Abstract
Six new diketopiperazines, (±)-7,8-epoxy-brevianamide Q ((±)-1), (±)-8-hydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-2), and (±)-8-epihydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-3), together with four known compounds, (±)-brevianamide R ((±)-4), versicolorin B (5) and averufin (6), were isolated from a marine-derived fungus strain Aspergillus versicolor MF180151, which was recovered from a sediment sample collected from the Bohai Sea, China. The chemical structures were established by 1D- and 2D-NMR spectra and HR-ESI-MS. 1 is the first sample of brevianamides with an epoxy moiety. Their bioactivities were evaluated against Candida albicans, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant S. aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Compounds 1–4 showed no activities against the pathogens, and compounds 5 and 6 showed moderate activities against S. aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
1. Introduction
Marine-derived fungi are revealed to be excellent resources for novel secondary metabolites and many lead compounds have been characterized for drug development [1,2,3]. Aspergillus versicolor, a slow-growing filamentous fungus, normally are found in air, soil, marine sediment, corrupted plants, and agricultural products. Previous chemical investigations on the fungus Aspergillus versicolor from different environments have resulted in the identification of new secondary metabolites with a variety of structures, such as alkaloids [4,5,6,7,8,9], anthraquinones [10,11,12,13,14], xanthones [15,16,17,18,19], diphenyl ethers [20,21], lactones [22,23,24,25,26], peptides [27], polyketide [28], terpenoids [29,30], and varicuothiols [31].
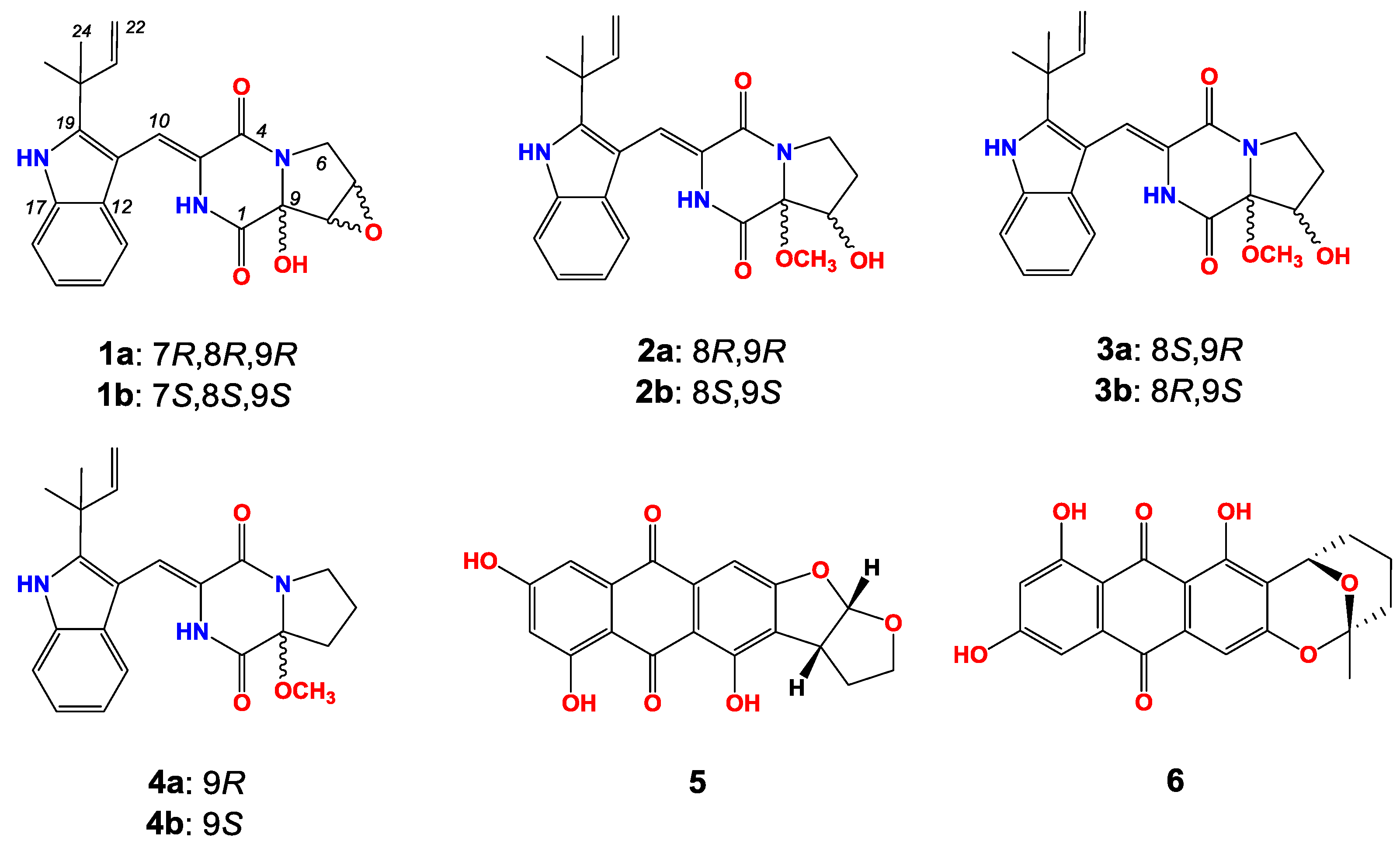
During our continuous screening of new secondary metabolites from marine Aspergillus versicolor, six new diketopiperazines ((±)-1–(±)-3) named as (±)-7,8-epoxy-brevianamide Q, (±)-8-hydroxy-brevianamide R, and (±)-8-epihydroxy-brevianamide R along with four known compounds (±)-brevianamide R, versicolorin B and averufin ((±)-4–6, Figure 1) were isolated from the culture material of a marine-derived fungus strain Aspergillus versicolor MF180151. Compound 1 is the first sample of brevianamides with an epoxy moiety. In this paper, we describe the fermentation, isolation, structure elucidation and preliminary bioactivities of these compounds.
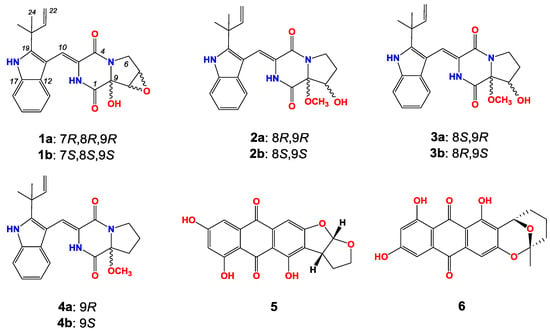
Figure 1.
The structures of compounds 1–6.
2. Results
2.1. Characterization and Identification of the Isolated Strain MF180151
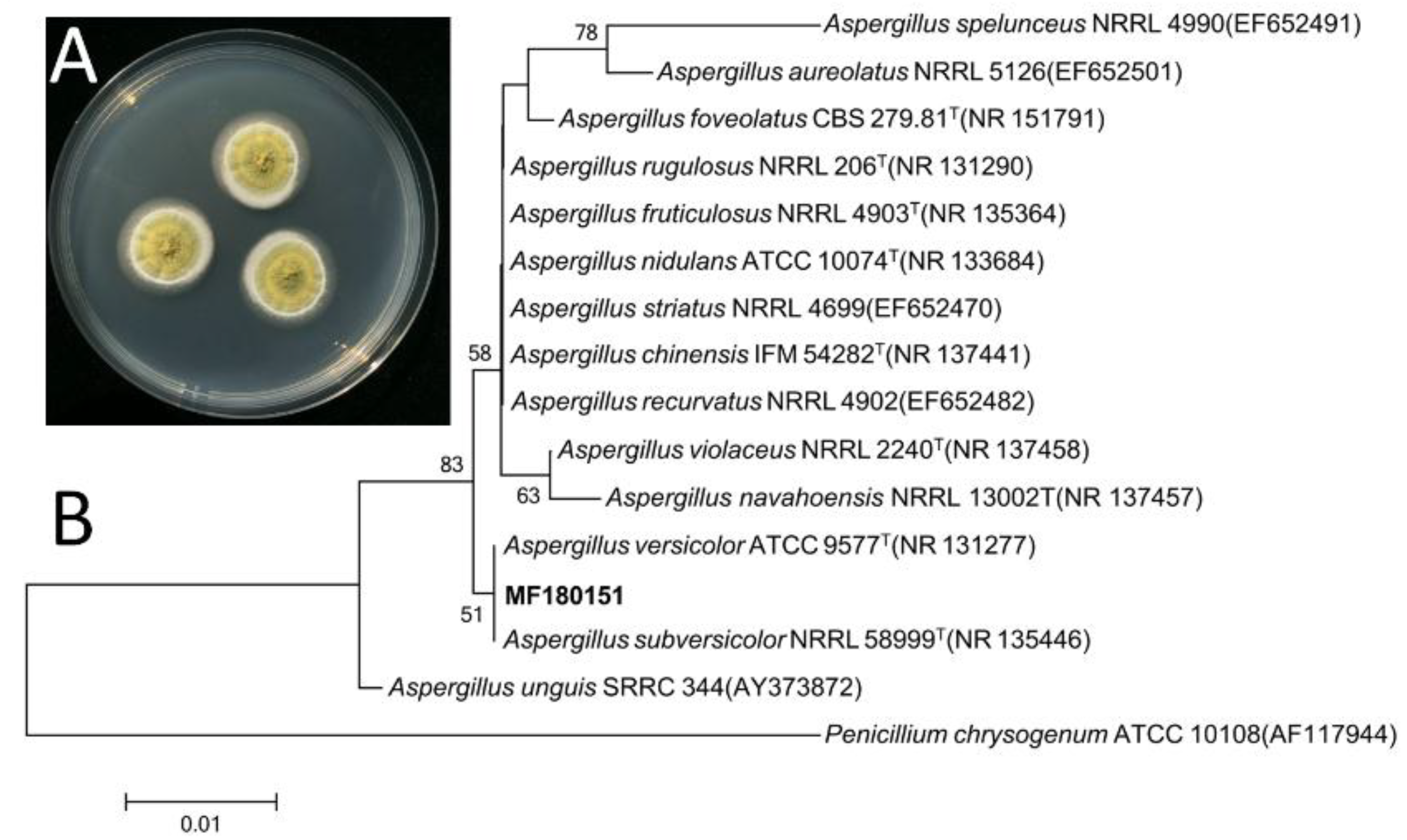
The strain MF180151 was isolated from a marine sediment sample from the Bohai Sea, China. The identification of the strain was performed based on the morphology and phylogenetic analysis.
