Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) genotyping, a critical examen for the treatment decisions of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), is commonly assayed by next-generation sequencing (NGS), but this global approach takes time. To determine whether rapid EGFR genotyping tests by the IdyllaTM system guides earlier therapy decisions, EGFR mutations were assayed by both the IdyllaTM system and NGS in 223 patients with NSCLC in a bicentric prospective study. IdyllaTM demonstrated agreement with the NGS method in 187/194 cases (96.4%) and recovered 20 of the 26 (77%) EGFR mutations detected using NGS. Regarding the seven missed EGFR mutations, five were not detected by the IdyllaTM system, one was assayed in a sample with insufficient tumoral cells, and the last was in a sample not validated by the IdyllaTM system (a bone metastasis). IdyllaTM did not detect any false positives. The average time between EGFR genotyping results from IdyllaTM and the NGS method was 9.2 ± 2.2 working days (wd) (12.6 ± 4.0 calendar days (cd)). Subsequently, based on the IdyllaTM method, the timeframe from tumor sampling to the initiation of EGFR-TKI was 7.7 ± 1.2 wd (11.4 ± 3.1 cd), while it was 20.3 ± 6.7 wd (27.2 ± 8.3 cd) with the NGS method (p < 0.001). We thus demonstrated here that the IdyllaTM system contributes to improving the therapeutic care of patients with NSCLC by the early screening of EGFR mutations.
1. Introduction
Lung carcinoma remains the most common cause of cancer death worldwide. Nearly 85% of lung cancers are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and 15% are small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Accounting for approximately 50% of cases of NSCLC, adenocarcinoma (ADC) is the most prevalent histological subtype [1].
All histology combined, the prognosis of patients with NSCLC remains poor, with a five-year survival rate of 15%, NSCLC being most often diagnosed at an advanced (stages III and IV) and metastatic stage [2]. Surgery is therefore insufficient for the therapeutic care of these patients, who can then benefit from chemotherapy based on platinum salts, immunotherapy according to the tumor expression of PDL1 (programmed death-ligand 1), or targeted therapy depending on the molecular abnormalities detected in their tumor. PD-1 blockade alone or with platinum-based chemotherapy is indeed the first-line therapy (depending on the level of PDL1 expression) for non-targetable metastatic NSCLC, while never-smoking patients with NSCLC more often harbor a targetable molecular aberration. The natural history of NSCLC is actually linked to the occurrence of “driver” molecular abnormalities, among which are KRAS (24%), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; 15%), ERBB2 (<5%), or BRAF (<5%) gene mutations; MET amplification (<5%); MET exon 14 skipping (<5%) and ALK (<5%), ROS1 (<2%), or RET (<1%) gene rearrangements [3]. Patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutations or ALK or ROS1 gene rearrangement are eligible for first-line targeted therapy with the respective appropriate drug, resulting in greatly improved clinical outcomes [4,5,6]. The optimal therapy for each patient must be promptly identified to improve patient outcomes in advanced NSCLC. Considering this objective, the mutational profile of NSCLC tumors is essential for developing a more targeted approach in lung cancer treatment. The guidelines recommend searching for EGFR (exons 18–21), ROS1, KRAS, ALK, and PDL1 status in all new diagnosed advanced non-squamous NSCLC and advanced squamous cell carcinomas in never-smokers. The molecular testing turnaround time should not exceed 10 working days according to oncology and pathology societies [7]. Following the ADAURA study, EGFR mutation testing is also now recommended in patients with stage IB to IIIA resected NSCLC [8], but with less urgency in terms of the expected timeframe for the result.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) using dedicated gene panels is the most common approach to detect EGFR mutations. This is a global analysis that detects other genomic alterations of interest (KRAS, HER2, BRAF, MET, STK11, PIK3CA, etc.). However, this approach is time consuming. The average expected time of a result of the analysis is ~15 days, when these results are necessary for initiation of treatment of patients. Alternative techniques have been developed, such as the IdyllaTM EGFR mutation assay, i.e., an automated real-time polymerase chain reaction detecting EGFR mutations with minimal delays for guiding clinical decisions and starting targeted therapies earlier. This assay detects both EGFR mutations (exon 19 deletions, exon 21 (L858R and L861Q), and exon 18 (G719A/C/S) mutations) associated with sensitivity to EGFR-TKIs [9,10,11] as the main mutations (mainly T790M and insertions in exon 20), predicting the resistance to EGFR-TKIs from the first or second generation but only the response to EGFR-TKIs from the third generation [10,11].
Previous studies have already reported the high concordance (from 94% to 100%) between the IdyllaTM system and other methods routinely used for EGFR mutation detection from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue of human lung cancer (NGS: [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]; pyrosequencing: [23]; Therascreen® EGFR RGQ PCR: [24]; droplet digital PCR: [22]; ARMS PCR: [25]; fragment PCR: [26,27]; multiplex PCR: [28]; real-time PCR (cobas® EGFR Mutation Test): [29]; Sanger sequencing: [29,30]), usually through a retrospective and monocenter study, although sometimes prospective [13,18,28,29,31] and rarely multicentric [15]. Previous studies have thus evaluated the sensitivity, concordance, and reproducibility between NGS and the alternative technical approaches of EGFR genotyping, but whether the early genotyping of EGFR can initiate more quickly the treatment of patients with NSCLC is not clearly answered in the literature.
