Effects of Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Exercise on Self-Reported Pain and Mechanical Hyperalgesia in Older Adults with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
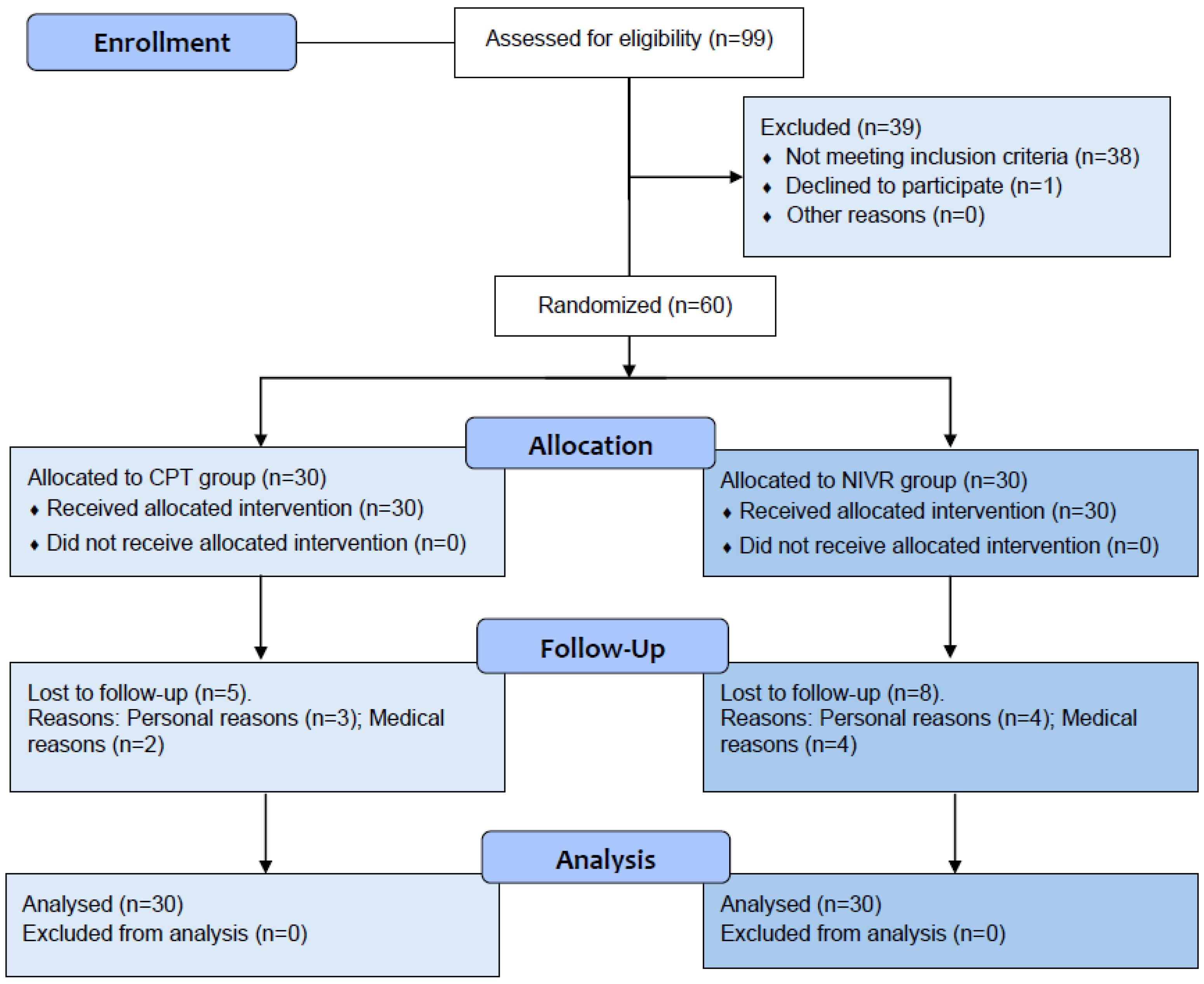
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Overview
2.2. Participant Recruitment
2.3. Group Allocation
2.4. Intervention Protocol
- Control group: CPT sessions included physical agents (e.g., TENS, hot packs), warm-up, structured exercises (aerobics, strength, balance, and flexibility), and a cool-down. Individualized adaptations ensured the exercises matched participants’ capacities.
