Maternal and Fetal–Neonatal Complications of Romanian Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Retrospective Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Laboratory Characteristics
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDM | Gestational diabetes mellitus |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| PCOS | Polycystic ovary syndrome |
| PIH | Pregnancy-induced hypertension |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HELLP | Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets |
| LGA | Large for gestational age |
References
- Lende, M.; Rijhsinghani, A. Gestational Diabetes: Overview with Emphasis on Medical Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powe, C.E.; Allard, C.; Battista, M.C.; Doyon, M.; Bouchard, L.; Ecker, J.L.; Perron, P.; Florez, J.C.; Thadhani, R.; Hivert, M.F. Heterogeneous Contribution of Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion Defects to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 11th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 201: Pregestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 132, e228–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, L.E.; Hussey, J.M.; Crandell, J.L.; Brooks, J.L.; Bryant, A.G. Contraceptive use among women with prediabetes and diabetes in a US national sample. J. Midwifery Womens Health 2019, 64, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andes, L.J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Rolka, D.B.; Gregg, E.W.; Imperatore, G. Prevalence of Prediabetes Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States, 2005–2016. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e194498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, F.N.; Faramarzi, M.; Bakhtiari, A.; Omidvar, S. Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2018, 15, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, A.; Stefan, A.G.; Vladu, I.M.; Fortofoiu, M.C.; Clenciu, D.; Fortofoiu, M.; Gheorghe, I.O.; Comanescu, A.C.; Mota, M. Analysis of Risk Factors for the Development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Group of Romanian Patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 2367213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, G.; Basile, G.; Cucinella, G.; Greco, M.E.; Perino, A.; Chiantera, V.; Marinelli, S. Fresh vs. frozen embryo transfer in assisted reproductive techniques: A single center retrospective cohort study and ethical-legal implications. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 6809–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullo, G.; Scaglione, M.; Laganà, A.S.; Perino, A.; Andrisani, A.; Chiantera, V.; Cucinella, G.; Gitas, G.; Barra, F.; Riemma, G. Assisted Reproductive Techniques and Risk of Congenital Heart Diseases in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Reprod. Sci. 2023, 30, 2896–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kowalcze, K.; Burgio, S.; Ott, J.; Gullo, G.; Zaami, S.; Krysiak, R. The Impact of Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Minipuberty in Boys. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gherbon, A.; Frandes, M.; Lungeanu, D.; Nicula, M.; Timar, R. Transient Hyperthyroidism following the ingestion of complementary medications containing kelp seaweed: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e17058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicula, M.; Pacala, N.; Stef, L.; Pet, I.; Iancu, T.; Dronca, D.; Ahmadi, M.; Gherbon, A.; Deleanu, B. In vivo Experiments (Carassius gibelio Bloch) on Copper Homeostasis Alteration After Lead Intoxication and Natural Biologic-active Principles Treatments. Aquat. (Water Waste) 2017, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskovi-Kaplan, Z.A.; Ozgu-Erdinc, A.S. Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. In Diabetes: From Research to Clinical Practice; Islam, M.d.S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 4, pp. 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Luo, C.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F. Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 377, e067946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, J.; Shubrook, J. International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Coding for Diabetes. Clin. Diabetes 2017, 35, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes: The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group (IADPSG) Working Group on Outcome Definitions; Feig, D.S.; Corcoy, R.; Jensen, D.M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Nolan, C.J.; Oats, J.J.; Sacks, D.A.; Caimari, F.; McIntyre, H.D. Diabetes in pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and proposed codification of definitions. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, A.M.; Bogdanet, D.; Griffin, T.P.; Kgosidialwa, O.; Cervar-Zivkovic, M.; Dempsey, E.; Allotey, J.; Alvarado, F.; Clarson, C.; Cooray, S.D.; et al. A core outcome set for studies of gestational diabetes mellitus prevention and treatment. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Neonatal and Perinatal Mortality: Country, Regional and Global Estimates; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Basic Newborn Resuscitation: A Practical Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. The Prevention and Elimination of Disrespect and Abuse During Facility-Based Childbirth; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lamminpää, R.; Vehviläinen-Julkunen, K.; Gissler, M.; Selander, T.; Heinonen, S. Pregnancy outcomes in women aged 35 years or older with gestational diabetes—A registry-based study in Finland. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer-Graf, U.; Napoli, A.; Nolan, C.J. Diabetes in pregnancy: A new decade of challenges ahead. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdoe, M.B.; Kibusi, S.M.; Munyogwa, M.J.; Ernest, A.I. Prevalence and predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus among pregnant women attending antenatal clinic in Dodoma region, Tanzania: An analytical cross-sectional study. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2021, 4, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, A.; Serra, A.; Herrero, T.; Pan, D.; Ogunyemi, D. Pre-gestational versus gestational diabetes: A population-based study on clinical and demographic differences. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kwak, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, J.S.; Chung, H.R.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Jang, H.C. Pregnancy Outcomes of Women Additionally Diagnosed as Gestational Diabetes by the International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Criteria. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyari, M.; Abu-Romman, H.; Ajlouni, K. Maternal and Fetal Outcomes in Diabetic Pregnant Women. J. R. Med. Serv. 2013, 20, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zyl, H.; Levitt, N.S. Pregnancy outcome in patients with pregestational and gestational diabetes attending Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town, South Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. 2018, 108, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stogianni, A.; Lendahls, L.; Landin-Olsson, M.; Thunander, M. Obstetric and perinatal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, and control pregnancies, in Kronoberg, Sweden. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualdani, E.; Di Cianni, G.; Seghieri, M.; Francesconi, P.; Seghieri, G. Pregnancy outcomes and maternal characteristics in women with pregestational and gestational diabetes: A retrospective study on 206,917 singleton live births. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liu, B. Association between maternal diabetes mellitus and the risk of congenital malformations: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Zhao, M.; Lee, P.M.Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Xi, B.; Li, J. Maternal hypertensive disorders during pregnancy and the risk of offspring diabetes mellitus in childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood: A nationwide population-based cohort study. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, L.A.; Sedar, J.; Carmody, L.; Dunne, F. Comparing type 1 and type 2 diabetes in pregnancy- similar conditions or is a separate approach required? BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovesen, P.G.; Jensen, D.M.; Damm, P.; Rasmussen, S.; Kesmodel, U.S. Maternal and neonatal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes. a nation-wide study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 28, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 14. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S183–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, A.S.; Monti, N.; Fedeli, V.; Gullo, G.; Bizzarri, M. Does Alpha-lipoic acid improve effects on polycystic ovary syndrome? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coldebella, D.; Buzzaccarini, G.; Sleiman, Z.; Ferrari, J.; D’Alterio, M.; Della Corte, L.; Cucinella, G.; Gullo, G. Inositols administration: Further insights on their biological role. Gynaecol. Obstet. Ital. J. Narrat. Rev. 2023, 35, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yan, J.; Yang, H. Inositol Nutritional Supplementation for the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, C.; Song, Y.; Wang, X. Vitamin D Supplementation for the Outcomes of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Neonates: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2023, 2023, 1907222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gullo, G.; Scaglione, M.; Cucinella, G.; Perino, A.; Chiantera, V.; D’Anna, R.; Laganà, A.S.; Buzzaccarini, G. Impact of assisted reproduction techniques on the neuro-psycho-motor outcome of newborns: A critical appraisal. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 42, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medenica, S.; Abazovic, D.; Ljubić, A.; Vukovic, J.; Begovic, A.; Cucinella, G.; Zaami, S.; Gullo, G. The Role of Cell and Gene Therapies in the Treatment of Infertility in Patients with Thyroid Autoimmunity. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 4842316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mackeen, D.A.; Trauffer, P.M.; Berghella, V. (Eds.) Maternal-Fetal Evidence-Based Guidelines, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
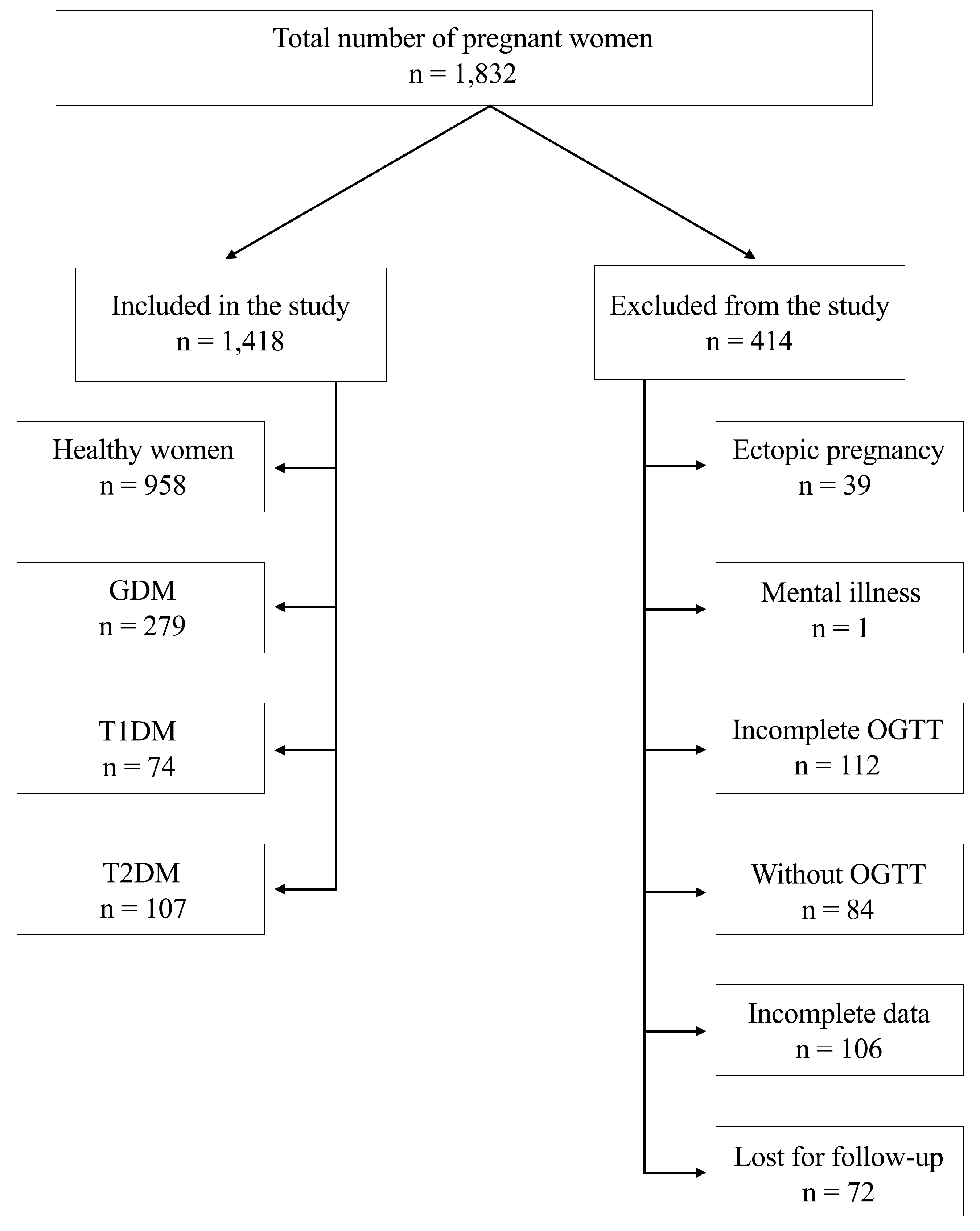
| Parameters | GDM | Control Group | p-Value (GDM vs. Control Group) | T1DM | p-Value (GDM vs. T1DM) | T2DM | p-Value (GDM vs. T2DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 279 | 958 | 74 | 107 | |||
| Age (years) | 31.78 ± 5.60 | 29.64 ± 5.91 | <0.001 | 31.08 ± 6.14 | 0.308 | 33.18 ± 6.24 | 0.048 |
| Areas | 0.239 | 0.140 | 0.152 | ||||
| 140 (50.18%) | 519 (54.17%) | 30 (40.54%) | 45 (42.05%) | |||
| 139 (49.82%) | 439 (45.83%) | 44 (59.46%) | 62 (57.95%) | |||
| Number of pregnancies | 0.342 | 0.0001 | 0.990 | ||||
| 138 (49.46%) | 443 (46.24%) | 56 (75.67%) | 53 (49.53%) | |||
| 141 (50.54%) | 515 (53.76%) | 18 (24.33%) | 54 (50.47%) | |||