Herein, through a prospective bicentric study, we aimed to assess the benefits of the early diagnosis of EGFR mutations in the therapeutic initiation in 225 patients with NSCLC, and thus define this benefit from the patient’s point of view by evaluating delays in pathology processing and in initiation of therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients from the ID-MUT Study and Paraffin-Embedded Specimens
From January 2019 to August 2020, 223 patients with NSCLC diagnosed by pathologists from Caen University Hospital (CHU; n = 79) and the François Baclesse Center (CFB; n = 144) were routinely tested to evaluate EGFR mutations with both reference methods, i.e., NGS and the IdyllaTM system (Table 1).

Table 1.
Patients’ characteristics.
All tumor samples were fixed in formalin for 6 to 48 h: (i) “biopsy” type samples (including bone samples) were addressed to the pathology department from the Caen University Hospital or from the CFB in formalin buffered at 4%, (ii) the “fine needle aspiration” type samples were addressed to the pathology departments in a fixing liquid (CytoRichTM, BD, Le Pont de Claix, France); the cells were pelleted by centrifugation then incubated in 4% buffered formalin. Following the fixation step, the bone samples undergwent an additional decalcification step by being incubated in a buffered EDTA solution (OsteosoftTM, Merck, Germany). After fixation (and decalcification for bone samples), the tumor samples were embedded with paraffin. Sections of paraffin-embedded specimens for EGFR mutation testing by NGS method were performed before those for EGFR mutation testing by the IdyllaTM system. At the end of the two series of sections, a slide for hematoxyllin, eosin, saffron (HES) staining and morphological verification of the residual tumor material was systematically carried out.
The clinical data were recovered from electronic medical records, including the date of (1) tumor sampling, (2) multidisciplinary consultation meetings, (3) diagnosis announcement, and (4) initiation of anti-EGFR therapy.
Specific informed consent was obtained for the biological study (ID-MUT). The additional EGFR analysis by IdyllaTM was approved by the appropriate ethics committee (CPP Ref DC 2008-574 Nord-Ouest III, France and Local Health Research Ethics Committee (CLERS ref ID#1595), France). In accordance with the French law n° 2018-493 of 20 June 2018 relating to the protection of personal data, a formally complete declaration file was sent to the National Commission for Data Protection (declaration number: 2204611 v 0).
2.2. EGFR Mutation Assay by Next-Generation Sequencing Panel CLv3 (Colon and Lung Cancer Panel v3)
EGFR mutation testing by NGS method was centralized and carried out once a week in the Department of Genetics from the CHU de Caen. Tumor genomic DNA was extracted from three sections of 10 µm of the paraffin-embedded specimens using an RSC FFPE Plus DNA Kit (PromegaTM, Charbonnières-les-Bains, France) on a Maxwell RSC 48 automated system (PromegaTM) according to the manufacturer’s recommendation twice a week. The DNA concentration was measured with a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA).
NGS was performed using S5 Prime (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The average depth was >500×; on target >90%. Bioinformatic analyses (alignment, call of variants, and annotations) was run on LifeTechnologies: Torrent suite 5.10, Variant caller 5.10, Ion reporter 5.10—Nextgene (Softgenetics, State College, Pennsylvania, USA) 2.4.1.2. The copy number variant (CNV) analysis was expressed as the ratio of mean depths by amplicons ±2 standard deviations. The detection limit was set to 3% for punctual mutations and 5% for insertions/deletions for a minimum depth of 100× per amplicon. Variations of the sequences recognized as non-pathogenic (classes 1 and 2) were not mentioned. The allelic frequency of variants (VAF) of an alteration was evaluated, including panel CLv3 sequence exons 18–21 of the EGFR gene.
2.3. EGFR Mutation Assay by the IdyllaTM System
EGFR mutation testing by the IdyllaTM system was centralized and carried out every working day in the Department of Pathology from the CHU de Caen from unextracted paraffin-embedded specimens according to an adaptation of the manufacturer’s recommendation. Briefly, three sections of 20 µm thickness from the paraffin-embedded specimens were loaded into the IdyllaTM EGFR Mutation cartridge for the following fully automated test, previously described by others [32]. The tumor sample had to contain at least 10% of tumor cells; a macrodissection was carried out to enrich the sample with tumor cells when necessary. The EGFR mutations detected in the IdyllaTM EGFR Mutation cartridge are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
PCR curves were visualized through the web-based interphase IdyllaTM explore to evaluate the quantification cycle (CQ) from the mutation signal if present, the CQ for the internal control (total EGFR) signal, the difference between the two CQs (ΔCQ), the sigmoid aspect of the amplification curve of the mutation when found, and the maximal fluorescence, similarly to Momeni-Boroujeni et al. [32]. The total EGFR CQ for all samples ranged from 16 to 26.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Sensitivity and specificity were the proportion of concordant results against the sum of concordant and discordant results (true positives/(true positives + false negatives) and true negatives/(true negatives + false positives), as detailed by [24]. The male/female distribution, smoking status, and age of patients between NSCLC patients with or without EGFR mutation were evaluated using a chi-square test and a non-parametric test for unpaired data from Mann–Whitney. The influence of the used method (IdyllaTM or NGS) on the time required for delivering EGFR genotyping results was evaluated by a two-way (techniques and time) analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a post-hoc Bonferroni test (GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0 Software, San Diego, California, USA).
