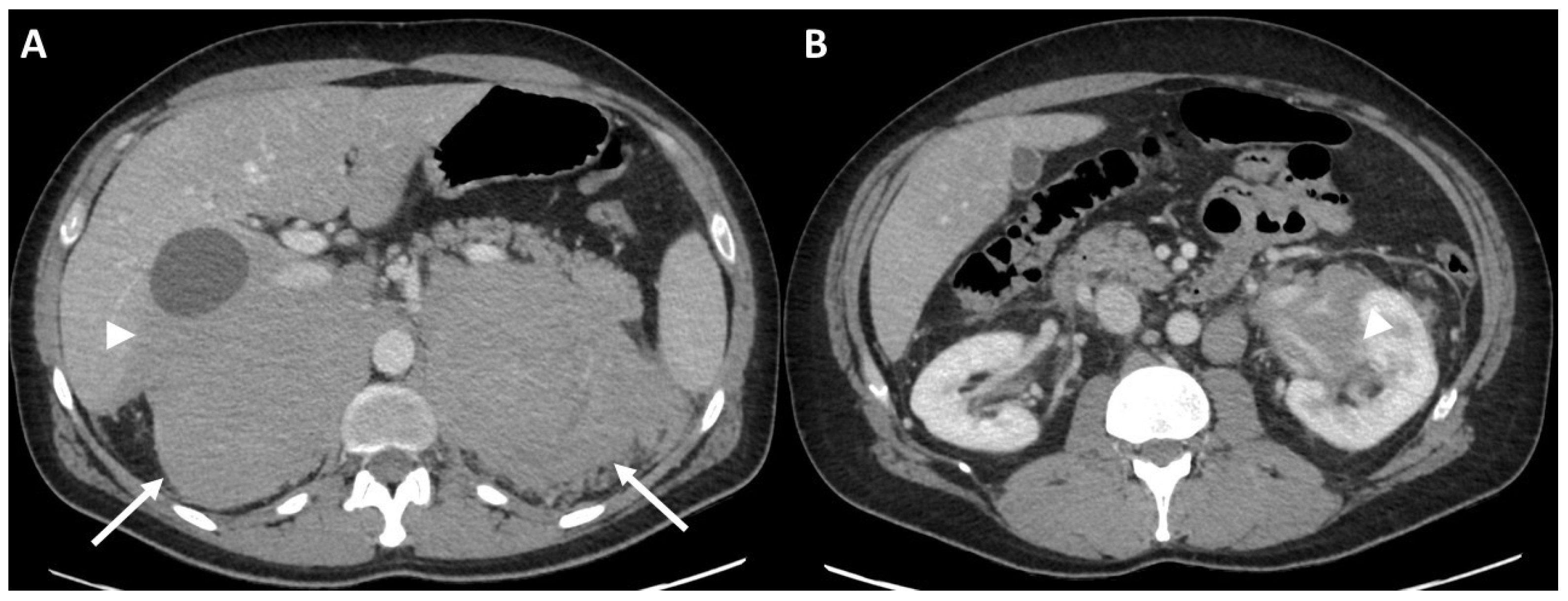
3.2.1. Initial Staging of Disease: Case #1
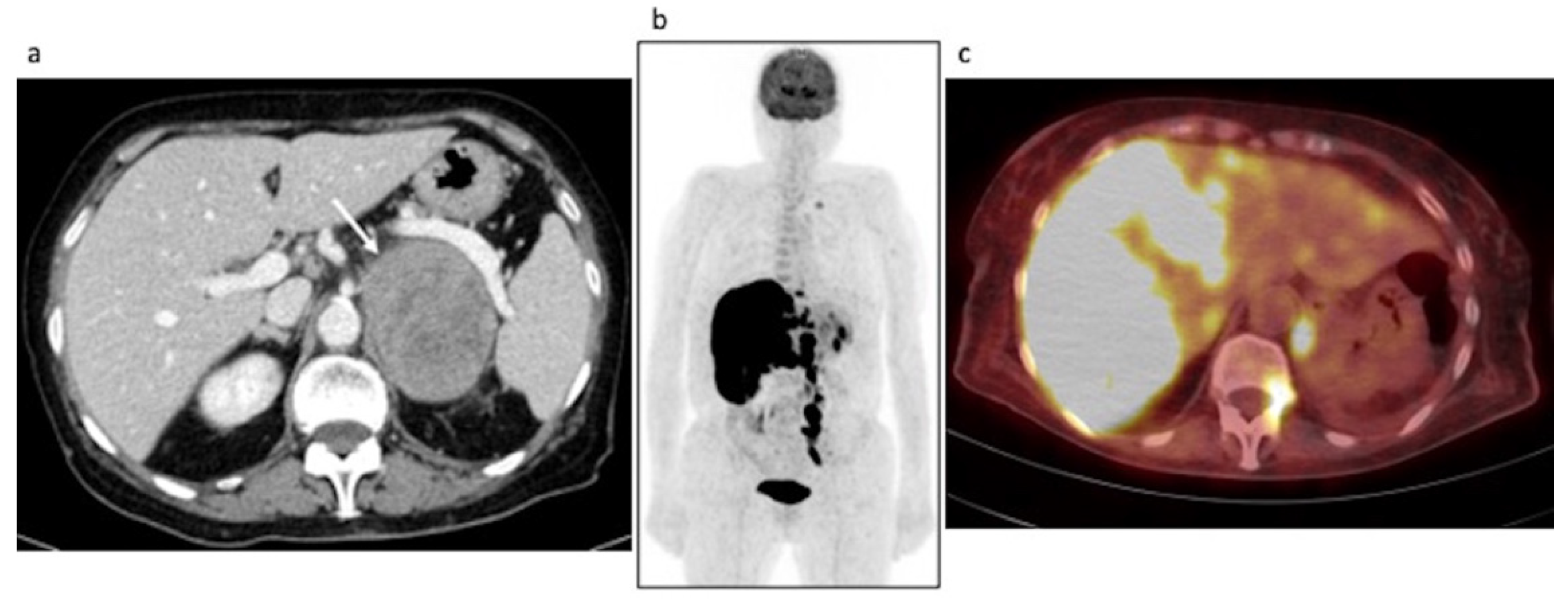
3.2.2. Restaging: Case #2
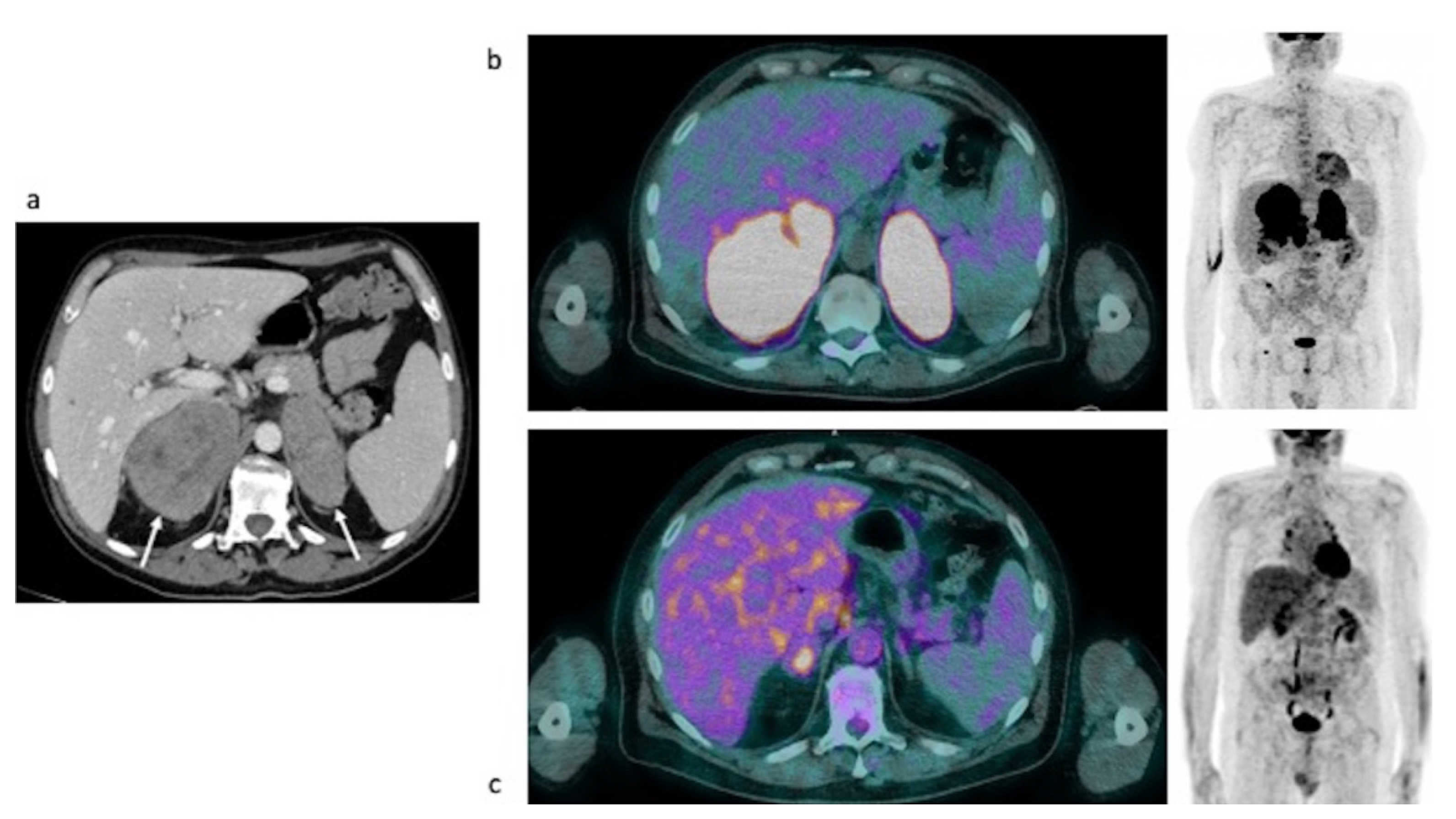
3.2.3. Evaluation of Response to Therapy: Case #3, Case #4 and Case #5
Case #3
Case #4
Case #5
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Essay, P. PET—CT of Extranodal Lymphoma. 2004, pp. 1579–1586.
- Rashidi, A.; Fisher, S.I. Primary adrenal lymphoma: A systematic review. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, N.; Rashid, O.; Farooq, S.; Ulhaq, I.; Islam, N. Primary adrenal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyroglou, A.; Schneider, H.J.; Mussack, T.; Reincke, M.; von Werder, K.; Beuschlein, F. Primary Adrenal Lymphoma: 3 Case Reports with Different Outcomes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2011, 119, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassnacht, M.; Arlt, W.; Bancos, I.; Dralle, H.; Newell-Price, J.; Sahdev, A.; Tabarin, A.; Terzolo, M.; Tsagarakis, S.; Dekkers, O.M. Management of adrenal incidentalomas: European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors [Internet]. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, G1–G34. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27390021/ (accessed on 27 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, N.; Zeynalova, S.; Nickelsen, M.; Kansara, R.; Villa, D.; Sehn, L.H.; Glass, B.; Scott, D.W.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Connors, J.M.; et al. CNS International Prognostic Index: A Risk Model for CNS Relapse in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With R-CHOP. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdová, E.; Ferda, J.; Baxa, J. 18 F-FDG-PET/MRI in lymphoma patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 94, A52–A63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidi, F.; Martino, S.; Kondakci, M.; Antke, C.; Haase, M.; Chortis, V.; Arlt, W.; Ronchi, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Laurent, C.; et al. Clinical spectrum of primary adrenal lymphoma: Results of a multicenter cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaliwal, R.; Goroshi, M.; Khadilkar, K.; Bakshi, G.; Rangarajan, V.; Malhotra, G.; Lila, A.; Bandgar, T.; Shah, N.S. Primary Adrenal Lymphoma: A Single-Center Experience. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinmakas, E.; Üçışık-Keser, F.E.; Medeiros, L.J.; Ng, C.S. CT and 18F- FDG-PET-CT Findings in Secondary Adrenal Lymphoma with Pathologic Correlation. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, e108–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, C.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; Martin, L.; Chauchet, A.; Ghesquieres, H.; Aussedat, G.; Fornecker, L.; Bologna, S.; Borot, S.; Bouillet, B.; et al. Adrenal lymphoma: Presentation, management and prognosis. QJM 2016, 110, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Xu, H.; Xiao, L.; Song, W.; Zhu, S.; Ma, X. Prognostic Value of Functional Parameters of 18F-FDG-PET Images in Patients with Primary Renal/Adrenal Lymphoma. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 2641627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Allolio, B.; Arlt, W.; Barthel, A.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Hammer, G.D.; Husebye, E.S.; Merke, D.P.; Murad, M.H.; Stratakis, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 364–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler-Sagie, M.; Bushelev, O.; Epelbaum, R.; Dann, E.J.; Haim, N.; Avivi, I.; Ben-Barak, A.; Ben-Arie, Y.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Israel, O. 18F-FDG Avidity in Lymphoma Readdressed: A Study of 766 Patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 51, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feres, C.C.P.; Nunes, R.F.; Teixeira, L.L.C.; Arcuri, L.J.; Perini, G.F. Baseline total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV) application in Hodgkin lymphoma: A review article. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2022, 10, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Triumbari, E.K.A.; Gatta, R.; Boldrini, L.; Racca, M.; Mayerhoefer, M.; Annunziata, S. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics in lymphoma. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2021, 9, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.F. The Incidentally Discovered Adrenal Mass. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandathil, A.; Wong, K.K.; Wale, D.J.; Zatelli, M.C.; Maffione, A.M.; Gross, M.D.; Rubello, D. Metabolic and anatomic characteristics of benign and malignant adrenal masses on positron emission tomography/computed tomography: A review of literature. Endocrine 2014, 49, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.G.; Vaidhyanath, R.; Kirke, R.; Rajesh, A. Extranodal Lymphoma from Head to Toe: Part 1, The Head and Spine. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.G.; Vaidhyanath, R.; Kirke, R.; Rajesh, A. Extranodal Lymphoma from Head to Toe: Part 2, The Trunk and Extremities. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Bai, Y.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T. CT and MRI of adrenal gland pathologies. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 853–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, M.A.; Cronin, C.G.; Boland, G.W. Adrenal Imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbanan, M.G.; Javadi, S.; Ganeshan, D.; Habra, M.A.; Korivi, B.R.; Faria, S.C.; Elsayes, K.M. Adrenal cortical adenoma: Current update, imaging features, atypical findings, and mimics. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 45, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.-W.; Pak, K.; Kim, I.-J.; Kim, K. Diagnostic accuracy of18F-FDG PET or PET/CT for the characterization of adrenal masses: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Authors | Ref | Year of Pub | Country | N of Patients | Scanner Type | Clinical Indication | Analysis of the Images | Main Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kasaliwal et al. | [10] | 2015 | India | 5 | PET/CT | Baseline and post-therapy | NA | The conclusions were not relative to FDG PET/CT. |
| Laurent et al. | [12] | 2017 | France | 10 | PET/CT | Initial staging | Visual and SUVmax | PET can visualize extra-adrenal locations of disease, more than CT. |
| Altinmakas et al. | [11] | 2019 | USA | 6 | PET/CT | Initial staging | Visual and SUVmax | Adrenal lymphoma has a high FDG uptake. |