The ITS gene region of ribosomal DNA of the strain was PCR-amplified and sequenced. By comparing the ITS sequence to GenBank, it was indicated that the strain MF180151 belonged to the genus Aspergillus and shared a highest similarity with Aspergillus versicolor (99.66%). The phylogenetic tree based on ITS gene sequence revealed that the strain MF180151 formed a distinct phylogenetic cluster with A. versicolor (Figure 2) with a bootstrap value above 95%.
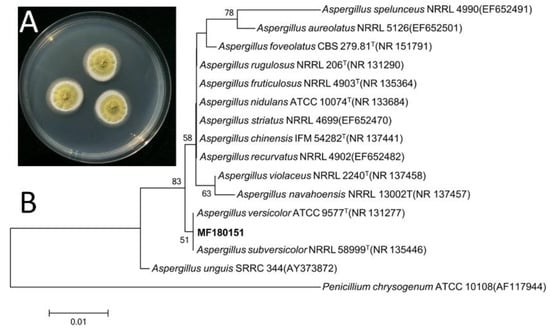
Figure 2.
Morphology and neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of strain MF180151. A: The morphology of the strain MF180151; B: The neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of strain MF180151, numbers at nodes indicate levels of bootstrap support (%) based on a neighbor-joining analysis of 1,000 resampled datasets; only values >50% are given.
2.2. Structure Elucidation
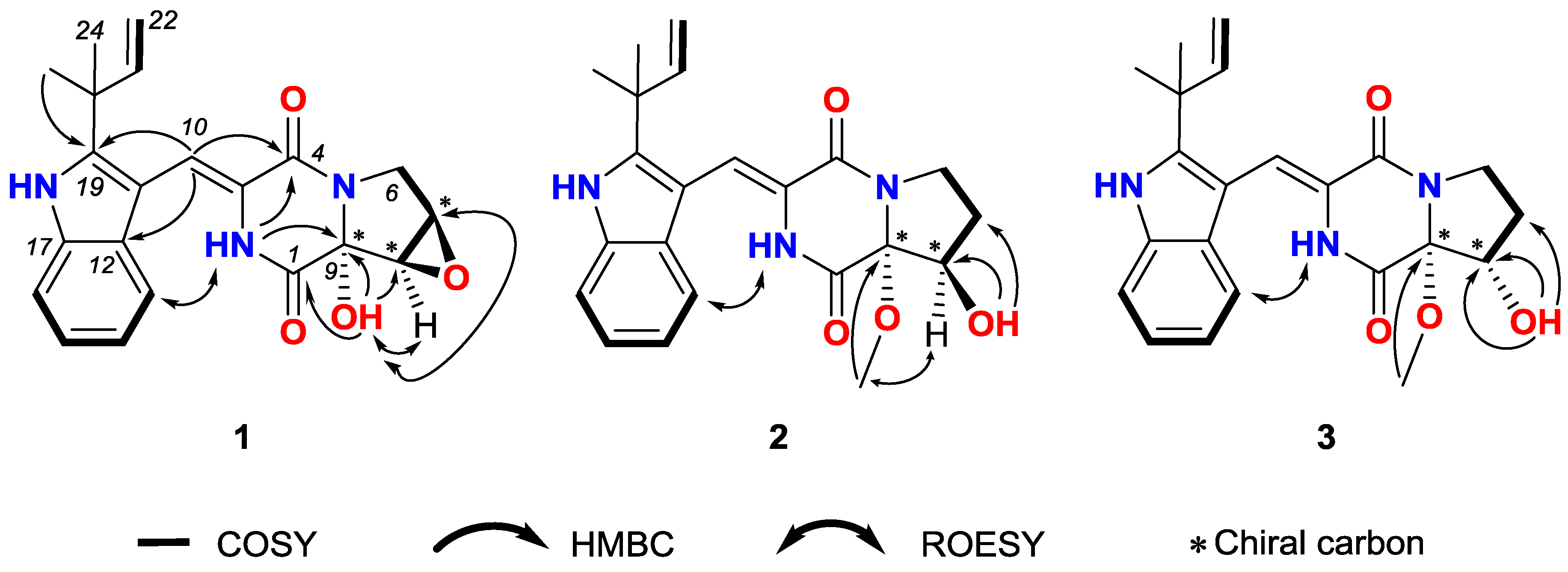
(±)-7,8-Epoxy-brevianamide Q ((±)-1) were isolated as a light yellow amorphous powder. The molecular formula of 1 was established as C21H21N3O4 by HRESIMS (m/z 380.1608 [M + H]+ showed in Figure S7, calcd for C21H22N3O4: 380.1605). The planar structure of 1 was determined by 1D and 2D NMR spectra analyses, including 1H, 13C, 1H-1H homonuclear correlated spectroscopy (COSY), heteronculear single quantum coherence (HSQC) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC, Figures S1–S5). The 1H