Statistical differences of the timeframe according to the method used for EGFR genotyping (IdyllaTM or NGS) were determined using a t-test (GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0 Software, San Diego, California, USA). Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
In total, 223 patients (126 men and 97 women; medium age at diagnosis: 65.4 ± 9.8 years old) newly diagnosed with NSCLC, mostly adenocarcinomas or probable adenocarcinomas (83.1%), were enrolled in the ID-MUT study from January 2019 to August 2020 (Table 1, Figure 1).
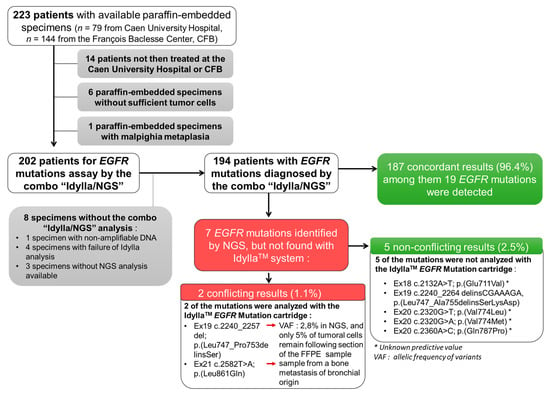
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the ID-MUT study and concordance between the IdyllaTM system and NGS genotyping for EGFR.
We excluded from this study: (i) patients not then treated at the CHU or CFB (n = 14), (ii) samples with insufficient material (tumor sample of less than 50 mm² and/or without sufficient tumor cells (less than 10% of tumoral cells); n = 6), (iii) a malpighia metaplasia sample (n = 1), and (iv) samples without results for both the IdyllaTM and NGS tests (n = 8) (Figure 1).
The final analysis was thus performed on 194 NSCLC samples (Figure 1). Of the 194 NSCLC samples tested, 149 (76.8%) were histological FFPE specimens and 45 (23.2%) were cytology specimens.
3.2. Concordance of EGFR Genotyping between the IdyllaTM and NGS Methods
Of the 194 NSCLC samples tested, 25 (12.8%) were positive for EGFR mutations (including a sample with a double mutation (EGFR_ex20 c.2360A > C; p. (Gln787Pro) (Q787P)/EGFR_ex20 c.2369C > T; p. (Thr790Met) (T790M)) and 169 negatives (87.2%) using NGS, the benchmark analysis (Figure 1). Among these 25 patients were a majority of women (n = 17 (68.0%); p < 0.01) and a majority of non-smokers (n = 15, (60%); p value < 0.001). With IdyllaTM, 19 (9.7%) and 175 (90.3%) cases were positive and negative, respectively, for EGFR mutations (Figure 1). Thus, IdyllaTM demonstrated agreement with the NGS method in 187/194 cases (96.4%) and recovered 20 of the 26 (74.1%) EGFR mutations detected using NGS: 11 deletions in exon 19, seven L858R mutations, one T790M mutation, and one insertion in exon 20 from EGFR. In addition, IdyllaTM did not detect any false positives.
However, seven EGFR mutations were detected by NGS but not by IdyllaTM; five of these missed mutations were not assayed by the IdyllaTM system and were therefore not true mismatches between IdyllaTM and NGS. The two other missed mutations were mutations evaluated by IdyllaTM. However, one of them was missed probably because, following the scraping of the FFPE block for IdyllaTM to analyze, only 5% of the tumor cells remained in the sample (the sensitivity threshold of the IdyllaTM technique is 10% of tumor cells), and the deletion of the exon 19 of the EGFR reported by NGS had a low allelic frequency of 2.80%. The second missed mutation was from a bone metastasis sample of an undifferentiated carcinoma presumed to be of pulmonary origin, because it was TTF1-positive. It should be noted that the IdyllaTM system has not been certified for such type of sample.
3.3. Consideration of the EGFR Genotyping by the IdyllaTM Method in the Treatment Decision
Among the 194 patients with EGFR mutations diagnosed by the combo “IdyllaTM/NGS”, 158 patients received first-line systemic treatment. For these 158 patients, EGFR genotyping results by Idylla® were all reported before those by NGS. For the majority of these patients, i.e., 118/158 of them (75%), the multidisciplinary consultation meeting leading to the therapeutic decision took place with the knowledge of EGFR genotyping by the IdyllaTM method and without the knowledge of the result of the analysis by NGS. For 23/158 patients, EGFR genotyping results were known (10/23 EGFR genotyping results were based only on the IdyllaTM method, 13/23 EGFR genotyping results were known from both NGS and IdyllaTM methods). Finally, 17/158 patients (11%) were discussed in the multidisciplinary consultation meeting before the results of the mutation status of EGFR.
3.4. Turnaround Time (TAT)
To appreciate the TAT of EGFR genotyping from the tumor sample to the initiation of EGFR-TKI treatment according to the NGS or IdyllaTM method, we then measured the timeframe between (1) tumor sampling and EGFR genotyping request, (2) EGFR genotyping request and result, (3) tumoral sampling and EGFR genotyping result, (4) results from both techniques, and (5) tumoral sampling and initiation of treatment (Figure 2).
