Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
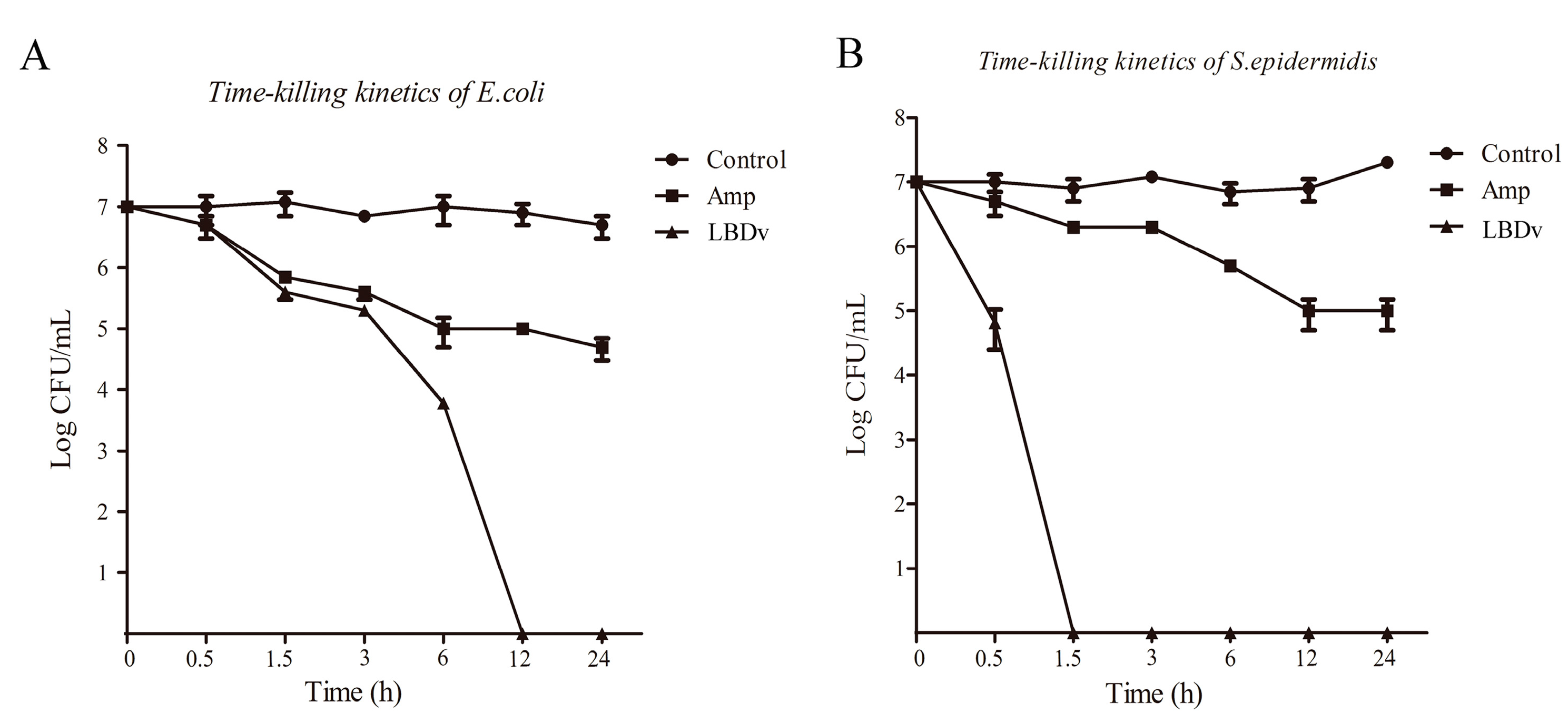
2.1. Antibacterial and Bactericidal Activity of LBDv Peptides
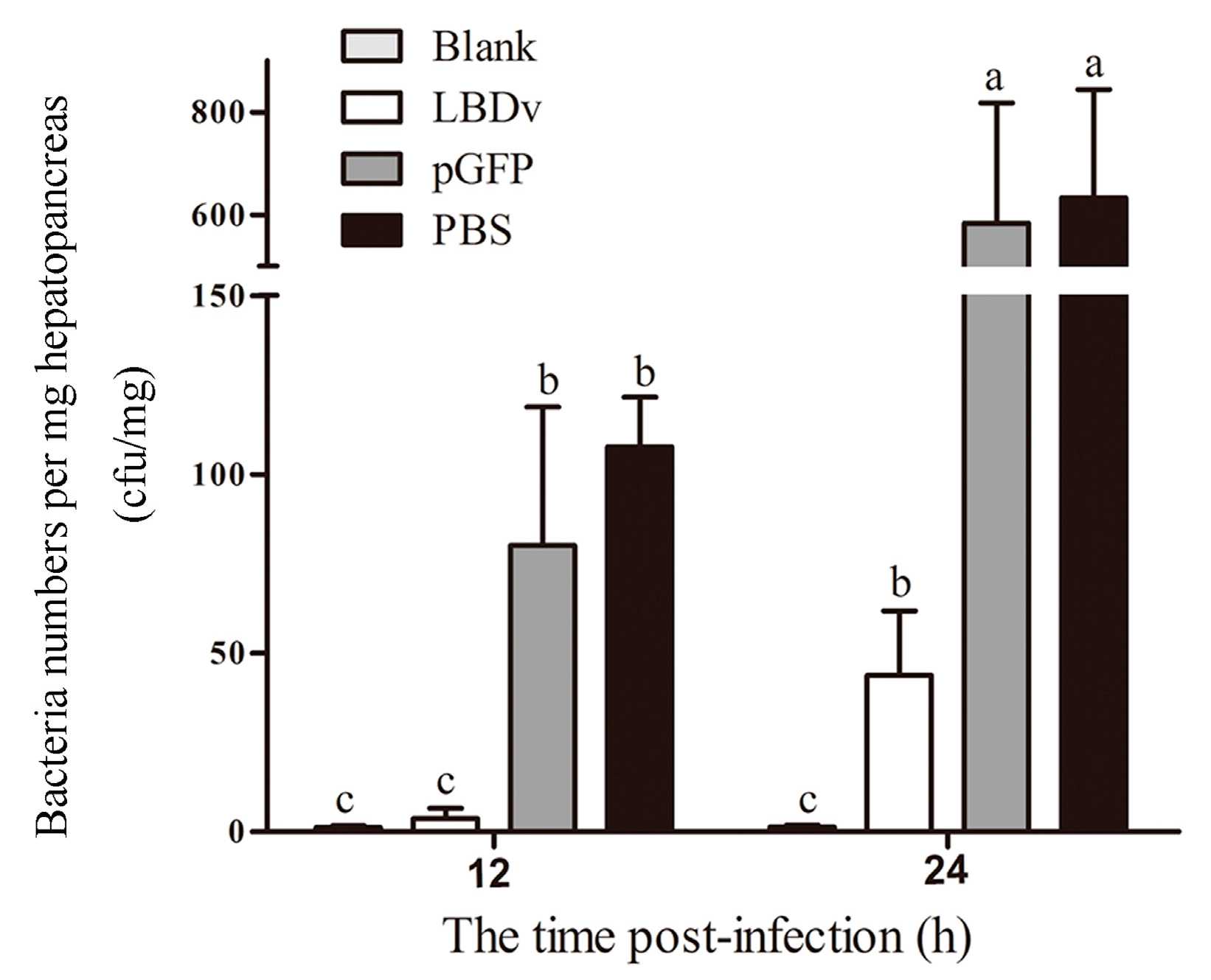
2.2. In Vivo Detection of the Antimicrobial Activity of LBDv Peptide
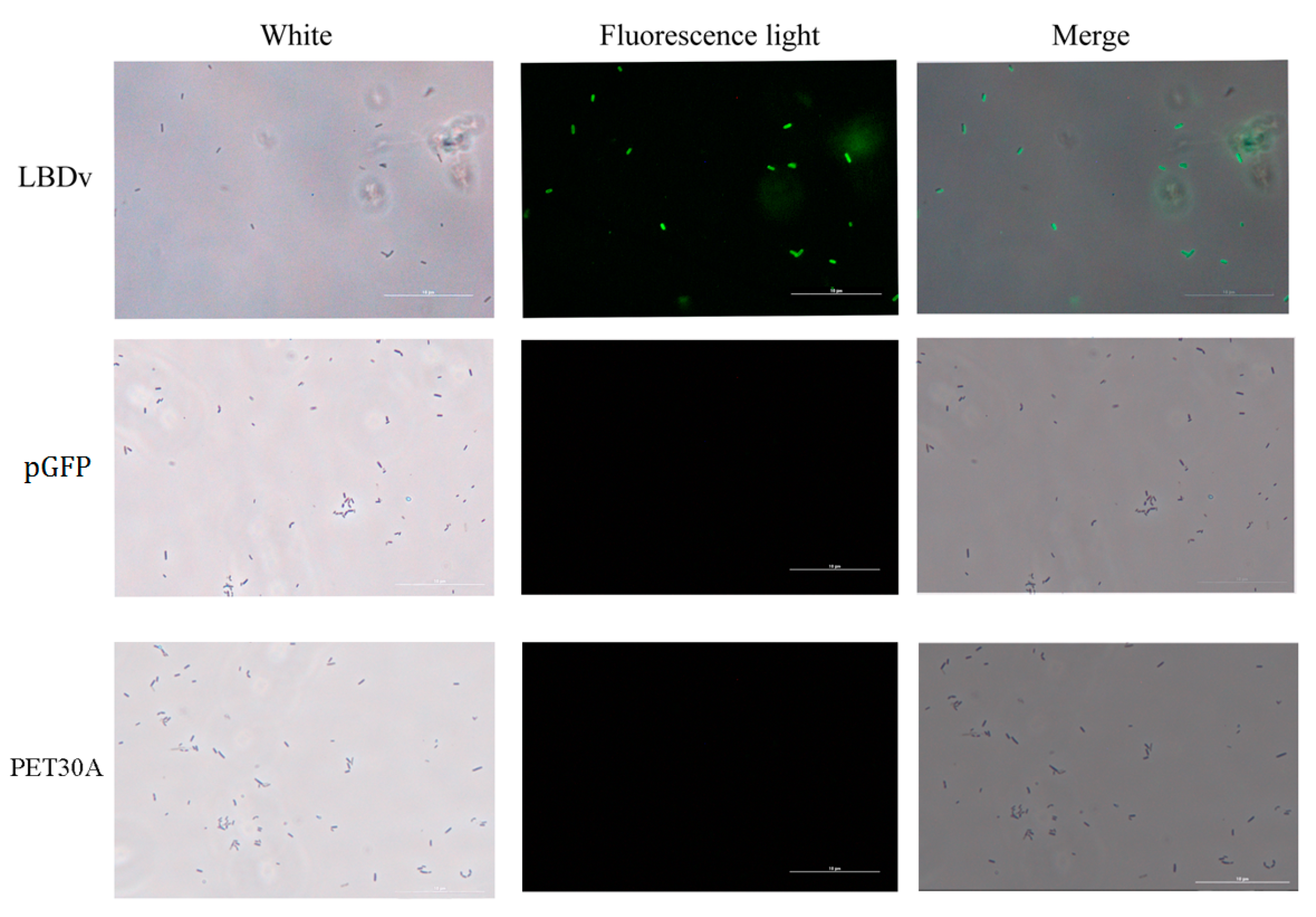
2.3. The Binding and Agglutination Activity of LBDv
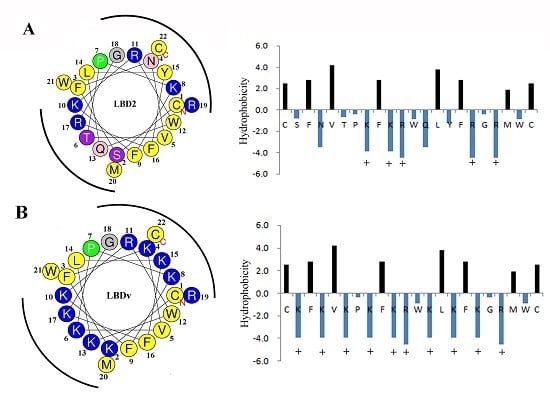
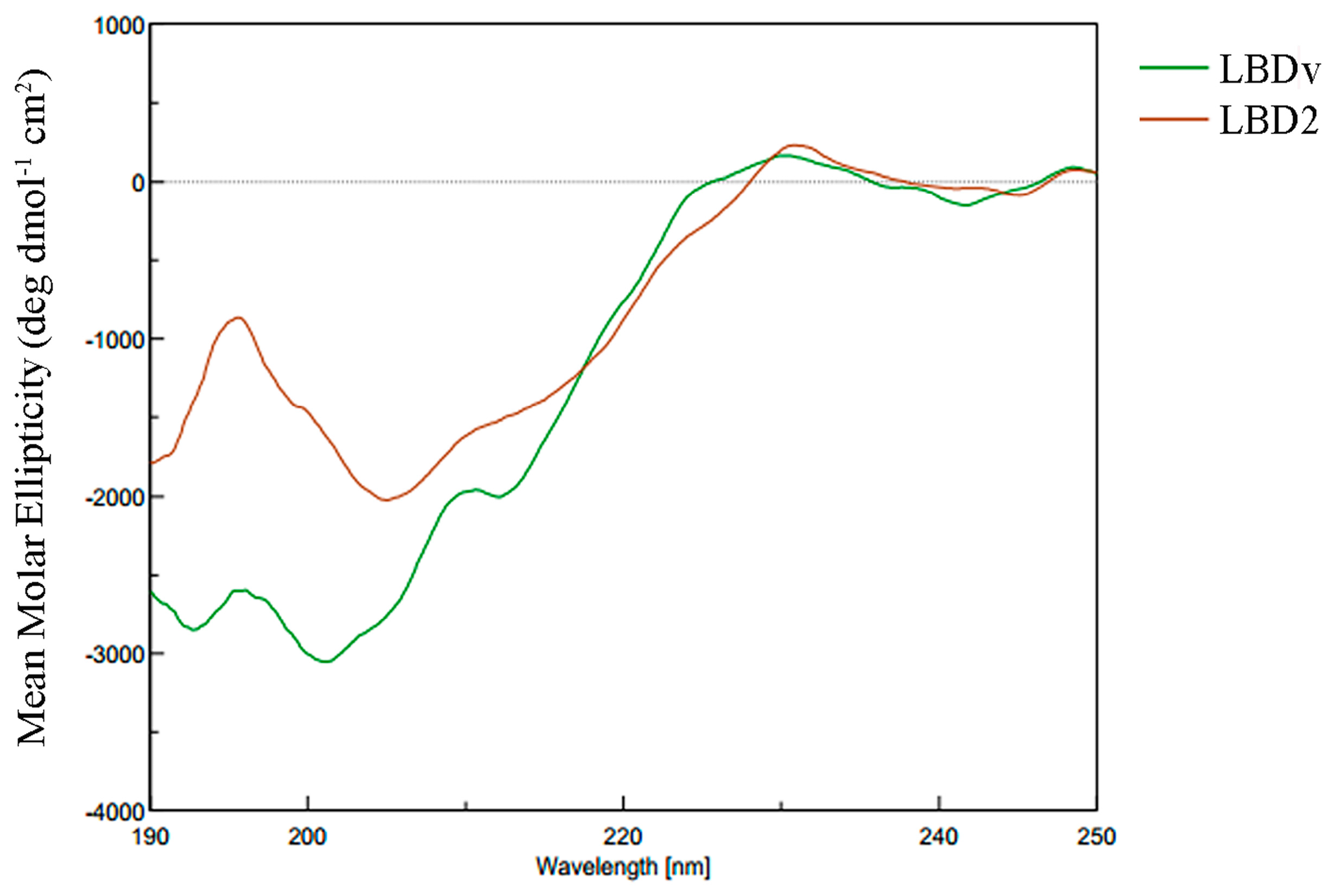
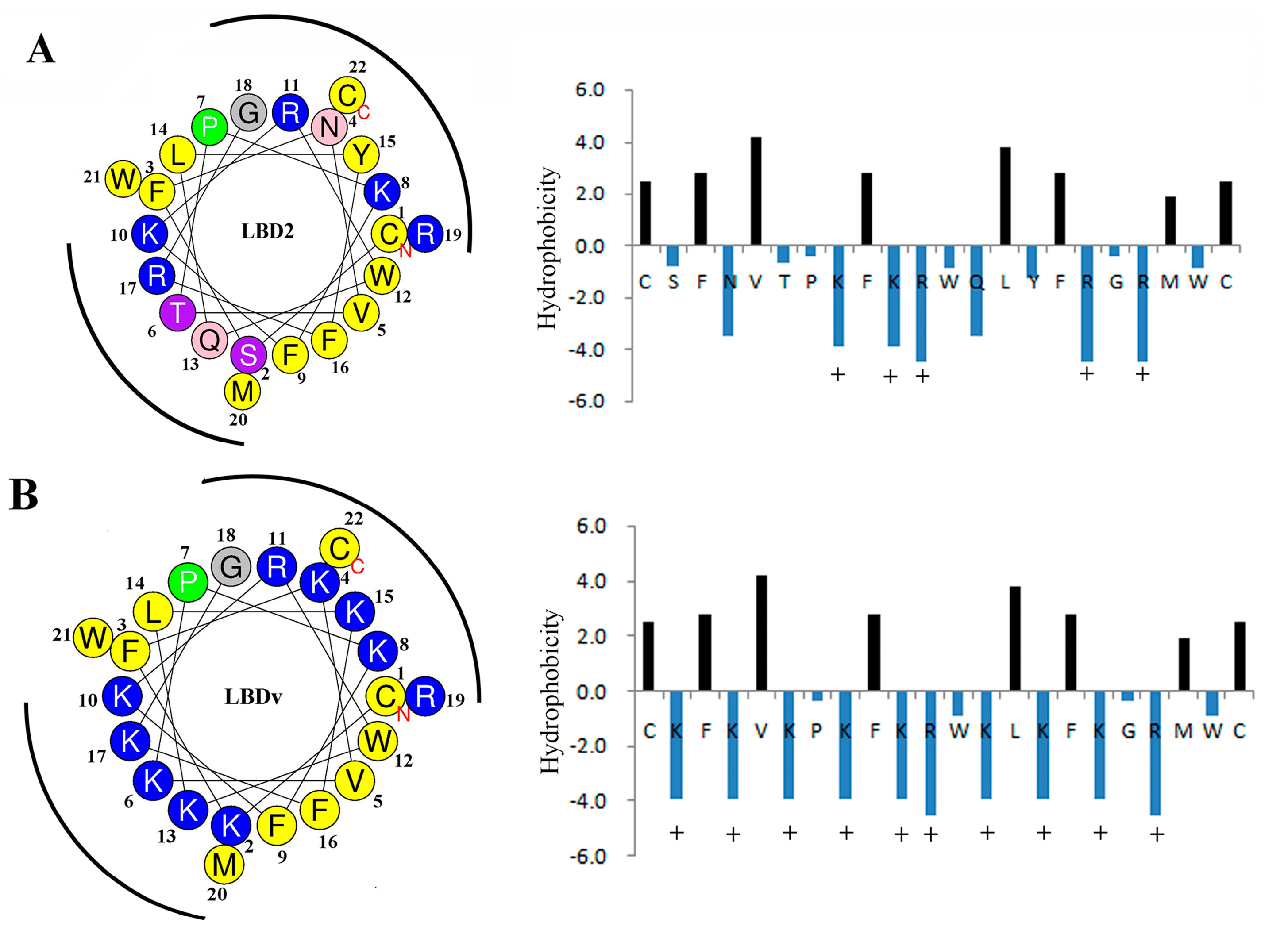
2.4. Structure Analysis of LBDv Peptide
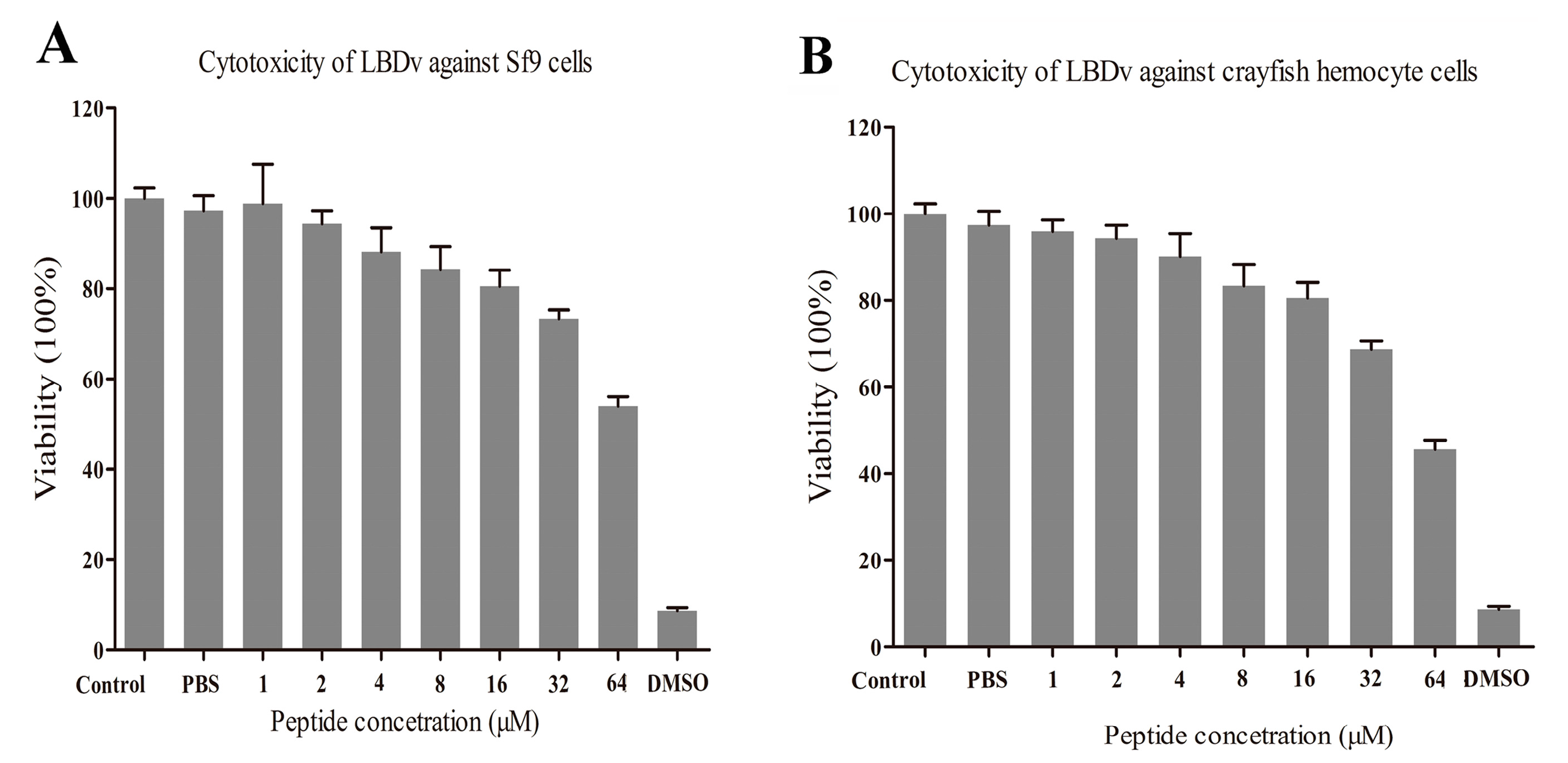
2.5. Evaluation on the Cytotoxicity of LBDv Peptide
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptides Synthesis
4.2. Antibacterial Activity Test
4.3. The Time-Killing Curve against Bacteria
4.4. Effects of the Peptides on Bacterial Infections
4.5. Bacteria Binding Assay
4.6. Bacterial Agglutination Experiment
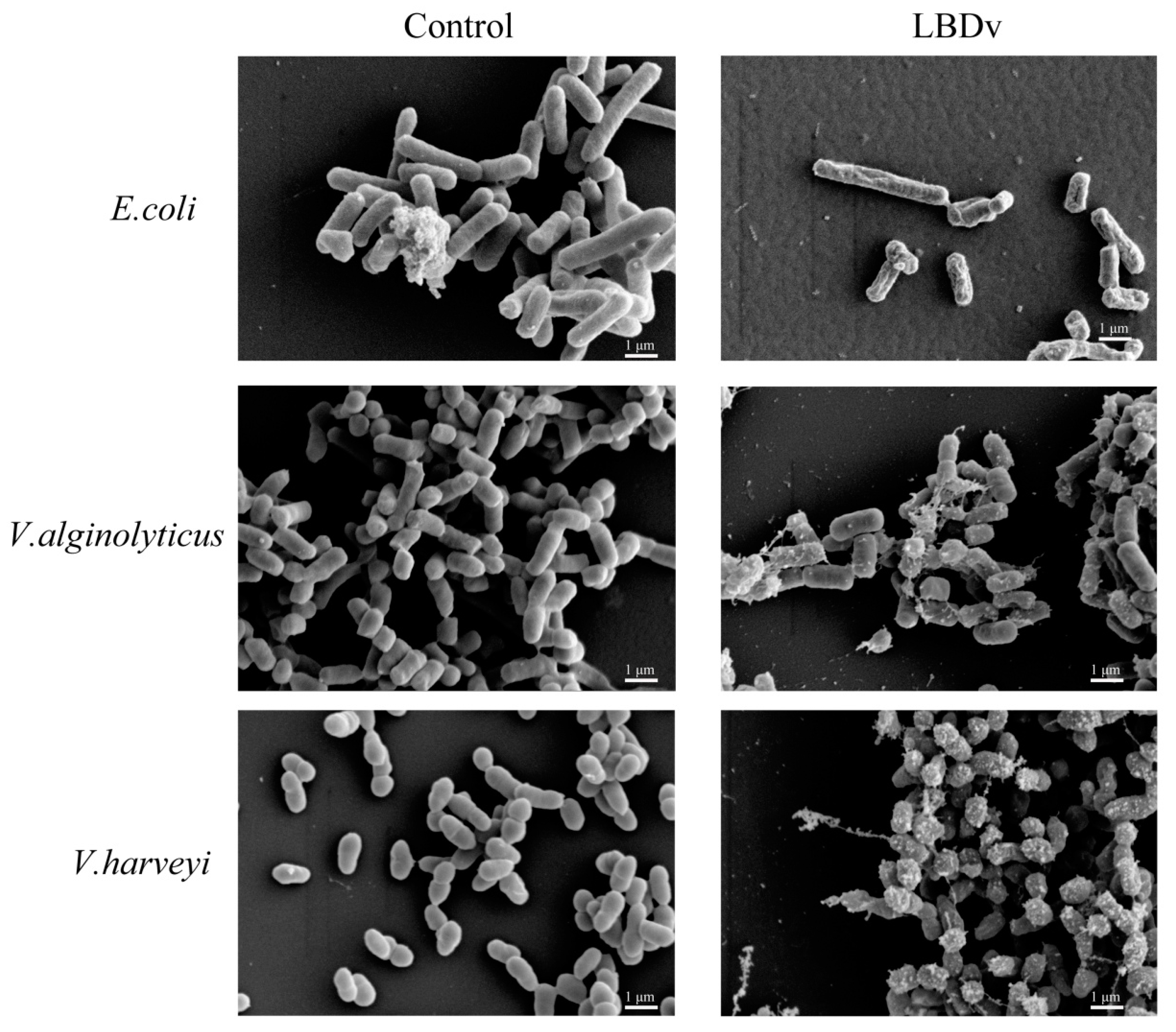
4.7. Morphology of the Bacteria Treated with LBDv
4.8. Structure Analysis on the Peptide LBDv and LBD2
4.9. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powers, J.-P.S.; Hancock, R.E. The relationship between peptide structure and antibacterial activity. Peptides 2003, 24, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boman, H.G. Peptide antibiotics and their role in innate immunity. Annu. Rev. Immonul. 1995, 13, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aley, S.B.; Zimmerman, M.; Hetsko, M.; Selsted, M.E.; Gillin, F.D. Killing of Giardia lamblia by cryptdins and cationic neutrophil peptides. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5397–5403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, F.V.; Noorwala, M.; Ahmad, V.U.; Sener, B. Bidesmosidic triterpenoidal saponins from the roots of Symphytum officinale. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, P.; Mor, A. Peptides as weapons against microorganisms in the chemical defense system of vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Immonul. 1995, 49, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boman, H. Antibacterial peptides: Basic facts and emerging concepts. J. Intern. Med. 2003, 254, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimarcq, J.L.; Bulet, P.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J. Cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides in invertebrates. Pept. Sci. 1998, 47, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E. Host Defence (bdCationic) Peptides. Drugs 1999, 57, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizet, V. Antimicrobial peptide resistance mechanisms of human bacterial pathogens. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2006, 8, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yount, N.Y.; Yeaman, M.R. Multidimensional signatures in antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7363–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.M.; Edwards, M.A.; Li, J.; Yip, C.M.; Deber, C.M. Roles of hydrophobicity and charge distribution of cationic antimicrobial peptides in peptide-membrane interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7738–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Vasil, A.I.; Vasil, M.L.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, K.L.; Hahm, K.S. Structure-antitumor and hemolytic activity relationships of synthetic peptides derived from cecropin A-magainin 2 and cecropin A-melittin hybrid peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 1997, 50, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dathe, M.; Nikolenko, H.; Meyer, J.; Beyermann, M.; Bienert, M. Optimization of the antimicrobial activity of magainin peptides by modification of charge. Febs. Lett. 2001, 501, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarovici, P.; Primor, N.; Loew, L.M. Purification and pore-forming activity of two hydrophobic polypeptides from the secretion of the Red Sea Moses sole (Pardachirus marmoratus). J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 16704–16713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeng, C.-Y.; Oh, M.S.; Park, I.H.; Hong, H.J. Purification and structural analysis of the hepatitis B virus preS1 expressed from Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslouches, B.; Steckbeck, J.D.; Craigo, J.K.; Doi, Y.; Mietzner, T.A.; Montelaro, R.C. Rational design of engineered cationic antimicrobial peptides consisting exclusively of arginine and tryptophan, and their activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, S.; Minaba, M.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Taichi, M.; Tamada, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Kato, Y. Generation of novel cationic antimicrobial peptides from natural non-antimicrobial sequences by acid-amide substitution. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2011, 10, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frecer, V.; Ho, B.; Ding, J.L. Interpretation of biological activity data of bacterial endotoxins by simple molecular models of mechanism of action. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, C.-F.; Yusof, M.Y. M.; Hassan, H.; Sekaran, S.D. In vitro properties of designed antimicrobial peptides that exhibit potent antipneumococcal activity and produces synergism in combination with penicillin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, T.