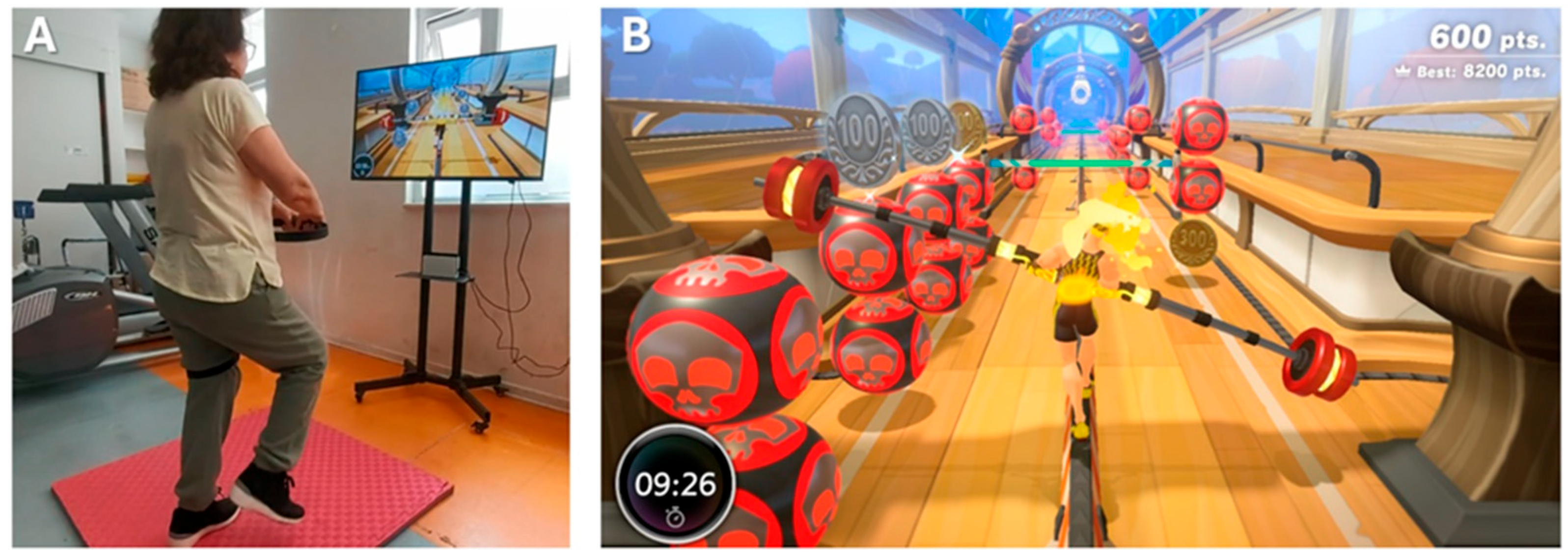
- Experimental group: CPT was complemented with 20 min of NIVR, replacing part of the CPT exercise block to maintain an equal session duration of 50 min. The NIVR included activities targeting strength, balance, flexibility, and aerobic endurance, delivered through Ring Fit Adventure (Nintendo Switch®, Nintendo Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan) on a 43-inch TV with real-time feedback (Figure 2). Specifically, the exercises performed using the NIVR device were as follows: Dorsal rotation, Rotation with inclination, Knee raises, Squats, Lunge with rotation, Lateral inclination, Squats with extension, The warrior, The chair, Crescent moon, Equilibrium, Moto adductors, Trunk swinging, Running path, Monster’s lair, and Jogging bridge.
2.5. Outcome Assessments
2.6. Statistical Anlysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
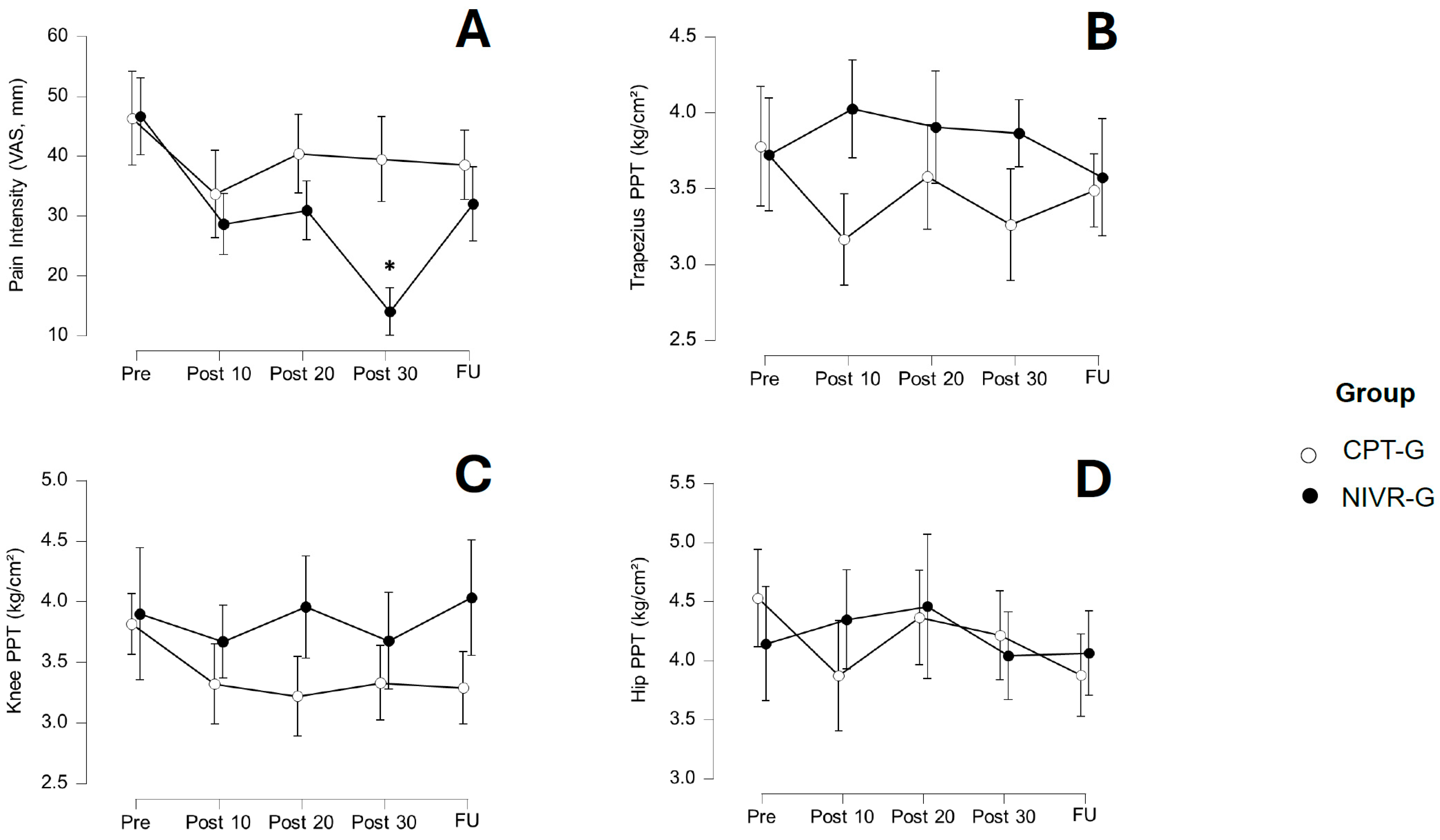
4.1. Self-Reported Pain Intensity
4.2. Mechanical Hyperalgesia
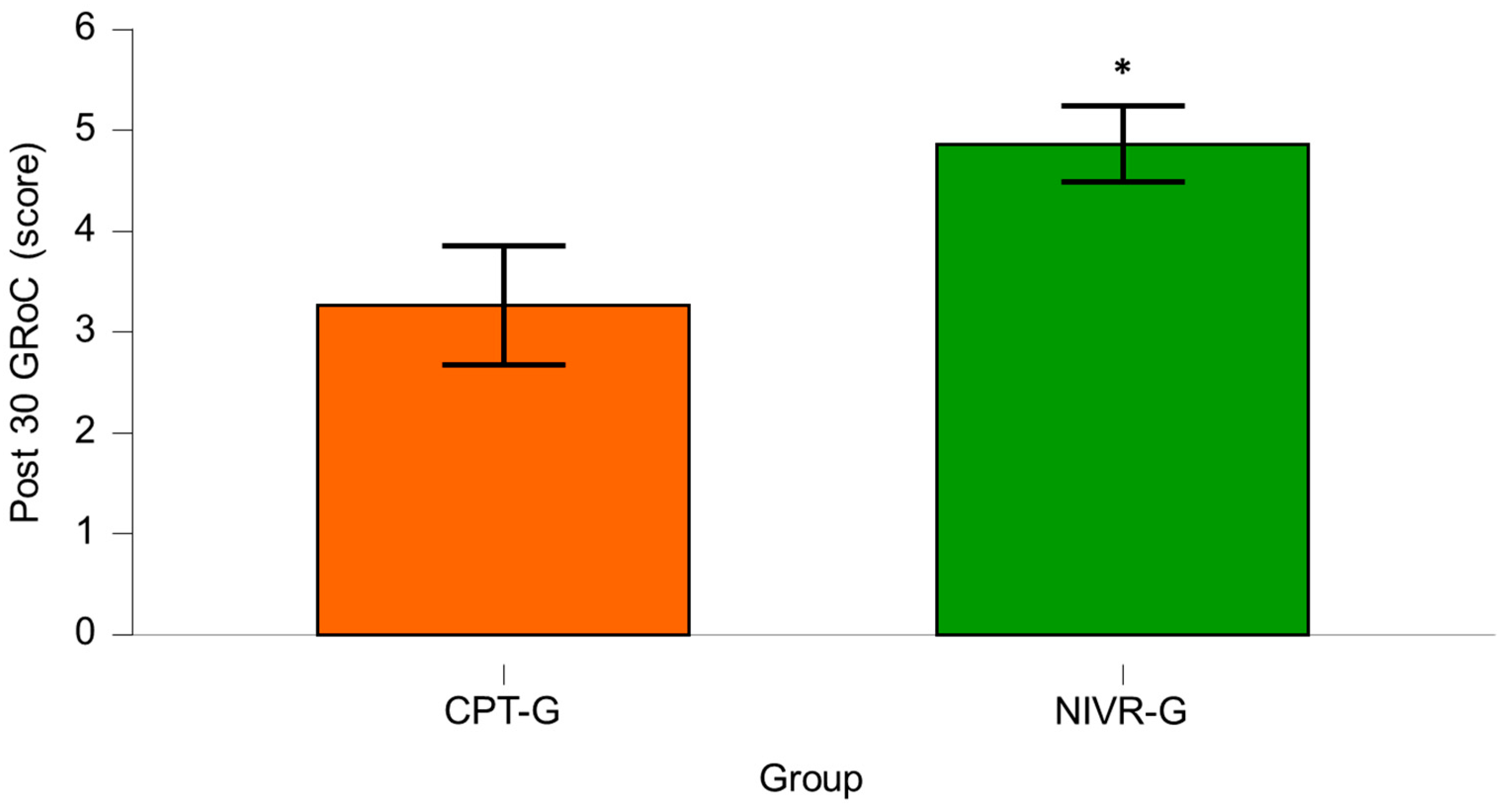
4.3. Minimal Clinically Important Difference
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| PPTs | Pressure pain thresholds |
| CS | Central Sensitization |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| NIVR | Non-immersive virtual reality |
| CPT | Conventional physical therapy |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| MCID | Minimum clinically important difference |
| GRoC | Global Rating of Change |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| ACSM | American College of Sports Medicine |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CPM | Conditioned pain modulation |
References
- Katz, J.N.; Arant, K.R.; Loeser, R.F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Hoy, D.; Buchbinder, R.; Mansournia, M.A.; Bettampadi, D.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Smith, E.; Sepidarkish, M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Neck Pain in the General Population, 1990-2017: Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMJ 2020, 368, m791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, M.; Smith, E.; Hoy, D.; Nolte, S.; Ackerman, I.; Fransen, M.; Bridgett, L.; Williams, S.; Guillemin, F.; Hill, C.L.; et al. The Global Burden of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jordan, J.M. Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 26, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, A.J.J.; McGrory, B.J.; Starz, T.W.; Vincent, K.R.; McCardel, B.; Golightly, Y.M. AAOS Appropriate Use Criteria: Optimizing the Non-Arthroplasty Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee. JAAOS—J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 22, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcieszek, A.; Kurowska, A.; Majda, A.; Liszka, H.; Gądek, A. The Impact of Chronic Pain, Stiffness and Difficulties in Performing Daily Activities on the Quality of Life of Older Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, G.A.; Stewart, L.; French, M.R.; Cibere, J.; Jordan, J.M.; March, L.; Suarez-Almazor, M.; Gooberman-Hill, R. Understanding the Pain Experience in Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis—An OARSI/OMERACT Initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogö Nyvang, J.; Naili, J.E.; Iversen, M.D.; Broström, E.W.; Hedström, M. Younger Age Is Associated with Greater Pain Expression among Patients with Knee or Hip Osteoarthritis Scheduled for a Joint Arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Severo, M.; Santos, R.A.; Barros, H.; Branco, J.; Lucas, R.; Costa, L.; Ramos, E. Knee and Hip Radiographic Osteoarthritis Features: Differences on Pain, Function and Quality of Life. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, P.H.; Buenaver, L.F.; Bounds, S.C.; Hussain, S.; Park, R.J.; Haque, U.J.; Campbell, C.M.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Edwards, R.R.; Smith, M.T. Discordance between Pain and Radiographic Severity in Knee Osteoarthritis: Findings from Quantitative Sensory Testing of Central Sensitization. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Shimo, K.; Niwa, Y.; Katsura, Y.; Tokiwa, Y.; Ohga, S.; Matsubara, T. Pain Sensitization and Neuropathic Pain-like Symptoms Associated with Effectiveness of Exercise Therapy in Patients with Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 4323045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, P.; Knight, E.; Wright, A. Subjects with Knee Osteoarthritis Exhibit Widespread Hyperalgesia to Pressure and Cold. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolio, L.; Lim, K.Y.; McKenzie, J.E.; Yan, M.K.; Estee, M.; Hussain, S.M.; Cicuttini, F.; Wluka, A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Neuropathic-like Pain and/or Pain Sensitization in People with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 1096–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingleton, C.; Smart, K.; Moloney, N.; Fullen, B.M.; Doody, C. Pain Sensitization in People with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J. Central Sensitization: Implications for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pain. Pain 2011, 152, S2–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Imamura, S.T.; Kaziyama, H.H.S.; Targino, R.A.; Hsing, W.T.; De Souza, L.P.M.; Cutait, M.M.; Fregni, F.; Camanho, G.L. Impact of Nervous System Hyperalgesia on Pain, Disability, and Quality of Life in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Controlled Analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Nie, H.; Laursen, M.B.; Laursen, B.S.; Madeleine, P.; Simonsen, O.H.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Sensitization in Patients with Painful Knee Osteoarthritis. Pain 2010, 149, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseng, T.; Vliet Vlieland, T.P.M.; Battista, S.; Beckwée, D.; Boyadzhieva, V.; Conaghan, P.G.; Costa, D.; Doherty, M.; Finney, A.G.; Georgiev, T.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Non-Pharmacological Core Management of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: 2023 Update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, S.L.; Neogi, T.; Hochberg, M.C.; Oatis, C.; Guyatt, G.; Block, J.; Callahan, L.; Copenhaver, C.; Dodge, C.; Felson, D.; et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudejko, T.; van der Esch, M.; Schrijvers, J.; Richards, R.; van den Noort, J.C.; Wrigley, T.; van der Leeden, M.; Roorda, L.D.; Lems, W.; Harlaar, J.; et al. The Immediate Effect of a Soft Knee Brace on Dynamic Knee Instability in Persons with Knee Osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2018, 57, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poenaru, D.; Sandulescu, M.I.; Potcovaru, C.G.; Cinteza, D. High-Intensity Laser Therapy in Pain Management of Knee Osteoarthritis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madry, H. Surgical Therapy in Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlgenannt, I.; Simons, A.; Stieglitz, S. Virtual Reality. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2020, 62, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byra, J.; Czernicki, K. The Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation in Patients with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guede-Rojas, F.; Andrades-Torres, B.; Aedo-Díaz, N.; González-Koppen, C.; Muñoz-Fuentes, M.; Enríquez-Enríquez, D.; Carvajal-Parodi, C.; Mendoza, C.; Alvarez, C.; Fuentes-Contreras, J. Effects of Exergames on Rehabilitation Outcomes in Patients with Osteoarthritis. A Systematic Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2025, 47, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, E.; Sari, Z. The Efficacy of Exergaming in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Physiother. Res. Int. 2022, 27, e1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manlapaz, D.G.; Sole, G.; Jayakaran, P.; Chapple, C.M. Risk Factors for Falls in Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. PM R 2019, 11, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Tang, H.; Luo, Y.; Yan, S.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, F.; Yang, S.; Yang, X. Efficacy of Virtual Reality Exercise in Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1424815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, O.; Başar, S. The Effect of Virtual Reality on Pain, Kinesiophobia and Function in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Knee 2023, 45, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; He, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, F. The Effectiveness of Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality Rehabilitation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2024, 39, 582–590.