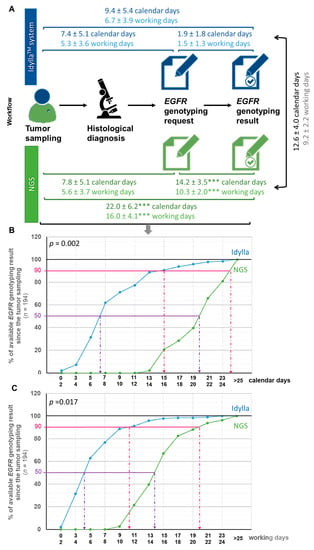
Figure 2.
Turnaround time from the tumor sample to the initiation of treatment according to the NGS or IdyllaTM method. (A) Workflow illustrating delays between each step toward the communication of EGFR genotyping result in calendar or working days (mean ± SD). Delays according to the IdyllaTM system or NGS assay was tested using a t-test (*** p < 0.001 when compared in the same timeframe to the IdyllaTM method). (B,C) Monitoring the availability of EGFR genotyping results by the IdyllaTM or NGS technique from tumor sampling in calendar days (B) or working days (C). The influence of the “technique” variable (IdyllaTM or NGS) on the time required to deliver EGFR genotyping result was evaluated by a two-way (techniques and time) analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a post-hoc Bonferroni test (GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
We expressed these time periods in both working (wd) and calendar (cd) days, calendar days being more representative for patients.
The TAT from tumor sampling to EGFR genotyping request was comparable whether genotyping was ordered from IdyllaTM or performed using the NGS method, with a timeframe of 5.3 ± 3.6 wd (7.4 ± 5.1 cd) and 5.6 ± 3.7 wd (7.8 ± 5.1 cd), respectively (Figure 2A). By contrast, the TAT from the EGFR genotyping request to the EGFR genotyping results was almost six times faster with IdyllaTM than with the NGS method, with a timeframe of 1.5 ± 1.3 wd (1.9 ± 1.8 cd) and 10.3 ± 2.0 wd (14.2 ± 3.5 cd), respectively (p < 0.001) (Figure 2A). The average time between EGFR genotyping results by IdyllaTM and the NGS method was thus 9.2 ± 2.2 wd (12.6 ± 4.0 cd) (Figure 2A). All these TAT (timeframe between (1) tumor sampling and EGFR genotyping prescriptionrequest, (2) EGFR genotyping prescription request and result, (3) tumoral sampling and EGFR geno-typing result, (4) results from both techniques, and (5) tumoral sampling and initiation of treatment) were comparable between the CHU and the CFB (p > 0.05).
Figure 2B,C illustrates the availability of EGFR genotyping since the tumor sampling in calendar days (Figure 2B) and working days (Figure 2C) from the point of view of patients (calendar days) and practitioners (working days), respectively. As shown, for half of the patients from the ID-MUT study, the EGFR genotyping result was determined to be 6–7 cd (4–5 wd) after the tumor sampling with the IdyllaTM method, against 19–20 cd (13–14 wd) for the NGS method. Similarly, for 90% of the patients from the ID-MUT study, the EGFR genotyping result was determined to be 15–16 cd (10–11 wd) after tumor sampling with the IdyllaTM method, against 23–24 cd (19–20 wd) for the NGS method. The influence of the “technique” used (IdyllaTM or NGS) on the time required to deliver EGFR genotyping results was evaluated by a two-way (technique and time) analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a post-hoc Bonferroni test, which confirmed statistically the time-saving benefit of the IdyllaTM technique whether evaluated in cd (p = 0.002) or wd (p = 0.0017).
During the first part of the ID-MUT study (the first nine months), in one of the centers (Caen University Hospital), the EGFR genotyping results by both the IdyllaTM and NGS methods were expected to initiate EGFR-TKI treatment, the time for the confirmation of EGFR genotyping concordance between the two methods in our hand. During the second part of this study, EGFR-TKI treatment was initiated on EGFR genotyping by IdyllaTM in both Caen University Hospital and the François Baclesse Center. For this reason, among the 22 NSCLC patients from the ID-MUT study with EGFR mutations treated by EGFR-TKI, 12 NSCLC patients harboring EGFR mutations received treatment following EGFR genotyping by the NGS method, while the other 10 patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutations received EGFR-TKI treatment according EGFR genotyping by the IdyllaTM system (i.e., before the EGFR genotyping result by NGS was known), allowing the evaluation of the contribution of the IdyllaTM system to improving the therapeutic care of patients with NSCLC by early screening of EGFR mutations (Table 2). Table 2 details the timeframes for the available EGFR genotyping according to the IdyllaTM or NGS method for each of the 22 patients, as well as the time required for the initiation of EGFR-TKI treatment since the tumor sample was processed.

Table 2.
Turnaround time of initiation of EGFR-TKI in patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations according to EGFR genotyping by the IdyllaTM system or the NGS method.
