Natural Products as a Source for New Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Compounds through the Inhibition of Purinergic P2X Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
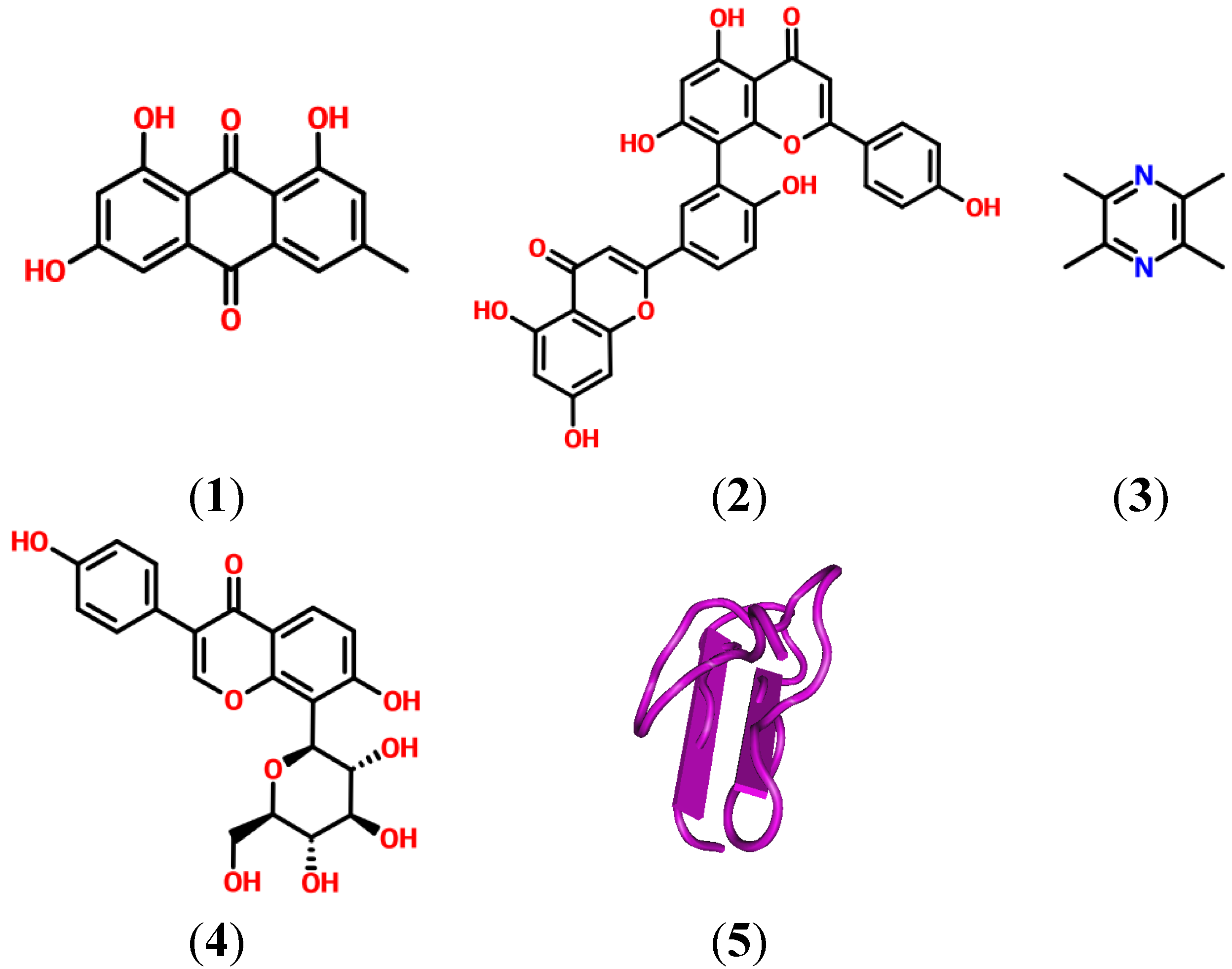
2. Natural Products and Their Potential as Modulators of the Inflammation and Pain Related P2X Receptor
3. Could an Antagonist to P2XR be Useful in the Treatment of Inflammatory and Pain Disorders?
4. Conclusions
References
- Itokawa, H.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Akiyama, T.; Lee, K.H. Plant-derived natural product research aimed at new drug discovery. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, N.M.; Masimirembwa, C.; Chibale, K. Identification and characterization of reactive metabolites in natural products-driven drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S. The role of natural product chemistry in drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J. Natural products in cancer chemotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklani, A.; Kutty, S.K. Plant-derived compounds in clinical trials. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.P.; Shrestha, S.; Foresman, T.W.; Singh, A. Global Biodiversity Data and Information. Available online: http://www.unescap.org/stat/envstat/stwes-26.pdf (Accessed on 18 April 2013).
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, V.C. Biodiversidade: Um componente essencial na descoberta de Fármacos. In Química de produtos naturais, novos fármacos e a moderna farmacognosia; UNIVALI, Ed.: Itajaí, Brazil, 2009; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, L.C. Fitoterapia. Revista eletrônica Com Ciência. Available online: http://www.comciencia.br/reportagens/fito/fito8.htm/ (Accessed on 23 November 2012).
