The Impact of Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Expression Patterns in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Associations with Pathological Response and Tumor Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Protocol
2.3. Pathological Evaluation
2.4. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of YAP1 Expression
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LABC | locally advanced breast cancer |
| NAC | neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| pCR | pathological complete response |
| YAP1 | Yes-associated protein-1 |
| TNBC | triple-negative breast cancer |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| HR | hormone receptor |
| PR | progesterone receptor |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| OR | odds ratio |
| DFS | disease-free survival |
| OS | overall survival |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 2019, 393, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Minckwitz, G.; Untch, M.; Blohmer, J.-U.; Costa, S.D.; Eidtmann, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Gerber, B.; Eiermann, W.; Hilfrich, J.; Huober, J.; et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.; Sagona, A.; De Carlo, C.; Fernandes, B.; Barbieri, E.; Grimaldi, S.D.M.; Jacobs, F.; Vatteroni, G.; Scardina, L.; Biondi, E.; et al. Pathologic response and residual tumor cellularity after neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict prognosis in breast cancer patients. Breast 2023, 69, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Yoo, T.-K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, J.; Chung, I.Y.; Ko, B.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.W.; Son, B.H. Prognostic value of residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: A comprehensive subtype-specific analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.-X.; Zhao, B.; Guan, K.L. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, M. Hippo pathway in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms, potential targets, and biomarkers. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhong, H.; Shi, Q.; Ruan, R.; Huang, C.; Wen, Q.; Zeng, S.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Xiong, J.; et al. YAP1-CPNE3 positive feedback pathway promotes gastric cancer cell progression. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fan, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, S.; Du, G.; Zhang, N. Advances in research on the carcinogenic mechanisms and therapeutic potential of YAP1 in bladder cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2025, 53, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Shang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, R. YAP1 expression in colorectal cancer confers the aggressive phenotypes via its target genes. Cell Cycle 2024, 23, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Dai, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. YAP1 activates SLC2A1 transcription and augments the malignant behavior of colorectal cancer cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Div. 2025, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Shao, Y.W.; Tong, X.; Wu, X.; Pang, J.; Feng, A.; Yang, Z. YAP1 amplification as a prognostic factor of definitive chemoradiotherapy in nonsurgical esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Narita, S.; Nara, T.; Mingguo, H.; Sato, H.; Koizumi, A.; Kanda, S.; Numakura, K.; Saito, M.; Inoue, T.; et al. Impact of nuclear YAP1 expression in residual cancer after neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy with docetaxel for high-risk localized prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Azzolin, L.; Forcato, M.; Rosato, A.; Frasson, C.; Inui, M.; Montagner, M.; Parenti, A.R.; Poletti, A.; et al. The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell 2011, 147, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Role of inhibitor of yes-associated protein 1 in triple-negative breast cancer with taxol-based chemoresistance. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.D.K.; Yi, C. YAP/TAZ Signaling and Resistance to Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Liu, L.; You, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yu, Z. WISP1 inhibition of YAP phosphorylation drives breast cancer growth and chemoresistance via TEAD4 activation. Anticancer. Drugs 2025, 36, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-Q.; Zhang, K.-J.; Wang, S.