The time to initiation of EGFR-TKI was defined as the time between the interventional procedures leading to the histological confirmation until initiation of TKIs for patients harboring EGFR mutations. The TAT from tumor sampling to initiation of EGFR-TKI was 7.7 ± 1.2 wd (11.4 ± 3.1 cd) when the decision was based on the IdyllaTM method, while it was 20.3 ± 6.7 wd (27.2 ± 8.3 cd) when the decision was based on the NGS method, i.e., reduced by more than two-fold with the IdyllaTM system (p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
In this study, we confirmed the good sensitivity and specificity of the rapid detection of EGFR mutations using the IdyllaTM system and mainly reported that EGFR mutation detection with this assay is associated with a significantly reduced turnaround time compared to the use of NGS testing. In turn, patients were observed to begin systemic EGFR-TKIs therapy an average of two weeks earlier than if waiting for the NGS result.
The good sensitivity and specificity of the rapid detection of EGFR mutations using the IdyllaTM system were previously reported in other publications on lung cancer, as well as on other cancers such as melanoma and colorectal cancer [17]. Similarly, as detailed in the introduction, the concordance of EGFR genotyping has already been reported between the IdyllaTM system and NGS [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] or other techniques [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. In our center, we chose to introduce the IdyllaTM system rather than another rapid assay, because our main objective was to reduce, at maximum, the result of the EGFR genotyping for clinicians and to reduce the need of DNA extraction being performed daily, not allowing this objective to be achieved. In fact, the IdyllaTM system is one of the rare solutions avoiding DNA extraction and allowing reliable EGFR genotyping directly from FFPE sample slides [20,25,33,34,35] in all patients with advanced NSCLC, mainly adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas in never-smokers, as in patients with stage IB to IIIA resected EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC [8]. However, the IdyllaTM system has several limitations. First, biological materials obtained from biopsies are often limited and can be an issue when multiple analyses are required. Indeed, the IdyllaTM assay requires additional sections of FFPE sample and therefore risks exhausting the tumor sample, especially because, contrary to what is recommended by Biocartis, which markets the IdyllaTM EGFR cartridge, we did not perform EGFR genotyping on a single section of 5 µm but on three sections of 20 µm thickness from the paraffin-embedded specimens, because, in our hands, during preliminary tests, we observed that, by following the recommendations of Biocartis, there was a risk of missing out on an EGFR mutation with low allelic frequency. This did not put the performance of the tests at risk because no analysis failure due to a saturation of a cartridge was reported. As we have an excellent agreement (96.4%) of results between the methods by the IdyllaTM system and NGS, we concluded that our procedure for EGFR mutation testing by the IdyllaTM system allowed us not to miss a mutation due to lack of sensitivity for the IdyllaTM method. The off-label use of CE-IVD methods was thoroughly validated before being used in routine testing during a retrospective study not reported here. The risk to exhaust the tumor sample could, however, be lifted by the reuse of H&E, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) diagnostic slides [36], by the use of plasma from patients with lung cancer [37,38] or of the DNA extracted from FFPE sections for NGS analysis [14,19,26,28,39]. Indeed, using the same DNA for IdyllaTM and NGS assays could discard divergent results linked to tumor heterogeneity and to the fact that the two analyses are not carried out on strictly the same part of the tumor sample. Moreover, only a little DNA is needed; Bocciarelli et al. reported that >25 ng of DNA and >10% of tumor cells are sufficient to detect EGFR mutations with the IdyllaTM method [19]. DNA use seems a good alternative, however, and this is also the second limitation of the IdyllaTM system—IdyllaTM EGFR cartridges are not certified for samples other than primary tumor biopsies included in FFPE. This lack of certification is regrettable, but like others [13,27,30,40], we also analyzed samples of other kinds (fine needle aspiration and metastasis of bronchial origin) on IdyllaTM EGFR cartridges and, except for one of them, the results of EGFR genotyping were consistent with the analysis by NGS. As long as the result of the EGFR genotyping is confirmed in a second step by another technique, it seems to us that this second limitation can therefore be avoided.
Studies comparing the IdyllaTM system and NGS performance [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] reported a concordance between the two techniques ranging from 94% to 100%, which is consistent with the 96.7% of concordant results between the IdyllaTM system and NGS that we evaluated here, especially because the seven apparent discordant results that we reported were not trues discordant: Five missed mutations were not detected by the IdyllaTM system, one missed mutation was assayed in a sample with insufficient tumoral cells, and the last missed mutation was sought in a sample not validated on the IdyllaTM system (a bone metastasis).