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretat, T.; Koller, C.; Hügle, T. Virtual Reality as a Treatment for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Syndromes. Jt. Bone Spine 2025, 92, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, H.G. Interacting with Virtual Objects via Embodied Avatar Hands Reduces Pain Intensity and Diverts Attention. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, B.; Ma, K.; Hu, L.; Lu, X. The Analgesic Effects and Neural Oscillatory Mechanisms of Virtual Reality Scenes Based on Distraction and Mindfulness Strategies in Human Volunteers. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 131, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditchburn, J.-L.; van Schaik, P.; Dixon, J.; MacSween, A.; Martin, D. The Effects of Exergaming on Pain, Postural Control, Technology Acceptance and Flow Experience in Older People with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: A Randomised Controlled Trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.T.; Makarewicz, N.; Wang, E.Y.; Zuniga-Hernandez, M.; Titzler, J.; Jackson, C.; Suen, M.Y.; Rosales, O.; Caruso, T.J. Virtual Reality Facilitated Exercise Improves Pain Perception: A Crossover Study. J. Clin. Anesth. 2023, 91, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, K.E.; Cervantes, X.A.; Boone, C.L.; Wind, B.; Naugle, K.M. The Acute Hypoalgesic Effects of Active Head-Mounted Display Virtual Reality Games. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.G.; Fontenot, M.R.; Garcia-Palacios, A.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Alhalabi, W.; Curatolo, M.; Flor, H. Adding Tactile Feedback Increases Avatar Ownership and Makes Virtual Reality More Effective at Reducing Pain in a Randomized Crossover Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, N.; Feng, J.y.; Liu, H.x.; Chen, X.y.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, H. Effects of Exergaming on Musculoskeletal Pain in Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR Serious Games 2023, 11, e42944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Parodi, C.; Mendoza, C.; Alvarez, C.; Soto-Martínez, A.; Ulloa-Díaz, D.; Jorquera-Aguilera, C.; Guede-Rojas, F. Effectiveness of Exergames on Functional Physical Performance in Older Adults with Knee/Hip Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Runhaar, J.; Kloppenburg, M.; Boers, M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; CREDO Expert Group. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performance of American College of Rheumatology, EULAR, and National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Criteria Against Clinically Relevant Knee Osteoarthritis: Data From the CHECK Cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2024, 76, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Bohnen, A.; Ginai, A.; Prins, A.; Verhaar, J. Validity of American College of Rheumatology Criteria for Diagnosing Hip Osteoarthritis in Primary Care Research. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, D.; Lavados, M.; Rojas, P.; Henríquez, C.; Silva, F.; Guillón, M.; Jiménez, D.; Lavados, M.; Rojas, P.; Henríquez, C.; et al. Performance of an Abbreviated Mini Mental Examination to Detect Dementia in Older People. Rev. Méd. Chile 2017, 145, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.