-M.; Guo, L. YAP1/MMP7/CXCL16 axis affects efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy via tumor environment immunosuppression in triple-negative breast cancer. Gland. Surg. 2021, 10, 2799–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Bae, S.J.; Kim, D.; Ahn, S.G.; Jeong, J.; Koo, J.S.; Yoo, T.-K.; Park, W.-C.; Lee, A.; Yoon, C.I. High Nuclear Expression of Yes-Associated Protein 1 Correlates with Metastasis in Patients with Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 609743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.G.; Chen, X.W.; Zhang, L.P.; Wang, J.; Diehn, M. Yap1 promotes the survival and self-renewal of breast tumor initiating cells via inhibiting Smad3 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9692–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Sun, P.L.; Yao, M.; Jia, M.; Gao, H. Expression of YES-associated protein (YAP) and its clinical significance in breast cancer tissues. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 68, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehn, S.; Tobin, N.P.; Sims, A.H.; Stål, O.; Jirström, K.; Axelson, H.; Landberg, G. Decreased expression of Yes-associated protein is associated with outcome in the luminal A breast cancer subgroup and with an impaired tamoxifen response. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zou, H.; Guo, Y.; Tong, T.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, P. The oncogenic roles and clinical implications of YAP/TAZ in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.Q.; Ding, N.H.; Xiao, Z. The Hippo Transducer YAP/TAZ as a Biomarker of Therapeutic Response and Prognosis in Trastuzumab-Based Neoadjuvant Therapy Treated HER-2 Positive Breast Cancer Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 537265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejben, A.; Kószó, R.; Kahán, Z.; Cserni, G.; Zombori, T. Examination of Tumor Regression Grading Systems in Breast Cancer Patients Who Received Neoadjuvant Therapy. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Huang, T.; Yuan, J.; Mao, J.; Duan, Y.; Liao, W.; Xiao, Z. Yes-associated protein expression in paired primary and local recurrent breast cancer and its clinical significance. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2019, 43, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, J.; Fang, J.Y.