That some mutations detected in the NGS panel were absent in the IdyllaTM test panel is unfortunate, but most of the time there are few consequences for the patient considering that approved therapies are missing for most of those missed mutations (insertion in exon 20 of the EGFR gene), and the others were finally found with the complementary analysis of the sample by NGS, such as the C797S mutation, a second acquired resistance mutation arising in tumors that have progressed after treatment for T790M+ disease and not detected in the IdyllaTM system [41]. For us, the IdyllaTM system or another rapid system of EGFR mutation detection is essential for reducing the timeframe of EGFR genotyping and initiating therapy in patients with lung cancer. However, it cannot be the only analysis realized to process this genotyping because of the risk of missing some EGFR mutations, either in samples with few tumor cells or rare EGFR mutations not detected by rapid genotyping, but for which we will soon know whether they do or do not predict the response to EGFR-TKIs, and because NGS allows the analysis of a large panel of genes whose alterations (mutations and copy gain) can also guide the treatment decisions of patients with lung cancer. Considering the simultaneous evaluation of numerous genomic alterations across several genes with NGS, and even if the system is presented as being available in any laboratory, because it does not require a molecular biologist, we believe that the links between these laboratories and platforms equipped with NGS technology must be preserved. NGS panels remain essential in molecular sub-type diagnosis of lung cancer and cannot be replaced due to the rapid emergence of new targeted therapies for different genomic alterations. Therefore, it can screen mutations that allow some patients to be included into clinical trials. Molecular testing is also essential in the treatment strategy because studies have demonstrated that immunotherapy before targeted therapies increases the occurrence of serious side effects [42,43,44]. While comprehensive molecular screening is essential in academic centers with access to clinical trials, it is questionable in smaller centers who do not have access to NGS assays. In those centers, IdyllaTM assays can be part of the solution to improving the time to initiate therapies.
Molecular testing requires a good-quality sample, enough tumor cells, and even multiple interventional procedures to be conclusive, which would lengthen delays. In 2016, a survey from the French National Cancer Institute showed that the median turnaround time (TAT) from test prescription to reception of results by the clinician for EGFR molecular test was 18 days [7]. A limitation with the NGS technique is that the TAT is usually longer than the TAT associated with a specific assay. However, a delayed turnaround time for biomarker reports can lead to delays in treatment initiation, decreased efficacy of treatment, and inappropriate treatment decisions. Indeed, EGFR mutations are an oncogenic driver occurring especially in patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma and never-smokers. For patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations, the development of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is an important improvement in therapeutic care, as shown by the increase in the progression-free survival (PFS) and limitation of toxicities using EGFR-TKIs for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC compared to chemotherapy [5], especially with the use of osimertinib versus first-line TKIs (gefitinib and erlotinib) [4,6]. However, a long delay to initiate EGFR-TKIs can result in rapid disease progression and deterioration in performance status associated with a worse prognosis [45]. Thus, it is essential to accelerate the availability of molecular sub-type results. Because pathology processing is reduced with rapid techniques, we were able obtain a result for EGFR genotyping 12.5 calendar days earlier with IdyllaTM compared to NGS assays. As a consequence, the TAT from tumor sampling to initiation of EGFR-TKIs was reduced by two weeks when the decision was based on the IdyllaTM method compared to when the decision was based on the NGS method. Besides faster delivery of the appropriate treatment for patients with NSCLC, therefore increasing their chance of survival, we can also assume that by improving the deadlines, we can improve patients’ adherence to participating in clinical trials.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated, for the first time and to the best of our knowledge, the benefit for the patient of the introduction into routine practice of the rapid EGFR genotyping test, in addition to NGS in the initiation of its therapeutic care. EGFR mutation assays by the IdyllaTM system, in addition to NGS testing, increase the costs of patient care but improve it through the timely completion of biomarker results and the facilitation of appropriate treatment decisions [46].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/curroncol28060376/s1, Table S1: Mutations detected with the IdyllaTM EGFR Mutation cartridge.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.B., E.B., R.G. and G.L.; methodology, C.P., A.R. and G.L.; software, C.P., A.R. and G.L.; validation, G.L.; formal analysis, C.P., A.R. and G.L.; investigation, C.P., G.R.-Z. and A.R.; resources, C.P., G.R.-Z., M.D., C.B.-F., S.D. and A.R.; data curation, C.P., G.R.-Z., A.R., M.D., C.B.-F., S.D. and N.R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.P., A.R. and G.L.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, F.B., E.B. and G.L.; project administration, G.L.; funding acquisition, F.B., E.B. and G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by AstraZeneca and INNOV_ECAIR, a unit from the Caen University Hospital Center.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The ID-MUT study was approved by the appropriate ethics committee (Avis favorable CLERS ref ID#1595, France). In accordance with the French law n° 2018-493 of 20 June 2018 relating to the protection of personal data, a formally complete declaration file was sent to the National Commission for Data Protection (CNIL; declaration number: 2204611 v 0).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
All data are stored at the CHU of Caen and CFB center and can be made available upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all of the onco-pulmonologists and anatomopathologists from Caen University Hospital and the François Baclesse Center that contributed to this study; Sylvie Lecot-Cotigny, Géraldine Lefevre, and Roseline Patey for their technical support in the realization of this study; and Vincent Léon, Clinical Research Associate at Caen University Hospital, for his support in this project.
Conflicts of Interest
G.L. received 22 batches of six EGFR IdyllaTM tests (Biocartis®) from AstraZeneca. FB received payment for participating in international meetings from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, MSD, and Sanofi. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hutchinson, B.; Shroff, G.S.; Truong, M.T.; Ko, J.P. Spectrum of lung adenocarcinoma. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2019, 40, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihimäki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Fallah, M.; Thomsen, H.; Sundquist, K. Metastatic sites and survival in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, E.M.; Doebele, R.C. Targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer: Emerging oncogene targets following the success of epidermal growth factor receptor. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Facchinetti, F.; Olaussen, K.A.; Besse, B.; Friboulet, L. Making the first move in EGFR-driven or ALK-driven NSCLC: First-generation or next-generation TKI? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INCa (French National Cancer Institute). Accès Aux Tests Moléculaires EGFR, RAS et BRAF/Résultats D’une Enquête Dans 5 Régions Françaises. 2016. Available online: https://www.e-cancer.fr/Expertises-et-publications/Catalogue-des-publications/Acces-aux-tests-moleculaires-EGFR-RAS-et-BRAF-Resultats-d-une-enquete-dans-5-regions-francaises (accessed on 1 January 2016).
