Agomelatine Ameliorates Cognitive and Behavioral Deficits in Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
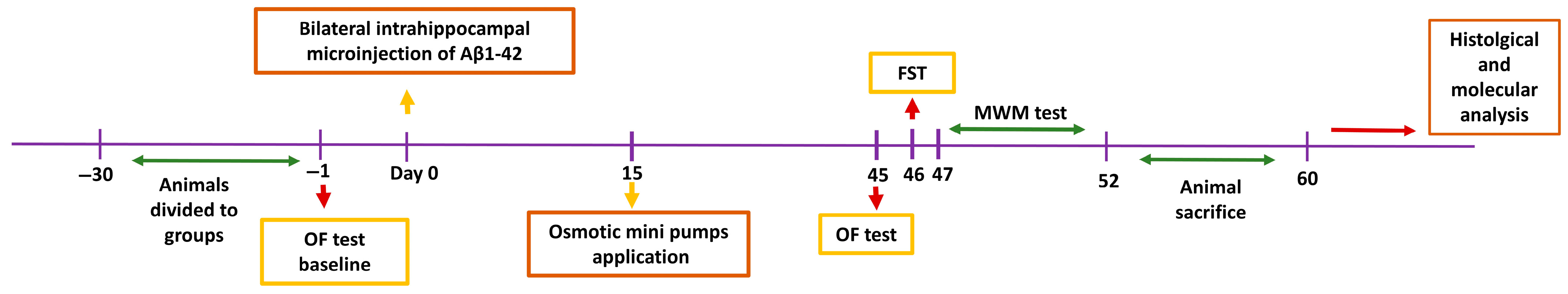
2.1. Experimental Design and Animals
2.2. Experimental AD Model
2.3. Administration of Drugs
2.4. Behavioral and Memory Tests
2.4.1. Open Field Test
2.4.2. Forced Swim Test
2.4.3. Morris Water Maze Test
2.5. Total RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcriptase (RT) Reaction, and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
2.6. Histological Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
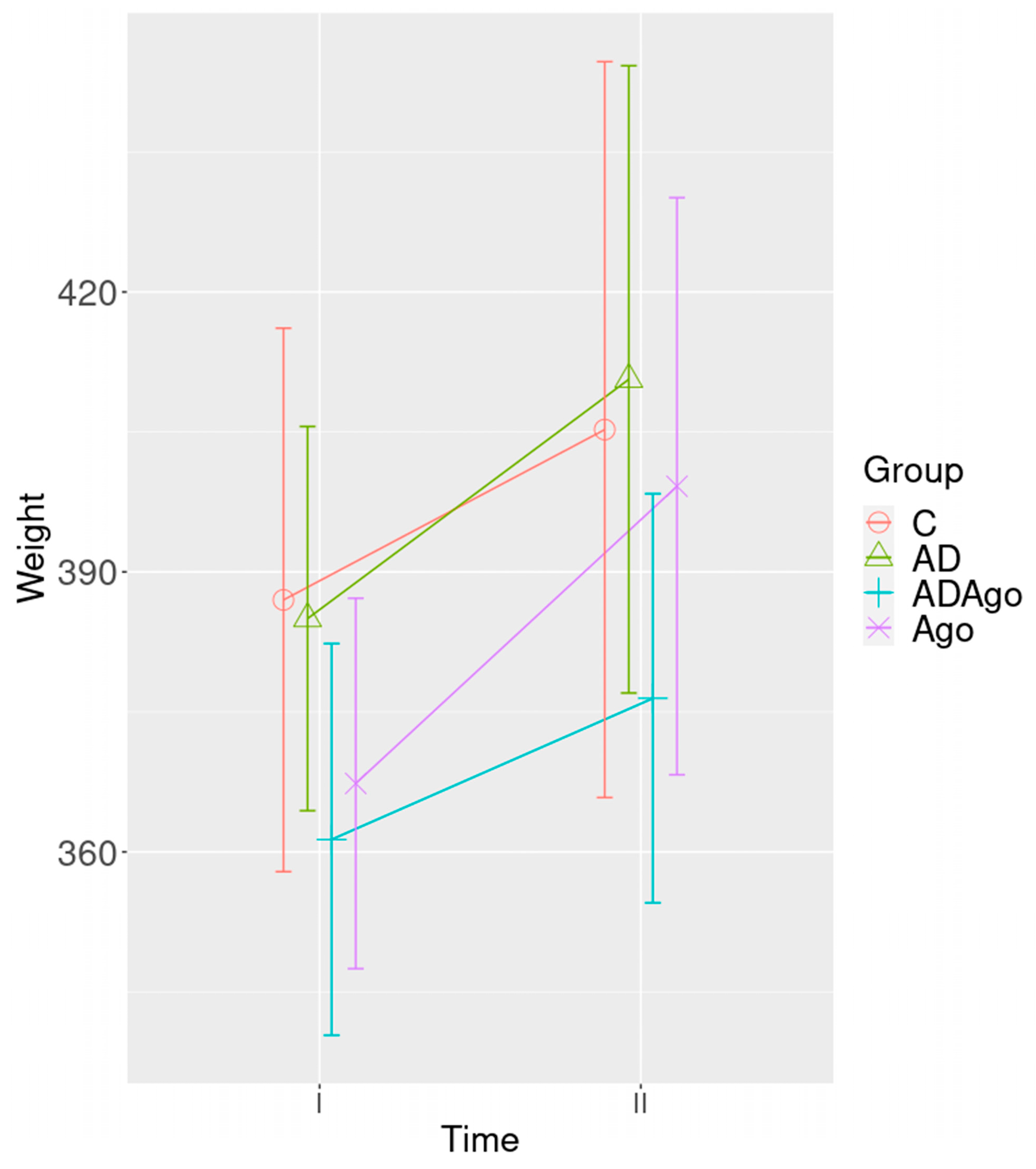
3.1. Weight Change
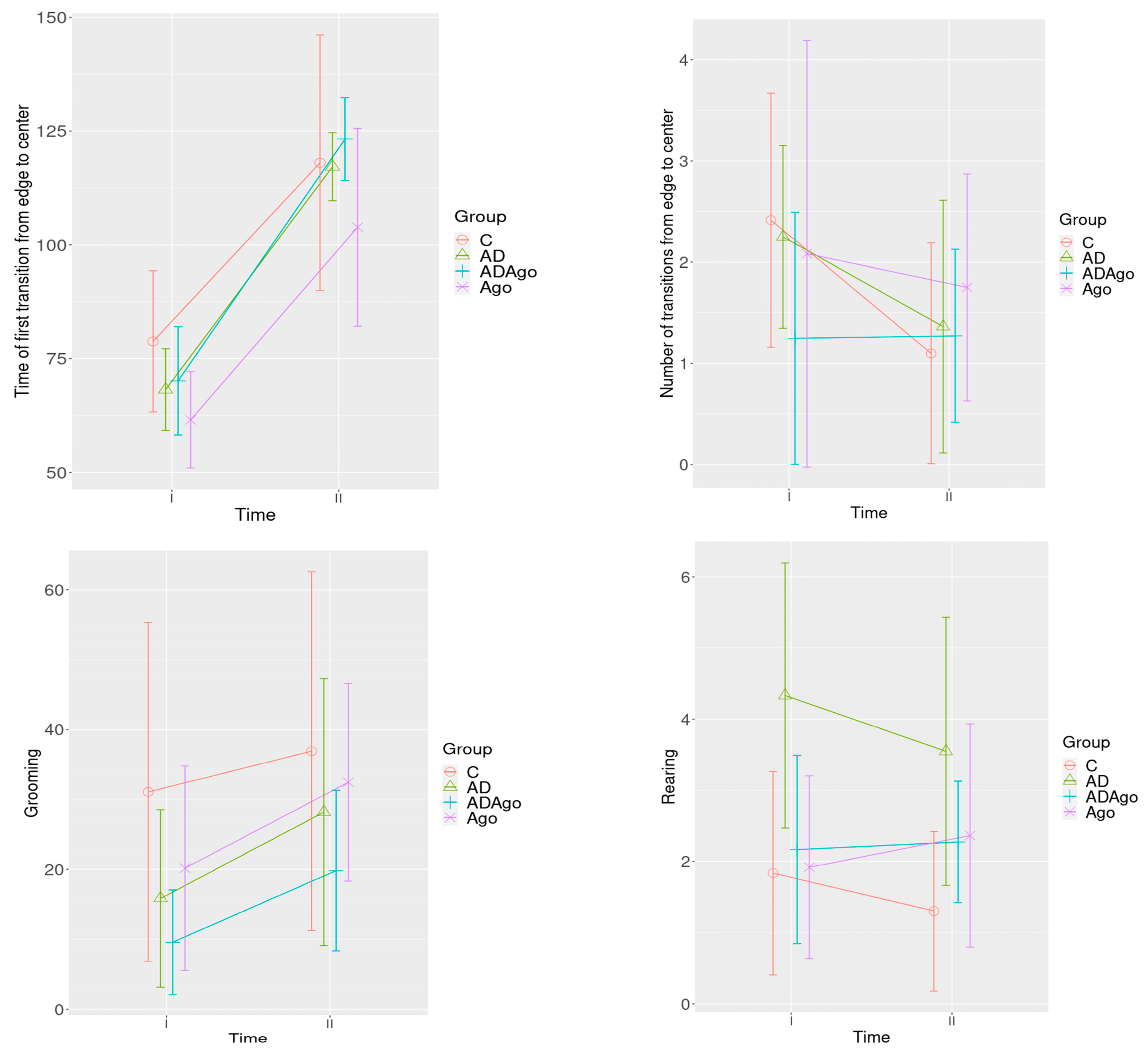
3.2. Open Field Test
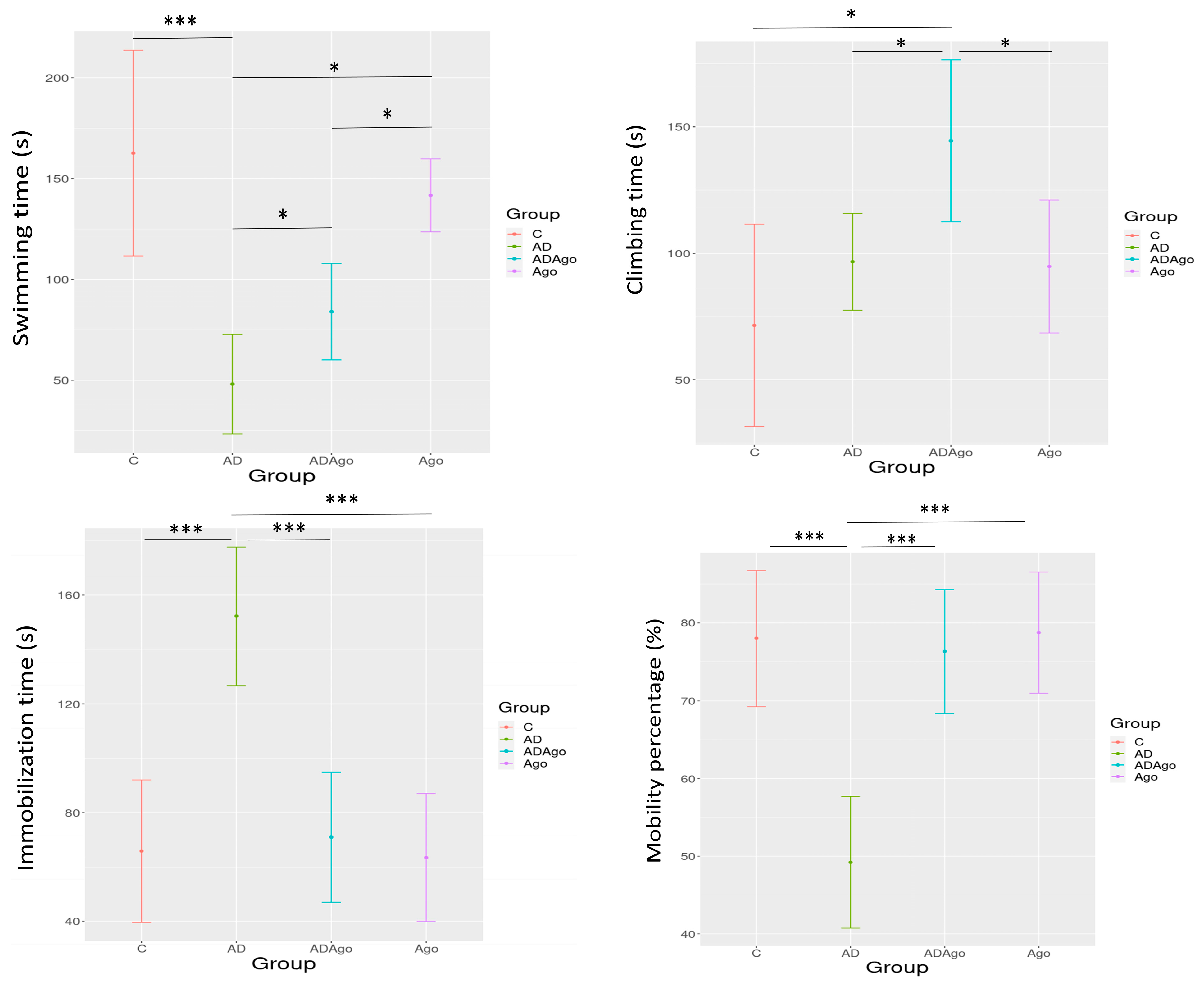
3.3. Force Swimming Test
3.4. Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
3.5. Gene Expression
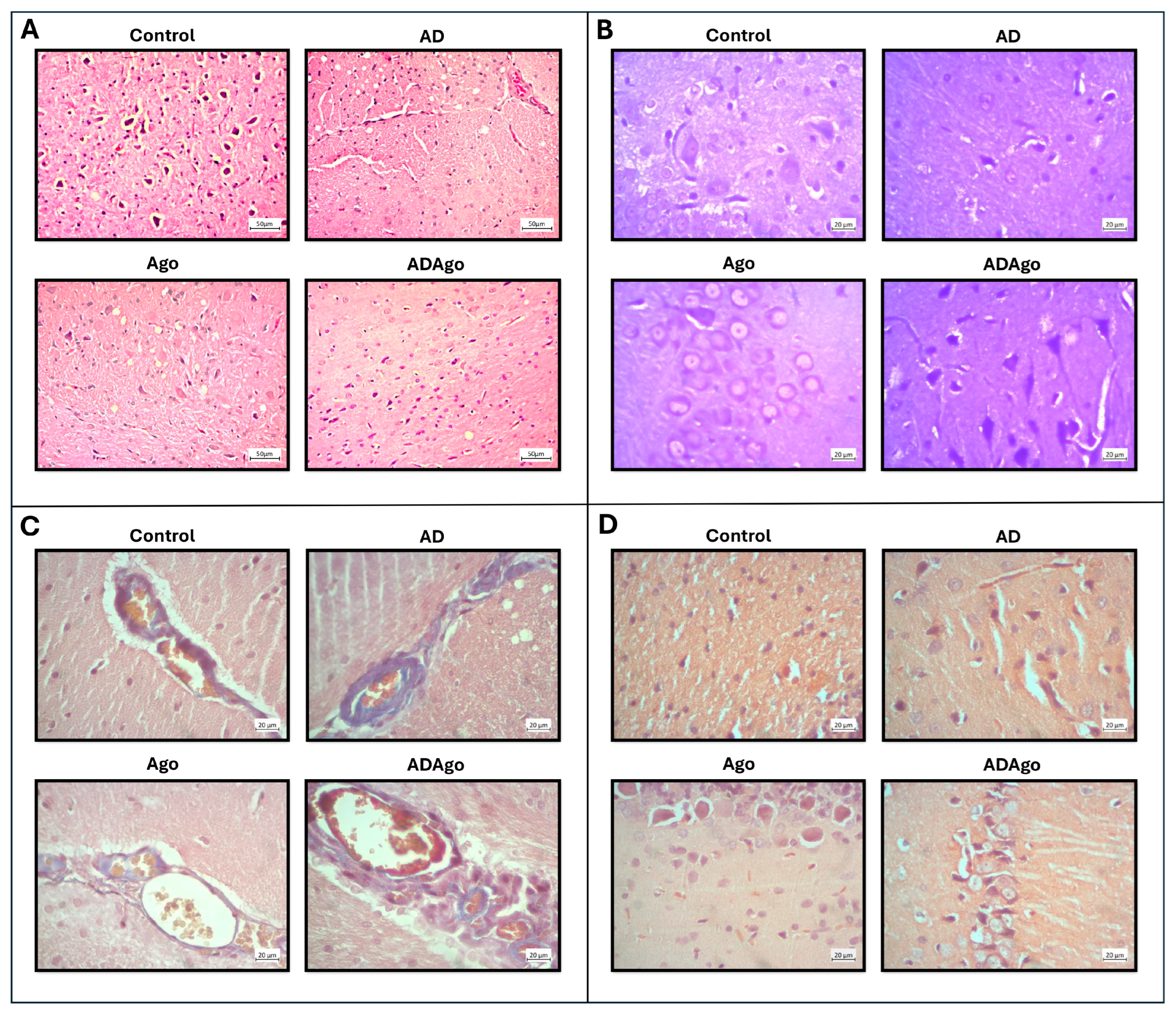
3.6. Histological Parameters
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colita, E.; Mateescu, V.O.; Olaru, D.-G.; Popa-Wagner, A. Cognitive Decline in Ageing and Disease: Risk Factors, Genetics and Treatments. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association Report 2024 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 3708–3821. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggu, S.; Bai, A.; Aida, M.; Rehman, H.; Pless, A.; Ware, D.; Deak, F.; Jiao, K.; Wang, Q. Monoamine Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease and Their Implications in Comorbid Neuropsychiatric Symptoms. GeroScience 2024, 47, 457–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, D.; Cumming, P. Mind Language Disturbances and PET-Signs of Depression vs Alzheimer’s Disease: Are There Any Common Patterns Identified? Psychiatry Danub. 2024, 36, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, G.-W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Guo, J.-H.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wu, M.-N.; Qi, J.-S. Agomelatine: A Potential Novel Approach for the Treatment of Memory Disorder in Neurodegenerative Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, A.; Gbahou, F.; Jockers, R. Melatonin Receptors, Brain Functions, and Therapies. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 179, pp. 345–356. ISBN 978-0-12-819975-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Zhou, J.-N.; Van Heerikhuize, J.; Jockers, R.; Swaab, D.F. Decreased MT1 Melatonin Receptor Expression in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaskan, E.; Ayoub, M.A.; Ravid, R.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Meier, F.; Eckert, A.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Jockers, R. Reduced Hippocampal MT2 Melatonin Receptor Expression in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zu, H. Melatonin Receptor Stimulation by Agomelatine Prevents A&β;-Induced Tau Phosphorylation and Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells. DDDT 2019, 13, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, B.; Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. The Protective Effects of Agomelatine against Aβ1-42 Oligomers-Induced Cellular Senescence Mediated by SIRT6 and Agomelatine’s Potential in AD Treatment. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, R.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Scuderi, C. An Animal Model of Alzheimer Disease Based on the Intrahippocampal Injection of Amyloid β-Peptide (1–42). In Neurotrophic Factors; Skaper, S.D., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1727, pp. 343–352. ISBN 978-1-4939-7570-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kheirbakhsh, R.; Haddadi, M.; Muhammadnejad, A.; Abdollahi, A.; Shahi, F.; Amanpour-Gharaei, B.; Abrahim-Habibi, A.; Barati, T.; Amanpour, S. Long-term Behavioral, Histological, Biochemical and Hematological Evaluations of Amyloid Beta-induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Rat. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2018, 78, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Prut, L.; Belzung, C. The Open Field as a Paradigm to Measure the Effects of Drugs on Anxiety-like Behaviors: A Review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solak, H.; Gormus, Z.I.S.; Koca, R.O.; Gunes, C.E.; Kutlu, S. Does Sertraline Affect Hypothalamic Food Intake Peptides in the Rat Experimental Model of Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression? Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 1299–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris Water Maze: Procedures for Assessing Spatial and Related Forms of Learning and Memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, S.L.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, L.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Mateus, J.M.; Fonseca-Gomes, J.; Soares, R.; Diógenes, M.J.; Solá, S.; Sebastião, A.M.; Ribeiro, F.F.; et al. Sustained Hippocampal Neural Plasticity Questions the Reproducibility of an Amyloid-β-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Model. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 82, 1183–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.; Bauer, B.; Abner, E.L.; Ashkenazy-Frolinger, T.; Hartz, A.M.S. A Comprehensive Behavioral Test Battery to Assess Learning and Memory in 129S6/Tg2576 Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimen, Y.; Ozdengul, F.; Gunes, C.; Kurar, E.; Gormus, Z.; Sak, K.; Kutlu, S. Investigation of Melatonin Receptors Gene Expression Levels in the Hippocampus and Hypothalamus in Rats with an Experimental Morphine Dependence Model. Ann. Med. Res. 2024, 31, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen Koca, R.; Solak Gormus, Z.I.; Solak, H.; Celik, F.S.; Kurar, E.; Kutlu, S. Are the Promnestic Effects of Neurokinin 3 Receptor Mediated by Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Aβ-induced Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease? Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2024, 84, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallemant, B.; Evrard, A.; Combescure, C.; Chapuis, H.; Chambon, G.; Raynal, C.; Reynaud, C.; Sabra, O.; Joubert, D.; Hollande, F.; et al. Reference Gene Selection for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Gene Expression Studies. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langnaese, K.; John, R.; Schweizer, H.; Ebmeyer, U.; Keilhoff, G. Selection of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR in a Rat Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Model. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Raymick, J.; Cuevas, E.; Rosas-Hernandez, H.; Hanig, J. Modification of methods to use Congo-red stain to simultaneously visualize amyloid plaques and tangles in human and rodent brain tissue sections. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola-Lemaitre, B.; De Bodinat, C.; Delagrange, P.; Millan, M.J.; Munoz, C.; Mocaër, E. Agomelatine: Mechanism of Action and Pharmacological Profile in Relation to Antidepressant Properties. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3604–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conboy, L.; Tanrikut, C.; Zoladz, P.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Sandi, C.; Diamond, D.M. The Antidepressant Agomelatine Blocks the Adverse Effects of Stress on Memory and Enables Spatial Learning to Rapidly Increase Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule (NCAM) Expression in the Hippocampus of Rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumuslu, E.; Mutlu, O.; Sunnetci, D.; Ulak, G.; Celikyurt, I.K.; Cine, N.; Akar, F.; Savli, H.; Erden, F. The Antidepressant Agomelatine Improves Memory Deterioration and Upregulates CREB and BDNF Gene Expression Levels in Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress (UCMS)-Exposed Mice. Drug Target Insights 2014, 8, DTI.S13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B.; Sharma, B. Neuroprotective Effects of Agomelatine and Vinpocetine Against Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Induced Vascular Dementia. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2015, 12, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertaina-Anglade, V.; Drieu-La-Rochelle, C.; Mocaër, E.; Seguin, L. Memory Facilitating Effects of Agomelatine in the Novel Object Recognition Memory Paradigm in the Rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 98, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaziz, M.; Mohamed, A.F.; Zaki, H.F.; Gad, S.S. Agomelatine Improves Memory and Learning Impairments in