Dieckol Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis Ameliorates Wrinkling and Improves Skin Hydration via MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathways in UVB-Irradiated Hairless Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
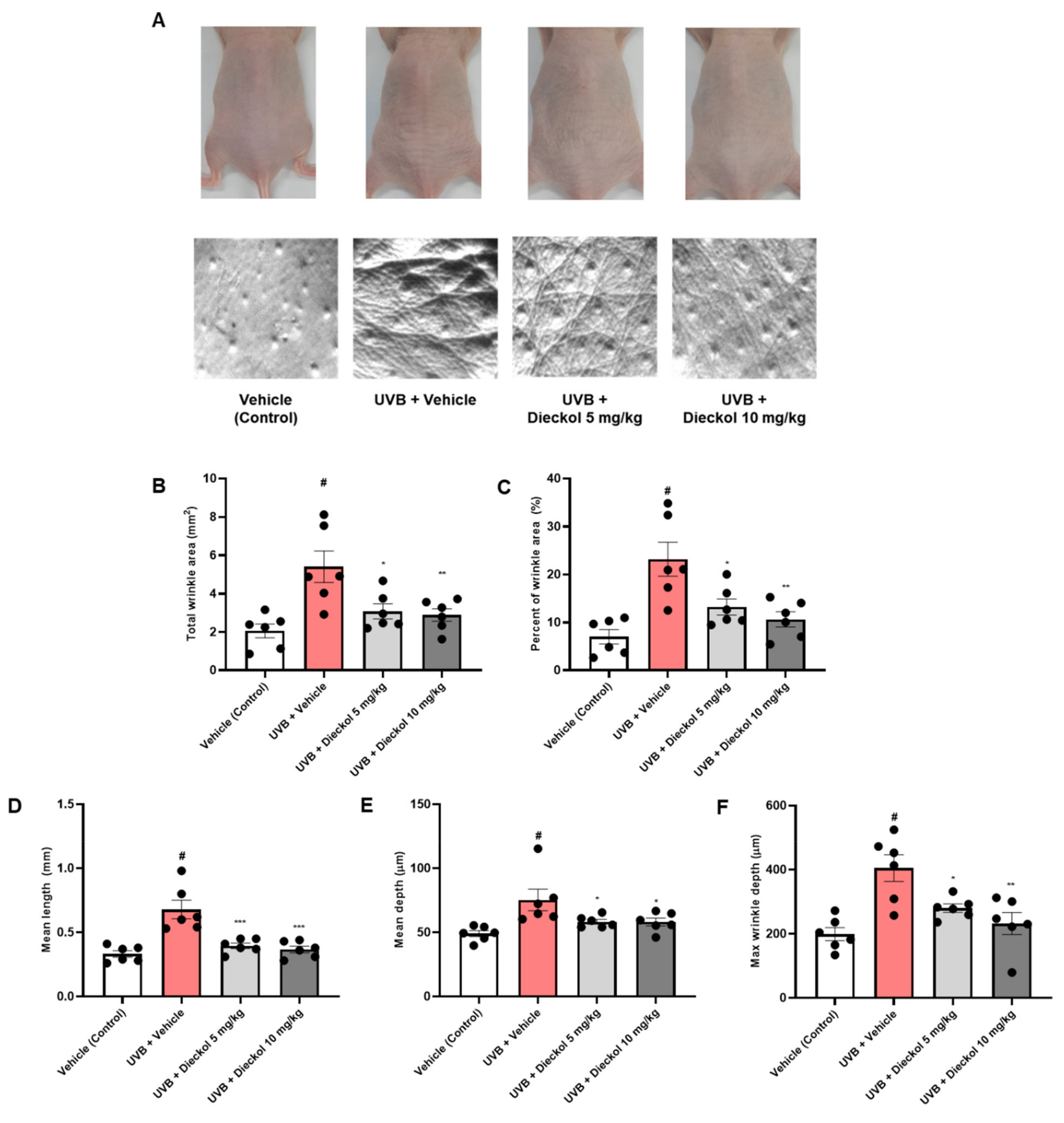
2.1. Dieckol Suppresses Skin Wrinkle Formation on the Dorsal Skin of UVB-Irradiated HR-1 Mice
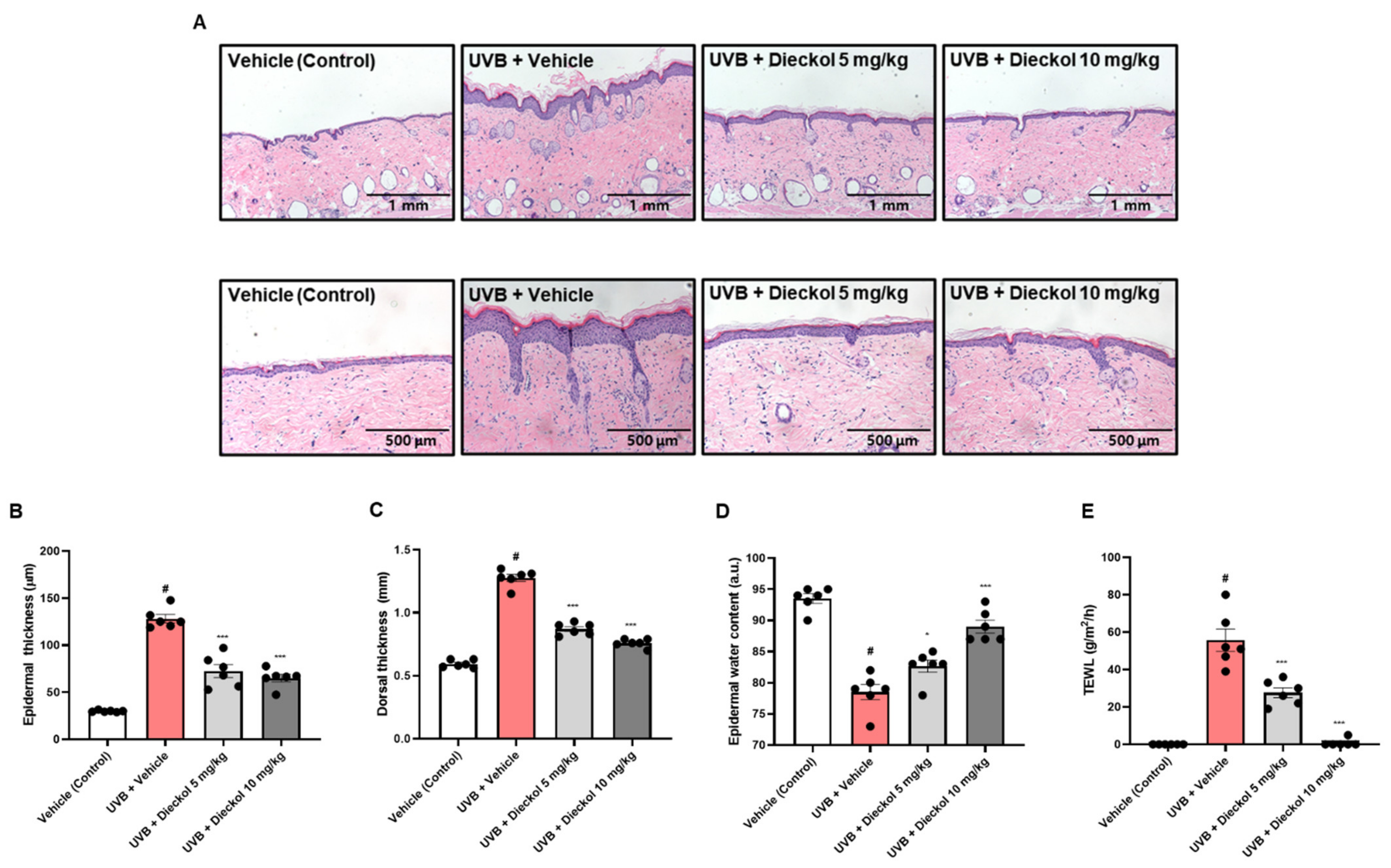
2.2. Dieckol Protects against Skin Thickening and Water Loss on the Dorsal Skin of UVB-Irradiated HR-1 Mice
2.3. Dieckol Inhibits Collagen Degradation in the Dorsal Skin of UVB-Irradiated HR-1 Mice
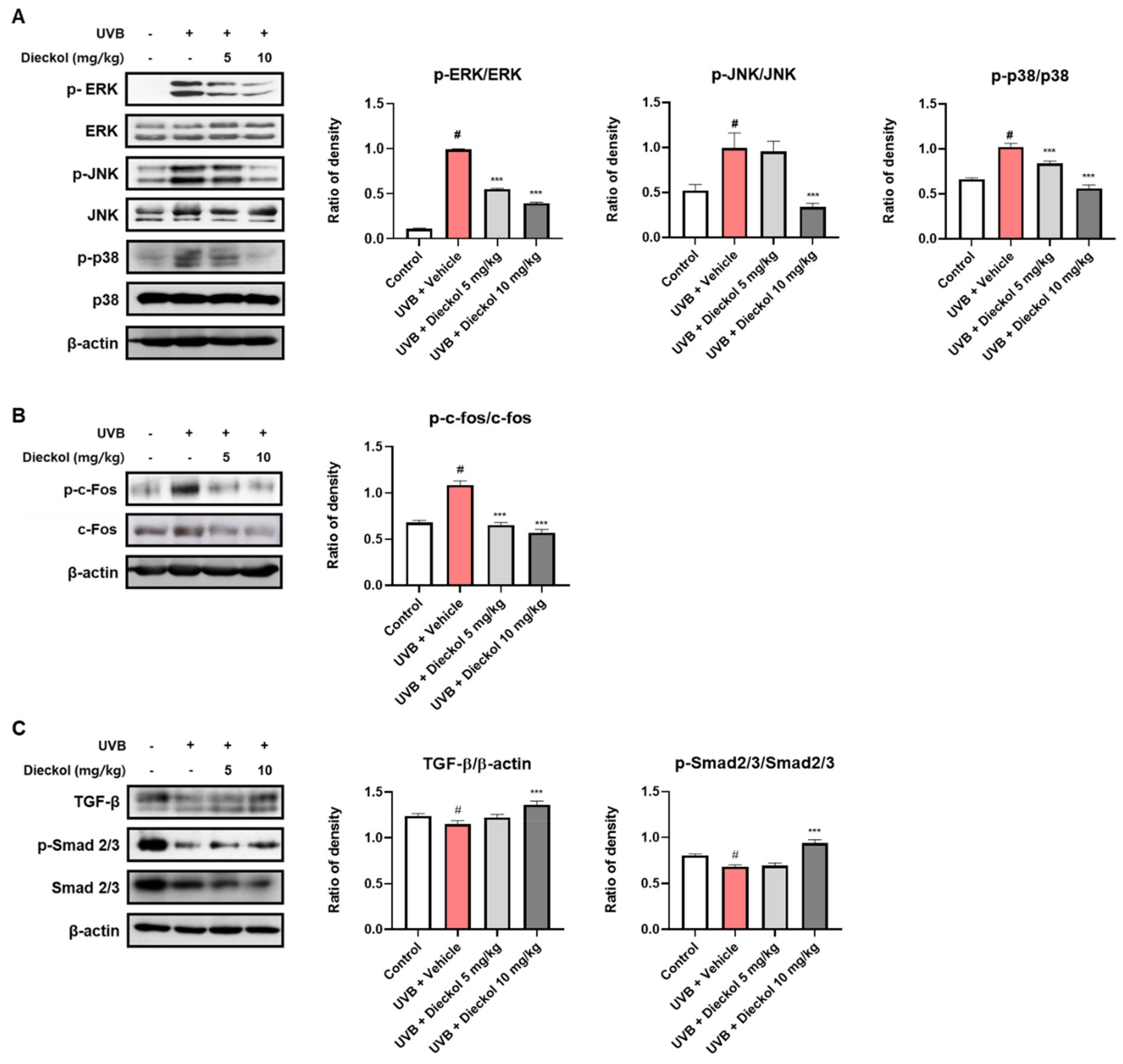
2.4. Dieckol Prevents UVB-Induced Activation of the MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathways in the Dorsal Skin of UVB-Irradiated HR-1 Mice
2.5. Dieckol Restores Hyaluronic Acid Production and HAS-1/-2 and HYAL-1/-2 mRNA Expression in the Dorsal Skin of UVB-Irradiated HR-1 Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
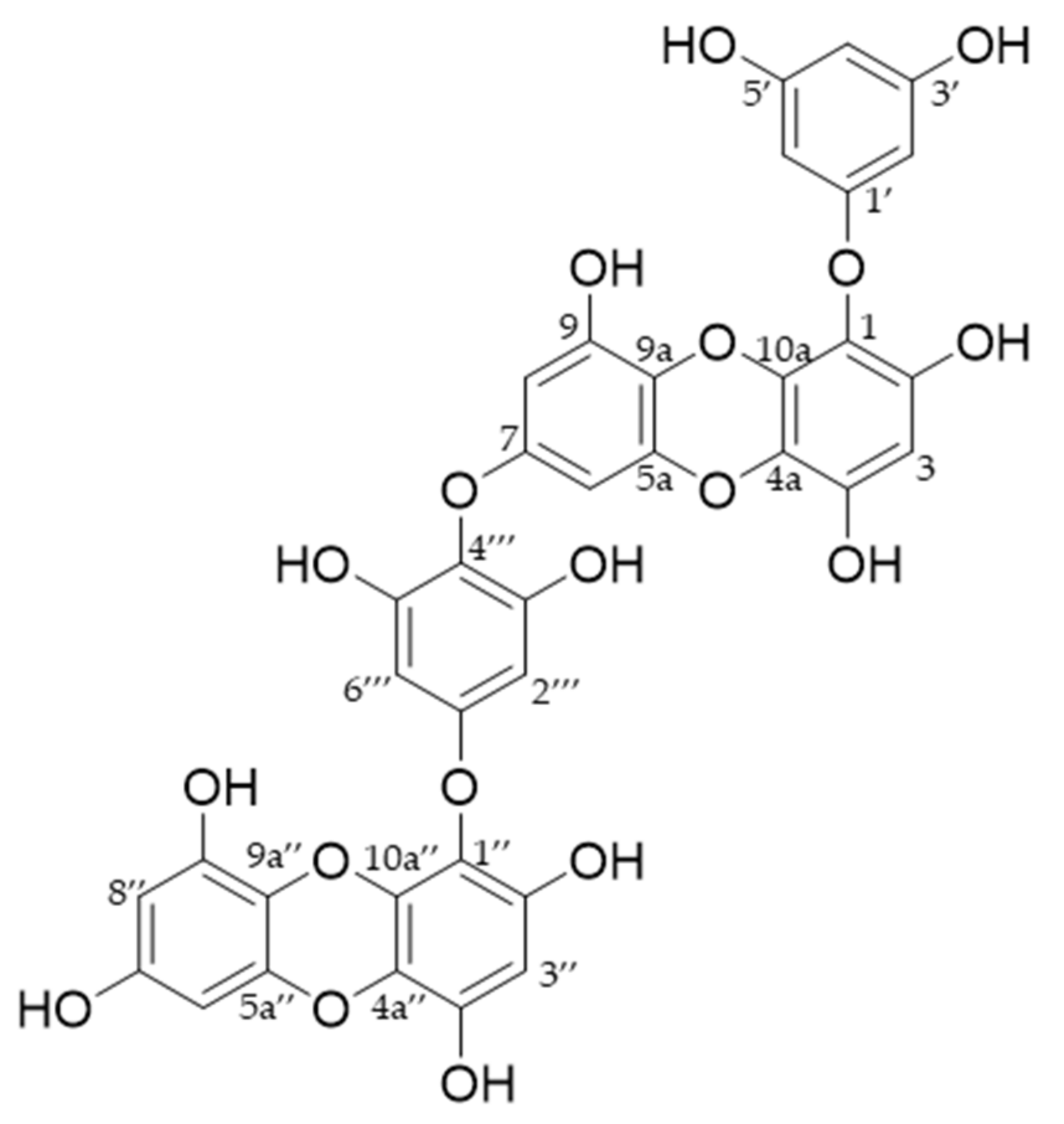
4.1. Preparation of Dieckol from E. bicyclis
4.2. Animals
4.3. Sample Treatment and UVB Irradiation
4.4. Analysis of Skin Wrinkle Formation
4.5. Histological Analysis
4.6. Assessment of Dorsal Skin Thickness, Epidermal Water Content, and Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
4.7. Measurement of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and Hyaluronic Acid Production
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mestrallet, G.; Rouas-Freiss, N.; LeMaoult, J.; Fortunel, N.O.; Martin, M.T. Skin Immunity and Tolerance: Focus on Epidermal Keratinocytes Expressing HLA-G. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 772516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khavkin, J.; Ellis, D.A. Aging skin: Histology, physiology, and pathology. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 19, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. Natural and sun-induced aging of human skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a015370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Derm.-Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Freudenberger, T.; Zipper, P.; Melchior, A.; Grether-Beck, S.; Rabausch, B.; de Groot, J.; Twarock, S.; Hanenberg, H.; Homey, B.; et al. Chronic ultraviolet B irradiation causes loss of hyaluronic acid from mouse dermis because of down-regulation of hyaluronic acid synthases. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.S.; Han, H.S.; Lee, S.B.; Myung, D.B.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.T. Chemical Constituents from Leaves of Hydrangea serrata and Their Anti-photoaging Effects on UVB-Irradiated Human Fibroblasts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiishi, M.; Sayo, T.; Yoshida, H.; Kusaka, A.; Kawabata, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Ishikawa, O.; Inoue, S. Changes in epidermal hyaluronan metabolism following UVB irradiation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 64, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, C.L.; Ullrich, S.E.; Kripke, M.L.; Ananthaswamy, H.N. p53 tumor suppressor gene: A critical molecular target for UV induction and prevention of skin cancer. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, F.; Peharda, V.; Kastelan, M.; Brajac, I. Occupational skin diseases caused by UV radiation. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. ADC 2007, 15, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama, H.; Waditee-Sirisattha, R. Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Aging Properties of Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms in the Protection of Skin-Aging. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.F.; Chen, W.Y.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Lin, Y.K.; Shih, H.C.; Fang, J.Y. Skin aging modulates percutaneous drug absorption: The impact of ultraviolet irradiation and ovariectomy. Age 2015, 37, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate treatment to mouse skin prevents UVB-induced infiltration of leukocytes, depletion of antigen-presenting cells, and oxidative stress. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.G.; Zhang, Z.Y. Redox regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase activity by hydroxyl radical. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonks, N.K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: From genes, to function, to disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, G.B. Interstitial collagen catabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8785–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, M. Attenuation of UV-induced skin photoaging in rats by walnut protein hydrolysates is linked to the modulation of MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathways. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, P.; O’Hara, C.; Magee, P.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Allsopp, P.J. Risks and benefits of consuming edible seaweeds. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, K.; Jeon, J.S.; Jho, E.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Nho, C.W.; Um, B.H. Isolation of phlorotannins from Eisenia bicyclis and their hepatoprotective effect against oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hyperoxide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, C.G.; Park, N.H. Antioxidant activity of various solvent fractions from edible brown alga, Eisenia bicyclis and its active compounds. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C679–C684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.W.; et al. In vitro antibacterial activity and synergistic antibiotic effects of phlorotannins isolated from Eisenia bicyclis against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytother. Res. PTR 2013, 27, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Jin, S.E.; Ahn, B.R.; Lee, C.M.; Choi, J.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis and its constituents fucosterol and phlorotannins in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2013, 59, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.R.; Moon, H.E.; Kim, H.R.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Neuroprotective effect of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis on amyloid beta peptide-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2012, 35, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.I.; Han, H.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, G.; Jang, Y.P.; Shin, Y.K.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.T. Eisenia bicyclis Extract Repairs UVB-Induced Skin Photoaging In Vitro and In Vivo: Photoprotective Effects. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Lewis, E.D.; Zakaria, N.; Pelipyagina, T.; Guthrie, N. A randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel study to evaluate the efficacy of a freshwater marine collagen on skin wrinkles and elasticity. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.C.; Fan, P.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; Shih, I.C.; Chiang, H.M. Ixora parviflora Protects against UVB-Induced Photoaging by Inhibiting the Expression of MMPs, MAP Kinases, and COX-2 and by Promoting Type I Procollagen Synthesis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2012, 2012, 417346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, S.A.; Yoo, T.; Hwang, J.S.; Kang, E.S.; Paek, K.S.; Park, C.; Kim, J.H.; Do, J.T.; Seo, H.G. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta modulates MMP-2 secretion and elastin expression in human dermal fibroblasts exposed to ultraviolet B radiation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 76, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Photoaging and Photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicker, K.T.; Gurski, L.A.; Pradhan-Bhatt, S.; Witt, R.L.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Hyaluronan: A simple polysaccharide with diverse biological functions. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, A.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Hyaluronic Acid: A Key Ingredient in the Therapy of Inflammation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengot-Carbo, M.; Hernandez-Martin, A.; Torrelo, A. The role of filaggrin in the skin barrier and disease development. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2015, 106, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, D.B.; Han, H.S.; Shin, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.T. Hydrangenol Isolated from the Leaves of Hydrangea serrata Attenuates Wrinkle Formation and Repairs Skin Moisture in UVB-Irradiated Hairless Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bech-Thomsen, N.; Wulf, H.C. Photoprotection due to pigmentation and epidermal thickness after repeated exposure to ultraviolet light and psoralen plus ultraviolet A therapy. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1995, 11, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biniek, K.; Levi, K.; Dauskardt, R.H. Solar UV radiation reduces the barrier function of human skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17111–17116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Shin, J.S.; Myung, D.B.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.T. Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Extract Attenuate UVB-Induced Photoaging through MAPK/AP-1 Inactivation in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Oresajo, C.; Hayward, J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: Roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebel, F.; Kaur, S.; Ruvolo, E.; Kollias, N.; Southall, M.D. Irradiation of skin with visible light induces reactive oxygen species and matrix-degrading enzymes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfle, U.; Seelinger, G.; Bauer, G.; Meinke, M.C.; Lademann, J.; Schempp, C.M. Reactive molecule species and antioxidative mechanisms in normal skin and skin aging. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Noh, E.M.; Song, H.K.; Lee, G.S.; Kwon, K.B.; Lee, Y.R. Reversine inhibits MMP-1 and MMP-3 expressions by suppressing of ROS/MAPK/AP-1 activation in UV-stimulated human keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Je, J.G.; Yang, H.W.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, S. Dieckol, an Algae-Derived Phenolic Compound, Suppresses UVB-Induced Skin Damage in Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Its Underlying Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Cruz, G.; Leon-Lopez, A.; Cruz-Gomez, V.; Jimenez-Alvarado, R.; Aguirre-Alvarez, G. Collagen Hydrolysates for Skin Protection: Oral Administration and Topical Formulation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massague, J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbow, U.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. The AP-1 site and MMP gene regulation: What is all the fuss about? Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 1997, 15, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J.; Quan, T. YAP/TAZ regulates TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling by induction of Smad7 via AP-1 in human skin dermal fibroblasts. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2018, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. UV-light-induced signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z.J.; Lee, S.H.; Li, Y.X.; Kim, S.K. Dieckol from Ecklonia cava Regulates Invasion of Human Fibrosarcoma Cells and Modulates MMP-2 and MMP-9 Expression via NF-kappaB Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2011, 2011, 140462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, L.; Kerscher, M. Native hyaluronic acid in dermatology--results of an expert meeting. J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. JDDG 2008, 6, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Abatangelo, G. Functions of hyaluronan in wound repair. Wound Repair Regen. Off. Publ. Wound Heal. Soc. Eur. Tissue Repair Soc. 1999, 7, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Yasuda, R.; Sayo, T.; Ishikawa, O.; Inoue, S. Hyaluronan exists in the normal stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itano, N.; Kimata, K. Mammalian hyaluronan synthases. IUBMB Life 2002, 54, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupkova, O.; Greutert, H.; Boos, N.; Lemcke, J.; Liebscher, T.; Wuertz-Kozak, K. Expression and activity of hyaluronidases HYAL-1, HYAL-2 and HYAL-3 in the human intervertebral disc. Eur. Spine J. Off. Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deform. Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 2020, 29, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, K.M. Skin barrier dysfunction and filaggrin. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kezic, S.; Jakasa, I. Filaggrin and Skin Barrier Function. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2016, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.-T.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, M.-M.; Kim, S.-K. Inhibitory effects of polyphenols isolated from marine alga Ecklonia cava on histamine release. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, J.M.; Kwon, H.