- Wu, Y.-L.; Tsuboi, M.; He, J.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Kato, T.; et al. Osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated non–small-cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.A.; Lam, D.C.L.; O’Toole, S.A.; Minna, J.D. Molecular biology of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5, S479–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Version 4.2019; NCCN Guidelines: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lambros, L.; Caumont, C.; Guibourg, B.; Barel, F.; Quintin-Roué, I.; Marcorelles, P.; Merlio, J.P.; Uguen, A. Evaluation of a fast and fully automated platform to diagnose EGFR and KRAS mutations in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded non-small cell lung cancer samples in less than one day. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas De Montpréville, V.; Ghigna, M.R.; Lacroix, L.; Lemoine, A.; Besse, B.; Mercier, O.; Fadel, É.; Dorfmuller, P.; Le Chevalier, T. EGFR and KRAS molecular genotyping for pulmonary carcinomas: Feasibility of a simple and rapid technique implementable in any department of pathology. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.; Rappa, A.G.; Gragnano, G.; Malapelle, U.; Troncone, G.; Barberis, M. Idylla Assay and next generation sequencing: An integrated EGFR mutational testing algorithm. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, S.M.; Taranchon-Clermont, E.; Rouquette, I.; Murray, S.; Dintner, S.; Nam-Apostolopoulos, Y.-C.; Bellosillo, B.; Varela, M.; Nadal, E.; Wiedorn, K.H.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of the fully automated PCR-based Idylla EGFR Mutation Assay on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue of human lung cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 21, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Turkmani, M.R.; Suriawinata, M.A.; Deharvengt, S.J.; Green, D.C.; Black, C.C.; Shirai, K.; Dragnev, K.H.; Tsongalis, G.J. Rapid EGFR mutation testing in lung cancer tissue samples using a fully automated system and single-use cartridge. Pract. Lab. Med. 2020, 20, e00156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colling, R.; Bancroft, H.; Langman, G.; Soilleux, E.J. Fully automated real-time PCR for EGFR testing in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2019, 474, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chevalier, L.M.; Billaud, A.; Passot, C.; Renoult, A.; Bigot, F.; Verrièle, V.; Morel, A. EGFR molecular characterization in non-small cell bronchic cancer: Comparative prospective study by NGS and Idylla platform technologies. Ann. Pathol. 2020, 40, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocciarelli, C.; Cohen, J.; Pelletier, R.; Tran Van Nhieu, J.; Derman, J.; Favre, L.; Bourgogne, A.; Monnet, I.; Chouaid, C.; Pujals, A. Evaluation of the Idylla system to detect the EGFRT790M mutation using extracted DNA. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haele, M.; Borght, S.V.; Ceulemans, A.; Wieërs, M.; Metsu, S.; Sagaert, X.; Weynand, B. Rapid clinical mutational testing of KRAS, BRAF and EGFR: A prospective comparative analysis of the Idylla technique with high-throughput next-generation sequencing. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 73, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiduk, T.; Brockmann, M.; Tillmann, R.L.; Pieper, M.; Lüsebrink, J.; Schildgen, V.; Schildgen, O. Comparison of Biocartis IDYLLATM cartridge assay with Qiagen GeneReader NGS for detection of targetable mutations in EGFR, KRAS/NRAS, and BRAF genes. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 120, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Jones, V.; Topkas, E.; Harraway, J. Reduced sensitivity for EGFR T790M mutations using the Idylla EGFR Mutation Test. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Butori, C.; Lassalle, S.; Heeke, S.; Piton, N.; Sabourin, J.C.; Tanga, V.; Washetine, K.; Long-Mira, E.; Maitre, P.; et al. Optimization of EGFR mutation detection by the fully-automated qPCR-based Idylla system on tumor tissue from patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103055–103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Garcia, M.; Weynand, B.; Gómez-Izquierdo, L.; Hernández, M.J.; Blanco, Á.M.; Varela, M.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Nadal, E.; Márquez-Lobo, B.; Alarcão, A.; et al. Clinical performance evaluation of the IdyllaTM EGFR Mutation Test on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaanane, H.; El Attar, H.; Louahabi, A.; Berradi, H.; Idrissi, H.H.; Khyatti, M.; Nadifi, S. Targeted methods for molecular characterization of EGFR mutational profile in lung cancer Moroccan cohort. Gene 2019, 705, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Gragnano, G.; Pisapia, P.; Vigliar, E.; Malapelle, U.; Bellevicine, C.; Troncone, G. EGFR mutation detection on lung cancer cytological specimens by the novel fully automated PCR-based Idylla EGFR Mutation Assay. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Conticelli, F.; Leone, A.; Gragnano, G.; Salatiello, M.; Galasso, P.; Pisapia, P.; Grillo, L.R.; Iaccarino, A.; Vigliar, E.; et al. Is the Idylla EGFR Mutation Assay feasible on archival stained cytological smears? A pilot study. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Azzolli, C.G.; Fintelmann, F.