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 98.97 ± 13.63 | 76.92 ± 8.62 | <0.001 | 180.63 ± 87.67 | <0.001 | 146.52 ± 65.99 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.45 ± 0.54 | 4.57 ± 0.33 | <0.001 | 8.23 ± 2.44 | <0.001 | 7.18 ± 2.00 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| 104 (37.28%) | 0 (0%) | 74 (100%) | 93 (86.91%) | |||
| 175 (62.72%) | 958 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 14 (13.09%) | |||
| Chronic hypertension | <0.001 | 0.300 | <0.001 | ||||
| 11 (3.94%) | 4 (0.42%) | 5 (6.76%) | 17 (15.89%) | |||
| 268 (96.06%) | 954 (99.58%) | 69 (93.24%) | 90 (84.11%) | |||
| Obesity | <0.001 | 0.584 | <0.001 | ||||
| 21 (7.53%) | 6 (0.63%) | 7 (9.46%) | 32 (29.91%) | |||
| 258 (92.47%) | 952 (99.37%) | 67 (90.54%) | 75 (70.09%) | |||
| Anemia | 0.003 | 0.238 | 0.051 | ||||
| 61 (21.86%) | 296 (30.90%) | 21 (28.38%) | 14 (13.08%) | |||
| 218 (78.14%) | 662 (69.10%) | 53 (71.62%) | 93 (86.92%) | |||
| Autoimmune thyroiditis | 0.145 | <0.001 | 0.094 | ||||
| 8 (2.87%) | 47 (4.9%) | 15 (20.27%) | 7 (6.54%) | |||
| 271 (97.13%) | 911 (95.1%) | 59 (79.73%) | 100 (93.46%) |
| Age Group | GDM (n = 279) | Control Group (n = 958) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14–20 years | 9 (3.22%) | 67 (7%) | 0.021 |
| 21–25 years | 27 (9.67%) | 169 (17.64%) | 0.136 |
| 26–30 years | 79 (28.31%) | 296 (30.90%) | 0.408 |
| 31–35 years | 88 (31.55%) | 261 (27.24%) | 0.160 |
| 36–40 years | 65 (23.30%) | 141 (14.71%) | 0.0007 |
| 41–45 years | 11 (3.95%) | 24 (2.5%) | 0.202 |
| Maternal and Fetal–Neonatal Complications | GDM (n = 279) | Control Group (n = 958) | p-Value (GDM vs. Control Group) | T1DM (n = 74) | p-Value (GDM vs. T1DM) | T2DM (n = 107) | p-Value (GDM vs. T2DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal complications | |||||||
| Type of birth | 0.0035 | 0.0001 | 0.043 | ||||
| 152 (54.48%) | 427 (44.57%) | 22 (29.72%) | 46 (43%) | |||
| 127 (45.52%) | 531 (55.43%) | 52 (70.27%) | 61 (57%) | |||
| Abortion | 0.008 | 0.030 | 0.031 | ||||
| 2 (0.72%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (4.05%) | 4 (3.74%) | |||
| 277 (99.28%) | 958 (100%) | 71 (95.95%) | 103 (96.26%) | |||
| Premature birth | 0.088 | 0.004 | 0.014 | ||||
| 43 (15.41%) | 111 (11.59%) | 22 (29.73%) | 28 (26.17%) | |||
| 236 (84.59%) | 847 (88.41%) | 52 (70.27%) | 79 (73.83%) | |||
| Pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.007 | ||||
| 117 (41.93%) | 35 (3.65%) | 12 (16.22%) | 29 (27.1%) | |||
| 162 (58.07%) | 923 (96.35%) | 62 (83.78%) | 78 (72.9%) | |||
| Preeclampsia | <0.001 | 0.487 | 0.576 | ||||
| 23 (8.24%) | 5 (0.52%) | 8 (10.81%) | 7 (6.54%) | |||
| 256 (91.76%) | 953 (99.48%) | 66 (89.19%) | 100 (93.46%) | |||
| Hypoglycemia | 0.106 | 0.841 | 0.902 | ||||
| 3 (1.07%) | 3 (0.31%) | 1 (1.35%) | 1 (0.93%) | |||