a Rat Model of LPS-Induced Neurotoxicity by Modulating the ERK/SorLA/BDNF/TrkB Pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchekalarova, J.; Nenchovska, Z.; Atanasova, D.; Atanasova, M.; Kortenska, L.; Stefanova, M.; Alova, L.; Lazarov, N. Consequences of Long-Term Treatment with Agomelatine on Depressive-like Behavior and Neurobiological Abnormalities in Pinealectomized Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 302, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, Ö.D.; Üçel, U.İ.; Demir Özkay, Ü.; Ulupınar, E. The Effect of Agomelatine Treatment on Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats: Concomitant Alterations in the Hippocampal Neuron Numbers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilieva, K.; Tchekalarova, J.; Atanasova, D.; Kortenska, L.; Atanasova, M. Antidepressant Agomelatine Attenuates Behavioral Deficits and Concomitant Pathology Observed in Streptozotocin-Induced Model of Alzheimer’s Disease in Male Rats. Horm. Behav. 2019, 107, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, A.; Cardona, X.; Martin-Baranera, M.; Leon, L.; Caballol, N.; Millet, P.; Bello, J. Agomelatine for Depression in Parkinson Disease: Additional Effect on Sleep and Motor Dysfunction. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 35, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir Özkay, Ü.; Söztutar, E.; Can, Ö.D.; Üçel, U.I.; Öztürk, Y.; Ulupinar, E. Effects of Long-Term Agomelatine Treatment on the Cognitive Performance and Hippocampal Plasticity of Adult Rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2015, 26, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, S.; Zhao, G.; Ma, Y. 7.0T Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Evaluation of the Amyloid Beta (1-40) Animal Model of Alzheimer′s Disease: Comparison of Cytology Verification. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douichene, S.; Djebli, N.; Zerrouki, K. Neuroprotective Effect Of Curcumin With A Fixator Of Absorption Against Both Aluminium Neurotoxicity And Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 2012, 3837–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami Mahmoudian, Z.; Komaki, A.; Rashidi, I.; Amiri, I.; Ghanbari, A. The Effect of Minocycline on Beta-Amyloid-Induced Memory and Learning Deficit in Male Rats: A Behavioral, Biochemical, and Histological Study. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2022, 125, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarahian, N.; Khodagholi, F.; Valian, N.; Ahmadiani, A. Interplay of MeCP2/REST/Synaptophysin-BDNF and Intranasal Oxytocin Influence on Aβ-Induced Memory and Cognitive Impairments. Behav. Brain Res. 2025, 476, 115235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompili, M.; Serafini, G.; Innamorati, M.; Venturini, P.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Sher, L.; Amore, M.; Girardi, P. Agomelatine, a Novel Intriguing Antidepressant Option Enhancing Neuroplasticity: A Critical Review. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 14, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagytė, G.; Trentani, A.; Postema, F.; Luiten, P.G.; Den Boer, J.A.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaër, E.; Meerlo, P.; Van Der Zee, E.A. The Novel Antidepressant Agomelatine Normalizes Hippocampal Neuronal Activity and Promotes Neurogenesis in Chronically Stressed Rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 16, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molteni, R.; Calabrese, F.; Pisoni, S.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Racagni, G.; Riva, M.A. Synergistic Mechanisms in the Modulation of the Neurotrophin BDNF in the Rat Prefrontal Cortex Following Acute Agomelatine Administration. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 11, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnitskaya, E.A.; Maksimova, K.Y.; Muraleva, N.A.; Logvinov, S.V.; Yanshole, L.V.; Kolosova, N.G.; Stefanova, N.A. Beneficial Effects of Melatonin in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, K.; Ryu, J.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, A.Y.; Woo, R.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Hyun, J.W.; Hahn, S.