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Farago, A.F.; Gainor, J.F.; Jiang, G.; Piotrowska, Z.; Heist, R.S.; Lennes, I.T.; et al. Clinical utility of rapid EGFR genotyping in advanced lung cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.; Silveira, C.; Janeiro, A.; Malveiro, S.; Oliveira, A.R.; Felizardo, M.; Nogueira, F.; Teixeira, E.; Martins, J.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Detection of rare and novel EGFR mutations in NSCLC patients: Implications for treatment-decision. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boureille, A.; Ferraro-Peyret, C.; Pontarollo, G.; Confavreux, C.; Pialat, J.-B.; Isaac, S.; Forest, F.; Yvorel, V.; Watkin, E.; Girard, N.; et al. Rapid detection of EGFR mutations in decalcified lung cancer bone metastasis. J. Bone Oncol. 2020, 21, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle, S.; Hofman, V.; Heeke, S.; Benzaquen, J.; Long, E.; Poudenx, M.; Lantéri, E.; Boutros, J.; Tanga, V.; Zahaf, K.; et al. Targeted assessment of the EGFR status as reflex testing in treatment-naive non-squamous cell lung carcinoma patients: A single laboratory experience (LPCE, Nice, France). Cancers 2020, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Momeni-Boroujeni, A.; Salazar, P.; Zheng, T.; Mensah, N.; Rijo, I.; Dogan, S.; Yao, J.; Moung, C.; Vanderbilt, C.; Benhamida, J.; et al. Rapid EGFR mutation detection using the Idylla platform: Single-institution experience of 1200 cases analyzed by an in-house developed pipeline and comparison with concurrent next-generation sequencing results. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeke, S.; Hofman, P. EGFR mutation analysis in non-small cell lung carcinoma from tissue samples using the fully automated IdyllaTM qPCR system. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2054, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Springborn, S.; Haug, K.; Bartow, K.; Samra, H.; Menon, S.; Mackinnon, A.C. Evaluation, validation, and implementation of the Idylla system as rapid molecular testing for precision medicine. J. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 21, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, P.; Stevenson, T.; Powari, M. Use of the Idylla EGFR mutation test for variant detection in non–small cell lung cancer samples. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 156, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnari, J.; Graziano, P.; Muscarella, L.A.; Rossi, A.; Grillo, L.R.; Montrone, G.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Bronzini, M.; Leone, A. Rapid EGFR evaluation from used H&E, IHC and FISH diagnostic slides with the Idylla platform. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeke, S.; Hofman, V.; Benzaquen, J.; Otto, J.; Tanga, V.; Zahaf, K.; Allegra, M.; Long-Mira, E.; Lassalle, S.; Marquette, C.-H.; et al. Detection of EGFR mutations from plasma of NSCLC patients using an automatic cartridge-based PCR system. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 657743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, P.; Saurel, C.; Salleron, J.; Husson, M.; Demange, J.; Merlin, J.-L.; Harlé, A. Evaluation of the Idylla ctEGFR Mutation Assay to detect EGFR mutations in plasma from patients with non-small cell lung cancers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.; Stanley, A.; Balbi, K.; Gerrard, G.; Bennett, P. Performance evaluation of the Biocartis Idylla EGFR Mutation Test using pre-extracted DNA from a cohort of highly characterised mutation positive samples. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Yang, S.-R.; Momeni, A.; Mata, D.A.; Salazar, P.; Chan, R.; Elezovic, D.; Benayed, R.; Zehir, A.; Buonocore, D.J.; et al. Ultrarapid EGFR mutation screening followed by comprehensive next-generation sequencing: A feasible, informative approach for lung carcinoma cytology specimens with a high success rate. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tsui, S.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to third-generation inhibitors in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisberg, A.; Cummings, A.; Goldman, J.; Bornazyan, K.; Reese, N.; Wang, T.; Coluzzi, P.; Ledezma, B.; Mendenhall, M.; Hunt, J.; et al. A phase II study of pembrolizumab in EGFR-mutant, PD-L1+, tyrosine kinase inhibitor naïve patients with advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.J.; Chin, E.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ferris, L.A.; Kamesan, V.; Lennes, I.T.; Sequist, L.V.; Heist, R.S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Gainor, J.F.; et al. Increased hepatotoxicity associated with sequential immune checkpoint inhibitor and crizotinib therapy in patients with non–small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Tanimoto, T.; Yuji, K.; Tojo, A. EGFR–TKI-associated interstitial pneumonitis in nivolumab-treated patients with non–small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blanc-Durand, F.; Florescu, M.; Tehfe, M.; Routy, B.; Alameddine, R.; Tran-Thanh, D.; Blais, N. Improvement of EGFR Testing over the last decade and impact of delaying TKI initiation. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Flahec, G.; Guibourg, B.; Marcorelles, P.; Uguen, A. Financial implications of Idylla testing in colorectal cancer, lung cancer and melanoma: A French laboratory point of view. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).