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Limulus anti-LPS factor: An anticoagulant which inhibits the endotoxin-mediated activation of Limulus coagulation system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982, 105, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoess, R.H. Phage display of peptides and protein domains: Current opinion in structural biology. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1993, 3, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supungul, P.; Klinbunga, S.; Pichyangkura, R.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Tassanakajon, A. Antimicrobial peptides discovered in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon using the EST approach. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 61, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Functional Diversity of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor Isoforms in Shrimp and Their Characters Related to Antiviral Activity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Lv, X.; Xiang, J. Recombinant expression and functional analysis of an isoform of anti-lipopolysaccharide factors (FcALF5) from Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Boze, H.; Chemardin, P.; Padilla, A.; Moulin, G.; Tassanakajon, A.; Pugnière, M.; Roquet, F.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Gueguen, Y. NMR structure of Ralf-Pm3, an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from shrimp: Model of the possible lipid A-binding site. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaree, P.; Tassanakajon, A.; Somboonwiwat, K. Effect of the anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 3 (ALFPm3) from Penaeus monodon on Vibrio harveyi cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Characterization and function analysis of an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALF) from the Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maróti, G.; Kereszt, A.; Kondorosi, E.; Mergaert, P. Natural roles of antimicrobial peptides in microbes, plants and animals. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dathe, M.; Wieprecht, T.; Nikolenko, H.; Handel, L.; Maloy, W.L.; MacDonald, D.L.; Beyermann, M.; Bienert, M. Hydrophobicity, hydrophobic moment and angle subtended by charged residues modulate antibacterial and haemolytic activity of amphipathic helical peptides. FEBS Lett. 1997, 403, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, H.; Pei, D.; Cong, M.; Li, F.; Ji, C.; Zhao, J. A defensin from clam Venerupis philippinarum: Molecular characterization, localization, antibacterial activity, and mechanism of action. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somboonwiwat, K.; Bachère, E.; Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Tassanakajon, A. Localization of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALFPm3) in tissues of the black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon, and characterization of its binding properties. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehlbaum, P.; Bulet, P.; Chernysh, S.; Briand, J.-P.; Roussel, J.-P.; Letellier, L.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A. Structure-activity analysis of thanatin, a 21-residue inducible insect defense peptide with sequence homology to frog skin antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shai, Y. Mode of action of membrane active antimicrobial peptides. Pept. Sci. 2002, 66, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K. Magainins as paradigm for the mode of action of pore forming polypeptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1376, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Maier, E.; Benz, R.; Hancock, R.E. Mechanism of interaction of different classes of cationic antimicrobial peptides with planar bilayers and with the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7235–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozek, A.; Powers, J.