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Neuritin Attenuates Cognitive Function Impairments in Tg2576 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Li, G.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Huang, J. miR-199a Decreases Neuritin Expression Involved in the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease in APP/PS1 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, S.; Gong, D.; Yang, M.; Qiu, Q.; Luo, J.; Chen, T. Curcumin Improves Neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice via the Upregulation of Wnt/β-Catenin and BDNF. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.S.; Shetty, A.K. Efficacy of Doublecortin as a Marker to Analyse the Absolute Number Anddendritic Growth of Newly Generated Neurons in the Adult Dentate Gyrus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annita, A.; Revilla, G.; Ali, H.; Almurdi, A. The Effect of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Nestin and Sox-2 Gene Expression and Spatial Learning (Percent Alternation Y-Maze Test) against AlCl3-Induced Alzheimer’s-like Pathology in a Rat Model. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 49, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, P.; Sözer-Topcular, N.; Jockers, R.; Ravid, R.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Eckert, A.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Savaskan, E. Pineal and Cortical Melatonin Receptors MT1 and MT2 Are Decreased in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Histochem. 2006, 50, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Matsubara, E.; Vidal, R.; Pacheco-Quinto, J.; Poeggeler, B.; Zagorski, M.; Sambamurti, K. Melatonin Treatment Enhances Aβ Lymphatic Clearance in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Amyloidosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Mean ± SD | C | AD | ADAgo | Ago | p-Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swimming time | 162.63 ± 61.01 | 48.11 ± 32.14 | 84.00 ± 25.86 | 141.70 ± 25.2 | <0.001 |
| Climbing time | 71.50 ± 47.86 | 96.67 ± 24.89 | 144.43 ± 34.64 | 94.80 ± 36.68 | 0.010 |
| Immobilization time | 65.88 ± 31.38 | 152.22 ± 33.08 | 71.00 ± 25.87 | 63.50 ± 32.93 | <0.001 |