and 13C NMR data of 1 is tabulated in Table 1, which revealed the moieties of indole, diketopiperazine, prenyl, and one isolated double bond. Further analyses of 2D NMR data confirmed these moieties. Additionally, the HMBC correlations from the methyl groups (δH 1.50 and 1.45, H3-23 and H3-24) to C-19 (δC 144.6), C-20 (δC 39.0) and C-21 (δC 145.1) suggested that C-20 of the prenyl was attached to C-19 of the indole moiety. The HMBC crossing peaks from H-10 (δH 7.02) to C-12 (δC 126.2), C-19 (δC 144.6) and C-4 (δC 160.2) revealed that the diketopiperazine and indole moieties were connected by double bond of C-3 (δC 124.5) and C-10 (δC 113.4). The connectivity among C-1, C-9 and C-8 was confirmed by the HMBC correlations from 9-OH (δH 7.54) to C-1 (δC 163.1), C-9 (δC 86.0) and C-8 (δC 57.4). Thus the planar structure of 1 was assigned as shown in Figure 1. The rotating frame overhauser effect spectroscopy (ROESY, Figure S6) correlation between 2-NH (δH 9.37) and H-13 (δH 7.32) suggested the cis form of the double bond between C-3 and C-10. The ROESY signal from 9-OH (δH 7.54) to H-7 (δH 3.95)/H-8 (δH 3.93) revealed the relative configurations of 1 (Figure 3).

Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR data (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) for compounds 1–3.
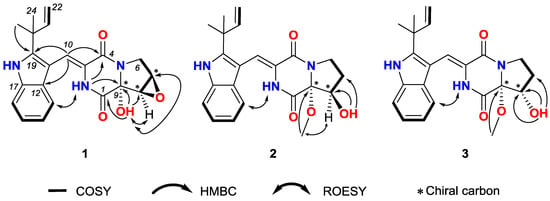
Figure 3.
COSY, Key HMBC and ROESY correlations of compounds 1–3.
