A Population-Based Study on the Association between Periodontal Disease and Major Lifestyle-Related Comorbidities in South Korea: An Elderly Cohort Study from 2002–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic and Economic Factors Associated with Periodontal Disease
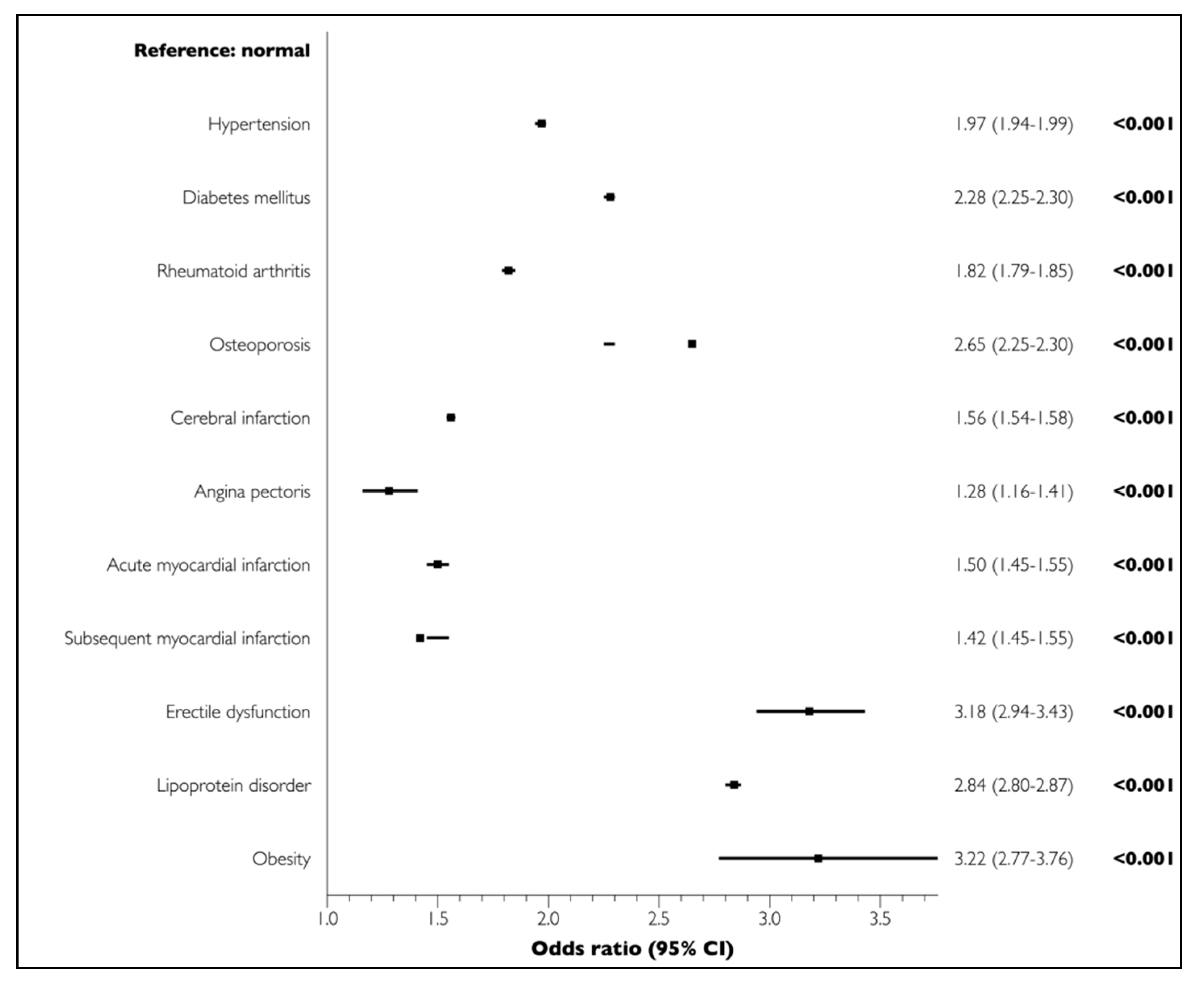
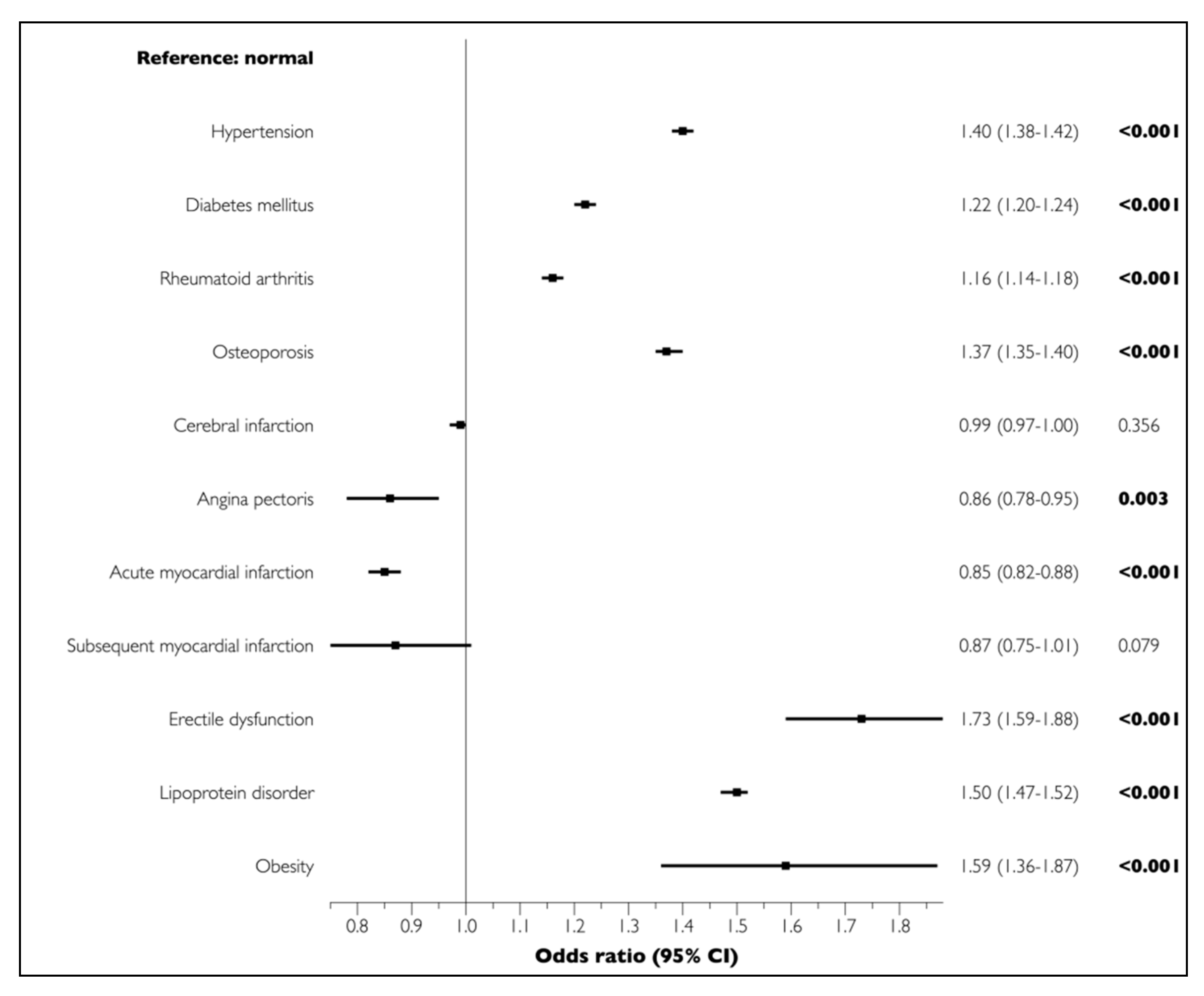
3.2. Lifestyle-Related Comorbidities Associated with Periodontal Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.A.; Kong, E.F.; Meiller, T.F.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Periodontal diseases: Bug induced, host promoted. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.T.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N.; Lee, J.H. Association between health status and tooth loss in korean adults: Longitudinal results from the national health insurance service-health examinee cohort, 2002-2015. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2019, 49, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, B.K.; Berger, S.L.; Brunet, A.; Campisi, J.; Cuervo, A.M.; Epel, E.S.; Franceschi, C.; Lithgow, G.J.; Morimoto, R.I.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Geroscience: Linking aging to chronic disease. Cell 2014, 159, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, S.N.; Choi, S.H. Predictive data mining for diagnosing periodontal disease: The korea national health and nutrition examination surveys (knhanes v and vi) from 2010 to 2015. J. Public Health Dent. 2019, 79, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigbede, A.O.; Babatope, B.O.; Bamidele, M.K. Periodontitis and systemic diseases: A literature review. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2012, 16, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; D’Aiuto, F.; Deanfield, J.; Fernandez-Aviles, F. European workshop in periodontal health and cardiovascular disease-scientific evidence on the association between periodontal and cardiovascular diseases: A review of the literature. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2010, 12, B3-CB12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, L.; Cervino, G.; Laino, L.; D’Amico, C.; Mauceri, R.; Tozum, T.F.; Gaeta, M.; Cicciu, M. Porphyromonas gingivalis, periodontal and systemic implications: A systematic review. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, G.; Polizzi, A.; Patini, R.; Ferlito, S.; Alibrandi, A.; Palazzo, G. Association among serum and salivary a. Actinomycetemcomitans specific immunoglobulin antibodies and periodontitis. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, C.; Lobos, O.; Hubert, E.; Gonzalez, C.; Matus, S.; Pereira, M.; Hasbun, S.; Descouvieres, C. Periodontal pathogens in atheromatous plaques isolated from patients with chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2006, 41, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Khalaf, H.; Sirsjo, A.; Bengtsson, T. Gingipains from the periodontal pathogen porphyromonas gingivalis play a significant role in regulation of angiopoietin 1 and angiopoietin 2 in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, G.; Alibrandi, A.; Curro, M.; Matarese, M.; Ricca, S.; Matarese, G.; Ientile, R.; Kocher, T. Evaluation of salivary and serum adma levels in patients with periodontal and cardiovascular disease as subclinical marker of cardiovascular risk. J. Periodontol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Polizzi, A.; Iorio-Siciliano, V.; Alibrandi, A.; Ramaglia, L.; Leonardi, R. Effectiveness of a nutraceutical agent in the non-surgical periodontal therapy: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Mai, W.; Li, M.; Hu, Y. Association between prediabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016, 355, i5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.C.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, S.K.; Khang, Y.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Cohort profile: The national health insurance service-national health screening cohort (nhis-heals) in korea. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, K.A.; Clem, D.S., 3rd; American Academy of Periodontology. Guidelines for the management of patients with periodontal diseases. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, Y.T.; Choi, S.H. Association of lifestyle-related comorbidities with periodontitis: A nationwide cohort study in korea. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015, 94, e1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Youk, T.M.; Jeong, S.N.; Kim, Y.T.; Choi, S.H. Association between periodontal disease and non-communicable diseases: A 12-year longitudinal health-examinee cohort study in south korea. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopino, A.M.; Cutler, C.W. Pathophysiological relationships between periodontitis and systemic disease: Recent concepts involving serum lipids. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, G.J.; Ford, P.J.; Cullinan, M.P.; Leishman, S.; Yamazaki, K. Relationship between periodontal infections and systemic disease. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13 (Suppl. 4), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G. Periodontitis: From microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albandar, J.M. Global risk factors and risk indicators for periodontal diseases. Periodontol. 2000 2002, 29, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, E.; Burnett, A.L.; Platz, E.A. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the us. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellesarian, S.V.; Kellesarian, T.V.; Ros Malignaggi, V.; Al-Askar, M.; Ghanem, A.; Malmstrom, H.; Javed, F. Association between periodontal disease and erectile dysfunction: A systematic review. Am. J. Mens Health 2018, 12, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cao, F.; Lin, Z.; Wu, D. Updated evidence of association between periodontal disease and incident erectile dysfunction. J. Sex Med. 2019, 16, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlstein, M.I.; Bissada, N.F. Influence of obesity and hypertension on the severity of periodontitis in rats. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1977, 43, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffee, B.W.; Weston, S.J. Association between chronic periodontal disease and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1708–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.; Rohde, J.F.; Raymond, K.; Heitmann, B.L. Association between periodontal disease and overweight and obesity: A systematic review. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cabezas, R.; Seelam, N.; Petit, C.; Agossa, K.; Gaertner, S.; Tenenbaum, H.; Davideau, J.L.; Huck, O. Association between periodontitis and arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. Heart J. 2016, 180, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamster, I.B.; Pagan, M. Periodontal disease and the metabolic syndrome. Int. Dent. J. 2017, 67, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.C.; Srivastava, R.; Verma, P.K.; Gautam, A. Metabolic syndrome and periodontal disease: An overview for physicians. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 3492–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, S.; Suvan, J.; Deschner, J. The association of periodontal diseases with metabolic syndrome and obesity. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 83, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genest, J. Lipoprotein disorders and cardiovascular risk. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2003, 26, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Interrelationship between diabetes and periodontitis: Role of hyperlipidemia. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preshaw, P.M.; Alba, A.L.; Herrera, D.; Jepsen, S.; Konstantinidis, A.; Makrilakis, K.; Taylor, R. Periodontitis and diabetes: A two-way relationship. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, B.; Park, B.; Bartold, P.M. Periodontitis and type ii diabetes: A two-way relationship. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2013, 11, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Kim, Y.T.; Kweon, H.I.; Park, E.C.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Effect of periodontitis on the development of osteoporosis: Results from a nationwide population-based cohort study (2003–2013). BMC Womens Health 2017, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wactawski-Wende, J. Periodontal diseases and osteoporosis: Association and mechanisms. Ann. Periodontol. 