- Almeida, M.C. Setor de fitomedicamentos deve faturar R$ 400 milhões. Diário Comércio Indústria & Serviços. Available online: http://www.cdcc.usp.br/cda/sessao-astronomia/sessao-astronomia-padrao/referencia-bibliografica-ufrgs.htm/ (Accessed on 14 September 2009).
- Chaves, M.H. Plantas Medicinais: importância e desafios. Saplência. Available online: http://www.fapepi.pi.gov.br/novafapepi/sapiencia10/artigos3.php/ (Accessed on 23 November 2012).
- Cunha, P.A. Farmacognosia nos estudos farmacêuticos; Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian: Lisboa, Portugal, 2005; pp. 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Galvez-Llompart, M.; Zanni, R.; Garcia-Domenech, R. Modeling natural anti-inflammatory compounds by molecular topology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 9481–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.X.; Ferreira, L.G.B.; Soares-Bezerra, R.J.; Frutuoso, V.S.; Alves, L.A. Action of natural products on P2 receptors: A reinvented era for drug discovery. Molecules 2012, 17, 13009–13025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andó, R.D.; Mehesz, B.; Gyires, K.; Illes, P.; Sperlagh, B. A comparative analysis of the activity of ligands acting at P2X and P2Y receptor subtypes in models of neuropathic, acute and inflammatory pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; North, R.A. Neuromodulation by extracellular ATP and P2X receptors in the CNS. Neuron 2012, 76, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CADD Group Chemoinformatics Tools and User Services, Chemical Identifier Resolver beta 4. USA: National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. 2009. Available online: http://cactus.nci.nih.gov/chemical/structure/ (Accessed on 5 March 2013).