(±)-8-Hydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-2) were isolated as a light yellow amorphous powder. The molecular formula of 2 was established as C22H25N3O4 by HRESIMS (m/z 396.1912 [M + H]+ showed in Figure S15, calcd for C22H26N3O4: 396.1918). Analyses of the 1H, 13C, COSY and HSQC NMR data (Table 1, Figures S9–S11, S13) revealed that 2 possessed the same carbon skeleton as that of 1. By comparing the NMR data of 2 with those of brevianamide U [9] and brevianamide R [32], it was revealed that 2 was methylated at the 9-hydroxyl group of brevianamide U, which was confirmed by the HMBC (Figure S12) crossing peak from 9-OMe (δH 3.23) to C-9 (δC 94.5). The 8-hydroxyl group was confirmed by the HMBC correlations from 8-OH (δH 5.52) to C-7 (δC 28.4), C-8 (δC 74.0) and C-9 (δC 94.5). Thus, the planer structure of 2 was assigned. In the ROESY (Figure S14) spectrum of 2, the correlation between 2-NH (δH 9.25) and H-13 (δH 7.14) suggested the cis form of double bond between C-3 and C-10. And the ROESY correlations between 9-OMe (δH 3.23) and H-8 (δH 4.22), and the absence between 9-OMe (δH 3.23) and 8-OH (δH 5.52) indicated that 9-OMe and H-8 were cis form. Therefore, the relative configurations of 2 was established as shown in Figure 3.
(±)-8-Epihydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-3) were isolated as a light yellow amorphous powder. The molecular formula of 3 was established as C22H25N3O4 by HRESIMS (m/z 396.1921 [M+H]+ showed in Figure S22, calcd for C22H26N3O4: 396.1918). By comparing the 1H, 13C NMR, COSY and HSQC data (Table 1, Figures S17–S19, S21) of 3 with those of 2, it is revealed that 3 possessed the similar structure as that of 2. Analyses of the 2D NMR data suggested the same planer structure of 3 and 2. The 8-hydroxyl group was confirmed by the HMBC (Figure S20) correlations from 8-OH (δH 5.14) to C-7 (δC 27.6), C-8 (δC 73.6) and C-9 (δC 87.1). And the HMBC signal from 9-OMe (δH 3.42) to C-9 (δC 87.1) revealed the methyoxyl group at C-9. In the ROESY (Figure S22) spectrum of 3, the correlation between 2-NH (δH 9.35) and H-13 (δH 7.22) suggested the cis form of double bond between C-3 and C-10. By comparison the chemical shift of C-9 for 3 with that of 2, 3 was established as an epimer of 2, with the relative configuration of 9-OCH3 and 8-OH being cis and named as (±)-8-epihydroxy-brevianamide R which was shown in Figure 3.
(±)-1–(±)-3 did not show significant CD spectra absorption (Figure S8, S16, and S23) and optical rotations, +3.00 (c 0.1, CH3OH) for (±)-1, +1.00 (c 0.1, CH3OH) for (±)-2, and +2.00 (c 0.1, CH3OH) for (±)-3, which indicated that (±)-1–(±)-3 were racemic mixtures.
Additionally, the structures of the three known compounds were identified as (±)-brevianamide R ((±)-4) [32], versicolorin B (5) [33] and averufin (6) [34] based on its HRESIMS, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR data and comparing with previous reports.
2.3. Biological Activities
The biological activity of those compounds were evaluated against pathogens of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), C. albicans, B. subtilis, S. aureus, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), and P. aeruginosa. The new diketopiperazines (±)-1–(±)-3 and (±)-brevianamide R ((±)-4) showed no significant antibacterial activities against those pathogens. Versicolorin B (5) exhibited moderate activities against S. aureus and MRSA with the MIC values of 6.25 µg/mL and 12.5 µg/mL. Simultaneously, averufin (6) exhibited moderate activities against S. aureus and MRSA with the MIC values of 6.25 µg/mL and 25 µg/mL (Table 2).

Table 2.
Antimicrobial Activities of 1–6.