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J.B.; Zhu, Z.P. Expression characteristics of the yes-associated protein in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vici, P.; Ercolani, C.; Di Benedetto, A.; Pizzuti, L.; Di Lauro, L.; Sperati, F.; Terrenato, I.; Gamucci, T.; Natoli, C.; Di Filippo, F.; et al. Topographic expression of the Hippo transducers TAZ and YAP in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaogullari, S.Y.; Topal, U.; Ozturk, F.; Gok, M.; Oz, B.; Akcan, A.C. The relationship of patients, giving or not giving a pathological full response, with YAP (Yes Associated Protein) in breast cancer cases to which neo-adjuvant chemotherapy is applied. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2022, 92, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.A.; Smits, D.; Haughton, P.D.; Koorman, T.; Jansen, K.A.; Verhagen, M.P.; van der Net, M.; van Zwieten, K.; Enserink, L.; Jansen, L.; et al. A YAP-centered mechanotransduction loop drives collective breast cancer cell invasion. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Es, H.A.; Cox, T.R.; Sarafraz-Yazdi, E.; Thiery, J.P.; Warkiani, M.E. Pirfenidone Reduces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Spheroid Formation in Breast Carcinoma through Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs). Cancers 2021, 13, 5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Huang, Q.; Jia, W.; Feng, S.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Tao, D.; Xie, D. YAP1 induces invadopodia formation by transcriptionally activating TIAM1 through enhancer in breast cancer. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3830–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, G.R.; Sethi, I.; Sadida, H.Q.; Rah, B.; Mir, R.; Algehainy, N.; Albalawi, I.A.; Masoodi, T.; Subbaraj, G.K.; Jamal, F.; et al. Cancer cell plasticity: From cellular, molecular, and genetic mechanisms to tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 197–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.G.; Bilici, A.; Olmez, O.F.; Oven, B.B.; Acikgoz, O.; Cakir, T.; Basim, P.; Cakir, A.; Kutlu, Y.; Hamdard, J. The Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Predicting the Neoadjuvant Treatment Response in Patients with Locally Advanced Breast Cancer. Breast Care 2022, 17, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E.R.; Morikawa, T.; Butler, B.L.; Shrestha, K.; De