| Mobility percentage | 78.00 ± 10.45 | 49.23 ± 11.03 | 76.31 ± 8.61 | 78.75 ± 10.87 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD | C | AD | ADAgo | Ago | p-Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
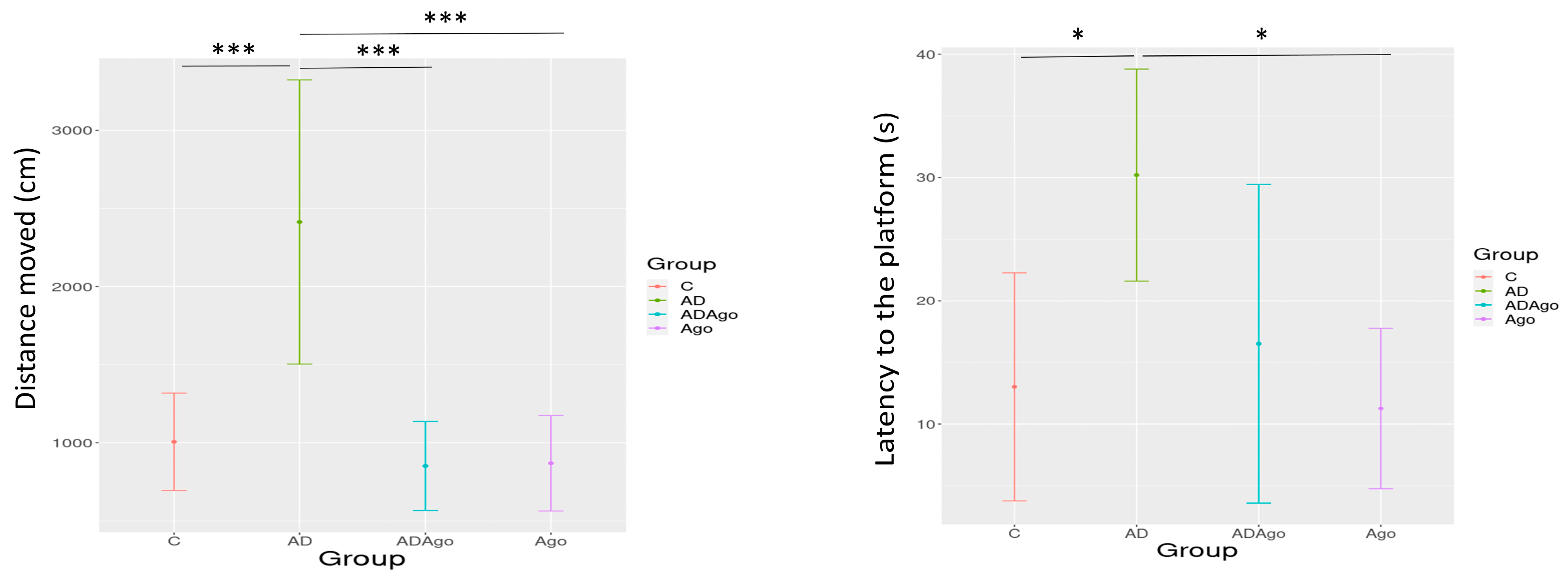
| Distance moved (cm) | 1006.52 ± 405.43 | 2413.45 ± 1183.26 | 851.74 ± 370.05 | 869.22 ± 365.58 | <0.001 |
| Latency to the platform (s) | 13.01 ± 8.82 | 30.19 ± 9.30 | 16.51 ± 10.41 | 11.25 ± 6.22 | 0.019 |
| Velocity | 29.63 ± 12.31 | 35.16 ± 8.55 | 25.10 ± 11.33 | 25.24 ± 10.63 | 0.34 |
| Time spent in the target quadrant (s) | 17.19 ± 6.43 | 11.11 ± 3.01 | 16.94 ± 5.99 | 17.48 ± 5.37 | 0.039 |
| First transition time to target quadrant (s) | 6.27 ± 4.59 | 4.57 ± 2.59 | 7.45 ± 3.86 | 2.18 ± 1.37 | 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozen Koca, R.; Solak Gormus, Z.I.; Solak, H.; Gultekin, B.; Ozdemir, A.; Eroglu Gunes, C.; Kurar, E.; Kutlu, S. Agomelatine Ameliorates Cognitive and Behavioral Deficits in Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Rat Model. Medicina 2025, 61, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081315
Ozen Koca R, Solak Gormus ZI, Solak H, Gultekin B, Ozdemir A, Eroglu Gunes C, Kurar E, Kutlu S. Agomelatine Ameliorates Cognitive and Behavioral Deficits in Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Rat Model. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081315
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzen Koca, Raviye, Z. Isik Solak Gormus, Hatice Solak, Burcu Gultekin, Ayse Ozdemir, Canan Eroglu Gunes, Ercan Kurar, and Selim Kutlu. 2025. "Agomelatine Ameliorates Cognitive and Behavioral Deficits in Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Rat Model" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081315
APA StyleOzen Koca, R., Solak Gormus, Z. I., Solak, H., Gultekin, B., Ozdemir, A., Eroglu Gunes, C., Kurar, E., & Kutlu, S. (2025). Agomelatine Ameliorates Cognitive and Behavioral Deficits in Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Rat Model. Medicina, 61(8), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081315