| Wang et al. | [13] | 2019 | China | 8 | PET/CT | Initial staging | PET metrics (also radiomics) | Texture analysis may be used for the prediction of OS. |
| Majidi et al. | [9] | 2020 | USA | 18 | PET/CT | Initial staging | Visual and SUVmax | PET can visualize extra-adrenal locations of disease, more than CT. |
| Authors, Ref | Risk of Bias | Applicability Problems | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Selection | Study Test | Standard of Reference | Flux and Timing | Patient Selection | Study Test | Standard of Reference | |
| Kasaliwal et al. [10] | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low |
| Laurent et al. [12] | High | Low | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low | Unclear |
| Altinmakas et al. [11] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear |
| Wang et al. [13] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Majidi et al. [9] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Endocrine Parameters | Patient #1 | Patient #2 | Patient #3 | Patient #4 | Patient #5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Imaging | Before Imaging | Before Imaging | After Chemotherapy | Before Imaging | After Chemotherapy | Before Imaging | After Chemotherapy | |
| ACTH (10–50 ng/l) | 319 | 145 | 105 | 97 | 129 | 30 | 89.4 | 56.1 |
| Serum cortisol (138–690 nmol/l) | 291 | 378 | 90 | 326 | 262 | 354 | 277 | 396 |
| Na (136–145 mmol/l) | 112 | 121 | 132 | 143 | 136 | 140 | 113 | 137 |
| K (3.4–4.5 mmol/l) | 6.8 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 4.5 | 5.4 | 4.4 |
| Cortisol post Synacthen test t0′→ t60′ (>500 nmol/l) | 363→374 | NA | 306→339 | 285→461 | 252→337 | 480→563 | 326→333 | 378→470 |
| Renin (4.4–46.1 mIU/l) | 85.1 | 2.2 | 30.3 | NA | 72.4 | 38 | 262.4 | 161.8 |
| Aldosterone (70–1086 pmol/l) | 168 | 61.9 | 138 | NA | 156 | 297 | 62.2 | 281 |
| Patient #1 | Patient #2 | Patient #3 | Patient #4 | Patient #5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | SUVmax (LAG) | 20.3 | NA | 19.7 | 30 | 48.43 |
| SUVmean (LAG) | 6.73 | NA | 5.09 | 4.37 | 9.8 | |
| MTV (LAG) | 2393.94 | NA | 800 | 960.35 | 75.99 | |