| 276 (98.93%) | 955 (99.69%) | 73 (98.65%) | 106 (99.07%) | |||
| Infections | <0.001 | 0.136 | 0.475 | ||||
| 11 (3.94%) | 6 (0.63%) | 6 (8.1%) | 6 (5.6%) | |||
| 268 (96.06%) | 952 (99.37%) | 68 (91.9%) | 101 (94.4%) | |||
| Fetal–neonatal complications | |||||||
| Apgar score | 0.668 | 0.016 | 2 | 0.002 | |||
| 28 (10.03%) | 88 (9.18%) | 15 (20.27%) | 3 (21.5%) | |||
| 251 (89.97%) | 870 (90.82%) | 59 (79.73%) | 84 (78.5%) | |||
| Birth weight | |||||||
| 31 (11.11%) | 112 (11.7%) | 0.789 | 12 (16.22%) | 0.232 | 18 (16.82%) | 0.131 |
| 211 (75.63%) | 799 (83.4%) | 50 (67.56%) | 69 (64.48%) | |||
| 37 (13.26%) | 47 (4.9%) | <0.001 | 12 (16.22%) | 0.513 | 20 (18.7%) | 0.178 |
| Fetal death | 0.706 | 0.017 | 0.079 | ||||
| 3 (1.07%) | 8 (0.83%) | 4 (5.4%) | 4 (3.74%) | |||
| 276 (98.93%) | 950 (99.17%) | 70 (94.6%) | 103 (96.26%) | |||
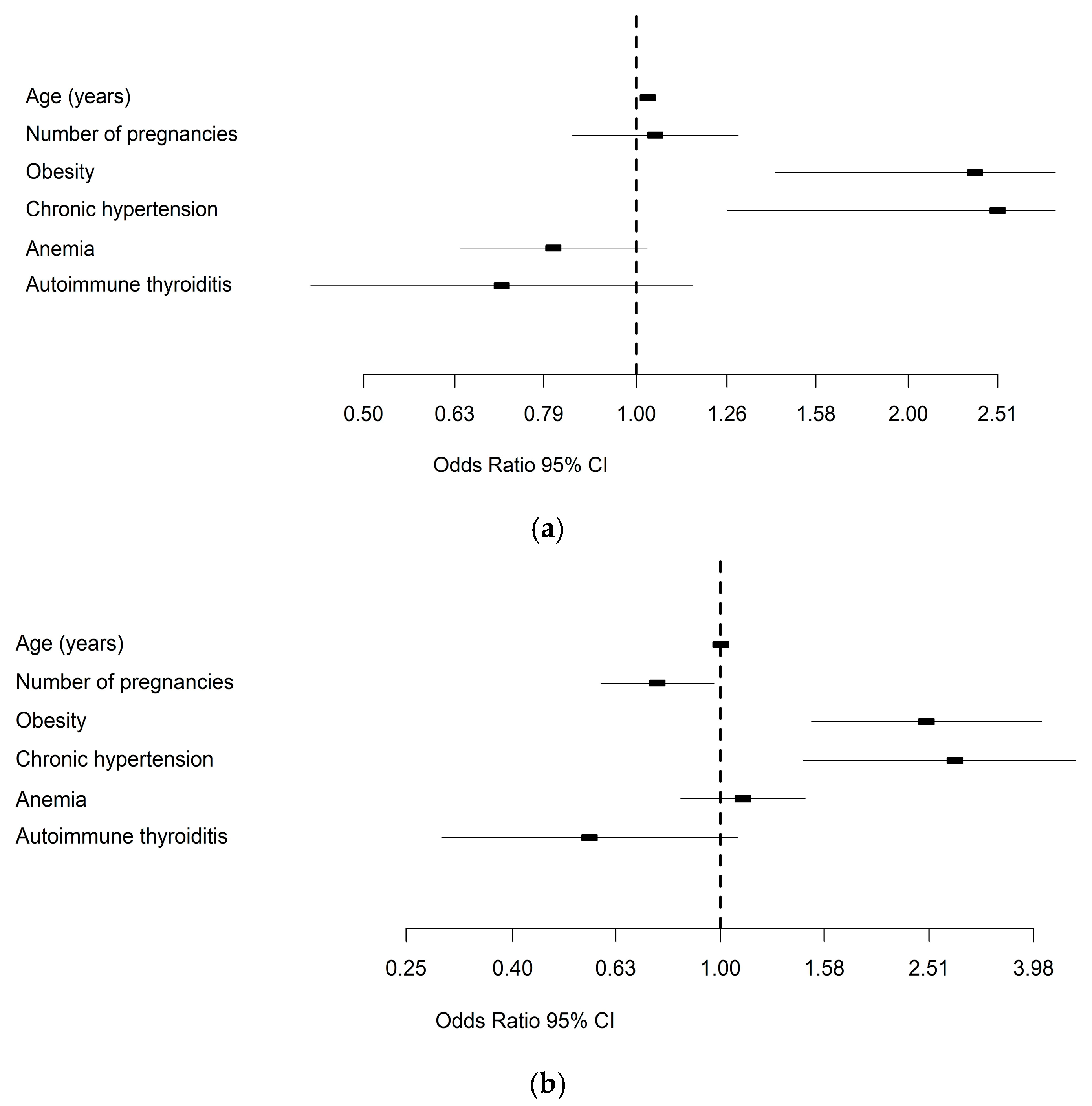
| Maternal Complications | Fetal–Neonatal Complications | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictor | OR | Lower | Upper | p-Value | OR | Lower | Upper | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 1.03 | 1.011 | 1.047 | 0.002 | 1.001 | 0.98 | 1.022 | 0.942 |
| Number of pregnancies | 1.05 | 0.849 | 1.294 | 0.663 | 0.757 | 0.59 | 0.971 | 0.028 |
| Obesity | 2.37 | 1.424 | 3.942 | <0.001 | 2.481 | 1.493 | 4.12 | <0.001 |
| Chronic hypertension | 2.51 | 1.262 | 5.002 | 0.009 | 2.813 | 1.44 | 5.495 | 0.002 |
| Anemia | 0.81 | 0.64 | 1.031 | 0.088 | 1.104 | 0.839 | 1.453 | 0.48 |
| Autoimmune thyroiditis | 0.71 | 0.436 | 1.152 | 0.165 | 0.561 | 0.292 | 1.076 | 0.082 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gherbon, A.; Frandes, M.; Toderescu, C.D.; Dirpes, D.; Timar, R.; Nicula, M.N.; Dascau, C.; Daniluc, R.; Timar, B. Maternal and Fetal–Neonatal Complications of Romanian Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071190
Gherbon A, Frandes M, Toderescu CD, Dirpes D, Timar R, Nicula MN, Dascau C, Daniluc R, Timar B. Maternal and Fetal–Neonatal Complications of Romanian Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071190
Chicago/Turabian StyleGherbon, Adriana, Mirela Frandes, Corina Dalia Toderescu, Darius Dirpes, Romulus Timar, Marioara Neagu Nicula, Calin Dascau, Razvan Daniluc, and Bogdan Timar. 2025. "Maternal and Fetal–Neonatal Complications of Romanian Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Retrospective Comparative Study" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071190
APA StyleGherbon, A., Frandes, M., Toderescu, C. D., Dirpes, D., Timar, R., Nicula, M. N., Dascau, C., Daniluc, R., & Timar, B. (2025). Maternal and Fetal–Neonatal Complications of Romanian Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Medicina, 61(7), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071190