2001, 6, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Maestre, M.A.; Gonzalez-Cejudo, C.; Machuca, G.; Torrejon, R.; Castelo-Branco, C. Periodontitis and osteoporosis: A systematic review. Climacteric 2010, 13, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahanian, V.; Shamami, M.S.; Shamami, M.S. Relationship between osteoporosis and periodontal disease: Review of the literature. J. Dent. (Tehran) 2012, 9, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, L.; Goyal, T.; Gupta, N.D. Osteoporosis and periodontitis in postmenopausal women: A systematic review. J. Midlife Health 2017, 8, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Ferreira, R.; de Brito Silva, R.; Magno, M.B.; Carvalho Almeida, A.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Maia, L.C.; Lima, R.R. Does periodontitis represent a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2019, 11, 1759720X19858514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, S.; Putz, N.; Jurianz, E.; Schaller, H.G.; Reichert, S. Are there any common genetic risk markers for rheumatoid arthritis and periodontal diseases? A case-control study. Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 2907062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.D.; Fernandes, G.R.; Calderaro, D.C.; Mendonca, S.M.S.; Silva, J.M.; Albiero, M.L.; Cunha, F.Q.; Xiao, E.; Ferreira, G.A.; Teixeira, A.L.; et al. Oral microbial dysbiosis linked to worsened periodontal condition in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. Complement and dysbiosis in periodontal disease. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, M.W.; Listl, S.; Bartols, A.; Schubert, I.; Blaschke, K.; Haux, C.; Van Der Zande, M.M. Current knowledge on correlations between highly prevalent dental conditions and chronic diseases: An umbrella review. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2019, 16, E132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freisinger, E.; Malyar, N.M.; Reinecke, H. Peripheral artery disease is associated with high in-hospital mortality particularly in males with acute myocardial infarction in a nationwide real-world setting. VASA 2016, 45, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Canut, P.; Lorca, A.; Magan, R. Smoking and periodontal disease severity. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanur, E. Effects of smoking on the prevalence and severity of periodontal disease. Tex. Dent. J. 2001, 118, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, J.A.; Barua, R.S. The pathophysiology of cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease: An update. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | PD Participants | Periodontally Healthy Participants | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Total | 149,785 | 100.0 | 408,362 | 100.0 | |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 65,817 | 43.9 | 167,765 | 40.3 | <0.001 |
| Female | 83,968 | 56.1 | 243,597 | 59.7 | |
| Age group (years) | |||||
| 60–64 | 75,716 | 50.5 | 120,400 | 29.5 | <0.001 |
| 65–69 | 44,322 | 29.6 | 103,039 | 25.2 | |
| 70–74 | 20,179 | 13.5 | 77,478 | 19.0 | |
| 75–79 | 7234 | 4.8 | 53,983 | 13.2 | |
| 80–84 | 1970 | 1.3 | 33,245 | 8.1 | |
| ≥85 | 364 | 0.2 | 20,217 | 5.0 | |