| SUVmax (RAG) | 21.3 | NA | 21.6 | 28.3 | 53.22 | |
| SUVmean (RAG) | 6.98 | NA | 4.82 | 4.88 | 4.88 | |
| MTV (RAG) | 3310.61 | NA | 344.94 | 1348.02 | 255.43 | |
| Post-therapy | SUVmax (LAG) | NA | NA | 4.96 | no uptake | no uptake |
| SUVmean (LAG) | NA | NA | 2.48 | no uptake | no uptake | |
| MTV (LAG) | NA | NA | 26.02 | no uptake | no uptake | |
| SUVmax (RAG) | NA | NA | no uptake | 6.03 | no uptake | |
| SUVmean (RAG) | NA | NA | no uptake | 2.43 | no uptake | |
| MTV (RAG) | NA | NA | no uptake | 16.17 | no uptake | |
| Metabolic response | - | - | PMR * | PMR * | CMR * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evangelista, L.; Crimì, F.; Visentin, A.; Voltan, G.; Trentin, L.; Lacognata, C.; Cecchin, D.; Ceccato, F. [18F]FDG PET/CT and PET/MR in Patients with Adrenal Lymphoma: A Systematic Review of Literature and a Collection of Cases. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7887-7899. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100623
Evangelista L, Crimì F, Visentin A, Voltan G, Trentin L, Lacognata C, Cecchin D, Ceccato F. [18F]FDG PET/CT and PET/MR in Patients with Adrenal Lymphoma: A Systematic Review of Literature and a Collection of Cases. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7887-7899. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100623
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvangelista, Laura, Filippo Crimì, Andrea Visentin, Giacomo Voltan, Livio Trentin, Carmelo Lacognata, Diego Cecchin, and Filippo Ceccato. 2022. "[18F]FDG PET/CT and PET/MR in Patients with Adrenal Lymphoma: A Systematic Review of Literature and a Collection of Cases" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7887-7899. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100623
APA StyleEvangelista, L., Crimì, F., Visentin, A., Voltan, G., Trentin, L., Lacognata, C., Cecchin, D., & Ceccato, F. (2022). [18F]FDG PET/CT and PET/MR in Patients with Adrenal Lymphoma: A Systematic Review of Literature and a Collection of Cases. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7887-7899. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100623