La Rosa, R.; Yan, K.S.; Fuchs, C.S.; Magness, S.T.; Smits, R.; Ogino, S.; et al. Restriction of intestinal stem cell expansion and the regenerative response by YAP. Nature 2013, 493, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhu, L.; Rong, Y.; Shen, H.; Luk, J.M.; et al. Targeting Hippo pathway by specific interruption of YAP-TEAD interaction using cyclic YAP-like peptides. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, O.J.; Huang, S.M.; Kwon, J.L.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Seong, I.O.; Song, K.S.; Kim, K.H. Differential expression of Yes-associated protein and phosphorylated Yes-associated protein is correlated with expression of Ki-67 and phospho-ERK in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Histol. Histopathol. 2013, 28, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Li, X. Verteporfin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in different subtypes of breast cancer cell lines without light activation. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, Q.; Su, P.; Duan, M.; Xue, M.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; et al. Regulation of Hippo signaling and triple negative breast cancer progression by an ubiquitin ligase RNF187. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
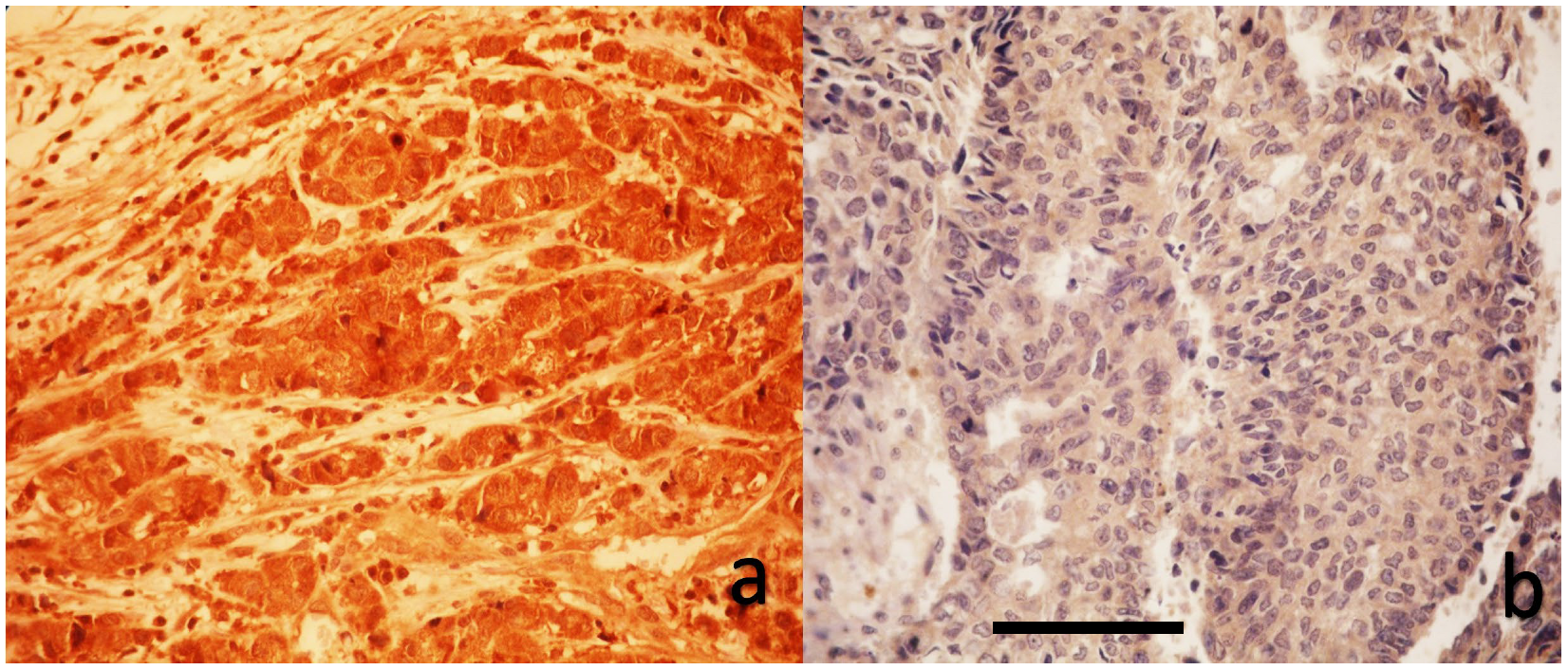
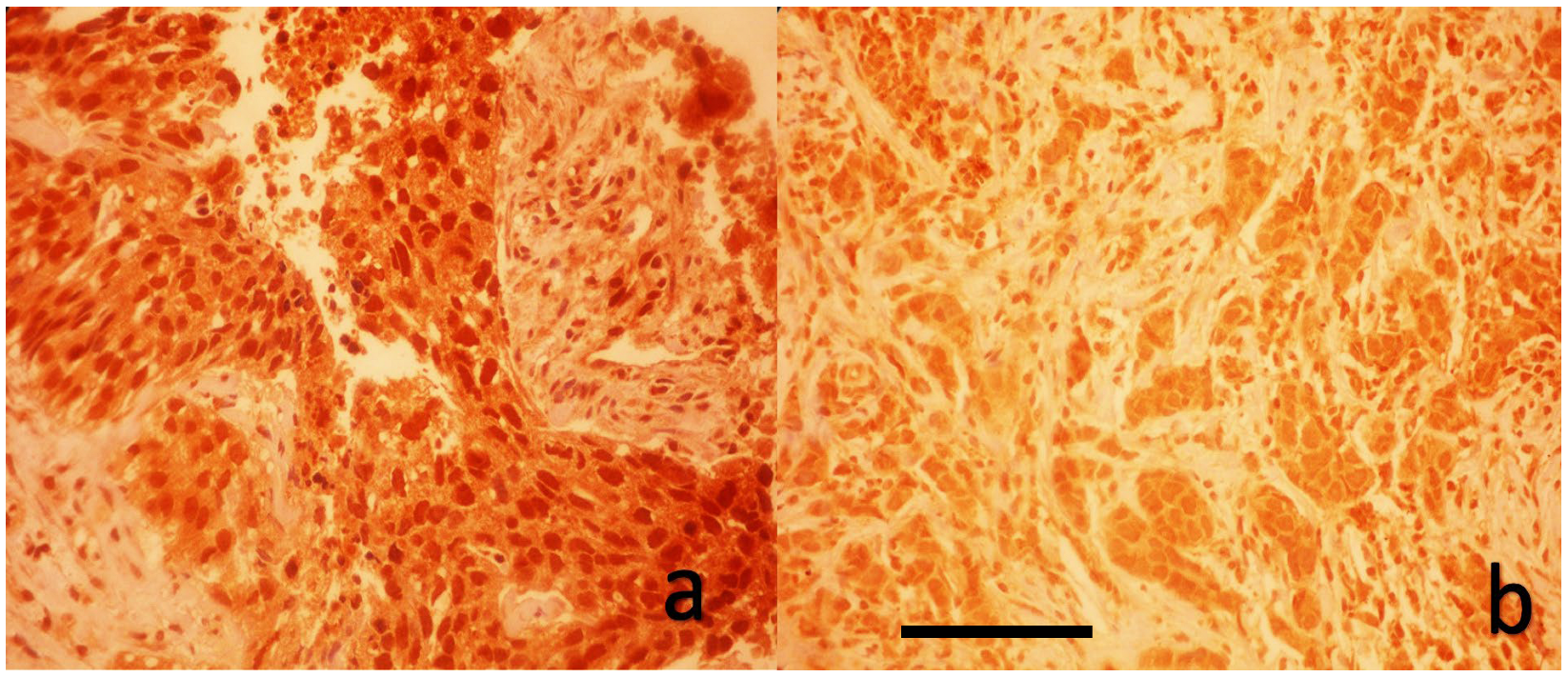
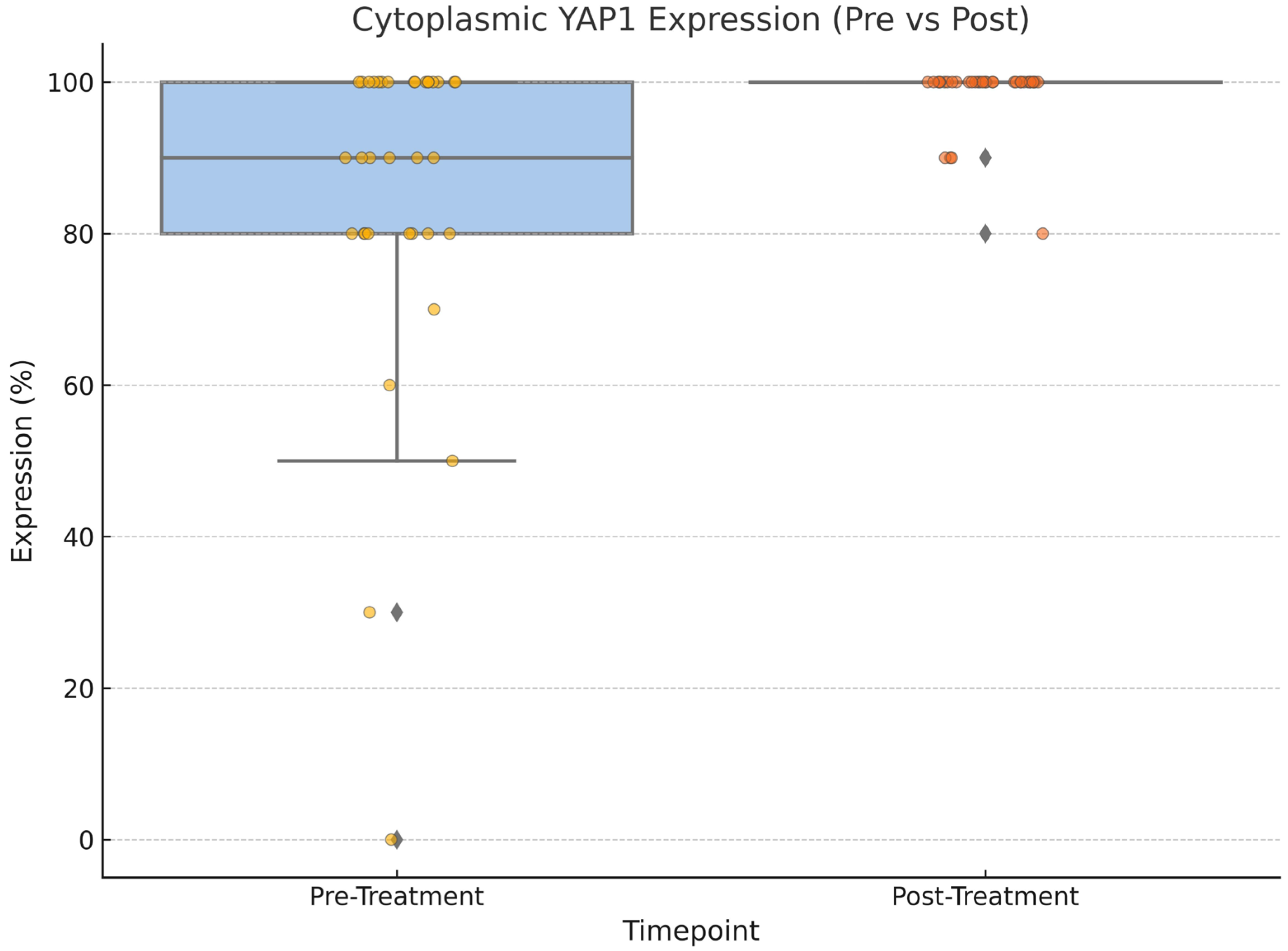

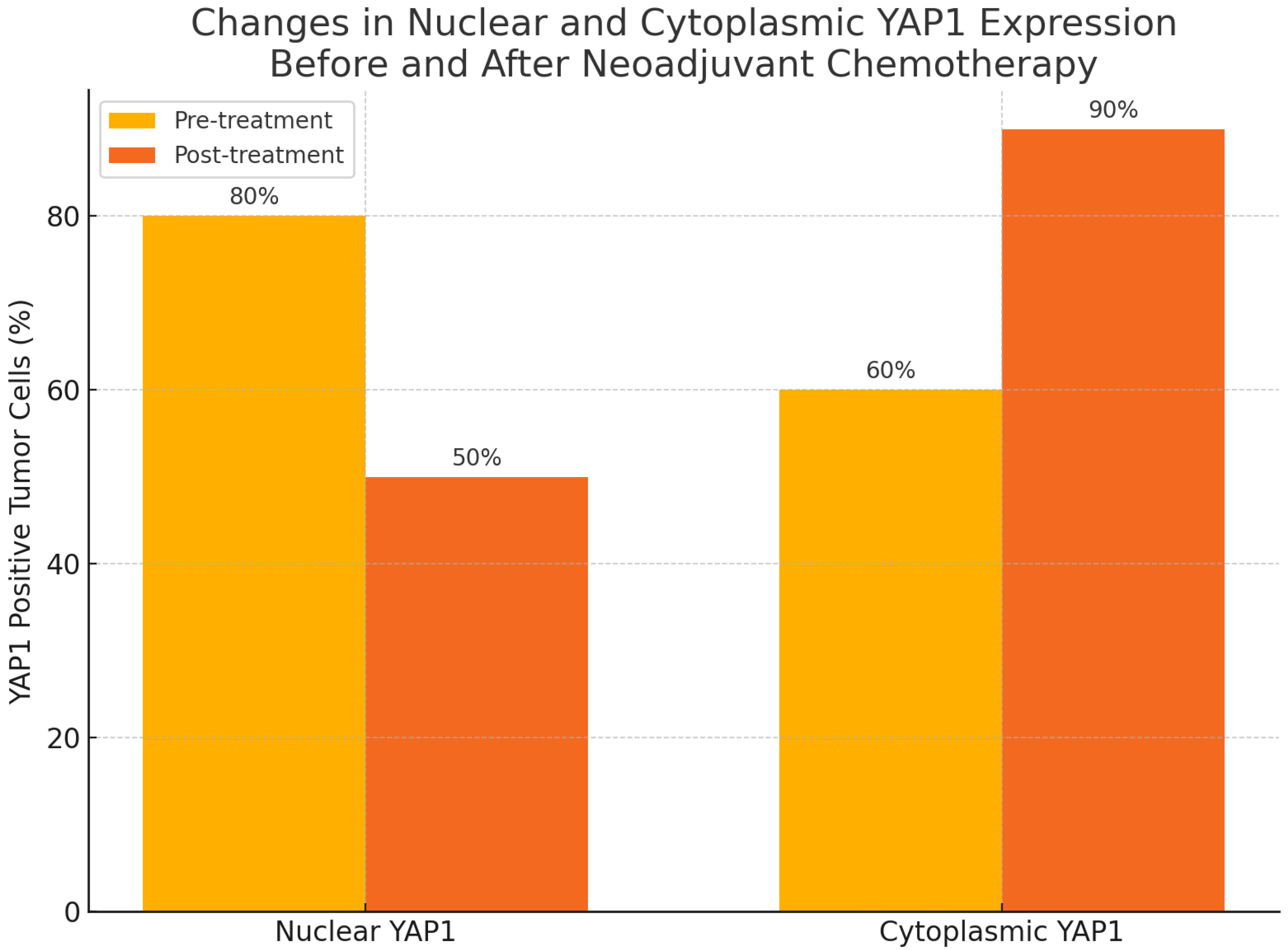
| Characteristics (N = 50) | |
| Age, median (range) | 49.5 (24–72) |
| Menopausal status, n (%) | |
| Premenopausal | 24 (48) |
| Postmenopausal | 26 (52) |
| Tumor location, n (%) | |
| Left | 23 (46) |
| Right | 27 (54) |
| Tumor size (mm) | 28 (20–36) |
| Baseline T stage (clinical) | |
| T1 | 7 (14) |
| T2 | 20 (40) |
| T3 | 18 (36) |
| T4 | 5 (10) |
| Baseline N stage (clinical) | |
| N1 | 24 (48) |
| N2 | 15 (30) |
| N3 | 11 (22) |
| Molecular phenotype, n (%) | |
| Luminal type | 27 (54) |
| HR-positive/HER-2-positive | 7 (14) |
| HER-2-positive/HR-negative | 7 (14) |
| Triple-negative | 9 (18) |
| ER positivity, n (%) | 34 (68) |
| PR positivity, n (%) | 30 (60) |
| HER-2 positivity, n (%) | 14 (28) |
| Baseline Ki-67, median (range) | 35 (10–90) |
| Axillary pCR, n (%) | 20 (40.0) |
| Breast pCR, n (%) | 11 (22) |