- North, R.A. P2X3 receptors and peripheral pain mechanisms. J. Physiol. 2004, 554, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.C.; Pelegrini-da-Silva, A.; Tambeli, C.H.; Parada, C.A. Peripheral mechanisms underlying the essential role of P2X3,2/3 receptors in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Pain 2009, 141, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, F.C.; Araldi, D.; Vieira, A.S.; Oliveira-Fusaro, M.C.; Tambeli, C.H.; Parada, C.A. Neuronal P2X3 receptor activation is essential to the hyperalgesia induced by prostaglandins and sympathomimetic amines released during inflammation. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Fusaro, M.C.; Pelegrini-da-Silva, A.; Araldi, D.; Parada, C.A.; Tambeli, C.H. P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors mediate mechanical hyperalgesia induced by bradykinin, but not by pro-inflammatory cytokines, PGE(2) or dopamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.D.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.S.; Xu, B.H.; Mu, S.N. Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on acute nociception mediated by signaling of P2X receptor activation in rat. Brain Res. 2004, 995, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.D.; Xu, C.S.; Zhou, T.; Liu, H.Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.L. Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits ATP-activated currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res. 2005, 1040, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Liang, S.; Zhang, A.; Mu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wan, F. Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on primary afferent transmission mediated by P2X3 receptor in neuropathic pain states. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 77, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, K.; Li, G.; Wan, F.; Liu, S.; Lin, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liang, S. Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on DRG neuron P2X3 receptor involved in transmitting pain after burn. Burns 2010, 36, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, S. Effect of puerarin on P2X3 receptor involved in hyperalgesia after burn injury in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xu, W.; Xu, H.; Xiong, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Tu, G.; Peng, H.; Qiu, S.; Liang, S. Role of puerarin in the signalling of neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3 receptor of dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Deng, L.; Zhu, G.; Xu, C.; Li, G.; Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Kong, F.; Wu, R.; Liang, S. Effect of emodin on neuropathic pain transmission mediated by P2X2/3 receptor of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 84, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L. H.; Li, J. Inhibition of ATP-induced macrophage death by emodin via antagonizing P2X7 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 640, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, H.A.; Vasylevs'kyi, A.A.; Pluzhnykov, K.A.; Korol'kova Iu, V.; Mamenko, M.V.; Volkova, T.M.; Maksymiuk, O.P.; Boichuk Ia, A.; Hrishyn Ie, V.; Kryshtal, O.O. Peptide components of Geolycosa spider venom modulate P2X receptor activity of rat sensory neurons. Fiziol. Zh. 2009, 55, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Grishin, E.V.; Savchenko, G.A.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Boychuk, Y.A.; Viatchenko-Karpinski, V.Y.; Nadezhdin, K.D.; Arseniev, A.S.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Kulyk, V.B.; et al. Novel peptide from spider venom inhibits P2X3 receptors and inflammatory pain. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 680–683. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, M.; Kuboyama, K.; Inoue, T.; Nagata, K.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Inoue, K. Behavioral phenotypes of mice lacking purinergic P2X4 receptors in acute and chronic pain assays. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Wan, X.; Salter, M.W. P2X4-receptor-mediated synthesis and release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in microglia is dependent on calcium and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3518–3528. [Google Scholar]
- Trang, T.; Salter, M.W. P2X4 purinoceptor signaling in chronic pain. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Olmos, V.; Abdelrahman, A.; El-Tayeb, A.; Freudendahl, D.; Weinhausen, S.; Muller, C.E. N-substituted phenoxazine and acridone derivatives: structure-activity relationships of potent P2X4 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9576–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, A.; Tsukimoto, M.; Mori, D.; Noguchi, T.; Harada, H.; Takenouchi, T.; Kitani, H.; Kojima, S. Regulation of P2X7-dependent inflammatory functions by P2X4 receptor in mouse macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulme, E.; Tsuda, M.; Khakh, B.S.; Inoue, K. On the role of ATP-gated P2X receptors in acute, inflammatory and neuropathic pain. In Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man; Kruger, L., Light, A.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vitiello, L.; Gorini, S.; Rosano, G.; la Sala, A. Immunoregulation through extracellular nucleotides. Blood 2012, 120, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.A. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 1013–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Labasi, J.M.; Petrushova, N.; Donovan, C.; McCurdy, S.; Lira, P.; Payette, M.M.; Brissette, W.; Wicks, J.R.; Audoly, L.; Gabel, C.A. Absence of the P2X7 receptor alters leukocyte function and attenuates an inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 6436–6445. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.A.; Alvarez, A.J.; Estes, D.M. The P2X7 purinergic receptor on bovine macrophages mediates mycobacterial death. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 78, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.B.; Hart, J.; Wewers, M.D. ATP-stimulated release of interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-18 requires priming by lipopolysaccharide and is independent of caspase-1 cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3820–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudipaty, L.; Munetz, J.; Verhoef, P.A.; Dubyak, G.R. Essential role for Ca2+ in regulation of IL-1beta secretion by P2X7 nucleotide receptor in monocytes, macrophages, and HEK-293 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 285, C286–C299. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, H.L.; Francis, S.E.; Dower, S.K.; Crossman, D.C. Secretion of intracellular IL-1 receptor antagonist (type 1) is dependent on P2X7 receptor activation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Chessell, I.P.; Hatcher, J.P.; Bountra, C.; Michel, A.D.; Hughes, J.P.; Green, P.; Egerton, J.; Murfin, M.; Richardson, J.; Peck, W.L.; et al. Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2005, 114, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, W.H.; Namiki, S.; Ostrom, R.S.; Insel, P.A. Hypertonic stress increases T cells interleukin-2 expression through a mechanism that involves ATP release, P2 receptor, and p38 MAPK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4590–4596. [Google Scholar]
- Sluyter, R.; Shemon, A.N.; Barden, J.A.; Wiley, J.S. Extracellular ATP increases cation fluxes in human erythrocytes by activation of the P2X7 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44749–44755. [Google Scholar]
- Bulanova, E.; Budagian, V.; Orinska, Z.; Hein, M.; Petersen, F.; Thon, L.; Adam, D.; Bulfone-Paus, S. Extracellular ATP induces cytokine expression and apoptosis through P2X7 receptor in murine mast cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3880–3890. [Google Scholar]
- Coddou, C.; Yan, Z.; Obsil, T.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Activation and regulation of purinergic P2X receptor channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 641–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.A.; Fidalgo-Neto, A.A.; Faria, R.X.; Simões, A.; Calheiros, A.S.; Bérenger, A.L.; Faria-Neto, H.C.; Figueiredo, M.R.; Frutuoso, V.S.; Alves, L.A. Effect of Rheedia longifolia leaf extract and fractions on the P2X(7) receptor in vitro: novel antagonists? J. Med. Food. 2011, 14, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gever, J.R.; Cockayne, D.A.; Dillon, M.P.; Burnstock, G.; Ford, A.P. Pharmacology of P2X channels. Pflugers Arch. 2006, 452, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunosewoyo, H.; Kassiou, M. P2X purinergic receptor ligands: recently patented compounds. Expert Opin Ther. Pat. 2010, 20, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Gregg, R.J.; Kort, M.E.; Perez-Medrano, A.; Voight, E.A.; Wang, Y.; Grayson, G.; Namovic, M.T.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Niforatos, W.; et al. Structure-activity relationship studies on a series of novel, substituted 1-benzyl-5-phenyltetrazole P2X7 antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, T.C.; Bloom, B.J.; Wei, N.; Ishaq, S.; Park, W.; Wang, X.; Gupta, P.; Mebus, C.A. Efficacy and safety of CE-224,535, an antagonist of P2X7 receptor, in treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis inadequately controlled by methotrexate. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Soares-Bezerra, R.J.; Calheiros, A.S.; Da Silva Ferreira, N.C.; Da Silva Frutuoso, V.; Alves, L.A. Natural Products as a Source for New Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Compounds through the Inhibition of Purinergic P2X Receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 650-658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050650
Soares-Bezerra RJ, Calheiros AS, Da Silva Ferreira NC, Da Silva Frutuoso V, Alves LA. Natural Products as a Source for New Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Compounds through the Inhibition of Purinergic P2X Receptors. Pharmaceuticals. 2013; 6(5):650-658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoares-Bezerra, Rômulo José, Andrea Surrage Calheiros, Natiele Carla Da Silva Ferreira, Valber Da Silva Frutuoso, and Luiz Anastacio Alves. 2013. "Natural Products as a Source for New Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Compounds through the Inhibition of Purinergic P2X Receptors" Pharmaceuticals 6, no. 5: 650-658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050650
APA StyleSoares-Bezerra, R. J., Calheiros, A. S., Da Silva Ferreira, N. C., Da Silva Frutuoso, V., & Alves, L. A. (2013). Natural Products as a Source for New Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Compounds through the Inhibition of Purinergic P2X Receptors. Pharmaceuticals, 6(5), 650-658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050650