3. Discussion
Brevianamides belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazine alkaloids, which are mainly produced by fungi of Penicillium and Aspergillus [6,9,32,35,36]. In this research, three pairs of new brevianamides ((±)-1–(±)-3) were isolated and their relative configurations were elucidated according to the 1D, 2D NMR, HRESIMS, UV. But, the specific optical rotation analysis and CD showed that these compounds were racemic mixtures. In more than 24 brevianamides, the hydroxy-substitution were mainly occurred at C-8 or/and C-9. In our research, (±)-7,8-epoxy-brevianamide Q ((±)-1) was discovered as the first brevianamide analogues with an epoxy substitution. Compounds (±)-1–(±)-4 did not exhibit antifungal and antibacterial activities against C. albicans, B. subtilis, S. aureus, MRSA, P. aeruginosa and Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (MIC >100 µg/mL). Versicolorin B (5) exhibited moderate activities against S. aureus and MRSA with the MIC values of 6.25 µg/mL and 12.5 µg/mL. Simultaneously, averufin (6) exhibited moderate activities against S. aureus and MRSA with the MIC values of 6.25 µg/mL and 25 µg/mL.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Details
Specific optical rotations ([α]D) were measured on AntonPaar MCP 200 polarimeter (Anton Paar GmbH, Graz, Austria) in a 100 × 2 mm cell. CD spectra were measured on Chirascan spectropolarimeter (Applied Photophysics Ltd., Leatherhead, UK) in 1 mm quartz cells. UV-visible spectra were obtained on a Cary 50 spectrophotometer (Varian Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) in 1 cm quartz cells. NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker Avance DRX600 spectrometer (Bruker BioSpin Corp., Billerica, MA, USA) at 600 MHz for 1H and 13C NMR. Chemical shifts were calibrated using residual solvent signals (DMSO-d6: δC 39.5, δH 2.50). High-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry measurements were obtained on an Agilent 6520QTOF mass spectrometer (Aglient Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). TLC H silica (Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China), Sephadex LH-20 (GE Healthcare BioSciences AB, Uppsala, Sweden) were used for purification. Analytical and semipreparative HPLC was performed using Agilent 1100 or 1200 Series separations modules equipped with Agilent 1100 or 1200 Series diode array detectors and fraction collectors, controlled using ChemStation Rev.B.02.01 (Aglient Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA).
4.2. Fungal Culture and Identification
The strain MF180151 was isolated from a marine sediment sample from the Bohai Sea, China. It was incubated on potato dextrose agar (PDA) plate consisting (0.4% potato starch, 2% dextrose, and 2% agar) at 28 °C. The identification was performed based on the morphology and phylogenetic analysis. The whole genomic DNA of the strain was extracted using the E.Z.N.A. kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA). A pair of primers (ITS4: 5″-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3″; ITS5: 5″-GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG-3″) was used to amplify the ITS region of MF180151. PCR amplification (50.0 μL final volume: 25 μL 2 × Taq Master Mix, 2 μL of 10 μM of each primer, 5.0 μL DNA template and 16 μL ddH2O) of the ITS sequence was performed on Bio-gener PCR Thermal Cycler with the initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, 32 cycles of denaturation (94 °C, 15 s), annealing (60 °C, 15 s), and elongation (72 °C, 60 s), and a final elongation at 72 °C for 5 min. After multiple alignments of ITS sequence of the related species by CLUSTAL W [37], phylogenetic analysis was constructed using neighbor-joining method with bootstrap values based on 1000 replications by MEGA 5.0 [38,39].
The strain was deposited at the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The nucleotide sequences of ITS gene (accession number MK680178) of A. versicolor MF180151 were deposited in GenBank.
4.3. Fermentation, Extraction and Isolation
The strain MF180151 was cultured on potato dextrose agar plate at 28 °C for 7 days. Mature colonies were cut into small pieces (about 1 cm2) under aseptic conditions. Then, three piece of the strain was inoculated into three 250 mL conical flasks, each containing 40 mL of liquid medium consisting of potato infusion (20%), glucose (2.0%), artificial sea salt (3.5%) and distilled artificial seawater, at 28 °C for 3 d on a rotary shaker at 160 rpm. An aliquot (5 mL) of the resultant seed culture was inoculated into twelve 1 L conical flasks, each containing solid medium consisting of rice (100 g) and artificial seawater (30 mL), and the flasks were incubated stationary for 28 d at 20 °C.
The whole culture media was extracted exhaustively with EtOAc:MeOH (80:20). The combined extracts were reduced to dryness in vacuo and the residue was partitioned between EtOAc and H2O. The EtOAc layer (10.3 g) was subjected to a normal phase silica gel chromatography (60 × 80 mm column, TLC H silica) using a stepwise gradient of 50–100% hexane/CH2Cl2 and then 0–100% MeOH/CH2Cl2 to afford 15 fractions (500 mL each). The ninth fraction was chromatographed over a Sephadex LH-20 column (700 × 30 mm) using an isocratic elution of hexane: CH2Cl2:MeOH (5:5:1), to give four subfractions (F1–F4; 100 mL each). Subfraction F3 (205.6 mg) was further purified by HPLC (Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 250 × 9.4 mm, 5 μm column, 3.0 mL/min, isocratic 65% MeCN/H2O) to yield 1 (3.5 mg), 2 (4.2 mg), 3 (5.7 mg), and 4 (4.8 mg). The eighth fraction was purified by HPLC (Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 250 × 9.4 mm, 5 μm column, 3.0 mL/min, isocratic 60% MeCN/H2O) to yield 5 (3.9 mg) and 6 (6.7 mg).