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, D.; Lee, W.S.; Ryu, Y.B. Dieckol, a SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibitor, isolated from the edible brown algae Ecklonia cava. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3730–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-M.; Chung, K.-S.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Jang, S.-Y.; Heo, S.-W.; Park, G.; Jang, Y.-P.; Ahn, H.-S.; Shin, Y.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. Dieckol Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis Ameliorates Wrinkling and Improves Skin Hydration via MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathways in UVB-Irradiated Hairless Mice. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120779
Kim J-M, Chung K-S, Yoon Y-S, Jang S-Y, Heo S-W, Park G, Jang Y-P, Ahn H-S, Shin Y-K, Lee S-H, et al. Dieckol Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis Ameliorates Wrinkling and Improves Skin Hydration via MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathways in UVB-Irradiated Hairless Mice. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(12):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120779
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jae-Min, Kyung-Sook Chung, Young-Seo Yoon, Seo-Yun Jang, So-Won Heo, Geonha Park, Young-Pyo Jang, Hye-Shin Ahn, Yu-Kyong Shin, Sun-Hee Lee, and et al. 2022. "Dieckol Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis Ameliorates Wrinkling and Improves Skin Hydration via MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathways in UVB-Irradiated Hairless Mice" Marine Drugs 20, no. 12: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120779
APA StyleKim, J.-M., Chung, K.-S., Yoon, Y.-S., Jang, S.-Y., Heo, S.-W., Park, G., Jang, Y.-P., Ahn, H.-S., Shin, Y.-K., Lee, S.-H., & Lee, K.-T. (2022). Dieckol Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis Ameliorates Wrinkling and Improves Skin Hydration via MAPK/AP-1 and TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathways in UVB-Irradiated Hairless Mice. Marine Drugs, 20(12), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120779