-P.S.; Friedrich, C.L.; Hancock, R.E. Structure-based design of an indolicidin peptide analogue with increased protease stability. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 14130–14138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.H.; Cho, Y.; Lehrer, R.I. Effects of pH and salinity on the antimicrobial properties of clavanins. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 2898–2903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maisetta, G.; Di Luca, M.; Esin, S.; Florio, W.; Brancatisano, F.L.; Bottai, D.; Campa, M.; Batoni, G. Evaluation of the inhibitory effects of human serum components on bactericidal activity of human beta defensin 3. Peptides 2008, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunasagar, I.; Pai, R.; Malathi, G.; Karunasagar, I. Mass mortality of Penaeus monodon larvae due to antibiotic-resistant Vibrio harveyi infection. Aquaculture 1994, 128, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, B.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Cationic amphiphiles, a new generation of antimicrobials inspired by the natural antimicrobial peptide scaffold. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4049–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossi, A.; Sandri, L.; Giangaspero, A. Amphipathic, α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Pept. Sci. 2000, 55, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, D.; Shukla, S.K.; Prakash, O.; Zhang, G. Structural determinants of host defense peptides for antimicrobial activity and target cell selectivity. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K. Control of cell selectivity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giangaspero, A.; Sandri, L.; Tossi, A. Amphipathic α helical antimicrobial peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5589–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiradharma, N.; Sng, M.; Khan, M.; Ong, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.Y. Rationally Designedα-Helical Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptides with Idealized Facial Amphiphilicity. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2013, 34, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nell, M.J.; Tjabringa, G.S.; Wafelman, A.R.; Verrijk, R.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Grote, J.J. Development of novel LL-37 derived antimicrobial peptides with LPS and LTA neutralizing and antimicrobial activities for therapeutic application. Peptides 2006, 27, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Lehrer, R. Cationic peptides: A new source of antibiotics. Trends. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, H.; Osuji, J.C. Phytochemical and in vitro antimicrobial assay of the leaf extract of Newbouldia laevis. Afr. J. Tradit. Complem. 2008, 4, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslouches, B.; Islam, K.; Craigo, J.K.; Paranjape, S.M.; Montelaro, R.C.; Mietzner, T.A. Activity of the de novo engineered antimicrobial peptide WLBU2 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human serum and whole blood: Implications for systemic applications. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3208–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
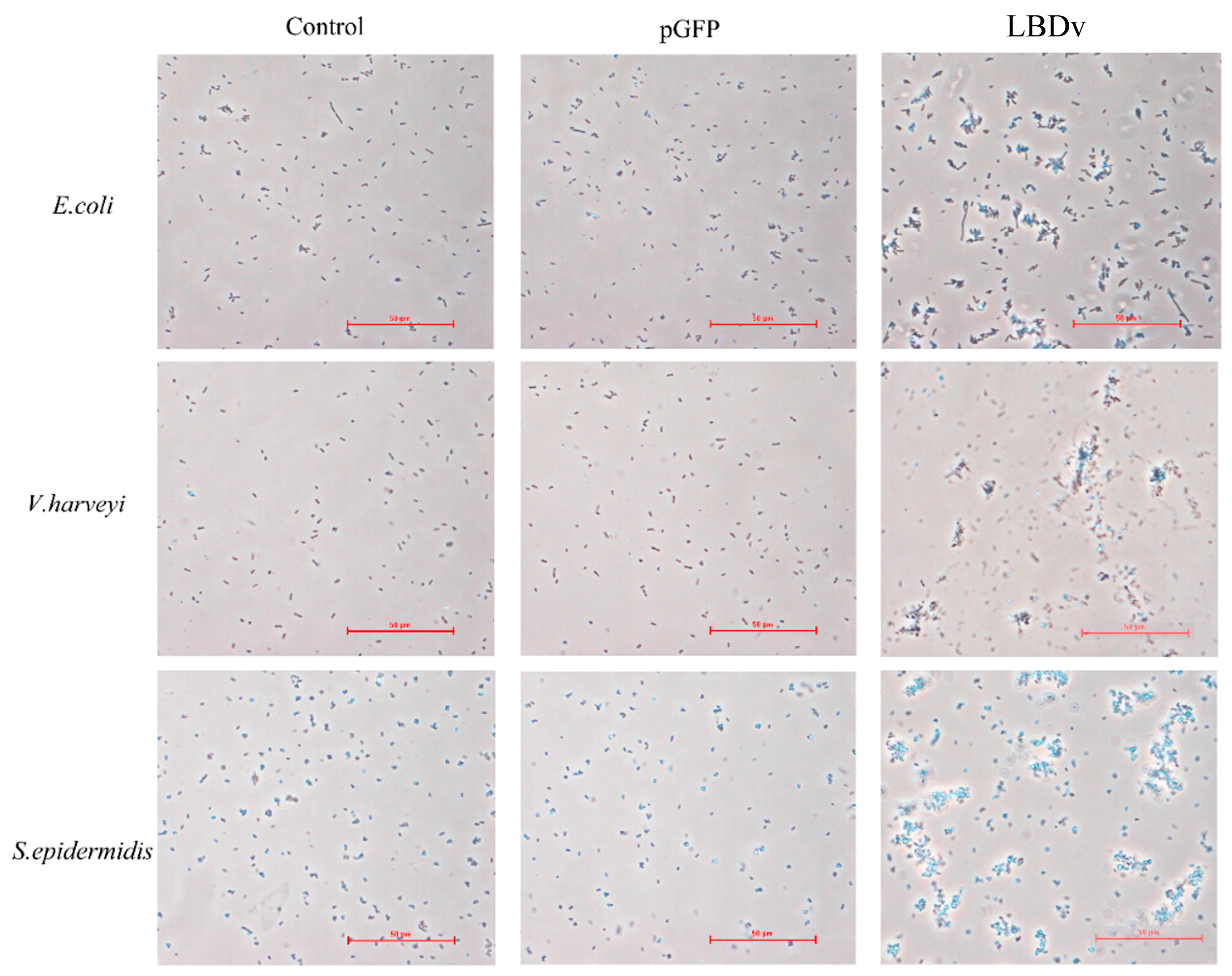

| Microorganisms | LBD2 (μM) | LBDv (μM) | Heated LBDv (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC a | MBC b | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | |
| Gram negative bacteria (G−): | ||||||
| Escherichia coli | >64 | >64 | 0.5–1 | 4–8 | 1–2 | 4–8 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | 2–4 | 16–32 | 1–2 | 8–16 | 2–4 | 8–16 |
| Vibrio harveyi | 2–4 | 16–32 | 1–2 | 2–4 | 2–4 | 2–4 |
| Vibrio Parahaemolyticus | 32–64 | 32–64 | 1–2 | 4–8 | 2–4 | 4–8 |
| Gram positive bacteria (G+): | ||||||
| Bacillus licheniformis | 16–32 | >64 | 8–16 | 32–64 | 16–32 | 32–64 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 32–64 | >64 | 4–8 | 16–32 | 4–8 | 16–32 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 2–4 | >64 | 4–8 | 16–32 | 4–8 | 16–32 |
| Peptide | Structure Content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-helical | β-sheet | β-turn | Random coil | |
| LBD2 | 0 | 79.7 | 0 | 20.3 |
| LBDv | 0 | 71.5 | 4.1 | 24.4 |
| Peptide | Sequence | NetC a | H b | HR (%) c | GRAVY d | μH e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBD2 | Ac-Y(CSFNVTPKFKRWQLYFRGRMWC)P-NH2 | 5 | 0.619 | 41 | −0.6042 | 0.103 |
| LBDv | Ac-Y(CKFKVKPKFKRWKLKFKGRMWC)P-NH2 | 10 | 0.398 | 41 | −0.9409 | 0.072 |
| pGFP | Ac-TTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFS-NH2 | 1 | 0.732 | 37 | 0.3333 | 0.314 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14050096
Yang H, Li S, Li F, Xiang J. Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(5):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14050096
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hui, Shihao Li, Fuhua Li, and Jianhai Xiang. 2016. "Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp" Marine Drugs 14, no. 5: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14050096
APA StyleYang, H., Li, S., Li, F., & Xiang, J. (2016). Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp. Marine Drugs, 14(5), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14050096