-M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghadir, A.; Anwer, S.; Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, Z. Test-Retest Reliability, Validity, and Minimum Detectable Change of Visual Analog, Numerical Rating, and Verbal Rating Scales for Measurement of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, H.; Smart, K.M.; Moloney, N.A.; Blake, C.; Doody, C.M. Pain Sensitization Associated with Nonresponse after Physiotherapy in People with Knee Osteoarthritis. PAIN 2018, 159, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, A.B.; Neogi, T.; Mikolaitis, R.A.; Block, J.A.; Shakoor, N. Somatosensation in OA: Exploring the Relationships of Pain Sensitization, Vibratory Perception and Spontaneous Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, N.J.; Booth, J.; Sturnieks, D.L.; Barry, B.K. Acute Resistance Exercise and Pressure Pain Sensitivity in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomised Crossover Trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Noor, A.S.; Englund, E.; Wretenberg, P.; Sjödén, G.O. Pressure-Pain Threshold Algometric Measurement in Patients With Greater Trochanteric Pain After Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. J. Pain 2008, 24, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamper, S.J.; Maher, C.G.; Mackay, G. Global Rating of Change Scales: A Review of Strengths and Weaknesses and Considerations for Design. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; White, I.R.; Carlin, J.B.; Spratt, M.; Royston, P.; Kenward, M.G.; Wood, A.M.; Carpenter, J.R. Multiple Imputation for Missing Data in Epidemiological and Clinical Research: Potential and Pitfalls. BMJ 2009, 338, b2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0-203-77158-7. [Google Scholar]
- da Cunha Nascimento, D.; Rolnick, N.; da Silva Almeida, I.; Junior, G.C.; Durigan, J.L. Frequentist, Bayesian Analysis and Complementary Statistical Tools for Geriatric and Rehabilitation Fields: Are Traditional Null-Hypothesis Significance Testing Methods Sufficient? Clin. Interv. Aging 2024, 19, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, G.; Williamson, P.; Batterham, A.M. Issues in the Determination of ‘Responders’ and ‘Non-Responders’ in Physiological Research. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, L.; Gui, C.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Tan, H.; Su, W.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Q. Virtual Reality Intervention for Patients With Neck Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e38256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brea-Gómez, B.; Laguna-González, A.; Pérez-Gisbert, L.; Valenza, M.C.; Torres-Sánchez, I. Virtual Reality Based Rehabilitation in Adults with Chronic Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Virtual Real. 2024, 28, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallari, B.; Spaeth, E.K.; Goh, H.; Boyd, B.S. Virtual Reality as an Analgesic for Acute and Chronic Pain in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2053–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.H.M.; Zhu, M.; Zou, Z.; Wong, C.L.; Lo, S.H.S.; Chung, V.C.-H.; Wong, S.Y.-S.; Sit, R.W.S. Immersive and Nonimmersive Virtual Reality–Assisted Active Training in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e48787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, N.; Randall, H.; Choksi, H.; Gao, A.; Vaughan, C.; Poronnik, P. Virtual Reality Interventions for Acute and Chronic Pain Management. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 114, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, N.; Aina, A.; May, S. The Benefits of Adding Manual Therapy to Exercise Therapy for Improving Pain and Function in Patients With Knee or Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2022, 52, 675-A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.P.; Williams, M.; Eyles, J.P.; Chen, J.S.; Makovey, J.; Hunter, D.J. Effectiveness of Knee Bracing in Osteoarthritis: Pragmatic Trial in a Multidisciplinary Clinic. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 19, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duivenvoorden, T.; van Raaij, T.M.; Horemans, H.L.D.; Brouwer, R.W.; Bos, P.K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Reijman, M. Do Laterally Wedged Insoles or Valgus Braces Unload the Medial Compartment of the Knee in Patients with Osteoarthritis? Clin. Orthop. 2015, 473, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Romero, E.A.; Fernández-Carnero, J.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Ochoa Sáez, V.; Burgos Caballero, V.; Pecos-Martín, D. Is a Combination of Exercise and Dry Needling Effective for Knee OA? Pain Med. 2020, 21, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado-Mateo, D.; Lavín-Pérez, A.M.; Peñacoba, C.; Del Coso, J.; Leyton-Román, M.; Luque-Casado, A.; Gasque, P.; Fernández-del-Olmo, M.