| YAP1-positive expression (pre-NAC), n (%) | 9 (18) |
| YAP1-negative expression (pre-NAC), n (%) | 41 (82) |
| Parameter | YAP1-Positive (n = 9) | YAP1-Negative (n = 41) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Axillary pCR, n (%) | 7 (77.8) | 13 (31.7) | 0.021 |
| Breast pCR, n (%) | 4 (44.4) | 7 (17.1) | 0.093 |
| Molecular Subtype, n (%) | 0.001 | ||
| Luminal (HR+/HER–2-) | 1 (11.1) | 26 (63.4) | |
| HR+/HER-2+ | 5 (55.6) | 2 (4.9) | |
| HR−/HER-2+ | 1 (11.1) | 6 (14.6) | |
| Triple-negative | 2 (22.2) | 7 (17.1) | |
| ER positivity, n (%) | 7 (77.8) | 33 (80.5) | NS |
| PR positivity, n (%) | 6 (66.7) | 30 (73.2) | NS |
| HER-2 positivity, n (%) | 6 (66.7) | 9 (22.0) | 0.01 |
| Ki-67 (Pre-NAC), median (%) | 75 | 55 | 0.028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erinc, O.; Goktas Aydin, S.; Erkinuresin, T.; Yilmaz, O.; Aydin, A.; Dagistanli, S.; Akarsu, M. The Impact of Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Expression Patterns in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Associations with Pathological Response and Tumor Features. Medicina 2025, 61, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071297
Erinc O, Goktas Aydin S, Erkinuresin T, Yilmaz O, Aydin A, Dagistanli S, Akarsu M. The Impact of Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Expression Patterns in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Associations with Pathological Response and Tumor Features. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071297
Chicago/Turabian StyleErinc, Osman, Sabin Goktas Aydin, Taskin Erkinuresin, Ozgur Yilmaz, Ahmet Aydin, Sevinc Dagistanli, and Murat Akarsu. 2025. "The Impact of Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Expression Patterns in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Associations with Pathological Response and Tumor Features" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071297
APA StyleErinc, O., Goktas Aydin, S., Erkinuresin, T., Yilmaz, O., Aydin, A., Dagistanli, S., & Akarsu, M. (2025). The Impact of Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1) Expression Patterns in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Associations with Pathological Response and Tumor Features. Medicina, 61(7), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071297






