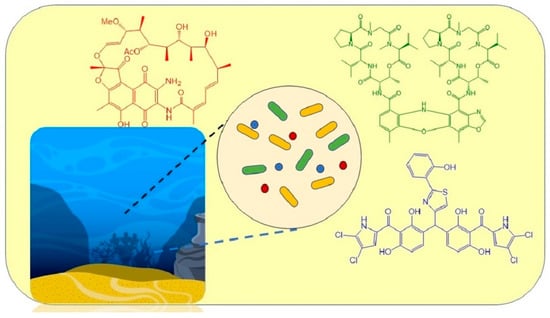
Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria with Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activities against Drug-Resistant Pathogens †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria Which Were Tested against Drug-Resistant Bacteria
2.1. Polyketides
2.1.1. Anthraquinones and Their Analogs
2.1.2. Naphthoquinones
2.1.3. Macrolides
2.1.4. Spirotetronates
2.2. Amino Acid Derivatives
2.2.1. Simple Amino Acid Derivatives
2.2.2. Linear Peptides
2.2.3. Cyclic Peptides
2.2.4. Alkaloids
2.3. Terpenoid Derivatives
2.4. Miscellaneous
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interests
References
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M.; et al. Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Stemming the Superbug Tide; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.; Wright, G.D. Intrinsic antibiotic resistance: Mechanisms, origins, challenges and solutions. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2006, 34, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, L.; Breidenstein, E.B.; Hancock, R.E. Creeping baselines and adaptive resistance to antibiotics. Drug Resist. Updates 2011, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance in the 21st Century. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2014, 6, S14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; An, R.; Wang, J.; Sun, N.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Kuai, J. Exploring novel bioactive compounds from marine microbes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.; Fenical, W. Marine Microorganisms and Drug Discovery: Current Status and Future Potential. In Drugs from the Sea; Fusetani, N., Ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Edrada-Ebel, R.; AEvarsson, A.; Polymenakou, P.; Hentschel, U.; Carettoni, D.; Day, J.; Green, D.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Harvey, L.; McNeil, B. SeaBioTech: From seabed to test-bed: Harvesting the potential of marine biodiversity for industrial biotechnology. In Grand Challenges in Marine Biotechnology; Rampelotto, P.H., Trincone, A., Eds.; Grand Challenges in Biology and Biotechnology; Springer International Publishing Ag: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 451–504. [Google Scholar]
- Schinke, C.; Martins, T.; Queiroz, S.C.N.; Melo, I.S.; Reyes, F.G.R. Antibacterial Compounds from Marine Bacteria, 2010–2015. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Nepal, K.K.; Chen, J.; Harmody, D.; Zhu, H.; McCarthy, P.J.; Wright, A.E.; Wang, G. Nocardiopsistins A-C: New angucyclines with anti-MRSA activity isolated from a marine sponge-derived Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, N.; Liu, Y.; Auckloo, B.N.; Shi, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, B. Stress-Driven Discovery of New Angucycline-Type Antibiotics from a Marine Streptomyces pratensis NA-ZhouS1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, S.; Ye, X.; Anjum, K.; Huang, H.; Lian, X.; Zhang, Z. Bioactive Polycyclic Quinones from Marine Streptomyces sp. 182SMLY. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Li, Z.; Cullum, R.; Molinski, T.F.; Eid, M.A.G.; Hebishy, A.M.S.; Faraag, A.H.I.; Moneim, A.E.A.; Abdelfattah, M.S.; Fenical, W. Chlororesistoflavins A and B, Chlorinated Benzopyrene Antibiotics Produced by the Marine-Derived Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. Strain EG32. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 85, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, M.; Sawa, R.; Umekita, M.; Hatano, M.; Arisaka, R.; Hayashi, C.; Ishizaki, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kato, C. Sealutomicins, new enediyne antibiotics from the deep-sea actinomycete Nonomuraea sp. MM565M-173N2. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Kwon, O.-S.; Chung, B.; Lee, J.; Sun, J.; Shin, J.; Oh, K.-B. Antibacterial Activity of Chromomycins from a Marine-Derived Streptomyces microflavus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Molina, D.; Ortiz-López, F.J.; Martín, J.; Oves-Costales, D.; Díaz, C.; de la Cruz, M.; Cautain, B.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. New Napyradiomycin Analogues from Streptomyces sp. Strain CA-271078. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dampier, M.F.; Whitlock, H.W. Electronegative groups at C-3 of rifamycin S enhance its activity toward DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 6254–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Dalisay, D.S.; Chen, J.; Polishchuck, E.A.; Patrick, B.O.; Narula, G.; Ko, M.; Av-Gay, Y.; Li, H.; Magarvey, N.; et al. Aminorifamycins and Sporalactams Produced in Culture by a Micromonospora sp. Isolated from a Northeastern-Pacific Marine Sediment Are Potent Antibiotics. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.W.; Torres, J.P.; Tun, J.O.; Flores, M.S.; Forteza, I.; Rosenberg, G.; Haygood, M.G.; Schmidt, E.W.; Concepcion, G.P. Synergistic anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) activity and absolute stereochemistry of 7,8-dideoxygriseorhodin C. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Cullum, R.; Hebishy, A.M.S.; Mohamed, H.A.; Faraag, A.H.I.; Salah, N.M.; Abdelfattah, M.S.; Fenical, W. Mersaquinone, A New Tetracene Derivative from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. EG1 Exhibiting Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Antibiotics 2020, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, V.; Martín, J.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; de la Cruz, M.; García, L.A.; Blanco, G.; Reyes, F. Anthracimycin B, a Potent Antibiotic against Gram-Positive Bacteria Isolated from Cultures of the Deep-Sea Actinomycete Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-169. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.H.; Nam, S.-J.; Locke, J.B.; Kauffman, C.A.; Beatty, D.S.; Paul, L.A.; Fenical, W. Anthracimycin, a Potent Anthrax Antibiotic from a Marine-Derived Actinomycete. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7822–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M. Chemical mining of heterotrophic Shewanella algae reveals anti-infective potential of macrocyclic polyketides against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 108, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Chai, W.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. A unique indolizinium alkaloid streptopertusacin A and bioactive bafilomycins from marine-derived Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E. Phytochemistry 2017, 144, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Anjum, K.; Chen, L.; Lian, X.-Y. Bioactive Bafilomycins and a New N-Arylpyrazinone Derivative from Marine-derived Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, X.; Duan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Shang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification and Proposed Relative and Absolute Configurations of Niphimycins C–E from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. IMB7-145 by Genomic Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, A.; Aszalos, A.; Dinya, Z.; Sudo, K. Structure elucidation of the antibiotic desertomycin through the use of new two-dimensional NMR techniques. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 8056–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braña, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Otero, L.; Palacios-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Fernández, J.; Mohamedi, Y.; Fontanil, T.; Salmón, M.; et al. Desertomycin G, a New Antibiotic with Activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Human Breast Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Streptomyces althioticus MSM3, Isolated from the Cantabrian Sea Intertidal Macroalgae Ulva sp. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braddock, A.A.; Theodorakis, E.A. Marine Spirotetronates: Biosynthetic Edifices That Inspire Drug Discovery. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bonilla, M.; Oves-Costales, D.; de la Cruz, M.; Kokkini, M.; Martín, J.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. Phocoenamicins B and C, New Antibacterial Spirotetronates Isolated from a Marine Micromonospora sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Ding, W.; Huang, H.; Gu, Y.-C.; Duan, Y.; Ju, J. Antimicrobial Spirotetronate Metabolites from Marine-Derived Micromonospora harpali SCSIO GJ089. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ling, C.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Q.; Wei, X.; Ju, J. Abyssomicin Monomers and Dimers from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinger, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miller, M.D.; Hall, R.E.; Van Lanen, S.G.; Phillips, G.N., Jr.; Thorson, J.S.; Elshahawi, S.I. Structure and Function of a Dual Reductase–Dehydratase Enzyme System Involved in p-Terphenyl Biosynthesis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Che, Q.; Xing, L.; Ma, C.; Han, Y.; Zhu, T.; Pfeifer, B.A.; Peng, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, D. Antibacterial p-Terphenyl with a Rare 2,2′-Bithiazole Substructure and Related Compounds Isolated from the Marine-Derived Actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. HDN154086. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Priyadharsini, S.; Sajayan, A.; Priyadharsini, G.B.; Poulose, N.; Selvin, J. Production of Lipopeptide Biosurfactant by a Marine Nesterenkonia sp. and Its Application in Food Industry. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Sajayan, A.; Priyadharshini, G.; Balakrishnan, A.; Prathiviraj, R.; Sabu, A.; Selvin, J. A novel anti-infective molecule nesfactin identified from sponge associated bacteria Nesterenkonia sp. MSA31 against multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 157, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareq, F.S.; Shin, H.J. Bacilotetrins A and B, anti-Staphylococcal cyclic-lipotetrapeptides from a marine-derived Bacillus subtilis. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2889–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tan, Y.; Hu, X.; He, H.; Xiao, C.; You, X.; Wang, Y.; Gan, M. Neo-actinomycins A and B, natural actinomycins bearing the 5H-oxazolo[4,5-b]phenoxazine chromophore, from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. IMB094. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.-H.; Yuan, W.; Li, Z.-Y.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J.-B.; Gui, Y.-H.; Wang, J.; Ye, B.-P.; Lin, H.-W. Anti-MRSA actinomycins D1-D4 from the marine sponge-associated Streptomyces sp. LHW52447. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 5914–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaz, A.W.; Yong, K.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Streptoindoles A–D, novel antimicrobial indole alkaloids from the marine-associated actinomycete Streptomyces sp. ZZ1118. Tetrahedron 2021, 104, 132598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wong, N.-K.; Ju, J. Chlorinated bis-indole alkaloids from deep-sea derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 11791 with antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Braun, D.R.; Chanana, S.; Rajski, S.R.; Bugni, T.S. Phallusialides A–E, Pyrrole-Derived Alkaloids Discovered from a Marine-Derived Micromonospora sp. Bacterium Using MS-Based Metabolomics Approaches. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3432–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Adnani, N.; Braun, D.R.; Ellis, G.A.; Barns, K.J.; Parker-Nance, S.; Guzei, I.A.; Bugni, T.S. Micromonohalimanes A and B: Antibacterial Halimane-Type Diterpenoids from a Marine Micromonospora Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2968–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Li, Q.; Song, T.; Chen, L.; Li, X.-C.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, X.-Y. Isolation, structure elucidation, and antibacterial evaluation of the metabolites produced by the marine-sourced Streptomyces sp. ZZ820. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xie, F.; Ren, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Liu, M.; Han, J.; Oyeleye, A.; et al. Anti-MRSA and anti-TB metabolites from marine-derived Verrucosispora sp. MS100047. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 7437–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, Z.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y. Maipomycin A, a Novel Natural Compound With Promising Anti-biofilm Activity Against Gram-Negative Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 598024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yi, W.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B. Bioactive Streptoglutarimides A–J from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. ZZ741. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asolkar, R.N.; Singh, A.; Jensen, P.R.; Aalbersberg, W.; Carté, B.K.; Feussner, K.-D.; Subramani, R.; DiPasquale, A.; Rheingold, A.L.; Fenical, W. Marinocyanins, cytotoxic bromo-phenazinone meroterpenoids from a marine bacterium from the streptomycete clade MAR4. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerna, N.M.; Miller, B.W.; Lim, A.L.; Tun, J.O.; Robes, J.M.D.; Cleofas, M.J.B.; Lin, Z.; Salvador-Reyes, L.A.; Haygood, M.G.; Schmidt, E.W.; et al. Mindapyrroles A–C, Pyoluteorin Analogues from a Shipworm-Associated Bacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| No. | Bacterial Strain | Source | Compounds and Their Activities | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bacillus subtilis 109GGC020 | Sediment sample from the Gageocho reef, Republic of Korea | 55 and 56 active against MRSA | [39] |
| 2. | Kibdelosporangium phytohabitans XY-R10 | Root sediments of a mangrove plant, Kandelia candel (L.) Druce, from Mai Po Inner Deep Bay Ramsar Site | 79 active against A. baumanii as antibiofilm | [48] |
| 3. | MAR4 clade within the Streptomycetaceae strains CNS-284 and CNY-960 | Sediment sample from Solomon Islands | 90–95 active against amphotericin B-resistant C. albicans | [50] |
| 4. | Micromonospora harpali SCSIO GJ089 | Sediment from Northern South China Sea | 43 and 44 active against MRSA | [33] |
| 5. | Micromonospora sp. CA-214671 | from the Canary Island | 40 and 41 active against MRSA | [32] |
| 6. | Micromonospora sp. RJA4480 | Marine sediment from Barkley Sound, British Columbia | 18–21 active against MRSA | [20] |
| 7. | Micromonospora sp. WMMA-2495 | Tunicate, Phallusia nigra, from Florida Keys | 71 and 72 active against MRSA | [44] |
| 8. | Micromonospora sp. WMMC-218 | Ascidian, Symplegma brakenhielmi, Florida at Stanblum State Park, USA | 74 active against MRSA | [45] |
| 9. | Nesterenkonia sp. MSA31 | Marine sponge, Fasciospongia cavernosa, from southwest coast of India | 54 against MDR-P.aeruginosa | [38] |
| 10. | Nocardiopsis sp. HDN154086 | Marine sediment from South China Sea | 52 and 53 active against MRSA, Proteus sp. and B. subtilis | [36] |
| 11. | Nocardiopsis sp. strain HB-J378 | Deep-sea sediment | 1–3 active against MRSA | [12] |