Á.; Amado-Alonso, D. Key Factors Associated with Adherence to Physical Exercise in Patients with Chronic Diseases and Older Adults: An Umbrella Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.J.; Rathod-Mistry, T.; Parry, E.L.; Pope, C.; Neogi, T.; Peat, G. Triggers for Acute Flare in Adults with, or at Risk of, Knee Osteoarthritis: A Web-Based Case-Crossover Study in Community-Dwelling Adults. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadzadeh, A.; Samad-Soltani, T.; Salahzadeh, Z.; Rezaei-Hachesu, P. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality-Based Exercise Therapy in Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 24, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, J.M.; Dennis, S.; Gibson, K.A.; Livings, R.; Mills, K.; Schabrun, S.M.; Sun, H.; Naylor, J.M. Knee Osteoarthritis Patient Perspectives of Their Care in an Australian Private Physiotherapy Setting: A Qualitative Exploratory Interview Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; You, J.; Yang, Y. Effect of Digital Exercise Therapy on the Pain and Physical Function of Patients With Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e66037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suokas, A.K.; Walsh, D.A.; McWilliams, D.F.; Condon, L.; Moreton, B.; Wylde, V.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Zhang, W. Quantitative Sensory Testing in Painful Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Shimo, K.; Niwa, Y.; Tokiwa, Y.; Matsubara, T. Association of Chronic Pain with Radiologic Severity and Central Sensitization in Hip Osteoarthritis Patients. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch, E.; Torres, R.; Nijs, J.; Van Oosterwijck, J. Evidence for Central Sensitization in Patients with Osteoarthritis Pain: A Systematic Literature Review. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, D.; Capone, G.; Marchettini, P.; Candrian, C.; Zaffagnini, S.; Filardo, G. High Prevalence of Pain Sensitization in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-Analysis with Meta-Regression. Cartilage 2022, 13, 19476035221087698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibulka, M.T.; Bloom, N.J.; Enseki, K.R.; Macdonald, C.W.; Woehrle, J.; McDonough, C.M. Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits-Hip Osteoarthritis: Revision 2017. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, A1–A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuni, B.; Wang, H.; Rickert, M.; Ewerbeck, V.; Schiltenwolf, M. Pain Threshold Correlates with Functional Scores in Osteoarthritis Patients. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, M.; Petersen, K.K.; Laursen, M.B.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Facilitated Temporal Summation of Pain Correlates with Clinical Pain Intensity after Hip Arthroplasty. Pain 2017, 158, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.D.; Sibille, K.T.; Goodin, B.R.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Glover, T.L.; Bartley, E.; Riley, J.L.; Herbert, M.S.; Sotolongo, A.; Schmidt, J.; et al. Experimental Pain Sensitivity Differs as a Function of Clinical Pain Severity in Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlesso, L.C.; Segal, N.A.; Frey-Law, L.; Zhang, Y.; Na, L.; Nevitt, M.; Lewis, C.E.; Neogi, T. Pain Susceptibility Phenotypes in Those Free of Knee Pain with or at Risk of Knee Osteoarthritis: The Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-Villalobos, P.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Navarro-Espigares, J.L.; Hernández-Torres, E.; Villalobos, M.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Arroyo-Morales, M. Normalization of Widespread Pressure Pain Hypersensitivity after Total Hip Replacement in Patients with Hip Osteoarthritis Is Associated with Clinical and Functional Improvements. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graven-Nielsen, T.; Wodehouse, T.; Langford, R.M.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Kidd, B.L. Normalization of Widespread Hyperesthesia and Facilitated Spatial Summation of Deep-Tissue Pain in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients after Knee Replacement. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Simonsen, O.; Wilder-Smith, O.; Laursen, M.B. Presurgical Assessment of Temporal Summation of Pain Predicts the Development of Chronic Postoperative Pain 12 Months after Total Knee Replacement. Pain 2015, 156, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, C.; Smart, K.M.; Doody, C.M. Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in People With Knee Osteoarthritis With Normal and Abnormal Conditioned Pain Modulation. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Lu, B.; Bathon, J.M.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Smith, M.T.; Page, G.G.; Edwards, R.R. Pain Sensitivity and Pain Reactivity in Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakorinne, P.; Haanpää, M.; Arokoski, J. Reliability of Pressure Pain, Vibration Detection, and Tactile Detection Threshold Measurements in Lower Extremities in Subjects with Knee Osteoarthritis and Healthy Controls. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 47, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geri, T.; Botticchio, A.; Rossettini, G.; Pournajaf, S.; Pellicciari, L.; Di Antonio, S.; Castaldo, M. Pressure Pain Threshold of the Upper Trapezius Trigger Point: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Baseline Values and Their Modification after Physical Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.A. Pressure Algometry over Normal Muscles. Standard Values, Validity and Reproducibility of Pressure Threshold. PAIN 1987, 30, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Simonsen, O.; Laursen, M.B.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Preoperative Pain Mechanisms Assessed by Cuff Algometry Are Associated with Chronic Postoperative Pain Relief after Total Knee Replacement. PAIN 2016, 157, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossipov, M.H.; Morimura, K.; Porreca, F. Descending Pain Modulation and Chronification of Pain. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2014, 8, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.M.; Uchida, P.M.; Barbosa, S.P. The Impact of Exergames on Emotional Experience: A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1209520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, M.B.; Neumann, H.; Buskbjerg, C.R.; Johannsen, M.; O’Toole, M.S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Zachariae, R. The Effect of Experimental Emotion Induction on Experimental Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain 2024, 165, e17–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.; Nijs, J.; Kosek, E.; Wideman, T.; Hasenbring, M.I.; Koltyn, K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Polli, A. Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Pain-Free and Chronic Pain Populations: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Pain 2019, 20, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, J.; Kosek, E.; Van Oosterwijck, J.; Meeus, M. Dysfunctional Endogenous Analgesia during Exercise in Patients with Chronic Pain: To Exercise or Not to Exercise? Pain Physician 2012, 15, ES205–ES213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, I.G.; Dixon, E.A.; Johnson, K.; Kong, J.-T. Dynamic Quantitative Sensory Testing to Characterize Central Pain Processing. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 120, 54452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arant, K.R.; Katz, J.N.; Neogi, T. Quantitative Sensory Testing: Identifying Pain Characteristics in Patients with Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belavy, D.L.; Van Oosterwijck, J.; Clarkson, M.; Dhondt, E.; Mundell, N.L.; Miller, C.T.; Owen, P.J. Pain Sensitivity Is Reduced by Exercise Training: Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.S.; Yamada, Y.; Kataoka, R.; Wong, V.; Spitz, R.W.; Bell, Z.W.; Loenneke, J.P. Training-Induced Hypoalgesia and Its Potential Underlying Mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 141, 104858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Stancati, A.; Silvestri, C.A.; Ciapetti, A.; Grassi, W. Minimal Clinically Important Changes in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Intensity Measured on a Numerical Rating Scale. Eur. J. Pain 2004, 8, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubach, F. Evaluation of Clinically Relevant Changes in Patient Reported Outcomes in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: The Minimal Clinically Important Improvement. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, T.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Mai, Y.; Fan, T.; Zeng, M.; Wen, X.; Han, W.; Lin, L.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Effectiveness and Associated Factors of Exercise on Symptoms in Osteoarthritis: A Pharmacodynamic Model-Based Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2024, 58, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelfort, X.; Torres-Claramunt, R.; Sánchez-Soler, J.F.; Hinarejos, P.; Leal-Blanquet, J.; Valverde, D.; Monllau, J.C. Pressure Algometry Is a Useful Tool to Quantify Pain in the Medial Part of the Knee: An Intra- and Inter-Reliability Study in Healthy Subjects. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CPT-G (n = 30) | NIVR-G (n = 30) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), M ± SD | 69.00 ± 5.56 | 68.73 ± 5.48 | 0.852 |
| BMI (kg/m2), M ± SD | 30.17 ± 4.35 | 29.83 ± 4.44 | 0.761 |
| Number of drugs, M ± SD | 2.53 ± 1.50 | 2.37 ± 1.56 | 0.675 |
| Number of comorbidities, M ± SD | 1.23 ± 0.86 | 1.27 ± 0.98 | 0.889 |
| Sex (female/male), n | 25/5 | 25/5 | 1.000 |
| Educational level | |||
| Primary, n (%) | 6 (20.00%) | 6 (20.00%) | 1.000 |
| Secondary, n (%) | 19 (63.33%) | 12 (40.00%) | 0.071 |
| Incomplete higher education, n (%) | 2 (6.67%) | 3 (10.00%) | 0.638 |
| Professionals, n (%) | 3 (10.00%) | 9 (30.00%) | 0.052 |
| Osteoarthritis diagnosis, n (%) | |||
| Knee | 15 (50.00%) | 19 (63.33%) | 0.298 |
| Hip | 6 (20.00%) | 7 (23.33%) | 0.756 |
| Knee + Hip | 9 (30.00%) | 4 (13.33%) | 0.116 |
| NIVR-G (n = 30) | CPT-G (n = 30) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post 10 | Post 20 | Post 30 | Follow-Up | Pre-Test | Post 10 | Post 20 | Post 30 | Follow-Up | |
| Pain Intensity | 46.67 ± 19.69 | 28.67 ± 16.39 * | 30.93 ± 20.78 | 14.03 ± 8.24 *,† | 32.03 ± 23.61 | 46.30 ± 24.11 | 33.67 ± 25.89 | 40.40 ± 327.43 | 39.47 ± 18.34 | 38.53 ± 26.57 |
| PPT-T | 3.72 ± 1.27 | 4.02 ± 1.21 | 3.90 ± 1.83 | 3.86 ± 1.09 | 3.57 ± 1.35 | 3.78 ± 1.14 | 3.16 ± 0.98 | 3.58 ± 1.32 | 3.26 ± 1.22 | 3.49 ± 1.12 |
| PPT-K | 3.90 ± 1.72 | 3.67 ± 1.11 | 3.96 ± 1.55 | 3.68 ± 1.21 | 4.03 ± 1.73 | 3.82 ± 0.87 | 3.32 ± 1.03 | 3.22 ± 1.28 | 3.33 ± 1.01 | 3.29 ± 1.22 |
| PPT-H | 4.14 ± 1.61 | 4.35 ± 1.46 | 4.46 ± 1.75 | 4.04 ± 1.58 | 4.06 ± 1.58 | 4.53 ± 1.67 | 3.87 ± 1.52 | 4.36 ± 1.56 | 4.21 ± 1.76 | 3.88 ± 1.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guede-Rojas, F.; Mendoza, C.; Rodríguez-Lagos, L.; Soto-Martínez, A.; Ulloa-Díaz, D.; Jorquera-Aguilera, C.; Carvajal-Parodi, C. Effects of Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Exercise on Self-Reported Pain and Mechanical Hyperalgesia in Older Adults with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicina 2025, 61, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071122
Guede-Rojas F, Mendoza C, Rodríguez-Lagos L, Soto-Martínez A, Ulloa-Díaz D, Jorquera-Aguilera C, Carvajal-Parodi C. Effects of Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Exercise on Self-Reported Pain and Mechanical Hyperalgesia in Older Adults with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071122
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuede-Rojas, Francisco, Cristhian Mendoza, Leonardo Rodríguez-Lagos, Adolfo Soto-Martínez, David Ulloa-Díaz, Carlos Jorquera-Aguilera, and Claudio Carvajal-Parodi. 2025. "Effects of Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Exercise on Self-Reported Pain and Mechanical Hyperalgesia in Older Adults with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071122
APA StyleGuede-Rojas, F., Mendoza, C., Rodríguez-Lagos, L., Soto-Martínez, A., Ulloa-Díaz, D., Jorquera-Aguilera, C., & Carvajal-Parodi, C. (2025). Effects of Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Exercise on Self-Reported Pain and Mechanical Hyperalgesia in Older Adults with Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicina, 61(7), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071122