| Household income 1 | |||||
| First quintile | 26,179 | 17.5 | 104,610 | 25.6 | <0.001 |
| Second quintile | 17,264 | 11.5 | 53,158 | 13.0 | |
| Third quintile | 21,944 | 14.7 | 59,686 | 14.6 | |
| Fourth quintile | 33,150 | 22.1 | 81,155 | 19.9 | |
| Fifth quintile | 51,248 | 34.2 | 109,753 | 26.9 | |
| Insurance status | |||||
| MAP beneficiary | 6057 | 4.0 | 39,369 | 9.6 | <0.001 |
| NHIS, employed | 83,003 | 55.4 | 194,955 | 47.7 | |
| NHIS, self-employed | 60,725 | 40.5 | 174,038 | 42.6 | |
| Health status 2 | |||||
| Healthy | 149,302 | 99.7 | 405,175 | 99.2 | <0.001 |
| Disabled | 483 | 0.3 | 3187 | 0.8 | |
| Living area 3 | |||||
| Seoul | 33,714 | 22.5 | 65,878 | 16.1 | <0.001 |
| Metropolitan area | 37,114 | 24.8 | 85,758 | 21.0 | |
| Other areas | 78,957 | 52.7 | 256,726 | 62.9 | |
| Variables | PD Participants | Periodontally Healthy Participants | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Total | 149,785 | 100.0 | 408,362 | 100.0 | |
| Hypertension | 104,257 | 69.6 | 188,989 | 46.3 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 67,946 | 45.4 | 108,968 | 26.7 | <0.001 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 27,971 | 18.7 | 45,638 | 11.2 | <0.001 |
| Osteoporosis | 67,623 | 45.1 | 120,281 | 29.5 | <0.001 |
| Cerebral infarction | 33,467 | 22.3 | 63,406 | 15.5 | <0.001 |
| Angina pectoris | 39,547 | 26.4 | 60,200 | 14.7 | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction | |||||
| Acute | 5433 | 3.6 | 9945 | 2.4 | <0.001 |
| Subsequent | 300 | 0.2 | 576 | 0.1 | <0.001 |
| Erectile dysfunction | 1373 | 0.9 | 1184 | 0.3 | <0.001 |
| Lipoprotein disorder | 76,465 | 51.0 | 109,618 | 26.8 | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 362 | 0.2 | 305 | 0.1 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-N. A Population-Based Study on the Association between Periodontal Disease and Major Lifestyle-Related Comorbidities in South Korea: An Elderly Cohort Study from 2002–2015. Medicina 2020, 56, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110575
Lee J-H, Jeong S-N. A Population-Based Study on the Association between Periodontal Disease and Major Lifestyle-Related Comorbidities in South Korea: An Elderly Cohort Study from 2002–2015. Medicina. 2020; 56(11):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110575
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jae-Hong, and Seong-Nyum Jeong. 2020. "A Population-Based Study on the Association between Periodontal Disease and Major Lifestyle-Related Comorbidities in South Korea: An Elderly Cohort Study from 2002–2015" Medicina 56, no. 11: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110575
APA StyleLee, J.-H., & Jeong, S.-N. (2020). A Population-Based Study on the Association between Periodontal Disease and Major Lifestyle-Related Comorbidities in South Korea: An Elderly Cohort Study from 2002–2015. Medicina, 56(11), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110575