| 12. | Nonomuraea sp. strain MM565M-173N2 | Deep-sea sediment from Japan trench | 10–13 active against MDR-E. coli and MDR-K. pneumoniae, MRSA, and VRE | [16] |
| 13. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 1682U.R.0a.27 | Gill tissue homogenate of the giant shipworm, Kuphus polythalamius, from Sultan Kudarat, Mindanao, Philippines | 96 and 97 active against MRSA. 96 also active against P. aeruginosa and E. faecium | [51] |
| 14. | Shewanella algae MTCC 12715 | Red algae, Hypnea valentiae, from the Gulf of Mannar, India | 28 and 29 active against MRSA and VRE | [25] |
| 15. | Streptomyces althioticus MSM3 | Seaweed, Ulva sp., from the Cantabrian Sea | 39 active against M. tuberculosis, S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, Clostridium perfringens, C. urealyticum, E. faecalis, E. Faecium, B. fragilis, H. influenzae and N. meningitidis | [30] |
| 16. | Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-169 | Gorgonian coral from Avilés submarine Canyon, Cantabrian Sea | 26 active against MRSA, MSSA, E. faecium, E. faecalis | [23] |
| 17. | Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802 | Marine sediment from Northern South China Sea | 50 and 51 active against MRSA | [34] |
| 18. | Streptomyces pratensis strain NA-ZhouS1 | Marine sediment in Zhoushan, East China Sea | 4 and 5 active against B. stubtilis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, MRSA, P. aeruginosa | [13] |
| 19. | Streptomyces sp. 1425S.R.1a.1 | Mollusk, Truncatella guerinii, from Cebu, Philippines | 24 active against MRSA | [21] |
| 20. | Streptomyces sp. 182SMLY | Marine sediment | 6 active against MRSA | [14] |
| 21. | Streptomyces sp. CA-271078 | - | 15 and 17 active against MRSA and M. tuberculosis | [18] |
| 22. | Streptomyces sp. EG1 | Marine sediment | 25 active against MRSA | [22] |
| 23. | Streptomyces sp. EG32 | Marine sediment from North Coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt | 8 and 9 active against MRSA | [15] |
| 24. | Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E | Seaweed Ulva pertusa from Turtle Islet Guangdong, China | 33 active against MRSA | [27] |
| 25. | Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E | Seaweed, Ulva pertusa, from Turtle Islet Guangdong, China | 30 and 31 active against MRSA | [26] |
| 26. | Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E | Seaweed, Ulva pertusa, from Turtle Islet Guangdong, China | 70 active against MRSA | [26] |
| 27. | Streptomyces sp. IMB094 | Marine sediment Heishijiao Bay, Dalian, China | 57 active against MRSA and VRE | [40] |
| 28. | Streptomyces sp. IMB7-145 | Marine sediment at -40 m in Heishijiao Bay, Dalian, China | 34–37 active against MRSA, MRSE, and VRE. 34 also active against MDR-TB | [28] |
| 29. | Streptomyces sp. LHW52447 | Marine sponge, Phyllospongia foliascens, in Xisha Islands in the South China Sea | 60–63 active against MRSA | [41] |
| 30. | Streptomyces sp. MBTI36 | Marine sediment | 14 active against MRSA | [17] |
| 31. | Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 11791 | Deep-sea sediment from South China Sea | 68 and 69 active against MRSA | [43] |
| 32. | Streptomyces sp. ZZ1118 | Marine shrimp (Penaeus sp.) in Zhoushan archipelago, Zhejiang, China | 64, 65, and 67 active against MRSA | [42] |
| 33. | Streptomyces sp. ZZ741 | Sea mud in Jintang Island Zhoushan, China | 80–89 active against MRSA | [49] |
| 34. | Streptomyces sp. ZZ820 | Coastal soil in Zhoushan Archipelago (Zhejiang, China) | 75–77 active against MRSA | [46] |
| 35. | Verrucosispora sp. strain MS100047 | Deep-sea sediment from South China Sea | 78 active against MRSA | [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wibowo, J.T.; Bayu, A.; Aryati, W.D.; Fernandes, C.; Yanuar, A.; Kijjoa, A.; Putra, M.Y. Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria with Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activities against Drug-Resistant Pathogens. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21010050
Wibowo JT, Bayu A, Aryati WD, Fernandes C, Yanuar A, Kijjoa A, Putra MY. Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria with Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activities against Drug-Resistant Pathogens. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleWibowo, Joko Tri, Asep Bayu, Widya Dwi Aryati, Carla Fernandes, Arry Yanuar, Anake Kijjoa, and Masteria Yunovilsa Putra. 2023. "Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria with Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activities against Drug-Resistant Pathogens" Marine Drugs 21, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21010050
APA StyleWibowo, J. T., Bayu, A., Aryati, W. D., Fernandes, C., Yanuar, A., Kijjoa, A., & Putra, M. Y. (2023). Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria with Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activities against Drug-Resistant Pathogens. Marine Drugs, 21(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21010050