4.4. Biological Activities
The biological activities of isolated compounds were assessed according to the previous report [9]. A panel of human pathogens were used for the assay, including B. subtilis (ATCC 6633), S. aureus (ATCC 6538), methicillin-resistant S. aureus (clinical strain from Chaoyang Hospital, Beijing, China), and Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (Pasteur 1173P2), P. aeruginosa (ATCC 15692), and fungus C. albicans (SC 5314).
For general antimicrobial assays, a single colony which was incubated on an LB agar overnight at 37 °C was picked up and suspended in Mueller-Hinton Broth to approximately 1 × 104 cfu/mL. For anti-C. albicans assay, a colony of C. albicans incubated on a YPD agar plate was picked and suspended in RPMI 1640 to a concentration of 1 × 104 cfu/mL. A twofold serial dilution of each compound to be tested was prepared, and an aliquot of each dilution (2μL) was added to a 96-well flat-bottom microtiter plate (Greiner). Vancomycin, ciprofloxacin and ketoconazole were used as the positive control and DMSO as the negative control. An aliquot (78 µL) of suspension was then added to each well (to give final compound concentrations of 100 to 0.78 µg/mL in 2.5% DMSO) and the plate was incubated at 37 °C aerobically for 16 h. The MIC was defined as the minimum concentration of the compound that prevented visible growth of the tested bacteria. All the experiments were performed in triplicate.
The strain Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (Pasteur 1173P2) used for the anti-BCG assay was transformed with green fluorescent protein (GFP) constitutive expression plasmid pUV3583c with direct readout of fluorescence as a measure of bacterial growth. The strain was incubated to mid log phase (7 d) at 37 °C in Middle brook 7H9 broth (40 mL; Difco) supplemented with 10% OADC enrichment (Becton Dickinson), 0.05% Tween-80 and 0.2% glycerol and then diluted to an OD600 of 0.025 with broth. Aliquots (80 μL) of the bacterial suspension were added to each well of the 96-well micro plates (clear flat-bottom), followed by adding compounds (2 μL in DMSO), which were serially twofold diluted. Isoniazid served as positive control and DMSO as negative control. The plate was incubated at 37 °C for 3 days, and GFP fluorescence was measured with Multi-label Plate Reader using the bottom read mode, with excitation at 485 nm and emission at 535 nm. MIC is defined as the minimum concentration of drug that inhibits more than 90% of bacterial growth reflected by fluorescence value.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/17/5/262/s1, Figures S1–S8: 1D, 2D NMR, HRESIMS, UV and CD spectra of (±)-7,8-epoxy-brevianamide Q ((±)-1), Figures S9–S16: 1D, 2D NMR, HRESIMS, UV and CD spectra of (±)-8-hydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-2), Figures S17–S23: 1D, 2D NMR, HRESIMS, UV and CD spectra of (±)-8-epihydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-3).
Author Contributions
Data curation, J.H. and Z.L.; Investigation, J.H., J.G., H.H., Z.L., H.D. and X.X.; Supervision, F.S., L.Z. and C.L.; Writing—original draft, J.H. and F.S.; review & editing, L.Z., C.L. and F.S.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0311002, 2017YFD0201203, 2017YFC1601300, 2017YFE0108200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31600136, 31430002, 31720103901), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Public Welfare Research Institutes (Z0547). Taishan Scholarship for Lixin Zhang and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities 22221818014.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Na. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Na. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Lefranc, F.; Kijjoa, A.; Kiss, R. Can some marine-derived fungal metabolites become actual anticancer agents? Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 3950–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, W.; Deng, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Qi, C.; Luo, Z.; Xue, Y.; et al. Asperversiamides, Linearly fused prenylated indole alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 8483–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.A.; Tao, X.; Wu, B. New compounds from a hydrothermal vent crab-associated fungus Aspergillus versicolor XZ-4. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; Ai, J.; Geng, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Prenylated indole diketopiperazines from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 7895–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Miao, M.M.; Du, G.; Li, X.N.; Shang, S.Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, G.Y.; Che, C.T.; Hu, Q.F.; et al. Aspergillines A-E, highly oxygenated hexacyclic indole-tetrahydrofuran-tetramic acid derivatives from Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5016–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.B.; Gui, Y.H.; Liu, L.; Su, Z.Y.; Jiao, W.H.; Li, L.; Sun, F.; Wang, S.P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.W. A new asymmetric diketopiperazine dimer from the sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus versicolor 16F-11. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Piggott, A.M.; Yu, K.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; et al. Brevianamides with antitubercular potential from a marine-derived isolate of Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4770–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, D.; Wang, H.; Jiao, Y.; Lou, H.; Wang, X. Metabolites from Aspergillus versicolor, an endolichenic fungus from the lichen Lobaria retigera. Drug Discov. Ther. 2014, 8, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawas, U.W.; El-Beih, A.A.; El-Halawany, A.M. Bioactive anthraquinones from endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor isolated from red sea algae. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Nong, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, S. Anti-HSV-1, antioxidant and antifouling phenolic compounds from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 41502. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, R.; Luo, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. Antimicrobial activity and molecular docking studies of a novel anthraquinone from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. Anthraquinone derivatives produced by marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor EN-7. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1774–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Yu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; et al. Three new sterigmatocystin analogues from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor MF359. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yu, G.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Peng, J.; Mo, X.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; et al. Versixanthones A-F, cytotoxic xanthone-chromanone dimers from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor HDN1009. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, W.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Versicones E-H and arugosin K produced by the mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor HDN11-84. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo). 2017, 70, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.H.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Lin, W.H. Antioxidant xanthones and anthraquinones isolated from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wu, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Che, Q.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D.; Zhang, G. Cytotoxic tetrahydroxanthone dimers from the mangrove-associated fungus Aspergillus versicolor HDN1009. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Zhou, L.; Cai, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Diorcinols B-E, new prenylated diphenyl ethers from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo). 2013, 66, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.B.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhu, R.X.; Chang, W.Q.; Yuan, H.Q.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, Z.T.; Lou, H.X. Identification and biological evaluation of secondary metabolites from the endolichenic fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Xu, P.; Li, T.; Liao, X.; He, S.; Xu, S. Asperfurandiones A and B, two antifungal furandione analogs from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.X.; Meng, D.D.; Wang, Y.; An, J.L.; Bai, J.F.; Jia, X.W.; Xu, C.P. Antioxidant coumarin and pyrone derivatives from the insect-associated fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, M.; Hao, H.; Lu, C. Avertoxins A-D, prenyl asteltoxin derivatives from Aspergillus versicolor Y10, an endophytic fungus of Huperzia serrat. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 3067–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Du, G.; Yang, H.Y.; Xia, C.F.; Yang, J.X.; Ye, Y.Q.; Gao, X.M.; Li, X.N.; Hu, Q.F. Antiviral butyrolactones from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Planta. Med. 2015, 81, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Lou, J.; Li, Y.K.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhou, K.; Ji, B.K.; Dong, W.; Gao, X.M.; Du, G.; Hu, Q.F. Versicolols A and B, two new prenylated isocoumarins from endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor and their cytotoxic activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Hai, Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Aspersymmetide A, a new centrosymmetric cyclohexapeptide from the marine-derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salendra, L.; Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Versispiroketal A, an unusual tetracyclic bridged spiroketal from the sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 41013. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2182–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Tan, M.H.; Liu, C.X.; Lv, M.M.; Deng, Z.S.; Cao, F.; Zou, K.; Proksch, P. Aspergoterpenins A⁻D: four new antimicrobial bisabolane sesquiterpenoid derivatives from an endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Molecules 2018, 23, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, W.; Deng, M.; Qi, C.; Chen, C.; Zhu, H.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y. Asperversins A and B, two novel meroterpenoids with an unusual 5/6/6/6 ring from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Varicuothiols A and B, new fungal metabolites from Aspergillus versicolor with anti-Inflammatory activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Y.; Li, L.M.; Yang, T.; Chen, X.Z.; Fang, D.M.; Zhang, G.L. Four New Alkaloids, Brevianamides O – R, from the Fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2010, 93, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšić, D.; Puel, O.; Canlet, C.; Kopjar, N.; Kosalec, I.; Klarić, M.Š. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of versicolorins and 5-methoxysterigmatocystin in A549 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Li, C.W.; Cui, C.B. Seven new and two known lipopeptides as well as five known polyketides: The activated production of silent metabolites in a marine-derived fungus by chemical mutagenesis strategy using diethyl sulphate. Mar. Drugs. 2014, 12, 1815–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Lan, M.; Zhu, W.; Sun, K. Diketopiperazine and diphenylether derivatives from marine algae-derived Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 by epigenetic activation. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Wang, J.; Qi, S. Brevianamides and mycophenolic acid serivatives from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium brevicompactum DFFSCS025. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTALW: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).